CHASQUI - I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chasqui I is a one-kilogram nano satellite project that was launched from the International Space Station during a
 The Nanosatellite Chasqui I research project is a satellite developed by students at the
The Nanosatellite Chasqui I research project is a satellite developed by students at the  Peru has large geographical diversity, which makes it very difficult to constantly monitor the situation of certain events, whether natural or man-made, such as permanent snow melting, deforestation of the Amazon, the protection of habitats of endangered species, combating
Peru has large geographical diversity, which makes it very difficult to constantly monitor the situation of certain events, whether natural or man-made, such as permanent snow melting, deforestation of the Amazon, the protection of habitats of endangered species, combating
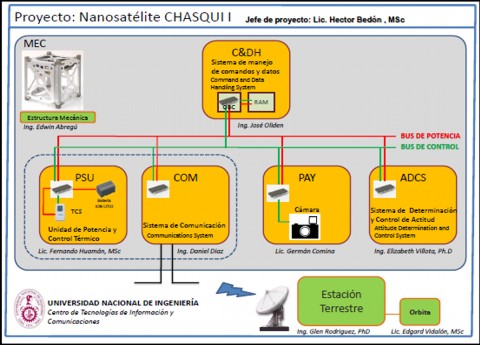
 The research group module mechanical structure (EMEC) is responsible for reviewing the state of art, comparative analysis of existing cases to the pico-satellite design and manufacture our own model based on the Standard Cubesat.
The pico-satellite contains the following modules:
*Central Control and Management Information (CCMI)
*Unit Power and Thermal Control (PCT)
*Communications System (SICOM)
*Imaging Management System (SIMA)
*System Identification and Attitude Control (SDCA)
The research group module mechanical structure (EMEC) is responsible for reviewing the state of art, comparative analysis of existing cases to the pico-satellite design and manufacture our own model based on the Standard Cubesat.
The pico-satellite contains the following modules:
*Central Control and Management Information (CCMI)
*Unit Power and Thermal Control (PCT)
*Communications System (SICOM)
*Imaging Management System (SIMA)
*System Identification and Attitude Control (SDCA)
 The first subsystem is the Power and is responsible for receiving, processing, storing, and distributing power to other subsystems in the Chasqui I. The objective of this subsystem is to ensure electricity supply for Chasqui I give it the energy needed at the right time.
The second subsystem is the Thermal Control and he is responsible for maintaining the temperature of the
The first subsystem is the Power and is responsible for receiving, processing, storing, and distributing power to other subsystems in the Chasqui I. The objective of this subsystem is to ensure electricity supply for Chasqui I give it the energy needed at the right time.
The second subsystem is the Thermal Control and he is responsible for maintaining the temperature of the
 The main objective of the research group is to obtain photographs of the Earth from Chasqui I. SIMA The module consists of two cameras, one visible range and the other in the near infrared range. Digital information is collected by the Central Control Module and Management Information (CCMI) and then sent to the Earth Station (ESTER).
Additionally, the Group is responsible for processing digital images obtained by the Chasqui I.
The main objective of the research group is to obtain photographs of the Earth from Chasqui I. SIMA The module consists of two cameras, one visible range and the other in the near infrared range. Digital information is collected by the Central Control Module and Management Information (CCMI) and then sent to the Earth Station (ESTER).
Additionally, the Group is responsible for processing digital images obtained by the Chasqui I.
 The SDCA maintains the pico-satellite stabilization and guidance to a desired direction when necessary. Specifically, we can say that SDCA is responsible for:
* Stabilize the pico-satellite after leaving the deployer through reduction (within 0.1rad / s) and control their angular velocities.
* Maintain a pointing accuracy of 3 degrees for taking pictures of Peru and, if technically possible, having a wide coverage of South America through maneuvers of 30 degrees in roll (roll) and 30 degrees pitch (pitch).
* Maintain a less demanding pointing accuracy (e.g. 20 degrees) to enable up / down data between the pico-satellite and ground station.
The SDCA enables the pico-satellite to determine its attitude, calculate the correction required to achieve the desired orientation and execute the necessary maneuvers using the actuators. The attitude determination system will use
The SDCA maintains the pico-satellite stabilization and guidance to a desired direction when necessary. Specifically, we can say that SDCA is responsible for:
* Stabilize the pico-satellite after leaving the deployer through reduction (within 0.1rad / s) and control their angular velocities.
* Maintain a pointing accuracy of 3 degrees for taking pictures of Peru and, if technically possible, having a wide coverage of South America through maneuvers of 30 degrees in roll (roll) and 30 degrees pitch (pitch).
* Maintain a less demanding pointing accuracy (e.g. 20 degrees) to enable up / down data between the pico-satellite and ground station.
The SDCA enables the pico-satellite to determine its attitude, calculate the correction required to achieve the desired orientation and execute the necessary maneuvers using the actuators. The attitude determination system will use
 This subsystem is not part of the satellite itself, but its existence and operation is necessary to achieve the objectives of Chasqui I. The set of facilities and wireless communication (radio) needed to communicate with the Chasqui I, and any satellite.
The main functions of this module are:
* Follow-up: radioforo hear the beacon or satellite for its position.
* Telemetry: Request state variables (temperature, voltage, etc..) To monitor and validate the satellite orbit calculation.
* Commando: Order to extend the satellite
This subsystem is not part of the satellite itself, but its existence and operation is necessary to achieve the objectives of Chasqui I. The set of facilities and wireless communication (radio) needed to communicate with the Chasqui I, and any satellite.
The main functions of this module are:
* Follow-up: radioforo hear the beacon or satellite for its position.
* Telemetry: Request state variables (temperature, voltage, etc..) To monitor and validate the satellite orbit calculation.
* Commando: Order to extend the satellite
 This module aims to simulate the trajectory of Chasqui I, which is calculated using differential equations of motion, which are then solved in
This module aims to simulate the trajectory of Chasqui I, which is calculated using differential equations of motion, which are then solved in
 The module aims to achieve the assembly of components developed by different modules of the project as circuit boards, cameras,
The module aims to achieve the assembly of components developed by different modules of the project as circuit boards, cameras,
National University of Engineering
Home of the public university located in Lima Peru.
CTIC – UNI
Center for Information & Communication Technologies (CTIC-UNI).
Project Official Site Chasqui 1
All information relating to the project. {{Use American English, date=January 2014 Student satellites CubeSats
spacewalk
Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. In the absence of a breathable atmosphere of Earth, Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environmen ...
on August 18, 2014. The concept satellite was equipped with two cameras, one for visible light and one infrared, equipped to take photos of the Earth.
The Chasqui I was developed by students at Peru's National University of Engineering
The National University of Engineering ( es, Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería, UNI) is a public engineering and science university located in the Rímac District of Lima, Peru.
History
The National University of Engineering was founded in 1 ...
(UNI) with assistance from the Russian Southwest State University (SWSU), Kursk. It was part of an educational project to acquire the experience and ability in developing satellites.
The name of the project refers to the ''Chasqui
The ''chasquis'' (also ) were the messengers of the Inca empire. Agile, highly trained and physically fit, they were in charge of carrying the , messages and gifts, up to 240 km per day through the relay system. ''Chasquis'' were not just messe ...
'', who served as messengers in the Inca Empire.
General objectives
Most of UNI's objectives in satellite technology were completed through nanosatellite Cubesat. Plans for the satellite Chasqui I included taking pictures of the Earth, with transmission to a ground station. Specific objectives include: * Establish contact and support to other universities and/or institutions involved in such projects. * To deepen the knowledge in information and communications technologies emerging. * To lead such projects in Latin America. * To demonstrate and validate new technologies. Goals include: * Design of the project profile. * Funding. * Capacity building. * Implementation of the Laboratory. * Development of the project. * Testing integrated. * Guidelines. * OperationProject
 The Nanosatellite Chasqui I research project is a satellite developed by students at the
The Nanosatellite Chasqui I research project is a satellite developed by students at the National University of Engineering
The National University of Engineering ( es, Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería, UNI) is a public engineering and science university located in the Rímac District of Lima, Peru.
History
The National University of Engineering was founded in 1 ...
based on CubeSat technology. The satellite is small, weighing less than 1 kg and it has a volume of up to 1 Lt. The project was designed to image Peruvian land using a CMOS camera that seeks to distinguish between fertile land and uncultivated areas. As a student project, Chasqui I was constructed using commercial components. It uses amateur radio frequency, making it possible to be located throughout the country. The Chasqui I students also developed a ground station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves fro ...
that allows for remote monitoring of the satellite, as well as satellite's of other universities.
 Peru has large geographical diversity, which makes it very difficult to constantly monitor the situation of certain events, whether natural or man-made, such as permanent snow melting, deforestation of the Amazon, the protection of habitats of endangered species, combating
Peru has large geographical diversity, which makes it very difficult to constantly monitor the situation of certain events, whether natural or man-made, such as permanent snow melting, deforestation of the Amazon, the protection of habitats of endangered species, combating narco-terrorism
Narcoterrorism, in its original context, is understood to refer to the attempts of narcotics traffickers to influence the policies of a government or a society through violence and intimidation, and to hinder the enforcement of anti-drug laws by t ...
, surveillance of borders and territorial sea, the prediction and mitigation of natural disasters, etc. UNI, with its project Chasqui I, are taking steps in the process of addressing problems such as crop monitoring and telecommunications areas.
Outline of the Project Development Modules

Project Modules
Mechanical Structure – EMEC
 The research group module mechanical structure (EMEC) is responsible for reviewing the state of art, comparative analysis of existing cases to the pico-satellite design and manufacture our own model based on the Standard Cubesat.
The pico-satellite contains the following modules:
*Central Control and Management Information (CCMI)
*Unit Power and Thermal Control (PCT)
*Communications System (SICOM)
*Imaging Management System (SIMA)
*System Identification and Attitude Control (SDCA)
The research group module mechanical structure (EMEC) is responsible for reviewing the state of art, comparative analysis of existing cases to the pico-satellite design and manufacture our own model based on the Standard Cubesat.
The pico-satellite contains the following modules:
*Central Control and Management Information (CCMI)
*Unit Power and Thermal Control (PCT)
*Communications System (SICOM)
*Imaging Management System (SIMA)
*System Identification and Attitude Control (SDCA)
Central Control and Information Management – CCMI
This module manages and monitors information from all subsystems Chasqui I. The module to meet the goals set must have within it a processor (called OBC: On-Board Computer), which fulfills the following functions in each module: * Camera (SIMA): Regulates the satellite image capture and storage in an external memory. * Attitude (SDCA): Orders and confirms, stabilization and spatial orientation. * Power (PCT): Manages and monitors satellite states of physical variables such as temperature, voltage and current. * Communication (SICOM): Ground-station receives orders and sends the information of camera data and pico-satellite states The data managed are: Data from the camera, Data Maintenance and commands.Power and Thermal Control – PCT
 The first subsystem is the Power and is responsible for receiving, processing, storing, and distributing power to other subsystems in the Chasqui I. The objective of this subsystem is to ensure electricity supply for Chasqui I give it the energy needed at the right time.
The second subsystem is the Thermal Control and he is responsible for maintaining the temperature of the
The first subsystem is the Power and is responsible for receiving, processing, storing, and distributing power to other subsystems in the Chasqui I. The objective of this subsystem is to ensure electricity supply for Chasqui I give it the energy needed at the right time.
The second subsystem is the Thermal Control and he is responsible for maintaining the temperature of the batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
and other components of the satellite in its operating range, in order to ensure the functioning of Chasqui I. The most critical task of this subsystem is to maintain the batteries to operate within its limit of operation (0 °C to 20 °C.). Through heaters specifically designed and constructed at the National University of Engineering.
Both subsystems were designed and built at the National Engineering University.
Communication System – SICOM
The TT & C module is responsible to provide a means of communication between the peak itself and the satellite earth station.Image Acquisition System – SIMA
 The main objective of the research group is to obtain photographs of the Earth from Chasqui I. SIMA The module consists of two cameras, one visible range and the other in the near infrared range. Digital information is collected by the Central Control Module and Management Information (CCMI) and then sent to the Earth Station (ESTER).
Additionally, the Group is responsible for processing digital images obtained by the Chasqui I.
The main objective of the research group is to obtain photographs of the Earth from Chasqui I. SIMA The module consists of two cameras, one visible range and the other in the near infrared range. Digital information is collected by the Central Control Module and Management Information (CCMI) and then sent to the Earth Station (ESTER).
Additionally, the Group is responsible for processing digital images obtained by the Chasqui I.
System Identification and Attitude Control – SDCA
 The SDCA maintains the pico-satellite stabilization and guidance to a desired direction when necessary. Specifically, we can say that SDCA is responsible for:
* Stabilize the pico-satellite after leaving the deployer through reduction (within 0.1rad / s) and control their angular velocities.
* Maintain a pointing accuracy of 3 degrees for taking pictures of Peru and, if technically possible, having a wide coverage of South America through maneuvers of 30 degrees in roll (roll) and 30 degrees pitch (pitch).
* Maintain a less demanding pointing accuracy (e.g. 20 degrees) to enable up / down data between the pico-satellite and ground station.
The SDCA enables the pico-satellite to determine its attitude, calculate the correction required to achieve the desired orientation and execute the necessary maneuvers using the actuators. The attitude determination system will use
The SDCA maintains the pico-satellite stabilization and guidance to a desired direction when necessary. Specifically, we can say that SDCA is responsible for:
* Stabilize the pico-satellite after leaving the deployer through reduction (within 0.1rad / s) and control their angular velocities.
* Maintain a pointing accuracy of 3 degrees for taking pictures of Peru and, if technically possible, having a wide coverage of South America through maneuvers of 30 degrees in roll (roll) and 30 degrees pitch (pitch).
* Maintain a less demanding pointing accuracy (e.g. 20 degrees) to enable up / down data between the pico-satellite and ground station.
The SDCA enables the pico-satellite to determine its attitude, calculate the correction required to achieve the desired orientation and execute the necessary maneuvers using the actuators. The attitude determination system will use magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, o ...
s, sun sensors and attitude determination algorithms for estimating positions and angular velocities
In physics, angular velocity or rotational velocity ( or ), also known as angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time (i.e. how quickly an object ...
. Using GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
and gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rota ...
s as sensors for determining attitude will also be evaluated. The attitude control system will use electromagnetic coil
An electromagnetic coil is an electrical Electrical conductivity, conductor such as a wire in the shape of a wiktionary:coil, coil (spiral or helix). Electromagnetic coils are used in electrical engineering, in applications where electric curre ...
s and permanent magnets as actuators, forming what are known as magnetorquers. The magnetorquers are especially important for the stabilization of the pico-satellite once it leaves the deployer. The inclusion of the permanent magnet can have a system of active-passive control. More than one control law will be studied for possible implementation. The use of magnetic materials
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...
and hysteretic
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of ...
also be evaluated.
Ground Station – ESTER
 This subsystem is not part of the satellite itself, but its existence and operation is necessary to achieve the objectives of Chasqui I. The set of facilities and wireless communication (radio) needed to communicate with the Chasqui I, and any satellite.
The main functions of this module are:
* Follow-up: radioforo hear the beacon or satellite for its position.
* Telemetry: Request state variables (temperature, voltage, etc..) To monitor and validate the satellite orbit calculation.
* Commando: Order to extend the satellite
This subsystem is not part of the satellite itself, but its existence and operation is necessary to achieve the objectives of Chasqui I. The set of facilities and wireless communication (radio) needed to communicate with the Chasqui I, and any satellite.
The main functions of this module are:
* Follow-up: radioforo hear the beacon or satellite for its position.
* Telemetry: Request state variables (temperature, voltage, etc..) To monitor and validate the satellite orbit calculation.
* Commando: Order to extend the satellite antenna
Antenna ( antennas or antennae) may refer to:
Science and engineering
* Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves
* Antennae Galaxies, the name of two collid ...
; order reset the system, order the taking and sending photos.
System Orbits – SORS
 This module aims to simulate the trajectory of Chasqui I, which is calculated using differential equations of motion, which are then solved in
This module aims to simulate the trajectory of Chasqui I, which is calculated using differential equations of motion, which are then solved in parallel
Parallel is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Computing
* Parallel algorithm
* Parallel computing
* Parallel metaheuristic
* Parallel (software), a UNIX utility for running programs in parallel
* Parallel Sysplex, a cluster of IBM ...
using two programs: Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The oracle ...
and Matlab.
This simulation is accomplished by taking into consideration the following phases:
* Considering the Earth as an inertial reference system, the quadrupole term of the gravitational potential and using Newton's second law, we obtained the equations of motion are nonlinear equations.
* Using the Runge-Kutta of order 4 with the Delphi program to solve the equations of motion energy remaining constant.
* Phase 2 was repeated with the Matlab program and with this software are carried out trajectory simulations Chasqui I.
Module Integration and Testing – MIP
 The module aims to achieve the assembly of components developed by different modules of the project as circuit boards, cameras,
The module aims to achieve the assembly of components developed by different modules of the project as circuit boards, cameras, batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
, antennas, sensors, and magnetorquers A magnetorquer or magnetic torquer (also known as a torque rod) is a satellite system for attitude control, detumbling, and stabilization built from electromagnetic coils. The magnetorquer creates a magnetic dipole that interfaces with an ambient ma ...
.
This goal can be achieved:
* Optimizing surfaces, volumes, masses, finding center of gravity, center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force may ...
.
* Planning and conducting standardized testing requirements.
* Perform field tests planned in the project.
See also
* List of CubeSatsReferences
External links
National University of Engineering
Home of the public university located in Lima Peru.
CTIC – UNI
Center for Information & Communication Technologies (CTIC-UNI).
Project Official Site Chasqui 1
All information relating to the project. {{Use American English, date=January 2014 Student satellites CubeSats