|
Circuit Boards
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers: each of the conductive layers is designed with an artwork pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto and/or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers in the shape designed to accept the component's terminals, generally by means of soldering, to both electrically connect and mechanically fasten them to it. Another manufacturing process adds vias: plated-through holes that allow interconnections between layers. Printed circuit boards are used in nearly all electronic products. Alternatives to PCBs include wire wrap a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEG DVD 430 - Printed Circuit Board-4276
SEG or seg may refer to: Organisations * Society of Economic Geologists * Society of Exploration Geophysicists * Semaphore Entertainment Group, co-founder of the Ultimate Fighting Championship * Southern Examining Group, a former English examining body * Special Escort Group (Metropolitan Police), England * Special Escort Group (Ministry of Defence Police) (SEG (MDP)), UK Other uses * Smart Export Guarantee, a scheme which rewards export of electricity by small-scale low-carbon generators in the United Kingdom * ''Supplementum Epigraphicum Graecum'', new studies of ancient Greek inscriptions * Penn Valley Airport IATA code * ''Ség.'', taxonomic author abbreviation of Jean-François Séguier (1703–1784), French botanist See also * Segment (other) * * * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etching
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types of material. As a method of printmaking, it is, along with engraving, the most important technique for old master prints, and remains in wide use today. In a number of modern variants such as microfabrication etching and photochemical milling it is a crucial technique in much modern technology, including circuit boards. In traditional pure etching, a metal plate (usually of copper, zinc or steel) is covered with a waxy ground which is resistant to acid. The artist then scratches off the ground with a pointed etching needle where the artist wants a line to appear in the finished piece, exposing the bare metal. The échoppe, a tool with a slanted oval section, is also used for "swelling" lines. The plate is then dipped in a bath of aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an educational institution, institution of higher education, higher (or Tertiary education, tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate education, undergraduate and postgraduate education, postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Cledo Brunetti Award
The IEEE Cledo Brunetti Award is an award is presented for outstanding contributions to nanotechnology and miniaturization in the electronics arts. It may be presented to an individual or a team of up to three. The award was established in 1975 by the IEEE Board of Directors. Recipients of this award receive bronze medal, a certificate and honorarium. Basis for judging: In the evaluation process, the following criteria are considered: innovation, development, social value, uniqueness of concept, other technical accomplishments, and the quality of the nomination. Nomination deadline: 31 January Notification: Recipients are typically approved during the June IEEE Board of Directors meeting, usually held towards the end of the month. Recipients and their nominators will be notified following the meeting. Subsequently, the nominators of unsuccessful candidates will be notified of the status of their nomination. Presentation: IEEE policy requires that its awards be presented at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
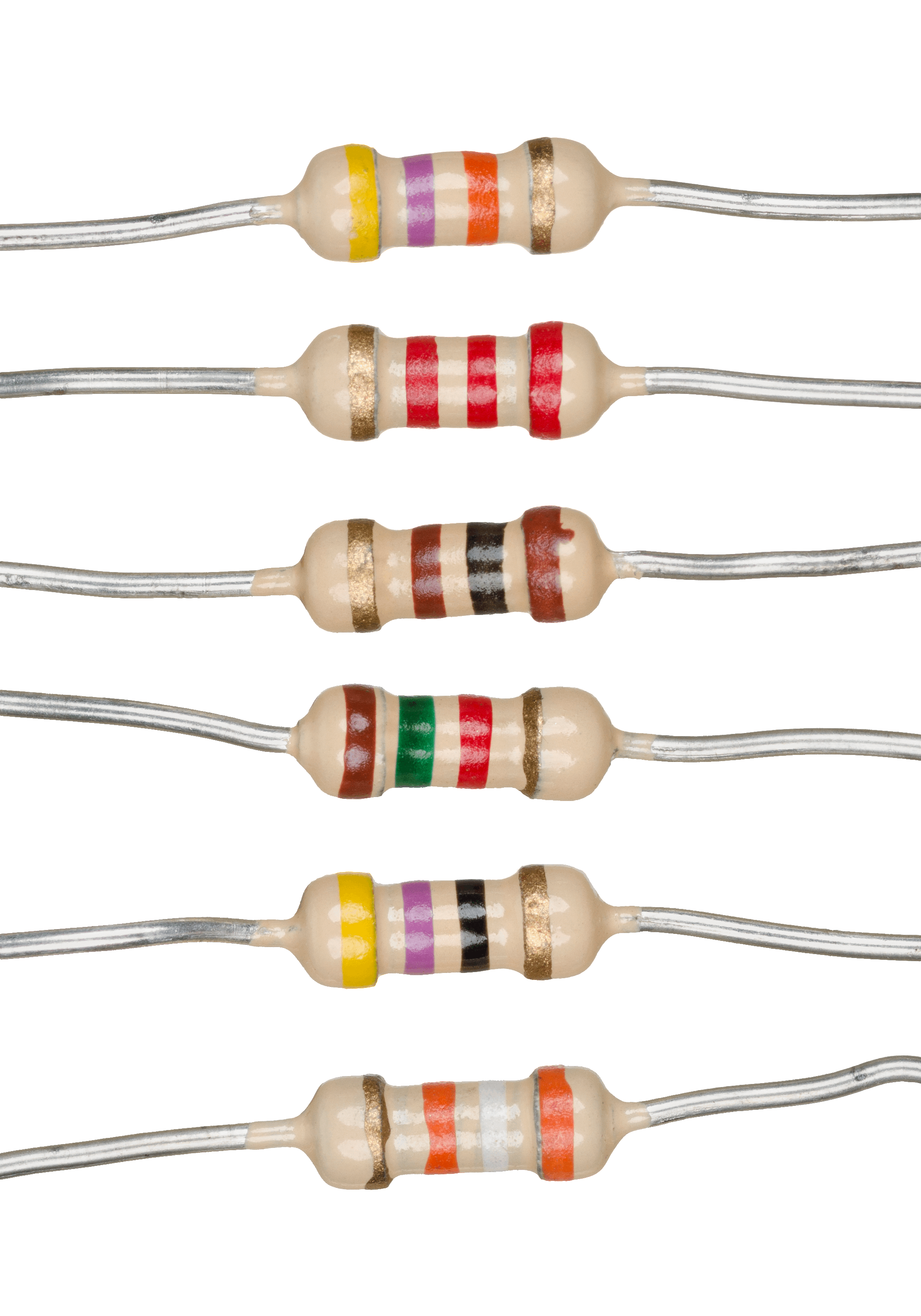
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screenprinting
Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink (or dye) onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact. This causes the ink to wet the substrate and be pulled out of the mesh apertures as the screen springs back after the blade has passed. One colour is printed at a time, so several screens can be used to produce a multi-coloured image or design. Traditionally, silk was used in the process. Currently, synthetic threads are commonly used in the screen printing process. The most popular mesh in general use is made of polyester. There are special-use mesh materials of nylon and stainless steel available to the screen-printer. There are also different types of mesh size which will determine the outcome and look of the fini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximity Fuze
A proximity fuze (or fuse) is a Fuze (munitions), fuze that detonates an Explosive material, explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such as planes, missiles, ships at sea, and ground forces. They provide a more sophisticated trigger mechanism than the common contact fuze or timed fuze. It is estimated that it increases the lethality by 5 to 10 times, compared to these other fuzes. Background Before the invention of the proximity fuze, detonation was induced by direct contact, a timer set at launch or an altimeter. All of these earlier methods have disadvantages. The probability of a direct hit on a small moving target is low; a shell that just misses the target will not explode. A time- or height-triggered fuze requires good prediction by the gunner and accurate timing by the fuze. If either is wrong, then even accurately aimed shells may explode harmlessly before reaching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any vessel or a particular vessel type, akin to anti-infantry vs. anti-vehicle mines. Naval mines can be used offensively, to hamper enemy shipping movements or lock vessels into a harbour; or defensively, to protect friendly vessels and create "safe" zones. Mines allow the minelaying force commander to concentrate warships or defensive assets in mine-free areas giving the adversary three choices: undertake an expensive and time-consuming minesweeping effort, accept the casualties of challenging the minefield, or use the unmined waters where the greatest concentration of enemy firepower will be encountered. Although international law requires signatory nations to declare mined areas, precise locations remain secret; and non-complying individ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Eisler
Paul Eisler (1907 – 26 October 1992, London) was an Austrian inventor born in Vienna. Among his innovations were the printed circuit board. In 2012, ''Printed Circuit Design & Fab'' magazine named its Hall of Fame after Eisler. Early life and education He graduated in engineering from Vienna University of Technology in 1930. Being Jewish, antisemitic German-Nationalist organizations prevented him from getting an engineering job in Vienna, so he obtained employment with the English recording technology firm (Gramaphone Company, EMI from March 1931) operating under its His Master's Voice brand in Belgrade. ; edited with notes by Mari Williams His task there was to eliminate radio interference on the music broadcast system on trains running from Belgrade to Niś. The project was a technical success but a financial failure because the Serbian railroad could only pay HMV by barter in grain, not pounds sterling, due a foreign exchange crisis. As a result, he had to return to Vienna. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCB Design And Realisation Smt And Through Hole
PCB may refer to: Science and technology * Polychlorinated biphenyl, an organic chlorine compound, now recognized as an environmental toxin and classified as a persistent organic pollutant * Printed circuit board, a board used in electronics * Plenum chamber burning, in some jet engines Computing * PCB (software), software to design printed circuit boards * PCBoard, bulletin board software for MS-DOS * Process control block, an operating system data structure Organizations * Pacific Coast Borax Company, an American mining company * Pakistan Cricket Board, national regulatory board for cricket in Pakistan * ''Partido Comunista Bolchevique'', the Bolshevik Communist Party in Mexico in the 1960s * ''Partido Comunista Brasileiro'', the Brazilian Communist Party * ''Partido Comunista de Bolivia'', the Communist Party of Bolivia * PCB Piezotronics, a manufacturer of piezoelectric sensors * Police Complaints Board, in England and Wales Places * Panama City Beach, Florida, US * Pondok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
