CCD imager on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an
 The basis for the CCD is the
The basis for the CCD is the
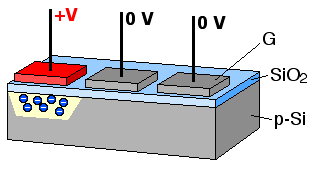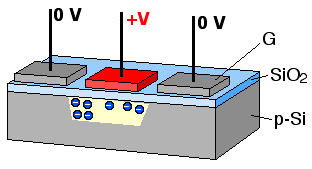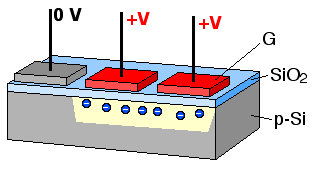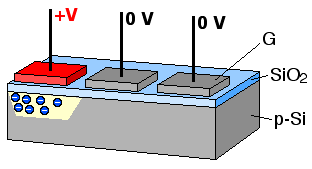 In a CCD for capturing images, there is a photoactive region (an
In a CCD for capturing images, there is a photoactive region (an
 The frame transfer CCD imager was the first imaging structure proposed for CCD Imaging by Michael Tompsett at Bell Laboratories. A frame transfer CCD is a specialized CCD, often used in
The frame transfer CCD imager was the first imaging structure proposed for CCD Imaging by Michael Tompsett at Bell Laboratories. A frame transfer CCD is a specialized CCD, often used in  A frame transfer CCD solves both problems: it has a shielded, not light sensitive, area containing as many cells as the area exposed to light. Typically, this area is covered by a reflective material such as aluminium. When the exposure time is up, the cells are transferred very rapidly to the hidden area. Here, safe from any incoming light, cells can be read out at any speed one deems necessary to correctly measure the cells' charge. At the same time, the exposed part of the CCD is collecting light again, so no delay occurs between successive exposures.
The disadvantage of such a CCD is the higher cost: the cell area is basically doubled, and more complex control electronics are needed.
A frame transfer CCD solves both problems: it has a shielded, not light sensitive, area containing as many cells as the area exposed to light. Typically, this area is covered by a reflective material such as aluminium. When the exposure time is up, the cells are transferred very rapidly to the hidden area. Here, safe from any incoming light, cells can be read out at any speed one deems necessary to correctly measure the cells' charge. At the same time, the exposed part of the CCD is collecting light again, so no delay occurs between successive exposures.
The disadvantage of such a CCD is the higher cost: the cell area is basically doubled, and more complex control electronics are needed.
(Hainaut is an astronomer at th
European Southern Observatory
CCD cameras used in
Journal Article On Basics of CCDs
More statistical properties
{{DEFAULTSORT:Charge-Coupled Device American inventions Integrated circuits Image processing Image sensors Image scanners Astronomical imaging MOSFETs
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge
Electric charge (symbol ''q'', sometimes ''Q'') is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative''. Like charges repel each other and ...
to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging
Digital imaging or digital image acquisition is the creation of a digital representation of the visual characteristics of an object, such as a physical scene or the interior structure of an object. The term is often assumed to imply or include ...
.
Overview
In a CCDimage sensor An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into s ...
, pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
(MOS) capacitors
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
. These MOS capacitor
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
s, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges.
Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required.
In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital camera
A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in Digital data storage, digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Dig ...
s, active pixel sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor, which was invented by Peter J.W. Noble in 1968, where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semico ...
s, also known as CMOS sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor, which was invented by Peter J.W. Noble in 1968, where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semic ...
s (complementary MOS sensors), are generally used.
However, the large quality advantage CCDs enjoyed early on has narrowed over time and since the late 2010s CMOS sensors are the dominant technology, having largely if not completely replaced CCD image sensors.
History
 The basis for the CCD is the
The basis for the CCD is the metal–oxide–semiconductor
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
(MOS) structure, with MOS capacitor
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
s being the basic building blocks of a CCD, and a depleted MOS structure used as the photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical ...
in early CCD devices.
In the late 1960s, Willard Boyle and George E. Smith
George Elwood Smith (May 10, 1930 – May 28, 2025) was an American scientist, applied physicist, and co-inventor of the charge-coupled device (CCD). He was awarded a one-quarter share in the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics for "the invention of an ...
at Bell Labs were researching MOS technology while working on semiconductor bubble memory
Bubble memory is a type of non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory that uses a thin film of a magnetic material to hold small magnetized areas, known as ''bubbles'' or ''domains'', each storing one bit of data. The material is arrange ...
. They realized that an electric charge was the analog of the magnetic bubble and that it could be stored on a tiny MOS capacitor. As it was fairly straightforward to fabricate a series of MOS capacitors in a row, they connected a suitable voltage to them so that the charge could be stepped along from one to the next. This led to the invention of the charge-coupled device by Boyle and Smith in 1969. They conceived of the design of what they termed, in their notebook, "Charge 'Bubble' Devices".See and
The initial paper describing the concept in April 1970 listed possible uses as memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembe ...
, a delay line, and an imaging device. The device could also be used as a shift register
A shift register is a type of digital circuit using a cascade of flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops where the output of one flip-flop is connected to the input of the next. They share a single clock signal, which causes the data stored in the syst ...
. The essence of the design was the ability to transfer charge along the surface of a semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
from one storage capacitor to the next. The concept was similar in principle to the bucket-brigade device
A bucket brigade or bucket-brigade device (BBD) is a discrete-time analogue delay line, developed in 1969 by F. Sangster and K. Teer of the Philips Research Labs in the Netherlands. It consists of a series of capacitance sections C0 to ...
(BBD), which was developed at Philips Research Labs during the late 1960s.
The first experimental device demonstrating the principle was a row of closely spaced metal squares on an oxidized
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
surface electrically accessed by wire bonds. It was demonstrated by Gil Amelio
Gilbert Frank Amelio (born March 1, 1943) is an American technology executive. Amelio worked at Bell Labs, Fairchild Semiconductor, and the semiconductor division of Rockwell International, and was also the CEO of National Semiconductor and Appl ...
, Michael Francis Tompsett and George Smith in April 1970. This was the first experimental application of the CCD in image sensor An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into s ...
technology, and used a depleted MOS structure as the photodetector. The first patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
() on the application of CCDs to imaging was assigned to Tompsett, who filed the application in 1971.
The first working CCD made with integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
technology was a simple 8-bit shift register, reported by Tompsett, Amelio and Smith in August 1970. This device had input and output circuits and was used to demonstrate its use as a shift register and as a crude eight pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
linear imaging device. Development of the device progressed at a rapid rate. By 1971, Bell researchers led by Michael Tompsett were able to capture images with simple linear devices.
Several companies, including Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument by the " traitorous eight" who defected from Shockley Semi ...
, RCA
RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded in 1919 as the Radio Corporation of America. It was initially a patent pool, patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghou ...
and Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
, picked up on the invention and began development programs. Fairchild's effort, led by ex-Bell researcher Gil Amelio, was the first with commercial devices, and by 1974 had a linear 500-element device and a 2D 100 × 100 pixel device. Peter Dillon, a scientist at Kodak Research Labs, invented the first color CCD image sensor by overlaying a color filter array on this Fairchild 100 x 100 pixel Interline CCD starting in 1974. Steven Sasson
Steve J. Sasson is an American electrical engineer and the inventor of the self-contained (portable) digital camera. He joined Kodak shortly after his graduation from engineering school and retired from Kodak in 2001.
Early life and education
S ...
, an electrical engineer working for the Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company, referred to simply as Kodak (), is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in film photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorporated i ...
Apparatus Division, invented a digital still camera using this same Fairchild CCD in 1975.
The interline transfer (ILT) CCD device was proposed by L. Walsh and R. Dyck at Fairchild in 1973 to reduce smear and eliminate a mechanical shutter. To further reduce smear from bright light sources, the frame-interline-transfer (FIT) CCD architecture was developed by K. Horii, T. Kuroda and T. Kunii at Matsushita (now Panasonic) in 1981.
The first KH-11 KENNEN
The KH-11 KENNEN (later renamed CRYSTAL,p.199-200 then Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System, and codenamed 1010 and Key Hole) is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 19 ...
reconnaissance satellite equipped with charge-coupled device array ( pixels) technology for imaging was launched in December 1976. Under the leadership of Kazuo Iwama, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
started a large development effort on CCDs involving a significant investment. Eventually, Sony managed to mass-produce CCDs for their camcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right side, hot-sw ...
s. Before this happened, Iwama died in August 1982. Subsequently, a CCD chip was placed on his tombstone to acknowledge his contribution. The first mass-produced consumer CCD video camera
A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos, as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film. Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of other ...
, the CCD-G5, was released by Sony in 1983, based on a prototype developed by Yoshiaki Hagiwara Yoshiaki Hagiwara (July 4, 1948 – ) is a Japanese scientist, engineer, and inventor who spent his career at Sony developing image sensors and related technologies.
Hagiwara was elected Fellow of the IEEE in 2001, "For pioneering work on, and deve ...
in 1981.
Early CCD sensors suffered from shutter lag
In photography, shutter lag is the delay between triggering the shutter and when the photograph is actually recorded, which includes all lag between when the shutter button is pressed and when the photo is taken, including metering and focus lag. ...
. This was largely resolved with the invention of the pinned photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and me ...
(PPD). It was invented by Nobukazu Teranishi, Hiromitsu Shiraki and Yasuo Ishihara at NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered at the NEC Supertower in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), Inte ...
in 1980. They recognized that lag can be eliminated if the signal carriers could be transferred from the photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and me ...
to the CCD. This led to their invention of the pinned photodiode, a photodetector structure with low lag, low noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
, high quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
and low dark current. It was first publicly reported by Teranishi and Ishihara with A. Kohono, E. Oda and K. Arai in 1982, with the addition of an anti-blooming structure. The new photodetector structure invented at NEC was given the name "pinned photodiode" (PPD) by B.C. Burkey at Kodak in 1984. In 1987, the PPD began to be incorporated into most CCD devices, becoming a fixture in consumer electronic
Consumer electronics, also known as home electronics, are electronic devices intended for everyday household use. Consumer electronics include those used for entertainment, communications, and recreation. Historically, these products were refer ...
video cameras
A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos, as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film. Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of other ...
and then digital still cameras. Since then, the PPD has been used in nearly all CCD sensors and then CMOS sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor, which was invented by Peter J.W. Noble in 1968, where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semic ...
s.
In January 2006, Boyle and Smith were awarded the National Academy of Engineering
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American Nonprofit organization, nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. It is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), along with the National Academ ...
Charles Stark Draper Prize
The U.S. National Academy of Engineering annually awards the Draper Prize, which is given for the advancement of engineering and the education of the public about engineering. It is one of three prizes that constitute the "Nobel Prizes of Enginee ...
, and in 2009 they were awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prize, Nobel Prizes establi ...
for their invention of the CCD concept. Michael Tompsett was awarded the 2010 National Medal of Technology and Innovation
The National Medal of Technology and Innovation (formerly the National Medal of Technology) is an honor granted by the president of the United States to American inventors and innovators who have made significant contributions to the development ...
, for pioneering work and electronic technologies including the design and development of the first CCD imagers. He was also awarded the 2012 IEEE Edison Medal
The IEEE Edison Medal is presented by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) "for a career of meritorious achievement in electrical science, electrical engineering, or the electrical arts." It is the oldest medal in this fi ...
for "pioneering contributions to imaging devices including CCD Imagers, cameras and thermal imagers".
Basics of operation
 In a CCD for capturing images, there is a photoactive region (an
In a CCD for capturing images, there is a photoactive region (an epitaxial
Epitaxy (prefix ''epi-'' means "on top of”) is a type of crystal growth or material deposition in which new crystalline layers are formed with one or more well-defined orientations with respect to the crystalline seed layer. The deposited cry ...
layer of silicon), and a transmission region made out of a shift register
A shift register is a type of digital circuit using a cascade of flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops where the output of one flip-flop is connected to the input of the next. They share a single clock signal, which causes the data stored in the syst ...
(the CCD, properly speaking).
An image is projected through a lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
onto the capacitor array (the photoactive region), causing each capacitor to accumulate an electric charge proportional to the light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
intensity at that location. A one-dimensional array, used in line-scan cameras, captures a single slice of the image, whereas a two-dimensional array, used in video and still cameras, captures a two-dimensional picture corresponding to the scene projected onto the focal plane of the sensor. Once the array has been exposed to the image, a control circuit causes each capacitor to transfer its contents to its neighbor (operating as a shift register). The last capacitor in the array dumps its charge into a charge amplifier
A charge amplifier is an electronic electric current, current integrator that produces a voltage output proportional to the integrated value of the input current, or the total charge injected.
The amplifier offsets the input current using a feed ...
, which converts the charge into a voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
. By repeating this process, the controlling circuit converts the entire contents of the array in the semiconductor to a sequence of voltages. In a digital device, these voltages are then sampled, digitized, and usually stored in memory; in an analog device (such as an analog video camera), they are processed into a continuous analog signal (e.g. by feeding the output of the charge amplifier into a low-pass filter), which is then processed and fed out to other circuits for transmission, recording, or other processing.
Detailed physics of operation
Charge generation
Before the MOS capacitors are exposed to light, they are biased into the depletion region; in n-channel CCDs, the silicon under the bias gate is slightly ''p''-doped or intrinsic. The gate is then biased at a positive potential, above the threshold for strong inversion, which will eventually result in the creation of an ''n'' channel below the gate as in aMOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
. However, it takes time to reach this thermal equilibrium: up to hours in high-end scientific cameras cooled at low temperature. Initially after biasing, the holes are pushed far into the substrate, and no mobile electrons are at or near the surface; the CCD thus operates in a non-equilibrium state called deep depletion. Chapter 13.6.
Then, when electron–hole pair
In solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fund ...
s are generated in the depletion region, they are separated by the electric field, the electrons move toward the surface, and the holes move toward the substrate. Four pair-generation processes can be identified:
* photo-generation (up to 95% of quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
),
* generation in the depletion region,
* generation at the surface, and
* generation in the neutral bulk.
The last three processes are known as dark-current generation, and add noise to the image; they can limit the total usable integration time. The accumulation of electrons at or near the surface can proceed either until image integration is over and charge begins to be transferred, or thermal equilibrium is reached. In this case, the well is said to be full. The maximum capacity of each well is known as the well depth, typically about 105 electrons per pixel. CCDs are normally susceptible to ionizing radiation and energetic particles which causes noise in the output of the CCD, and this must be taken into consideration in satellites using CCDs.
Design and manufacturing
The photoactive region of a CCD is, generally, anepitaxial
Epitaxy (prefix ''epi-'' means "on top of”) is a type of crystal growth or material deposition in which new crystalline layers are formed with one or more well-defined orientations with respect to the crystalline seed layer. The deposited cry ...
layer of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
. It is lightly ''p'' doped (usually with boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three ...
) and is grown upon a substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (aquatic environment), the earthy material that exi ...
material, often p++. In buried-channel devices, the type of design utilized in most modern CCDs, certain areas of the surface of the silicon are ion implanted with phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
, giving them an n-doped designation. This region defines the channel in which the photogenerated charge packets will travel. Simon Sze
Simon Min Sze, or Shi Min (; 21 March 1936 – 6 November 2023), was a Taiwanese-American electrical engineer. He is best known for inventing the floating-gate MOSFET with Korean electrical engineer Dawon Kahng in 1967.
Early life and educat ...
details the advantages of a buried-channel device:
This thin layer (= 0.2–0.3 micron) is fully depleted and the accumulated photogenerated charge is kept away from the surface. This structure has the advantages of higher transfer efficiency and lower dark current, from reduced surface recombination. The penalty is smaller charge capacity, by a factor of 2–3 compared to the surface-channel CCD.The gate oxide, i.e. the
capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator that can be Polarisability, polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric ...
, is grown on top of the epitaxial layer and substrate.
Later in the process, polysilicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry.
Polysilicon is produ ...
gates are deposited by chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high-quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (electro ...
, patterned with photolithography
Photolithography (also known as optical lithography) is a process used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. It involves using light to transfer a pattern onto a substrate, typically a silicon wafer.
The process begins with a photosensiti ...
, and etched in such a way that the separately phased gates lie perpendicular to the channels. The channels are further defined by utilization of the LOCOS
''Locos: A Comedy of Gestures'' is the first novel of Spanish-born American writer Felipe Alfau (1902–1999), written in 1928 and published in 1936. The metafictional novel remained out of print until 1988 when it was reprinted by Dalkey Arch ...
process to produce the channel stop region.
Channel stops are thermally grown oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s that serve to isolate the charge packets in one column from those in another. These channel stops are produced before the polysilicon gates are, as the LOCOS process utilizes a high-temperature step that would destroy the gate material. The channel stops are parallel to, and exclusive of, the channel, or "charge carrying", regions.
Channel stops often have a p+ doped region underlying them, providing a further barrier to the electrons in the charge packets (this discussion of the physics of CCD devices assumes an electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
transfer device, though hole transfer is possible).
The clocking of the gates, alternately high and low, will forward and reverse bias the diode that is provided by the buried channel (n-doped) and the epitaxial layer (p-doped). This will cause the CCD to deplete, near the p–n junction and will collect and move the charge packets beneath the gates—and within the channels—of the device.
CCD manufacturing and operation can be optimized for different uses. The above process describes a frame transfer CCD. While CCDs may be manufactured on a heavily doped p++ wafer it is also possible to manufacture a device inside p-wells that have been placed on an n-wafer. This second method, reportedly, reduces smear, dark current, and infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
and red response. This method of manufacture is used in the construction of interline-transfer devices.
Another version of CCD is called a peristaltic CCD. In a peristaltic charge-coupled device, the charge-packet transfer operation is analogous to the peristaltic contraction and dilation of the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
. The peristaltic CCD has an additional implant that keeps the charge away from the silicon/silicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundan ...
interface and generates a large lateral electric field from one gate to the next. This provides an additional driving force to aid in transfer of the charge packets.
Architecture
The CCD image sensors can be implemented in several different architectures. The most common are full-frame, frame-transfer, and interline. The distinguishing characteristic of each of these architectures is their approach to the problem of shuttering. In a full-frame device, all of the image area is active, and there is no electronic shutter. A mechanical shutter must be added to this type of sensor or the image smears as the device is clocked or read out. With a frame-transfer CCD, half of the silicon area is covered by an opaque mask (typically aluminum). The image can be quickly transferred from the image area to the opaque area or storage region with acceptable smear of a few percent. That image can then be read out slowly from the storage region while a new image is integrating or exposing in the active area. Frame-transfer devices typically do not require a mechanical shutter and were a common architecture for early solid-state broadcast cameras. The downside to the frame-transfer architecture is that it requires twice the silicon real estate of an equivalent full-frame device; hence, it costs roughly twice as much. The interline architecture extends this concept one step further and masks every other column of the image sensor for storage. In this device, only one pixel shift has to occur to transfer from image area to storage area; thus, shutter times can be less than a microsecond and smear is essentially eliminated. The advantage is not free, however, as the imaging area is now covered by opaque strips dropping the fill factor to approximately 50 percent and the effectivequantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
by an equivalent amount. Modern designs have addressed this deleterious characteristic by adding microlenses on the surface of the device to direct light away from the opaque regions and on the active area. Microlenses can bring the fill factor back up to 90 percent or more depending on pixel size and the overall system's optical design.
The choice of architecture comes down to one of utility. If the application cannot tolerate an expensive, failure-prone, power-intensive mechanical shutter, an interline device is the right choice. Consumer snap-shot cameras have used interline devices. On the other hand, for those applications that require the best possible light collection and issues of money, power and time are less important, the full-frame device is the right choice. Astronomers tend to prefer full-frame devices. The frame-transfer falls in between and was a common choice before the fill-factor issue of interline devices was addressed. Today, frame-transfer is usually chosen when an interline architecture is not available, such as in a back-illuminated device.
CCDs containing grids of pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s are used in digital camera
A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in Digital data storage, digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Dig ...
s, optical scanners, and video cameras as light-sensing devices. They commonly respond to 70 percent of the incident light (meaning a quantum efficiency of about 70 percent) making them far more efficient than photographic film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin photographic emulsion, emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the ...
, which captures only about 2 percent of the incident light.
Most common types of CCDs are sensitive to near-infrared light, which allows infrared photography
In infrared photography, the photographic film or image sensor used is sensitive to infrared light. The part of the spectrum used is referred to as near-infrared to distinguish it from far-infrared, which is the domain of thermal imaging. Wav ...
, night-vision devices, and zero lux
The lux (symbol: lx) is the unit of illuminance, or luminous flux per unit area, in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to one lumen per square metre. In photometry, this is used as a measure of the irradiance, as perceived by ...
(or near zero lux) video-recording/photography. For normal silicon-based detectors, the sensitivity is limited to 1.1 μm. One other consequence of their sensitivity to infrared is that infrared from remote control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operat ...
s often appears on CCD-based digital cameras or camcorders if they do not have infrared blockers.
Cooling reduces the array's dark current, improving the sensitivity of the CCD to low light intensities, even for ultraviolet and visible wavelengths. Professional observatories often cool their detectors with liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is nitrogen in a liquid state at cryogenics, low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, mobile liquid whose vis ...
to reduce the dark current, and therefore the thermal noise
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
, to negligible levels.
Frame transfer CCD
 The frame transfer CCD imager was the first imaging structure proposed for CCD Imaging by Michael Tompsett at Bell Laboratories. A frame transfer CCD is a specialized CCD, often used in
The frame transfer CCD imager was the first imaging structure proposed for CCD Imaging by Michael Tompsett at Bell Laboratories. A frame transfer CCD is a specialized CCD, often used in astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
and some professional video camera
A professional video camera (often called a television camera even though its use has spread beyond television) is a high-end device for creating electronic moving images (as opposed to a movie camera, that earlier recorded the images on film). O ...
s, designed for high exposure efficiency and correctness.
The normal functioning of a CCD, astronomical or otherwise, can be divided into two phases: exposure and readout. During the first phase, the CCD passively collects incoming photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s, storing electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s in its cells. After the exposure time is passed, the cells are read out one line at a time. During the readout phase, cells are shifted down the entire area of the CCD. While they are shifted, they continue to collect light. Thus, if the shifting is not fast enough, errors can result from light that falls on a cell holding charge during the transfer. These errors are referred to as rolling shutter effect
Rolling shutter describes the process of image capture in which a still picture (in a still camera) or each frame of a video (in a video camera) is captured not by taking a snapshot of the entire scene at a single instant in time but rather b ...
, making fast moving objects appear distorted. In addition, the CCD cannot be used to collect light while it is being read out. A faster shifting requires a faster readout, and a faster readout can introduce errors in the cell charge measurement, leading to a higher noise level.
 A frame transfer CCD solves both problems: it has a shielded, not light sensitive, area containing as many cells as the area exposed to light. Typically, this area is covered by a reflective material such as aluminium. When the exposure time is up, the cells are transferred very rapidly to the hidden area. Here, safe from any incoming light, cells can be read out at any speed one deems necessary to correctly measure the cells' charge. At the same time, the exposed part of the CCD is collecting light again, so no delay occurs between successive exposures.
The disadvantage of such a CCD is the higher cost: the cell area is basically doubled, and more complex control electronics are needed.
A frame transfer CCD solves both problems: it has a shielded, not light sensitive, area containing as many cells as the area exposed to light. Typically, this area is covered by a reflective material such as aluminium. When the exposure time is up, the cells are transferred very rapidly to the hidden area. Here, safe from any incoming light, cells can be read out at any speed one deems necessary to correctly measure the cells' charge. At the same time, the exposed part of the CCD is collecting light again, so no delay occurs between successive exposures.
The disadvantage of such a CCD is the higher cost: the cell area is basically doubled, and more complex control electronics are needed.
Intensified charge-coupled device
An intensified charge-coupled device (ICCD) is a CCD that is optically connected to an image intensifier that is mounted in front of the CCD. An image intensifier includes three functional elements: aphotocathode
A photocathode is a surface engineered to convert light (photons) into electrons using the photoelectric effect. Photocathodes are important in accelerator physics where they are utilised in a photoinjector to generate high brightness electron ...
, a micro-channel plate
A microchannel plate (MCP) is used to detect single particles (electrons, ions and neutrons) and photons (ultraviolet radiation and X-rays). It is closely related to an electron multiplier, as both intensify single particles or photons by the mul ...
(MCP) and a phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
screen. These three elements are mounted one close behind the other in the mentioned sequence. The photons which are coming from the light source fall onto the photocathode, thereby generating photoelectrons. The photoelectrons are accelerated towards the MCP by an electrical control voltage, applied between photocathode and MCP. The electrons are multiplied inside of the MCP and thereafter accelerated towards the phosphor screen. The phosphor screen finally converts the multiplied electrons back to photons which are guided to the CCD by a fiber optic or a lens.
An image intensifier inherently includes a shutter functionality: If the control voltage between the photocathode and the MCP is reversed, the emitted photoelectrons are not accelerated towards the MCP but return to the photocathode. Thus, no electrons are multiplied and emitted by the MCP, no electrons are going to the phosphor screen and no light is emitted from the image intensifier. In this case no light falls onto the CCD, which means that the shutter is closed. The process of reversing the control voltage at the photocathode is called ''gating'' and therefore ICCDs are also called gateable CCD cameras.
Besides the extremely high sensitivity of ICCD cameras, which enable single photon detection, the gateability is one of the major advantages of the ICCD over the EMCCD cameras. The highest performing ICCD cameras enable shutter times as short as 200 picoseconds.
ICCD cameras are in general somewhat higher in price than EMCCD cameras because they need the expensive image intensifier. On the other hand, EMCCD cameras need a cooling system to cool the EMCCD chip down to temperatures around . This cooling system adds additional costs to the EMCCD camera and often yields heavy condensation problems in the application.
ICCDs are used in night vision devices and in various scientific applications.
Electron-multiplying CCD
An electron-multiplying CCD (EMCCD, also known as an L3Vision CCD, a product commercialized by e2v Ltd., GB, L3CCD or Impactron CCD, a now-discontinued product offered in the past by Texas Instruments) is a charge-coupled device in which a gain register is placed between the shift register and the output amplifier. The gain register is split up into a large number of stages. In each stage, the electrons are multiplied byimpact ionization
Impact ionization is the process in a material by which one energetic charge carrier can lose energy by the creation of other charge carriers. For example, in semiconductors, an electron (or hole) with enough kinetic energy can knock a bound elec ...
in a similar way to an avalanche diode
In electronics, an avalanche diode is a diode (made from silicon or other semiconductor) that is designed to experience avalanche breakdown at a specified reverse bias voltage. The junction of an avalanche diode is designed to prevent current co ...
. The gain probability at every stage of the register is small (''P'' < 2%), but as the number of elements is large (N > 500), the overall gain can be very high (), with single input electrons giving many thousands of output electrons. Reading a signal from a CCD gives a noise background, typically a few electrons. In an EMCCD, this noise is superimposed on many thousands of electrons rather than a single electron; the devices' primary advantage is thus their negligible readout noise. The use of avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown (or the avalanche effect) is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwis ...
for amplification of photo charges had already been described in the in 1973 by George E. Smith/Bell Telephone Laboratories.
EMCCDs show a similar sensitivity to intensified CCDs (ICCDs). However, as with ICCDs, the gain that is applied in the gain register is stochastic and the ''exact'' gain that has been applied to a pixel's charge is impossible to know. At high gains (> 30), this uncertainty has the same effect on the signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to noise power, often expressed in deci ...
(SNR) as halving the quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
(QE) with respect to operation with a gain of unity. This effect is referred to as the Excess Noise Factor (ENF). However, at very low light levels (where the quantum efficiency is most important), it can be assumed that a pixel either contains an electron—or not. This removes the noise associated with the stochastic multiplication at the risk of counting multiple electrons in the same pixel as a single electron. To avoid multiple counts in one pixel due to coincident photons in this mode of operation, high frame rates are essential. The dispersion in the gain is shown in the graph on the right. For multiplication registers with many elements and large gains it is well modelled by the equation:
where ''P'' is the probability of getting ''n'' output electrons given ''m'' input electrons and a total mean multiplication register gain of ''g''. For very large numbers of input electrons, this complex distribution function converges towards a Gaussian.
Because of the lower costs and better resolution, EMCCDs are capable of replacing ICCDs in many applications. ICCDs still have the advantage that they can be gated very fast and thus are useful in applications like range-gated imaging. EMCCD cameras indispensably need a cooling system—using either thermoelectric cooling
Thermoelectric cooling uses the Peltier effect to create a heat flux at the junction of two different types of materials. A Peltier cooler, heater, or thermoelectric heat pump is a Solid-state physics, solid-state active heat pump which transfers ...
or liquid nitrogen—to cool the chip down to temperatures in the range of . This cooling system adds additional costs to the EMCCD imaging system and may yield condensation problems in the application. However, high-end EMCCD cameras are equipped with a permanent hermetic vacuum system confining the chip to avoid condensation issues.
The low-light capabilities of EMCCDs find use in astronomy and biomedical research, among other fields. In particular, their low noise at high readout speeds makes them very useful for a variety of astronomical applications involving low light sources and transient events such as lucky imaging
Lucky imaging (also called lucky exposures) is one form of speckle imaging used for astrophotography. Speckle imaging techniques use a high-speed camera with shutter speed, exposure times short enough (100 ms or less) so that the changes in ...
of faint stars, high speed photon counting
Photon counting is a technique in which individual photons are counted using a single-photon detector (SPD). A single-photon detector emits a pulse of signal for each detected photon. The counting efficiency is determined by the quantum efficienc ...
photometry, Fabry-Pérot spectroscopy and high-resolution spectroscopy. More recently, these types of CCDs have broken into the field of biomedical research in low-light applications including small animal imaging, single-molecule imaging, Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after physicist C. V. Raman) is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Ra ...
, super resolution microscopy
Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have resolutions higher than those imposed by the diffraction limit, which is due to the diffraction of light. Super-resolution imaging techni ...
as well as a wide variety of modern fluorescence microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. A fluorescence micro ...
techniques thanks to greater SNR in low-light conditions in comparison with traditional CCDs and ICCDs.
In terms of noise, commercial EMCCD cameras typically have clock-induced charge (CIC) and dark current (dependent on the extent of cooling) that together lead to an effective readout noise ranging from 0.01 to 1 electrons per pixel read. However, recent improvements in EMCCD technology have led to a new generation of cameras capable of producing significantly less CIC, higher charge transfer efficiency and an EM gain 5 times higher than what was previously available. These advances in low-light detection lead to an effective total background noise of 0.001 electrons per pixel read, a noise floor unmatched by any other low-light imaging device.
Use in astronomy
Due to the high quantum efficiencies of charge-coupled device (CCD) (the idealquantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
is 100%, one generated electron per incident photon), linearity of their outputs, ease of use compared to photographic plates, and a variety of other reasons, CCDs were very rapidly adopted by astronomers for nearly all UV-to-infrared applications.
Thermal noise and cosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
s may alter the pixels in the CCD array. To counter such effects, astronomers take several exposures with the CCD shutter closed and opened. The average of images taken with the shutter closed is necessary to lower the random noise. Once developed, the dark frame average image is then subtracted from the open-shutter image to remove the dark current and other systematic defects (dead pixel
A defective pixel or a dead pixel is a pixel on a liquid crystal display (LCD) that is not functioning properly. The International Organization for Standardization, ISO standard ISO 13406-2 distinguishes between three different types of defectiv ...
s, hot pixels, etc.) in the CCD. Newer Skipper CCDs counter noise by collecting data with the same collected charge multiple times and has applications in precision light Dark Matter
In astronomy, dark matter is an invisible and hypothetical form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is implied by gravity, gravitational effects that cannot be explained by general relat ...
searches and neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is an elementary particle that interacts via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that i ...
measurements.
The Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
, in particular, has a highly developed series of steps ("data reduction pipeline") to convert the raw CCD data to useful images.
(Hainaut is an astronomer at th
European Southern Observatory
CCD cameras used in
astrophotography
Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1839, but it was no ...
often require sturdy mounts to cope with vibrations from wind and other sources, along with the tremendous weight of most imaging platforms. To take long exposures of galaxies and nebulae, many astronomers use a technique known as auto-guiding. Most autoguiders use a second CCD chip to monitor deviations during imaging. This chip can rapidly detect errors in tracking and command the mount motors to correct for them.
An unusual astronomical application of CCDs, called drift-scanning, uses a CCD to make a fixed telescope behave like a tracking telescope and follow the motion of the sky. The charges in the CCD are transferred and read in a direction parallel to the motion of the sky, and at the same speed. In this way, the telescope can image a larger region of the sky than its normal field of view. The Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-spectral imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project began in 2000 a ...
is the most famous example of this, using the technique to produce a survey of over a quarter of the sky. The Gaia space telescope is another instrument operating in this mode, rotating about its axis at a constant rate of 1 revolution in 6 hours and scanning a 360° by 0.5° strip on the sky during this time; a star traverses the entire focal plane in about 40 seconds (effective exposure time).
In addition to imagers, CCDs are also used in an array of analytical instrumentation including spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure Spectrum, spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomeno ...
s and interferometers.
Color cameras
Digital color cameras, including the digital color cameras in smartphones, generally use an integral color image sensor, which has a color filter array fabricated on top of the monochrome pixels of the CCD. The most popular CFA pattern is known as theBayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color model, RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digit ...
, which is named for its inventor, Kodak scientist Bryce Bayer. In the Bayer pattern, each square of four pixels has one filtered red, one blue, and two green pixels (the human eye
The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to light, visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and Balance (ability), keeping balance.
The eye can be considered as a living ...
has greater acuity for luminance, which is more heavily weighted in green than in either red or blue). As a result, the luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls wit ...
information is collected in each row and column using a checkerboard pattern, and the color resolution is lower than the luminance resolution.
Better color separation can be reached by three-CCD devices (3CCD
A three-CCD (3CCD) camera is a camera whose imaging system uses three separate charge-coupled devices (CCDs), each one receiving filtered red, green, or blue color ranges. Light coming in from the lens is split by a beam-splitter prism into ...
) and a dichroic beam splitter prism, that splits the image
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be di ...
into red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–750 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a seconda ...
, green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a com ...
and blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB color model, RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB color model, RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between Violet (color), violet and cyan on the optical spe ...
components. Each of the three CCDs is arranged to respond to a particular color. Many professional video camcorders, and some semi-professional camcorders, use this technique, although developments in competing CMOS technology have made CMOS sensors, both with beam-splitters and Bayer filters, increasingly popular in high-end video and digital cinema cameras. Another advantage of 3CCD over a Bayer mask device is higher quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
(higher light sensitivity), because most of the light from the lens enters one of the silicon sensors, while a Bayer mask absorbs a high proportion (more than 2/3) of the light falling on each pixel location.
For still scenes, for instance in microscopy, the resolution of a Bayer mask device can be enhanced by microscanning Microscanning is a method for increasing resolution of digital cameras. With the color co-site sampling identically colored pixels in several frames of the specimen, obtained by moving the sensor with a piezo mechanism in a regular raster, are c ...
technology. During the process of color co-site sampling
Colour co-site sampling is a system of photographic colour sensing, wherein 4, 16 or 36 images are collected from the sensor and merged to form a single image. Each subsequent image physically moves the sensor by exactly one pixel, in order to col ...
, several frames of the scene are produced. Between acquisitions, the sensor is moved in pixel dimensions, so that each point in the visual field is acquired consecutively by elements of the mask that are sensitive to the red, green, and blue components of its color. Eventually every pixel in the image has been scanned at least once in each color and the resolution of the three channels become equivalent (the resolutions of red and blue channels are quadrupled while the green channel is doubled).
Sensor sizes
Sensors (CCD / CMOS) come in various sizes, or image sensor formats. These sizes are often referred to with an inch fraction designation such as 1/1.8″ or 2/3″ called theoptical format Optical format is a hypothetical measurement approximately 50% larger than the true diagonal size of a solid-state photo sensor. The use of the optical format means that a lens used with a particular size sensor will have approximately the same a ...
. This measurement originates back in the 1950s and the time of Vidicon tubes.
Blooming
When a CCD exposure is long enough, eventually the electrons that collect in the "bins" in the brightest part of the image will overflow the bin, resulting in blooming. The structure of the CCD allows the electrons to flow more easily in one direction than another, resulting in vertical streaking. Some anti-blooming features that can be built into a CCD reduce its sensitivity to light by using some of the pixel area for a drain structure. James M. Early developed a vertical anti-blooming drain that would not detract from the light collection area, and so did not reduce light sensitivity.See also
References
External links
Journal Article On Basics of CCDs
More statistical properties
{{DEFAULTSORT:Charge-Coupled Device American inventions Integrated circuits Image processing Image sensors Image scanners Astronomical imaging MOSFETs