Brunei Districts English on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak. It is separated into two parts by the Sarawak district of Limbang. Brunei is the only sovereign state entirely on Borneo; the remainder of the island is divided between Malaysia and Indonesia. , its population was 460,345, of whom about 100,000 live in the
Comparative Analysis of Documents about the Bornean Settlement Tradition By Talaguit Christian Jeo N. One of the earliest Chinese records of an independent kingdom in Borneo is the 977 AD letter to the Chinese emperor from the ruler of Boni, which some scholars believe to refer to Borneo. The Bruneians regained their independence from Srivijaya due to the onset of a Javanese-Sumatran war. In 1225, the Chinese official Zhao Rukuo reported that Boni had 100 warships to protect its trade, and that there was great wealth in the kingdom. Marco Polo suggested in his memoirs that the Great Khan or the ruler of the Mongol Empire, attempted and failed many times in invading "Great Java" which was the European name for Bruneian controlled Borneo. In the 1300s the Chinese annals, ''Nanhai zhi'', reported that Brunei invaded or administered Sarawak and Sabah as well as the Philippine kingdoms of Butuan,
 Brunei briefly rose to prominence in Southeast Asia when the Portuguese occupied
Brunei briefly rose to prominence in Southeast Asia when the Portuguese occupied  In March 1578, a fresh Spanish fleet had arrived from Mexico and settled at the Philippines, they were led by De Sande, acting as
In March 1578, a fresh Spanish fleet had arrived from Mexico and settled at the Philippines, they were led by De Sande, acting as
 The British have intervened in the affairs of Brunei on several occasions. Britain attacked Brunei in July 1846 due to internal conflicts over who was the rightful Sultan.
In the 1880s, the decline of the Bruneian Empire continued. The sultan granted land (now Sarawak) to James Brooke, who had helped him quell a rebellion, and allowed him to establish the Raj of Sarawak. Over time, Brooke and his nephews (who succeeded him) leased or annexed more land. Brunei lost much of its territory to him and his dynasty, known as the White Rajahs.
Sultan Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin appealed to the British to stop further encroachment by the Brookes. The "Treaty of Protection" was negotiated by Sir Hugh Low and signed into effect on 17 September 1888. The treaty said that the sultan "could not cede or lease any territory to foreign powers without British consent"; it provided Britain effective control over Brunei's external affairs, making it a British protected state (which continued until 1984). But, when the Raj of Sarawak annexed Brunei's Pandaruan District in 1890, the British did not take any action to stop it. They did not regard either Brunei or the Raj of Sarawak as 'foreign' (per the Treaty of Protection). This final annexation by Sarawak left Brunei with its current small land mass and separation into two parts.
British residents were introduced in Brunei under the Supplementary Protectorate Agreement in 1906. The residents were to advise the sultan on all matters of administration. Over time, the resident assumed more executive control than the sultan. The residential system ended in 1959.
The British have intervened in the affairs of Brunei on several occasions. Britain attacked Brunei in July 1846 due to internal conflicts over who was the rightful Sultan.
In the 1880s, the decline of the Bruneian Empire continued. The sultan granted land (now Sarawak) to James Brooke, who had helped him quell a rebellion, and allowed him to establish the Raj of Sarawak. Over time, Brooke and his nephews (who succeeded him) leased or annexed more land. Brunei lost much of its territory to him and his dynasty, known as the White Rajahs.
Sultan Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin appealed to the British to stop further encroachment by the Brookes. The "Treaty of Protection" was negotiated by Sir Hugh Low and signed into effect on 17 September 1888. The treaty said that the sultan "could not cede or lease any territory to foreign powers without British consent"; it provided Britain effective control over Brunei's external affairs, making it a British protected state (which continued until 1984). But, when the Raj of Sarawak annexed Brunei's Pandaruan District in 1890, the British did not take any action to stop it. They did not regard either Brunei or the Raj of Sarawak as 'foreign' (per the Treaty of Protection). This final annexation by Sarawak left Brunei with its current small land mass and separation into two parts.
British residents were introduced in Brunei under the Supplementary Protectorate Agreement in 1906. The residents were to advise the sultan on all matters of administration. Over time, the resident assumed more executive control than the sultan. The residential system ended in 1959.
 The Japanese invaded Brunei on 16 December 1941, eight days after their attack on Pearl Harbor and the United States Navy. They landed 10,000 troops of the Kawaguchi Detachment from Cam Ranh Bay at Kuala Belait. After six days' fighting, they occupied the entire country. The only Allied troops in the area were the 2nd Battalion of the
The Japanese invaded Brunei on 16 December 1941, eight days after their attack on Pearl Harbor and the United States Navy. They landed 10,000 troops of the Kawaguchi Detachment from Cam Ranh Bay at Kuala Belait. After six days' fighting, they occupied the entire country. The only Allied troops in the area were the 2nd Battalion of the  During the occupation, the Japanese had their language taught in schools, and Government officers were required to learn Japanese. The local currency was replaced by what was to become known as ''duit pisang'' (banana money). From 1943 hyper-inflation destroyed the currency's value and, at the end of the war, this currency was worthless. Allied attacks on shipping eventually caused trade to cease. Food and medicine fell into short supply, and the population suffered from famine and disease.
The airport runway was constructed by the Japanese during the occupation, and in 1943 Japanese naval units were based in
During the occupation, the Japanese had their language taught in schools, and Government officers were required to learn Japanese. The local currency was replaced by what was to become known as ''duit pisang'' (banana money). From 1943 hyper-inflation destroyed the currency's value and, at the end of the war, this currency was worthless. Allied attacks on shipping eventually caused trade to cease. Food and medicine fell into short supply, and the population suffered from famine and disease.
The airport runway was constructed by the Japanese during the occupation, and in 1943 Japanese naval units were based in  On 10 June 1945, the Australian 9th Division landed at Muara under
On 10 June 1945, the Australian 9th Division landed at Muara under
 In July 1953, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III formed a seven-member committee named ''Tujuh Serangkai'', to determine the citizens' views regarding a written constitution for Brunei. In May 1954, the Sultan, Resident and High Commissioner met to discuss the findings of the committee. They agreed to authorise the drafting of a constitution. In March 1959, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III led a delegation to London to discuss the proposed Constitution. The British delegation was led by Sir
In July 1953, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III formed a seven-member committee named ''Tujuh Serangkai'', to determine the citizens' views regarding a written constitution for Brunei. In May 1954, the Sultan, Resident and High Commissioner met to discuss the findings of the committee. They agreed to authorise the drafting of a constitution. In March 1959, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III led a delegation to London to discuss the proposed Constitution. The British delegation was led by Sir
 The plan also aided the development of public education. By 1958, expenditure on education totalled at $4 million. Communications were improved, as new roads were built and reconstruction at Berakas Airport was completed in 1954.
The second National Development Plan was launched in 1962. A major oil and gas field was discovered in 1963. Developments in the oil and gas sector have continued, and oil production has steadily increased since then. The plan also promoted the production of meat and eggs for consumption by citizens. The fishing industry increased its output by 25% throughout the course of the plan. The deepwater port at Muara was also constructed during this period. Power requirements were met, and studies were made to provide electricity to rural areas. Efforts were made to eradicate malaria, an endemic disease in the region, with the help of the World Health Organization. Malaria cases were reduced from 300 cases in 1953 to only 66 cases in 1959. The death rate was reduced from 20 per thousand in 1947 to 11.3 per thousand in 1953. Infectious disease has been prevented by public sanitation and improvement of drainage, and the provision of piped pure water to the population.
The plan also aided the development of public education. By 1958, expenditure on education totalled at $4 million. Communications were improved, as new roads were built and reconstruction at Berakas Airport was completed in 1954.
The second National Development Plan was launched in 1962. A major oil and gas field was discovered in 1963. Developments in the oil and gas sector have continued, and oil production has steadily increased since then. The plan also promoted the production of meat and eggs for consumption by citizens. The fishing industry increased its output by 25% throughout the course of the plan. The deepwater port at Muara was also constructed during this period. Power requirements were met, and studies were made to provide electricity to rural areas. Efforts were made to eradicate malaria, an endemic disease in the region, with the help of the World Health Organization. Malaria cases were reduced from 300 cases in 1953 to only 66 cases in 1959. The death rate was reduced from 20 per thousand in 1947 to 11.3 per thousand in 1953. Infectious disease has been prevented by public sanitation and improvement of drainage, and the provision of piped pure water to the population.
 On 7 January 1979, another treaty was signed between Brunei and the United Kingdom. It was signed with Lord Goronwy-Roberts being the representative of the UK. This agreement granted Brunei to take over international responsibilities as an independent nation. Britain agreed to assist Brunei in diplomatic matters. In May 1983, it was announced by the UK that the date of independence of Brunei would be 1 January 1984.
On 31 December 1983, a mass gathering was held on main mosques on all four of the districts of the country and at midnight, on 1 January 1984, the Proclamation of Independence was read by Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah. The sultan subsequently assumed the title " His Majesty", rather than the previous "
On 7 January 1979, another treaty was signed between Brunei and the United Kingdom. It was signed with Lord Goronwy-Roberts being the representative of the UK. This agreement granted Brunei to take over international responsibilities as an independent nation. Britain agreed to assist Brunei in diplomatic matters. In May 1983, it was announced by the UK that the date of independence of Brunei would be 1 January 1984.
On 31 December 1983, a mass gathering was held on main mosques on all four of the districts of the country and at midnight, on 1 January 1984, the Proclamation of Independence was read by Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah. The sultan subsequently assumed the title " His Majesty", rather than the previous "
 Brunei is a southeast Asian country consisting of two unconnected parts with a total area of on the island of Borneo. It has of coastline next to the South China Sea, and it shares a border with Malaysia. It has of territorial waters, and a exclusive economic zone.
About 97% of the population lives in the larger western part ( Belait, Tutong, and
Brunei is a southeast Asian country consisting of two unconnected parts with a total area of on the island of Borneo. It has of coastline next to the South China Sea, and it shares a border with Malaysia. It has of territorial waters, and a exclusive economic zone.
About 97% of the population lives in the larger western part ( Belait, Tutong, and
 Brunei's political system is governed by the constitution and the national tradition of the Malay Islamic Monarchy ('' Melayu Islam Beraja''; MIB). The three components of MIB cover Malay culture, Islamic religion, and the political framework under the monarchy. It has a legal system based on English common law, although Islamic law ('' shariah'') supersedes this in some cases. Brunei has a parliament but there are no elections; the last election was held in
Brunei's political system is governed by the constitution and the national tradition of the Malay Islamic Monarchy ('' Melayu Islam Beraja''; MIB). The three components of MIB cover Malay culture, Islamic religion, and the political framework under the monarchy. It has a legal system based on English common law, although Islamic law ('' shariah'') supersedes this in some cases. Brunei has a parliament but there are no elections; the last election was held in
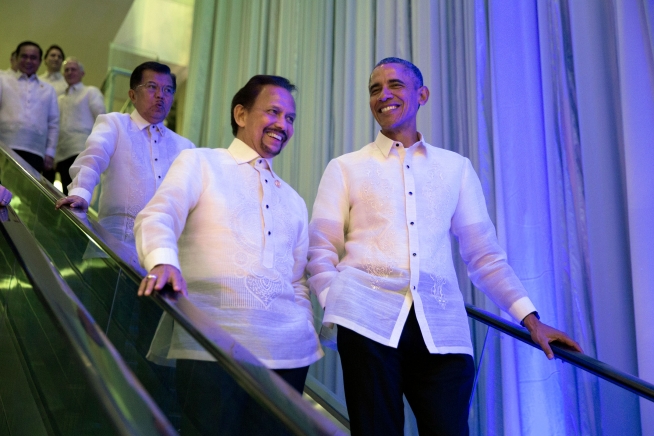

 Until 1979, Brunei's foreign relations were managed by the UK government. After that, they were handled by the Brunei Diplomatic Service. After independence in 1984, this Service was upgraded to ministerial level and is now known as the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Officially, Brunei's foreign policy is as follows:
* Mutual respect of others' territorial sovereignty, integrity and independence;
* The maintenance of friendly relations among nations;
* Non-interference in the internal affairs of other countries; and
* The maintenance and the promotion of peace, security and stability in the region.
With its traditional ties with the United Kingdom, Brunei became the 49th member of the
Until 1979, Brunei's foreign relations were managed by the UK government. After that, they were handled by the Brunei Diplomatic Service. After independence in 1984, this Service was upgraded to ministerial level and is now known as the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Officially, Brunei's foreign policy is as follows:
* Mutual respect of others' territorial sovereignty, integrity and independence;
* The maintenance of friendly relations among nations;
* Non-interference in the internal affairs of other countries; and
* The maintenance and the promotion of peace, security and stability in the region.
With its traditional ties with the United Kingdom, Brunei became the 49th member of the  Brunei shares a close relationship with Singapore and the Philippines. In April 2009, Brunei and the Philippines signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) that seeks to strengthen the bilateral co-operation of the two countries in the fields of agriculture and farm-related trade and investments.
Brunei is one of many nations to lay claim to some of the disputed Spratly Islands. The status of Limbang as part of Sarawak has been disputed by Brunei since the area was first annexed in 1890. The issue was reportedly settled in 2009, with Brunei agreeing to accept the border in exchange for Malaysia giving up claims to oil fields in Bruneian waters. The Brunei government denies this and says that their claim on Limbang was never dropped.
Brunei was the chair for ASEAN in 2013. It also hosted the ASEAN summit on that same year.
Brunei shares a close relationship with Singapore and the Philippines. In April 2009, Brunei and the Philippines signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) that seeks to strengthen the bilateral co-operation of the two countries in the fields of agriculture and farm-related trade and investments.
Brunei is one of many nations to lay claim to some of the disputed Spratly Islands. The status of Limbang as part of Sarawak has been disputed by Brunei since the area was first annexed in 1890. The issue was reportedly settled in 2009, with Brunei agreeing to accept the border in exchange for Malaysia giving up claims to oil fields in Bruneian waters. The Brunei government denies this and says that their claim on Limbang was never dropped.
Brunei was the chair for ASEAN in 2013. It also hosted the ASEAN summit on that same year.
US Department of State The law prohibits sexual harassment and stipulates that whoever assaults or uses criminal force, intending thereby to outrage or knowing it is likely to outrage the modesty of a person, shall be punished with imprisonment for as much as five years and
 In The Laws of Brunei, the right of non-Muslims to practice their faith is guaranteed by the 1959 Constitution. However, celebrations and prayers must be confined to places of worship and private residences. Upon adopting Sharia Penal Code, the Ministry of Religious Affairs banned Christmas decorations in public places, but did not forbid celebration of Christmas in places of worship and private premises.
On 25 December 2015, 4,000 out of 18,000 estimated local Catholics attended the mass of Christmas Day and Christmas Eve. The Brunei Times
In The Laws of Brunei, the right of non-Muslims to practice their faith is guaranteed by the 1959 Constitution. However, celebrations and prayers must be confined to places of worship and private residences. Upon adopting Sharia Penal Code, the Ministry of Religious Affairs banned Christmas decorations in public places, but did not forbid celebration of Christmas in places of worship and private premises.
On 25 December 2015, 4,000 out of 18,000 estimated local Catholics attended the mass of Christmas Day and Christmas Eve. The Brunei Times
In 2015, the then-

 Brunei has the second-highest Human Development Index among the
Brunei has the second-highest Human Development Index among the
 As of 2019, the country's road network constituted a total length of , out of which were paved. The highway from Muara Town to Kuala Belait is a
As of 2019, the country's road network constituted a total length of , out of which were paved. The highway from Muara Town to Kuala Belait is a
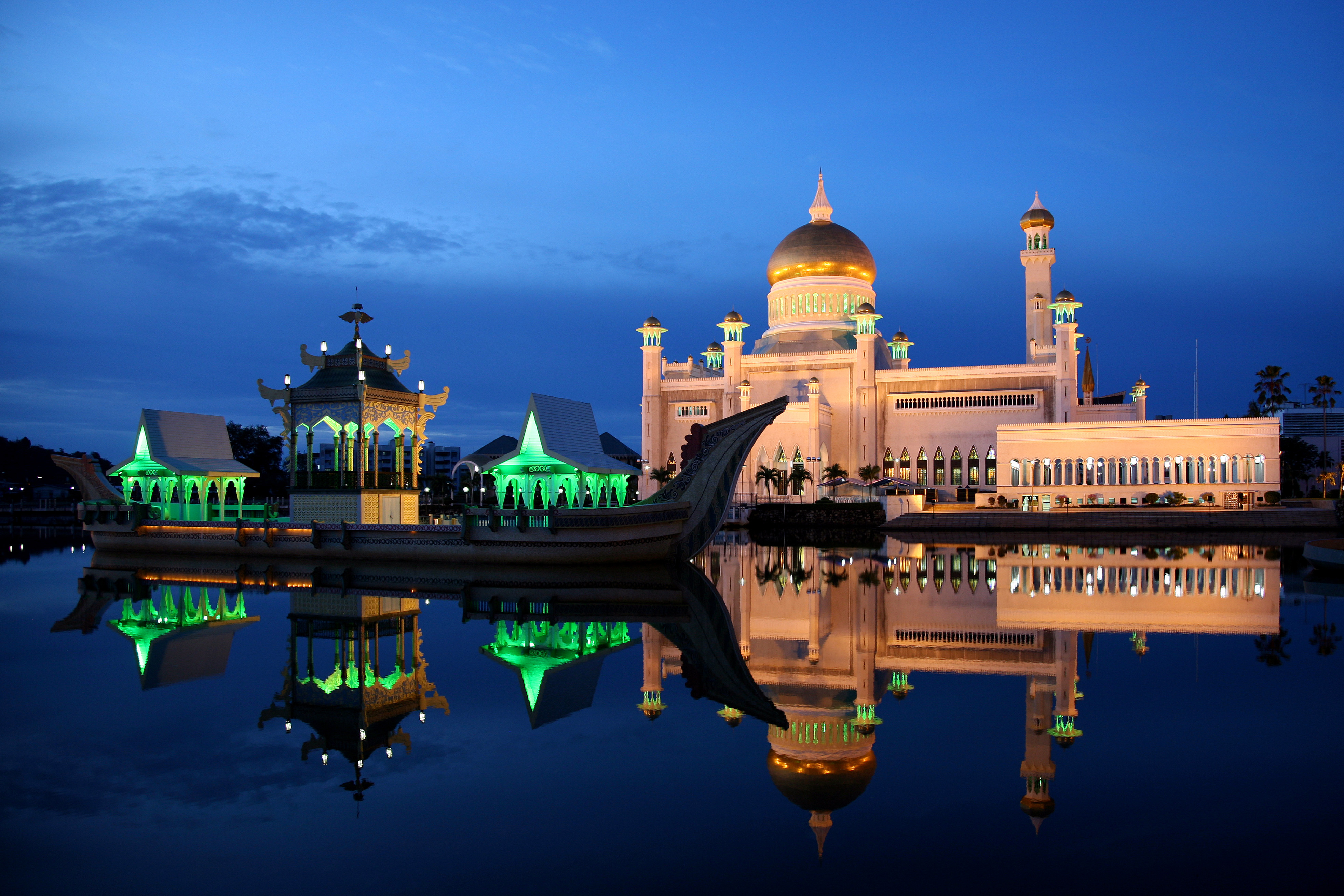 Ethnicities indigenous to Brunei include the Belait, Brunei Bisaya (not to be confused with the Bisaya/Visaya of the nearby Philippines), indigenous Bruneian Malay, Dusun, Kedayan, Lun Bawang, Murut and Tutong.
The population of Brunei in was , of which 76% live in urban areas. The rate of urbanisation is estimated at 2.13% per year from 2010 to 2015. The average life expectancy is 77.7 years. In 2014, 65.7% of the population were Malay, 10.3% are Chinese, 3.4% are indigenous, with 20.6% smaller groups making up the rest. There is a relatively large expatriate community.
Most expats come from non-
Ethnicities indigenous to Brunei include the Belait, Brunei Bisaya (not to be confused with the Bisaya/Visaya of the nearby Philippines), indigenous Bruneian Malay, Dusun, Kedayan, Lun Bawang, Murut and Tutong.
The population of Brunei in was , of which 76% live in urban areas. The rate of urbanisation is estimated at 2.13% per year from 2010 to 2015. The average life expectancy is 77.7 years. In 2014, 65.7% of the population were Malay, 10.3% are Chinese, 3.4% are indigenous, with 20.6% smaller groups making up the rest. There is a relatively large expatriate community.
Most expats come from non-
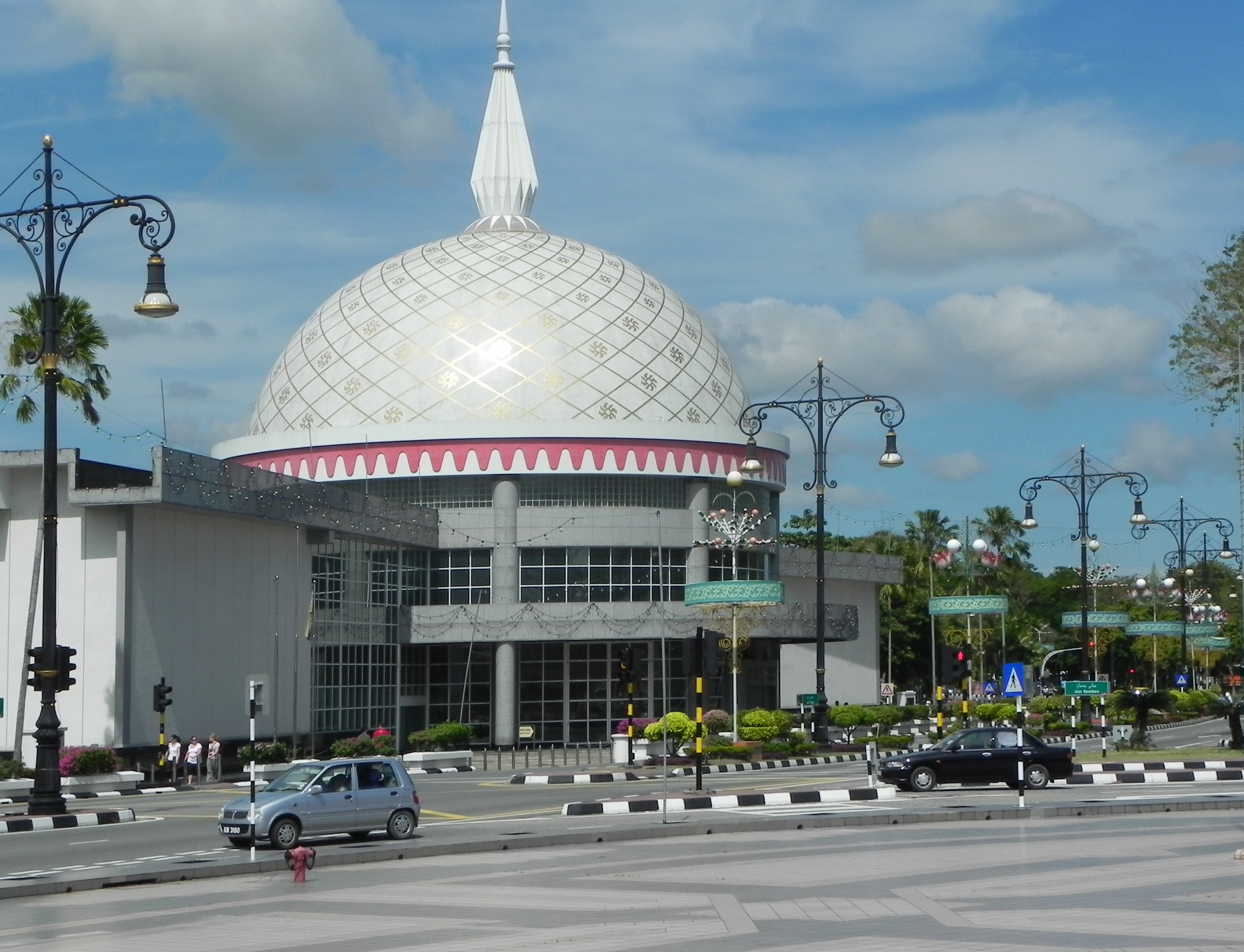 The culture of Brunei is predominantly Malay (reflecting its ethnicity), with heavy influences from
The culture of Brunei is predominantly Malay (reflecting its ethnicity), with heavy influences from
tourismbrunei.com Non-Muslims are allowed to bring in a limited amount of alcohol from their point of embarkation overseas for their own private consumption.
Prime Minister's Office of Brunei Darussalam
website
General information
Brunei
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Brunei profile
from the BBC News
Brunei
at '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' *
Key Development Forecasts for Brunei
from International Futures Travel
Brunei Tourism
website {{Coord, 4, 30, N, 114, 40, E, display=title 1888 establishments in the British Empire * Borneo Commonwealth monarchies Countries in Asia English-speaking countries and territories Former British colonies and protectorates in Asia Island countries Malay-speaking countries and territories Maritime Southeast Asia Member states of ASEAN Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Southeast Asian countries States and territories established in 1984 Sultanates
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city, Bandar Seri Begawan. The government is an absolute monarchy ruled by its Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
, entitled the Yang di-Pertuan, and implements a combination of English common law and sharia law
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the Five Pillars of Islam, religious precepts of Islam and is based on the Islamic holy books, sacred scriptures o ...
, as well as general Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
ic practices.
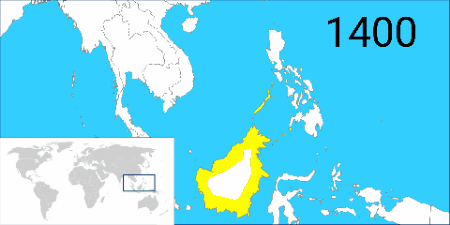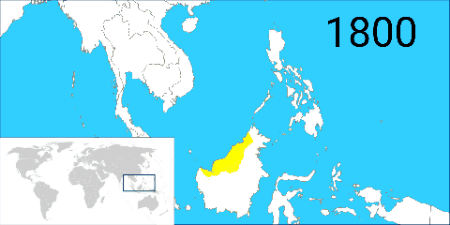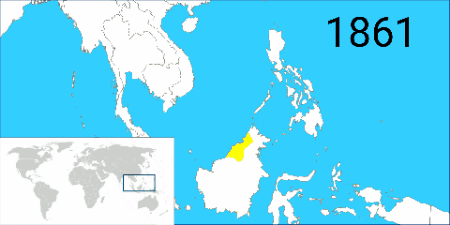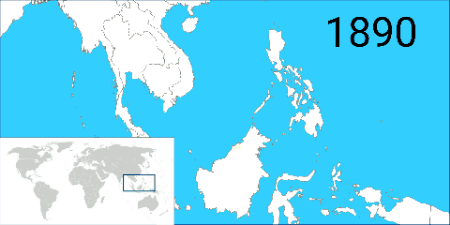
At the peak of the Bruneian Empire, Sultan Bolkiah
Bolkiah, also known as Nakhoda Ragam, was the 5th Sultan of Brunei. He ascended the throne upon the abdication of his father, Sultan Sulaiman, and ruled Brunei from 1485 to 1524. His reign marked the Golden Age of Brunei and saw the Sultanat ...
(reigned 1485–1528) is claimed to have had control over most regions of Borneo, including modern-day Sarawak and Sabah, as well as the Sulu Archipelago off the northeast tip of Borneo, and the islands off the northwest tip of Borneo. Claims also state that they had control over Seludong (or the Kingdom of Maynila, where the modern-day Philippine capital Manila now stands) but Southeast Asian scholars believe this refers to a settlement Mount Selurong in Indonesia.Abinales, Patricio N. and Donna J. Amoroso, State and Society in the Philippines. Maryland: Rowman and Littlefield, 2005. The maritime state of Brunei was visited by Spain's Magellan Expedition in 1521 and fought against Spain in the 1578 Castilian War
The Castilian War took place in 1570-1578 and represented the last crusade in Islamic history between the Spanish Empire and the Sultanate of Brunei; the Sultanate of Sulu, the Sultanate of Maguindanao, and the Ottoman Caliphate.
Sultan Saiful ...
.
During the 19th century, the Bruneian Empire began to decline. The Sultanate ceded Sarawak (Kuching
Kuching (), officially the City of Kuching, is the capital and the most populous city in the States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Sarawak in Malaysia. It is also the capital of Kuching Division. The city is on the Sarawak River ...
) to James Brooke and installed him as the White Rajah, and it ceded Sabah to the British North Borneo Chartered Company. In 1888, Brunei became a British protectorate and was assigned a British resident as colonial manager in 1906. After the Japanese occupation during World War II, in 1959 a new constitution was written. In 1962, a small armed rebellion against the monarchy was ended with the help of the British.
Brunei has been led by the Sultan of Brunei
The sultan of Brunei is the monarchical head of state of Brunei and head of government in his capacity as prime minister of Brunei. Since independence from the British in 1984, only one sultan has reigned, though the royal institution dates bac ...
Hassanal Bolkiah
Hassanal Bolkiah ibni Omar Ali Saifuddien III ( Jawi: ; born 15 July 1946) is the 29th and current Sultan and Yang di-Pertuan of Brunei since 1967 and the Prime Minister of Brunei since independence from the United Kingdom in 1984. He is one ...
since 1967, and had gained its independence as a British protectorate on 1 January 1984. The country is an autocratic absolute monarchy. Economic growth during the 1990s and 2000s, with the GDP increasing 56% from 1999 to 2008, transformed Brunei into an industrialised country. It has developed wealth from extensive petroleum and natural gas fields. Brunei has the second-highest Human Development Index among the Southeast Asian
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
nations, after Singapore, and is classified as a developed country
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Brunei is ranked fifth in the world by gross domestic product per capita at purchasing power parity. The IMF estimated in 2011 that Brunei was one of two countries (the other being Libya) with a public debt at 0% of the national GDP.
Etymology
According to local historiography, Brunei was founded by Awang Alak Betatar, later to be Sultan Muhammad Shah, reigning around AD 1400. He moved from Garang in the Temburong District to the Brunei River estuary, discovering Brunei. According to legend, upon landing he exclaimed, ''Baru nah'' (loosely translated as "that's it!" or "there"), from which the name "Brunei" was derived. He was the first Muslim ruler of Brunei. Before the rise of the Bruneian Empire under the Muslim Bolkiah Dynasty, Brunei is believed to have been under Buddhist rulers. It was renamed "Barunai" in the 14th century, possibly influenced by the Sanskrit word "'" (), meaning "seafarers". The word " Borneo" is of the same origin. In the country's full name, ', ' ( ar, دار السلام) means "abode of peace", while ' means "country" in Malay. A shortened version of the Malay official name, "Brunei Darussalam", has also entered common usage, particularly in official contexts, and is present in the United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names geographical database, as well as the official ASEAN and Commonwealth listings. The earliest recorded documentation by the West about Brunei is by an Italian known as Ludovico di Varthema. On his documentation back to 1550;History
Early history
The settlement known as Vijayapura was a vassal-state to the BuddhistSrivijaya
Srivijaya ( id, Sriwijaya) was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia), which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th t ...
empire and was thought to be located in Borneo's Northwest which flourished in the 7th Century. This alternate Srivijaya referring to Brunei, was known to Arabic sources as "Sribuza". The Arabic author Al Ya'akubi writing in 800 recorded that the kingdom of Musa (Muja, which is old Brunei) was in alliance with the kingdom of Mayd (Either Ma-i or Madja-as in the Philippines), against the Chinese Empire which they waged war against. In the aftermath of the Indian Chola invasion of Srivijaya, Datu Puti lead some dissident datus from Sumatra and Borneo in a rebellion against Rajah Makatunao who was a Chola appointed local Rajah or the descendant of Seri Maharajah (In Chinese records). The dissidents and their retinue tried to revive Srivijaya in a new country called Madja-as in the Visayas (an island archipelago named after Srivijaya) in the Philippines. After the 10 Datus established many towns in Panay
Panay is the sixth-largest and fourth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of and has a total population of 4,542,926 as of 2020 census. Panay comprises 4.4 percent of the entire population of the country. The City o ...
and Southern Luzon, according to Augustinian Friar Rev. Fr. Santaren recording in the Spanish era of this Pre-Spanish legendary history, that Datu Macatunao or Rajah Makatunao who was the "sultan of the Moros," and a relative of Datu Puti who seized the properties and riches of the ten datus was eventually killed by the warriors named Labaodungon and Paybare, after learning of this injustice from their father-in-law Paiburong, sailed to Odtojan in Borneo where Makatunaw ruled. The warriors sacked the city, killed Makatunaw and his family, retrieved the stolen properties of the 10 datus, enslaved the remaining population of Odtojan, and sailed back to Panay. Labaw Donggon and his wife, Ojaytanayon, later settled in a place called Moroboro.Mga Maragtas ng PanayComparative Analysis of Documents about the Bornean Settlement Tradition By Talaguit Christian Jeo N. One of the earliest Chinese records of an independent kingdom in Borneo is the 977 AD letter to the Chinese emperor from the ruler of Boni, which some scholars believe to refer to Borneo. The Bruneians regained their independence from Srivijaya due to the onset of a Javanese-Sumatran war. In 1225, the Chinese official Zhao Rukuo reported that Boni had 100 warships to protect its trade, and that there was great wealth in the kingdom. Marco Polo suggested in his memoirs that the Great Khan or the ruler of the Mongol Empire, attempted and failed many times in invading "Great Java" which was the European name for Bruneian controlled Borneo. In the 1300s the Chinese annals, ''Nanhai zhi'', reported that Brunei invaded or administered Sarawak and Sabah as well as the Philippine kingdoms of Butuan,
Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
, Ma-i (Mindoro), Malilu 麻裏蘆 (present-day Manila), Shahuchong 沙胡重 (present-day Siocon), Yachen 啞陳 ( Oton), and 文杜陵 Wenduling (present-day Mindanao), which would regain their independence at a later date.
In the 14th century, the Javanese manuscript '' Nagarakretagama'', written by Prapanca
Mpu Prapanca wrote the '' Nagarakretagama'', written in Old Javanese, which tells the story of the Majapahit Kingdom and other stories of ancient Hindu- Javanese kingdoms. The Buddhist monk Prapanca wrote the chronicle in 1365 (or 1287 Saka ye ...
in 1365, mentioned ''Barune'' as the constituent state of Hindu Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
, which had to make an annual tribute of 40 katis of camphor
Camphor () is a waxy, colorless solid with a strong aroma. It is classified as a terpenoid and a cyclic ketone. It is found in the wood of the camphor laurel ('' Cinnamomum camphora''), a large evergreen tree found in East Asia; and in the k ...
. In 1369, Sulu which was also formerly part of Majapahit, had successfully rebelled and then attacked Boni, and had invaded the Northeast Coast of Borneo and afterwards had looted the capital of its treasure and gold including sacking two sacred pearls. A fleet from Majapahit succeeded in driving away the Sulus, but Boni was left weaker after the attack. A Chinese report from 1371 described Boni as poor and totally controlled by Majapahit.
During the 15th century, Boni had seceded from Majapahit and then converted to Islam. Thus transforming into the independent Sultanate of Brunei. Brunei became a Hashemite state when she allowed the Arab Emir of Mecca, Sharif Ali, to become her third sultan. Scholars claim that the power of the Sultanate of Brunei was at its peak between the 15th and 17th centuries, with its power extending from northern Borneo to the southern Philippines (Sulu) and even in the northern Philippines (Manila) which Brunei incorporated via territorial acquisition accomplished through royal marriages. For political reasons, the historical rulers of Maynila maintained close cognatic ties through intermarriage with the ruling houses of the Sultanate of Brunei
This article includes a list of successive Islamic states and Muslim dynasties beginning with the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632 CE) and the early Muslim conquests that spread Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, and continui ...
, but Brunei's political influence over Maynila is not considered to have extended to military or political rule. Intermarriage was a common strategy for large thalassocratic states (maritime states) such as Brunei to extend their influence, and for local rulers such as those of Maynila to help strengthen their family claims to nobility. Sultan Bolkiah had extended Brunei's power to its greatest extent when it conquered Manila and Sulu as he even attempted but failed to conquer the Visayas islands even though Sultan Bolkiah was half-Visayan himself being descended from a Visayan mother and he was famously known as Sultan Ragam "The Singing Captain", his powerful musical voice was a trait he inherited from his Visayan lineage since Visayans were culturally obsessed with singing, with the best Visayan singers often also being members of their warrior castes too. However, Islamic Brunei's power was not uncontested in Borneo since it had a Hindu rival in a state founded by Indians called Kutai in the south which they overpowered but didn't destroy. Brunei's dominance in the Philippines was also challenged by two Indianized kingdoms, the Rajahanates of Cebu and Butuan which were also coincidentally allied with Kutai and were also at war with Brunei's dependencies; Sulu and Manila as well as their mutual ally, the Sultanate of Maguindanao. The Kedatuans of Madja-as and Dapitan were also belligerent against Brunei due to them being the targets of constant Muslim attacks organized from Maguindanao and Ternate, a Papuan speaking state in the vicinity of Oceania that grew wealthy by monopolizing spice production. Nevertheless, by the 16th century, Islam was firmly rooted in Brunei, and the country had built one of its biggest mosques. In 1578, Alonso Beltrán, a Spanish traveller, described it as being five stories tall and built on the water.
War with Spain and decline
 Brunei briefly rose to prominence in Southeast Asia when the Portuguese occupied
Brunei briefly rose to prominence in Southeast Asia when the Portuguese occupied Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
and thereby forced the wealthy and powerful but displaced Muslim refugees there to relocate to nearby Sultanates such as Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a s ...
and Brunei. The Bruneian Sultan then intervened in a territorial conflict between Hindu Tondo and Muslim Manila in the Philippines by appointing the Bruneian descended Rajah Ache of Manila as admiral of the Bruneian navy in a rivalry against Tondo and as the enforcer of Bruneian interests in the Philippines. He subsequently encountered the Magellan expedition wherein Antonio Pigafetta noted that under orders from his grandfather the Sultan of Brunei, Ache had previously sacked the Buddhist city of Loue in Southwest Borneo for being faithful to the old religion and rebelling against the authority of Sultanate. However, European influence gradually brought an end to Brunei's regional power, as Brunei entered a period of decline compounded by internal strife over royal succession. In the face of these invasions by European Christian powers, the Ottoman Caliphate aided the beleaguered Southeast Asian Sultanates by making Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a s ...
a protectorate and sending expeditions to reinforce, train and equip the local mujahideen
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term th ...
. Turks were routinely migrating to Brunei as evidenced by the complaints of Manila Oidor Melchor Davalos who in his 1585 report, say that Turks were coming to Sumatra, Borneo and Ternate every year, including defeated veterans from the Battle of Lepanto. The presence of Turks assisting Brunei against Habsburg Spain, makes the subsequent Castille War a part of the Ottoman–Habsburg wars.
Spain declared war in 1578, planning to attack and capture Kota Batu, Brunei's capital at the time. This was based in part on the assistance of two Bruneian noblemen, Pengiran Seri Lela and Pengiran Seri Ratna. The former had travelled to Manila, then the centre of the Spanish colony. Manila itself was captured from Brunei, Christianised and made a territory of the Viceroyalty of New Spain which was centered in Mexico City. Pengiran Seri Lela came to offer Brunei as a tributary to Spain for help to recover the throne usurped by his brother, Saiful Rijal. The Spanish agreed that if they succeeded in conquering Brunei, Pengiran Seri Lela would be appointed as the sultan, while Pengiran Seri Ratna would be the new Bendahara.
 In March 1578, a fresh Spanish fleet had arrived from Mexico and settled at the Philippines, they were led by De Sande, acting as
In March 1578, a fresh Spanish fleet had arrived from Mexico and settled at the Philippines, they were led by De Sande, acting as Capitán-General
Captain general (and its literal equivalent in several languages) is a high military rank of general officer grade, and a gubernatorial title.
History
The term "Captain General" started to appear in the 14th century, with the meaning of Command ...
, he organised an expedition from Manila for Brunei. The expedition consisted of 400 Spaniards and Mexicans, 1,500 Filipino natives and 300 Borneans. The campaign was one of many, which also included action in Mindanao and Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilāya sin Lupa' Sūg''; tl, Lalawigan ng Sulu), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamor ...
. The racial make-up of the Christian side was diverse since it were usually made up of Mestizos, Mulattoes and Amerindians (Aztecs
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
, Mayans and Incans) who were gathered and sent from Mexico and were led by Spanish officers who had worked together with native Filipinos in military campaigns across the Southeast Asia. The Muslim side though was also equally racially diverse. In addition to the native Malay warriors, the Ottomans had repeatedly sent military expeditions to nearby Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a s ...
. The expeditions were composed mainly of Turks, Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
, Swahilis
The Swahili people ( sw, WaSwahili) comprise mainly Bantu, Afro-Arab and Comorian ethnic groups inhabiting the Swahili coast, an area encompassing the Zanzibar archipelago and mainland Tanzania's seaboard, littoral Kenya, northern Mozambique, ...
, Somalis, Sindhis, Gujaratis and Malabars. These expeditionary forces had also spread to other nearby Sultanates such as Brunei and had taught new fighting tactics and techniques on how to forge cannons.
Eventually, the Spanish invaded the capital on 16 April 1578, with the help of Pengiran Seri Lela and Pengiran Seri Ratna, burning towns and raping populations. The Sultan Saiful Rijal and Paduka Seri Begawan Sultan Abdul Kahar were forced to flee to Meragang then to Jerudong. In Jerudong, they made plans to chase the conquering army away from Brunei. Suffering high fatalities due to a cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
or dysentery outbreak, the Spanish decided to abandon Brunei and returned to Manila on 26 June 1578, after 72 days. Before doing so, they burned the mosque, a high structure with a five-tier roof.
Pengiran Seri Lela died in August or September 1578, probably from the same illness suffered by his Spanish allies. There was suspicion that the legitimist sultan could have been poisoned by the ruling sultan. Seri Lela's daughter, a Bruneian princess, "Putri", had left with the Spanish, she abandoned her claim to the crown and then she married a Christian Tagalog
Tagalog may refer to:
Language
* Tagalog language, a language spoken in the Philippines
** Old Tagalog, an archaic form of the language
** Batangas Tagalog, a dialect of the language
* Tagalog script, the writing system historically used for Tagal ...
, named Agustín de Legazpi de Tondo. Agustin de Legaspi
Agustin de Legazpi is a prominent historical figure in the Philippines best known as the leader of the Tondo Conspiracy of 1587–1588, the last native ruler of Tondo, and the last individual to hold the title of paramount ruler in any of the In ...
along with his family and associates were soon implicated in the Conspiracy of the Maharlikas, an attempt by Filipinos to link up with the Brunei Sultanate and Japanese Shogunate to expel the Spaniards from the Philippines.Martinez, Manuel F. Assassinations & conspiracies : from Rajah Humabon to Imelda Marcos. Manila: Anvil Publishing, 2002. However, upon the Spanish suppression of the conspiracy, the Bruneian descended aristocracy of precolonial Manila were exiled to Guerrero, Mexico which consequently later became a center of the Mexican war of independence against Spain.
The local Brunei accounts of the Castilian War differ greatly from the generally accepted view of events. What was called the Castilian War was seen as a heroic episode, with the Spaniards being driven out by Bendahara Sakam, purportedly a brother of the ruling sultan, and a thousand native warriors. Most historians consider this to be a folk-hero
A folk hero or national hero is a type of hero – real, fictional or mythological – with their name, personality and deeds embedded in the popular consciousness of a people, mentioned frequently in folk songs, folk tales and other folklore; an ...
account, which probably developed decades or centuries after.
Brunei eventually descended into anarchy. The country suffered a civil war from 1660 to 1673.
British intervention
 The British have intervened in the affairs of Brunei on several occasions. Britain attacked Brunei in July 1846 due to internal conflicts over who was the rightful Sultan.
In the 1880s, the decline of the Bruneian Empire continued. The sultan granted land (now Sarawak) to James Brooke, who had helped him quell a rebellion, and allowed him to establish the Raj of Sarawak. Over time, Brooke and his nephews (who succeeded him) leased or annexed more land. Brunei lost much of its territory to him and his dynasty, known as the White Rajahs.
Sultan Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin appealed to the British to stop further encroachment by the Brookes. The "Treaty of Protection" was negotiated by Sir Hugh Low and signed into effect on 17 September 1888. The treaty said that the sultan "could not cede or lease any territory to foreign powers without British consent"; it provided Britain effective control over Brunei's external affairs, making it a British protected state (which continued until 1984). But, when the Raj of Sarawak annexed Brunei's Pandaruan District in 1890, the British did not take any action to stop it. They did not regard either Brunei or the Raj of Sarawak as 'foreign' (per the Treaty of Protection). This final annexation by Sarawak left Brunei with its current small land mass and separation into two parts.
British residents were introduced in Brunei under the Supplementary Protectorate Agreement in 1906. The residents were to advise the sultan on all matters of administration. Over time, the resident assumed more executive control than the sultan. The residential system ended in 1959.
The British have intervened in the affairs of Brunei on several occasions. Britain attacked Brunei in July 1846 due to internal conflicts over who was the rightful Sultan.
In the 1880s, the decline of the Bruneian Empire continued. The sultan granted land (now Sarawak) to James Brooke, who had helped him quell a rebellion, and allowed him to establish the Raj of Sarawak. Over time, Brooke and his nephews (who succeeded him) leased or annexed more land. Brunei lost much of its territory to him and his dynasty, known as the White Rajahs.
Sultan Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin appealed to the British to stop further encroachment by the Brookes. The "Treaty of Protection" was negotiated by Sir Hugh Low and signed into effect on 17 September 1888. The treaty said that the sultan "could not cede or lease any territory to foreign powers without British consent"; it provided Britain effective control over Brunei's external affairs, making it a British protected state (which continued until 1984). But, when the Raj of Sarawak annexed Brunei's Pandaruan District in 1890, the British did not take any action to stop it. They did not regard either Brunei or the Raj of Sarawak as 'foreign' (per the Treaty of Protection). This final annexation by Sarawak left Brunei with its current small land mass and separation into two parts.
British residents were introduced in Brunei under the Supplementary Protectorate Agreement in 1906. The residents were to advise the sultan on all matters of administration. Over time, the resident assumed more executive control than the sultan. The residential system ended in 1959.
Discovery of oil
Petroleum was discovered in 1929 after several fruitless attempts. Two men, F. F. Marriot and T. G. Cochrane, smelled oil near the Seria river in late 1926. They informed ageophysicist
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' som ...
, who conducted a survey there. In 1927, gas seepages were reported in the area. Seria Well Number One (S-1) was drilled on 12 July 1928. Oil was struck at on 5 April 1929. Seria Well Number 2 was drilled on 19 August 1929, and, , continues to produce oil. Oil production was increased considerably in the 1930s with the development of more oil fields. In 1940, oil production was at more than six million barrels. The British Malayan Petroleum Company (now Brunei Shell Petroleum
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New Yo ...
Company) was formed on 22 July 1922. The first offshore well was drilled in 1957. Oil and natural gas have been the basis of Brunei's development and wealth since the late 20th century.
Japanese occupation
15th Punjab Regiment
The 15th Punjab Regiment was a infantry regiment of the British Indian Army from 1922 to 1947 and of the Pakistan Army from 1947 to 1956. Following its allotment to Pakistan after the partition of India in 1947, it was amalgamated in 1956 with ...
based at Kuching
Kuching (), officially the City of Kuching, is the capital and the most populous city in the States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Sarawak in Malaysia. It is also the capital of Kuching Division. The city is on the Sarawak River ...
, Sarawak.
Once the Japanese occupied Brunei, they made an agreement with Sultan Ahmad Tajuddin
Ahmad Tajuddin Akhazul Khairi Waddien ( Jawi: ; August 22, 1913 – June 4, 1950) was the 27th Sultan of Brunei from 11 September 1924 until his death. After his death in 1950, he was then succeeded by his younger brother Omar Ali Saifuddien ...
over governing the country. Inche Ibrahim (known later as Pehin Datu Perdana Menteri Dato Laila Utama Awang Haji Ibrahim), a former Secretary to the British Resident, Ernest Edgar Pengilly, was appointed Chief Administrative Officer
A chief administrative officer (CAO) is a top-tier executive who supervises the daily operations of an organization and is ultimately responsible for its performance.
Government and non-profit
A CAO is responsible for administrative management of ...
under the Japanese Governor. The Japanese had proposed that Pengilly retain his position under their administration, but he declined. Both he and other British nationals still in Brunei were interned by the Japanese at Batu Lintang camp in Sarawak. While the British officials were under Japanese guard, Ibrahim made a point of personally shaking each one by the hand and wishing him well.
The Sultan retained his throne and was given a pension and honours by the Japanese. During the later part of the occupation, he resided at Tantuya, Limbang and had little to do with the Japanese. Most of the Malay government officers were retained by the Japanese. Brunei's administration was reorganised into five prefectures, which included British North Borneo
North Borneo (usually known as British North Borneo, also known as the State of North Borneo) was a British Protectorate, British protectorate in the northern part of the island of Borneo, which is present day Sabah. The territory of North Borneo ...
. The Prefectures included Baram, Labuan, Lawas, and Limbang. Ibrahim hid numerous significant government documents from the Japanese during the occupation. Pengiran Yusuf (later YAM Pengiran Setia Negara Pengiran Haji Mohd Yusuf
Pengiran Muhammad Yusuf bin Abdul Rahim (May 2, 1923 – April 11, 2016), pen name Yura Halim, was a Bruneian politician, civil servant, diplomat, and writer. He served as the Chief Minister (Menteri Besar) of Brunei from 1967 to 1972. Halim wrot ...
), along with other Bruneians, was sent to Japan for training. Although in the area the day of the atomic bombing of Hiroshima, Yusuf survived.
The British had anticipated a Japanese attack, but lacked the resources to defend the area because of their engagement in the war in Europe. The troops from the Punjab Regiment filled in the Seria oilfield oilwells with concrete in September 1941 to deny the Japanese their use. The remaining equipment and installations were destroyed when the Japanese invaded Malaya. By the end of the war, 16 wells at Miri and Seria had been restarted, with production reaching about half the pre-war level. Coal production at Muara was also recommenced, but with little success.
 During the occupation, the Japanese had their language taught in schools, and Government officers were required to learn Japanese. The local currency was replaced by what was to become known as ''duit pisang'' (banana money). From 1943 hyper-inflation destroyed the currency's value and, at the end of the war, this currency was worthless. Allied attacks on shipping eventually caused trade to cease. Food and medicine fell into short supply, and the population suffered from famine and disease.
The airport runway was constructed by the Japanese during the occupation, and in 1943 Japanese naval units were based in
During the occupation, the Japanese had their language taught in schools, and Government officers were required to learn Japanese. The local currency was replaced by what was to become known as ''duit pisang'' (banana money). From 1943 hyper-inflation destroyed the currency's value and, at the end of the war, this currency was worthless. Allied attacks on shipping eventually caused trade to cease. Food and medicine fell into short supply, and the population suffered from famine and disease.
The airport runway was constructed by the Japanese during the occupation, and in 1943 Japanese naval units were based in Brunei Bay
Brunei Bay ( ms, Teluk Brunei) is on the northwestern coast of Borneo island, in Brunei and Malaysia.
Brunei Bay is located 5°00'43.44", 115°17'26.66"; east of Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei.
It is the ocean gateway to the isolated Temburong Dis ...
and Labuan. The naval base was destroyed by Allied bombing, but the airport runway survived. The facility was developed as a public airport. In 1944 the Allies began a bombing campaign against the occupying Japanese, which destroyed much of the town and Kuala Belait, but missed Kampong Ayer.
Operation Oboe Six
The Battle of North Borneo took place during the Second World War between Allied and Japanese forces. Part of the wider Borneo campaign of the Pacific War, it was fought between 10 June and 15 August 1945 in North Borneo (later known as Saba ...
to recapture Borneo from the Japanese. They were supported by American air and naval units. Brunei town was bombed extensively and recaptured after three days of heavy fighting. Many buildings were destroyed, including the Mosque. The Japanese forces in Brunei, Borneo, and Sarawak, under Lieutenant-General Masao Baba, formally surrendered at Labuan on 10 September 1945. The British Military Administration took over from the Japanese and remained until July 1946.
Post-World War II
After World War II, a new government was formed in Brunei under the British Military Administration (BMA). It consisted mainly of Australian officers and servicemen. The administration of Brunei was passed to the Civil Administration on 6 July 1945. The Brunei State Council was also revived that year. The BMA was tasked to revive the Bruneian economy, which was extensively damaged by the Japanese during their occupation. They also had to put out the fires on the wells of Seria, which had been set by the Japanese prior to their defeat. Before 1941, the Governor of the Straits Settlements, based in Singapore, was responsible for the duties of British High Commissioner for Brunei, Sarawak, andNorth Borneo
North Borneo (usually known as British North Borneo, also known as the State of North Borneo) was a British Protectorate, British protectorate in the northern part of the island of Borneo, which is present day Sabah. The territory of North Borneo ...
(now Sabah). The first British High Commissioner for Brunei was the Governor of Sarawak, Sir Charles Ardon Clarke. The Barisan Pemuda ("Youth Movement"; abbreviated as BARIP) was the first political party to be formed in Brunei, on 12 April 1946. The party intended to "preserve the sovereignty of the Sultan and the country, and to defend the rights of the Malays
Malays may refer to:
* Malay race, a racial category encompassing peoples of Southeast Asia and sometimes the Pacific Islands
** Overseas Malays, people of Malay race ancestry living outside Malay archipelago home areas
** Cape Malays, a communit ...
". BARIP also contributed to the composition of the country's national anthem. The party was dissolved in 1948 due to inactivity.
In 1959, a new constitution was written declaring Brunei a self-governing state, while its foreign affairs, security, and defence remained the responsibility of the United Kingdom. A small rebellion
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
erupted against the monarchy in 1962, which was suppressed with help of the UK. Known as the Brunei Revolt, the rebellion contributed to the Sultan's decision to opt out of joining the emerging state now called Malaysia under the umbrella of North Borneo Federation.
Brunei gained its independence from the United Kingdom on 1 January 1984. The official National Day, which celebrates the country's independence, is held by tradition on 23 February.
Writing of the Constitution
 In July 1953, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III formed a seven-member committee named ''Tujuh Serangkai'', to determine the citizens' views regarding a written constitution for Brunei. In May 1954, the Sultan, Resident and High Commissioner met to discuss the findings of the committee. They agreed to authorise the drafting of a constitution. In March 1959, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III led a delegation to London to discuss the proposed Constitution. The British delegation was led by Sir
In July 1953, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III formed a seven-member committee named ''Tujuh Serangkai'', to determine the citizens' views regarding a written constitution for Brunei. In May 1954, the Sultan, Resident and High Commissioner met to discuss the findings of the committee. They agreed to authorise the drafting of a constitution. In March 1959, Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III led a delegation to London to discuss the proposed Constitution. The British delegation was led by Sir Alan Lennox-Boyd
Alan Tindal Lennox-Boyd, 1st Viscount Boyd of Merton, CH, PC, DL (18 November 1904 – 8 March 1983), was a British Conservative politician.
Background, education and military service
Lennox-Boyd was the son of Alan Walter Lennox-Boyd by his ...
, Secretary of State for the Colonies. The British Government later accepted the draft constitution.
On 29 September 1959, the Constitution Agreement was signed in Brunei Town
Bandar Seri Begawan (BSB; Jawi: بندر سري بڬاوان; ) is the capital city of Brunei. It is officially a municipal area () with an area of and an estimated population of 100,700 as of 2007. It is part of Brunei-Muara District, the sm ...
. The agreement was signed by Sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III and Sir Robert Scott, the Commissioner-General for Southeast Asia.
It included the following provisions:
* The Sultan was made the Supreme Head of State.
* Brunei was responsible for its internal administration.
* The British Government was responsible for foreign and defence affairs only.
* The post of Resident was abolished and replaced by a British High Commissioner.
Five councils were established:
* The Executive Council
* The Legislative Council of Brunei
* The Privy Council
* The Council of Succession
* The State Religious Council
National development plans
A series of National Development Plans was initiated by the 28th Sultan of Brunei, Omar Ali Saifuddien III. The first was introduced in 1953. A total sum of B$100 million was approved by the Brunei State Council for the plan. E.R. Bevington, from the Colonial Office inFiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, was appointed to implement it. A US$14 million Gas Plant was built under the plan. In 1954, survey and exploration work were undertaken by the Brunei Shell Petroleum on both offshore and onshore fields. By 1956, production reached 114,700 bpd.
 The plan also aided the development of public education. By 1958, expenditure on education totalled at $4 million. Communications were improved, as new roads were built and reconstruction at Berakas Airport was completed in 1954.
The second National Development Plan was launched in 1962. A major oil and gas field was discovered in 1963. Developments in the oil and gas sector have continued, and oil production has steadily increased since then. The plan also promoted the production of meat and eggs for consumption by citizens. The fishing industry increased its output by 25% throughout the course of the plan. The deepwater port at Muara was also constructed during this period. Power requirements were met, and studies were made to provide electricity to rural areas. Efforts were made to eradicate malaria, an endemic disease in the region, with the help of the World Health Organization. Malaria cases were reduced from 300 cases in 1953 to only 66 cases in 1959. The death rate was reduced from 20 per thousand in 1947 to 11.3 per thousand in 1953. Infectious disease has been prevented by public sanitation and improvement of drainage, and the provision of piped pure water to the population.
The plan also aided the development of public education. By 1958, expenditure on education totalled at $4 million. Communications were improved, as new roads were built and reconstruction at Berakas Airport was completed in 1954.
The second National Development Plan was launched in 1962. A major oil and gas field was discovered in 1963. Developments in the oil and gas sector have continued, and oil production has steadily increased since then. The plan also promoted the production of meat and eggs for consumption by citizens. The fishing industry increased its output by 25% throughout the course of the plan. The deepwater port at Muara was also constructed during this period. Power requirements were met, and studies were made to provide electricity to rural areas. Efforts were made to eradicate malaria, an endemic disease in the region, with the help of the World Health Organization. Malaria cases were reduced from 300 cases in 1953 to only 66 cases in 1959. The death rate was reduced from 20 per thousand in 1947 to 11.3 per thousand in 1953. Infectious disease has been prevented by public sanitation and improvement of drainage, and the provision of piped pure water to the population.
Independence
On 14 November 1971, SultanHassanal Bolkiah
Hassanal Bolkiah ibni Omar Ali Saifuddien III ( Jawi: ; born 15 July 1946) is the 29th and current Sultan and Yang di-Pertuan of Brunei since 1967 and the Prime Minister of Brunei since independence from the United Kingdom in 1984. He is one ...
left for London to discuss matters regarding the amendments to the 1959 constitution. A new agreement was signed on 23 November 1971 with the British representative being Anthony Royle.
Under this agreement, the following terms were agreed upon:
* Brunei was granted full internal self-government
* The UK would still be responsible for external affairs and defence.
* Brunei and the UK agreed to share the responsibility for security and defence.
This agreement also caused Gurkha units to be deployed in Brunei, where they remain up to this day.
 On 7 January 1979, another treaty was signed between Brunei and the United Kingdom. It was signed with Lord Goronwy-Roberts being the representative of the UK. This agreement granted Brunei to take over international responsibilities as an independent nation. Britain agreed to assist Brunei in diplomatic matters. In May 1983, it was announced by the UK that the date of independence of Brunei would be 1 January 1984.
On 31 December 1983, a mass gathering was held on main mosques on all four of the districts of the country and at midnight, on 1 January 1984, the Proclamation of Independence was read by Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah. The sultan subsequently assumed the title " His Majesty", rather than the previous "
On 7 January 1979, another treaty was signed between Brunei and the United Kingdom. It was signed with Lord Goronwy-Roberts being the representative of the UK. This agreement granted Brunei to take over international responsibilities as an independent nation. Britain agreed to assist Brunei in diplomatic matters. In May 1983, it was announced by the UK that the date of independence of Brunei would be 1 January 1984.
On 31 December 1983, a mass gathering was held on main mosques on all four of the districts of the country and at midnight, on 1 January 1984, the Proclamation of Independence was read by Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah. The sultan subsequently assumed the title " His Majesty", rather than the previous "His Royal Highness
Royal Highness is a style used to address or refer to some members of royal families, usually princes or princesses. Monarchs and their consorts are usually styled ''Majesty''.
When used as a direct form of address, spoken or written, it takes ...
". Brunei was admitted to the United Nations on 22 September 1984, becoming the organisation's 159th member.
21st century
In October 2013, Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah announced his intention to imposePenal Code
A criminal code (or penal code) is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that might ...
from the Sharia law
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the Five Pillars of Islam, religious precepts of Islam and is based on the Islamic holy books, sacred scriptures o ...
on the country's Muslims, which make up roughly two thirds of the country's population. This would be implemented in three phases, culminating in 2016, and making Brunei the first and only country in East Asia to introduce Sharia law into its penal code, excluding the subnational Indonesian special territory of Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a s ...
. The move attracted international criticism, the United Nations expressing "deep concern".
Geography
 Brunei is a southeast Asian country consisting of two unconnected parts with a total area of on the island of Borneo. It has of coastline next to the South China Sea, and it shares a border with Malaysia. It has of territorial waters, and a exclusive economic zone.
About 97% of the population lives in the larger western part ( Belait, Tutong, and
Brunei is a southeast Asian country consisting of two unconnected parts with a total area of on the island of Borneo. It has of coastline next to the South China Sea, and it shares a border with Malaysia. It has of territorial waters, and a exclusive economic zone.
About 97% of the population lives in the larger western part ( Belait, Tutong, and Brunei-Muara
Brunei-Muara District ( ms, Daerah Brunei dan Muara; Jawi: برونائی-موارا ضلع) or simply Brunei-Muara is one of the four districts of Brunei. It has the smallest area among the four districts, with , yet is the most populous, wi ...
), while only about 10,000 people live in the mountainous eastern part ( Temburong District). The total population of Brunei is approximately 408,000 , of which around 150,000 live in the capital Bandar Seri Begawan. Other major towns are the port town of Muara, the oil-producing town of Seria and its neighbouring town, Kuala Belait. In Belait District, the Panaga area is home to large numbers of Europeans expatriates, due to Royal Dutch Shell and British Army housing, and several recreational facilities are located there.
Most of Brunei is within the Borneo lowland rain forests ecoregion, which covers most of the island. Areas of mountain rain forests are located inland.
The climate of Brunei is tropical equatorial that is a Tropical rainforest climate more subject to the Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
than the trade winds and with no or rare cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anti ...
s. Brunei is exposed to the risks stemming from climate change along with other ASEAN member states.
Politics and government
 Brunei's political system is governed by the constitution and the national tradition of the Malay Islamic Monarchy ('' Melayu Islam Beraja''; MIB). The three components of MIB cover Malay culture, Islamic religion, and the political framework under the monarchy. It has a legal system based on English common law, although Islamic law ('' shariah'') supersedes this in some cases. Brunei has a parliament but there are no elections; the last election was held in
Brunei's political system is governed by the constitution and the national tradition of the Malay Islamic Monarchy ('' Melayu Islam Beraja''; MIB). The three components of MIB cover Malay culture, Islamic religion, and the political framework under the monarchy. It has a legal system based on English common law, although Islamic law ('' shariah'') supersedes this in some cases. Brunei has a parliament but there are no elections; the last election was held in 1962
Events January
* January 1 – Western Samoa becomes independent from New Zealand.
* January 3 – Pope John XXIII excommunicates Fidel Castro for preaching communism.
* January 8 – Harmelen train disaster: 93 die in the wors ...
.
Under Brunei's 1959 constitution, His Majesty Hassanal Bolkiah
Hassanal Bolkiah ibni Omar Ali Saifuddien III ( Jawi: ; born 15 July 1946) is the 29th and current Sultan and Yang di-Pertuan of Brunei since 1967 and the Prime Minister of Brunei since independence from the United Kingdom in 1984. He is one ...
is the head of state with full executive authority. Since 1962
Events January
* January 1 – Western Samoa becomes independent from New Zealand.
* January 3 – Pope John XXIII excommunicates Fidel Castro for preaching communism.
* January 8 – Harmelen train disaster: 93 die in the wors ...
, this authority has included emergency powers, which are renewed every two years. Brunei has technically been under martial law since the Brunei Revolt of 1962. Hassanal Bolkiah
Hassanal Bolkiah ibni Omar Ali Saifuddien III ( Jawi: ; born 15 July 1946) is the 29th and current Sultan and Yang di-Pertuan of Brunei since 1967 and the Prime Minister of Brunei since independence from the United Kingdom in 1984. He is one ...
also serves as the state's prime minister, finance minister and defence minister
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
.
Foreign relations

 Until 1979, Brunei's foreign relations were managed by the UK government. After that, they were handled by the Brunei Diplomatic Service. After independence in 1984, this Service was upgraded to ministerial level and is now known as the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Officially, Brunei's foreign policy is as follows:
* Mutual respect of others' territorial sovereignty, integrity and independence;
* The maintenance of friendly relations among nations;
* Non-interference in the internal affairs of other countries; and
* The maintenance and the promotion of peace, security and stability in the region.
With its traditional ties with the United Kingdom, Brunei became the 49th member of the
Until 1979, Brunei's foreign relations were managed by the UK government. After that, they were handled by the Brunei Diplomatic Service. After independence in 1984, this Service was upgraded to ministerial level and is now known as the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Officially, Brunei's foreign policy is as follows:
* Mutual respect of others' territorial sovereignty, integrity and independence;
* The maintenance of friendly relations among nations;
* Non-interference in the internal affairs of other countries; and
* The maintenance and the promotion of peace, security and stability in the region.
With its traditional ties with the United Kingdom, Brunei became the 49th member of the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
immediately on the day of its independence on 1 January 1984. As one of its first initiatives toward improved regional relations, Brunei joined ASEAN on 7 January 1984, becoming the sixth member. To achieve recognition of its sovereignty and independence, it joined the United Nations as a full member on 21 September of that same year.
As an Islamic country, Brunei became a full member of the Organisation of the Islamic Conference (now the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation) in January 1984 at the Fourth Islamic Summit held in Morocco.
After its accession to the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum (APEC) in 1989, Brunei hosted the APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting in November 2000 and the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) in July 2002. Brunei became a founding member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) on 1 January 1995, and is a major player in BIMP-EAGA, which was formed during the Inaugural Ministers' Meeting in Davao, Philippines, on 24 March 1994.
 Brunei shares a close relationship with Singapore and the Philippines. In April 2009, Brunei and the Philippines signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) that seeks to strengthen the bilateral co-operation of the two countries in the fields of agriculture and farm-related trade and investments.
Brunei is one of many nations to lay claim to some of the disputed Spratly Islands. The status of Limbang as part of Sarawak has been disputed by Brunei since the area was first annexed in 1890. The issue was reportedly settled in 2009, with Brunei agreeing to accept the border in exchange for Malaysia giving up claims to oil fields in Bruneian waters. The Brunei government denies this and says that their claim on Limbang was never dropped.
Brunei was the chair for ASEAN in 2013. It also hosted the ASEAN summit on that same year.
Brunei shares a close relationship with Singapore and the Philippines. In April 2009, Brunei and the Philippines signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) that seeks to strengthen the bilateral co-operation of the two countries in the fields of agriculture and farm-related trade and investments.
Brunei is one of many nations to lay claim to some of the disputed Spratly Islands. The status of Limbang as part of Sarawak has been disputed by Brunei since the area was first annexed in 1890. The issue was reportedly settled in 2009, with Brunei agreeing to accept the border in exchange for Malaysia giving up claims to oil fields in Bruneian waters. The Brunei government denies this and says that their claim on Limbang was never dropped.
Brunei was the chair for ASEAN in 2013. It also hosted the ASEAN summit on that same year.
Defence
Brunei maintains three infantry battalions stationed around the country. The Brunei navy has several "Ijtihad"-class patrol boats purchased from a German manufacturer. The United Kingdom also maintains a base in Seria, the centre of the oil industry in Brunei. A Gurkha battalion consisting of 1,500 personnel is stationed there. United Kingdom military personnel are stationed there under a defence agreement signed between the two countries. ABell 212
The Bell 212 (also known as the ''Twin Two-Twelve'') is a two-blade, medium helicopter that first flew in 1968. Originally manufactured by Bell Helicopter in Fort Worth, Texas, United States, production was moved to Mirabel, Quebec, Canada in ...
operated by the air force crashed in Kuala Belait on 20 July 2012 with the loss of 12 of the 14 crew on board. The cause of the accident has yet to be ascertained. The crash is the worst aviation incident in the history of Brunei.
The Army is currently acquiring new equipment, including UAVs and S-70i Black Hawks.
Brunei's Legislative Council proposed an increase of the defence budget for the 2016–17 fiscal year of about five percent to 564 million Brunei dollars ($408 million). This amounts to about ten per cent of the state's total national yearly expenditure and represents around 2.5 per cent of GDP.
Administrative divisions
Brunei is divided into fourdistricts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
(), namely Brunei-Muara
Brunei-Muara District ( ms, Daerah Brunei dan Muara; Jawi: برونائی-موارا ضلع) or simply Brunei-Muara is one of the four districts of Brunei. It has the smallest area among the four districts, with , yet is the most populous, wi ...
, Belait, Tutong and Temburong. Brunei-Muara District is the smallest yet the most populous, and home to the country's capital Bandar Seri Begawan. Belait is the birthplace and centre for the country's oil and gas industry. Temburong is an exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
and separated from the rest of the country by the Brunei Bay
Brunei Bay ( ms, Teluk Brunei) is on the northwestern coast of Borneo island, in Brunei and Malaysia.
Brunei Bay is located 5°00'43.44", 115°17'26.66"; east of Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei.
It is the ocean gateway to the isolated Temburong Dis ...
and Malaysian state of Sarawak. Tutong is home to Tasek Merimbun, the country's largest natural lake.
Each district is divided into several mukims
A mukim is a type of administrative division used in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore. The word ''mukim'' is a loanword in English. However, it was also originally a loanword in Malay from the Arabic word: (meaning ''resident''). The clo ...
. Altogether there are 39 mukims in Brunei. Each mukim encompasses several villages ( or ).
Bandar Seri Begawan and towns in the country (except Muara and Bangar) are administered as Municipal Board areas (). Each municipal area may constitute villages or mukims, partially or as a whole. Bandar Seri Begawan and a few of the towns also function as capitals of the districts where they are located.
A district and its constituent mukims and villages are administered by a District Office (). Meanwhile, municipal areas are governed by Municipal Departments (). Both District Offices and Municipal Departments are government departments under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
Legal system
Brunei has numerous courts in its judicial branch. The highest court, though subject in civil cases to the appellate jurisdiction of the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, is the Supreme Court, which consists of the Court of Appeal and High Court. Both of these have a chief justice and two judges.Women and children
The U.S. Department of State has stated that discrimination against women is a problem in Brunei.2010 Human Rights Report: Brunei DarussalamUS Department of State The law prohibits sexual harassment and stipulates that whoever assaults or uses criminal force, intending thereby to outrage or knowing it is likely to outrage the modesty of a person, shall be punished with imprisonment for as much as five years and
caning
Caning is a form of corporal punishment consisting of a number of hits (known as "strokes" or "cuts") with a single Stick-fighting, cane usually made of rattan, generally applied to the offender's bare or clothed buttocks (see spanking) or ha ...
. The law stipulates imprisonment of up to 30 years, and caning with not fewer than 12 strokes for rape. The law does not criminalise spousal rape; it explicitly states that sexual intercourse by a man with his wife, as long as she is not under 13 years of age, is not rape. Protections against sexual assault by a spouse are provided under the amended Islamic Family Law Order 2010 and Married Women Act Order 2010. The penalty for breaching a protection order is a fine not exceeding BN$2,000 or imprisonment not exceeding six months. By law, sexual intercourse with a female under 14 years of age constitutes rape and is punishable by imprisonment for not less than eight years and not more than 30 years and not less than 12 strokes of the cane. The intent of the law is to protect girls from exploitation through prostitution and "other immoral purposes", including pornography.
Bruneian citizenship is derived through parents' nationality rather than ''jus soli
''Jus soli'' ( , , ; meaning "right of soil"), commonly referred to as birthright citizenship, is the right of anyone born in the territory of a state to nationality or citizenship.
''Jus soli'' was part of the English common law, in contras ...
''. Parents with stateless status are required to apply for a special pass for a child born in the country. Failure to register a child may make it difficult to enroll the child in school.
LGBT rights
Male and female homosexuality is illegal in Brunei. Sexual relations between men are punishable by death or whipping; sex between women is punishable by caning or imprisonment. In May 2019, the Brunei government extended its existing moratorium on the death penalty to the Sharia criminal code as well that made homosexual acts punishable with death by stoning.Religious rights
 In The Laws of Brunei, the right of non-Muslims to practice their faith is guaranteed by the 1959 Constitution. However, celebrations and prayers must be confined to places of worship and private residences. Upon adopting Sharia Penal Code, the Ministry of Religious Affairs banned Christmas decorations in public places, but did not forbid celebration of Christmas in places of worship and private premises.
On 25 December 2015, 4,000 out of 18,000 estimated local Catholics attended the mass of Christmas Day and Christmas Eve. The Brunei Times
In The Laws of Brunei, the right of non-Muslims to practice their faith is guaranteed by the 1959 Constitution. However, celebrations and prayers must be confined to places of worship and private residences. Upon adopting Sharia Penal Code, the Ministry of Religious Affairs banned Christmas decorations in public places, but did not forbid celebration of Christmas in places of worship and private premises.
On 25 December 2015, 4,000 out of 18,000 estimated local Catholics attended the mass of Christmas Day and Christmas Eve. The Brunei TimesIn 2015, the then-
head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may ...
of the Catholic Church in Brunei told '' The Brunei Times'', "To be quite honest there has been no change for us this year; no new restrictions have been laid down, although we fully respect and adhere to the existing regulations that our celebrations and worship be onfinedto the compounds of the church and private residences".
Brunei's revised penal code came into force in phases, commencing on 22 April 2014 with offences punishable by fines or imprisonment. The complete code, due for final implementation later, stipulated the death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
for numerous offenses (both violent and non-violent), such as insult or defamation of Muhammad, insulting any verses of the Quran and Hadith, blasphemy
Blasphemy is a speech crime and religious crime usually defined as an utterance that shows contempt, disrespects or insults a deity, an object considered sacred or something considered inviolable. Some religions regard blasphemy as a religiou ...
, declaring oneself a prophet or non-Muslim, robbery, rape, adultery, sodomy, extramarital sexual relations for Muslims, and murder. Stoning to death was the specified "method of execution for crimes of a sexual nature". Rupert Colville, spokesperson for the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) declared that, "Application of the death penalty for such a broad range of offences contravenes international law."
Animal rights
Brunei is the first country in Asia to have banned shark finning nationwide. Brunei has retained most of its forests, compared to its neighbours that share Borneo island. There is a public campaign calling to protectpangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smut ...
s which are considered a threatened treasure in Brunei.
Economy
 Brunei has the second-highest Human Development Index among the
Brunei has the second-highest Human Development Index among the Southeast Asian
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
nations, after Singapore. Crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
and natural gas production account for about 90% of its GDP. About of oil are produced every day, making Brunei the fourth-largest producer of oil in Southeast Asia. It also produces approximately of liquified natural gas per day, making Brunei the ninth-largest gas exporter in the world. '' Forbes'' also ranks Brunei as the fifth-richest nation out of 182, based on its petroleum and natural gas fields.
Substantial income from overseas investment supplements income from domestic production. Most of these investments are made by the Brunei Investment Agency, an arm of the Ministry of Finance. The government provides for all medical services, and subsidises rice and housing.
The national air carrier, Royal Brunei Airlines, is trying to develop Brunei as a hub for international travel between Europe and Australia/New Zealand. Central to this strategy is the position that the airline maintains at London Heathrow Airport. It holds a daily slot at the highly capacity-controlled airport, which it serves from Bandar Seri Begawan via Dubai. The airline also has services to major Asian destinations including Shanghai, Bangkok, Singapore and Manila.
Brunei depends heavily on imports such as agricultural products (e.g. rice, food products, livestock, etc.), vehicles and electrical products from other countries. Brunei imports 60% of its food; of that amount, around 75% come from other ASEAN countries.
Brunei's leaders are concerned that increasing integration in the world economy will undermine internal social cohesion and have therefore pursued an isolationist policy. However, it has become a more prominent player by serving as chairman for the 2000 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum. Brunei's leaders plan to upgrade the labour force, reduce unemployment, which was at 6.9% in 2014; strengthen the banking and tourism sectors, and, in general, broaden the economic base. A long-term development plan aims to diversify growth.
The government of Brunei has also promoted food self-sufficiency, especially in rice. Brunei renamed its Brunei Darussalam Rice 1 as Laila Rice during the launch of the "Padi Planting Towards Achieving Self-Sufficiency of Rice Production in Brunei Darussalam" ceremony at the Wasan padi fields in April 2009. In August 2009, the Royal Family reaped the first few Laila padi stalks, after years of attempts to boost local rice production, a goal first articulated about half a century ago. In July 2009 Brunei launched its national halal branding scheme, Brunei Halal, with a goal to export to foreign markets.
In 2020, Brunei's electricity production was largely based on fossil fuels; renewable energy accounted for less than 1% of produced electricity in the country.
Infrastructure
 As of 2019, the country's road network constituted a total length of , out of which were paved. The highway from Muara Town to Kuala Belait is a
As of 2019, the country's road network constituted a total length of , out of which were paved. The highway from Muara Town to Kuala Belait is a dual carriageway
A dual carriageway ( BE) or divided highway ( AE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are ...
.
Brunei is accessible by air, sea, and land transport. Brunei International Airport is the main entry point to the country. Royal Brunei Airlines is the national carrier. There is another airfield, the Anduki Airfield, located in Seria. The ferry terminal at Muara services regular connections to Labuan (Malaysia). Speedboats provide passenger and goods transportation to the Temburong district. The main highway running across Brunei is the Tutong-Muara Highway. The country's road network is well developed. Brunei has one main sea port located at Muara.
The airport in Brunei is currently being extensively upgraded. Changi Airport International is the consultant working on this modernisation, which planned cost is currently $150 million. This project is slated to add of new floorspace and includes a new terminal and arrival hall. With the completion of this project, the annual passenger capacity of the airport is expected to double from 1.5 to 3 million.
With one private car for every 2.09 persons, Brunei has one of the highest car ownership rates in the world. This has been attributed to the absence of a comprehensive transport system, low import tax, and low unleaded petrol price of B$0.53 per litre.
A new roadway connecting the Muara and Temburong districts of Brunei is slated to be completed in 2019. Fourteen kilometres (9 mi) of this roadway would be crossing the Brunei Bay
Brunei Bay ( ms, Teluk Brunei) is on the northwestern coast of Borneo island, in Brunei and Malaysia.
Brunei Bay is located 5°00'43.44", 115°17'26.66"; east of Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei.
It is the ocean gateway to the isolated Temburong Dis ...
. The bridge cost is $1.6 billion.
Banking
Bank of China received permission to open a branch in Brunei in April 2016.Citibank
Citibank, N. A. (N. A. stands for " National Association") is the primary U.S. banking subsidiary of financial services multinational Citigroup. Citibank was founded in 1812 as the City Bank of New York, and later became First National City ...
, which entered in 1972, closed its operations in Brunei in 2014. HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc is a British multinational universal bank and financial services holding company. It is the largest bank in Europe by total assets ahead of BNP Paribas, with US$2.953 trillion as of December 2021. In 2021, HSBC had $10.8 tri ...
, which had entered in 1947, closed its operation in Brunei in November 2017. May Bank of Malaysia, RHB Bank of Malaysia, Standard Chartered Bank of United Kingdom, United Overseas Bank of Singapore and Bank of China are currently operating in Brunei.
Demographics
 Ethnicities indigenous to Brunei include the Belait, Brunei Bisaya (not to be confused with the Bisaya/Visaya of the nearby Philippines), indigenous Bruneian Malay, Dusun, Kedayan, Lun Bawang, Murut and Tutong.
The population of Brunei in was , of which 76% live in urban areas. The rate of urbanisation is estimated at 2.13% per year from 2010 to 2015. The average life expectancy is 77.7 years. In 2014, 65.7% of the population were Malay, 10.3% are Chinese, 3.4% are indigenous, with 20.6% smaller groups making up the rest. There is a relatively large expatriate community.
Most expats come from non-
Ethnicities indigenous to Brunei include the Belait, Brunei Bisaya (not to be confused with the Bisaya/Visaya of the nearby Philippines), indigenous Bruneian Malay, Dusun, Kedayan, Lun Bawang, Murut and Tutong.
The population of Brunei in was , of which 76% live in urban areas. The rate of urbanisation is estimated at 2.13% per year from 2010 to 2015. The average life expectancy is 77.7 years. In 2014, 65.7% of the population were Malay, 10.3% are Chinese, 3.4% are indigenous, with 20.6% smaller groups making up the rest. There is a relatively large expatriate community.
Most expats come from non-Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
countries such as Australia, United Kingdom, South Korea, Japan, The Philippines, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam and India.
Religion
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
is the official religion of Brunei, specifically that of the Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
denomination and the Shafi'i school of Islamic jurisprudence. More than 80% of the population, including the majority of Bruneian Malays
Bruneian MalaysBrunei Malay in its various forms can be identified with a nation, an ethnic group and a
region. ( ms, Orang Melayu Brunei, Jawi: ) are a native Malay ethnic group that lives in Brunei, the federal territory of Labuan, the so ...
and Kedayans identify as Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
. Other faiths practised are Buddhism (7%, mainly by the Chinese) and Christianity (7.1%). Freethinkers, mostly Chinese, form about 7% of the population. Although most of them practise some form of religion with elements of Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism, they prefer to present themselves as having practised no religion officially, hence labelled as atheists in official censuses. Followers of indigenous religions are about 2% of the population.
Languages
The official language of Brunei is Standard Malay, for which both the Latin alphabet (Rumi
Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Rūmī ( fa, جلالالدین محمد رومی), also known as Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Balkhī (), Mevlânâ/Mawlānā ( fa, مولانا, lit= our master) and Mevlevî/Mawlawī ( fa, مولوی, lit= my ma ...
) and the Arabic alphabet ( Jawi) are used. Initially, Malay was written in Jawi script
Jawi (; ace, Jawoë; Kelantan-Pattani Malay, Kelantan-Pattani: ''Yawi''; ) is a writing system used for writing several languages of Southeast Asia, such as Acehnese language, Acehnese, Banjar language, Banjarese, Kerinci language, Kerinci, ...
before it was switched in to Latin alphabet around 1941.
The principal spoken language is ''Melayu Brunei'' ( Brunei Malay). Brunei Malay is rather divergent from standard Malay and the rest of the Malay dialects, being about 84% cognate with standard Malay,P.W. Martin and G. Poedjosoedarmo (1996). An overview of the language situation in Brunei Darussalam. In P.W. Martin, C. Ozog & G. Poedjosoedarmo (Eds.), ''Language use & language change in Brunei Darussalam'' (pp. 1–23). Athens, Ohio: Ohio University Center for International Studies. p. 7. and is mostly mutually intelligible with it.
English is widely used as a business and official language and it is spoken by a majority of the population in Brunei. English is used in business as a working language and as the language of instruction from primary to tertiary education.
Chinese languages are also widely spoken, and the Chinese minority in Brunei speak a number of varieties of Chinese.
Arabic is the religious language of Muslims and is taught in schools, particularly religious schools, and also in institutes of higher learning. As of 2004, there are six Arabic schools and one religious teachers' college in Brunei. A majority of Brunei's Muslim population has had some form of formal or informal education in the reading, writing and pronunciation of the Arabic language as part of their religious education.
Other languages and dialects spoken include Kedayan Malay
The Brunei Malay language, or Kedayan (, Jawi: ) is the most widely spoken language in Brunei and a lingua franca in some parts of Sarawak and Sabah, such as Labuan, Limbang, Lawas, Sipitang and Papar.Clynes, A. (2014). Brunei Malay: An Overvi ...
dialect, Tutong Malay dialect, Murut, and Dusun.
Culture
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, but is seen as much more conservative than Indonesia and Malaysia. Influences to Bruneian culture come from the Malay cultures of the Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago (Indonesian/Malay: , tgl, Kapuluang Malay) is the archipelago between mainland Indochina and Australia. It has also been called the " Malay world," "Nusantara", "East Indies", Indo-Australian Archipelago, Spices Archipe ...
. Four periods of cultural influence have occurred: animist, Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Islamic, and Western. Islam had a very strong influence, and was adopted as Brunei's ideology and philosophy.
As a Sharia
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the H ...
country, the sale and public consumption of alcohol is banned.Brunei Tourism Website (Government appointed)tourismbrunei.com Non-Muslims are allowed to bring in a limited amount of alcohol from their point of embarkation overseas for their own private consumption.
Media
Media in Brunei are said to be pro-government; press criticism of the government and monarchy is rare. The country ranks "Not Free" in media byFreedom House
Freedom House is a non-profit, majority U.S. government funded organization in Washington, D.C., that conducts research and advocacy on democracy, political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, and Wendell Wil ...
. Nonetheless, the press is not overtly hostile toward alternative viewpoints and is not restricted to publishing only articles regarding the government. The government allowed a printing and publishing company, Brunei Press PLC, to form in 1953. The company continues to print the English daily '' Borneo Bulletin''. This paper began as a weekly community paper and became a daily in 1990 Apart from The ''Borneo Bulletin'', there is also the '' Media Permata'' and Pelita Brunei, the local Malay newspapers which are circulated daily. '' The Brunei Times'' is another English independent newspaper published in Brunei since 2006.
The Brunei government owns and operates three television channels with the introduction of digital TV using DVB-T (RTB Perdana, RTB Aneka and RTB Sukmaindera) and five radio stations (National FM, Pilihan FM, Nur Islam FM, Harmony FM and Pelangi FM). A private company has made cable television available (Astro-Kristal) as well as one private radio station, Kristal FM.
It also has an online campus radio station, '' UBD FM'', that streams from its first university, Universiti Brunei Darussalam.
Sport
The most popular sport in Brunei is association football. The Brunei national football team joinedFIFA
FIFA (; stands for ''Fédération Internationale de Football Association'' ( French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was found ...
in 1969, but has not had much success. The top two football leagues are the Brunei Super League and the Brunei Premier League.
Brunei debuted at the Olympics in 1996; it has competed at all subsequent Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The inau ...
except 2008. The country has competed in badminton, shooting, swimming, and track-and-field, but has yet to win any medals. Brunei has had slightly more success at the Asian Games, winning four bronze medals. The first major international sporting event to be hosted in Brunei was the 1999 Southeast Asian Games
The 1999 Southeast Asian Games ( ms, Sukan Asia Tenggara 1999), officially known as the 20th Southeast Asian Games, was a Southeast Asian multi-sport event held in Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei Darussalam. This was the first time Brunei hosted th ...
. According to the all-time Southeast Asian Games medal table
The Southeast Asian Games, also known as the SEA Games, is a biennial multi-sport event involving participants from the current 11 countries of Southeast Asia. The games are under the regulation of the Southeast Asian Games Federation with supe ...
, Bruneian athletes have won a total of 14 gold, 55 silver and 163 bronze medals at the games.
See also
* List of Brunei-related topics *Outline of Brunei
The location of Brunei
The following outline is provided as an overview of and a topical guide to Brunei:
Brunei is a sovereign country located on the north coast of the Island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its coastline with the ...
Notes
References
Sources * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
GovernmentPrime Minister's Office of Brunei Darussalam
website
General information
Brunei
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Brunei profile
from the BBC News
Brunei
at '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' *
Key Development Forecasts for Brunei
from International Futures Travel
Brunei Tourism
website {{Coord, 4, 30, N, 114, 40, E, display=title 1888 establishments in the British Empire * Borneo Commonwealth monarchies Countries in Asia English-speaking countries and territories Former British colonies and protectorates in Asia Island countries Malay-speaking countries and territories Maritime Southeast Asia Member states of ASEAN Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Southeast Asian countries States and territories established in 1984 Sultanates