Bernardin Gigault de Bellefonds on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bernardin Gigault, Marquis de Bellefonds (1630–1694) was a French nobleman, soldier and courtier of the 17th century, who was appointed
 While the family came from
While the family came from
 In the first half of the 17th century, France was divided internally and threatened externally; while it largely stayed out of the 1618–1648
In the first half of the 17th century, France was divided internally and threatened externally; while it largely stayed out of the 1618–1648 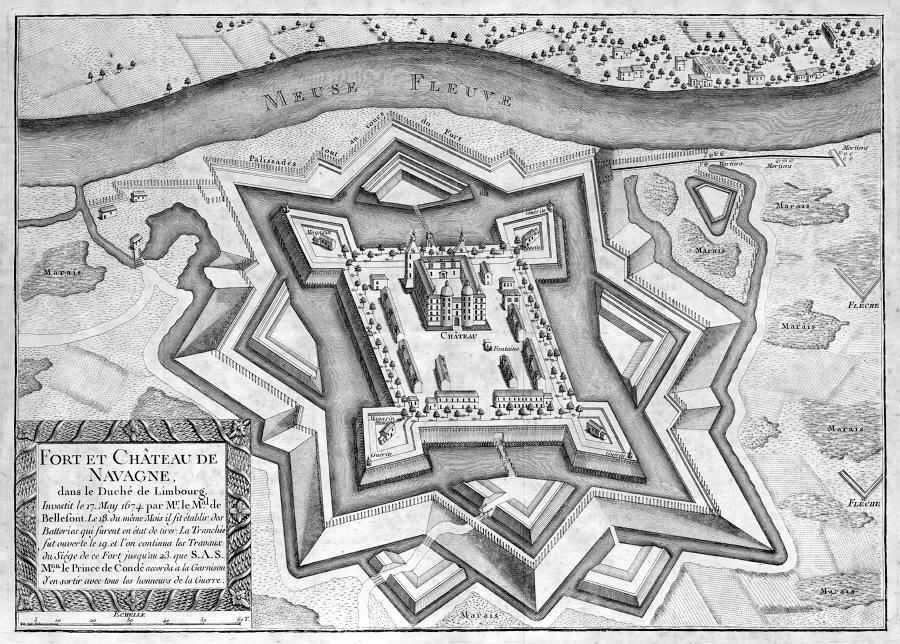 In the latter stages of the Franco-Spanish war, he served in
In the latter stages of the Franco-Spanish war, he served in  While he never recovered his previous office in the Maison du Roi, in 1680 he was appointed head of household or ''Grand Ecuyer'' to La Dauphine, Maria Anna of Bavaria, a position he held until her death in April 1690. In the 1683–1684
While he never recovered his previous office in the Maison du Roi, in 1680 he was appointed head of household or ''Grand Ecuyer'' to La Dauphine, Maria Anna of Bavaria, a position he held until her death in April 1690. In the 1683–1684
 Bellefonds was considered by contemporaries to be a man of morality but inflexible once he had decided on a course of action, which led to his banishment in 1672 and removal from command in 1674. He was known for religious piety, financing Notre-Dame-des-Anges, a convent near
Bellefonds was considered by contemporaries to be a man of morality but inflexible once he had decided on a course of action, which led to his banishment in 1672 and removal from command in 1674. He was known for religious piety, financing Notre-Dame-des-Anges, a convent near
Marshal of France
Marshal of France (french: Maréchal de France, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished (1 ...
in 1668 and held a number of senior positions in the personal household of Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
.
Life
Bellefonds
Bellefonds () is a commune in the Vienne department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region in western France.
See also
*Communes of the Vienne department
The following is a list of the 266 communes of the Vienne department of France
...
, in the central French department of Nouvelle-Aquitaine
Nouvelle-Aquitaine (; oc, Nòva Aquitània or ; eu, Akitania Berria; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Novéle-Aguiéne'') is the largest administrative region in France, spanning the west and southwest of the mainland. The region was created by t ...
, Bernadin's branch settled in Chef-du-Pont
Chef-du-Pont () is a former commune in the Manche department in Normandy in north-western France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the commune of Sainte-Mère-Église.
During World War 2, as part of the opening phase of Operation Overlord, du ...
, near Valognes, in Normandy. His paternal grandfather Bernardin Gigault de Bellefonds (1580–1639) was Governor of Valognes and Caen
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
.
Bernadin was the only child of Henri-Robert Gigault (?–1643), also Governor of Valognes and Caen, and Marie d'Avoynes, who brought the Servigny properties into the family. His father was one of eight and he had a wide circle of relatives in Normandy and Acquitaine.
He married Madeleine Fouquet de Chalain (1639–1716) in 1655 and they had 9 children; Jean (1660–1668), Louis-Christophe, killed at Steenkerque in 1692, Marie-Éléonore (?–1717), Thérèse-Marie (1667–1733), Jeanne-Susanne (1665–1698), Louise (?), Bernardine-Thérèse (?–1717), Françoise Bonne (1676–1693) and Marie-Armande-Agnès. His titles and estates were inherited by his grandson, Louis-Charles Bernadin (1685–1710).
Career
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
, support for the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
in its war of independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List of o ...
from Spain eventually led to the 1635–1659 Franco-Spanish War. At home, the French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estim ...
that had ended with the 1590 Edict of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed pr ...
flared up again in a series of domestic Huguenot rebellions
The Huguenot rebellions, sometimes called the Rohan Wars after the Huguenot leader Henri de Rohan, were a series of rebellions of the 1620s in which French Calvinist Protestants (Huguenots), mainly located in southwestern France, revolted agains ...
in the 1620s.
The accession of the five-year old Louis XIV in 1643 caused a power struggle between his regents, headed by his mother, Anne of Austria
Anne of Austria (french: Anne d'Autriche, italic=no, es, Ana María Mauricia, italic=no; 22 September 1601 – 20 January 1666) was an infanta of Spain who became Queen of France as the wife of King Louis XIII from their marriage in 1615 unti ...
and Cardinal Mazarin
Cardinal Jules Mazarin (, also , , ; 14 July 1602 – 9 March 1661), born Giulio Raimondo Mazzarino () or Mazarini, was an Italian cardinal, diplomat and politician who served as the chief minister to the Kings of France Louis XIII and Louis X ...
, opposed by regional magnates like Condé. This resulted in the 1648–1653 civil war known as the Fronde
The Fronde () was a series of civil wars in France between 1648 and 1653, occurring in the midst of the Franco-Spanish War, which had begun in 1635. King Louis XIV confronted the combined opposition of the princes, the nobility, the law cour ...
; Bellefonds became Governor of Valognes
Valognes () is a commune in the Manche department in Normandy in north-western France.
Geography
Valognes is situated in the Cotentin Peninsula, southeast of Cherbourg. Valognes station has rail connections to Caen, Paris and Cherbourg.
History ...
after his father's death in 1643 and in 1649 held it against rebel troops or ''Frondeurs''. Similarly, in November 1651 he defended Cognac
Cognac ( , also , ) is a variety of brandy named after the Communes of France, commune of Cognac, France. It is produced in the surrounding wine-growing region in the Departments of France, departments of Charente and Charente-Maritime.
Cog ...
in Nouvelle-Aquitaine
Nouvelle-Aquitaine (; oc, Nòva Aquitània or ; eu, Akitania Berria; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Novéle-Aguiéne'') is the largest administrative region in France, spanning the west and southwest of the mainland. The region was created by t ...
when besieged by Frondeurs under Condé, until it was relieved by the Comte d'Harcourt {{Unreferenced, date=June 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
When the Viking chieftain Rollo obtained via the Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte the territories which would later make up Normandy, he distributed them as estates among his main supporters. Amo ...
in early December.
 In the latter stages of the Franco-Spanish war, he served in
In the latter stages of the Franco-Spanish war, he served in Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the north ...
and Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
, including the decisive Battle of the Dunes in June 1658, which led to the 1659 Treaty of the Pyrenees and he was promoted Lieutenant-General in 1659. He was also employed in maritime operations, acting as deputy to the duc de Guise
Count of Guise and Duke of Guise (pronounced �ɥiz were titles in the French nobility.
Originally a seigneurie, in 1417 Guise was erected into a county for René, a younger son of Louis II of Anjou.
While disputed by the House of Luxembourg (1 ...
in his failed attempt to capture Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
in 1654 and in 1666 was sent to the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
to discuss joint fleet operations against England.
In 1663, he was appointed head of the Maison du Roi
The Maison du Roi (, "King's Household") was the royal household of the King of France. It comprised the military, domestic, and religious entourage of the French royal family during the Ancien Régime and Bourbon Restoration.
Organisation ...
or the King's household; given its proximity to Louis XIV, this was a position of great importance, held by an individual of proven loyalty. In the 1667–1668 War of Devolution
In the 1667 to 1668 War of Devolution (, ), France occupied large parts of the Spanish Netherlands and Franche-Comté, both then provinces of the Holy Roman Empire (and properties of the King of Spain). The name derives from an obscure law known ...
, France quickly over-ran Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté (, ; ; Frainc-Comtou: ''Fraintche-Comtè''; frp, Franche-Comtât; also german: Freigrafschaft; es, Franco Condado; all ) is a cultural and historical region of eastern France. It is composed of the modern departments of Doubs, ...
and much of the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the Ha ...
; after the capture of Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region, the Pref ...
in 1667, Turenne
Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne (11 September 161127 July 1675), commonly known as Turenne , was a French general and one of only six Marshals to have been promoted Marshal General of France. The most illustrious member of the ...
detached a cavalry force under Bellefonds and de Créquy to cut off the Spanish retreat. They inflicted nearly 2,000 casualties, with Louis looking on; in 1668, Bellefonds, de Créquy and Humières
Humières () is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regio ...
were all created Marshals of France
Marshal of France (french: Maréchal de France, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished (1 ...
.
However, the Dutch preferred a weak Spain as a neighbour in the Spanish Netherlands, to a strong and ambitious France; with England and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, they formed the Triple Alliance obliging Louis to return most of his gains in the 1668 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle. Angered by what he viewed as ingratitude for previous French support against Spain, Louis made preparations to invade the Netherlands.
In April 1672, Turenne was appointed ''general en chef'' or senior commander of French forces in the Netherlands; this caused problems, as the convention was Marshalls did not serve under other Marshalls. Bellefonds, Humières and de Créquy refused to serve under Turenne, arguing that to do so would diminish their personal prestige and the position of Marshal; all three were banished to their estates, while Bellefonds also lost his position as head of the ''Maison du Roi''.
When the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
began in May 1672, the French over-ran much of the Dutch Republic and initially seemed to have achieved an overwhelming victory. By late July, the Dutch position had stabilised and they gained the support of Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohenz ...
, Emperor Leopold
Leopold I (Leopold Ignaz Joseph Balthasar Franz Felician; hu, I. Lipót; 9 June 1640 – 5 May 1705) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia. The second son of Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, by his first wife, Maria An ...
and Charles II of Spain
Charles II of Spain (''Spanish: Carlos II,'' 6 November 1661 – 1 November 1700), known as the Bewitched (''Spanish: El Hechizado''), was the last Habsburg ruler of the Spanish Empire. Best remembered for his physical disabilities and the War o ...
. With new fronts opening in Spain and the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
, Louis decided to withdrew from the Dutch Republic by the end of 1673.
Bellefonds and his two colleagues had been taken back into service in November 1672 and he was put in charge of operations in the Netherlands. All Dutch towns held by the French were evacuated except for Grave
A grave is a location where a dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of burial, such as grave ...
and Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
, providing him with an army of 15,000 troops. Ignoring orders to remain on the defensive, in May 1674 he attacked and captured Fort Navagne and Argenteau, Spanish-held positions on the Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
between Maastricht and Liège
Liège ( , , ; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is a major city and municipality of Wallonia and the capital of the Belgian province of Liège.
The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from b ...
. A large Allied army was based nearby, which left his force dangerously exposed; Conde managed to reinforce him first but Bellefonds was removed from command.
War of the Reunions
The War of the Reunions (1683–84) was a conflict between France, Spain and the Holy Roman Empire, with limited involvement by Genoa. It can be seen as a continuation of the 1667–1668 War of Devolution and the 1672–1678 Franco–Dutch War, ...
, he once again commanded the French army in Catalonia and besieged the town of Girona
Girona (officially and in Catalan language, Catalan , Spanish: ''Gerona'' ) is a city in northern Catalonia, Spain, at the confluence of the Ter River, Ter, Onyar, Galligants, and Güell rivers. The city had an official population of 103,369 in ...
, although he was forced to retreat in May 1684, shortly before the Truce of Ratisbon
The Truce of Ratisbon, or Truce of Regensburg, concluded the War of the Reunions, fought by France against Spain and the Holy Roman Empire. The Truce was signed on 15 August 1684 at the Dominican convent in Ratisbon (now in Bavaria) between Louis X ...
.
Bellefonds had been acquainted with James II of England
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Gloriou ...
since the 1650s and following his exile to France in the 1688 Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
, accompanied him on religious retreats to La Trappe Abbey
La Trappe Abbey, also known as La Grande Trappe, is a monastery in Soligny-la-Trappe, Orne, France. It is known for being the house of origin of the Trappists, to whom it gave its name.
History
The site of the famous La Trappe Abbey was for cen ...
. In 1690, he was nominated general of French forces fighting in the Williamite War in Ireland
The Williamite War in Ireland (1688–1691; ga, Cogadh an Dá Rí, "war of the two kings"), was a conflict between Jacobite supporters of deposed monarch James II and Williamite supporters of his successor, William III. It is also called th ...
to restore James to his throne but the Marquis de St Ruth
Charles Chalmot de Saint-RuheLecestre, L. (ed.) (1921). ''Memoires de Saint-Simon'', v. 19, Hachette et cie, p. 135 (c. 165012 July 1691) was a French cavalry officer, serving in the armies of Louis XIV.
Despite a long career, Saint-Ruhe is re ...
was selected instead and was killed at Aughrim in July 1691. In 1692, he was given command of the expeditionary corps assembled at Saint-Vaast-la-Hougue
Saint-Vaast-la-Hougue is a commune in the Manche department in Normandy in north-western France.
Toponymy
Saint-Vaast is the Norman name of Saint Vedast and Hougue is a Norman language word meaning a "mound" or "loaf" and comes from the Old Norse ...
to support a proposed invasion of England. This ended after an inconclusive naval battle between the French and a combined Anglo-Dutch fleet at Barfleur on 29 May; a few days later, 12 French ships that had taken refuge at La Hogue were destroyed, while French land forces failed to intervene. Clearly fearing he would be blamed, Bellefonds wrote a lengthy explanation to the naval minister, the Comte de Pontchartrain
''Comte'' is the French, Catalan and Occitan form of the word 'count' (Latin: ''comes''); ''comté'' is the Gallo-Romance form of the word 'county' (Latin: ''comitatus'').
Comte or Comté may refer to:
* A count in French, from Latin ''comes''
* A ...
.
Regardless of who was to blame, this was his final military command; he died on 4 December 1694 at the Château de Vincennes
The Château de Vincennes () is a former fortress and royal residence next to the town of Vincennes, on the eastern edge of Paris, alongside the Bois de Vincennes. It was largely built between 1361 and 1369, and was a preferred residence, after ...
and buried in Sainte-Chapelle de Vincennes
The Sainte-Chapelle de Vincennes is a Gothic royal chapel within the fortifications of the Château de Vincennes on the east edge of Paris, France. It was inspired by the Sainte-Chapelle, the royal chapel within the Palais de la Cité in Paris. ...
, next to his daughter Françoise Bonne who died in 1693. His eldest son Louis-Christophe was killed at Steenkerque in 1692 and his titles and estates were inherited by his grandson, Louis-Charles Bernadin (1685–1710).
Legacy
 Bellefonds was considered by contemporaries to be a man of morality but inflexible once he had decided on a course of action, which led to his banishment in 1672 and removal from command in 1674. He was known for religious piety, financing Notre-Dame-des-Anges, a convent near
Bellefonds was considered by contemporaries to be a man of morality but inflexible once he had decided on a course of action, which led to his banishment in 1672 and removal from command in 1674. He was known for religious piety, financing Notre-Dame-des-Anges, a convent near Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of ...
established in 1650 by his aunt, Laurence Gigault de Bellefonds (1610–1683). He was also associated with the abbey of Port-Royal-des-Champs
Port-Royal-des-Champs was an abbey of Cistercian nuns in Magny-les-Hameaux, in the Vallée de Chevreuse southwest of Paris that launched a number of culturally important institutions.
History
The abbey was established in 1204, but became fa ...
, a centre of Jansenist
Jansenism was an early modern theological movement within Catholicism, primarily active in the Kingdom of France, that emphasized original sin, human depravity, the necessity of divine grace, and predestination. It was declared a heresy by th ...
thought, a then popular doctrine within French Catholicism controversial for its similarities to Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Cal ...
. Finally, he was close to Jacques-Bénigne Bossuet
Jacques-Bénigne Lignel Bossuet (; 27 September 1627 – 12 April 1704) was a French bishop and theologian, renowned for his sermons and other addresses. He has been considered by many to be one of the most brilliant orators of all time and a m ...
, Bishop to the Court at Versailles, and like him supported the decision of Louis' mistress Louise de La Vallière
Françoise ''Louise'' de La Vallière, Duchess of La Vallière and Vaujours, born Françoise Louise de La Baume Le Blanc de La Vallière, Mademoiselle de La Vallière (6 August 1644 – 7 June 1710) was a French noblewoman and the first mistress ...
to enter a Carmelite
, image =
, caption = Coat of arms of the Carmelites
, abbreviation = OCarm
, formation = Late 12th century
, founder = Early hermits of Mount Carmel
, founding_location = Mount Car ...
convent in Paris in 1675.
His letters to and from Louis XIV concerning the education of the Dauphin were later collected and published in ''Lettres sur l'éducation du dauphin; suivies de Lettres au maréchal de Belle-fonds et au roi. Introd. et notes de E. Levesque.''
The Rue de Bellefond in Paris is named after his daughter Marie-Éléonore, Abbess of nearby Montmartre Abbey
Montmartre Abbey (french: Abbaye de Montmartre) was a 12th-century Benedictine monastery established in the Montmartre district of Paris within the Diocese of Paris.
In 1133, King Louis VI purchased the Merovingian church of Saint Peter of Mo ...
, demolished in 1794.
References
Sources
* * * ; * ; * * ; * * ; * * ; * ; * ; {{DEFAULTSORT:Bellefonds, Bernardin Gigault de 1630 births 1694 deaths People from Manche Marshals of FranceAncien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for "ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
Order of the Holy Spirit
French military personnel of the Franco-Dutch War
French military personnel of the Nine Years' War