Battle Of The Crimea (1944) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Crimean offensive (8 April – 12 May 1944), known in German sources as the Battle of the Crimea, was a series of offensives by the Red Army directed at the German-held Crimea. The Red Army's 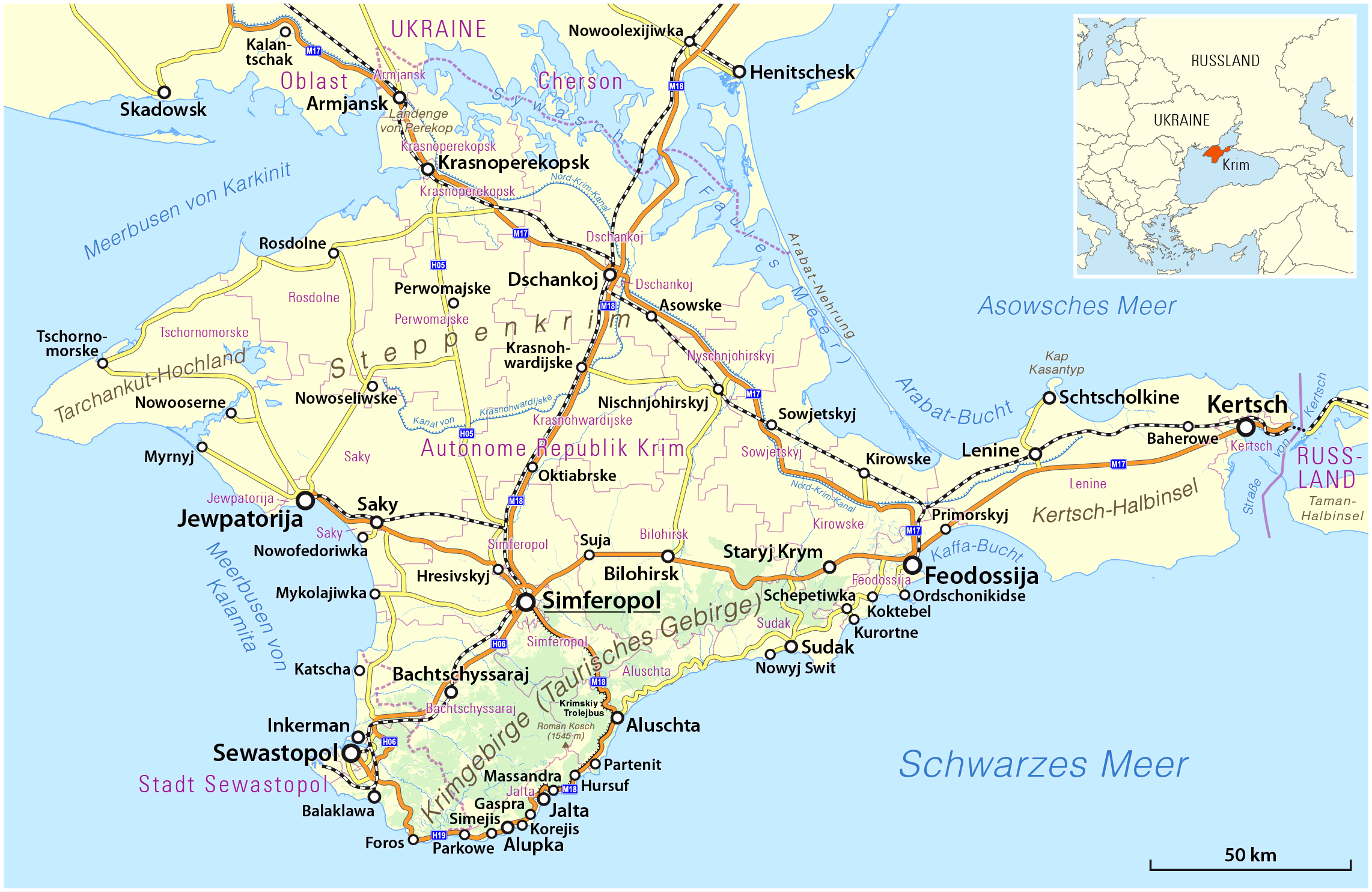

 The evacuation of the Crimea in April–May 1944 was the most complex and extensive operation of the Romanian Navy during the Second World War. From 15 April to 14 May, numerous German and Romanian warships escorted many convoys between Constanța and Sevastopol. The scale and importance of the operation can be attested by the usage in combat of all four Romanian destroyers, the largest Axis warships in the Black Sea. The last phase of the evacuation (10–14 May) saw the fiercest combat, as Axis ships transported, under constant attacks from Soviet aircraft and shore artillery, over 30,000 troops. Of these, 18,000 were transported by Romanian ships. On 11 May, the German tanker ''Friederike'' was torpedoed and heavily damaged by Soviet submarine L-4, preventing her participation.
In total, Romanian and German convoys evacuated over 113,000 Axis troops from the Crimea, most of them (over 63,000) during the first phase of the evacuation (15–25 April). No Romanian Navy warships were lost during the evacuation, however the destroyer ''Regele Ferdinand'' came close to being sunk. She was struck by a large aerial bomb, which fell in her fuel tanks, but failed to detonate. The bomb was extracted several days after the end of the operation. Two naval actions involving the Romanian Navy took place during the second phase of the evacuation (25 April–10 May), near Sevastopol. On 18 April, the Soviet ''Leninets''-class submarine ''L-6'' was twice attacked with depth charges and damaged by the Romanian gunboat '' Ghiculescu'', numerous bubbles emerged from the depths after each attack, before being finished off by the German submarine hunter ''UJ-104''. During the night of 27 April, a convoy escorted by the Romanian gunboat ''Ghiculescu'', the German submarine hunter ''UJ-115'', one R-boat, two KFK naval trawlers and 19 MFPs (including the Romanian ''PTA-404'' and ''PTA-406'') engaged the Soviet
The evacuation of the Crimea in April–May 1944 was the most complex and extensive operation of the Romanian Navy during the Second World War. From 15 April to 14 May, numerous German and Romanian warships escorted many convoys between Constanța and Sevastopol. The scale and importance of the operation can be attested by the usage in combat of all four Romanian destroyers, the largest Axis warships in the Black Sea. The last phase of the evacuation (10–14 May) saw the fiercest combat, as Axis ships transported, under constant attacks from Soviet aircraft and shore artillery, over 30,000 troops. Of these, 18,000 were transported by Romanian ships. On 11 May, the German tanker ''Friederike'' was torpedoed and heavily damaged by Soviet submarine L-4, preventing her participation.
In total, Romanian and German convoys evacuated over 113,000 Axis troops from the Crimea, most of them (over 63,000) during the first phase of the evacuation (15–25 April). No Romanian Navy warships were lost during the evacuation, however the destroyer ''Regele Ferdinand'' came close to being sunk. She was struck by a large aerial bomb, which fell in her fuel tanks, but failed to detonate. The bomb was extracted several days after the end of the operation. Two naval actions involving the Romanian Navy took place during the second phase of the evacuation (25 April–10 May), near Sevastopol. On 18 April, the Soviet ''Leninets''-class submarine ''L-6'' was twice attacked with depth charges and damaged by the Romanian gunboat '' Ghiculescu'', numerous bubbles emerged from the depths after each attack, before being finished off by the German submarine hunter ''UJ-104''. During the night of 27 April, a convoy escorted by the Romanian gunboat ''Ghiculescu'', the German submarine hunter ''UJ-115'', one R-boat, two KFK naval trawlers and 19 MFPs (including the Romanian ''PTA-404'' and ''PTA-406'') engaged the Soviet
Killed and missing: 31,700
Wounded: 33,400
Total: 65,100 Romanian:
Killed and missing: 25,800
Wounded: 5,800
Total: 31,600 Total:
Killed and missing: 57,500
Wounded: 39,200
Total: 96,700 Soviet losses Killed and missing: 17,754
Wounded: 67,065
Total: 84,819 Tanks: 171
Artillery: 521
Aircraft: 179
4th Ukrainian Front
The 4th Ukrainian Front (Russian: Четвёртый Украинский фронт) was the name of two distinct Red Army strategic army groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II.
The front was first formed on 20 October 1943, by ...
engaged the German 17th Army of Army Group A, which consisted of Wehrmacht and Romanian formations. The battles ended with the evacuation of the Crimea by the Germans. German and Romanian forces suffered considerable losses during the evacuation.

Prelude
The Germans took control of the Crimean Peninsula after the Crimean Campaign in 1942.Kerch-Eltigen operation
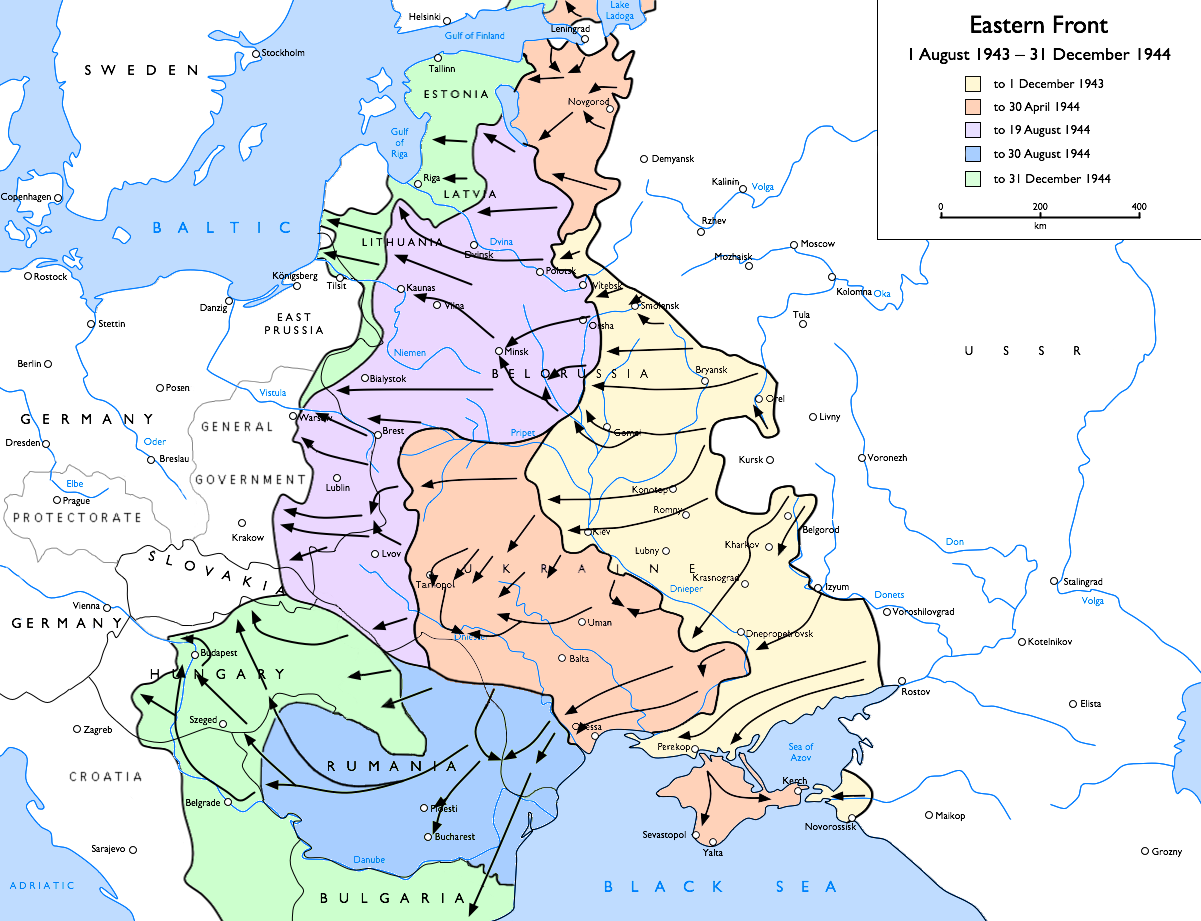
During late 1943 and early 1944, the Wehrmacht was pressed back along its entire front line in the east. In October 1943, the 17th Army withdrew from the Kuban bridgehead across the Kerch Strait into the Crimea. During the following months, the Red Army pushed back the Wehrmacht in southern Ukraine, eventually cutting off the land-based connection of 17th Army through the Perekop Isthmus in November 1943. The Wehrmacht was able to successfully hold on to the Crimea even after it had been cut off by land due to their ability to supply it via the Black Sea. Holding the Crimea was considered important as its loss would negatively affect the attitude of Turkey and put Romanian oilfields under risk of Soviet air attacks. Aside from Soviet landings across the Kerch Strait and in the north-eastern sector near Sivash at the end of 1943, the Soviet Army largely ignored the Crimea for the next five months. Paul Ludwig Ewald von Kleist was removed from the command of Army Group A on March 30, 1944. He was succeeded by Ferdinand Schörner.Progress of the battle
An assault across the Perekop Isthmus was launched on 8 April by elements of the4th Ukrainian Front
The 4th Ukrainian Front (Russian: Четвёртый Украинский фронт) was the name of two distinct Red Army strategic army groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II.
The front was first formed on 20 October 1943, by ...
's 2nd Guards and 51st Armies. The 17th Army defended but was unable to stop the advance. Kerch was reached by the Separate Coastal Army on 11 April; Simferopol, about northeast of Sevastopol, followed two days later. The 17th Army was retreating toward Sevastopol by 16 April, with remaining Axis forces in the Crimea concentrating around the city by the end of the third week of April.
The OKH intended to hold Sevastopol as a fortress, as the Red Army had done during the first Crimean campaign in 1941–42. However, the fortifications of the city had never been restored and Sevastopol was not the strong defensive position that it had been in 1941. Fighting broke out in the city outskirts towards the end of April and the city fell on 9 May, less than a month after the start of the offensive. The Axis sea evacuation to Constanța
Constanța (, ; ; rup, Custantsa; bg, Кюстенджа, Kyustendzha, or bg, Констанца, Konstantsa, label=none; el, Κωνστάντζα, Kōnstántza, or el, Κωνστάντια, Kōnstántia, label=none; tr, Köstence), histo ...
was attacked by Soviet land-based bombers.
Evacuation of the Crimea

G-5-class motor torpedo boat
The G-5 was a Soviet motor torpedo boat design built before and during World War II. Approximately 300 were built, of which 73 were lost during the war. Four were exported to the Spanish Republican Navy during the Spanish Civil War and others ...
s ''TKA-332'', ''TKA-343'' and ''TKA-344'', after the three attacked and damaged the German submarine hunter ''UJ-104''. ''Ghiculescu'' opened fire with tracer rounds, enabling the entire escort group to locate the two Soviet MTBs and open fire. ''TKA-332'' was hit and sunk. Over 12 Soviet aircraft were also shot down during the evacuation, including two by the minelaying destroyer escort ''Amiral Murgescu''. The last Axis pockets in the Crimea were destroyed on 12 May. The last Axis warship to leave the peninsula was ''Amiral Murgescu'', carrying on board 1,000 Axis troops, including the German General Walter Hartmann.
Consequences
In a meeting with Adolf Hitler in Berchtesgaden, 17th Army commander Erwin Jaenecke had insisted that Sevastopol should be evacuated and his cut off Army of 235,000 men withdrawn. After the loss of the Crimea, he was held responsible, arrested in Romania and court-martialed. Only the intervention of Heinz Guderian saved his life. He was dismissed from the army on 31 January 1945. The German and Romanian formations suffered the loss of 57,000 men, many of whom drowned during the evacuation. The sinking of the '' Totila'' and '' Teja'' on 10 May alone caused up to 10,000 deaths. In total, the German losses at sea amounted to five cargo ships, one tanker, three tugs, three lighters, three motorboats and four submarine hunters, while the Romanians lost three cargo ships. The partially successful evacuation of Axis troops from the Crimea earned the commander of the Romanian Navy, Rear Admiral Horia Macellariu, theKnight's Cross of the Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (german: Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II.
The Knight' ...
.Spencer C. Tucker, ''World War II at Sea: An Encyclopedia'', p. 633 The table below is based on information from Glantz/House ''When Titans Clashed''.:
Axis losses
German:Killed and missing: 31,700
Wounded: 33,400
Total: 65,100 Romanian:
Killed and missing: 25,800
Wounded: 5,800
Total: 31,600 Total:
Killed and missing: 57,500
Wounded: 39,200
Total: 96,700 Soviet losses Killed and missing: 17,754
Wounded: 67,065
Total: 84,819 Tanks: 171
Artillery: 521
Aircraft: 179
Land formations and units involved

Soviet
*4th Ukrainian Front
The 4th Ukrainian Front (Russian: Четвёртый Украинский фронт) was the name of two distinct Red Army strategic army groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II.
The front was first formed on 20 October 1943, by ...
** 2nd Guards Army
The 2nd Guards Army was a field army of the Soviet Union's Red Army that fought in World War II, most notably at Stalingrad.
History
The 2nd Guards Army was formed according to the order of the Staff of the Supreme High Command (Stavka) from Oc ...
** 51st Army
** 4th Air Army
Fourth or the fourth may refer to:
* the ordinal form of the number 4
* ''Fourth'' (album), by Soft Machine, 1971
* Fourth (angle), an ancient astronomical subdivision
* Fourth (music), a musical interval
* ''The Fourth'' (1972 film), a Sovie ...
* Black Sea Fleet
Chernomorskiy flot
, image = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet
, dates = May 13, ...
* Separate Coastal Army
* Partisans
Axis
German
* Army Group A ** 17th ArmyRomanian
* Romanian Mountain Corps ** 1st Mountain Division ** 2nd Mountain DivisionCitations
Bibliography
* * * * Ziemke, E.F. ''Stalingrad to Berlin'' * {{coord missing, Ukraine World War II aerial operations and battles of the Eastern Front Battles and operations of the Soviet–German War Strategic operations of the Red Army in World War II Crimea in World War II Naval battles of World War II involving the Soviet Union Naval battles of World War II involving Germany Naval battles of World War II involving Romania 1944 in Russia April 1944 events May 1944 events