|
Ferdinand Schörner
Ferdinand Schörner (12 June 1892 – 2 July 1973) was a German military commander and convicted war criminal, who held the rank of ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (Field Marshal) in the ''Wehrmacht'' of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was the only German soldier to rise to this rank from his initial status of '' Einjährig-Freiwilliger'' (One-year volunteer). He commanded several army groups and was the final Commander-in-chief of the German Army and the last man promoted to the rank of Field Marshal in the Wehrmacht. Schörner was a dedicated Nazi and became well known for his ruthlessness. By the end of World War II, he was Hitler's favourite commander. Following the war he was convicted of war crimes by courts in the Soviet Union and West Germany, and was imprisoned in the Soviet Union, East Germany and West Germany. Early life Schörner was born on 12 June 1892 in Munich, Kingdom of Bavaria, German Empire. He entered the Bavarian Army in October 1911 as a one-year volunt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberkommando Des Heeres
The (; abbreviated OKH) was the high command of the Army of Nazi Germany. It was founded in 1935 as part of Adolf Hitler's rearmament of Germany. OKH was ''de facto'' the most important unit within the German war planning until the defeat at Moscow in December 1941. During World War II, OKH had the responsibility of strategic planning of Armies and Army Groups. The General Staff of the OKH managed operational matters. Each German Army also had an Army High Command ( or AOK). The Armed Forces High Command () then took over this function for theatres other than the Eastern front. The OKH commander held the title of Commander-in-chief of the Army (). After the Battle of Moscow, the OKH commander Field marshal Walther von Brauchitsch was removed from office, and Hitler appointed himself as Commander-in-Chief of the Army. From 1938, OKH was, together with () and () formally subordinated to the . OKH vs OKW OKH had been independent until February 1938, when Hitler creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
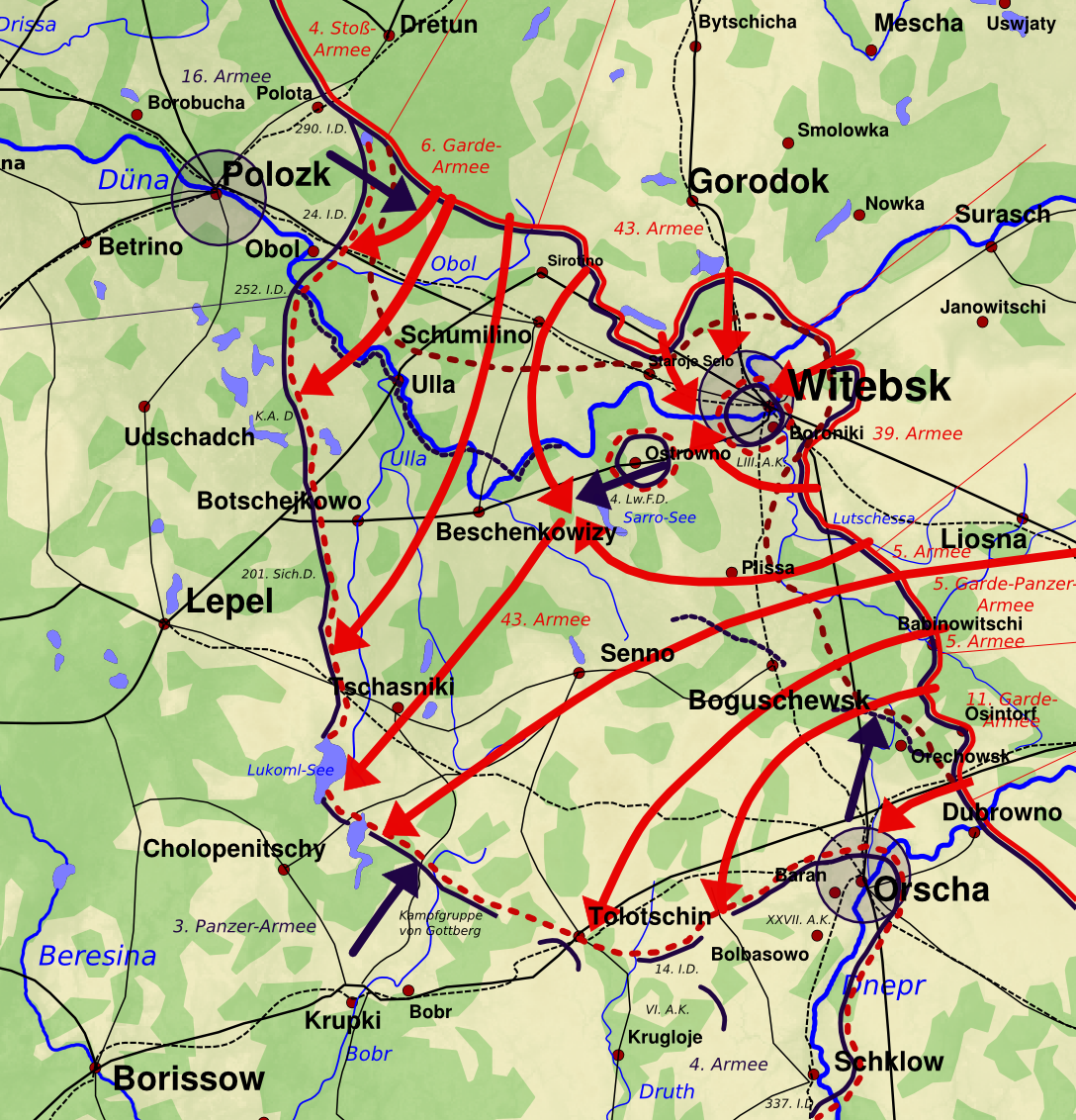
Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration () was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (), a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, just over two weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west. It was during this operation that Nazi Germany was forced to fight simultaneously on two major fronts for the first time since the war began. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of the divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. The overall engagement is the largest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while setting the stage for the subsequent isolation of 300,000 German soldiers in the Courland Pocket. On 22 June 1944, the Red Army attacked Army Group Centre in Byelorussia, with the objective of encircling and destroying its main component armies. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Crete
The Battle of Crete (, ), codenamed Operation Mercury (), was a major Axis Powers, Axis Airborne forces, airborne and amphibious assault, amphibious operation during World War II to capture the island of Crete. It began on the morning of 20 May 1941, with multiple Nazi Germany, German airborne landings on Crete. Hellenic Army, Greek and other Allies of World War II, Allied forces, along with Cretan civilians, defended the island. After only one day of fighting, the Germans had suffered heavy casualties and the Allied troops were confident that they would defeat the invasion. The next day, through communication failures, Allied tactical hesitation, and German offensive operations, Maleme Airfield in western Crete fell, enabling the Germans to land reinforcements and overwhelm the defensive positions on the north of the island. Allied forces withdrew to the south coast. More than half were evacuated by the British Royal Navy and the remainder surrendered or joined the Cretan resista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Thermopylae (1941)
The Battle of Thermopylae, on 24–25 April 1941, was part of the German invasion of Greece during World War II. Background Following the retreat of Allied forces from the mountain passes at Olympus and Servia, British Commonwealth forces began to set up defensive positions at the coastal pass at Thermopylae, famous for the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. The New Zealand Army's 2nd Infantry Division under Lieutenant-General Bernard Freyberg was given the task of defending the pass, while elements of the Australian 6th Infantry Division, under Major General Iven Mackay, defended the village of Brallos. In the New Zealand sector, the 5th Brigade was deployed in the foothills along the coastal road south of Lamia near the Spercheios River, covering the bridges on the road to Larisa. The 4th Brigade was positioned on the right flank, where it had established coast-watching patrols. The 6th Brigade was in reserve. The Australian force defending Brallos was composed pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tempe Gorge
The Battle of Tempe Gorge, also known as the Battle of Pinios Gorge, was a rearguard action fought by Australian and New Zealand troops during the German invasion of Greece on 18 April 1941. The battle was fought amidst the advance of German forces through central Greece, and saw a brigade-sized element dubbed "Anzac Force" fight a delaying action against elements of two German divisions, supported by armoured forces. During a day of hard fighting, the defending Anzacs suffered heavy casualties and were forced back from the gorge, but their stand allowed other Allied forces to withdraw through Larissa, and afterwards a new defensive position was established around Thermopylae. Background As the main Allied contingent retreated from German forces towards the south of Greece, a holding action was determined to be needed to delay the pursuing Germans at Tempe Gorge, a site deemed suitable for the defence. The force allocated for this action was dubbed "Anzac Force". It was relativel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Metaxas Line
The Battle of the Metaxas Line (), also known in Greece as the Battle of the Forts (), was the first battle during the German invasion of Greece in World War II. The Germans succeeded in capturing several individual forts but failed to breach the fortified Metaxas Line in general. The 2nd Panzer division ( XVIII Mountain Corps) with an enveloping move crossed the Yugoslavian borders, overcame Yugoslav and Greek resistance and captured Thessaloniki on the 9th of April. The capture of Thessaloniki forced the Greek East Macedonia Army Section to surrender on the 10th of April and the Metaxas Line battle was over. German General Wilhelm List, commander of the German forces attacking Greece, admired the bravery and courage of these soldiers. He refrained from taking the Greek soldiers prisoner and declared that the army was free to leave with their war flags, on condition that they surrender their arms and supplies. He also ordered his soldiers and officers to salute the Greek sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Greece
The German invasion of Greece or Operation Marita (), were the attacks on Greece by Italy and Germany during World War II. The Italian invasion in October 1940, which is usually known as the Greco-Italian War, was followed by the German invasion in April 1941. German landings on the island of Crete (May 1941) came after Allied forces had been defeated in mainland Greece. These battles were part of the greater Balkans Campaign of the Axis powers and their associates. Following the Italian invasion on 28 October 1940, Greece, with British air and material support, repelled the initial Italian attack and a counter-attack in March 1941. When the German invasion, known as Operation Marita, began on 6 April, the bulk of the Greek Army was on the Greek border with Albania, then a vassal of Italy, from which the Italian troops had attacked. German troops invaded from Bulgaria, creating a second front. Greece received a small reinforcement from British, Australian and New Zealand fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lwów (1939)
The Battle of Lwów (sometimes called the ''Siege of Lwów'') was a World War II battle for the control over the Poland, Polish city of Lviv, Lwów (now Lviv, Ukraine) between the Polish Army and the invading Wehrmacht and the Red Army. The city was seen as the key to the so-called Romanian Bridgehead and was defended at all costs. First clashes Initially, the city was not to be defended, as it was considered to be too deep behind the Polish lines and too important to Polish culture for warfare. However, the speed of the Nazi invasion and the almost-complete disintegration of the Polish reserve Prusy Army after the Battle of Łódź (1939), Battle of Łódź resulted in the city being in danger of a German assault. On September 7, 1939, General Władysław Langner started to organise the defence of the city., see also general reference No. 2 Initially, the Polish forces were to defend the Bełżec, Lublin Voivodeship, Bełżec – Rawa Ruska – Maheriv, Magierów line against th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |