B cell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of
 B cells undergo two types of selection while developing in the bone marrow to ensure proper development, both involving B cell receptors (BCR) on the surface of the cell. Positive selection occurs through antigen-independent signalling involving both the pre-BCR and the BCR. If these receptors do not bind to their
B cells undergo two types of selection while developing in the bone marrow to ensure proper development, both involving B cell receptors (BCR) on the surface of the cell. Positive selection occurs through antigen-independent signalling involving both the pre-BCR and the BCR. If these receptors do not bind to their 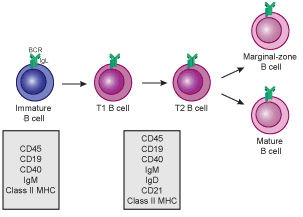
 B cell activation occurs in the
B cell activation occurs in the
 Once activated, B cells participate in a two-step differentiation process that yields both short-lived plasmablasts for immediate protection and long-lived plasma cells and memory B cells for persistent protection. The first step, known as the extrafollicular response, occurs outside lymphoid follicles but still in the SLO. During this step activated B cells proliferate, may undergo immunoglobulin class switching, and differentiate into plasmablasts that produce early, weak antibodies mostly of class IgM.
Once activated, B cells participate in a two-step differentiation process that yields both short-lived plasmablasts for immediate protection and long-lived plasma cells and memory B cells for persistent protection. The first step, known as the extrafollicular response, occurs outside lymphoid follicles but still in the SLO. During this step activated B cells proliferate, may undergo immunoglobulin class switching, and differentiate into plasmablasts that produce early, weak antibodies mostly of class IgM.
 The second step consists of activated B cells entering a lymphoid follicle and forming a germinal center (GC), which is a specialized microenvironment where B cells undergo extensive proliferation, immunoglobulin class switching, and
The second step consists of activated B cells entering a lymphoid follicle and forming a germinal center (GC), which is a specialized microenvironment where B cells undergo extensive proliferation, immunoglobulin class switching, and
 ; Plasmablast: A short-lived, proliferating antibody-secreting cell arising from B cell differentiation. Plasmablasts are generated early in an infection and their antibodies tend to have a weaker affinity towards their target antigen compared to plasma cell. Plasmablasts can result from T cell-independent activation of B cells or the extrafollicular response from T cell-dependent activation of B cells.
;
; Plasmablast: A short-lived, proliferating antibody-secreting cell arising from B cell differentiation. Plasmablasts are generated early in an infection and their antibodies tend to have a weaker affinity towards their target antigen compared to plasma cell. Plasmablasts can result from T cell-independent activation of B cells or the extrafollicular response from T cell-dependent activation of B cells.
;
 B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
of the lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
. B cells produce antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptor
The B cell receptor (BCR) is a transmembrane protein on the surface of a B cell. A B cell receptor is composed of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin molecule and a signal transduction moiety. The former forms a type 1 transmembrane receptor protein, ...
s. When a naïve or memory B cell
In immunology, a memory B cell (MBC) is a type of B lymphocyte that forms part of the adaptive immune system. These cells develop within germinal centers of the secondary lymphoid organs. Memory B cells circulate in the blood stream in a quiescen ...
is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s. In mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, B cells mature in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
, which is at the core of most bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
s. In bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ...
s, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius In birds, the bursa of Fabricius (Latin: ''bursa cloacalis'' or ''bursa fabricii'') is the site of hematopoiesis. It is a specialized organ that, as first demonstrated by Bruce Glick and later by Max Dale Cooper and Robert Good, is necessary fo ...
, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed.
B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s and natural killer cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and repres ...
s, express B cell receptors (BCRs) on their cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
. BCRs allow the B cell to bind
BIND () is a suite of software for interacting with the Domain Name System (DNS). Its most prominent component, named (pronounced ''name-dee'': , short for ''name daemon''), performs both of the main DNS server roles, acting as an authoritative ...
to a foreign antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
, against which it will initiate an antibody response. B cell receptors are extremely specific, with all BCRs on a B cell recognizing the same epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The p ...
.
Development
B cells develop from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that originate frombone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
. HSCs first differentiate into multipotent progenitor
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, which are one of the five types of white blood cells (WBCs). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.
Disruption in lymphopoiesis can lead t ...
(MPP) cells, then common lymphoid progenitor
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, which are one of the five types of white blood cells (WBCs). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.
Disruption in lymphopoiesis can lead t ...
(CLP) cells. From here, their development into B cells occurs in several stages (shown in image to the right), each marked by various gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The ...
patterns and immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
H chain and L chain gene loci arrangements, the latter due to B cells undergoing V(D)J recombination
V(D)J recombination is the mechanism of somatic recombination that occurs only in developing lymphocytes during the early stages of T and B cell maturation. It results in the highly diverse repertoire of antibodies/immunoglobulins and T cell re ...
as they develop.
 B cells undergo two types of selection while developing in the bone marrow to ensure proper development, both involving B cell receptors (BCR) on the surface of the cell. Positive selection occurs through antigen-independent signalling involving both the pre-BCR and the BCR. If these receptors do not bind to their
B cells undergo two types of selection while developing in the bone marrow to ensure proper development, both involving B cell receptors (BCR) on the surface of the cell. Positive selection occurs through antigen-independent signalling involving both the pre-BCR and the BCR. If these receptors do not bind to their ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
, B cells do not receive the proper signals and cease to develop. Negative selection occurs through the binding of self-antigen with the BCR; If the BCR can bind strongly to self-antigen, then the B cell undergoes one of four fates: clonal deletion
In immunology, clonal deletion is the removal through apoptosis of B cells and T cells that have expressed receptors for self before developing into fully immunocompetent lymphocytes. This prevents recognition and destruction of self host cells, ...
, receptor editing Receptor editing is a process that occurs during the maturation of B cells, which are part of the adaptive immune system. This process forms part of central tolerance to attempt to change the specificity of the antigen receptor of self reactive imma ...
, anergy
In immunology, anergy is a lack of reaction by the body's defense mechanisms to foreign substances, and consists of a direct induction of peripheral lymphocyte tolerance. An individual in a state of anergy often indicates that the immune syste ...
, or ignorance (B cell ignores signal and continues development). This negative selection process leads to a state of central tolerance
In immunology, central tolerance (also known as negative selection) is the process of eliminating any ''developing'' T or B lymphocytes that are autoreactive, i.e. reactive to the body itself. Through elimination of autoreactive lymphocytes, to ...
, in which the mature B cells do not bind self antigens present in the bone marrow.
To complete development, immature B cells migrate from the bone marrow into the spleen as transitional B cells, passing through two transitional stages: T1 and T2. Throughout their migration to the spleen and after spleen entry, they are considered T1 B cells. Within the spleen, T1 B cells transition to T2 B cells. T2 B cells differentiate into either follicular (FO) B cells or marginal zone (MZ) B cells depending on signals received through the BCR and other receptors. Once differentiated, they are now considered mature B cells, or naive B cells.
Activation
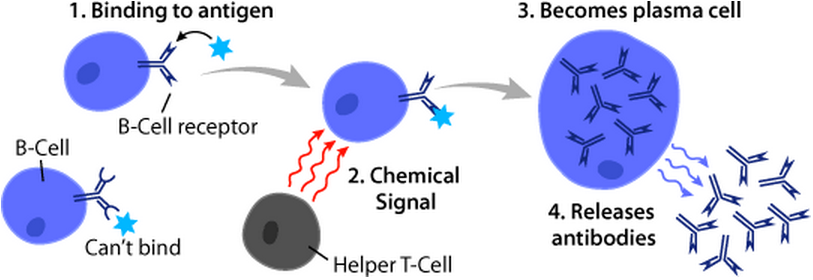
 B cell activation occurs in the
B cell activation occurs in the secondary lymphoid organs
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid ...
(SLOs), such as the spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
and lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
. After B cells mature in the bone marrow, they migrate through the blood to SLOs, which receive a constant supply of antigen through circulating lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to ...
. At the SLO, B cell activation begins when the B cell binds to an antigen via its BCR. Although the events taking place immediately after activation have yet to be completely determined, it is believed that B cells are activated in accordance with the kinetic segregation model , initially determined in T lymphocytes. This model denotes that before antigen stimulation, receptors diffuse through the membrane coming into contact with Lck
Lck (or lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase) is a 56 kDa protein that is found inside specialized cells of the immune system called lymphocytes. The Lck is a member of Src kinase family (SFK), it is important for the activation of the T ...
and CD45
Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, C also known as PTPRC is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ''PTPRC'' gene. PTPRC is also known as CD45 antigen (CD stands for cluster of differentiation), which was originally called leuko ...
in equal frequency, rendering a net equilibrium of phosphorylation and non-phosphorylation. It is only when the cell comes in contact with an antigen presenting cell that the larger CD45 is displaced due to the close distance between the two membranes. This allows for net phosphorylation of the BCR and the initiation of the signal transduction pathway. Of the three B cell subsets, FO B cells preferentially undergo T cell-dependent activation while MZ B cells and B1 B cells preferentially undergo T cell-independent activation.
B cell activation is enhanced through the activity of CD21
Complement receptor type 2 (CR2), also known as complement C3d receptor, Epstein-Barr virus receptor, and CD21 (cluster of differentiation 21), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR2 gene.
CR2 is involved in the complement system. It ...
, a surface receptor in complex with surface proteins CD19 and CD81 (all three are collectively known as the B cell coreceptor complex). When a BCR binds an antigen tagged with a fragment of the C3 complement protein, CD21 binds the C3 fragment, co-ligates with the bound BCR, and signals are transduced through CD19 and CD81 to lower the activation threshold of the cell.
T cell-dependent activation
Antigens that activate B cells with the help of T-cell are known as T cell-dependent (TD) antigens and include foreign proteins. They are named as such because they are unable to induce a humoral response in organisms that lack T cells. B cell responses to these antigens takes multiple days, though antibodies generated have a higher affinity and are more functionally versatile than those generated from T cell-independent activation. Once a BCR binds a TD antigen, the antigen is taken up into the B cell throughreceptor-mediated endocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME), also called clathrin-mediated endocytosis, is a process by which cells absorb metabolites, hormones, proteins – and in some cases viruses – by the inward budding of the plasma membrane (invagination). Thi ...
, degraded, and presented to T cells as peptide pieces in complex with MHC-II molecules on the cell membrane. T helper (TH) cells, typically follicular T helper (TFH) cells recognize and bind these MHC-II-peptide complexes through their T cell receptor (TCR). Following TCR-MHC-II-peptide binding, T cells express the surface protein CD40L
CD154, also called CD40 ligand or CD40L, is a protein that is primarily expressed on activated T cells and is a member of the TNF superfamily of molecules. It binds to CD40 on antigen-presenting cells (APC), which leads to many effects dependin ...
as well as cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-21. CD40L serves as a necessary co-stimulatory factor for B cell activation by binding the B cell surface receptor CD40
Cluster of differentiation 40, CD40 is a costimulatory protein found on antigen-presenting cells and is required for their activation. The binding of CD154 ( CD40L) on TH cells to CD40 activates antigen presenting cells and induces a variety of d ...
, which promotes B cell proliferation, immunoglobulin class switching
Immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class-switch recombination (CSR), is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the ...
, and somatic hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes), as seen during class switching. A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM div ...
as well as sustains T cell growth and differentiation. T cell-derived cytokines bound by B cell cytokine receptor
Cytokine receptors are receptors that bind to cytokines.
In recent years, the cytokine receptors have come to demand the attention of more investigators than cytokines themselves, partly because of their remarkable characteristics, and partly be ...
s also promote B cell proliferation, immunoglobulin class switching, and somatic hypermutation as well as guide differentiation. After B cells receive these signals, they are considered activated.  Once activated, B cells participate in a two-step differentiation process that yields both short-lived plasmablasts for immediate protection and long-lived plasma cells and memory B cells for persistent protection. The first step, known as the extrafollicular response, occurs outside lymphoid follicles but still in the SLO. During this step activated B cells proliferate, may undergo immunoglobulin class switching, and differentiate into plasmablasts that produce early, weak antibodies mostly of class IgM.
Once activated, B cells participate in a two-step differentiation process that yields both short-lived plasmablasts for immediate protection and long-lived plasma cells and memory B cells for persistent protection. The first step, known as the extrafollicular response, occurs outside lymphoid follicles but still in the SLO. During this step activated B cells proliferate, may undergo immunoglobulin class switching, and differentiate into plasmablasts that produce early, weak antibodies mostly of class IgM.
 The second step consists of activated B cells entering a lymphoid follicle and forming a germinal center (GC), which is a specialized microenvironment where B cells undergo extensive proliferation, immunoglobulin class switching, and
The second step consists of activated B cells entering a lymphoid follicle and forming a germinal center (GC), which is a specialized microenvironment where B cells undergo extensive proliferation, immunoglobulin class switching, and affinity maturation
In immunology, affinity maturation is the process by which TFH cell-activated B cells produce antibodies with increased affinity for antigen during the course of an immune response. With repeated exposures to the same antigen, a host will produc ...
directed by somatic hypermutation. These processes are facilitated by TFH cells within the GC and generate both high-affinity memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells. Resultant plasma cells secrete large amounts of antibody and either stay within the SLO or, more preferentially, migrate to bone marrow.
T cell-independent activation
Antigens that activate B cells without T cell help are known as T cell-independent (TI) antigens and include foreign polysaccharides and unmethylated CpG DNA. They are named as such because they are able to induce a humoral response in organisms that lack T cells. B cell response to these antigens is rapid, though antibodies generated tend to have lower affinity and are less functionally versatile than those generated from T cell-dependent activation. As with TD antigens, B cells activated by TI antigens need additional signals to complete activation, but instead of receiving them from T cells, they are provided either by recognition and binding of a common microbial constituent to toll-like receptors (TLRs) or by extensive crosslinking of BCRs to repeated epitopes on a bacterial cell. B cells activated by TI antigens go on to proliferate outside lymphoid follicles but still in SLOs (GCs do not form), possibly undergo immunoglobulin class switching, and differentiate into short-lived plasmablasts that produce early, weak antibodies mostly of class IgM, but also some populations of long-lived plasma cells.Memory B cell activation
Memory B cell activation begins with the detection and binding of their target antigen, which is shared by their parent B cell. Some memory B cells can be activated without T cell help, such as certain virus-specific memory B cells, but others need T cell help. Upon antigen binding, the memory B cell takes up the antigen through receptor-mediated endocytosis, degrades it, and presents it to T cells as peptide pieces in complex with MHC-II molecules on the cell membrane. Memory T helper (TH) cells, typically memory follicular T helper (TFH) cells, that were derived from T cells activated with the same antigen recognize and bind these MHC-II-peptide complexes through their TCR. Following TCR-MHC-II-peptide binding and the relay of other signals from the memory TFH cell, the memory B cell is activated and differentiates either into plasmablasts and plasma cells via an extrafollicular response or enter a germinal center reaction where they generate plasma cells and more memory B cells. It is unclear whether the memory B cells undergo further affinity maturation within these secondary GCs. ''In vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology an ...
'' activation of memory B cells can be achieved through stimulation with various activators, such as pokeweed mitogen or anti-CD40
Cluster of differentiation 40, CD40 is a costimulatory protein found on antigen-presenting cells and is required for their activation. The binding of CD154 ( CD40L) on TH cells to CD40 activates antigen presenting cells and induces a variety of d ...
monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodies ca ...
, however, a study found a combination of R-848 and recombinant human IL-2 to be the most efficient activator.
B cell types
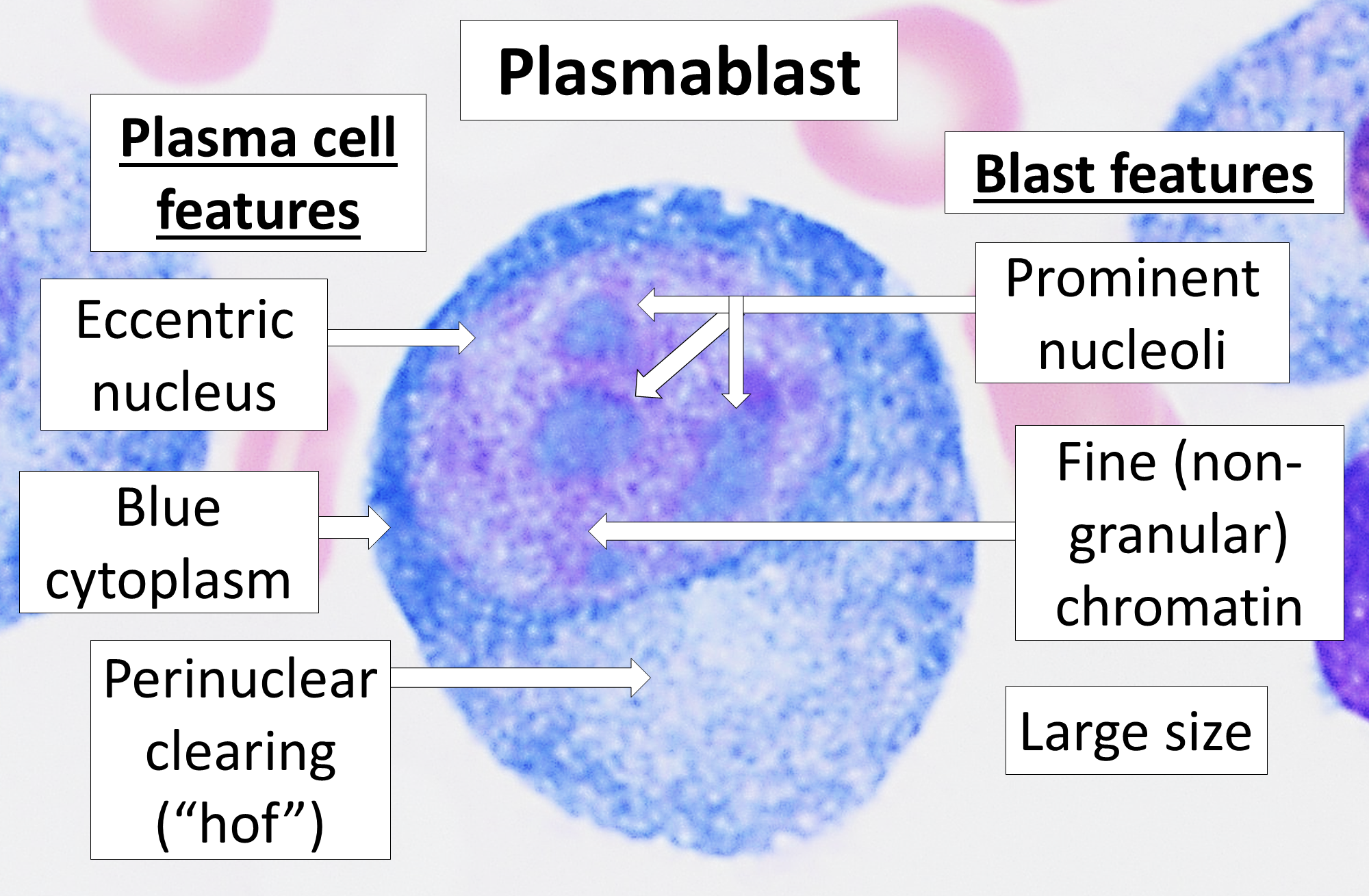
 ; Plasmablast: A short-lived, proliferating antibody-secreting cell arising from B cell differentiation. Plasmablasts are generated early in an infection and their antibodies tend to have a weaker affinity towards their target antigen compared to plasma cell. Plasmablasts can result from T cell-independent activation of B cells or the extrafollicular response from T cell-dependent activation of B cells.
;
; Plasmablast: A short-lived, proliferating antibody-secreting cell arising from B cell differentiation. Plasmablasts are generated early in an infection and their antibodies tend to have a weaker affinity towards their target antigen compared to plasma cell. Plasmablasts can result from T cell-independent activation of B cells or the extrafollicular response from T cell-dependent activation of B cells.
; Plasma cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B lymphocytes and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substan ...
: A long-lived, non-proliferating antibody-secreting cell arising from B cell differentiation. There is evidence that B cells first differentiate into a plasmablast-like cell, then differentiate into a plasma cell. Plasma cells are generated later in an infection and, compared to plasmablasts, have antibodies with a higher affinity towards their target antigen due to affinity maturation in the germinal center (GC) and produce more antibodies. Plasma cells typically result from the germinal center reaction from T cell-dependent activation of B cells, though they can also result from T cell-independent activation of B cells.
; Lymphoplasmacytoid cell: A cell with a mixture of B lymphocyte and plasma cell morphological features that is thought to be closely related to or a subtype of plasma cells. This cell type is found in pre-malignant and malignant plasma cell dyscrasia
Plasma cell dyscrasias (also termed plasma cell disorders and plasma cell proliferative diseases) are a spectrum of progressively more severe monoclonal gammopathies in which a clone or multiple clones of pre-malignant or malignant plasma cells (s ...
s that are associated with the secretion of IgM
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is one of several isotypes of antibody (also known as immunoglobulin) that are produced by vertebrates. IgM is the largest antibody, and it is the first antibody to appear in the response to initial exposure to an antig ...
monoclonal proteins; these dyscrasias include IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia.
; Memory B cell
In immunology, a memory B cell (MBC) is a type of B lymphocyte that forms part of the adaptive immune system. These cells develop within germinal centers of the secondary lymphoid organs. Memory B cells circulate in the blood stream in a quiescen ...
: Dormant B cell arising from B cell differentiation. Their function is to circulate through the body and initiate a stronger, more rapid antibody response (known as the anamnestic secondary antibody response) if they detect the antigen that had activated their parent B cell (memory B cells and their parent B cells share the same BCR, thus they detect the same antigen). Memory B cells can be generated from T cell-dependent activation through both the extrafollicular response and the germinal center reaction as well as from T cell-independent activation of B1 cells.
; B-2 cell: FO B cells and MZ B cells.
:; Follicular (FO) B cell (also known as a B-2 cell): Most common type of B cell and, when not circulating through the blood, is found mainly in the lymphoid follicles of secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs). They are responsible for generating the majority of high-affinity antibodies during an infection.
:; Marginal-zone (MZ) B cell: Found mainly in the marginal zone of the spleen and serves as a first line of defense against blood-borne pathogens, as the marginal zone receives large amounts of blood from the general circulation. They can undergo both T cell-independent and T cell-dependent activation, but preferentially undergo T cell-independent activation.
; B-1 cell
B1 cells are a sub-class of B cell lymphocytes that are involved in the humoral immune response. They are not part of the adaptive immune system, as they have no memory, but otherwise, B1 cells perform many of the same roles as other B cells: maki ...
: Arises from a developmental pathway different from FO B cells and MZ B cells. In mice, they predominantly populate the peritoneal cavity
The peritoneal cavity is a potential space between the parietal peritoneum (the peritoneum that surrounds the abdominal wall) and visceral peritoneum (the peritoneum that surrounds the internal organs). The parietal and visceral peritonea are la ...
and pleural cavity
The pleural cavity, pleural space, or interpleural space is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication bet ...
, generate natural antibodies (antibodies produced without infection), defend against mucosal pathogens, and primarily exhibit T cell-independent activation. A true homologue of mouse B-1 cells has not been discovered in humans, though various cell populations similar to B-1 cells have been described.
; Regulatory B (Breg) cell: An immunosuppressive
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
B cell type that stops the expansion of pathogenic, pro-inflammatory lymphocytes through the secretion of IL-10, IL-35, and TGF-β. Also, it promotes the generation of regulatory T (Treg) cells by directly interacting with T cells to skew their differentiation towards Tregs. No common Breg cell identity has been described and many Breg cell subsets sharing regulatory functions have been found in both mice and humans. It is currently unknown if Breg cell subsets are developmentally linked and how exactly differentiation into a Breg cell occurs. There is evidence showing that nearly all B cell types can differentiate into a Breg cell through mechanisms involving inflammatory signals and BCR recognition.
B cell-related pathology
Autoimmune disease can result from abnormal B cell recognition of self-antigens followed by the production of autoantibodies. Autoimmune diseases where disease activity is correlated with B cell activity includescleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas ...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This d ...
, systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
, type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar ...
, post-infectious IBS, and rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involv ...
.
Malignant transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as ''malignant degeneration'' of a previously existing benign tumor.
Causes
There are ...
of B cells and their precursors can cause a host of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), hairy cell leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon hematological malignancy characterized by an accumulation of abnormal B lymphocytes. It is usually classified as a subtype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Hairy cell leukemia makes up about 2% of all leu ...
, follicular lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is a cancer that involves certain types of white blood cells known as lymphocytes. The cancer originates from the uncontrolled division of specific types of B-cells known as centrocytes and centroblasts. These cells normal ...
, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of hematological malignancy, blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes, fever ...
, Hodgkin's lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition wa ...
, and plasma cell malignancies such as multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, an ...
, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, and certain forms of amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weight ...
.
Abnormal B cells may be relatively large and some diseases include this in their names, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a cancer of B cells, a type of lymphocyte that is responsible for producing antibody, antibodies. It is the most common form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma among adults, with an annual Incidence (epidemiology), in ...
s (DLBCLs) and intravascular large B-cell lymphoma
Intravascular lymphomas (IVL) are rare cancers in which malignant lymphocytes proliferate and accumulate within blood vessels. Almost all other tyes of lymphoma involve the proliferation and accumulation of malignant lymphocytes in lymph nodes, ...
.
Patients with B cell alymphocytosis are predisposed to infections.
Epigenetics
A study that investigated the methylome of B cells along their differentiation cycle, using whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS), showed that there is a hypomethylation from the earliest stages to the most differentiated stages. The largest methylation difference is between the stages of germinal center B cells and memory B cells. Furthermore, this study showed that there is a similarity between B cell tumors and long-lived B cells in theirDNA methylation
DNA methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. When located in a gene promoter, DNA methylation typically acts t ...
signatures.
See also
*A20 cells
A20 cells, also called ATCC TIB-208, is a cell line originally derived from B-cell lymphoma in an old BALB/c mouse. AT20 cells are BALB/c lymphoma cells derived from spontaneous reticulum cell neoplasm. ATCC TIB-208 cells originated from B-cell ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:B Cell B cells Lymphocytes Human cells Immunology Immune system