Byronosaurus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Byronosaurus'' is a
 ''Byronosaurus'' was a small dinosaur, measuring about long and tall; it weighed only about . Unlike most other troodontids, its teeth seem to lack serrations just like its closest relative ''
''Byronosaurus'' was a small dinosaur, measuring about long and tall; it weighed only about . Unlike most other troodontids, its teeth seem to lack serrations just like its closest relative ''
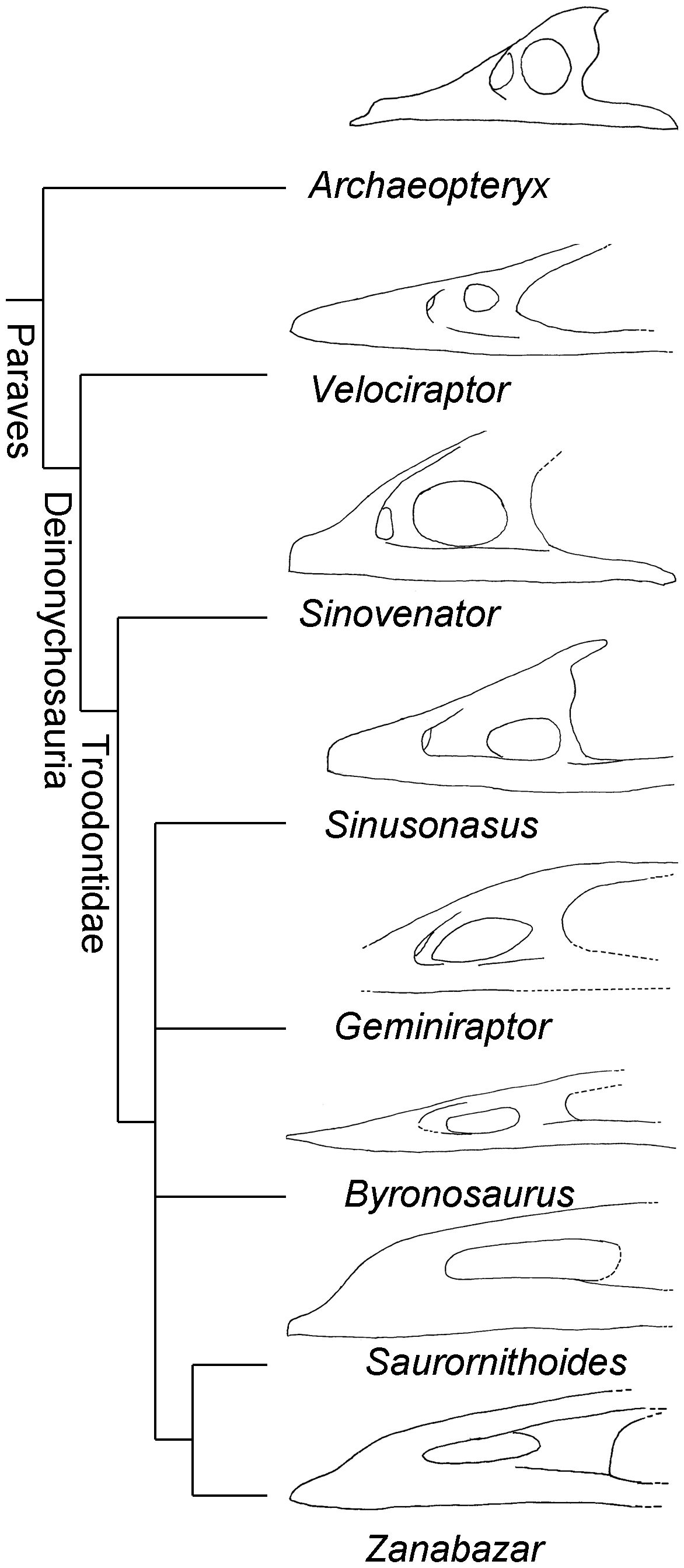 The following
The following
 Due to their large brains, possible
Due to their large brains, possible

Dinosauria.com
{{Taxonbar, from=Q134297 Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia Djadochta fauna Troodontids Fossil taxa described in 2000 Taxa named by Mark Norell
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of troodontid
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil discov ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
from the Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
Period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
.
Discovery and naming
In 1993, Michael Novacek, a member of anAmerican Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 inter ...
expedition to the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
, discovered the skeleton of a small theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
at Ukhaa Tolgod. This was further excavated in 1994 and 1995. The find was illustrated in a publication in 1994. On 15 July 1996, at the Bolor's Hill site, about eight kilometers (five miles) away from the original location, a second specimen was discovered, a skull.
In 2000, Mark Norell
Mark Allen Norell (born July 26, 1957) is an American paleontologist, acknowledged as one of the most important living vertebrate paleontologists. He is currently the chairman of paleontology and a research associate at the American Museum of Na ...
, Peter Makovicky and James Clark named and described the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
''Byronosaurus jaffei''. The species name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ...
as a whole honoured Byron Jaffe, "in recognition of his family's support for the Mongolian Academy of Sciences-American Museum of Natural History Paleontological Expeditions".
The holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
, IGM 100/983, was found in a layer of the Djadochta Formation
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 milli ...
dating from the late Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian s ...
. It consists of a partial skeleton with skull. It contains a partial skull with lower jaws, three neck vertebrae, three back vertebrae, a piece of a sacral vertebra, four partial tail vertebrae, ribs, the lower end of a thighbone, the upper ends of a shinbone and calf bone, a second metatarsal and three toe phalanges. The paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represents, but it is not the holotype (and in botany is also neither an isotype nor a syntype). Of ...
, specimen IGM 100/984, is the skull found in 1996, of which only the snout has been preserved. Both specimens are of adult individuals.
In 2003, the type specimen of ''Byronosaurus'' was described in detail. Makovicky and his colleagues found that ''Byronosaurus'' had a pneumatised snout with a sinus in each maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
.
In 2009, two front skulls and lower jaws of very young, perhaps newly hatched, individuals, specimens IGM 100/972 and IGM 100/974, were referred to ''Byronosaurus'', after originally having been identified as ''Velociraptor
''Velociraptor'' (; ) is a genus of small dromaeosaurid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. Two species are currently recognized, although others have been assigned in the pa ...
'' exemplars. Bever and Norell estimated that the skull length of IGM 100/972 and IGM 100/974 were about and , respectively.
In 2017, the researchers who described a troodontid ''Almas ukhaa
''Almas'' is a genus of troodontid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. It contains a single species, ''Almas ukhaa'', named in 2017 by Pei Rui and colleagues, based on a partial articulated skeleton. The only known specimen w ...
'' suggested that the specimens described by Bever and Norell (2009) don't belong to ''Byronosaurus'' based on different features found in the skull such as the number of maxillary teeth in both specimens being significantly fewer than this genus. They argued that these specimens are more closely related to ''A. ukhaa'' than to ''B. jaffei''.
Description
 ''Byronosaurus'' was a small dinosaur, measuring about long and tall; it weighed only about . Unlike most other troodontids, its teeth seem to lack serrations just like its closest relative ''
''Byronosaurus'' was a small dinosaur, measuring about long and tall; it weighed only about . Unlike most other troodontids, its teeth seem to lack serrations just like its closest relative ''Xixiasaurus
''Xixiasaurus'' () is a genus of troodontid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now China. The only known specimen was discovered in Xixia County, Henan Province, in central China, and became the holotype of th ...
'', probably a plesiomorph
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, and ...
ic trait among troodontids. The Ukhaa perinates show that ''Byronosaurus'' had a buccal maxillary groove and a recessed interfenestral bar.
Classification
 The following
The following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ...
shows the position of ''Byronosaurus'' within Troodontidae according to a 2017 analysis by the palaeontologist Caizhi Shen and colleagues:
Palaeobiology
Troodontids had some of the highestencephalization quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed to predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regressi ...
s (a measure of the ratio between actual brain size and the brain size predicted from body size) among non-avian
Avian may refer to:
*Birds or Aves, winged animals
*Avian (given name) (russian: Авиа́н, link=no), a male forename
Aviation
*Avro Avian, a series of light aircraft made by Avro in the 1920s and 1930s
*Avian Limited, a hang glider manufacture ...
dinosaurs. As suggested by their large eye-sockets and well-developed middle-ears, they appear to have had keen senses. They also had proportionately long legs, which indicates they were agile.
Diet
 Due to their large brains, possible
Due to their large brains, possible stereoscopic vision
Stereopsis () is the component of depth perception retrieved through binocular vision.
Stereopsis is not the only contributor to depth perception, but it is a major one. Binocular vision happens because each eye receives a different image becaus ...
, grasping hands, and enlarged sickle-claws, troodontids were generally assumed to have been predatory. In 1998, the palaeontologist Thomas R. Holtz
Thomas Richard Holtz Jr. (born September 13, 1965) is an American vertebrate palaeontologist, author, and principal lecturer at the University of Maryland, College Park, University of Maryland's Department of Geology. He has published extensively ...
and colleagues pointed out that the serrations on the teeth of troodontids were different from those of typical, carnivorous theropods in their large size and wide spacing, which is similar to the condition in herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
dinosaurs (including therizinosaurid
Therizinosauridae (meaning 'scythe lizards')Translated paper
is a family of derived (advanc ...
theropods) and lizards rather than carnivorous dinosaurs. They suggested that this difference in coarseness may be related to the size and resistance of plant and meat fibres, and that troodontids may have been herbivorous or is a family of derived (advanc ...
omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutri ...
. They also pointed out that some features that had been interpreted as predatory adaptations in troodontids were also found in herbivorous and omnivorous animals, such as primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
s and raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
s.
In 2001, the palaeontologists Philip J. Currie
Philip John Currie (born March 13, 1949) is a Canadian palaeontologist and museum curator who helped found the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology in Drumheller, Alberta and is now a professor at the University of Alberta in Edmonton. In the ...
and Dong Zhiming
Dong Zhiming (Chinese: 董枝明, Pinyin: ''Dǒng Zhimíng''; born January 1937) is a Chinese vertebrate paleontologist formerly employed at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) in Beijing. He began working at the ...
rejected the idea that troodontids could have been herbivorous. They stated that troodontid anatomy was consistent with a carnivorous lifestyle, and pointed out that the structure of their serrations was not much different from those of other theropods. They noted that troodontid features such as sharply pointed serrations that curved up towards the tip of the teeth, razor sharp enamel between the serrations, and at the bases, were not seen in herbivorous dinosaurs, which had simpler, cone shaped serrations. Lü and colleagues discussed the previous studies of troodontid diet, and suggested that the loss of serrations in the teeth of ''Byronosaurus'' and some other troodontids was related to a change in their diet. Since the teeth would appear to have lost their typical ability to slice meat, at least these troodontids may therefore have been either herbivorous or omnivorous. In 2015, the palaeontologist Christophe Hendrickx and colleagues suggested that basal (or "primitive") troodontids with unserrated teeth were herbivorous, whereas more derived troodontids with serrated teeth were carnivorous or omnivorous.
Reproduction

Mark Norell
Mark Allen Norell (born July 26, 1957) is an American paleontologist, acknowledged as one of the most important living vertebrate paleontologists. He is currently the chairman of paleontology and a research associate at the American Museum of Na ...
and colleagues described two "perinate" (hatchlings or embryos close to hatching) specimens of ''Byronosaurus'' (specimens IGM 100/972 and IGM 100/974) in 1994. The two specimens were found in a nest of oviraptorid
Oviraptoridae is a group of bird-like, herbivorous and omnivorous maniraptoran dinosaurs. Oviraptorids are characterized by their toothless, parrot-like beaks and, in some cases, elaborate crests. They were generally small, measuring between one ...
eggs in the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
"Flaming Cliffs" of the Djadochta Formation
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 milli ...
of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
. The nest is quite certainly that of an oviraptorosaur
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like s ...
, since an oviraptorid embryo is still preserved inside one of the eggs. The two partial skulls were first described by Norell et al. (1994) as dromaeosaurids, but reassigned to ''Byronosaurus'' after further study. The juvenile skulls were either from hatchlings or embryos, and fragments of eggshell are adhered to them although it seems to be oviraptorid eggshell. The presence of tiny ''Byronosaurus'' skulls in an oviraptorid nest was considered an enigma. Hypotheses explaining how they came to be there included that they were the prey of the adult oviraptorid, that they were there to prey on oviraptorid hatchlings, or that an adult ''Byronosaurus'' may have laid eggs in a ''Citipati
''Citipati'' (; meaning "funeral pyre lord") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. It is mainly known from the Ukhaa Tolgod locality at the Djadokhta F ...
'' nest (see nest parasite
Brood parasites are animals that rely on others to raise their young. The strategy appears among birds, insects and fish. The brood parasite manipulates a host, either of the same or of another species, to raise its young as if it were its own ...
). However, these interpretations have all been shown to not be the case. In 2011, Norell stated that the ''Byronosaurus'' nest was found two metres uphill from the oviraptorid nest, with the oviraptorid nest at the end of a drainage course from the ''Byronosaurus'' nest, suggesting that the baby ''Byronosaurus'' skulls must have been washed from one nest to the other. This claim has been already confirmed in 2005 by Gerald Grellet-Tinner who noted the presence of a troodontid nest (IGM 100/1003x) close to the ''Citipati'' nest containing the juvenile troodontid skulls. Norell is officially preparing to publish this information with more important details. Not only is the claim regarding nest parasitism considered dubious, but other researchers have pointed out the differences in skull morphology, suggesting that these specimens do not belong to this genus. The eggs of ''Byronosaurus'' and other troodontids are not paired unlike oviraptorids like ''Citipati'', but are "nearly vertically embedded with their round poles" up and are exposed barely above the sediment.
See also
*Timeline of troodontid research
This timeline of troodontid research is a chronological listing of events in the History of paleontology, history of paleontology focused on the troodontids, a group of bird-like theropod dinosaurs including animals like ''Troodon''. Troodontid re ...
References
Dinosauria.com
{{Taxonbar, from=Q134297 Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia Djadochta fauna Troodontids Fossil taxa described in 2000 Taxa named by Mark Norell