By Rote on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
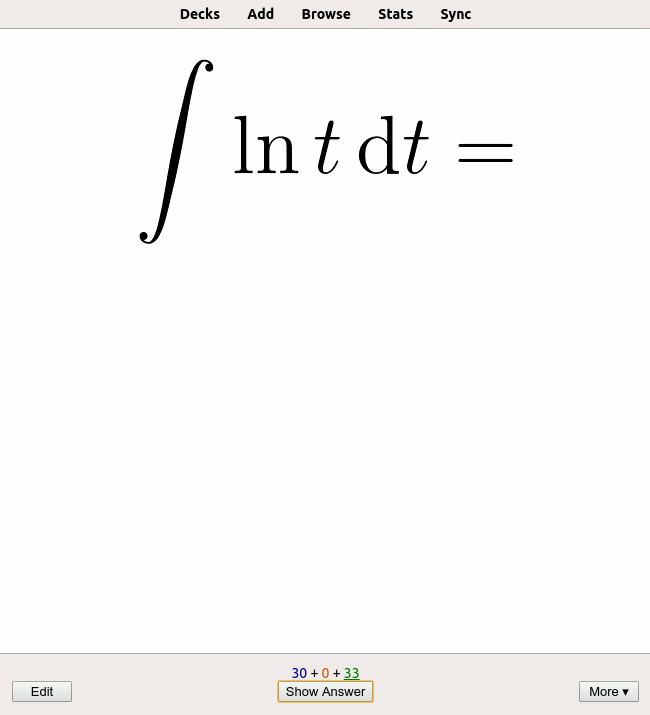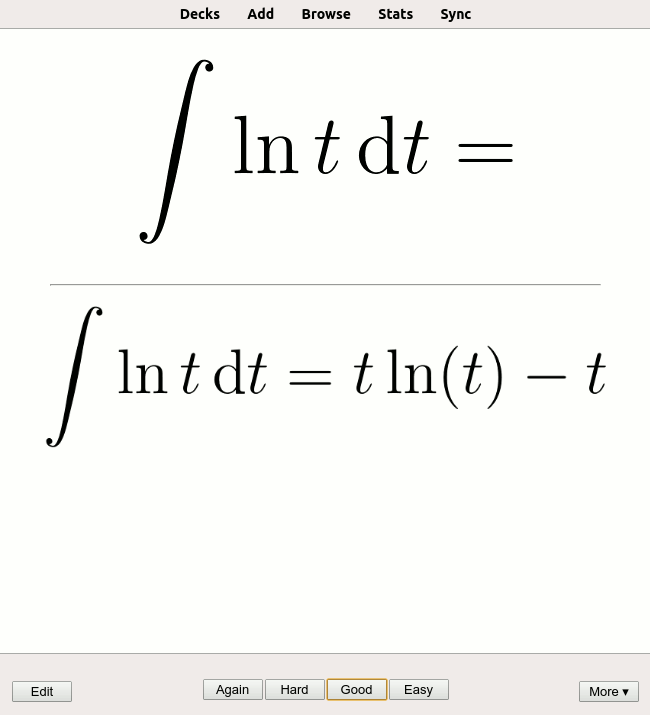 Rote learning is a
Rote learning is a
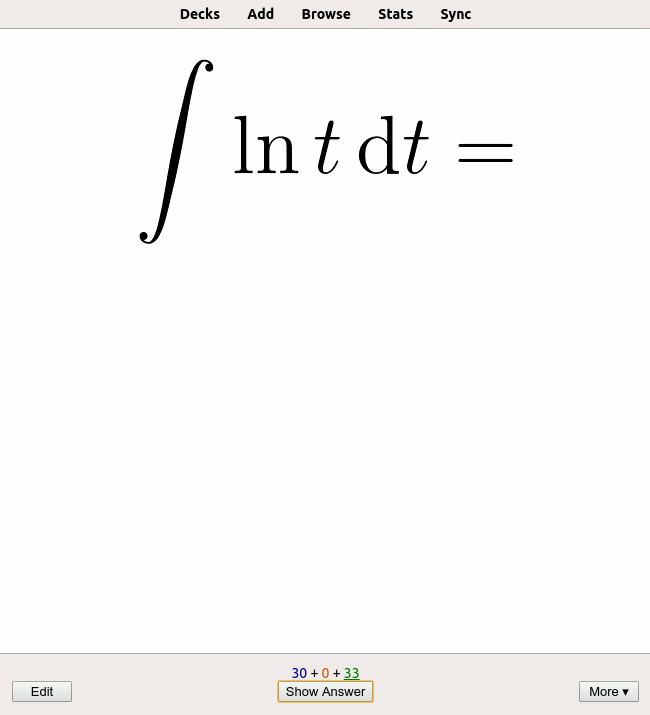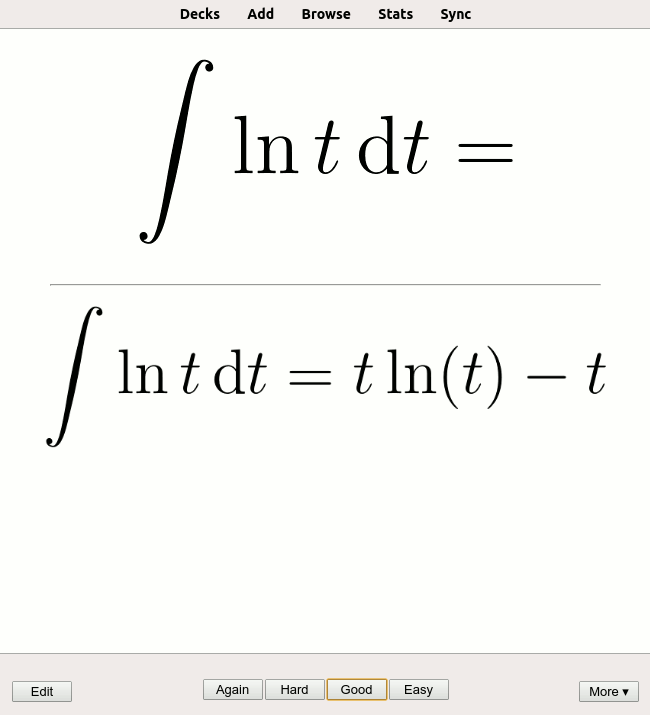 Rote learning is a
Rote learning is a memorization
Memorization is the process of committing something to memory. It is a mental process undertaken in order to store in memory for later recall visual, auditory, or tactical information.
The scientific study of memory is part of cognitive neuros ...
technique based on repetition. The method rests on the premise that the recall of repeated material becomes faster the more one repeats it. Some of the alternatives to rote learning include meaningful learning, associative learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of l ...
, spaced repetition
Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique that is usually performed with flashcards. Newly introduced and more difficult flashcards are shown more frequently, while older and less difficult flashcards are shown less frequently i ...
and active learning
Active learning is "a method of learning in which students are actively or experientially involved in the learning process and where there are different levels of active learning, depending on student involvement." states that "students partici ...
.
Versus critical thinking
Rote learning is widely used in the mastery of foundationalknowledge
Knowledge can be defined as Descriptive knowledge, awareness of facts or as Procedural knowledge, practical skills, and may also refer to Knowledge by acquaintance, familiarity with objects or situations. Knowledge of facts, also called pro ...
. Examples of school topics where rote learning is frequently used include phonics
Phonics is a method for teaching people how to read and write an alphabetic language (such as English, Arabic or Russian). It is done by demonstrating the relationship between the sounds of the spoken language (phonemes), and the letters or g ...
in reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of letters, symbols, etc., especially by sight or touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process involving such areas as word recognition, orthography (spelling ...
, the periodic table in chemistry, multiplication tables in mathematics, anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
in medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
, cases or statutes in law, basic formulae
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwee ...
in any science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
, etc. By definition, rote learning eschews comprehension, so by itself it is an ineffective tool in mastering any complex subject at an advanced level. For instance, one illustration of rote learning can be observed in preparing quickly for exams, a technique which may be colloquially referred to as " cramming".
Rote learning is sometimes disparaged with the derogative terms ''parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoide ...
fashion'', '' regurgitation'', ''cramming'', or ''mugging'' because one who engages in rote learning may give the wrong impression of having understood what they have written or said. It is strongly discouraged by many new curriculum standards. For example, science and mathematics standards in the United States specifically emphasize the importance of deep understanding over the mere recall of facts
Recall of facts is a value of education which is to be de-emphasized in reform of science according to new American national curriculum standards. Recall facts is often associated with rote learning.
Science in the United States
According to "The ...
, which is seen to be less important. The National Council of Teachers of Mathematics
Founded in 1920, The National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) is a professional organization for schoolteachers of mathematics in the United States. One of its goals is to improve the standards of mathematics in education. NCTM holds an ...
stated: More than ever, mathematics must include the mastery of concepts instead of mere memorization and the following of procedures. More than ever, school mathematics must include an understanding of how to use technology to arrive meaningfully at solutions to problems instead of endless attention to increasingly outdated computational tedium.However, advocates of
traditional education
Traditional education, also known as back-to-basics, conventional education or customary education, refers to long-established customs that society has traditionally used in schools. Some forms of education reform promote the adoption of progressiv ...
have criticized the new American standards as slighting learning basic facts and elementary arithmetic
The operators in elementary arithmetic are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The operators can be applied on both real numbers and imaginary numbers. Each kind of number is represented on a number line designated to the type ...
, and replacing content with process-based skills. In math and science, rote methods are often used, for example to memorize formulas. There is greater understanding if students commit a formula to memory through exercises that use the formula rather than through rote repetition of the formula. Newer standards often recommend that students derive formulas themselves to achieve the best understanding. Nothing is faster than rote learning if a formula must be learned quickly for an imminent test and rote methods can be helpful for committing an understood fact to memory. However, students who learn with understanding are able to transfer their knowledge to tasks requiring problem-solving with greater success than those who learn only by rote....
On the other side, those who disagree with the inquiry-based philosophy maintain that students must first develop computational skills before they can understand concepts of mathematics. These people would argue that time is better spent practicing skills rather than in investigations inventing alternatives, or justifying more than one correct answer or method. In this view, estimating
Estimation (or estimating) is the process of finding an estimate or approximation, which is a value that is usable for some purpose even if input data may be incomplete, uncertain, or unstable. The value is nonetheless usable because it is der ...
answers is insufficient and, in fact, is considered to be dependent on strong foundational skills
Foundationalism concerns philosophical theories of knowledge resting upon non-inferential justified belief, or some secure foundation of certainty such as a conclusion inferred from a basis of sound premises.Simon Blackburn, ''The Oxford Dictio ...
. Learning abstract concepts of mathematics is perceived to depend on a solid base of knowledge of the tools of the subject. Thus, these people believe that rote learning is an important part of the learning process.
In computer science
Rote learning is also used to describe a simple learning pattern used inmachine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
, although it does not involve repetition, unlike the usual meaning of rote learning. The machine is programmed to keep a history of calculations and compare new input against its history of inputs and outputs, retrieving the stored output if present. This pattern requires that the machine can be modeled as a pure function
In computer programming, a pure function is a function that has the following properties:
# the function return values are identical for identical arguments (no variation with local static variables, non-local variables, mutable reference argume ...
— always producing same output for same input — and can be formally described as follows:
:f() → () → store ((),())
Rote learning was used by Samuel's Checkers on an IBM 701, a milestone in the use of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
.
Learning methods for school
The flashcard, outline, andmnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imag ...
device are traditional tools for memorizing course material and are examples of rote learning.Schunk, Dale H. (2008). ''Learning Theories: An Educational Perspective'', Prentice Hall, .
See also
*References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rote Learning Academic pressure in East Asian culture Education reform Learning methods Memory Pedagogy