Butterfly Sleeves on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Butterflies are
 The ''
The ''
File:Prodryas.png, ''

 Butterfly adults are characterized by their four scale-covered wings, which give the Lepidoptera their name (
Butterfly adults are characterized by their four scale-covered wings, which give the Lepidoptera their name (
 Many butterflies, such as the
Many butterflies, such as the

 Butterflies in their adult stage can live from a week to nearly a year depending on the species. Many species have long larval life stages while others can remain dormant in their pupal or egg stages and thereby survive winters. The Melissa Arctic (''Oeneis melissa'') overwinters twice as a caterpillar. Butterflies may have one or more broods per year. The number of generations per year varies from
Butterflies in their adult stage can live from a week to nearly a year depending on the species. Many species have long larval life stages while others can remain dormant in their pupal or egg stages and thereby survive winters. The Melissa Arctic (''Oeneis melissa'') overwinters twice as a caterpillar. Butterflies may have one or more broods per year. The number of generations per year varies from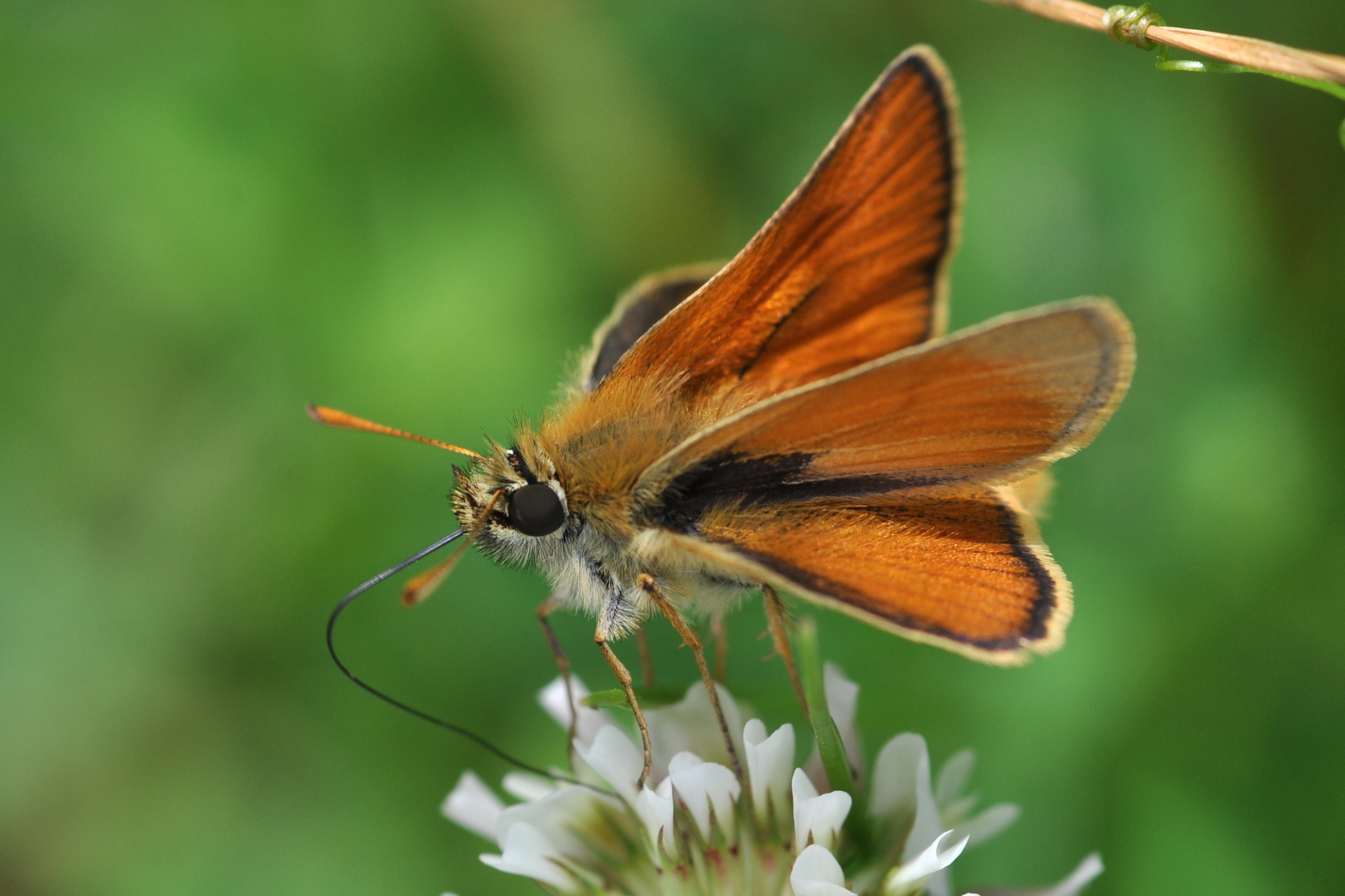 

 Butterfly eggs are protected by a hard-ridged outer layer of shell, called the ''chorion''. This is lined with a thin coating of wax which prevents the egg from drying out before the larva has had time to fully develop. Each egg contains a number of tiny funnel-shaped openings at one end, called ''micropyles''; the purpose of these holes is to allow sperm to enter and fertilize the egg. Butterfly eggs vary greatly in size and shape between species, but are usually upright and finely sculptured. Some species lay eggs singly, others in batches. Many females produce between one hundred and two hundred eggs.
Butterfly eggs are fixed to a leaf with a special glue which hardens rapidly. As it hardens it contracts, deforming the shape of the egg. This glue is easily seen surrounding the base of every egg forming a meniscus. The nature of the glue has been little researched but in the case of ''
Butterfly eggs are protected by a hard-ridged outer layer of shell, called the ''chorion''. This is lined with a thin coating of wax which prevents the egg from drying out before the larva has had time to fully develop. Each egg contains a number of tiny funnel-shaped openings at one end, called ''micropyles''; the purpose of these holes is to allow sperm to enter and fertilize the egg. Butterfly eggs vary greatly in size and shape between species, but are usually upright and finely sculptured. Some species lay eggs singly, others in batches. Many females produce between one hundred and two hundred eggs.
Butterfly eggs are fixed to a leaf with a special glue which hardens rapidly. As it hardens it contracts, deforming the shape of the egg. This glue is easily seen surrounding the base of every egg forming a meniscus. The nature of the glue has been little researched but in the case of ''
 Butterfly larvae, or caterpillars, consume plant leaves and spend practically all of their time searching for and eating food. Although most caterpillars are herbivorous, a few species are
Butterfly larvae, or caterpillars, consume plant leaves and spend practically all of their time searching for and eating food. Although most caterpillars are herbivorous, a few species are  Some larvae, especially those of the
Some larvae, especially those of the  Caterpillars mature through a series of developmental stages known as
Caterpillars mature through a series of developmental stages known as
 When the larva is fully grown, hormones such as
When the larva is fully grown, hormones such as
 The reproductive stage of the insect is the winged adult or
The reproductive stage of the insect is the winged adult or
 Butterflies feed primarily on nectar from flowers. Some also derive nourishment from pollen, tree sap, rotting fruit, dung, decaying flesh, and dissolved minerals in wet sand or dirt. Butterflies are important as pollinators for some species of plants. In general, they do not carry as much pollen load as bees, but they are capable of moving pollen over greater distances. Flower constancy has been observed for at least one species of butterfly.
Adult butterflies consume only liquids, ingested through the proboscis. They sip water from damp patches for hydration and feed on nectar from flowers, from which they obtain sugars for energy, and sodium and other minerals vital for reproduction. Several species of butterflies need more sodium than that provided by nectar and are attracted by sodium in salt; they sometimes land on people, attracted by the salt in human sweat. Some butterflies also visit dung and scavenge rotting fruit or carcasses to obtain minerals and nutrients. In many species, this mud-puddling behaviour is restricted to the males, and studies have suggested that the nutrients collected may be provided as a nuptial gift, along with the spermatophore, during mating.
In Hill-topping (biology), hilltopping, males of some species seek hilltops and ridge tops, which they patrol in search for females. Since it usually occurs in species with low population density, it is assumed these landscape points are used as meeting places to find mates.
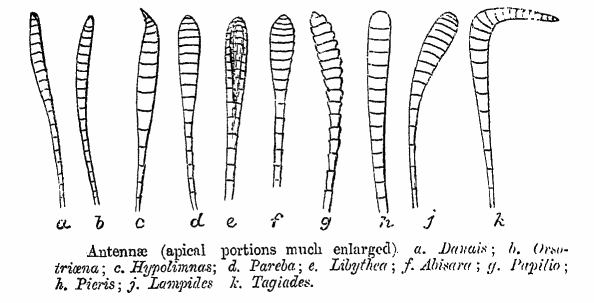
Butterflies use their antennae to sense the air for wind and scents. The antennae come in various shapes and colours; the hesperiids have a pointed angle or hook to the antennae, while most other families show knobbed antennae. The antennae are richly covered with sensory organs known as sensillum, sensillae. A butterfly's sense of taste is coordinated by chemoreceptors on the Arthropod leg#Insects, tarsi, or feet, which work only on contact, and are used to determine whether an egg-laying insect's offspring will be able to feed on a leaf before eggs are laid on it. Many butterflies use chemical signals,
Butterflies feed primarily on nectar from flowers. Some also derive nourishment from pollen, tree sap, rotting fruit, dung, decaying flesh, and dissolved minerals in wet sand or dirt. Butterflies are important as pollinators for some species of plants. In general, they do not carry as much pollen load as bees, but they are capable of moving pollen over greater distances. Flower constancy has been observed for at least one species of butterfly.
Adult butterflies consume only liquids, ingested through the proboscis. They sip water from damp patches for hydration and feed on nectar from flowers, from which they obtain sugars for energy, and sodium and other minerals vital for reproduction. Several species of butterflies need more sodium than that provided by nectar and are attracted by sodium in salt; they sometimes land on people, attracted by the salt in human sweat. Some butterflies also visit dung and scavenge rotting fruit or carcasses to obtain minerals and nutrients. In many species, this mud-puddling behaviour is restricted to the males, and studies have suggested that the nutrients collected may be provided as a nuptial gift, along with the spermatophore, during mating.
In Hill-topping (biology), hilltopping, males of some species seek hilltops and ridge tops, which they patrol in search for females. Since it usually occurs in species with low population density, it is assumed these landscape points are used as meeting places to find mates.
Butterflies use their antennae to sense the air for wind and scents. The antennae come in various shapes and colours; the hesperiids have a pointed angle or hook to the antennae, while most other families show knobbed antennae. The antennae are richly covered with sensory organs known as sensillum, sensillae. A butterfly's sense of taste is coordinated by chemoreceptors on the Arthropod leg#Insects, tarsi, or feet, which work only on contact, and are used to determine whether an egg-laying insect's offspring will be able to feed on a leaf before eggs are laid on it. Many butterflies use chemical signals,  Many species of butterfly maintain territories and actively chase other species or individuals that may stray into them. Some species will bask or perch on chosen perches. The flight styles of butterflies are often characteristic and some species have courtship flight displays. Butterflies can only fly when their temperature is above ; when it is cool, they can position themselves to expose the underside of the wings to the sunlight to heat themselves up. If their body temperature reaches , they can orientate themselves with the folded wings edgewise to the sun. Basking is an activity which is more common in the cooler hours of the morning. Some species have evolved dark wingbases to help in gathering more heat and this is especially evident in alpine forms.
As in many other insects, the lift (force), lift generated by butterflies is more than can be accounted for by steady-state, non-transitory aerodynamics. Studies using ''Vanessa atalanta'' in a wind tunnel show that they use a wide variety of aerodynamic mechanisms to generate force. These include wake capture, vortices at the wing edge, rotational mechanisms and the Torkel Weis-Fogh, Weis-Fogh 'clap-and-fling' mechanism. Butterflies are able to change from one mode to another rapidly.
Many species of butterfly maintain territories and actively chase other species or individuals that may stray into them. Some species will bask or perch on chosen perches. The flight styles of butterflies are often characteristic and some species have courtship flight displays. Butterflies can only fly when their temperature is above ; when it is cool, they can position themselves to expose the underside of the wings to the sunlight to heat themselves up. If their body temperature reaches , they can orientate themselves with the folded wings edgewise to the sun. Basking is an activity which is more common in the cooler hours of the morning. Some species have evolved dark wingbases to help in gathering more heat and this is especially evident in alpine forms.
As in many other insects, the lift (force), lift generated by butterflies is more than can be accounted for by steady-state, non-transitory aerodynamics. Studies using ''Vanessa atalanta'' in a wind tunnel show that they use a wide variety of aerodynamic mechanisms to generate force. These include wake capture, vortices at the wing edge, rotational mechanisms and the Torkel Weis-Fogh, Weis-Fogh 'clap-and-fling' mechanism. Butterflies are able to change from one mode to another rapidly.

, official website Ocybadistes knightorum, Black grass-dart butterfly ''(Ocybadistes knightorum)'' is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is endemic to New South Wales. It has a very limited distribution in the Boambee, New South Wales, Boambee area.
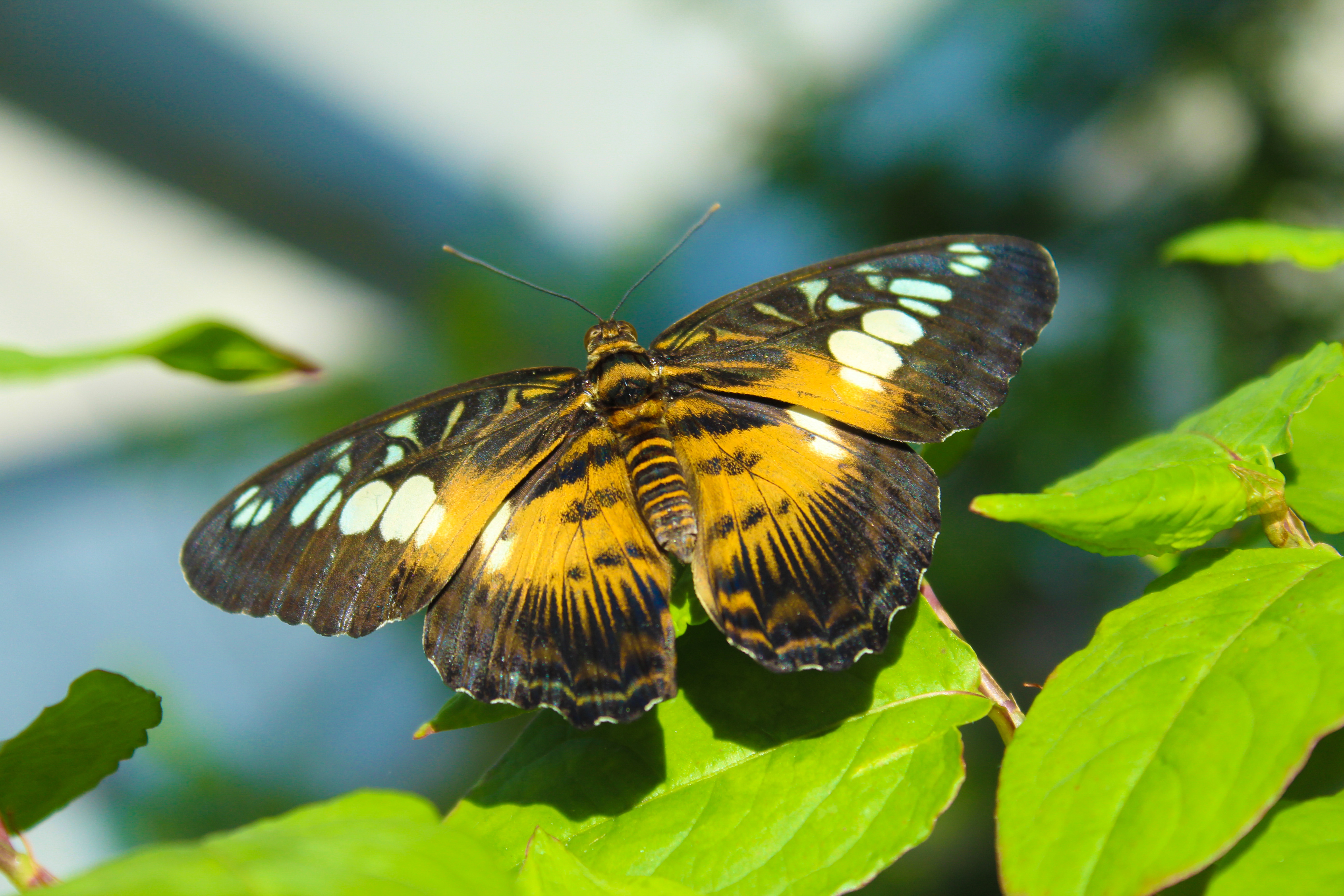
 Butterflies protect themselves from predators by a variety of means.
Butterflies protect themselves from predators by a variety of means.
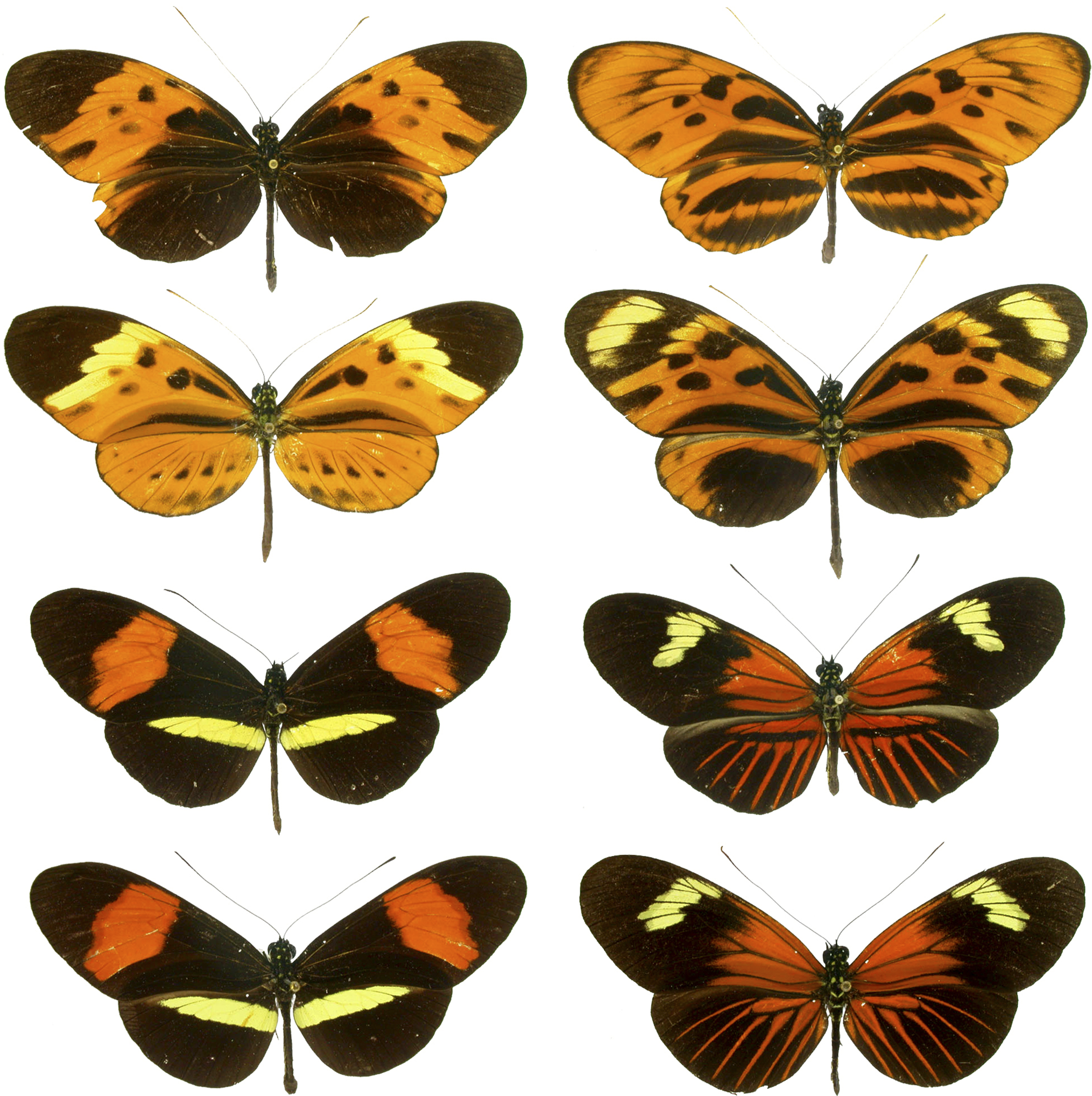
 Chemical defences are widespread and are mostly based on chemicals of plant origin. In many cases the plants themselves evolved these toxic substances as plant defense against herbivory, protection against herbivores. Butterflies have evolved mechanisms to sequester these plant toxins and use them instead in their own defence. These defence mechanisms are effective only if they are well advertised; this has led to the evolution of bright colours in unpalatable butterflies ( aposematism). This signal is commonly mimicry, mimicked by other butterflies, usually only females. A Batesian mimicry, Batesian mimic imitates another species to enjoy the protection of that species' aposematism. The Papilio polytes, common Mormon of India has female morphs which imitate the unpalatable red-bodied swallowtails, the Pachliopta aristolochiae, common rose and the Pachliopta hector, crimson rose. Müllerian mimicry occurs when aposematic species evolve to resemble each other, presumably to reduce predator sampling rates; ''
Chemical defences are widespread and are mostly based on chemicals of plant origin. In many cases the plants themselves evolved these toxic substances as plant defense against herbivory, protection against herbivores. Butterflies have evolved mechanisms to sequester these plant toxins and use them instead in their own defence. These defence mechanisms are effective only if they are well advertised; this has led to the evolution of bright colours in unpalatable butterflies ( aposematism). This signal is commonly mimicry, mimicked by other butterflies, usually only females. A Batesian mimicry, Batesian mimic imitates another species to enjoy the protection of that species' aposematism. The Papilio polytes, common Mormon of India has female morphs which imitate the unpalatable red-bodied swallowtails, the Pachliopta aristolochiae, common rose and the Pachliopta hector, crimson rose. Müllerian mimicry occurs when aposematic species evolve to resemble each other, presumably to reduce predator sampling rates; '' Camouflage is found in many butterflies. Some like the oakleaf butterfly and Doleschallia bisaltide, autumn leaf are remarkable imitations of leaves. As caterpillars, many defend themselves by freezing and appearing like sticks or branches. Others have deimatic behaviours, such as rearing up and waving their front ends which are marked with eyespots as if they were snakes. Some papilionid caterpillars such as the giant swallowtail (''Papilio cresphontes'') resemble bird droppings so as to be passed over by predators. Some caterpillars have hairs and bristly structures that provide protection while others are gregarious and form dense aggregations. Some species are myrmecophiles, forming Symbiosis, mutualistic associations with
Camouflage is found in many butterflies. Some like the oakleaf butterfly and Doleschallia bisaltide, autumn leaf are remarkable imitations of leaves. As caterpillars, many defend themselves by freezing and appearing like sticks or branches. Others have deimatic behaviours, such as rearing up and waving their front ends which are marked with eyespots as if they were snakes. Some papilionid caterpillars such as the giant swallowtail (''Papilio cresphontes'') resemble bird droppings so as to be passed over by predators. Some caterpillars have hairs and bristly structures that provide protection while others are gregarious and form dense aggregations. Some species are myrmecophiles, forming Symbiosis, mutualistic associations with
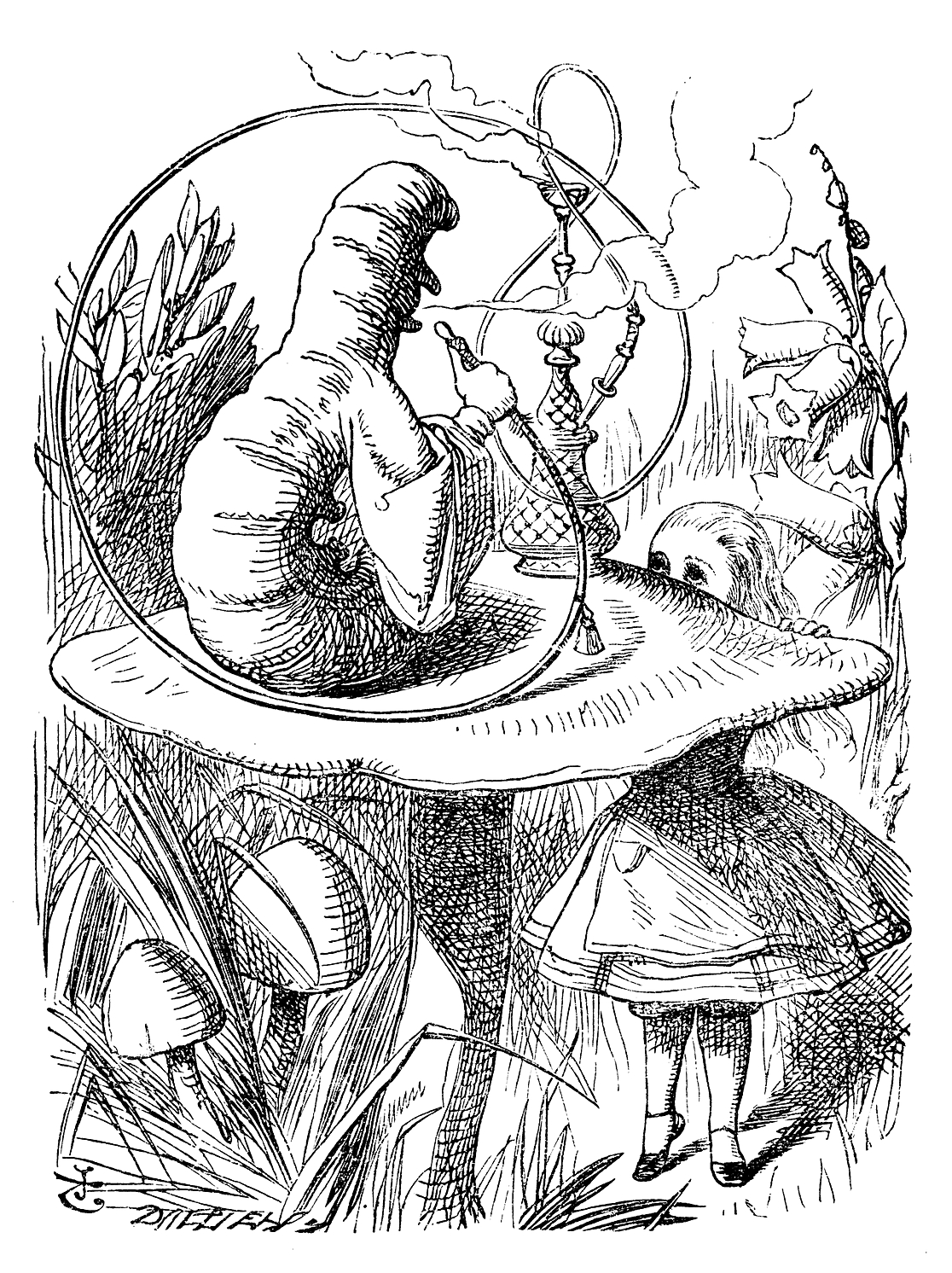 Sir John Tenniel drew a famous illustration of Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), Alice meeting a Caterpillar (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), caterpillar for Lewis Carroll's ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, Alice in Wonderland'', c. 1865. The caterpillar is seated on a toadstool and is smoking a hookah; the image can be read as showing either the forelegs of the larva, or as suggesting a face with protruding nose and chin. Eric Carle's children's book ''The Very Hungry Caterpillar'' portrays the larva as an extraordinarily hungry animal, while also teaching children how to count (to five) and the days of the week.
A butterfly appeared in one of Rudyard Kipling's ''Just So Stories'', "The Butterfly that Stamped".
One of the most popular, and most often recorded, songs by Sweden's eighteenth-century bard, Carl Michael Bellman, is "Fjäriln vingad syns på Haga" (The butterfly wingèd is seen in Haga), one of his ''Fredman's Songs''.
''Madam Butterfly'' is a 1904 opera by Giacomo Puccini about a romantic young Japanese bride who is deserted by her American officer husband soon after they are married. It was based on John Luther Long's short story written in 1898.
Sir John Tenniel drew a famous illustration of Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), Alice meeting a Caterpillar (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), caterpillar for Lewis Carroll's ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, Alice in Wonderland'', c. 1865. The caterpillar is seated on a toadstool and is smoking a hookah; the image can be read as showing either the forelegs of the larva, or as suggesting a face with protruding nose and chin. Eric Carle's children's book ''The Very Hungry Caterpillar'' portrays the larva as an extraordinarily hungry animal, while also teaching children how to count (to five) and the days of the week.
A butterfly appeared in one of Rudyard Kipling's ''Just So Stories'', "The Butterfly that Stamped".
One of the most popular, and most often recorded, songs by Sweden's eighteenth-century bard, Carl Michael Bellman, is "Fjäriln vingad syns på Haga" (The butterfly wingèd is seen in Haga), one of his ''Fredman's Songs''.
''Madam Butterfly'' is a 1904 opera by Giacomo Puccini about a romantic young Japanese bride who is deserted by her American officer husband soon after they are married. It was based on John Luther Long's short story written in 1898.
 According to Lafcadio Hearn, a butterfly was seen in Japan as the personification of a person's soul; whether they be living, dying, or already dead. One Japanese superstition says that if a butterfly enters your guest room and perches behind the bamboo screen, the person whom you most love is coming to see you. Large numbers of butterflies are viewed as bad omens. When Taira no Masakado was secretly preparing for his famous revolt, there appeared in Kyoto so vast a swarm of butterflies that the people were frightened—thinking the apparition to be a portent of coming evil.
According to Lafcadio Hearn, a butterfly was seen in Japan as the personification of a person's soul; whether they be living, dying, or already dead. One Japanese superstition says that if a butterfly enters your guest room and perches behind the bamboo screen, the person whom you most love is coming to see you. Large numbers of butterflies are viewed as bad omens. When Taira no Masakado was secretly preparing for his famous revolt, there appeared in Kyoto so vast a swarm of butterflies that the people were frightened—thinking the apparition to be a portent of coming evil.
 Diderot's ''Encyclopédie'' cites butterflies as a symbol for the soul. A Roman sculpture depicts a butterfly exiting the mouth of a dead man, representing the Roman belief that the soul leaves through the mouth. In line with this, the ancient Greek word for "butterfly" is ψυχή (''psȳchē''), which primarily means "soul" or "mind". According to Mircea Eliade, some of the Naga people, Nagas of Manipur claim ancestry from a butterfly.Rabuzzi, M. 1997. Butterfly etymology. Cultural Entomology November 1997 Fourth issu
Diderot's ''Encyclopédie'' cites butterflies as a symbol for the soul. A Roman sculpture depicts a butterfly exiting the mouth of a dead man, representing the Roman belief that the soul leaves through the mouth. In line with this, the ancient Greek word for "butterfly" is ψυχή (''psȳchē''), which primarily means "soul" or "mind". According to Mircea Eliade, some of the Naga people, Nagas of Manipur claim ancestry from a butterfly.Rabuzzi, M. 1997. Butterfly etymology. Cultural Entomology November 1997 Fourth issu
online
In some cultures, butterflies symbolise Reincarnation, rebirth. The butterfly is a symbol of being transgender, because of the transformation from caterpillar to winged adult. In the English county of Devon, people once hurried to kill the first butterfly of the year, to avoid a year of bad luck. In the Philippines, a lingering black or dark butterfly or moth in the house is taken to mean an impending or recent death in the family. Several American states have chosen an List of U.S. state butterflies, official state butterfly.
 "Collecting" means preserving dead specimens, not keeping butterflies as pets. Collecting butterflies was once a popular hobby; it has now largely been replaced by photography, recording, and rearing butterflies for release into the wild. The zoological illustrator Frederick William Frohawk succeeded in rearing all the butterfly species found in Britain, at a rate of four per year, to enable him to draw every stage of each species. He published the results in the folio sized handbook ''The Natural History of British Butterflies'' in 1924.
Butterflies and
"Collecting" means preserving dead specimens, not keeping butterflies as pets. Collecting butterflies was once a popular hobby; it has now largely been replaced by photography, recording, and rearing butterflies for release into the wild. The zoological illustrator Frederick William Frohawk succeeded in rearing all the butterfly species found in Britain, at a rate of four per year, to enable him to draw every stage of each species. He published the results in the folio sized handbook ''The Natural History of British Butterflies'' in 1924.
Butterflies and
Papilionoidea on the Tree of Life
Butterfly species and observations on iNaturalist
*
Rhopalocera
at insectoid.info
North America
AfricaGhana
* Asia
Indo-ChinaSulawesiTurkey
{{Authority control Butterflies, Articles containing video clips Extant Lutetian first appearances Insects in culture
insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three ...
s in the macrolepidoptera
Macrolepidoptera is a group within the insect order Lepidoptera. Traditionally used for the larger butterflies and moths as opposed to the "microlepidoptera", this group is artificial. However, it seems that by moving some taxa about, a monophy ...
n clade Rhopalocera from the order Lepidoptera, which also includes moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ...
s. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises the large superfamily Papilionoidea
The superfamily Papilionoidea (from the genus '' Papilio'', meaning "butterfly") contains all the butterflies except for the moth-like Hedyloidea.
The members of the Papilionoidea may be distinguished by the following combination of character ...
, which contains at least one former group, the skippers (formerly the superfamily "Hesperioidea"), and the most recent analyses suggest it also contains the moth-butterflies (formerly the superfamily "Hedyloidea"). Butterfly fossils date to the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
, about 56 million years ago.
Butterflies have a four-stage life cycle, as like most insects they undergo complete metamorphosis
Holometabolism, also called complete metamorphosis, is a form of insect development which includes four life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and imago (or adult). Holometabolism is a synapomorphic trait of all insects in the superorder Endopterygo ...
. Winged adults lay eggs on the food plant on which their larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e, known as caterpillars, will feed. The caterpillars grow, sometimes very rapidly, and when fully developed, pupa
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in thei ...
te in a chrysalis. When metamorphosis is complete, the pupal skin splits, the adult insect climbs out, and after its wings have expanded and dried, it flies off. Some butterflies, especially in the tropics, have several generations in a year, while others have a single generation, and a few in cold locations may take several years to pass through their entire life cycle.
Butterflies are often polymorphic, and many species make use of camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
, mimicry, and aposematism to evade their predators. Some, like the monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power i ...
and the painted lady
''Vanessa cardui'' is the most widespread of all butterfly species. It is commonly called the painted lady, or formerly in North America the cosmopolitan.
Description
File:Vanessa cardui MHNT CUT 2013 3 14 Pontfaverger-Moronvilliers Dos. ...
, migrate over long distances. Many butterflies are attacked by parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s or parasitoids, including wasps
A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder. ...
, protozoans, flies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced m ...
, and other invertebrates, or are preyed upon by other organisms. Some species are pests because in their larval stages they can damage domestic crops or trees; other species are agents of pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, birds, a ...
of some plants. Larvae of a few butterflies (e.g., harvesters
Harvester may refer to:
Agriculture and forestry
* Combine harvester, a machine commonly used to harvest grain crops
* Forage harvester, a machine used to harvest forage
* Harvester (forestry), a type of heavy vehicle employed in cut-to-length lo ...
) eat harmful insects, and a few are predators of ant
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of ...
s, while others live as mutualists
Mutualism describes the ecological Biological interaction, interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of ecological interaction. Prominent examples include most vascular plants engag ...
in association with ants. Culturally, butterflies are a popular motif in the visual and literary arts. The Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
says "butterflies are certainly one of the most appealing creatures in nature".
Etymology
 The ''
The ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a co ...
'' derives the word straightforwardly from Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
''butorflēoge'', butter-fly; similar names in Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aroun ...
and Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
show that the name is ancient, but modern Dutch and German use different words (''vlinder'' and ''Schmetterling'') and the common name often varies substantially between otherwise closely-related languages. A possible source of the name is the bright yellow male of the brimstone (''Gonepteryx rhamni
''Gonepteryx rhamni'' (known as the common brimstone) is a butterfly of the family Pieridae. It lives throughout the Palearctic zone and is commonly found across Europe, Asia, and North Africa. Across much of its range, it is the only species ...
''); another is that butterflies were on the wing in meadows during the spring and summer butter season while the grass was growing.
Paleontology
The earliest Lepidoptera fossils date to theTriassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
-Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
boundary, around 200 million years ago. Butterflies evolved from moths, so while the butterflies are monophyletic (forming a single clade), the moths are not. The oldest known butterfly is '' Protocoeliades kristenseni'' from the Palaeocene aged Fur Formation
The Fur Formation is a marine geological formation of Ypresian ( Lower Eocene Epoch, c. 56.0-54.5 Ma) age which crops out in the Limfjord region of Denmark from Silstrup via Mors and Fur to Ertebølle, and can be seen in many cliffs and quarries ...
of Denmark, approximately 55 million years old, which belongs to the family Hesperiidae (skippers). Molecular clock
The molecular clock is a figurative term for a technique that uses the mutation rate of biomolecules to deduce the time in prehistory when two or more life forms diverged. The biomolecular data used for such calculations are usually nucleo ...
estimates suggest that butterflies originated sometime in the mid-Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
, but only significantly diversified during the Cenozoic. The oldest American butterfly is the Late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "daw ...
''Prodryas persephone
''Prodryas persephone'' is an extinct species of brush-footed butterfly, known from a single specimen from the Chadronian-aged Florissant Shale Lagerstatte of Late Eocene Colorado. ''P. persephone'' is the first fossil butterfly to be found in ...
'' from the Florissant Fossil Beds
The Florissant Formation is a sedimentary geologic formation outcropping around Florissant, Teller County, Colorado. The formation is noted for the abundant and exceptionally preserved insect and plant fossils that are found in the mudstones and ...
, approximately 34 million years old.
Prodryas persephone
''Prodryas persephone'' is an extinct species of brush-footed butterfly, known from a single specimen from the Chadronian-aged Florissant Shale Lagerstatte of Late Eocene Colorado. ''P. persephone'' is the first fossil butterfly to be found in ...
'', a Late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "daw ...
butterfly from the Florissant Fossil Beds
The Florissant Formation is a sedimentary geologic formation outcropping around Florissant, Teller County, Colorado. The formation is noted for the abundant and exceptionally preserved insect and plant fossils that are found in the mudstones and ...
, 1887 engraving
File:PZSL1889Plate31 Fossil Papilionid Butterfly Lithopsyche antiqua from Early Oligocene Bembridge Marls.png, ''Lithopsyche antiqua
''Lithopsyche'' is a fossil butterfly known from Oligocene-aged strata of the Isle of Wight, England. The sole specimen is too incomplete to allow a certain assignment of a family (biology), family, but it was placed on its description as a geom ...
'', an Early Oligocene
The Rupelian is, in the geologic timescale, the older of two ages or the lower of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between . It is preceded by the Priabonian Stage (part of the Eocene) and is followed by the Chatti ...
butterfly from the Bembridge Marls, Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isle of ...
, 1889 engraving
Taxonomy and phylogeny
Traditionally, butterflies have been divided into thesuperfamily
SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, str ...
Papilionoidea
The superfamily Papilionoidea (from the genus '' Papilio'', meaning "butterfly") contains all the butterflies except for the moth-like Hedyloidea.
The members of the Papilionoidea may be distinguished by the following combination of character ...
excluding the smaller groups of the Hesperiidae (skippers) and the more moth-like Hedylidae
Hedylidae, the "American moth-butterflies", is a family of insects in the order Lepidoptera, representing the superfamily Hedyloidea. They have traditionally been viewed as an extant sister group of the butterfly superfamily Papilionoidea. In 198 ...
of America. Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
analysis suggests that the traditional Papilionoidea is paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
with respect to the other two groups, so they should both be included within Papilionoidea, to form a single butterfly group, thereby synonymous with the clade Rhopalocera.
Biology

General description

 Butterfly adults are characterized by their four scale-covered wings, which give the Lepidoptera their name (
Butterfly adults are characterized by their four scale-covered wings, which give the Lepidoptera their name (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
λεπίς lepís, scale + πτερόν pterón, wing). These scales give butterfly wings their colour: they are pigmented with melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
s that give them blacks and browns, as well as uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of ...
derivatives and flavones
Flavones (from Latin ''flavus'' "yellow") are a class of flavonoids based on the backbone of 2-phenylchromen-4-one (2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one) (as shown in the first image of this article).
Flavones are common in foods, mainly from spices, and ...
that give them yellows, but many of the blues, greens, reds and iridescent colours are created by structural coloration
Structural coloration in animals, and a few plants, is the production of colour by microscopically structured surfaces fine enough to interfere with visible light instead of pigments, although some structural coloration occurs in combination wit ...
produced by the micro-structures of the scales and hairs.
As in all insects, the body is divided into three sections: the head, thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the cre ...
, and abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. ...
. The thorax is composed of three segments, each with a pair of legs. In most families of butterfly the antennae are clubbed, unlike those of moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ...
s which may be threadlike or feathery. The long proboscis can be coiled when not in use for sipping nectar from flowers.
Nearly all butterflies are diurnal, have relatively bright colours, and hold their wings vertically above their bodies when at rest, unlike the majority of moths which fly by night, are often cryptically coloured (well camouflaged), and either hold their wings flat (touching the surface on which the moth is standing) or fold them closely over their bodies. Some day-flying moths, such as the hummingbird hawk-moth
The hummingbird hawk-moth (''Macroglossum stellatarum'') is a species of hawk moth found across temperate regions of Eurasia. The species is named for its similarity to hummingbirds, as they feed on the nectar of tube-shaped flowers using their ...
, are exceptions to these rules.
Butterfly larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e, caterpillars, have a hard (sclerotised
Sclerotin is a component of the cuticle of various Arthropoda, most familiarly insects. It is formed by cross-linking members of particular classes of protein molecules, a biochemical process called sclerotization, a form of tanning in which qui ...
) head with strong mandibles used for cutting their food, most often leaves. They have cylindrical bodies, with ten segments to the abdomen, generally with short prolegs on segments 3–6 and 10; the three pairs of true legs on the thorax have five segments each. Many are well camouflaged; others are aposematic with bright colours and bristly projections containing toxic chemicals obtained from their food plants. The pupa
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in thei ...
or chrysalis, unlike that of moths, is not wrapped in a cocoon.
Many butterflies are sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
. Most butterflies have the ZW sex-determination system
The ZW sex-determination system is a chromosomal system that determines the sex of offspring in birds, some fish and crustaceans such as the giant river prawn, some insects (including butterflies and moths), the schistosome family of flatworms, ...
where females are the heterogametic sex (ZW) and males homogametic (ZZ).
Distribution and migration
Butterflies are distributed worldwide except Antarctica, totalling some 18,500 species. Of these, 775 areNearctic
The Nearctic realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting the Earth's land surface.
The Nearctic realm covers most of North America, including Greenland, Central Florida, and the highlands of Mexico. The parts of North America t ...
; 7,700 Neotropical
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.
Definition
In bioge ...
; 1,575 Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Sibe ...
; 3,650 Afrotropical
The Afrotropical realm is one of Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the majority of the Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, southern Iran and extreme southwestern Pakistan, and the island ...
; and 4,800 are distributed across the combined Oriental
The Orient is a term for the East in relation to Europe, traditionally comprising anything belonging to the Eastern world. It is the antonym of ''Occident'', the Western World. In English, it is largely a metonym for, and coterminous with, the ...
and Australian
Australian(s) may refer to:
Australia
* Australia, a country
* Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia
** European Australians
** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists
** Aboriginal Au ...
/Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
regions. The monarch butterfly
The monarch butterfly or simply monarch (''Danaus plexippus'') is a milkweed butterfly (subfamily Danainae) in the family Nymphalidae. Other common names, depending on region, include milkweed, common tiger, wanderer, and black-veined brown. It ...
is native to the Americas, but in the nineteenth century or before, spread across the world, and is now found in Australia, New Zealand, other parts of Oceania, and the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
. It is not clear how it dispersed; adults may have been blown by the wind or larvae or pupae may have been accidentally transported by humans, but the presence of suitable host plants in their new environment was a necessity for their successful establishment.

 Many butterflies, such as the
Many butterflies, such as the painted lady
''Vanessa cardui'' is the most widespread of all butterfly species. It is commonly called the painted lady, or formerly in North America the cosmopolitan.
Description
File:Vanessa cardui MHNT CUT 2013 3 14 Pontfaverger-Moronvilliers Dos. ...
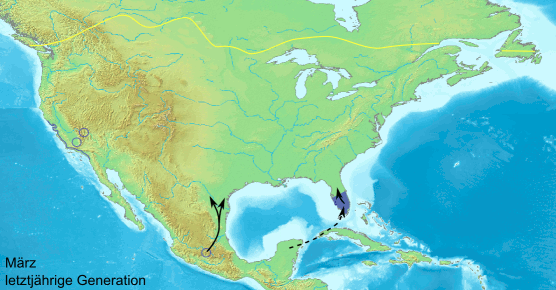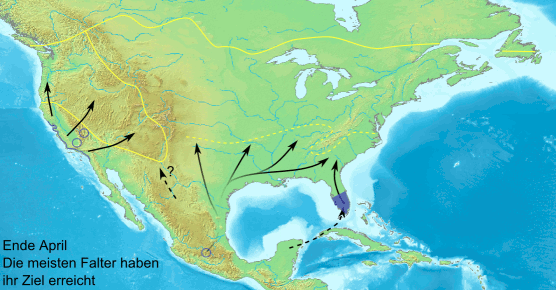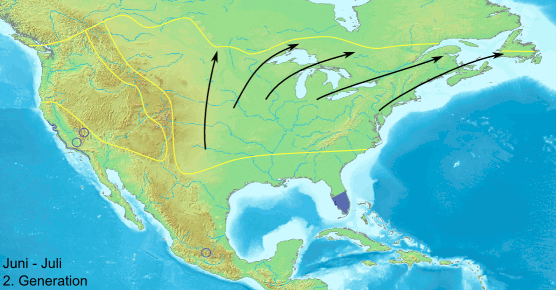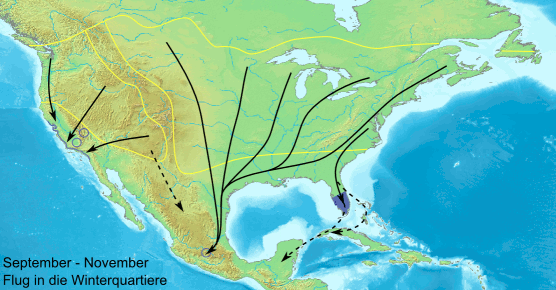
, monarch, and several danaine migrate for long distances. These migrations take place over a number of generations and no single individual completes the whole trip. The eastern North American population of monarchs can travel thousands of miles south-west to overwintering sites in Mexico. There is a reverse migration in the spring. It has recently been shown that the British painted lady undertakes a 9,000-mile round trip in a series of steps by up to six successive generations, from tropical Africa to the Arctic Circle — almost double the length of the famous migrations undertaken by monarch. Spectacular large-scale migrations associated with the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
are seen in peninsular India. Migrations have been studied in more recent times using wing tags and also using stable hydrogen isotopes.
Butterflies navigate using a time-compensated sun compass. They can see polarized light and therefore orient even in cloudy conditions. The polarized light near the ultraviolet spectrum appears to be particularly important. Many migratory butterflies live in semi-arid areas where breeding seasons are short. The life histories of their host plants also influence butterfly behaviour.
Life cycle
temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
to tropical regions
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred t ...
with tropical regions showing a trend towards multivoltinism.
Courtship
Courtship is the period wherein some couples get to know each other prior to a possible marriage. Courtship traditionally may begin after a betrothal and may conclude with the celebration of marriage. A courtship may be an informal and private m ...
is often aerial and often involves pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s. Butterflies then land on the ground or on a perch to mate. Copulation takes place tail-to-tail and may last from minutes to hours. Simple photoreceptor cells located at the genitals are important for this and other adult behaviours. The male passes a spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophores ...
to the female; to reduce sperm competition, he may cover her with his scent, or in some species such as the Apollos (''Parnassius
''Parnassius'' is a genus of northern circumpolar and montane (alpine and Himalayan) butterflies usually known as Apollos or snow Apollos. They can vary in colour and form significantly based on their altitude. They also show an adaptation to h ...
'') plugs her genital opening to prevent her from mating again.
The vast majority of butterflies have a four-stage life cycle; egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
, larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
(caterpillar), pupa
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in thei ...
(chrysalis) and imago
In biology, the imago (Latin for "image") is the last stage an insect attains during its metamorphosis, its process of growth and development; it is also called the imaginal stage, the stage in which the insect attains maturity. It follows the f ...
(adult). In the genera ''Colias
''Colias'' is a genus of butterflies in the family Pieridae. They are often called clouded yellows; the North American name "sulphurs" is elsewhere used for Coliadinae in general. The closest living relative is the genus '' Zerene'', which is so ...
'', ''Erebia
''Erebia'' is a Holarctic genus of brush-footed butterflies, family Nymphalidae. Most of the about 90–100 species (see also below) are dark brown or black in color, with reddish-brown to orange or more rarely yellowish wing blotches or ban ...
'', ''Euchloe
''Euchloe'' is a genus of pierid butterflies from the orangetip tribe (Anthocharini). They are Holarctic in distribution, with most species in Europe, Central Asia, and North America. Like other Anthocharini, the American species are usually c ...
'', and ''Parnassius'', a small number of species are known that reproduce semi-parthenogenetically; when the female dies, a partially developed larva emerges from her abdomen.
Egg
 Butterfly eggs are protected by a hard-ridged outer layer of shell, called the ''chorion''. This is lined with a thin coating of wax which prevents the egg from drying out before the larva has had time to fully develop. Each egg contains a number of tiny funnel-shaped openings at one end, called ''micropyles''; the purpose of these holes is to allow sperm to enter and fertilize the egg. Butterfly eggs vary greatly in size and shape between species, but are usually upright and finely sculptured. Some species lay eggs singly, others in batches. Many females produce between one hundred and two hundred eggs.
Butterfly eggs are fixed to a leaf with a special glue which hardens rapidly. As it hardens it contracts, deforming the shape of the egg. This glue is easily seen surrounding the base of every egg forming a meniscus. The nature of the glue has been little researched but in the case of ''
Butterfly eggs are protected by a hard-ridged outer layer of shell, called the ''chorion''. This is lined with a thin coating of wax which prevents the egg from drying out before the larva has had time to fully develop. Each egg contains a number of tiny funnel-shaped openings at one end, called ''micropyles''; the purpose of these holes is to allow sperm to enter and fertilize the egg. Butterfly eggs vary greatly in size and shape between species, but are usually upright and finely sculptured. Some species lay eggs singly, others in batches. Many females produce between one hundred and two hundred eggs.
Butterfly eggs are fixed to a leaf with a special glue which hardens rapidly. As it hardens it contracts, deforming the shape of the egg. This glue is easily seen surrounding the base of every egg forming a meniscus. The nature of the glue has been little researched but in the case of ''Pieris brassicae
''Pieris brassicae'', the large white, also called cabbage butterfly, cabbage white, cabbage moth (erroneously), or in India the large cabbage white, is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It is a close relative of the small white, ''Pieris ra ...
'', it begins as a pale yellow granular secretion containing acidophilic proteins. This is viscous and darkens when exposed to air, becoming a water-insoluble, rubbery material which soon sets solid. Butterflies in the genus ''Agathymus
''Agathymus'' is a genus of butterflies in the skipper family, Hesperiidae. They occur in the North American deserts. The genus was described by Hugh Avery Freeman in 1959. The larvae bore into the stems of agave plants.
These butterflies have ...
'' do not fix their eggs to a leaf, instead the newly laid eggs fall to the base of the plant.
Eggs are almost invariably laid on plants. Each species of butterfly has its own host plant range and while some species of butterfly are restricted to just one species of plant, others use a range of plant species, often including members of a common family. In some species, such as the great spangled fritillary
The great spangled fritillary (''Speyeria cybele'') is a North American butterfly of the family Nymphalidae.
Description
Its wingspan ranges from . It is characterized by its orange color above with five black dashes near forewing base and sev ...
, the eggs are deposited close to but not on the food plant. This most likely happens when the egg overwinters before hatching and where the host plant loses its leaves in winter, as do violets
Violet identifies various plant taxa, particularly species in the genus ''Viola'', within which the common violet is the best known member in Eurasia and the common blue violet and common purple violet are the best known members in North America ...
in this example.
The egg stage lasts a few weeks in most butterflies, but eggs laid close to winter, especially in temperate regions, go through a diapause
In animal dormancy, diapause is the delay in development in response to regular and recurring periods of adverse environmental conditions.Tauber, M.J., Tauber, C.A., Masaki, S. (1986) ''Seasonal Adaptations of Insects''. Oxford University Press It ...
(resting) stage, and the hatching may take place only in spring. Some temperate region butterflies, such as the Camberwell beauty, lay their eggs in the spring and have them hatch in the summer.
Caterpillar larva
predators
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
: ''Spalgis epius
''Spalgis epius'', the apefly, is a small butterfly found in the Indomalayan realm that belongs to the lycaenids or blues family. It gets its name from the supposed resemblance of its pupa to the face of an ape.
Description
Male
Upperside: du ...
'' eats scale insect
Scale insects are small insects of the order Hemiptera, suborder Sternorrhyncha. Of dramatically variable appearance and extreme sexual dimorphism, they comprise the infraorder Coccomorpha which is considered a more convenient grouping than the ...
s, while lycaenids such as ''Liphyra brassolis
''Liphyra brassolis'', the moth butterfly, is a butterfly found in South Asia, Southeast Asia and Australia that belongs to the lycaenid family. The larvae are predatory and feed on ant larvae. This is one of the largest species of lycaenid butt ...
'' are myrmecophilous
Myrmecophily ( , ) is the term applied to positive interspecies associations between ants and a variety of other organisms, such as plants, other arthropods, and fungi. Myrmecophily refers to mutualistic associations with ants, though in its ...
, eating ant larvae.
 Some larvae, especially those of the
Some larvae, especially those of the Lycaenidae
Lycaenidae is the second-largest family of butterflies (behind Nymphalidae, brush-footed butterflies), with over 6,000 species worldwide, whose members are also called gossamer-winged butterflies. They constitute about 30% of the known butterfl ...
, form mutual associations with ants. They communicate with the ants using vibrations that are transmitted through the substrate as well as using chemical signals. The ants provide some degree of protection to these larvae and they in turn gather honeydew secretions. Large blue
The large blue (''Phengaris arion'') is a species of butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. The species was first defined in 1758 and first recorded in Britain in 1795. In 1979 the species became mostly extinct in Britain but has been successfully ...
(''Phengaris arion'') caterpillars trick '' Myrmica'' ants into taking them back to the ant colony
An ant colony is a population of a single ant species capable to maintain its complete lifecycle. Ant colonies are eusocial, communal, and efficiently organized and are very much like those found in other social Hymenoptera, though the vario ...
where they feed on the ant eggs and larvae in a parasitic relationship.
 Caterpillars mature through a series of developmental stages known as
Caterpillars mature through a series of developmental stages known as instar
An instar (, from the Latin '' īnstar'', "form", "likeness") is a developmental stage of arthropods, such as insects, between each moult (''ecdysis''), until sexual maturity is reached. Arthropods must shed the exoskeleton in order to grow or ass ...
s. Near the end of each stage, the larva undergoes a process called apolysis
Apolysis ( grc, ἀπόλυσις "discharge, lit. absolution") is the separation of the cuticle from the epidermis in arthropods and related groups (Ecdysozoa). Since the cuticle of these animals is also the skeletal support of the body and is in ...
, mediated by the release of a series of neurohormone A neurohormone is any hormone produced and released by neuroendocrine cells (also called neurosecretory cells) into the blood. By definition of being hormones, they are secreted into the circulation for systemic effect, but they can also have a role ...
s. During this phase, the cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
, a tough outer layer made of a mixture of chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
and specialized protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s, is released from the softer epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
beneath, and the epidermis begins to form a new cuticle. At the end of each instar, the larva moults, the old cuticle splits and the new cuticle expands, rapidly hardening and developing pigment. Development of butterfly wing patterns begins by the last larval instar.
Caterpillars have short antennae and several simple eyes. The mouthparts are adapted for chewing with powerful mandibles and a pair of maxillae, each with a segmented palp. Adjoining these is the labium-hypopharynx which houses a tubular spinneret which is able to extrude silk. Caterpillars such as those in the genus ''Calpodes
''Calpodes'' is a genus of skipper butterflies in the family Hesperiidae.
Species
Recognised species in the genus ''Calpodes'' include:
*''Calpodes ethlius
''Calpodes ethlius'', the Brazilian skipper, larger canna leafroller or canna skippe ...
'' (family Hesperiidae) have a specialized tracheal system on the 8th segment that function as a primitive lung. Butterfly caterpillars have three pairs of true legs on the thoracic segments and up to six pairs of proleg
A proleg is a small, fleshy, stub structure found on the ventral surface of the abdomen of most larval forms of insects of the order Lepidoptera, though they can also be found on other larval insects such as sawflies and a few other types of in ...
s arising from the abdominal segments. These prolegs have rings of tiny hooks called crochets that are engaged hydrostatically and help the caterpillar grip the substrate. The epidermis bears tufts of seta
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. Th ...
e, the position and number of which help in identifying the species. There is also decoration in the form of hairs, wart-like protuberances, horn-like protuberances and spines. Internally, most of the body cavity is taken up by the gut, but there may also be large silk glands, and special glands which secrete distasteful or toxic substances. The developing wings are present in later stage instars and the gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
s start development in the egg stage.
Pupa
 When the larva is fully grown, hormones such as
When the larva is fully grown, hormones such as prothoracicotropic hormone Prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) was the first insect hormone to be discovered.The chemical symbol for prothoracicotropic hormone is (C64H102N16O19S2). It was originally described simply as "brain hormone" by early workers such as Stefan Kopeć (1 ...
(PTTH) are produced. At this point the larva stops feeding, and begins "wandering" in the quest for a suitable pupation site, often the underside of a leaf or other concealed location. There it spins a button of silk which it uses to fasten its body to the surface and moults for a final time. While some caterpillars spin a cocoon to protect the pupa, most species do not. The naked pupa, often known as a chrysalis, usually hangs head down from the cremaster, a spiny pad at the posterior end, but in some species a silken girdle may be spun to keep the pupa in a head-up position. Most of the tissues and cells of the larva are broken down inside the pupa, as the constituent material is rebuilt into the imago. The structure of the transforming insect is visible from the exterior, with the wings folded flat on the ventral surface and the two halves of the proboscis, with the antennae and the legs between them.
The pupal transformation into a butterfly through metamorphosis has held great appeal to mankind. To transform from the miniature wings visible on the outside of the pupa into large structures usable for flight, the pupal wings undergo rapid mitosis and absorb a great deal of nutrients. If one wing is surgically removed early on, the other three will grow to a larger size. In the pupa, the wing forms a structure that becomes compressed from top to bottom and pleated from proximal to distal ends as it grows, so that it can rapidly be unfolded to its full adult size. Several boundaries seen in the adult colour pattern are marked by changes in the expression of particular transcription factors in the early pupa.
Adult
 The reproductive stage of the insect is the winged adult or
The reproductive stage of the insect is the winged adult or imago
In biology, the imago (Latin for "image") is the last stage an insect attains during its metamorphosis, its process of growth and development; it is also called the imaginal stage, the stage in which the insect attains maturity. It follows the f ...
. The surface of both butterflies and moths is covered by scales, each of which is an outgrowth from a single epidermal
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water relea ...
cell. The head is small and dominated by the two large compound eyes
A compound eye is a visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens, and photoreceptor cells which distin ...
. These are capable of distinguishing flower shapes or motion but cannot view distant objects clearly. Colour perception is good, especially in some species in the blue/violet range. The antennae are composed of many segments and have clubbed tips (unlike moths that have tapering or feathery antennae). The sensory receptors are concentrated in the tips and can detect odours. Taste receptors are located on the palps and on the feet. The mouthparts are adapted to sucking and the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
s are usually reduced in size or absent. The first maxillae are elongated into a tubular proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elong ...
which is curled up at rest and expanded when needed to feed. The first and second maxillae bear palps which function as sensory organs. Some species have a reduced proboscis or maxillary palps and do not feed as adults.
Many ''Heliconius
''Heliconius'' comprises a colorful and widespread genus of brush-footed butterflies commonly known as the longwings or heliconians. This genus is distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the New World, from South America a ...
'' butterflies also use their proboscis to feed on pollen; in these species only 20% of the amino acids used in reproduction come from larval feeding, which allow them to develop more quickly as caterpillars, and gives them a longer lifespan of several months as adults.
The thorax of the butterfly is devoted to locomotion. Each of the three thoracic segments has two legs (among nymphalids, the first pair is reduced and the insects walk on four legs). The second and third segments of the thorax bear the wings. The leading edges of the forewings have thick veins to strengthen them, and the hindwings are smaller and more rounded and have fewer stiffening veins. The forewings and hindwings are not hooked together ( as they are in moths) but are coordinated by the friction of their overlapping parts. The front two segments have a pair of spiracle Spiracle or spiraculum may refer to:
* Spiracle (arthropods), opening in the exoskeletons of some arthropods
* Spiracle (vertebrates), openings on the surface of some vertebrates
* Spiraculum, a genus of land snails in family Cyclophoridae
Cycl ...
s which are used in respiration.
The abdomen consists of ten segments and contains the gut and genital organs. The front eight segments have spiracles and the terminal segment is modified for reproduction. The male has a pair of clasping organs attached to a ring structure, and during copulation, a tubular structure is extruded and inserted into the female's vagina. A spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophores ...
is deposited in the female, following which the sperm make their way to a seminal receptacle where they are stored for later use. In both sexes, the genitalia are adorned with various spines, teeth, scales and bristles, which act to prevent the butterfly from mating with an insect of another species. After it emerges from its pupal stage, a butterfly cannot fly until the wings are unfolded. A newly emerged butterfly needs to spend some time inflating its wings with hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod (invertebrate) body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which ...
and letting them dry, during which time it is extremely vulnerable to predators.
Pattern formation
The colorful patterns on many butterfly wings tell potential predators that they are toxic. Hence, the genetic basis of wingpattern formation
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, ( statistically) orderly outcomes of self-organization and the common principles behind similar patterns in nature.
In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of ...
can illuminate both the evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
of butterflies as well as their developmental biology. The color of butterfly wings is derived from tiny structures called scales, each of which have their own pigments. In ''Heliconius
''Heliconius'' comprises a colorful and widespread genus of brush-footed butterflies commonly known as the longwings or heliconians. This genus is distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the New World, from South America a ...
'' butterflies, there are three types of scales: yellow/white, black, and red/orange/brown scales. Some mechanism of wing pattern formation are now being solved using genetic techniques. For instance, a gene called ''cortex'' determines the color of scales: deleting ''cortex'' turned black and red scales yellow. Mutations, e.g. Transposable element, transposon insertions of the non-coding DNA around the ''cortex'' gene can turn a black-winged butterfly into a butterfly with a yellow wing band.
Behaviour
 Butterflies feed primarily on nectar from flowers. Some also derive nourishment from pollen, tree sap, rotting fruit, dung, decaying flesh, and dissolved minerals in wet sand or dirt. Butterflies are important as pollinators for some species of plants. In general, they do not carry as much pollen load as bees, but they are capable of moving pollen over greater distances. Flower constancy has been observed for at least one species of butterfly.
Adult butterflies consume only liquids, ingested through the proboscis. They sip water from damp patches for hydration and feed on nectar from flowers, from which they obtain sugars for energy, and sodium and other minerals vital for reproduction. Several species of butterflies need more sodium than that provided by nectar and are attracted by sodium in salt; they sometimes land on people, attracted by the salt in human sweat. Some butterflies also visit dung and scavenge rotting fruit or carcasses to obtain minerals and nutrients. In many species, this mud-puddling behaviour is restricted to the males, and studies have suggested that the nutrients collected may be provided as a nuptial gift, along with the spermatophore, during mating.
In Hill-topping (biology), hilltopping, males of some species seek hilltops and ridge tops, which they patrol in search for females. Since it usually occurs in species with low population density, it is assumed these landscape points are used as meeting places to find mates.
Butterflies use their antennae to sense the air for wind and scents. The antennae come in various shapes and colours; the hesperiids have a pointed angle or hook to the antennae, while most other families show knobbed antennae. The antennae are richly covered with sensory organs known as sensillum, sensillae. A butterfly's sense of taste is coordinated by chemoreceptors on the Arthropod leg#Insects, tarsi, or feet, which work only on contact, and are used to determine whether an egg-laying insect's offspring will be able to feed on a leaf before eggs are laid on it. Many butterflies use chemical signals,
Butterflies feed primarily on nectar from flowers. Some also derive nourishment from pollen, tree sap, rotting fruit, dung, decaying flesh, and dissolved minerals in wet sand or dirt. Butterflies are important as pollinators for some species of plants. In general, they do not carry as much pollen load as bees, but they are capable of moving pollen over greater distances. Flower constancy has been observed for at least one species of butterfly.
Adult butterflies consume only liquids, ingested through the proboscis. They sip water from damp patches for hydration and feed on nectar from flowers, from which they obtain sugars for energy, and sodium and other minerals vital for reproduction. Several species of butterflies need more sodium than that provided by nectar and are attracted by sodium in salt; they sometimes land on people, attracted by the salt in human sweat. Some butterflies also visit dung and scavenge rotting fruit or carcasses to obtain minerals and nutrients. In many species, this mud-puddling behaviour is restricted to the males, and studies have suggested that the nutrients collected may be provided as a nuptial gift, along with the spermatophore, during mating.
In Hill-topping (biology), hilltopping, males of some species seek hilltops and ridge tops, which they patrol in search for females. Since it usually occurs in species with low population density, it is assumed these landscape points are used as meeting places to find mates.
Butterflies use their antennae to sense the air for wind and scents. The antennae come in various shapes and colours; the hesperiids have a pointed angle or hook to the antennae, while most other families show knobbed antennae. The antennae are richly covered with sensory organs known as sensillum, sensillae. A butterfly's sense of taste is coordinated by chemoreceptors on the Arthropod leg#Insects, tarsi, or feet, which work only on contact, and are used to determine whether an egg-laying insect's offspring will be able to feed on a leaf before eggs are laid on it. Many butterflies use chemical signals, pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s; some have specialized scent scales (androconia) or other structures (coremata or "hair pencils" in the Danaidae). Vision is well developed in butterflies and most species are sensitive to the ultraviolet spectrum. Many species show sexual dimorphism in the patterns of UV reflective patches. Colour vision may be widespread but has been demonstrated in only a few species. Some butterflies have organs of hearing and some species make Stridulation, stridulatory and clicking sounds.
 Many species of butterfly maintain territories and actively chase other species or individuals that may stray into them. Some species will bask or perch on chosen perches. The flight styles of butterflies are often characteristic and some species have courtship flight displays. Butterflies can only fly when their temperature is above ; when it is cool, they can position themselves to expose the underside of the wings to the sunlight to heat themselves up. If their body temperature reaches , they can orientate themselves with the folded wings edgewise to the sun. Basking is an activity which is more common in the cooler hours of the morning. Some species have evolved dark wingbases to help in gathering more heat and this is especially evident in alpine forms.
As in many other insects, the lift (force), lift generated by butterflies is more than can be accounted for by steady-state, non-transitory aerodynamics. Studies using ''Vanessa atalanta'' in a wind tunnel show that they use a wide variety of aerodynamic mechanisms to generate force. These include wake capture, vortices at the wing edge, rotational mechanisms and the Torkel Weis-Fogh, Weis-Fogh 'clap-and-fling' mechanism. Butterflies are able to change from one mode to another rapidly.
Many species of butterfly maintain territories and actively chase other species or individuals that may stray into them. Some species will bask or perch on chosen perches. The flight styles of butterflies are often characteristic and some species have courtship flight displays. Butterflies can only fly when their temperature is above ; when it is cool, they can position themselves to expose the underside of the wings to the sunlight to heat themselves up. If their body temperature reaches , they can orientate themselves with the folded wings edgewise to the sun. Basking is an activity which is more common in the cooler hours of the morning. Some species have evolved dark wingbases to help in gathering more heat and this is especially evident in alpine forms.
As in many other insects, the lift (force), lift generated by butterflies is more than can be accounted for by steady-state, non-transitory aerodynamics. Studies using ''Vanessa atalanta'' in a wind tunnel show that they use a wide variety of aerodynamic mechanisms to generate force. These include wake capture, vortices at the wing edge, rotational mechanisms and the Torkel Weis-Fogh, Weis-Fogh 'clap-and-fling' mechanism. Butterflies are able to change from one mode to another rapidly.
Ecology

Parasitoids, predators, and pathogens
Butterflies are threatened in their early stages by parasitoids and in all stages by predators, diseases and environmental factors. Braconidae, Braconid and other parasitic wasps lay their eggs in lepidopteran eggs or larvae and the wasps' parasitoid larvae devour their hosts, usually pupating inside or outside the desiccated husk. Most wasps are very specific about their host species and some have been used as biological controls of pest butterflies like the Pieris brassicae, large white butterfly. When the Pieris rapae, small cabbage white was accidentally introduced to New Zealand, it had no natural enemies. In order to control it, some pupae that had been parasitised by a chalcid wasp were imported, and natural control was thus regained. Some flies lay their eggs on the outside of caterpillars and the newly hatched fly larvae bore their way through the skin and feed in a similar way to the parasitoid wasp larvae. Predators of butterflies include ants, spiders, wasps, and birds. Caterpillars are also affected by a range of bacterial, viral and fungal diseases, and only a small percentage of the butterfly eggs laid ever reach adulthood. The bacterium ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' has been used in sprays to reduce damage to crops by the caterpillars of the large white butterfly, and the entomopathogenic fungus ''Beauveria bassiana'' has proved effective for the same purpose.Endangered species
Queen Alexandra's birdwing is the largest butterfly in the world. The species is List of endangered insects#Other Lepidoptera species, endangered, and is one of only three insects (the other two being butterflies as well) to be listed on CITES#Appendix I, Appendix I of CITES, making international trade illegal.CITES appendices I, II and III, official website Ocybadistes knightorum, Black grass-dart butterfly ''(Ocybadistes knightorum)'' is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is endemic to New South Wales. It has a very limited distribution in the Boambee, New South Wales, Boambee area.
Defences
Heliconius
''Heliconius'' comprises a colorful and widespread genus of brush-footed butterflies commonly known as the longwings or heliconians. This genus is distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the New World, from South America a ...
'' butterflies from the Americas are a good example.
ant
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of ...
s and gaining their protection. Behavioural defences include perching and angling the wings to reduce shadow and avoid being conspicuous. Some female Nymphalid butterflies guard their eggs from parasitoidal wasps.
The Lycaenidae have a false head consisting of eyespots and small tails (false antennae) to deflect attack from the more vital head region. These may also cause ambush predators such as spiders to approach from the wrong end, enabling the butterflies to detect attacks promptly. Many butterflies have Eyespot (mimicry), eyespots on the wings; these too may deflect attacks, or may serve to attract mates.
Auditory defences can also be used, which in the case of the grizzled skipper refers to vibrations generated by the butterfly upon expanding its wings in an attempt to communicate with ant predators.
Many tropical butterflies have seasonal polyphenism, seasonal forms for dry and wet seasons. These are switched by the hormone ecdysone. The dry-season forms are usually more cryptic, perhaps offering better camouflage when vegetation is scarce. Dark colours in wet-season forms may help to absorb solar radiation.
Butterflies without defences such as toxins or mimicry protect themselves through a flight that is more bumpy and unpredictable than in other species. It is assumed this behavior makes it more difficult for predators to catch them, and is caused by the turbulence created by the small whirlpools formed by the wings during flight.
Declining numbers
Declining butterfly populations have been noticed in many areas of the world, and this phenomenon is consistent with the decline in insect populations, rapidly decreasing insect populations around the world. At least in the Western United States, this collapse in the number of most species of butterflies has been determined to be driven by global climate change, specifically, by warmer autumns.In culture
In art and literature
Butterflies have appeared in art from 3500 years ago in ancient Egypt. In the ancient Mesoamerican city of Teotihuacan, the brilliantly coloured image of the butterfly was carved into many temples, buildings, jewellery, and emblazoned on Censer, incense burners. The butterfly was sometimes depicted with the maw of a jaguar, and some species were considered to be the reincarnations of the souls of dead warriors. The close association of butterflies with fire and warfare persisted into the Aztec civilisation; evidence of similar jaguar-butterfly images has been found among the Zapotec peoples, Zapotec and Maya civilisations. Butterflies are widely used in objects of art and jewellery: mounted in frames, embedded in resin, displayed in bottles, laminated in paper, and used in some mixed media artworks and furnishings. The Norwegians, Norwegian naturalist Kjell B. Sandved, Kjell Sandved compiled a photographic ''Butterfly Alphabet'' containing all 26 letters and the numerals 0 to 9 from the wings of butterflies. Sir John Tenniel drew a famous illustration of Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), Alice meeting a Caterpillar (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), caterpillar for Lewis Carroll's ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, Alice in Wonderland'', c. 1865. The caterpillar is seated on a toadstool and is smoking a hookah; the image can be read as showing either the forelegs of the larva, or as suggesting a face with protruding nose and chin. Eric Carle's children's book ''The Very Hungry Caterpillar'' portrays the larva as an extraordinarily hungry animal, while also teaching children how to count (to five) and the days of the week.
A butterfly appeared in one of Rudyard Kipling's ''Just So Stories'', "The Butterfly that Stamped".
One of the most popular, and most often recorded, songs by Sweden's eighteenth-century bard, Carl Michael Bellman, is "Fjäriln vingad syns på Haga" (The butterfly wingèd is seen in Haga), one of his ''Fredman's Songs''.
''Madam Butterfly'' is a 1904 opera by Giacomo Puccini about a romantic young Japanese bride who is deserted by her American officer husband soon after they are married. It was based on John Luther Long's short story written in 1898.
Sir John Tenniel drew a famous illustration of Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), Alice meeting a Caterpillar (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), caterpillar for Lewis Carroll's ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, Alice in Wonderland'', c. 1865. The caterpillar is seated on a toadstool and is smoking a hookah; the image can be read as showing either the forelegs of the larva, or as suggesting a face with protruding nose and chin. Eric Carle's children's book ''The Very Hungry Caterpillar'' portrays the larva as an extraordinarily hungry animal, while also teaching children how to count (to five) and the days of the week.
A butterfly appeared in one of Rudyard Kipling's ''Just So Stories'', "The Butterfly that Stamped".
One of the most popular, and most often recorded, songs by Sweden's eighteenth-century bard, Carl Michael Bellman, is "Fjäriln vingad syns på Haga" (The butterfly wingèd is seen in Haga), one of his ''Fredman's Songs''.
''Madam Butterfly'' is a 1904 opera by Giacomo Puccini about a romantic young Japanese bride who is deserted by her American officer husband soon after they are married. It was based on John Luther Long's short story written in 1898.
In mythology and folklore
 According to Lafcadio Hearn, a butterfly was seen in Japan as the personification of a person's soul; whether they be living, dying, or already dead. One Japanese superstition says that if a butterfly enters your guest room and perches behind the bamboo screen, the person whom you most love is coming to see you. Large numbers of butterflies are viewed as bad omens. When Taira no Masakado was secretly preparing for his famous revolt, there appeared in Kyoto so vast a swarm of butterflies that the people were frightened—thinking the apparition to be a portent of coming evil.
According to Lafcadio Hearn, a butterfly was seen in Japan as the personification of a person's soul; whether they be living, dying, or already dead. One Japanese superstition says that if a butterfly enters your guest room and perches behind the bamboo screen, the person whom you most love is coming to see you. Large numbers of butterflies are viewed as bad omens. When Taira no Masakado was secretly preparing for his famous revolt, there appeared in Kyoto so vast a swarm of butterflies that the people were frightened—thinking the apparition to be a portent of coming evil.
 Diderot's ''Encyclopédie'' cites butterflies as a symbol for the soul. A Roman sculpture depicts a butterfly exiting the mouth of a dead man, representing the Roman belief that the soul leaves through the mouth. In line with this, the ancient Greek word for "butterfly" is ψυχή (''psȳchē''), which primarily means "soul" or "mind". According to Mircea Eliade, some of the Naga people, Nagas of Manipur claim ancestry from a butterfly.Rabuzzi, M. 1997. Butterfly etymology. Cultural Entomology November 1997 Fourth issu
Diderot's ''Encyclopédie'' cites butterflies as a symbol for the soul. A Roman sculpture depicts a butterfly exiting the mouth of a dead man, representing the Roman belief that the soul leaves through the mouth. In line with this, the ancient Greek word for "butterfly" is ψυχή (''psȳchē''), which primarily means "soul" or "mind". According to Mircea Eliade, some of the Naga people, Nagas of Manipur claim ancestry from a butterfly.Rabuzzi, M. 1997. Butterfly etymology. Cultural Entomology November 1997 Fourth issuonline
In some cultures, butterflies symbolise Reincarnation, rebirth. The butterfly is a symbol of being transgender, because of the transformation from caterpillar to winged adult. In the English county of Devon, people once hurried to kill the first butterfly of the year, to avoid a year of bad luck. In the Philippines, a lingering black or dark butterfly or moth in the house is taken to mean an impending or recent death in the family. Several American states have chosen an List of U.S. state butterflies, official state butterfly.
Collecting, recording, and rearing
 "Collecting" means preserving dead specimens, not keeping butterflies as pets. Collecting butterflies was once a popular hobby; it has now largely been replaced by photography, recording, and rearing butterflies for release into the wild. The zoological illustrator Frederick William Frohawk succeeded in rearing all the butterfly species found in Britain, at a rate of four per year, to enable him to draw every stage of each species. He published the results in the folio sized handbook ''The Natural History of British Butterflies'' in 1924.
Butterflies and
"Collecting" means preserving dead specimens, not keeping butterflies as pets. Collecting butterflies was once a popular hobby; it has now largely been replaced by photography, recording, and rearing butterflies for release into the wild. The zoological illustrator Frederick William Frohawk succeeded in rearing all the butterfly species found in Britain, at a rate of four per year, to enable him to draw every stage of each species. He published the results in the folio sized handbook ''The Natural History of British Butterflies'' in 1924.
Butterflies and moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ...
s can be reared for recreation or for release.
In technology
Study of thestructural coloration
Structural coloration in animals, and a few plants, is the production of colour by microscopically structured surfaces fine enough to interfere with visible light instead of pigments, although some structural coloration occurs in combination wit ...
of the wing scales of swallowtail butterflies has led to the development of more efficient light-emitting diodes, and is inspiring nanotechnology research to produce paints that do not use toxic pigments and the development of new display technologies.
References
External links
Papilionoidea on the Tree of Life
Butterfly species and observations on iNaturalist
*
Rhopalocera
at insectoid.info
Regional lists
North America
Africa
* Asia
{{Authority control Butterflies, Articles containing video clips Extant Lutetian first appearances Insects in culture