Butadienes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula (CH2=CH)2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to
 This process was the basis for the Soviet Union's synthetic rubber industry during and after World War II, and it remained in limited use in Russia and other parts of eastern Europe until the end of the 1970s. At the same time this type of manufacture was canceled in Brazil. As of 2017, no butadiene was produced industrially from ethanol.
In the other, two-step process, developed by the Russian emigre chemist Ivan Ostromislensky, ethanol is oxidized to
This process was the basis for the Soviet Union's synthetic rubber industry during and after World War II, and it remained in limited use in Russia and other parts of eastern Europe until the end of the 1970s. At the same time this type of manufacture was canceled in Brazil. As of 2017, no butadiene was produced industrially from ethanol.
In the other, two-step process, developed by the Russian emigre chemist Ivan Ostromislensky, ethanol is oxidized to  This process was one of the three used in the United States to produce "government rubber" during World War II, although it is less economical than the butane or butene routes for the large volumes. Still, three plants with a total capacity of 200,000 tons per year were constructed in the U.S. ( Institute, West Virginia, Louisville, Kentucky, and Kobuta, Pennsylvania) with start-ups completed in 1943, the Louisville plant initially created butadiene from acetylene generated by an associated calcium carbide plant. The process remains in use today in China and India.
This process was one of the three used in the United States to produce "government rubber" during World War II, although it is less economical than the butane or butene routes for the large volumes. Still, three plants with a total capacity of 200,000 tons per year were constructed in the U.S. ( Institute, West Virginia, Louisville, Kentucky, and Kobuta, Pennsylvania) with start-ups completed in 1943, the Louisville plant initially created butadiene from acetylene generated by an associated calcium carbide plant. The process remains in use today in China and India.
 The most stable conformer of 1,3-butadiene is the ''s''-''trans'' conformation, in which the molecule is planar, with the two pairs of double bonds facing opposite directions. This conformation is most stable because orbital overlap between double bonds is maximized, allowing for maximum conjugation, while steric effects are minimized. Conventionally, the ''s-trans'' conformation is considered to have a C2-C3 dihedral angle of 180°. In contrast, the ''s''-''cis'' conformation, in which the dihedral angle is 0°, with the pair of double bonds facing the same direction is approximately 16.5 kJ/mol (3.9 kcal/mol) higher in energy, due to steric hindrance. This geometry is a local energy maximum, so in contrast to the ''s-trans'' geometry, it is not a conformer. The ''gauche'' geometry, in which the double bonds of the ''s-cis'' geometry are twisted to give a dihedral angle of around 38°, is a second conformer that is around 12.0 kJ/mol (2.9 kcal/mol) higher in energy than the ''s-trans'' conformer. Overall, there is a barrier of 24.8 kJ/mol (5.9 kcal/mol) for isomerization between the two conformers. This increased rotational barrier and strong overall preference for a near-planar geometry is evidence for a delocalized π system and a small degree of partial double bond character in the C–C single bond, in accord with resonance theory.
Despite the high energy of the ''s-cis'' conformation, 1,3-butadiene needs to assume this conformation (or one very similar) before it can participate as the four-electron component in concerted cycloaddition reactions like the Diels-Alder reaction.
Similarly, a combined experimental and computational study has found that the double bond of ''s-trans-''butadiene has a length of 133.8 pm, while that for ethylene has a length of 133.0 pm. This was taken as evidence of a π-bond weakened and lengthened by delocalization, as depicted by the resonance structures shown below.
The most stable conformer of 1,3-butadiene is the ''s''-''trans'' conformation, in which the molecule is planar, with the two pairs of double bonds facing opposite directions. This conformation is most stable because orbital overlap between double bonds is maximized, allowing for maximum conjugation, while steric effects are minimized. Conventionally, the ''s-trans'' conformation is considered to have a C2-C3 dihedral angle of 180°. In contrast, the ''s''-''cis'' conformation, in which the dihedral angle is 0°, with the pair of double bonds facing the same direction is approximately 16.5 kJ/mol (3.9 kcal/mol) higher in energy, due to steric hindrance. This geometry is a local energy maximum, so in contrast to the ''s-trans'' geometry, it is not a conformer. The ''gauche'' geometry, in which the double bonds of the ''s-cis'' geometry are twisted to give a dihedral angle of around 38°, is a second conformer that is around 12.0 kJ/mol (2.9 kcal/mol) higher in energy than the ''s-trans'' conformer. Overall, there is a barrier of 24.8 kJ/mol (5.9 kcal/mol) for isomerization between the two conformers. This increased rotational barrier and strong overall preference for a near-planar geometry is evidence for a delocalized π system and a small degree of partial double bond character in the C–C single bond, in accord with resonance theory.
Despite the high energy of the ''s-cis'' conformation, 1,3-butadiene needs to assume this conformation (or one very similar) before it can participate as the four-electron component in concerted cycloaddition reactions like the Diels-Alder reaction.
Similarly, a combined experimental and computational study has found that the double bond of ''s-trans-''butadiene has a length of 133.8 pm, while that for ethylene has a length of 133.0 pm. This was taken as evidence of a π-bond weakened and lengthened by delocalization, as depicted by the resonance structures shown below.
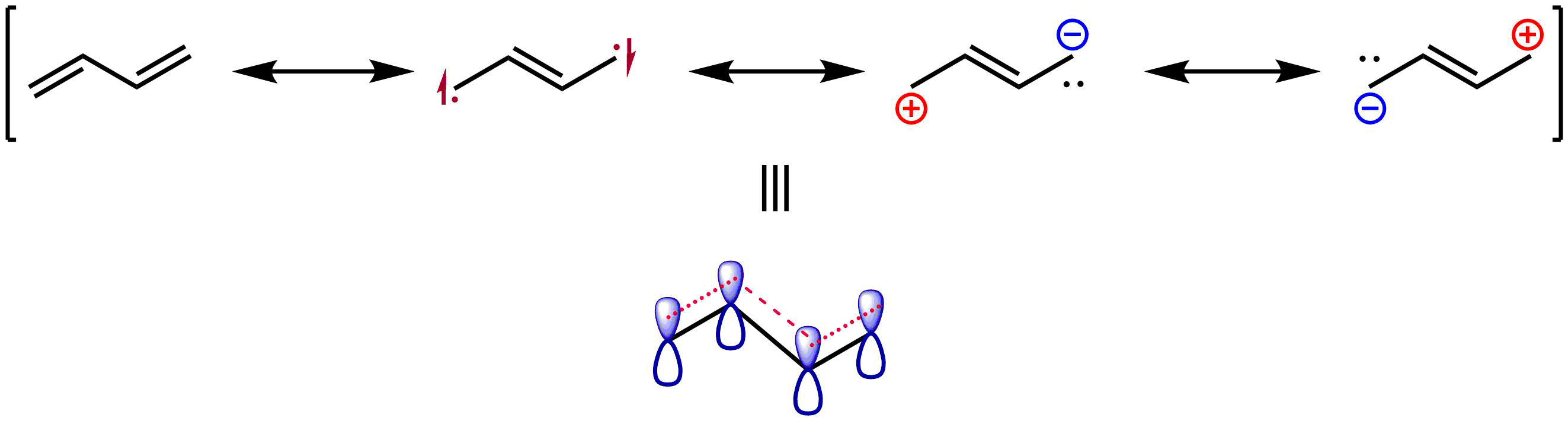 A qualitative picture of the molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene is readily obtained by applying Hückel theory. (The article on
A qualitative picture of the molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene is readily obtained by applying Hückel theory. (The article on
EPA website
/ref> 1,3-Butadiene is recognized as a Highly Reactive Volatile Organic Compound (HRVOC) for its potential to readily form ozone, and as such, emissions of the chemical are highly regulated by TCEQ in parts of the Houston-Brazoria-Galveston Ozone Non-Attainment Areabr>
1,3-Butadiene
– Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
– CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
{{DEFAULTSORT:Butadiene, 1, 3- Alkadienes Hazardous air pollutants Monomers IARC Group 1 carcinogens U.S. Synthetic Rubber Program Commodity chemicals Petrochemicals Conjugated dienes
synthetic rubber
A synthetic rubber is an artificial elastomer. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum byproducts. About 32-million metric tons of rubbers are produced annually in the United States, and of that amount two thirds are synthetic. Synthetic rubbe ...
. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene.
Although butadiene breaks down quickly in the atmosphere, it is nevertheless found in ambient air in urban and suburban areas as a consequence of its constant emission
Emission may refer to:
Chemical products
* Emission of air pollutants, notably:
**Flue gas, gas exiting to the atmosphere via a flue
** Exhaust gas, flue gas generated by fuel combustion
** Emission of greenhouse gases, which absorb and emit radi ...
from motor vehicle
A motor vehicle, also known as motorized vehicle or automotive vehicle, is a self-propelled land vehicle, commonly wheeled, that does not operate on Track (rail transport), rails (such as trains or trams) and is used for the transportation of pe ...
s.
The name butadiene can also refer to the isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
Iso ...
, 1,2-butadiene, which is a cumulated diene with structure H2C=C=CH−CH3. This allene has no industrial significance.
History
In 1863, the French chemist E. Caventou isolated butadiene from the pyrolysis of amyl alcohol. This hydrocarbon was identified as butadiene in 1886, after Henry Edward Armstrong isolated it from among the pyrolysis products of petroleum. In 1910, the Russian chemist Sergei Lebedev polymerized butadiene and obtained a material with rubber-like properties. This polymer was, however, found to be too soft to replace natural rubber in many applications, notably automobile tires. The butadiene industry originated in the years leading up to World War II. Many of the belligerent nations realized that in the event of war, they could be cut off from rubber plantations controlled by the British Empire, and sought to reduce their dependence on natural rubber. In 1929, Eduard Tschunker and Walter Bock, working forIG Farben
Interessengemeinschaft Farbenindustrie AG (), commonly known as IG Farben (German for 'IG Dyestuffs'), was a German chemical and pharmaceutical conglomerate (company), conglomerate. Formed in 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies—BASF, ...
in Germany, made a copolymer of styrene and butadiene that could be used in automobile tires. Worldwide production quickly ensued, with butadiene being produced from grain alcohol in the Soviet Union and the United States, and from coal-derived acetylene
Acetylene (systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure ...
in Germany.
Production
Extraction from C4 hydrocarbons
In the United States, western Europe, and Japan, butadiene is produced as a byproduct of thesteam cracking
Steam cracking is a petrochemical process in which saturated hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller, often unsaturated, hydrocarbons. It is the principal industrial method for producing the lighter alkenes (or commonly olefins), including ethe ...
process used to produce ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
and other alkenes. When mixed with steam and briefly heated to very high temperatures (often over 900 °C), aliphatic hydrocarbons give up hydrogen to produce a complex mixture of unsaturated hydrocarbons, including butadiene. The quantity of butadiene produced depends on the hydrocarbons used as feed. Light feeds, such as ethane, give primarily ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
when cracked, but heavier feeds favor the formation of heavier olefins, butadiene, and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Butadiene is typically isolated from the other four-carbon hydrocarbons produced in steam cracking by extractive distillation using a polar aprotic solvent such as acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not clas ...
, ''N''-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, furfural
Furfural is an organic compound with the formula C4H3OCHO. It is a colorless liquid, although commercial samples are often brown. It has an aldehyde group attached to the 2-position of furan. It is a product of the dehydration of sugars, as occurs ...
, or dimethylformamide, from which it is then stripped by distillation.Sun, H.P. Wristers, J.P. (1992). Butadiene. In J.I. Kroschwitz (Ed.), ''Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 4th ed.'', vol. 4, pp. 663–690. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
From dehydrogenation of ''n''-butane
Butadiene can also be produced by the catalytic dehydrogenation of normal butane (''n''-butane). The first such post-war commercial plant, producing 65,000 tons per year of butadiene, began operations in 1957 in Houston, Texas.Beychok, M.R. and Brack, W.J., "First Postwar Butadiene Plant", ''Petroleum Refiner'', June 1957. Prior to that, in the 1940s theRubber Reserve Company
Kenneth Stanley "Boots" Adams (August 31, 1899 – March 30, 1975) was an American business executive, University of Kansas booster, and civic philanthropist of Bartlesville, Oklahoma. Adams began his career with the Phillips Petroleum Compa ...
, a part of the United States government, constructed several plants in Borger, Texas, Toledo, Ohio, and El Segundo, California
El Segundo ( , ; ) is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States. Located on Santa Monica Bay, it was incorporated on January 18, 1917, and is part of the South Bay Cities Council of Governments. The population was 16,731 as of th ...
, to produce synthetic rubber for the war effort as part of the United States Synthetic Rubber Program.Herbert, Vernon, "Synthetic Rubber: A Project That Had to Succeed", Greenwood Press, 1985, Total capacity was 68 KMTA (Kilo Metric Tons per Annum).
Today, butadiene from ''n''-butane is commercially produced using the Houdry Catadiene process, which was developed during World War II. This entails treating butane over alumina and chromia at high temperatures.
From ethanol
In other parts of the world, including South America, Eastern Europe, China, and India, butadiene is also produced from ethanol. While not competitive with steam cracking for producing large volumes of butadiene, lower capital costs make production from ethanol a viable option for smaller-capacity plants. Two processes were in use. In the single-step process developed by Sergei Lebedev, ethanol is converted to butadiene, hydrogen, and water at 400–450 °C over any of a variety of metal oxide catalysts:Kirshenbaum, I. (1978). Butadiene. In M. Grayson (Ed.), ''Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 3rd ed.'', vol. 4, pp. 313–337. New York: John Wiley & Sons. :acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the mos ...
, which reacts with additional ethanol over a tantalum-promoted porous silica catalyst at 325–350 °C to yield butadiene:
: This process was one of the three used in the United States to produce "government rubber" during World War II, although it is less economical than the butane or butene routes for the large volumes. Still, three plants with a total capacity of 200,000 tons per year were constructed in the U.S. ( Institute, West Virginia, Louisville, Kentucky, and Kobuta, Pennsylvania) with start-ups completed in 1943, the Louisville plant initially created butadiene from acetylene generated by an associated calcium carbide plant. The process remains in use today in China and India.
This process was one of the three used in the United States to produce "government rubber" during World War II, although it is less economical than the butane or butene routes for the large volumes. Still, three plants with a total capacity of 200,000 tons per year were constructed in the U.S. ( Institute, West Virginia, Louisville, Kentucky, and Kobuta, Pennsylvania) with start-ups completed in 1943, the Louisville plant initially created butadiene from acetylene generated by an associated calcium carbide plant. The process remains in use today in China and India.
From butenes
1,3-Butadiene can also be produced by catalytic dehydrogenation of normal butenes. This method was also used by the U.S. Synthetic Rubber Program (USSRP) during World War II. The process was much more economical than the alcohol or n-butane route but competed with aviation gasoline for available butene molecules (butenes were plentiful thanks tocatalytic cracking
Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) is the conversion process used in petroleum refineries to convert the high-boiling point, high-molecular weight hydrocarbon fractions of petroleum (crude oils) into gasoline, olefinic gases, and other petroleum prod ...
). The USSRP constructed several plants in Baton Rouge
Baton Rouge ( ; ) is a city in and the capital of the U.S. state of Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-sma ...
and Lake Charles, Louisiana; Houston, Baytown, and Port Neches, Texas; and Torrance, California. Total annual production was 275 KMTA.
In the 1960s, a Houston company known as "Petro-Tex" patented a process to produce butadiene from normal butenes by oxidative dehydrogenation using a proprietary catalyst. It is unclear if this technology is practiced commercially.
After World War II, the production from butenes became the major type of production in USSR.
For laboratory use
1,3-Butadiene is inconvenient for laboratory use because it is gas. Laboratory procedures have been optimized for its generation from nongaseous precursors. It can be produced by the retro- Diels-Alder reaction of cyclohexene.Sulfolene
Sulfolene, or butadiene sulfone is a cyclic organic chemical with a sulfone functional group. It is a white, odorless, crystalline, indefinitely storable solid, which dissolves in water and many organic solvents. The compound is used as a source o ...
is a convenient solid storable source for 1,3-butadiene in the laboratory. It releases the diene and sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
upon heating.
Uses
Most butadiene is used to make synthetic rubbers for the manufacture of tyres, grommets and elastic bands. The conversion of butadiene to synthetic rubbers is called polymerization, a process by which small molecules (monomers) are linked to make large ones (polymers). The mere polymerization of butadiene givespolybutadiene
Polybutadiene utadiene rubber BRis a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tir ...
, which is a very soft, almost liquid material. The polymerization of butadiene ''and'' other monomers gives copolymers, which are more valued. The polymerization of butadiene and styrene and/or acrylonitrile, such as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
A ...
(ABS), nitrile-butadiene (NBR), and styrene-butadiene (SBR). These copolymers are tough and/or elastic depending on the ratio of the monomers used in their preparation. SBR is the material most commonly used for the production of automobile tyres. Precursors to still other synthetic rubbers are prepared from butadiene. One is chloroprene.
Smaller amounts of butadiene are used to make adiponitrile, a precursor to some nylons. The conversion of butadiene to adiponitrile entails the addition of hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide, sometimes called prussic acid, is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structure . It is a colorless, extremely poisonous, and flammable liquid that boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is produced on an ...
to each of the double bonds in butadiene. The process is called hydrocyanation.
Butadiene is used to make the solvent sulfolane
Sulfolane (also ''tetramethylene sulfone'', systematic name: 1λ6-thiolane-1,1-dione) is an organosulfur compound, formally a cyclic sulfone, with the formula (CH2)4SO2. It is a colorless liquid commonly used in the chemical industry as a solvent ...
.
Butadiene is also useful in the synthesis of cycloalkanes and cycloalkenes, as it reacts with double and triple carbon-carbon bonds through Diels-Alder reactions. The most widely used such reactions involve reactions of butadiene with one or two other molecules of butadiene, i.e., dimerization and trimerization respectively. Via dimerizatiion butadiene is converted to 4-vinylcyclohexene and cyclooctadiene
A cyclooctadiene (sometimes abbreviated COD) is any of several cyclic diene with the formula (CH2)4(C2H2)2. Focusing only on cis derivatives, four isomers are possible: 1,2-, which is an allene, 1,3-, 1,4-, and 1,5-. Commonly encountered isomers ar ...
. In fact, vinylcyclohexene is a common impurity that accumulates when butadiene is stored. Via trimerization, butadiene is converted to cyclododecatriene. Some of these processes employ nickel- or titanium-containing catalysts.
Structure, conformation, and stability
 The most stable conformer of 1,3-butadiene is the ''s''-''trans'' conformation, in which the molecule is planar, with the two pairs of double bonds facing opposite directions. This conformation is most stable because orbital overlap between double bonds is maximized, allowing for maximum conjugation, while steric effects are minimized. Conventionally, the ''s-trans'' conformation is considered to have a C2-C3 dihedral angle of 180°. In contrast, the ''s''-''cis'' conformation, in which the dihedral angle is 0°, with the pair of double bonds facing the same direction is approximately 16.5 kJ/mol (3.9 kcal/mol) higher in energy, due to steric hindrance. This geometry is a local energy maximum, so in contrast to the ''s-trans'' geometry, it is not a conformer. The ''gauche'' geometry, in which the double bonds of the ''s-cis'' geometry are twisted to give a dihedral angle of around 38°, is a second conformer that is around 12.0 kJ/mol (2.9 kcal/mol) higher in energy than the ''s-trans'' conformer. Overall, there is a barrier of 24.8 kJ/mol (5.9 kcal/mol) for isomerization between the two conformers. This increased rotational barrier and strong overall preference for a near-planar geometry is evidence for a delocalized π system and a small degree of partial double bond character in the C–C single bond, in accord with resonance theory.
Despite the high energy of the ''s-cis'' conformation, 1,3-butadiene needs to assume this conformation (or one very similar) before it can participate as the four-electron component in concerted cycloaddition reactions like the Diels-Alder reaction.
Similarly, a combined experimental and computational study has found that the double bond of ''s-trans-''butadiene has a length of 133.8 pm, while that for ethylene has a length of 133.0 pm. This was taken as evidence of a π-bond weakened and lengthened by delocalization, as depicted by the resonance structures shown below.
The most stable conformer of 1,3-butadiene is the ''s''-''trans'' conformation, in which the molecule is planar, with the two pairs of double bonds facing opposite directions. This conformation is most stable because orbital overlap between double bonds is maximized, allowing for maximum conjugation, while steric effects are minimized. Conventionally, the ''s-trans'' conformation is considered to have a C2-C3 dihedral angle of 180°. In contrast, the ''s''-''cis'' conformation, in which the dihedral angle is 0°, with the pair of double bonds facing the same direction is approximately 16.5 kJ/mol (3.9 kcal/mol) higher in energy, due to steric hindrance. This geometry is a local energy maximum, so in contrast to the ''s-trans'' geometry, it is not a conformer. The ''gauche'' geometry, in which the double bonds of the ''s-cis'' geometry are twisted to give a dihedral angle of around 38°, is a second conformer that is around 12.0 kJ/mol (2.9 kcal/mol) higher in energy than the ''s-trans'' conformer. Overall, there is a barrier of 24.8 kJ/mol (5.9 kcal/mol) for isomerization between the two conformers. This increased rotational barrier and strong overall preference for a near-planar geometry is evidence for a delocalized π system and a small degree of partial double bond character in the C–C single bond, in accord with resonance theory.
Despite the high energy of the ''s-cis'' conformation, 1,3-butadiene needs to assume this conformation (or one very similar) before it can participate as the four-electron component in concerted cycloaddition reactions like the Diels-Alder reaction.
Similarly, a combined experimental and computational study has found that the double bond of ''s-trans-''butadiene has a length of 133.8 pm, while that for ethylene has a length of 133.0 pm. This was taken as evidence of a π-bond weakened and lengthened by delocalization, as depicted by the resonance structures shown below.
 A qualitative picture of the molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene is readily obtained by applying Hückel theory. (The article on
A qualitative picture of the molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene is readily obtained by applying Hückel theory. (The article on Hückel theory Hückel or Huckel may refer to:
* Erich Hückel (1896-1980), German physicist and chemist
** Debye–Hückel equation (named after Peter Debye and Erich Hückel), in chemistry, a method of calculating activity coefficients
** Hückel method (name ...
gives a derivation for the butadiene orbitals.)
1,3-Butadiene is also thermodynamically stabilized. While a monosubstituted double bond releases about 30.3 kcal/mol of heat upon hydrogenation, 1,3-butadiene releases slightly less (57.1 kcal/mol) than twice this energy (60.6 kcal/mol), expected for two isolated double bonds. That implies a stabilization energy of 3.5 kcal/mol. Similarly, the hydrogenation of the terminal double bond of 1,4-pentadiene releases 30.1 kcal/mol of heat, while hydrogenation of the terminal double bond of conjugated (''E'')-1,3-pentadiene releases only 26.5 kcal/mol, implying a very similar value of 3.6 kcal/mol for the stabilization energy. The ~3.5 kcal/mol difference in these heats of hydrogenation can be taken to be the resonance energy of a conjugated diene.
Reactions
The industrial uses illustrate the tendency of butadiene to polymerize. Its susceptibility to 1,4-addition reactions is illustrated by its hydrocyanation. Like many dienes, it undergoes Pd-catalyzed reactions that proceed via allyl complexes. It is a partner in Diels-Alder reactions, e.g. with maleic anhydride to give tetrahydrophthalic anhydride. Like other dienes, butadiene is a ligand for low-valent metal complexes, e.g. the derivatives Fe(butadiene)(CO)3 and Mo(butadiene)3.Environmental health and safety
Butadiene is of low acute toxicity. LC50 is 12.5–11.5 vol% for inhalation by rats and mice. Long-term exposure has been associated with cardiovascular disease. There is a consistent association with leukemia, as well as a significant association with other cancers. IARC has designated 1,3-Butadiene as a Group 1 carcinogen ('carcinogenic to humans'), and the Agency for Toxic Substances Disease Registry and the US EPA also list the chemical as a carcinogen.Health Effects https://www.osha.gov/SLTC/butadiene/index.html The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) lists the chemical as a suspected carcinogen. The Natural Resource Defense Council (NRDC) lists some disease clusters that are suspected to be associated with this chemical. Some researchers have concluded it is the most potent carcinogen incigarette smoke
Tobacco smoke is a sooty aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of tobacco during the smoking of cigarettes and other tobacco products. Temperatures in burning cigarettes range from about 400 °C between puffs to about 900 °C d ...
, twice as potent as the runner up acrylonitrile
1,3-Butadiene is also a suspected human teratogen. Prolonged and excessive exposure can affect many areas in the human body; blood, brain, eye, heart, kidney, lung, nose and throat have all been shown to react to the presence of excessive 1,3-butadiene. Animal data suggest that women have a higher sensitivity to possible carcinogenic effects of butadiene over men when exposed to the chemical. This may be due to estrogen receptor impacts. While these data reveal important implications to the risks of human exposure to butadiene, more data are necessary to draw conclusive risk assessments. There is also a lack of human data for the effects of butadiene on reproductive and development shown to occur in mice, but animal studies have shown breathing butadiene during pregnancy can increase the number of birth defects, and humans have the same hormone systems as animals./ref> 1,3-Butadiene is recognized as a Highly Reactive Volatile Organic Compound (HRVOC) for its potential to readily form ozone, and as such, emissions of the chemical are highly regulated by TCEQ in parts of the Houston-Brazoria-Galveston Ozone Non-Attainment Areabr>
Data sheet
See also
* Cyclobutadiene *Polybutadiene
Polybutadiene utadiene rubber BRis a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tir ...
*Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) is an oligomer of butadiene terminated at each end with a hydroxyl functional group. It reacts with isocyanates to form polyurethane polymers.
HTPB is a translucent liquid with a color similar to wax paper a ...
References
External links
1,3-Butadiene
– Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
– CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
{{DEFAULTSORT:Butadiene, 1, 3- Alkadienes Hazardous air pollutants Monomers IARC Group 1 carcinogens U.S. Synthetic Rubber Program Commodity chemicals Petrochemicals Conjugated dienes