Bunyips on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
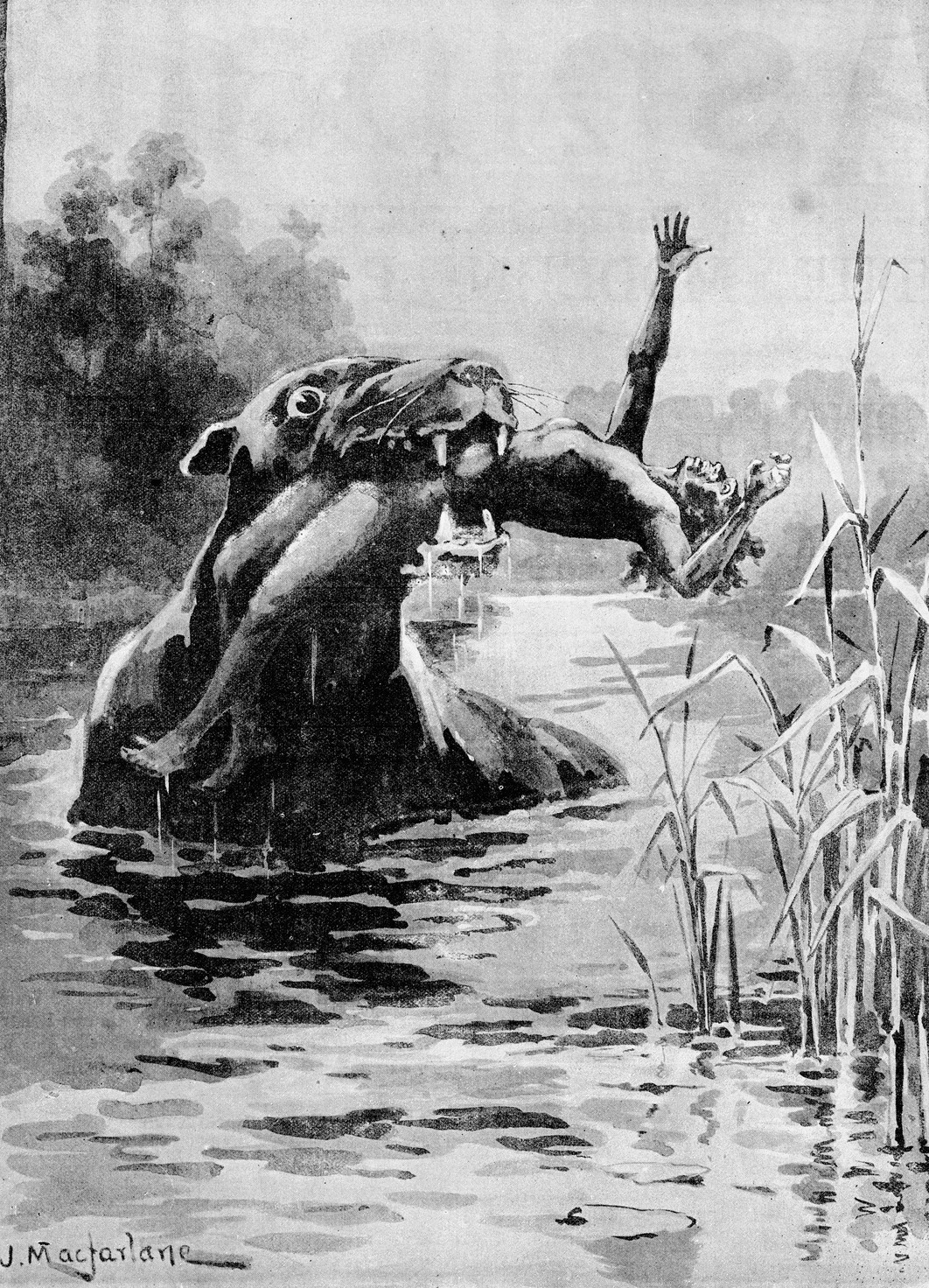 The bunyip is a creature from the aboriginal mythology of southeastern Australia, said to lurk in
The bunyip is a creature from the aboriginal mythology of southeastern Australia, said to lurk in
 In January 1846, a peculiar skull was taken by a settler from the banks of Murrumbidgee River near Balranald, New South Wales. Initial reports suggested that it was the skull of something unknown to science. The squatter who found it remarked, "all the natives to whom it was shown called ta bunyip". By July 1847, several experts, including W. S. Macleay and Professor Owen, had identified the skull as the deformed foetal skull of a foal or calf. At the same time, the purported bunyip skull was put on display in the Australian Museum (Sydney) for two days. Visitors flocked to see it, and '' The Sydney Morning Herald'' reported that many people spoke out about their "bunyip sightings". Reports of this discovery used the phrase 'Kine Pratie' as well as Bunyip. Explorer William Hovell, who examined the skull, also called it a 'katen-pai'.
In March of that year "a bunyip or an immense Platibus" ( Platypus) was sighted "sunning himself on the placid bosom of the Yarra, just opposite the Custom House" in Melbourne. "Immediately a crowd gathered" and three men set off by boat "to secure the stranger" which "disappeared" when they were "about a yard from him".
In January 1846, a peculiar skull was taken by a settler from the banks of Murrumbidgee River near Balranald, New South Wales. Initial reports suggested that it was the skull of something unknown to science. The squatter who found it remarked, "all the natives to whom it was shown called ta bunyip". By July 1847, several experts, including W. S. Macleay and Professor Owen, had identified the skull as the deformed foetal skull of a foal or calf. At the same time, the purported bunyip skull was put on display in the Australian Museum (Sydney) for two days. Visitors flocked to see it, and '' The Sydney Morning Herald'' reported that many people spoke out about their "bunyip sightings". Reports of this discovery used the phrase 'Kine Pratie' as well as Bunyip. Explorer William Hovell, who examined the skull, also called it a 'katen-pai'.
In March of that year "a bunyip or an immense Platibus" ( Platypus) was sighted "sunning himself on the placid bosom of the Yarra, just opposite the Custom House" in Melbourne. "Immediately a crowd gathered" and three men set off by boat "to secure the stranger" which "disappeared" when they were "about a yard from him".
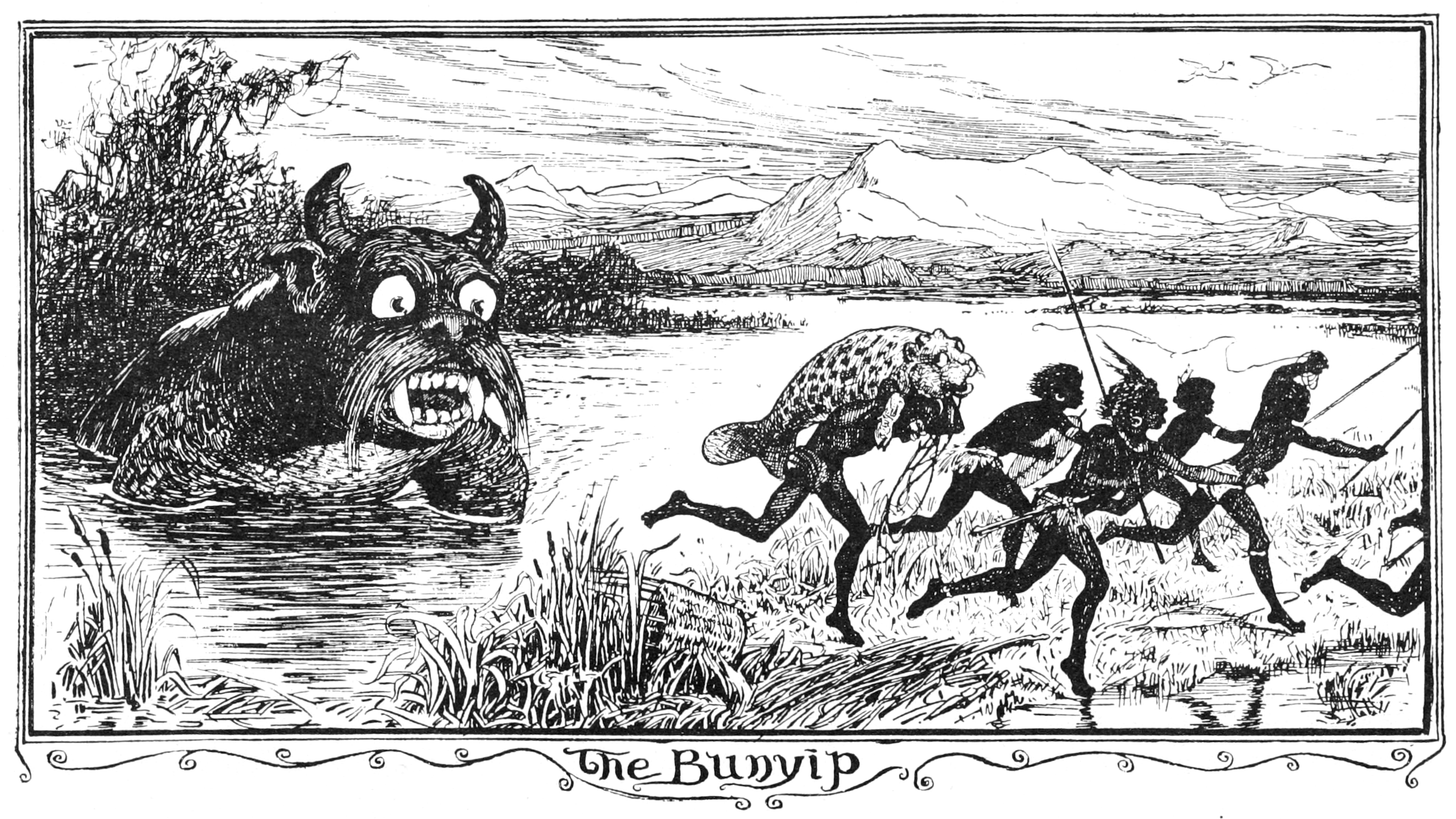 Numerous tales of the bunyip in written literature appeared in the 19th and early 20th centuries. One of the earliest known is a story in Andrew Lang's '' The Brown Fairy Book'' (1904), adapted from a tale collected and published in the Journal of the Anthropological Institute in 1899.
Numerous tales of the bunyip in written literature appeared in the 19th and early 20th centuries. One of the earliest known is a story in Andrew Lang's '' The Brown Fairy Book'' (1904), adapted from a tale collected and published in the Journal of the Anthropological Institute in 1899.
 * Well known Australian author Colin Thiele wrote ''Gloop The Gloomy Bunyip'' an illustrated children's book published in 1962.
* The character Alexander Bunyip, created by children's author and illustrator Michael Salmon, first appeared in print in ''The Monster That Ate Canberra'' (1972). Salmon featured the Bunyip character in many other books and adapted his work as a live-action television series, ''
* Well known Australian author Colin Thiele wrote ''Gloop The Gloomy Bunyip'' an illustrated children's book published in 1962.
* The character Alexander Bunyip, created by children's author and illustrator Michael Salmon, first appeared in print in ''The Monster That Ate Canberra'' (1972). Salmon featured the Bunyip character in many other books and adapted his work as a live-action television series, '' * (1937) Bibhutibhushan Bandyopadhyay wrote a
* (1937) Bibhutibhushan Bandyopadhyay wrote a
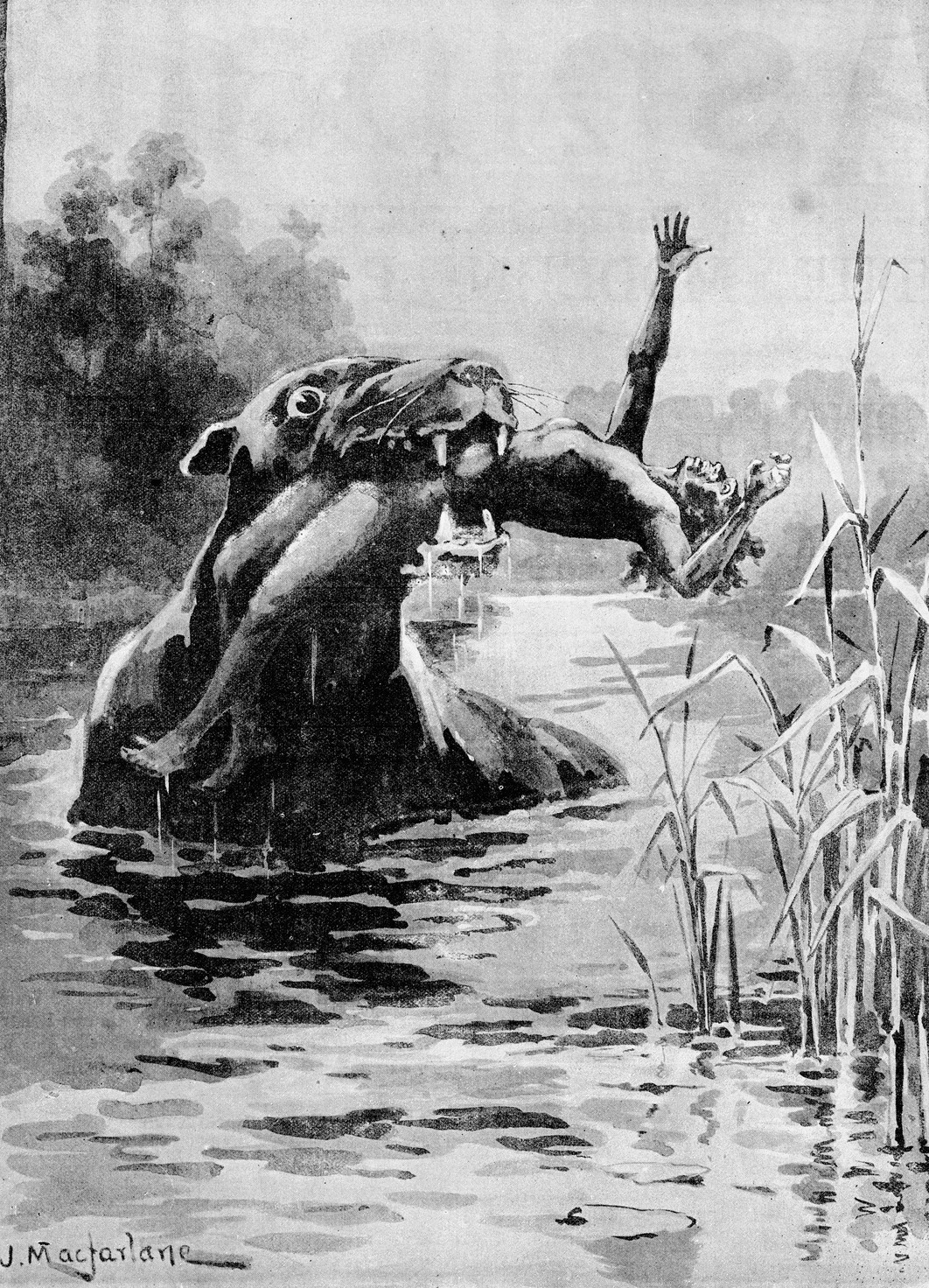 The bunyip is a creature from the aboriginal mythology of southeastern Australia, said to lurk in
The bunyip is a creature from the aboriginal mythology of southeastern Australia, said to lurk in swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
s, billabongs, creeks, riverbeds, and waterhole
A waterhole is a depression in the ground in which water can collect, or a more permanent pool in the bed of an ephemeral river.
Waterhole or water hole may refer to:
* Water hole (radio), an especially quiet region of the electromagnetic spect ...
s.
Name
The origin of the word ''bunyip'' has been traced to the Wemba-Wemba or Wergaia language of the Aboriginal people of Victoria, in South-Eastern Australia. The word ''bunyip'' is usually translated by Aboriginal Australians today as "devil" or "evil spirit". This contemporary translation may not accurately represent the role of the bunyip in pre-contact Aboriginal mythology or its possible origins before written accounts were made. Some modern sources allude to a linguistic connection between the bunyip andBunjil
Bunjil, also spelt Bundjil, is a creator deity, culture hero and ancestral being, often depicted as a wedge-tailed eagle in Australian Aboriginal mythology of some of the Aboriginal peoples of Victoria.
Creation stories
In the Kulin nation ...
, "a mythic 'Great Man' who made the mountains, rivers, man, and all the animals".
The word ''bahnyip'' first appeared in the '' Sydney Gazette'' in 1812. It was used by James Ives to describe "a large black animal like a seal, with a terrible voice which creates terror among the blacks".
Distribution
The bunyip is part of traditional Aboriginal beliefs and stories throughout Australia, while its name varies according to tribal nomenclature. In his 2001 book, writer Robert Holden identified at least nine regional variations of the creature known as the bunyip across Aboriginal Australia.Characteristics
The bunyip has been described asamphibious
Amphibious means able to use either land or water. In particular it may refer to:
Animals
* Amphibian, a vertebrate animal of the class Amphibia (many of which live on land and breed in water)
* Amphibious caterpillar
* Amphibious fish, a fish ...
, almost entirely aquatic, inhabiting lakes, rivers, swamps, lagoons, billabongs, creeks, waterhole
A waterhole is a depression in the ground in which water can collect, or a more permanent pool in the bed of an ephemeral river.
Waterhole or water hole may refer to:
* Water hole (radio), an especially quiet region of the electromagnetic spect ...
s, sometimes "particular waterholes in the riverbeds".
Physical descriptions of bunyips vary widely. George French Angus may have collected a description of a bunyip in his account of a "water spirit" from the Moorundi people of the Murray River before 1847, stating it is "much dreaded by them ... It inhabits the Murray; but ... they have some difficulty describing it. Its most usual form ... is said to be that of an enormous starfish." The Challicum bunyip, an outline image of a bunyip carved by Aboriginal people into the bank of Fiery Creek, near Ararat
Ararat or in Western Armenian Ararad may refer to:
Personal names
* Ararat ( hy, Արարատ), a common first name for Armenian males (pronounced Ararad in Western Armenian)
* Ararat or Araratian, a common family name for Armenians (pronounced A ...
, Victoria, was first recorded by '' The Australasian'' newspaper in 1851. According to the report, the bunyip had been speared after killing an Aboriginal man. Antiquarian Reynell Johns claimed that until the mid-1850s, Aboriginal people made a "habit of visiting the place annually and retracing the outlines of the figure f the bunyipwhich is about 11 paces long and 4 paces in extreme breadth". The outline image no longer exists. Robert Brough Smyth's ''Aborigines of Victoria'' (1878) devoted ten pages to the bunyip, but concluded "in truth little is known among the blacks respecting its form, covering or habits; they appear to have been in such dread of it as to have been unable to take note of its characteristics". Eugénie Louise McNeil recalled from her childhood memory in the 1890s that the bunyip supposedly had a snout like an owl ("a mopoke"), and was probably a nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
creature by her estimation.
The bunyips presumably seen by witnesses, according to their descriptions, most commonly fit one of two categories: 60% of sightings resemble seals or swimming dogs, and 20% of sightings are of long-necked creatures with small heads; the remaining descriptions are ambiguous beyond categorisation. The seal-dog variety is most often described as being between 4 and 6 feet long with a shaggy black or brown coat
A coat typically is an outer garment for the upper body as worn by either gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners, toggles, a ...
. According to reports, these bunyips have round heads resembling a bulldog, prominent ears, no tail, and whiskers like a seal or otter. The long-necked variety is allegedly between 5 and 15 feet long, and is said to have black or brown fur, large ears, small tusks, a head like a horse or emu
The emu () (''Dromaius novaehollandiae'') is the second-tallest living bird after its ratite relative the ostrich. It is endemic to Australia where it is the largest native bird and the only extant member of the genus ''Dromaius''. The emu' ...
, an elongated, maned neck about three feet long and with many folds of skin, and a horse-like tail. The bunyip has been described by natives as amphibious
Amphibious means able to use either land or water. In particular it may refer to:
Animals
* Amphibian, a vertebrate animal of the class Amphibia (many of which live on land and breed in water)
* Amphibious caterpillar
* Amphibious fish, a fish ...
, nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
, and inhabiting lakes, rivers, and swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
s. Bunyips, according to Aboriginal mythology, can swim swiftly with fins or flippers, have a loud, roaring call, and feed on crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the clade Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. In some locations, they are also known as crawfish, craydids, crawdaddies, crawdads, freshwater lobsters, mountain lobsters, rock lobsters, mu ...
, though some legends portray them as bloodthirsty predators of humans, particularly women and children. Bunyip eggs are allegedly laid in platypus nests.
The bunyip appears in Ngarrindjeri dreaming as a water spirit called the Mulyawonk, which would get anyone who took more than their fair share of fish from the waterways, or take children if they got too close to the water. The stories taught practical means of ensuring long-term survival for the Ngarrindjeri, embodying care for country and its people.
Debate over origins
There have been various attempts to understand and explain the origins of the bunyip as a physical entity over the past 150 years. Writing in 1933, Charles Fenner suggested that it was likely that the "actual origin of the bunyip myth lies in the fact that from time to time seals have made their way up the Murray and Darling (Rivers)". He provided examples of seals found as far inland asOverland Corner
Overland Corner is a locality in the Australian state of South Australia located in the state’s east about north-east of the state capital of Adelaide and about west of the municipal seat in Berri.
It is located on the Murray River in the R ...
, Loxton, and Conargo
Conargo is a town in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia. The town is in the Edward River Council local government area. It is on Billabong Creek, a tributary of the Edward River. The nearest towns are Jerilderie and Deniliquin. ...
and reminded readers that "the smooth fur, prominent 'apricot' eyes, and the bellowing cry are characteristic of the seal", especially southern elephant seals and leopard seals.
Another suggestion is that the bunyip may be a cultural memory of extinct Australian marsupials such as the '' Diprotodon'', ''Zygomaturus
''Zygomaturus'' is an extinct genus of giant marsupial belonging to the family Diprotodontidae which inhabited Australia from the Late Miocene to Late Pleistocene.
Description
It was a large animal, weighing 500 kg (1100 lbs) or ...
'', ''Nototherium
''Nototherium'' ("Southern Beast") is an extinct genus of diprotodontid marsupial from Australia and New Guinea. This mammal had hypsodont molars and weighed around 500kg.Ross D.E. MacPhee, Hans-Dieter Sues, 1999,
Extinctions in Near Time, p.251 ...
'', or ''Palorchestes
''Palorchestes'' ("ancient leaper or dancer") is an extinct genus of terrestrial animal, terrestrial, herbivorous marsupials of the family (biology), family Palorchestidae. The genus was endemic to Australia, living from the Miocene through to th ...
''. This connection was first formally made by Dr George Bennett of the Australian Museum in 1871. In the early 1990s, palaeontologist Pat Vickers-Rich and geologist Neil Archbold also cautiously suggested that Aboriginal legends "perhaps had stemmed from an acquaintance with prehistoric bones or even living prehistoric animals themselves ... When confronted with the remains of some of the now extinct Australian marsupials, Aborigines would often identify them as the bunyip." They also note that "legends about the'' mihirung paringmal'' of western Victorian Aborigines ... may allude to the ... extinct giant birds the Dromornithidae
Dromornithidae, known as mihirungs and informally as thunder birds or demon ducks, were a clade of large, flightless Australian birds of the Oligocene through Pleistocene Epochs. All are now extinct. They were long classified in Struthioniform ...
."
In a 2017 '' Australian Birdlife'' article, Karl Brandt suggested Aboriginal encounters with the southern cassowary
The southern cassowary (''Casuarius casuarius''), also known as double-wattled cassowary, Australian cassowary or two-wattled cassowary, is a large flightless black bird. It is one of the three living species of cassowary, alongside the dwarf c ...
inspired the myth. According to the first written description of the bunyip from 1845, the creature, which laid pale blue eggs of immense size, possessed deadly claws, powerful hind legs, a brightly coloured chest, and an emu
The emu () (''Dromaius novaehollandiae'') is the second-tallest living bird after its ratite relative the ostrich. It is endemic to Australia where it is the largest native bird and the only extant member of the genus ''Dromaius''. The emu' ...
-like head, characteristics shared with the Australian cassowary. As the creature's bill was described as having serrated projections, each "like the bone of the stingray
Stingrays are a group of sea rays, which are cartilaginous fish related to sharks. They are classified in the suborder Myliobatoidei of the order Myliobatiformes and consist of eight families: Hexatrygonidae (sixgill stingray), Plesiobatidae ( ...
", this bunyip was associated with the indigenous people of Far North Queensland
Far North Queensland (FNQ) is the northernmost part of the Australian state of Queensland. Its largest city is Cairns and it is dominated geographically by Cape York Peninsula, which stretches north to the Torres Strait, and west to the Gulf C ...
, renowned for their spears tipped with stingray barbs and their proximity to the cassowary's Australian range.
Another association to the bunyip is the shy Australasian bittern (''Botaurus poiciloptilus
The Australasian bittern (''Botaurus poiciloptilus''), also known as the brown bittern or matuku hūrepo, and also nicknamed the " bunyip bird", is a large bird in the heron family Ardeidae. A secretive bird with a distinctive booming call, it i ...
''). During the breeding season, the male call of this marsh-dwelling bird is a "low pitched boom"; hence, it is occasionally called the "bunyip bird".
Early accounts of European settlers
During the early settlement of Australia by Europeans, the notion became commonly held that the bunyip was an unknown animal that awaited discovery. Unfamiliar with the sights and sounds of the island continent's peculiar fauna, early Europeans believed that the bunyip described to them was one more strange Australian animal and they sometimes attributed unfamiliar animal calls or cries to it. Scholars suggest also that 19th-century bunyip lore was reinforced by imported European folklore, such as that of the Irish Púca. A large number of bunyip sightings occurred during the 1840s and 1850s, particularly in the southeastern colonies of Victoria, New South Wales and South Australia, as European settlers extended their reach. The following is not an exhaustive list of accounts:Hume find of 1818
One of the earliest accounts relating to a large unknown freshwater animal was in 1818, when Hamilton Hume and James Meehan found some large bones atLake Bathurst
Lake Bathurst ( Aboriginal: ''Bundong'') is a shallow lake located south-east of Goulburn, New South Wales in Australia. It is also the name of a nearby locality in the Goulburn Mulwaree Council.
Features and location
The surface area of the la ...
in New South Wales. They did not call the animal a bunyip, but described the remains indicating the creature as very much like a hippopotamus or manatee. The Philosophical Society of Australasia later offered to reimburse Hume for any costs incurred in recovering a specimen of the unknown animal, but for various reasons, Hume did not return to the lake. Ancient '' Diprotodon'' skeletons have sometimes been compared to the hippopotamus; they are a land animal, but have sometimes been found in a lake or water course.
Wellington Caves fossils, 1830
More significant was the discovery of fossilised bones of "some quadruped much larger than the ox or buffalo" in theWellington Caves
The Wellington Caves are a group of limestone caves located south of Wellington, New South Wales, Australia.
History
The Wellington region was long inhabited by the 'Binjang mob' of the Wiradjuri people. While there is no direct evidence th ...
in mid-1830 by bushman George Ranken and later by Thomas Mitchell. Sydney's Reverend John Dunmore Lang
John Dunmore Lang (25 August 1799 – 8 August 1878) was a Scottish-born Australian Presbyterian minister, writer, historian, politician and activist. He was the first prominent advocate of an independent Australian nation and of Australian re ...
announced the find as "convincing proof of the deluge", referring to Biblical accounts of the Flood. But British anatomist Sir Richard Owen identified the fossils as the gigantic marsupials ''Nototherium
''Nototherium'' ("Southern Beast") is an extinct genus of diprotodontid marsupial from Australia and New Guinea. This mammal had hypsodont molars and weighed around 500kg.Ross D.E. MacPhee, Hans-Dieter Sues, 1999,
Extinctions in Near Time, p.251 ...
'' and '' Diprotodon''. At the same time, some settlers observed that "all natives throughout these ... districts have a tradition (of) a very large animal having at one time existed in the large creeks and rivers and by many it is said that such animals now exist."
First written use of the word ''bunyip'', 1845
In July 1845, ''The Geelong Advertiser'' announced the discovery of fossils found nearGeelong
Geelong ( ) (Wathawurrung: ''Djilang''/''Djalang'') is a port city in the southeastern Australian state of Victoria, located at the eastern end of Corio Bay (the smaller western portion of Port Phillip Bay) and the left bank of Barwon River, ...
, under the headline "Wonderful Discovery of a new Animal". This was a continuation of a story on 'fossil remains' from the previous issue. The newspaper continued, "On the bone being shown to an intelligent black, he at once recognised it as belonging to the bunyip, which he declared he had seen. On being requested to make a drawing of it, he did so without hesitation." The account noted a story of an Aboriginal woman being killed by a bunyip and the "most direct evidence of all" – that of a man named Mumbowran "who showed several deep wounds on his breast made by the claws of the animal".
The account provided this description of the creature:
Shortly after this account appeared, it was repeated in other Australian newspapers. This appears to be the first use of the word ''bunyip'' in a written publication.
Australian Museum's bunyip of 1847
 In January 1846, a peculiar skull was taken by a settler from the banks of Murrumbidgee River near Balranald, New South Wales. Initial reports suggested that it was the skull of something unknown to science. The squatter who found it remarked, "all the natives to whom it was shown called ta bunyip". By July 1847, several experts, including W. S. Macleay and Professor Owen, had identified the skull as the deformed foetal skull of a foal or calf. At the same time, the purported bunyip skull was put on display in the Australian Museum (Sydney) for two days. Visitors flocked to see it, and '' The Sydney Morning Herald'' reported that many people spoke out about their "bunyip sightings". Reports of this discovery used the phrase 'Kine Pratie' as well as Bunyip. Explorer William Hovell, who examined the skull, also called it a 'katen-pai'.
In March of that year "a bunyip or an immense Platibus" ( Platypus) was sighted "sunning himself on the placid bosom of the Yarra, just opposite the Custom House" in Melbourne. "Immediately a crowd gathered" and three men set off by boat "to secure the stranger" which "disappeared" when they were "about a yard from him".
In January 1846, a peculiar skull was taken by a settler from the banks of Murrumbidgee River near Balranald, New South Wales. Initial reports suggested that it was the skull of something unknown to science. The squatter who found it remarked, "all the natives to whom it was shown called ta bunyip". By July 1847, several experts, including W. S. Macleay and Professor Owen, had identified the skull as the deformed foetal skull of a foal or calf. At the same time, the purported bunyip skull was put on display in the Australian Museum (Sydney) for two days. Visitors flocked to see it, and '' The Sydney Morning Herald'' reported that many people spoke out about their "bunyip sightings". Reports of this discovery used the phrase 'Kine Pratie' as well as Bunyip. Explorer William Hovell, who examined the skull, also called it a 'katen-pai'.
In March of that year "a bunyip or an immense Platibus" ( Platypus) was sighted "sunning himself on the placid bosom of the Yarra, just opposite the Custom House" in Melbourne. "Immediately a crowd gathered" and three men set off by boat "to secure the stranger" which "disappeared" when they were "about a yard from him".
William Buckley's account of bunyips, 1852
Another early written account is attributed to escaped convict William Buckley in his 1852 biography of thirty years living with the Wathaurong people. His 1852 account records "in ... Lake Moodewarri ow Lake Modewarreas well as in most of the others inland ... is a ... very extraordinary amphibious animal, which the natives call Bunyip." Buckley's account suggests he saw such a creature on several occasions. He adds, "I could never see any part, except the back, which appeared to be covered with feathers of a dusky grey colour. It seemed to be about the size of a full grown calf ... I could never learn from any of the natives that they had seen either the head or tail." Buckley also claimed the creature was common in the Barwon River and cites an example he heard of an Aboriginal woman being killed by one. He emphasized the bunyip was believed to have supernatural powers.Stocqueler's sightings and drawings, 1857
In an article titled, 'The Bunyip', a newspaper reported on the drawings made by Edwin Stocqueler as he travelled on the Murray and Goulburn rivers: 'Amongst the latter drawings we noticed a likeness of the Bunyip, or rather a view of the neck and shoulders of the animal. Mr. Stocqueler informs us that the Bunyip is a large freshwater seal, having two small padules or fins attached to the shoulders, a long swan like neck, a head like a dog, and a curious bag hanging under the jaw, resembling the pouch of the pelican. The animal is covered with hair, like the platypus, and the colour is a glossy black. Mr. Stocqueler saw no less than six of these curious animals at different times; his boat was within thirty feet of one near M'Guire's punt on the Goulburn, and he fired at the Bunyip, but did not succeed in capturing him. The smallest appeared to be about five feet in length, and the largest exceeded fifteen feet. The head of the largest was the size of a bullock's head, and three feet out of water. After taking a sketch of the animal, Mr. Stocqueler showed it to several blacks of the Goulburn tribe, who declared that the picture was "Bunyip's brother," meaning a duplicate or likeness of the bunyip. The animals moved against the current, at the rate of about seven miles an hour, and Mr. Stockqueler states that he could have approached close to the specimens he observed, had he not been deterred by the stories of the natives concerning the power and fury of the bunyip, and by the fact that his gun had only a single barrel, and his boat was of a very frail description.' The description varied across newspaper accounts: 'The great Bunyip question seems likely to be brought to a close, as a Mr. Stocqueler, an artist and gentleman, who has come up the Murray in a small boat, states that he saw one, and was enabled to take a drawing of this "vexed question," but could not succeed in catching him. We have seen the sketch, and it puts us in mind of an hybrid between the water mole and the great sea serpent.' 'Mr. Stocqueler, an artist, and his mother are on an expedition down the Murray, for the purpose of making some faithful sketches of the views on this fine stream, as well as of the creatures frequenting it. I have seen some of their productions, and as they pourtray localities with which I am well acquainted, can pronounce the drawings faithful representations. Mother and son go down the stream in a canoe. The lady paints flowers, &c.; the son devotes himself to choice views on the river's side. One of the drawings represents a singular creature, which the artist is unable to classify. It has the appearance in miniature of the famous sea-serpent, as that animal is described by navigators. Mr. Stocqueler was about twenty-five yards distant from it at first sight as it lay placidly on the water. On being observed, the stranger set-off, working his paddles briskly, and rapidly disappeared. Captain Cadell has tried to solve the mystery, but is not yet satisfied as to what the animal really is. Mr. Stocqueler states that there were about two feet of it above water when he first saw it, and he estimated its length at from five to six feet. The worthy Captain says, that unless the creature is the "Musk Drake" (so called from giving off a very strong odour of musk), he cannot account for the novelty.' Stocqueler disputed the newspaper descriptions in a letter; stating that he never called the animal a bunyip, it did not have a swan like neck, and he never said anything about the size of the animal as he never saw the whole body. He went on to write that all would be revealed in his diorama as an 'almost life size portrait of the beast' would be included. The diorama took him four years to paint and was reputed to be a mile (1.6 km) long and made of 70 individual pictures. The diorama has long since disappeared and may no longer exist.Figure of speech and eponymy
By the 1850s, ''bunyip'' was also used as a "synonym for impostor, pretender, humbug and the like", although this use of the word is now obsolete in Australian English. The term '' bunyip aristocracy'' was first coined in 1853 to describe Australians aspiring to be aristocrats. In the early 1990s, Prime Minister Paul Keating used this term to describe members of the conservative Liberal Party of Australia opposition. The word ''bunyip'' can still be found in a number of Australian contexts, including place names such as theBunyip River
The Bunyip River is a perennial river of the Western Port catchment, located in the West Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria.
Location and features
The Bunyip River rises below Mount Beenak, part of the southern portion of the Y ...
(which flows into Westernport Bay
Western Port, (Boonwurrung: ''Warn Marin'') commonly but unofficially known as Western Port Bay, is a large tidal bay in southern Victoria, Australia, opening into Bass Strait. It is the second largest bay in the state. Geographically, it is ...
in southern Victoria) and the town of Bunyip, Victoria.
In popular culture and fiction
* ''The Bunyip'' newspaper is a local weekly newspaper published in the town of Gawler, South Australia. First published as a pamphlet by the Gawler Humbug Society in 1863, the name was chosen because "the Bunyip is the true type of Australian Humbug!" * The House of the Gentle Bunyip, built in the 1860s, is located in Clifton Hill, Victoria. It has been redeveloped as housing for low-income people. Numerous tales of the bunyip in written literature appeared in the 19th and early 20th centuries. One of the earliest known is a story in Andrew Lang's '' The Brown Fairy Book'' (1904), adapted from a tale collected and published in the Journal of the Anthropological Institute in 1899.
Numerous tales of the bunyip in written literature appeared in the 19th and early 20th centuries. One of the earliest known is a story in Andrew Lang's '' The Brown Fairy Book'' (1904), adapted from a tale collected and published in the Journal of the Anthropological Institute in 1899.
 * Well known Australian author Colin Thiele wrote ''Gloop The Gloomy Bunyip'' an illustrated children's book published in 1962.
* The character Alexander Bunyip, created by children's author and illustrator Michael Salmon, first appeared in print in ''The Monster That Ate Canberra'' (1972). Salmon featured the Bunyip character in many other books and adapted his work as a live-action television series, ''
* Well known Australian author Colin Thiele wrote ''Gloop The Gloomy Bunyip'' an illustrated children's book published in 1962.
* The character Alexander Bunyip, created by children's author and illustrator Michael Salmon, first appeared in print in ''The Monster That Ate Canberra'' (1972). Salmon featured the Bunyip character in many other books and adapted his work as a live-action television series, ''Alexander Bunyip's Billabong
''Alexander Bunyip's Billabong'' is an Australian television series for children which screened on the Australian Broadcasting Corporation, ABC from 1978 to 1988. It followed the adventures of Alexander Bunyip, a mythical Australian creature who f ...
''.
*A statue of Alexander Bunyip was installed in front of the Gungahlin Library in 2011.
*The artwork by Anne Ross, called ''A is for Alexander, B is for Bunyip, C is for Canberra'', was commissioned by the ACT Government for Gungahlin's $3.8 million town park.
*(1916) ragtime musical comedy Bunyip (musical) or the long title 'the enchantment of fairy princess wattle blossom' by Ella Palzier Campbell (AKA Ella Airlie) toured nine venues in three states for a year with Fuller Brothers theatre circuit. Music was supplied by a number of Australian Stage Personalities including Vince Courtney, Herbert De Pinna, Fred Monument and James Kendis.
The Australian tourism boom of the 1970s brought a renewed interest in bunyip mythology.
* (1972) A coin-operated bunyip was built by Dennis Newell at Murray Bridge Murray Bridge may refer to.
*Murray Bridge, South Australia, a city and locality
*Rural City of Murray Bridge, a local government area in South Australia
*Corporate Town of Murray Bridge, a former local government area in South Australia
See also
...
, South Australia, at Sturt Reserve on the town's riverfront.
* Jenny Wagner published a children's picture book, ''The Bunyip of Berkeley's Creek'' (1973).
* (1977) The film ''Dot and the Kangaroo'' contains a song "The Bunyip (Bunyip Moon)". The bunyip was the subject of '' Dot and the Smugglers'' where the title character, Dot, and her animal friends foiling a circus- ringmaster's plan to capture a bunyip. The bunyip featured turned out to be a gentle, shy creature.
* (1982) Children's picture book ''The Ballad of the Blue Lake Bunyip''
* (1996) Australian children's author Jackie French
Jacqueline Anne Ffrench (born 29 November 1953), known professionally as Jackie French, is an Australian author who has written across a number of genres for both adults and children. Her most notable works include '' Rain Stones, Diary of a ...
wrote several bunyip tales, including the short story "Bunyip's Gift", collected in the anthology ''Mind's Eye''.
* An episode of The Silver Brumby (TV series)
''The Silver Brumby'' is an Australian animated children's television series written by Jon Stephens, Judy Malmgren and Paul Williams based on Elyne Mitchell's Silver Brumby books. A total of 39 episodes were produced by Media World Features be ...
featured a friendly, prank-playing bunyip.
* Wommy, a character on Noah's Island keeps mentioning bunyips and mistook Noah, the noble polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear specie ...
who's the title character, and feral cats
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact: it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens ...
for bunyips.
* (1986) The Australian film ''Frog Dreaming
''Frog Dreaming'' is a 1986 Australian family adventure film written by Everett De Roche and directed by Brian Trenchard-Smith. It starred Henry Thomas, Tony Barry, Rachel Friend and Tamsin West.
Plot
An American boy, Cody (Thomas), whose pare ...
'' centres around the search for a bunyip called Donkegin.
* (2016) The independent Australian film ''Red Billabong
''Red Billabong'' is a 2016 independent Australian horror thriller film, written and directed by Luke Sparke in his feature debut. Based on an Australian legend, ''Red Billabong'' follows two estranged brothers who find themselves stalked by ...
'' was released in 2016. It tells about two estranged brothers who find themselves stalked by the Bunyip.
Bunyip stories have also been published outside Australia.
 * (1937) Bibhutibhushan Bandyopadhyay wrote a
* (1937) Bibhutibhushan Bandyopadhyay wrote a Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
novel ''Chander Pahar
''Chander Pahar'' () is a Bengali adventure novel written by Bibhutibhushan Bandopadhyay and published in 1937. The novel follows the adventures of a young Bengali man in the forests of Africa. The novel is one of the most-loved adventure nove ...
'' ( Mountain of The Moon ) that included an account of a bunyip. The novel was adapted as a film of the same name, released in late 2013. The bunyip was portrayed as the primary threat to the treasure seekers in the wilderness of the Richtersveld
The Richtersveld is a desert landscape characterised by rugged kloofs and high mountains, situated in the north-western corner of South Africa’s Northern Cape province. It is full of changing scenery from flat, sandy, coastal plains, to crag ...
mountains in southern Africa. In the novel, the bunyip is described as a three-toed ape-like hominid
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the east ...
.
* From 1954 to 1966, Bertie the Bunyip was the lead puppet character on a popular children's series on Channel 3 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
* (1992) The role playing game, ''Werewolf: The Apocalypse'', appropriates the Bunyip legend, having the Bunyip actually be a tribe of Australian native Garou, or werewolves. However, they are not playable in the game as, according to the game's lore, they were driven to extinction by the European werewolves during the colonisation of Australia.
The Bunyip has been featured in films as well.
* In 1978 Ozsploitation eco-horror film ''The Long Weekend'', a bunyip is featured as a creature that terrorizes the main couple in the film, who trash a peaceful Australian beach.
In the 21st century the bunyip has been featured in works around the world.
* (2002) The video game series Ty the Tasmanian Tiger
''Ty the Tasmanian Tiger'' is a 2002 3D platforming game developed by Krome Studios and published by EA Games for the GameCube, PlayStation 2 and Xbox systems. The game was remastered in HD for Microsoft Windows and was made available through ...
portrays Bunyips as peaceful mystical elders who inhabit the world of The Dreaming, though not as ferocious as their namesake and resembling primates. The robotic suits that Ty can pilot in Ty the Tasmanian Tiger 2: Bush Rescue and Ty the Tasmanian Tiger 3: Night of the Quinkan are named after the Bunyips, such as Shadow Gunyip, Battle Gunyip and Missile Gunyips.
* (2009) A character named Bruce Bunyip appears in the children's book ''The Neddiad'' by American Daniel Pinkwater. He is initially described as "big and swarthy, and had tiny eyes, a scowl and his eyebrows grew together" and later says he is a monster.
* (2009) Bunyips appeared as the focus cryptids in an episode of '' The Secret Saturdays''; however, they were depicted as small, troublemaking creatures instead of monsters.
* (2010) Bunyips appear in Naomi Novik
Naomi Novik (born April 30, 1973) is an American author of speculative fiction. She is known for the ''Temeraire'' series (2006–2016), an alternate history of the Napoleonic Wars involving dragons, and her ''Scholomance'' fantasy series (2020 ...
's fantasy novel ''Tongues of Serpents
''Tongues of Serpents'' is the sixth novel in the '' Temeraire'' alternate history/fantasy series by American author Naomi Novik. This installment follows William Laurence and his dragon, Temeraire's adventures in Australia.
''Tongues of Serpen ...
'', where they are depicted as relatives of dragons that have adapted to the extreme conditions of the Outback.
* (2011) An episode of '' Prank Patrol (Australia)'' Season 2 involved a prank called Bunyip Hunters.
* (2014) In the novel ''Afterworlds'' one of the characters is the author of a fictional book named ''Bunyip''.
* (2014) The fantasy novel, ''Queen of the Dark Things'', by C. Robert Cargill, features the Bunyip throughout the story.
* (2016) A "tri-horned" bunyip appears in the '' My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic'' episode "P.P.O.V (Pony Point Of View)" after being revealed to be the cause of a shipwreck that is recollected differently by three of the series' main characters.
* (2022) In the novel ''The Island'' by Adrian McKinty
Adrian McKinty is a Northern Irish writer of crime and mystery novels and young adult fiction, best known for his 2020 award-winning thriller, ''The Chain'', and the Sean Duffy novels set in Northern Ireland during The Troubles. He is a winner ...
, which takes place in Australia, an antagonist fearfully refers to the bunyip before dying.
See also
*Drop bear
The drop bear (sometimes dropbear) is a hoax in contemporary Australian folklore featuring a predatory, carnivorous version of the koala. This imaginary animal is commonly spoken about in tall tales designed to scare tourists. While koalas are t ...
, a fictitious Australian mammal
* Min Min light
Min Min is a light phenomenon that has often been reported in outback Australia.
History
Stories about the lights can be found in several Aboriginal Australian cultures predating the European colonisation of Australia, and have since become ...
, a natural phenomenon that may have influenced Australian Aboriginal mythology
* Nargun, a living stone creature from Australian Aboriginal mythology
* Rainbow Serpent, a common motif in the art and mythology of Aboriginal Australia
* Underwater panther, a similar North American creature of legend
* Yara-ma-yha-who, a vampiric creature from Australian Aboriginal mythology
* P. A. Yeomans
Percival Alfred Yeomans (1905 - November 1984) was an Australian inventor known for the Keyline system for the development of land and increasing the fertility of that land. As a mining engineer and gold assayer, Yeomans had developed a keen sen ...
, inventor of the Bunyip Slipper Imp, a plough for developing watersheds
* Yowie, or Wowee, a "Big Foot" style of creature that has its origins in Australian Aboriginal mythology
Explanatory notes
Citations
General and cited references
* * * *Further reading
*External links
* {{Authority control Australian Aboriginal legendary creatures Australian Aboriginal words and phrases Demons Mythological marsupials Water spirits vi:Quỷ