Budget Spending on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual or collective needs of the community, is classed as government final consumption expenditure. Government acquisition of goods and services intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending, is classed as government investment (government gross capital formation). These two types of government spending, on final consumption and on gross capital formation, together constitute one of the major components of gross domestic product.
Government spending can be financed by
 Government spending can be a useful economic policy tool for governments. Fiscal policy can be defined as the use of government spending and/or taxation as a mechanism to influence an economy. There are two types of fiscal policy: expansionary fiscal policy, and contractionary fiscal policy. Expansionary fiscal policy is an increase in government spending or a decrease in taxation, while contractionary fiscal policy is a decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes. Expansionary fiscal policy can be used by governments to stimulate the economy during a recession. For example, an increase in government spending directly increases demand for goods and services, which can help increase output and
Government spending can be a useful economic policy tool for governments. Fiscal policy can be defined as the use of government spending and/or taxation as a mechanism to influence an economy. There are two types of fiscal policy: expansionary fiscal policy, and contractionary fiscal policy. Expansionary fiscal policy is an increase in government spending or a decrease in taxation, while contractionary fiscal policy is a decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes. Expansionary fiscal policy can be used by governments to stimulate the economy during a recession. For example, an increase in government spending directly increases demand for goods and services, which can help increase output and
''Statistics Explained'' European Union Statistics Directorate, European Commission Acquisition of goods and services is made through production by the government (using the government's labour force, fixed assets and purchased goods and services for intermediate consumption) or through purchases of goods and services from market producers. In economic theory or in
/ref>
OECD Government spending statistics
Canadian Governments Compared
Eurostat's government spending per sector
{{DEFAULTSORT:Government Spending Government finances Fiscal policy
government borrowing
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
, taxes, custom duties, the sale or lease of natural resources, and various fees like national park entry fees or licensing fees. When Governments choose to borrow money, they have to pay interest on the money borrowed. Changes in government spending is a major component of fiscal policy used to stabilize the macroeconomic business cycle.
Macroeconomic fiscal policy
 Government spending can be a useful economic policy tool for governments. Fiscal policy can be defined as the use of government spending and/or taxation as a mechanism to influence an economy. There are two types of fiscal policy: expansionary fiscal policy, and contractionary fiscal policy. Expansionary fiscal policy is an increase in government spending or a decrease in taxation, while contractionary fiscal policy is a decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes. Expansionary fiscal policy can be used by governments to stimulate the economy during a recession. For example, an increase in government spending directly increases demand for goods and services, which can help increase output and
Government spending can be a useful economic policy tool for governments. Fiscal policy can be defined as the use of government spending and/or taxation as a mechanism to influence an economy. There are two types of fiscal policy: expansionary fiscal policy, and contractionary fiscal policy. Expansionary fiscal policy is an increase in government spending or a decrease in taxation, while contractionary fiscal policy is a decrease in government spending or an increase in taxes. Expansionary fiscal policy can be used by governments to stimulate the economy during a recession. For example, an increase in government spending directly increases demand for goods and services, which can help increase output and employment
Employment is a relationship between two parties regulating the provision of paid labour services. Usually based on a contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any othe ...
. On the other hand, contractionary fiscal policy can be used by governments to cool down the economy during an economic boom. A decrease in government spending can help check inflation. During economic downturns, in the short run, government spending can be changed either via automatic stabilization In macroeconomics, automatic stabilizers are features of the structure of modern government budgets, particularly income taxes and welfare spending, that act to damp out fluctuations in real GDP.
The size of the government budget deficit tends t ...
or discretionary stabilization. Automatic stabilization is when existing policies automatically change government spending or taxes in response to economic changes, without the additional passage of laws. A primary example of an automatic stabilizer is unemployment insurance, which provides financial assistance to unemployed workers. Discretionary stabilization is when a government takes actions to change government spending or taxes in direct response to changes in the economy. For instance, a government may decide to increase government spending as a result of a recession. With discretionary stabilization, the government must pass a new law to make changes in government spending.
John Maynard Keynes was one of the first economists to advocate for government deficit spending as part of the fiscal policy response to an economic contraction. According to Keynesian economics, increased government spending raises aggregate demand
In macroeconomics, aggregate demand (AD) or domestic final demand (DFD) is the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time. It is often called effective demand, though at other times this term is distinguished. This is ...
and increases consumption, which leads to increased production and faster recovery from recessions. Classical economists, on the other hand, believe that increased government spending exacerbates an economic contraction by shifting resources from the private sector, which they consider productive, to the public sector, which they consider unproductive.
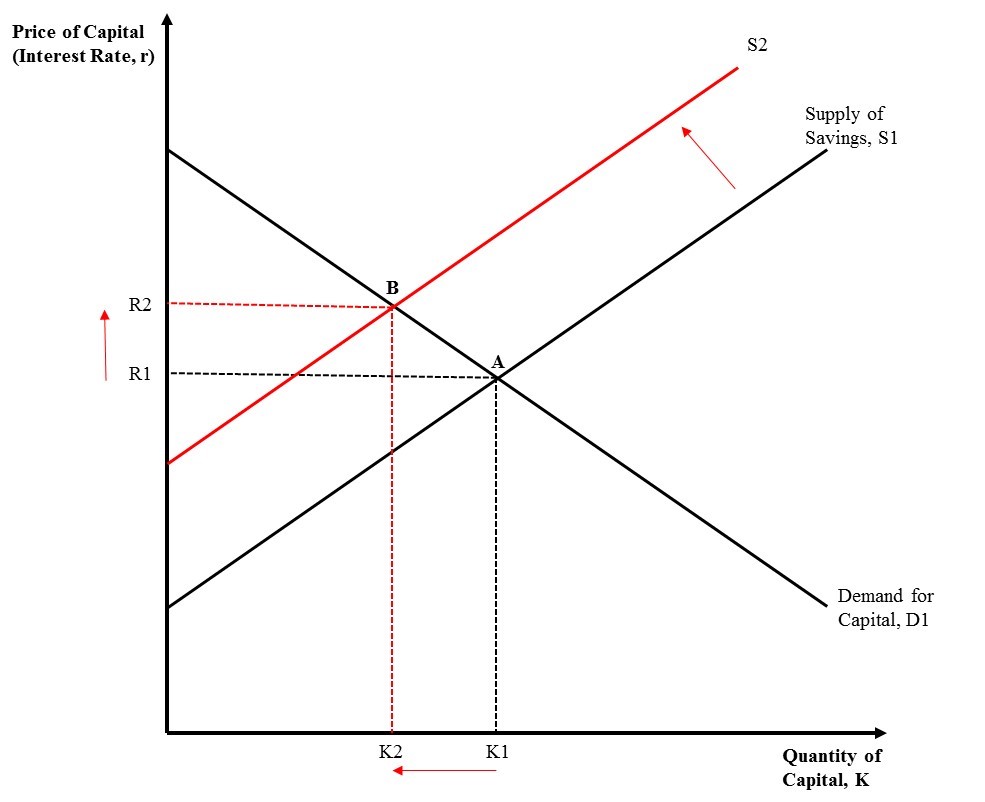
In economics, the potential "shifting" in resources from the private sector to the public sector as a result of an increase in government deficit spending is called crowding out. The figure to the right depicts the market for capital, otherwise known as the market for loanable funds. The downward sloping demand curve
In economics, a demand curve is a graph depicting the relationship between the price of a certain commodity (the ''y''-axis) and the quantity of that commodity that is demanded at that price (the ''x''-axis). Demand curves can be used either for ...
D1 represents demand for private capital by firms and investors, and the upward sloping supply curve
In economics, supply is the amount of a resource that firms, producers, labourers, providers of financial assets, or other economic agents are willing and able to provide to the marketplace or to an individual. Supply can be in produced goods, la ...
S1 represents savings by private individuals. The initial equilibrium in this market is represented by point A, where the equilibrium quantity of capital is K1 and the equilibrium interest rate is R1. If the government increases deficit spending, it will borrow money from the private capital market
A capital market is a financial market in which long-term debt (over a year) or equity-backed securities are bought and sold, in contrast to a money market where short-term debt is bought and sold. Capital markets channel the wealth of savers t ...
and reduce the supply of savings to S2. The new equilibrium is at point B, where the interest rate has increased to R2 and the quantity of capital available to the private sector has decreased to K2. The government has essentially made borrowing more expensive and has taken away savings from the market, which "crowds out" some private investment. The crowding out of private investment could limit the economic growth from the initial increase government spending.
Current use: final consumption
Government spending on goods and services for current use to directly satisfy individual or collective needs of the members of the community is called government final consumption expenditure (GFCE.) It is a purchase from the national accounts "use of income account" for goods and services directly satisfying of individual needs (''individual consumption'') or collective needs of members of the community (''collective consumption''). GFCE consists of the value of the goods and services produced by the government itself other than own-account capital formation and sales and of purchases by the government of goods and services produced by market producers that are supplied to households—without any transformation—as "social transfers" in kind. Government spending or government expenditure can be divided into three primary groups, government consumption, transfer payments, and interest payments. # Government consumption are government purchases of goods and services. Examples include road and infrastructure repairs, national defence, schools, healthcare, and government workers’ salaries. # Investments in sciences and strategic technological innovations to serve the public needs. # Transfer payments are government payments to individuals. Such payments are made without the exchange of good or services, for example Old Age Security payments, Employment Insurance benefits, veteran and civil service pensions, foreign aid, and social assistance payments. Subsidies to businesses are also included in this category. # Interest payments are the interest paid to the holders of government bonds, such as Saving Bonds and Treasury bills.National defense spending
The United States spends vastly more than other countries on national defense. For example, In 2019 the United States approved a budget of 686.1 billion in discretionary military spending, China was second with an estimated 261 billion dollars in military spending. The table below shows the top 10 countries with the largest military expenditures as of 2015, the most recent year with publicly available data. As the table suggests, the United States spent nearly 3 times as much on the military asChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, the country with the next largest military spending. The U.S. military budget dwarfed spending by all other countries in the top 10, with 8 out of countries spending less than $100 billion in 2016. In 2022, the omnibus spending package increased the military budget by another $42 billion further increasing the United States as the largest defense spenders.
Healthcare and medical research
Research Australia found 91% of Australians think 'improving hospitals and the health system' should be the Australian Government's first spending priority. Crowding 'in' also happens in university life science research Subsidies, funding and government business or projects like this are often justified on the basis of their positive return on investment. Life science crowding in contrasts with crowding out in public funding of research more widely: "10% increase in government R&D funding reduced private R&D expenditure by 3%...In Australia, the average cost of public funds is estimated to be $1.20 and $1.30 for each dollar raised (Robson, 2005). The marginal cost is probably higher, but estimates differ widely depending on the tax that is increased". In the US the total investment in medical and health research and development (R&D) in the US had grown by 27% over the five years from 2013 to 2017, and it is led by industry and the federal government. However, the industry accounted for 67% of total spending in 2017, followed by the federal government at 22%. According to the National Institute of Health (NIH) accounted for the lion's share of federal spending in medical and health research in 2017 was $32.4 billion or 82.1%. Also, academic and research institutions, this includes colleges, and universities, independent research (IRIs), and independent hospital medical research centres also increased spending, dedicating more than $14.2 billion of their own funds (endowment, donations etc.) to medical and health R&D in 2017. Although other funding sources - foundations, state and local government, voluntary health associations and professional societies - accounted for 3.7% of total medical and health R&D expenditure. On the other hand, global health spending continues to increase and rise rapidly – to US$7.8 trillion in 2017 or about 10% of GDP and $1.80 per capita – up from US£7.6 trillion in 2016. In addition, about 605 of this spending was public and 40% private, with donor funding representing less than 0.2% of the total although the health spending in real terms has risen by 3.79% in a year while global GDP had grown by 3.0%. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), the increase in health spending in low-income countries, and it rose by 7.8% a year between 2000 and 2017 while their economy grew by 6.4%, it is explained in the figure. However, the middle-income economies health spending grew more than 6%, and average annual growth in high-income countries was 3.5%, which is about twice as fast as economic growth. In contrast, health spending by the high-income countries continues to represent to be the largest share of global spending, which is about 81%, despite it covers only 16% of world's population; although it down from 87% in 2000. The primary driver of this change in global spending on healthcare is India and China, which they moved to higher-income groups. Furthermore, just over 40% of the world population lived in low-income countries, which is now they dropped to 10%. Moreover, significant spending increment was in upper-middle-income economies population share has more than doubled over the period of, and share of global health spending nearly also doubled due to China and India's vast population joining that group. Unfortunately, all other spending share income groups had declined. From the continent view, North America, Western Europe, and Oceanic countries have the highest levels of spending, and West Central Asia, and East Africa the lowest, which is followed closely by South Asia, it is explained in the figure. It is also true that fast economic growth is associated with increased health spending and sustained rapid economic growth between 2000 and 2017. Even more, fast economic growth which is generally associated with the higher government revenues and health spending is mostly located in Asia such as China, India and Indonesia followed by the Middle East and Latin America. In these countries, the real health spending per capita grew by 2.2 times and increased by 0.6 percentage point as per a share of GDP from 2000 to 2017.Infrastructure and investment: gross fixed capital formation
Government acquisition intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending, is called gross fixed capital formation, or government investment, which usually is the largest part of the government."Gross capital formation"''Statistics Explained'' European Union Statistics Directorate, European Commission Acquisition of goods and services is made through production by the government (using the government's labour force, fixed assets and purchased goods and services for intermediate consumption) or through purchases of goods and services from market producers. In economic theory or in
macroeconomics
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
For example, using interest rates, taxes, and ...
, investment is the amount purchased of goods which are not consumed but are to be used for future production (i.e. capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
). Examples include railroad or factory construction.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
spending is considered government investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing i ...
because it will usually save money in the long run, and thereby reduce the net present value of government liabilities.
Spending on physical infrastructure in the U.S. returns an average of about $1.92 for each $1.00 spent on nonresidential construction because it is almost always less expensive to maintain than repair or replace once it has become unusable.
Likewise, government spending on social infrastructure, such as preventative health care
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental hea ...
, can save several hundreds of billions of dollars per year in the U.S., because for example cancer patients are more likely to be diagnosed at Stage I where curative treatment is typically a few outpatient visits, instead of at Stage III or later in an emergency room
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ...
where treatment can involve years of hospitalization and is often terminal.
Per capita spending
In 2010 national governments spent an average of $2,376 per person, while the average for the world's 20 largest economies (in terms of GDP) was $16,110 per person. Norway and Sweden expended the most at $40,908 and $26,760 per capita respectively. The federal government of the United States spent $11,041 per person. Other large economy country spending figures include South Korea ($4,557), Brazil ($2,813), Russia ($2,458), China ($1,010), and India ($226). The figures below of 42% of GDP spending and a GDP per capita of $54,629 for the U.S. indicate a total per person spending including national, state, and local governments was $22,726 in the U.S.As a percentage of GDP
This is a list of countries by government spending as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) for the listed countries, according to the ''2014Index of Economic Freedom
The ''Index of Economic Freedom'' is an annual index and ranking created in 1995 by The Heritage Foundation and ''The Wall Street Journal'' to measure the degree of economic freedom in the world's nations. The creators of the index claim to tak ...
'' by The Heritage Foundation and '' The Wall Street Journal''. Tax revenue is included for comparison. These statistics utilize the United Nations' System of National Accounts
The System of National Accounts (often abbreviated as SNA; formerly the United Nations System of National Accounts or UNSNA) is an international standard system of national accounts, the first international standard being published in 1953. Handbo ...
(SNA), which measures the government sector differently than the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official economy of the United States, macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic ...
(BEA). The SNA counts as government spending the gross cost of public services such as state universities and public hospitals. For example, the SNA counts the entire cost of running the public-university system, not just what legislators appropriate to supplement students' tuition payments. Those adjustments push up the SNA's measure of spending by roughly 4 percent of GDP compared with the standard measure tallied by the BEA.
Public social spending by country
Public social spending comprises cash benefits, direct in-kind provision of goods and services, and tax breaks with social purposes provided by general government (that is central, state, and local governments, including social security funds).OECD data/ref>
Research, assessments and transparency
There is research into government spending such as their efficacies or effective design or comparisons to other options as well as research containing conclusions of public spending-related recommendations. Examples of such are studies outlining benefits of participation in bioeconomy innovation or identifying potential "misallocations" or "misalignments". Often, such spending may be broad – indirect in terms of national interests – such as with human resources/education-related spending or establishments of novel reward systems. In some cases, various goals and expenditures are made public to various degrees, referred to "budget transparency" or "government spending transparency". ;Informed and optimized allocations A study suggests "Greater attention to the development of methods and evidence to better inform the allocation of public sector spending between departments" may be needed and that decisions about public spending may miss opportunities to improve social welfare from existing budgets. ;Underlying drivers of spending alterations A study investigated funding allocations forpublic investment
Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual o ...
in energy research, development and demonstration reported insights about past impacts of its drivers, that may be relevant to adjusting (or facilitating) "investment in clean energy" "to come close to achieving meaningful global decarbonization". The investigated drivers can be broadly described as crisis responses, cooperations and competitions.
Principles and ethics
Studies and organizations have called for systemtically applying principles to spending decisions or to take current issues and goals such asclimate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing Greenhouse gas emissions, emissions of greenhouse gases or Carbon sink, removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly caus ...
into account in all such decisions. For example:
* scientists have suggested in '' Nature'' that governments should withstand various pressures and influences and "only support agriculture and food system
The term food system describes the interconnected systems and processes that influence nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients ...
s that deliver on the SDGs (in line with "public funds for public goods")"
* a campaign by the FSFE calls for a principle of "Public Money, Public Code" – that software created using taxpayers' money is developed as free and open source software
* Plan S calls for a requirement for scientific publications that result from research funded by public grants being published as open access
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 definition), or libre op ...
Public sector ethics may also concern government spending, affecting the shares and intentions of government spending or their respective rationales (beyond ethical principles or implications of the contextual socioeconomic structures), as well as corruption or diversion of public funds.
Other areas of spending
Science funding
Governments fund various research beyond healthcare and medical research and defense research . Sometimes, relevant funding decision-making makes use of coordinative and prioritizing tools, data or methods, such as evaluated relevances to global issues or international goals or national goals or major causes of human diseases and early deaths (health impacts).Energy infrastructure
See also
*Rahn curve
The Rahn curve is a graph used to illustrate an economic theory, proposed in 1996 by American economist Richard W. Rahn, which suggests that there is a level of government spending that maximizes economic growth. The theory is used by classical ...
* Open government
* Government operations
* Public expenditure
* Public finance
* Government budget
A government budget is a document prepared by the government and/or other political entity presenting its anticipated tax revenues (Inheritance tax, income tax, corporation tax, import taxes) and proposed spending/expenditure (Healthcare, Educa ...
* Government waste
* Fiscal policy
* Fiscal council
* Sovereign wealth fund
* Tax
* Mandatory spending
* Taxpayers unions
* Eurostat
Eurostat ('European Statistical Office'; DG ESTAT) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg, Luxembourg, Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statis ...
* Government spending in the United Kingdom
* Government spending in the United States
* List of countries by government spending as percentage of GDP
References
External links
OECD Government spending statistics
Canadian Governments Compared
Eurostat's government spending per sector
{{DEFAULTSORT:Government Spending Government finances Fiscal policy