Brussels Capital Region on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region
[ (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.)] (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest), is a
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
of
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
comprising
19 municipalities, including the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
, which is the capital of Belgium.
The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country and is a part of both the
French Community of Belgium
In Belgium, the French Community (french: Communauté française; ) refers to one of the three constituent constitutional linguistic communities. Since 2011, the French Community has used the name Wallonia-Brussels Federation (french: Fédé ...
and the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
, but is separate from the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
(within which it forms an
enclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
) and the
Walloon Region
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
.
Brussels is the most densely populated region in Belgium, and although it has the highest
GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
,
it has the lowest available income per household.
The Brussels Region covers , a relatively small area compared to the two other regions, and has a population of over 1.2 million.
The five times larger
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
of Brussels comprises over 2.5 million people, which makes it the largest in Belgium.
[ Population of all municipalities in Belgium on 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 18 October 2008.][ Definitions of metropolitan areas in Belgium. The metropolitan area of Brussels is divided into three levels. First, the central agglomeration (''geoperationaliseerde agglomeratie'') with 1,451,047 inhabitants (2008-01-01, adjusted to municipal borders). Adding the closest surroundings (suburbs, ''banlieue'' or ''buitenwijken'') gives a total of 1,831,496. And, including the outer commuter zone (''forensenwoonzone'') the population is 2,676,701.] It is also part of a large
conurbation
A conurbation is a region comprising a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ca ...
extending towards
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
,
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, ,
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic ...
and
Walloon Brabant
Walloon Brabant (french: Brabant wallon ; nl, Waals-Brabant ; wa, Roman Payis) is a province located in Belgium's French-speaking region of Wallonia. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the province of Flemish Brabant (Flemish Region) and ...
, home to over 5 million people.
Brussels grew from a small rural settlement on the river
Senne Senne may refer to:
Places
* Senne (Germany), a natural region of Germany
*Senne, a district of Bielefeld, Germany
* Senne (river), a river of Belgium
*Senné (disambiguation), places in Slovakia
People with the name
*Yōkō Senne, a 13th-centur ...
to become an important city-region in Europe. Since the end of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, it has been a major centre for
international politics
International relations (IR), sometimes referred to as international studies and international affairs, is the Scientific method, scientific study of interactions between sovereign states. In a broader sense, it concerns all activities betwe ...
and home to numerous international organisations, politicians,
diplomat
A diplomat (from grc, δίπλωμα; romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state or an intergovernmental institution such as the United Nations or the European Union to conduct diplomacy with one or more other states or internati ...
s and
civil servant
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil servants hired on professional merit rather than appointed or elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leaders ...
s.
Brussels is the ''
de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' capital of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, as it hosts a number of principal
EU institutions
The institutions of the European Union are the seven principal decision-making bodies of the European Union and the Euratom. They are, as listed in Article 13 of the Treaty on European Union:
* the European Parliament,
* the European Council ...
, including its
administrative-legislative,
executive-political, and
legislative
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as p ...
branches (though the judicial branch is located in
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
, and the European Parliament meets for a minority of the year in
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the Eu ...
).
Because of this, its name is sometimes used
metonymically
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name ...
to describe the EU and its institutions. The secretariat of the
Benelux
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a politico-economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in western Europe: B ...
and the
headquarters
Headquarters (commonly referred to as HQ) denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the to ...
of
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
are also located in Brussels.
As the economic capital of Belgium and a top financial centre of Western Europe with
Euronext Brussels
The Brussels Stock Exchange (french: Bourse de Bruxelles, nl, Beurs van Brussel), abbreviated to BSE, was founded in Brussels, Belgium, by decree of Napoleon in 1801. In 2002, the BSE merged with the Amsterdam, Lisbon and Paris stock exchanges ...
, Brussels is classified as an ''Alpha''
global city. It is also a national and international hub for rail, road and air traffic, and are sometimes considered, together with Belgium, as the geographic, economic and cultural crossroads of Europe. The
Brussels Metro
The Brussels Metro (french: Métro de Bruxelles, nl, Brusselse metro) is a rapid transit system serving a large part of the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It consists of four conventional metro lines and three ''premetro'' lines. The me ...
is the only
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
system in Belgium. In addition, both its
airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface ...
and
railway stations
A train station, railway station, railroad station or depot is a railway facility where trains stop to load or unload passengers, freight or both. It generally consists of at least one platform, one track and a station building providing such ...
are the largest and busiest in the country.
Historically Dutch-speaking, Brussels saw a
language shift to French from the late 19th century. Nowadays, the Brussels-Capital Region is officially bilingual in French and Dutch, even though French is the ''
lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
'' with over 90% of the inhabitants being able to speak it.
Brussels is also increasingly becoming multilingual. English is spoken as a second language by nearly a third of the population and many migrants and
expatriate
An expatriate (often shortened to expat) is a person who resides outside their native country. In common usage, the term often refers to educated professionals, skilled workers, or artists taking positions outside their home country, either ...
s speak other languages as well.
[O'Donnell, Paul; Toebosch, AnneMarie. ''Multilingualism in Brussels: "I'd Rather Speak English"''. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, 2008, v. 29 n. 2 p. 154-169.]
Brussels is known for its cuisine and gastronomic offer (including its local
waffle
A waffle is a dish made from leavened batter or dough that is cooked between two plates that are patterned to give a characteristic size, shape, and surface impression. There are many variations based on the type of waffle iron and recipe used ...
, its
chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civ ...
, its
French fries
French fries (North American English), chips (British English), finger chips ( Indian English), french-fried potatoes, or simply fries, are '' batonnet'' or ''allumette''-cut deep-fried potatoes of disputed origin from Belgium and France. Th ...
and its numerous types of
beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
s), as well as its historical and architectural landmarks; some of them are registered as
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s. Principal attractions include its historic
Grand-Place/Grote Markt (main square), ''
Manneken Pis
''Manneken Pis'' (; ) is a landmark bronze fountain sculpture in central Brussels, Belgium, depicting a puer mingens; a naked little boy urinating into the fountain's basin. Though its existence is attested as early as the 15th century, it wa ...
'', the
Atomium
The Atomium ( , , ) is a landmark building in Brussels, Belgium, originally constructed for the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (Expo '58). It is located on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Laeken (northern part of the City of Brussels), where the exh ...
, and cultural institutions such as
La Monnaie/De Munt and the
Museums of Art and History. Due to its long tradition of
Belgian comics
Belgian comics are a distinct subgroup in the comics history, and played a major role in the development of European comics, alongside France with whom they share a long common history. While the comics in the two major language groups and regio ...
, Brussels is also hailed as a capital of the
comic strip
A comic strip is a sequence of drawings, often cartoons, arranged in interrelated panels to display brief humor or form a narrative, often serialized, with text in balloons and captions. Traditionally, throughout the 20th and into the 21st ...
.
Toponymy
Etymology
The most common theory of the origin of the name ''Brussels'' is that it derives from the
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aroun ...
, or , meaning "marsh" ( / ) and "home" or "settlement" ( / / ) or "settlement in the marsh".
[Zo ontstond Brussel]
Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie - Commission of the Flemish Community in Brussels Saint Vindicianus, the Bishop of
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department and in the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, regio ...
, made the first recorded reference to the place in 695, when it was still a
hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
. The names of all the municipalities in the Brussels-Capital Region are also of
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
origin, except for
Evere
Evere (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium). On 1 January 2006, the municipality had a total population of 33,462. The total area is which gives a population density of . In common with all of Brussels' m ...
, which is
Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
.
Pronunciation
In
French, is pronounced (the ''x'' is pronounced , like in
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, and the final ''s'' is silent) and in Dutch, is pronounced . Inhabitants of Brussels are known in French as (pronounced ) and in Dutch as (pronounced ). In the
Brabantian dialect
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic or Brabantine ( nl, Brabants, Standard Dutch pronunciation: , ), is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant, which corresponded mainly to the Dutch provi ...
of Brussels (known as
Brusselian, and also sometimes referred to as Marols or Marollien),
[Jeanine Treffers-Daller, ''Mixing Two Languages: French-Dutch Contact in a Comparative Perspective'' (Walter de Gruyter, 1994), 25.] they are called ''Brusseleers'' or ''Brusseleirs''.
Originally, the written ''x'' noted the group . In the
Belgian French
Belgian French (french: français de Belgique) is the variety of French spoken mainly among the French Community of Belgium, alongside related Oïl languages of the region such as Walloon, Picard, Champenois, and Lorrain (Gaumais). The Frenc ...
pronunciation as well as in Dutch, the ''k'' eventually disappeared and ''z'' became ''s'', as reflected in the current
Dutch spelling, whereas in the more conservative
French form, the spelling remained. The pronunciation in French only dates from the 18th century, but this modification did not affect the traditional Brussels usage. In
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, the pronunciations and (for ) are often heard, but are rather rare in Belgium.
[Alain Lerond, ''Dictionnaire de la prononciation'' (1980), Larousse, pp. 477.]
History
Early history
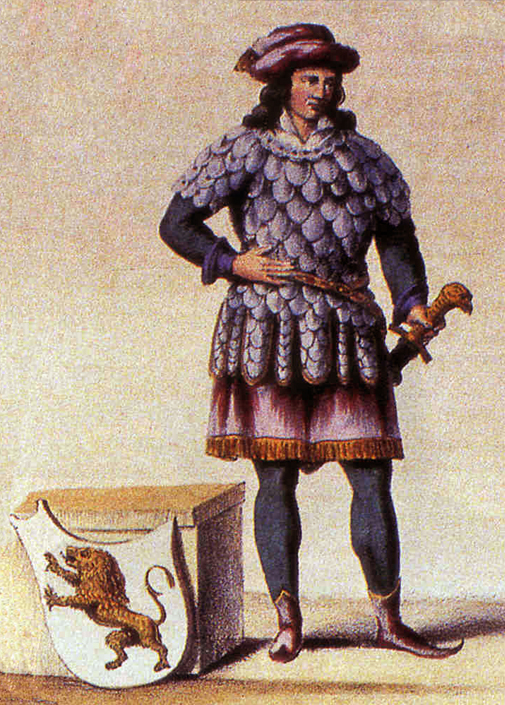

The history of Brussels is closely linked to that of
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
. Traces of human settlement go back to the
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
, with vestiges and place-names related to the civilisation of
megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
s,
dolmen
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
s and
standing stones
A menhir (from Brittonic languages: ''maen'' or ''men'', "stone" and ''hir'' or ''hîr'', "long"), standing stone, orthostat, or lith is a large human-made upright stone, typically dating from the European middle Bronze Age. They can be foun ...
(Plattesteen in the city centre and
Tomberg in
Woluwe-Saint-Lambert
Woluwe-Saint-Lambert () or Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe (Dutch, ) is one of the nineteen municipalities in the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It is a prosperous residential area, with a mixture of flats and detached, semi-detached and terraced hous ...
, for example). During
late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, the region was home to
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
occupation, as attested by archaeological evidence discovered on the current site of
Tour & Taxis
Tour & Taxis (french: Tour et Taxis, nl, Thurn en Taxis) is a large former industrial site in Brussels, Belgium. It is situated on the Brussels Canal in the City of Brussels, just north-west of the city centre, immediately adjacent to Laek ...
, north-west of the
Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon (from the Greek πέντε ''pente'' meaning ''five'' and γωνία ''gonia'' meaning ''angle'') is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simpl ...
. Following the decline of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
, it was incorporated into the
Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
.
According to local legend, the origin of the settlement which was to become Brussels lies in
Saint Gaugericus
Saint Gaugericus, in French Saint Géry (also known as Gorik, Gau; in Walloon, Djèri) ( 550 – August 11, 619) was a bishop of Cambrai, France.
Biography
He was born to Roman parents, Gaudentius and Austadiola, at ''Eposium'' (present Ca ...
' construction of a chapel on
an island in the river
Senne Senne may refer to:
Places
* Senne (Germany), a natural region of Germany
*Senne, a district of Bielefeld, Germany
* Senne (river), a river of Belgium
*Senné (disambiguation), places in Slovakia
People with the name
*Yōkō Senne, a 13th-centur ...
around 580. The official founding of Brussels is usually said to be around 979, when
Duke Charles of Lower Lorraine transferred the
relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangi ...
s of the
martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
Saint Gudula
Saint Gudula was born in the pagus of Brabant (in present-day Belgium). According to her 11th-century biography ( Vita Gudilae), written by a monk of the abbey of Hautmont between 1048 and 1051, she was the daughter of a duke of Lotharingia call ...
from
Moorsel
Moorsel is a village in the Denderstreek in the province East Flanders in Belgium, a '' deelgemeente'' of the city of Aalst. The village belongs to a league of neighbouring villages, which call themselves the ''Faluintjesgemeenten''. Moorsel is ...
(located in today's province of
East Flanders
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of Oost-Vlaanderen.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van O ...
) to Saint Gaugericus' chapel. When
King Lothair II appointed the same Charles (his brother) to become Duke of
Lower Lotharingia
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as ''Lothier'' or ''Lottier'' in 977, Charles ordered the construction of the city's first permanent fortification, doing so on that same island.
Middle Ages
Lambert I of Leuven
Count Lambert "the Bearded" (c. 950 - 12 September 1015) was the first person to be described as a count of Leuven (French ''Louvain'') in a surviving contemporary record, being described this way relatively late in life, in 1003. He is also the ...
,
Count of Leuven, gained the County of Brussels around 1000, by marrying Charles' daughter. Because of its location on the banks of the Senne, on an important trade route between
Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
and
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
, and
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 m ...
, Brussels became a commercial centre specialised in the textile trade. The town grew quite rapidly and extended towards the upper town (Treurenberg,
Coudenberg
The Palace of Coudenberg (french: Palais du Coudenberg, nl, Coudenbergpaleis) was a royal residence situated on the Coudenberg or Koudenberg (; Dutch for "Cold Hill"), a small hill in what is today the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium.
F ...
and
Sablon/Zavel areas), where there was a smaller risk of floods. As it grew to a population of around 30,000, the surrounding marshes were drained to allow for further expansion. Around this time, work began on what is now the
Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula
nl, Kathedraal van Sint-Michiel en Sint-Goedele
, native_name_lang =
, image = Saints-Michel-et-Gudule Luc Viatour.jpg
, imagesize = 200px
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, landscape ...
(1225), replacing an older
Romanesque church. In 1183, the Counts of Leuven became
Dukes of Brabant
The Duke of Brabant (, ) was the ruler of the Duchy of Brabant since 1183/1184. The title was created by the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in favor of Henry I of the House of Reginar, son of Godfrey III of Leuven (who was duke of Low ...
. Brabant, unlike the county of Flanders, was not fief of the king of France but was incorporated into the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
.
In the early 13th century, the
first walls of Brussels
The Fortifications of Brussels (french: Fortifications de Bruxelles, nl, Vestingwerken van Brussel) refers to the medieval city walls that surrounded Brussels, Belgium, built primarily to defend the city but also for administrative reasons. The ...
were built, and after this, the city grew significantly. To let the city expand,
a second set of walls was erected between 1356 and 1383. Traces of these walls can still be seen, although the
Small Ring
The Small Ring (french: Petite Ceinture, nl, Kleine Ring) inner ring road, formally R20 and N0 is a series of roadways in central Brussels, Belgium, surrounding the historic city centre. The city centre is usually defined as the area within t ...
, a series of boulevards bounding the historical city centre, follows their former course.
Early modern

In the 15th century, the marriage between heiress
Margaret III of Flanders
Margaret III (13 April 1350 – 16/21 March 1405) was a ruling Countess of Flanders, Countess of Artois, and Countess of Auvergne and Boulogne between 1384 and 1405. She was the last Countess of Flanders of the House of Dampierre.
She was ...
and
Philip the Bold
Philip II the Bold (; ; 17 January 1342 – 27 April 1404) was Duke of Burgundy and '' jure uxoris'' Count of Flanders, Artois and Burgundy. He was the fourth and youngest son of King John II of France and Bonne of Luxembourg.
Philip II was ...
,
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy (french: duc de Bourgogne) was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by France in 1477, and later by Holy Roman Emperors and Kings of Spain from the House of Habsburg ...
, produced a new Duke of Brabant of the
House of Valois
The Capetian house of Valois ( , also , ) was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. They succeeded the House of Capet (or "Direct Capetians") to the List of French monarchs, French throne, and were the royal house of France from 1328 to 1589 ...
(namely
Antoine
Antoine is a French given name (from the Latin ''Antonius'' meaning 'highly praise-worthy') that is a variant of Danton, Titouan, D'Anton and Antonin.
The name is used in France, Switzerland, Belgium, Canada, West Greenland, Haiti, French Guiana ...
, their son). In 1477, the Burgundian duke
Charles the Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477.
...
perished in the
Battle of Nancy
The Battle of Nancy was the final and decisive battle of the Burgundian Wars, fought outside the walls of Nancy on 5 January 1477 by Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, against René II, Duke of Lorraine, and the Swiss Confederacy.
René's ...
. Through the marriage of his daughter
Mary of Burgundy
Mary (french: Marie; nl, Maria; 13 February 1457 – 27 March 1482), nicknamed the Rich, was a member of the House of Valois-Burgundy who ruled a collection of states that included the duchies of Limburg, Brabant, Luxembourg, the counties of ...
(who was born in Brussels) to
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
Maximilian I, the
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
fell under
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
sovereignty. Brabant was integrated into this composite state, and Brussels flourished as the Princely Capital of the prosperous
Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and ...
, also known as the
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (Fre ...
. After the death of Mary in 1482, her son
Philip the Handsome
Philip the Handsome, es, Felipe, french: Philippe, nl, Filips (22 July 1478 – 25 September 1506), also called the Fair, was ruler of the Burgundian Netherlands and titular ruler, titular Duke of Burgundy from 1482 to 1506, as well as the fir ...
succeeded as Duke of Burgundy and Brabant.
Philip died in 1506, and he was succeeded by his son
Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
who then also became
King of Spain
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
(crowned in the
Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula
nl, Kathedraal van Sint-Michiel en Sint-Goedele
, native_name_lang =
, image = Saints-Michel-et-Gudule Luc Viatour.jpg
, imagesize = 200px
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, landscape ...
) and even Holy Roman Emperor at the death of his grandfather Maximilian I in 1519. Charles was now the ruler of a
Habsburg Empire
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
"on which the sun never sets" with Brussels serving as one of his main capitals. It was in the
Coudenberg Palace that Charles V was declared of age in 1515, and it was there in 1555 that he abdicated all of his possessions and passed the
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last House of Valois-Burgundy, Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary of Burgu ...
to
King Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, K ...
. This impressive palace, famous all over Europe, had greatly expanded since it had first become the seat of the Dukes of Brabant, but it was destroyed by fire in 1731.

In the 16th and 17th centuries, Brussels was a centre for the
lace
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is divided into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted o ...
industry. In addition,
Brussels tapestry
Brussels tapestry workshops produced tapestry from at least the 15th century, but the city's early production in the Late Gothic International style was eclipsed by the more prominent tapestry-weaving workshops based in Arras and Tournai. In 1 ...
hung on the walls of castles throughout Europe. In 1695, during the
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
,
King Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Ve ...
sent troops to
bombard Brussels with artillery. Together with the resulting fire, it was the most destructive event in the entire history of Brussels. The
Grand-Place
The Grand-Place (French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or Grote Markt (Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque guildhalls of the former Guilds of Brussels and two larger ...
was destroyed, along with 4,000 buildings—a third of all the buildings in the city. The reconstruction of
the city centre, effected during subsequent years, profoundly changed its appearance and left numerous traces still visible today.
Following the
Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne o ...
in 1713, Spanish sovereignty over the Southern Netherlands was transferred to the Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg. This event started the era of the
Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The p ...
. Brussels
was captured by France in 1746, during the
War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George's W ...
, but was handed back to Austria three years later. It remained with Austria until 1795, when the Southern Netherlands were captured and annexed by France, and the city became the capital of the
department of the Dyle. The French rule ended in 1815, with the defeat of
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
on the
battlefield of Waterloo, located south of today's Brussels-Capital Region. With the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
, the Southern Netherlands joined the
United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
, under
King William I of Orange. The former Dyle department became the province of
South Brabant
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
, with Brussels as its capital.
Late modern
In 1830, the
Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
T ...
began in Brussels, after a performance of
Auber's opera ''
La Muette de Portici
''La muette de Portici'' (''The Mute Girl of Portici'', or ''The Dumb Girl of Portici''), also called ''Masaniello'' () in some versions, is an opera in five acts by Daniel Auber, with a libretto by Germain Delavigne, revised by Eugène Scribe.
...
'' at the
Royal Theatre of La Monnaie. The city became the capital and seat of government of the new nation. South Brabant was renamed simply
Brabant Brabant is a traditional geographical region (or regions) in the Low Countries of Europe. It may refer to:
Place names in Europe
* London-Brabant Massif, a geological structure stretching from England to northern Germany
Belgium
* Province of Bra ...
, with Brussels as its administrative centre. On 21 July 1831,
Leopold I, the first
King of the Belgians
Belgium is a constitutional, hereditary, and popular monarchy. The monarch is titled king or queen of the Belgians ( nl, Koning(in) der Belgen, french: Roi / Reine des Belges}, german: König(in) der Belgier) and serves as the country's h ...
, ascended the throne, undertaking the destruction of the city walls and the construction of many buildings.
Following independence, Brussels underwent many more changes. It became a financial centre, thanks to the dozens of companies launched by the ''
Société Générale de Belgique
The ' ( nl, Generale Maatschappij van België; literally "General Company of Belgium") was a large Belgian bank and later holdings company which existed between 1822 and 2003.
The ''Société générale'' was originally founded as an investm ...
''. The
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
and the opening of the
Brussels–Charleroi Canal in 1832 brought prosperity to the city through commerce and manufacturing. The
Free University of Brussels University of Brussels may refer to several institutions in Brussels, Belgium: Current institutions
* Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), a French-speaking university established as a separate entity in 1970
*Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), a D ...
was established in 1834 and
Saint-Louis University in 1858. In 1835, the
first passenger railway built outside England linked the municipality of
Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, from which it is separated ...
with
Mechelen
Mechelen (; french: Malines ; traditional English name: MechlinMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical contex ...
.
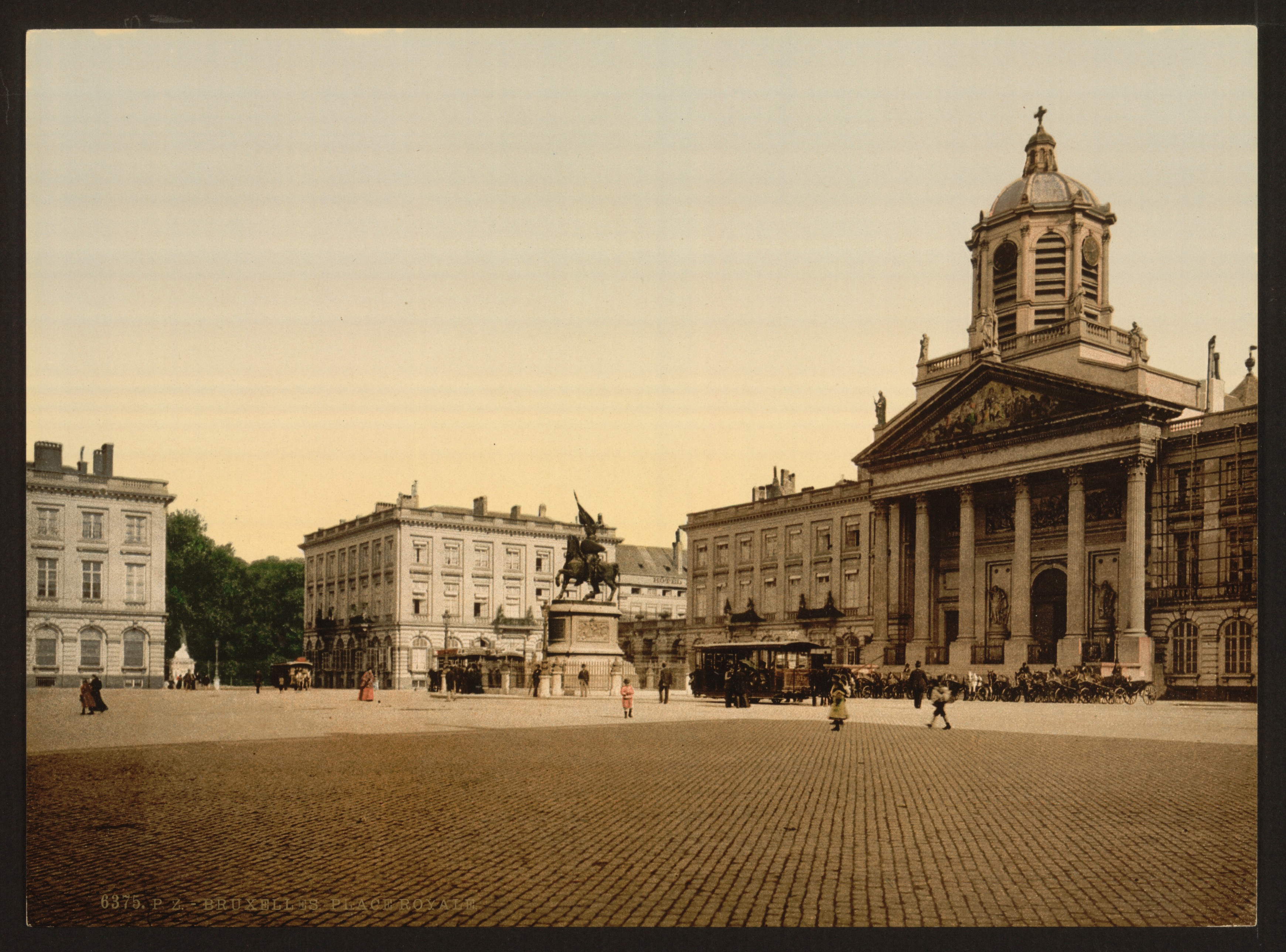

During the 19th century, the population of Brussels grew considerably; from about 80,000 to more than 625,000 people for the city and its surroundings. The Senne had become a serious
health hazard
A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would allow them, even just theoretically, to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probabi ...
, and from 1867 to 1871, under the tenure of the
city's then-mayor,
Jules Anspach
Baron Jules Victor Anspach (20 July 1829 – 19 May 1879) was a Belgian politician and mayor of the City of Brussels, best known for his renovations surrounding the covering of the river Senne (1867–1871). He is buried in Brussels Cemetery.
A ...
, its entire course through the urban area was
completely covered over. This allowed
urban renewal
Urban renewal (also called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address urban decay in cities. Urban renewal involves the clearing out of blighte ...
and the construction of modern buildings of ''
Haussmann Hausmann is a German word with former meanings "householder" and "freeholder" and current meaning "house-husband."
Hausmann (Hausman), Haussmann (Haussman), Haußmann, Hauszmann, etc. are German-origin surnames that may refer to:
Hausmann
* C ...
-esque'' style along grand
central boulevards, characteristic of downtown Brussels today. Buildings such as the
Brussels Stock Exchange
The Brussels Stock Exchange (french: Bourse de Bruxelles, nl, Beurs van Brussel), abbreviated to BSE, was founded in Brussels, Belgium, by decree of Napoleon in 1801. In 2002, the BSE merged with the Amsterdam, Lisbon and Paris stock exchang ...
(1873), the
Palace of Justice (1883) and
Saint Mary's Royal Church
nl, Koninklijke Sint-Mariakerk
, native_name_lang =
, image = Koninklijke Sint-Mariakerk Schaarbeek 2011 09 01 02.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, imagealt =
, caption = St. Mary's Royal Church in Schaerbeek
, coordinates =
, country = Belgiu ...
(1885) date from this period. This development continued throughout the reign of
King Leopold II
* german: link=no, Leopold Ludwig Philipp Maria Viktor
, house = Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
, father = Leopold I of Belgium
, mother = Louise of Orléans
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Brussels, Belgium
, death_date = ...
. The
International Exposition of 1897 contributed to the promotion of the infrastructure. Among other things, the (today's
Royal Museum for Central Africa
The Royal Museum for Central Africa or RMCA ( nl, Koninklijk Museum voor Midden-Afrika or KMMA; french: Musée royal de l'Afrique centrale or MRAC; german: Königliches Museum für Zentralafrika or KMZA), also officially known as the AfricaMuse ...
), in the suburb of
Tervuren
Tervuren () is a municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant, in Flanders, Belgium. The municipality comprises the villages of Duisburg, Tervuren, Vossem and Moorsel. On January 1, 2006, Tervuren had a total population of 20,636. The total a ...
, was connected to the capital by the construction of an
grand alley.
Brussels became one of the major European cities for the development of the
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
style in the 1890s and early 1900s. The architects
Victor Horta
Victor Pierre Horta (; Victor, Baron Horta after 1932; 6 January 1861 – 8 September 1947) was a Belgian architect and designer, and one of the founders of the Art Nouveau movement. His Hôtel Tassel in Brussels, built in 1892–93, is often ...
,
Paul Hankar
Paul Hankar (11 December 1859 – 17 January 1901) was a Belgian architect and furniture designer, and an innovator in the Art Nouveau style.
Career
Hankar was born at Frameries, in Hainaut, Belgium, the son of a stonemason. He studied at the ...
, and
Henry van de Velde
Henry Clemens van de Velde (; 3 April 1863 – 15 October 1957) was a Belgian painter, architect, interior designer, and art theorist. Together with Victor Horta and Paul Hankar, he is considered one of the founders of Art Nouveau in Belgium.'' ...
became particularly famous for their designs, many of which survive today.
20th century
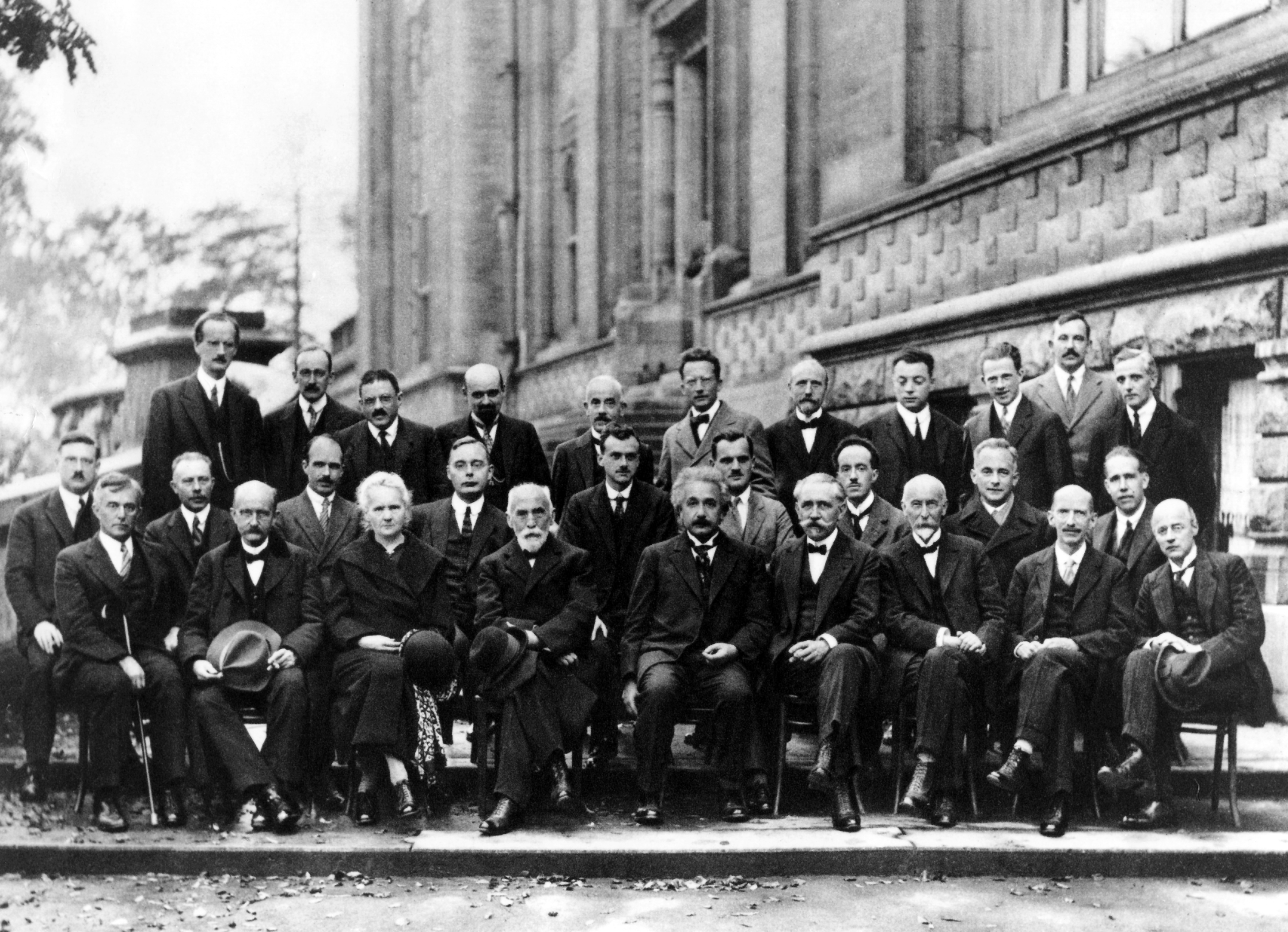

During the 20th century, the city hosted various fairs and conferences, including the
Solvay Conference
The Solvay Conferences (french: Conseils Solvay) have been devoted to outstanding preeminent open problems in both physics and chemistry. They began with the historic invitation-only 1911 Solvay Conference on Physics, considered a turning point i ...
on Physics and on Chemistry, and three
world's fair
A world's fair, also known as a universal exhibition or an expo, is a large international exhibition designed to showcase the achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specif ...
s: the
Brussels International Exposition of 1910, the
Brussels International Exposition of 1935 and the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (
Expo '58
Expo 58, also known as the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (french: Exposition Universelle et Internationale de Bruxelles de 1958, nl, Brusselse Wereldtentoonstelling van 1958), was a world's fair held on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Brussels, Bel ...
). During
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Brussels was an
occupied
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October ...
city, but German troops did not cause much damage. During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, it was again
occupied by German forces, and spared major damage, before it was liberated by the British
Guards Armoured Division
The Guards Armoured Division was an armoured division of the British Army during the Second World War. The division was created in the United Kingdom on 17 June 1941 during the Second World War from elements of the Guards units, the Grenadier G ...
on 3 September 1944.
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport, nl, Luchthaven Brussel, vls, Vliegpling Brussel, german: Flughafen Brüssel is an international airport northeast of Brussels, the capital of Belgium. In 2019, more than 26 million passengers arrived or departed at Bruss ...
, in the suburb of
Zaventem
Zaventem () is a Belgian municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant. It is located in the Dijleland area, one of the three large recreational areas which together form the '' Groene Gordel'' ("Green Belt") around the Brussels-Capital Region. ...
, dates from the occupation.
After the war, Brussels underwent extensive modernisation. The construction of the
North–South connection
The North–South connection (french: Jonction Nord-Midi, nl, Noord-Zuidverbinding) is a railway link of national and international importance through central Brussels, Belgium, that connects the major railway stations in the city. It is line ...
, linking the main railway stations in the city, was completed in 1952, while the first ''
premetro
A premetro is a tramway or light railway which includes segments built to rapid transit standards, generally as part of a process of conversion to a metro-standards railway usually by the construction of tunnels in the central city area.
Hist ...
'' (underground tram) service was launched in 1969,
and the first
Metro
Metro, short for metropolitan, may refer to:
Geography
* Metro (city), a city in Indonesia
* A metropolitan area, the populated region including and surrounding an urban center
Public transport
* Rapid transit, a passenger railway in an urba ...
line was opened in 1976.
Starting from the early 1960s, Brussels became the ''de facto'' capital of what would become the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
(EU), and many modern offices were built. Development was allowed to proceed with little regard to the aesthetics of newer buildings, and numerous architectural landmarks were demolished to make way for newer buildings that often clashed with their surroundings, giving name to the process of
Brusselisation
In urban planning, Brusselization ( UK and US) or Brusselisation ( UK variant) (french: bruxellisation, nl, verbrusseling) is "the indiscriminate and careless introduction of modern high-rise buildings into gentrified neighbourhoods" and has b ...
.
Contemporary
The Brussels-Capital Region was formed on 18 June 1989, after a constitutional reform in 1988. It is one of the three
federal regions of Belgium, along with
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
and
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
, and has bilingual status.
The
yellow iris
''Iris pseudacorus'', the yellow flag, yellow iris, or water flag, is a species of flowering plant in the family Iridaceae. It is native to Europe, western Asia and northwest Africa. Its specific epithet ''pseudacorus'' means "false acorus", ref ...
is the emblem of the region (referring to the presence of these flowers on the city's original site) and a stylised version is featured on its official flag.
In recent years, Brussels has become an important venue for international events. In 2000, it was named
European Capital of Culture alongside eight other European cities. In 2013, the city was the site of the
Brussels Agreement. In 2014, it hosted the
40th G7 summit
The 40th G7 summit was held 4–5 June, 2014 in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally scheduled to be held as the “40th G8 summit” and be hosted by Russia in the Black Sea resort of Sochi. However, the other seven countries decided on 24 March t ...
,
and in 2017, 2018 and 2021 respectively the
28th,
29th and
31st NATO Summits.
, three coordinated
nail bomb
A nail bomb is an anti-personnel explosive device containing nails to increase its effectiveness at harming victims. The nails act as shrapnel, leading almost certainly to more injury in inhabited areas than the explosives alone would. A nai ...
ings were detonated by
ISIL
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
in Brussels—two at
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport, nl, Luchthaven Brussel, vls, Vliegpling Brussel, german: Flughafen Brüssel is an international airport northeast of Brussels, the capital of Belgium. In 2019, more than 26 million passengers arrived or departed at Bruss ...
in
Zaventem
Zaventem () is a Belgian municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant. It is located in the Dijleland area, one of the three large recreational areas which together form the '' Groene Gordel'' ("Green Belt") around the Brussels-Capital Region. ...
and one at
Maalbeek/Maelbeek metro station
Maelbeek (French, former Dutch spelling) or Maalbeek (Dutch, ) is a Brussels Metro station in the City of Brussels, Belgium. Its name originates from the Maalbeek stream.
The station opened as a ''premetro'' (underground tram) station on 17 D ...
—resulting in 32 victims and three
suicide bombers
A suicide attack is any violent attack, usually entailing the attacker detonating an explosive, where the attacker has accepted their own death as a direct result of the attacking method used. Suicide attacks have occurred throughout histor ...
killed, and 330 people were injured. It was the deadliest act of
terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
in Belgium.
Geography
Location and topography

Brussels lies in the north-central part of Belgium, about from the Belgian coast and about from Belgium's southern tip. It is located in the heartland of the Brabantian Plateau, about south of
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, (
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
), and north of
Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593. (
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
). Its average
elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vert ...
is above
sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
, varying from a low point in the valley of the almost completely covered
Senne Senne may refer to:
Places
* Senne (Germany), a natural region of Germany
*Senne, a district of Bielefeld, Germany
* Senne (river), a river of Belgium
*Senné (disambiguation), places in Slovakia
People with the name
*Yōkō Senne, a 13th-centur ...
, which cuts the Brussels-Capital Region from east to west, up to high points in the
Sonian Forest
The Sonian Forest or Sonian Wood ( nl, Zoniënwoud, french: Forêt de Soignes, ) is a forest at the southeast edge of Brussels, Belgium.
The Sonian Forest was a favorite hunting ground of the Habsburg Imperial family, and as such features promi ...
, on its southeastern side. In addition to the Senne, tributary streams such as the
Maalbeek
The Maelbeek or Maalbeek () is a stream that runs through several municipalities in Brussels, including Etterbeek, Ixelles, Saint-Josse-ten-Noode, Schaerbeek. It is a tributary of the Zenne, which it joins up in Schaerbeek, from its source locat ...
and the
Woluwe
The Woluwe (; ) is a stream that goes through several municipalities in the southeast and east of Brussels and is a right tributary of the Senne/Zenne (in Vilvoorde). The Kleine Maalbeek is a tributary of the Woluwe (in Kraainem). Many ponds fo ...
, to the east of the region, account for significant elevation differences.
Brussels' central boulevards are above sea level. Contrary to popular belief, the highest point (at ) is not near the / in
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
, but at the / in the Sonian Forest.
Climate
Brussels experiences an
oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
(
Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
: ''Cfb'') with warm summers and cool winters.
Proximity to coastal areas influences the area's climate by sending marine air masses from the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
. Nearby wetlands also ensure a maritime temperate climate. On average (based on measurements in the period 1981–2010), there are approximately 135 days of rain per year in the Brussels-Capital Region. Snowfall is infrequent, averaging 24 days per year. The city also often experiences violent thunderstorms in summer months.
Brussels as a capital
Despite its name, the Brussels-Capital Region is not the capital of
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
. Article 194 of the
Belgian Constitution
The Constitution of Belgium ( nl, Belgische Grondwet, french: Constitution belge, german: Verfassung Belgiens) dates back to 1831. Since then Belgium has been a parliamentary monarchy that applies the principles of ministerial responsibility f ...
establishes that the capital of Belgium is the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
, the municipality in the region that is the city's core.
The City of Brussels is the location of many national institutions. The
Royal Palace of Brussels
The Royal Palace of Brussels (french: Palais royal de Bruxelles, , nl, Koninklijk Paleis van Brussel , german: Königlicher Palast von Brüssel) is the official palace of the King and Queen of the Belgians in the centre of the nation's capita ...
, where the
King of the Belgians
Belgium is a constitutional, hereditary, and popular monarchy. The monarch is titled king or queen of the Belgians ( nl, Koning(in) der Belgen, french: Roi / Reine des Belges}, german: König(in) der Belgier) and serves as the country's h ...
exercises his prerogatives as head of state, is situated alongside
Brussels' Park (not to be confused with the
Royal Palace of Laeken
The Palace of Laeken or Castle of Laeken (french: Château de Laeken, nl, Kasteel van Laken, german: Schloss zu Laeken) is the official residence of the King of the Belgians and the Belgian Royal Family. It lies in the Brussels-Capital Regio ...
, the official home of the
Belgian Royal Family
Belgium is a constitutional, hereditary, and popular monarchy. The monarch is titled king or queen of the Belgians ( nl, Koning(in) der Belgen, french: Roi / Reine des Belges}, german: König(in) der Belgier) and serves as the country's he ...
). The
Palace of the Nation
The Federal Parliament is the bicameral parliament of Belgium. It consists of the Chamber of Representatives (Dutch: , french: Chambre des Représentants, german: Abgeordnetenkammer) and the Senate (Dutch: , french: Sénat, german: Senat). It s ...
is located on the opposite side of this park, and is the seat of the
Belgian Federal Parliament
The Federal Parliament is the bicameral parliament of Belgium. It consists of the Chamber of Representatives (Dutch: , french: Chambre des Représentants, german: Abgeordnetenkammer) and the Senate (Dutch: , french: Sénat, german: Senat). It sit ...
. The office of the
Prime Minister of Belgium
german: Premierminister von Belgien
, insignia = State Coat of Arms of Belgium.svg
, insigniasize = 100px
, insigniacaption = Coat of arms
, insigniaalt =
, flag = Government ...
, colloquially called ''Law Street 16'' (french: 16, rue de la Loi, link=no, nl, Wetstraat 16, link=no), is located adjacent to this building. It is also where the
Council of Ministers
A council is a group of people who come together to consult, deliberate, or make decisions. A council may function as a legislature, especially at a town, city or county/ shire level, but most legislative bodies at the state/provincial or nati ...
holds its meetings. The
Court of Cassation
A court of cassation is a high-instance court that exists in some judicial systems. Courts of cassation do not re-examine the facts of a case, they only interpret the relevant law. In this they are appellate courts of the highest instance. In th ...
, Belgium's main court, has its seat in the
Palace of Justice. Other important institutions in the City of Brussels are the
Constitutional Court
A constitutional court is a high court that deals primarily with constitutional law. Its main authority is to rule on whether laws that are challenged are in fact unconstitutional, i.e. whether they conflict with constitutionally established ...
, the
Council of State
A Council of State is a governmental body in a country, or a subdivision of a country, with a function that varies by jurisdiction. It may be the formal name for the cabinet or it may refer to a non-executive advisory body associated with a head o ...
, the
Court of Audit A Court of Audit or Court of Accounts is a Supreme audit institution, i.e. a government institution performing financial and/or legal audit (i.e. Statutory audit or External audit) on the executive branch of power.
See also
*Most of those in ...
, the
Royal Belgian Mint
The Royal Mint of Belgium ( French: ''La Monnaie Royale de Belgique''; Dutch: ''De Koninklijke Munt van België'') was responsible for minting all official coins of Kingdom of Belgium from 1832 to 2017. As of 2018 the official legal tender of Be ...
and the
National Bank of Belgium
The National Bank of Belgium (NBB; nl, Nationale Bank van België, french: Banque nationale de Belgique, german: Belgische Nationalbank) has been the central bank of Belgium since 1850. The National Bank of Belgium was established with 100% pr ...
.
The City of Brussels is also the capital of both the
French Community of Belgium
In Belgium, the French Community (french: Communauté française; ) refers to one of the three constituent constitutional linguistic communities. Since 2011, the French Community has used the name Wallonia-Brussels Federation (french: Fédé ...
and the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
.
The
Flemish Parliament
The Flemish Parliament (Dutch: , formerly called Flemish Council or ''Vlaamse Raad'') constitutes the legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic region and as a cultural communi ...
and
Flemish Government
The Flemish Government ( nl, Vlaamse regering ) is the executive branch of the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region of Belgium. It consists of a government cabinet, headed by the Minister-President and accountable to the Flemish Parliament, a ...
have their seats in Brussels, and so do the
Parliament of the French Community
The Parliament of the French Community (french: Parlement de la Communauté française or PCF) is the legislative assembly of the French Community of Belgium based in the Quartier Royal. It consists of all 75 members of the Walloon Parliament exce ...
and the
Government of the French Community
The Cabinet of the French Community of Belgium (french: Gouvernement de la Communauté française ) is the executive branch of the French Community of Belgium, and it sits in Brussels. It consists of a number of ministers chosen by the Parliamen ...
.

Municipalities
The 19
municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
(french: communes, link=no, nl, gemeenten, link=no) of the Brussels-Capital
Region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
are political subdivisions with individual responsibilities for the handling of local level duties, such as law enforcement and the upkeep of schools and roads within its borders.
Municipal administration is also conducted by a mayor, a council, and an executive.
In 1831, Belgium was divided into 2,739 municipalities, including the 19 in the Brussels-Capital Region.
Unlike most of the municipalities in Belgium, the ones located in the Brussels-Capital Region were not merged with others during mergers occurring in 1964, 1970, and 1975.
However, several municipalities outside the Brussels-Capital Region have been merged with the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
throughout its history, including
Laeken
() or () is a residential suburb in the north-western part of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It belongs to the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality of the City of Brussels and is mostly identified by the ...
,
Haren and
Neder-Over-Heembeek
Neder-Over-Heembeek (; ) is a northern part of the City of Brussels municipality, inside the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It is a former municipality which lost its municipality status when it was merged with the City of Brussels. ...
in 1921.
The largest municipality in area and population is the City of Brussels, covering and with 145,917 inhabitants; the least populous is
Koekelberg
Koekelberg (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren, Jette and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean. In common with all ...
with 18,541 inhabitants. The smallest in area is
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode () or Sint-Joost-ten-Node (), often simply called Saint-Josse or Sint-Joost, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the Ci ...
, which is only , but still has the highest population density in the region, with .
Watermael-Boitsfort
Watermael-Boitsfort () or Watermaal-Bosvoorde () is a residential suburb of the city of Brussels in Belgium, and one of the 19 municipalities which form the Brussels-Capital Region.
The municipality has a total area of of which 58 percent is cov ...
has the lowest population density in the region, with .
There is much controversy on the division of 19 municipalities for a highly urbanised region, which is considered as (half of) one city by most people. Some politicians mock the "19 baronies" and want to merge the municipalities under one city council and one mayor. That would lower the number of politicians needed to govern Brussels, and centralise the power over the city to make decisions easier, thus reduce the overall running costs. The current municipalities could be transformed into districts with limited responsibilities, similar to the current structure of
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, or to structures of other capitals like the
boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
in
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
or ''
arrondissements
An arrondissement (, , ) is any of various administrative divisions of France, Belgium, Haiti, certain other Francophone countries, as well as the Netherlands.
Europe
France
The 101 French departments are divided into 342 ''arrondissements'', ...
'' in
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, to keep politics close enough to the citizen.
In early 2016,
Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, from which it is separated ...
held a reputation as a safe haven for
jihadists
Jihadism is a neologism which is used in reference to "militant Islamic movements that are perceived as existentially threatening to the West" and "rooted in political Islam."Compare: Appearing earlier in the Pakistani and Indian media, Wes ...
in relation to the support shown by some residents towards the bombers who carried out the
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
and
Brussels attacks.
File:Town hall of Anderlecht (DSC 2233).jpg, Anderlecht
Anderlecht (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the south-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Forest, Molenbeek-Saint-Jean, and Saint-Gilles, as well as the ...
File:Auderghem CH2.jpg, Auderghem
Auderghem (former Dutch spelling, now used in French; pronounced ) or Oudergem () is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium).
Located to the southeast of the region, along the Woluwe valley and at the entrance to t ...
(Oudergem)
File:SintAgathaBerchemMC7229.jpg, Berchem-Sainte-Agathe (Sint-Agatha-Berchem)
File:Brussels, townhall oeg2043-00090 foto3 2015-06-07 08.38.jpg, City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
File:Town hall of Etterbeek (DSC 2183).jpg, Etterbeek
Etterbeek (French: ; Dutch: ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the municipalities of Auderghem, the City of Brussels, Ixelles, Schaerbeek, Wolu ...
File:EvereTownHall.jpg, Evere
Evere (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium). On 1 January 2006, the municipality had a total population of 33,462. The total area is which gives a population density of . In common with all of Brussels' m ...
File:MaisonCommunaleForest.jpg, Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
(Vorst)
File:Ganshoren town hall.jpg, Ganshoren
Ganshoren (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Jette, Koekelberg, and Sint-Agatha-Berchem, as well as the Flemish municipality of As ...
File:Town Hall Ixelles 1.jpg, Ixelles
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Brussels' city centre, it is geographically bisected by the City of Brussels. It is also bordered by the muni ...
(Elsene)
File:Jette voormalig gemeentehuis 27-04-2013.jpg, Jette
Jette (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Ganshoren, Koekelberg, and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean, as well as the Flemi ...
File:DSP.Maison communale.Koekelberg.JPG, Koekelberg
Koekelberg (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren, Jette and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean. In common with all ...
File:Gemeentehuis St Jans Molenbeek.jpg, Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, from which it is separated ...
(Sint-Jans-Molenbeek)
File:StGillesTownHall.jpg, Saint-Gilles (Sint-Gillis)
File:3592sintJosseTownHall.jpg, Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode () or Sint-Joost-ten-Node (), often simply called Saint-Josse or Sint-Joost, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the Ci ...
(Sint-Joost-ten-Node)
File:Hôtel communal de Schaerbeek (2) - 2264-0007-0.jpg, Schaerbeek
(French language, French and History of Dutch orthography, archaic Dutch, ) or (contemporary Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Re ...
(Schaarbeek)
File:3557uccleTownHall.jpg, Uccle
Uccle () or Ukkel () is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch). It is generally considered an affluent area of the city a ...
(Ukkel)
File:WatermaelBoitsfortTownHall.jpg, Watermael-Boitsfort
Watermael-Boitsfort () or Watermaal-Bosvoorde () is a residential suburb of the city of Brussels in Belgium, and one of the 19 municipalities which form the Brussels-Capital Region.
The municipality has a total area of of which 58 percent is cov ...
(Watermaal-Bosvoorde)
File:Town hall of Woluwe-Saint-Lambert during golden hour (DSC 2171).jpg, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert
Woluwe-Saint-Lambert () or Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe (Dutch, ) is one of the nineteen municipalities in the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It is a prosperous residential area, with a mixture of flats and detached, semi-detached and terraced hous ...
(Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe)
File:Mais.Comm.W-S-P.01.JPG, Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
Woluwe-Saint-Pierre () or Sint-Pieters-Woluwe () is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by Etterbeek, Auderghem and Woluwe-Saint-Lambert, as well as th ...
(Sint-Pieters-Woluwe)
Brussels-Capital Region

Political status
The Brussels-Capital Region is one of the three federated regions of Belgium, alongside the
Walloon Region
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
and the
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region ( nl, Vlaams Gewest, ),; german: Flämische Region usually simply referred to as Flanders ( nl, link=no, Vlaanderen ) ; german: link=no, Flandern is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and t ...
. Geographically and linguistically, it is a bilingual
enclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
in the monolingual Flemish Region. Regions are one component of Belgium's institutions; the three communities being the other component. Brussels' inhabitants deal with either the
French Community
The French Community (1958–1960; french: Communauté française) was the constitutional organization set up in 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which ...
or the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
for matters such as culture and education, as well as a
Common Community for competencies which do not belong exclusively to either Community, such as healthcare and social
welfare
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
.
Since the split of
Brabant Brabant is a traditional geographical region (or regions) in the Low Countries of Europe. It may refer to:
Place names in Europe
* London-Brabant Massif, a geological structure stretching from England to northern Germany
Belgium
* Province of Bra ...
in 1995, the Brussels Region does not belong to any of the
provinces of Belgium
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province and nor is it subdivided into provinces. Inst ...
, nor is it subdivided into provinces itself. Within the Region, 99% of the areas of provincial jurisdiction are assumed by the Brussels regional institutions and community commissions. Remaining is only the
governor of Brussels-Capital and some aides, analogously to provinces. Its status is roughly akin to that of a
federal district
A federal district is a type of administrative division of a federation, usually under the direct control of a federal government and organized sometimes with a single municipal body. Federal districts often include capital districts, and they e ...
.
Institutions

The Brussels-Capital Region is governed by a
parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
of 89 members (72 French-speaking, 17 Dutch-speaking—parties are organised on a linguistic basis) and an eight-member regional cabinet consisting of a
minister-president
A minister-president or minister president is the head of government in a number of European countries or subnational governments with a parliamentary or semi-presidential system of government where they preside over the council of ministers. It ...
, four ministers and three
state secretaries. By law, the cabinet must comprise two French-speaking and two Dutch-speaking ministers, one Dutch-speaking secretary of state and two French-speaking secretaries of state. The minister-president does not count against the language quota, but in practice every minister-president has been a bilingual francophone. The regional parliament can enact
ordinances (french: ordonnances, link=no, nl, ordonnanties, link=no), which have equal status as a national legislative act.
19 of the 72 French-speaking members of the Brussels Parliament are also members of the
Parliament of the French Community of Belgium, and, until 2004, this was also the case for six Dutch-speaking members, who were at the same time members of the
Flemish Parliament
The Flemish Parliament (Dutch: , formerly called Flemish Council or ''Vlaamse Raad'') constitutes the legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic region and as a cultural communi ...
. Now, people voting for a Flemish party have to vote separately for 6 directly elected members of the Flemish Parliament.
Agglomeration of Brussels
Before the creation of the Brussels-Capital Region, regional competences in the 19 municipalities were performed by the Brussels Agglomeration. The Brussels Agglomeration was an administrative division established in 1971. This decentralised administrative public body also assumed jurisdiction over areas which, elsewhere in Belgium, were exercised by municipalities or provinces.
The Brussels Agglomeration had a separate legislative council, but the by-laws enacted by it did not have the status of a legislative act. The only election of the council took place on 21 November 1971. The working of the council was subject to many difficulties caused by the linguistic and socio-economic tensions between the two communities.
After the creation of the Brussels-Capital Region, the Brussels Agglomeration was never formally abolished, although it no longer has a purpose.
French and Flemish communities

The
French Community
The French Community (1958–1960; french: Communauté française) was the constitutional organization set up in 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which ...
and the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
exercise their powers in Brussels through two community-specific public authorities: the
French Community Commission
The ''Commission communautaire française'' (COCOF) or the French Community Commission is the local representative of the French-speaking authorities in the Brussels-Capital Region, one of the three regions of Belgium.
On 3 December 2001, the ''A ...
(french: Commission communautaire française, link=no or COCOF) and the
Flemish Community Commission
The Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie (or VGC, or, in English, the Flemish Community Commission) is the local representative of the Flemish authorities in the Brussels-Capital Region, one of the three regions of Belgium. The VGC depends on the Flemish ...
( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie, link=no or VGC). These two bodies each have an assembly composed of the members of each linguistic group of the
Parliament of the Brussels-Capital Region
The Parliament of the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (French: ''Parlement de la Région de Bruxelles-Capitale'', Dutch: ''Parlement van het Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewe ...
. They also have a board composed of the ministers and secretaries of state of each linguistic group in the Government of the Brussels-Capital Region.
The French Community Commission has also another capacity: some legislative powers of the French Community have been devolved to the Walloon Region (for the French language area of Belgium) and to the French Community Commission (for the bilingual language area). The Flemish Community, however, did the opposite; it merged the Flemish Region into the Flemish Community. This is related to different conceptions in the two communities, one focusing more on the Communities and the other more on the Regions, causing an asymmetrical
federalism
Federalism is a combined or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments (Province, provincial, State (sub-national), state, Canton (administrative division), can ...
. Because of this devolution, the French Community Commission can enact
decree
A decree is a legal proclamation, usually issued by a head of state (such as the president of a republic or a monarch), according to certain procedures (usually established in a constitution). It has the force of law. The particular term used for ...
s, which are legislative acts.
Common Community Commission
A bi-communitarian public authority, the
Common Community Commission
The Common Community Commission (french: Commission communautaire commune, nl, Gemeenschappelijke Gemeenschapscommissie) is responsible for Brussels community matters that are common to both the French Community and the Flemish Community and for i ...
(french: Commission communautaire commune, link=no, COCOM, nl, Gemeenschappelijke Gemeenschapscommissie, link=no, GGC) also exists. Its assembly is composed of the members of the regional parliament, and its board are the ministers—not the secretaries of state—of the region, with the minister-president not having the right to vote. This commission has two capacities: it is a decentralised administrative public body, responsible for implementing cultural policies of common interest. It can give subsidies and enact
by-law
A by-law (bye-law, by(e)law, by(e) law), or as it is most commonly known in the United States bylaws, is a set of rules or law established by an organization or community so as to regulate itself, as allowed or provided for by some higher authorit ...
s. In another capacity, it can also enact ordinances, which have equal status as a national legislative act, in the field of the welfare powers of the communities: in the Brussels-Capital Region, both the French Community and the Flemish Community can exercise powers in the field of welfare, but only in regard to institutions that are unilingual (for example, a private French-speaking retirement home or the Dutch-speaking hospital of the
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) () is a Dutch and English-speaking research university located in Brussels, Belgium.The Vrije Universiteit Brussel is one of the five universities officially recognised by the Flemish Community, Flemish gov ...
). The Common Community Commission is responsible for policies aiming directly at private persons or at bilingual institutions (for example, the centres for social welfare of the 19 municipalities). Its ordinances have to be enacted with a majority in both linguistic groups. Failing such a majority, a new vote can be held, where a majority of at least one third in each linguistic group is sufficient.
Brussels and the European Union

Brussels serves as ''
de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' capital of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
(EU), hosting the major political
institutions of the Union. The EU has not declared a capital formally, though the
Treaty of Amsterdam
The Treaty of Amsterdam, officially the Treaty of Amsterdam amending the Treaty on European Union, the Treaties establishing the European Communities and certain related acts, was signed on 2 October 1997, and entered into force on 1 May 1999; i ...
formally gives Brussels the seat of the
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body o ...
(the executive branch of government) and the
Council of the European Union
The Council of the European Union, often referred to in the treaties and other official documents simply as the Council, and informally known as the Council of Ministers, is the third of the seven Institutions of the European Union (EU) as ...
(a legislative institution made up from executives of member states).
[European Commission publication: ''Europe in Brussels'' 2007] It locates the formal seat of
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adopts ...
in
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the Eu ...
, where votes take place, with the council, on the proposals made by the commission. However, meetings of political groups and committee groups are formally given to Brussels, along with a set number of plenary sessions. Three quarters of Parliament sessions now take place at its
Brussels hemicycle. Between 2002 and 2004, the
European Council
The European Council (informally EUCO) is a collegiate body that defines the overall political direction and priorities of the European Union. It is composed of the heads of state or government of the EU member states, the President of the E ...
also fixed its seat in the city.
In 2014, the Union hosted a
G7 summit
The Group of Seven (G7) is an inter-governmental, intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated membe ...
in the city.

Brussels, along with
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
and Strasbourg, began to host European institutions in 1957, soon becoming the centre of activities, as the Commission and Council based their activities in what has become the
European Quarter, in the east of the city.
Early building in Brussels was sporadic and uncontrolled, with little planning. The current major buildings are the
Berlaymont building
The Berlaymont () is an office building in Brussels, Belgium, which houses the headquarters of the European Commission, the executive branch of the European Union (EU). The structure is located on the Robert Schuman Roundabout at 200, rue de l ...
of the commission, symbolic of the quarter as a whole, the
Europa building
The Europa building is the seat of the European Council and Council of the European Union, located on the Rue de la Loi/Wetstraat in the European Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. Its defining feature is the multi-storey "lantern-shaped" constr ...
of the Council and the
Espace Léopold
The Espace Léopold (French; commonly used in English) or Leopoldruimte (Dutch; ) is the complex of parliament buildings in Brussels, Belgium, housing the European Parliament, a legislative chamber of the European Union (EU). It consists of a ...
of the Parliament.
Today, the presence has increased considerably, with the Commission alone occupying within the European Quarter (a quarter of the total office space in Brussels). The concentration and density has caused concern that the presence of the institutions has created a ''
ghetto
A ghetto, often called ''the'' ghetto, is a part of a city in which members of a minority group live, especially as a result of political, social, legal, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished t ...
effect'' in that part of the city.
However, the European presence has contributed significantly to the importance of Brussels as an international centre.
International institutions
Brussels has, since
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, become the administrative centre of many international organisations. The city is the political and administrative centre of the
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two Nor ...
(NATO).
NATO's Brussels headquarters houses
29 embassies and brings together over 4,500 staff from allied nations, their militaries, and civil service personnel. Many other international organisations such as the
World Customs Organization
The World Customs Organization (WCO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. The WCO works on customs-related matters including the development of international conventions, instruments, and tools on topics suc ...
and
Eurocontrol
The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol (stylised ''EUROCONTROL''), is an international organisation working to achieve safe and seamless air traffic management across Europe. Founded in 1960, Eur ...
, as well as international corporations, have their main institutions in the city. In addition, the main international
trade union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
confederations have their headquarters there: the
European Trade Union Confederation
The European Trade Union Confederation (ETUC) is the major trade union organisation representing workers at the European level. In its role as a European social partner, the ETUC works both in a consulting role with the European Commission and n ...
(ETUC), the
International Confederation of Free Trade Unions
The International Confederation of Free Trade Unions (ICFTU) was an international trade union. It came into being on 7 December 1949 following a split within the World Federation of Trade Unions (WFTU), and was dissolved on 31 October 2006 when ...
(ICFTU) and the
World Confederation of Labour
The World Confederation of Labour (WCL) was an international labour organization founded in 1920 and based in Europe. Totalitarian governments of the 1930s repressed the federation and imprisoned many of its leaders, limiting operations until the ...
(WCL).
Brussels is third in the number of international conferences it hosts,
also becoming one of the largest convention centres in the world.
The presence of the EU and the other international bodies has, for example, led to there being more ambassadors and journalists in Brussels than in
Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
The city hosts 120 international institutions, 181
embassies
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually deno ...
() and more than 2,500
diplomat
A diplomat (from grc, δίπλωμα; romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state or an intergovernmental institution such as the United Nations or the European Union to conduct diplomacy with one or more other states or internati ...
s, making it the second centre of diplomatic relations in the world (after
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
).
International school
An international school is an institution that promotes education in an international environment or framework. Although there is no uniform definition or criteria, international schools are usually characterized by a multinational student body a ...
s have also been established to serve this presence.
The "international community" in Brussels numbers at least 70,000 people. In 2009, there were an estimated 286
lobbying
In politics, lobbying, persuasion or interest representation is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agency, regulatory agencie ...
consultancies known to work in Brussels. Finally, Brussels has more than 1,400
NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in h ...
s.
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation

The
Treaty of Brussels
The Treaty of Brussels, also referred to as the Brussels Pact, was the founding treaty of the Western Union (alliance), Western Union (WU) between 1948 and 1954, when it was amended as the Modified Brussels Treaty (MTB) and served as the foundin ...
, which was signed on 17 March 1948 between Belgium,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
,
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
, the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, was a prelude to the establishment of the
intergovernmental military alliance
A military alliance is a formal Alliance, agreement between nations concerning national security. Nations in a military alliance agree to active participation and contribution to the defense of others in the alliance in the event of a crisis. ...
which later became the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Today, the alliance consists of 29 independent member countries across
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and Europe. Several countries also have diplomatic missions to NATO
through embassies in Belgium. Since 1949, a number of
NATO Summits
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
have been held in Brussels, the most recent taking place in June 2021.
The organisation's political and administrative
headquarters
Headquarters (commonly referred to as HQ) denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the to ...
are located on the / in
Haren, on the north-eastern perimeter of the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
. A new €750 million headquarters building begun in 2010 and was completed in 2017.
Eurocontrol

The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol, is an
international organisation
An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states an ...
which coordinates and plans
air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airs ...
across European
airspace
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as aerospace, which is the ...
. The corporation was founded in 1960 and has 41 member states.
Its headquarters are located in Haren, Brussels.
Demographics
Population

Brussels is located in one of the most
urbanised regions of Europe, between
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
,
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, the
Rhine-Ruhr
The Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region (german: Metropolregion Rhein-Ruhr) is the largest metropolitan region in Germany, with over ten million inhabitants. A polycentric conurbation with several major urban concentrations, the region covers ...
(Germany), and the
Randstad
The Randstad (; "Rim" or "Edge" City) is a roughly crescent-shaped conurbation in the central-western Netherlands, consisting primarily of the four largest Dutch cities (Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, and Utrecht); their suburbs, and many tow ...
(Netherlands). The Brussels-Capital Region has a population of around 1.2 million and has witnessed, in recent years, a remarkable increase in its population. In general, the population of Brussels is younger than the national average, and the gap between rich and poor is wider.
Brussels is the core of a built-up area that extends well beyond the region's limits. Sometimes referred to as the urban area of Brussels (french: aire urbaine de Bruxelles, link=no, nl, stedelijk gebied van Brussel, link=no) or Greater Brussels (french: Grand-Bruxelles, link=no, nl, Groot-Brussel, link=no), this area extends over a large part of the two Brabant provinces, including much of the surrounding
arrondissement of Halle-Vilvoorde and some small parts of the
arrondissement of Leuven
The Leuven Arrondissement (; ) is one of two arrondissements in the Belgian province of Flemish Brabant. It lies east of the Brussels-Capital Region. The arrondissement has an area of and has (as of January 1, 2017) 502,602 inhabitants.
Munici ...
in
Flemish Brabant
Flemish Brabant ( nl, Vlaams-Brabant ; french: Brabant flamand ) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Haina ...
, as well as the northern part of
Walloon Brabant
Walloon Brabant (french: Brabant wallon ; nl, Waals-Brabant ; wa, Roman Payis) is a province located in Belgium's French-speaking region of Wallonia. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the province of Flemish Brabant (Flemish Region) and ...
.
The metropolitan area of Brussels is divided into three levels. Firstly, the central agglomeration (within the regional borders), with a population of 1,218,255 inhabitants.
Adding the closest suburbs (french: banlieues, link=no, nl, buitenwijken, link=no) gives a total population of 1,831,496. Including the outer
commuter zone (
Brussels Regional Express Network
The Brussels S-train, also known as the Brussels Regional Express Network (french: Réseau Express Régional Bruxellois or RER); ( nl, Gewestelijk ExpresNet or GEN) is a suburban rail system in the Brussels Capital Region. It will offer fast conne ...
(RER/GEN) area), the population is 2,676,701.
Brussels is also part of a wider
diamond-shaped conurbation
A conurbation is a region comprising a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ca ...
, with
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
,
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, and
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic ...
, which has about 4.4 million inhabitants (a little more than 40% of the Belgium's total population).
Nationalities
There have been numerous migrations towards Brussels since the end of the 18th century, when the city acted as a common destination for
political refugees
The right of asylum (sometimes called right of political asylum; ) is an ancient juridical concept, under which people persecuted by their own rulers might be protected by another sovereign authority, like a second country or another ent ...
from neighbouring or more distant countries, particularly France. From 1871, many of the
Paris Communards fled to Brussels, where they received political asylum. Other notable international exiles living in Brussels at the time included
Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
,
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
,
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (, , ; 15 January 1809, Besançon – 19 January 1865, Paris) was a French socialist,Landauer, Carl; Landauer, Hilde Stein; Valkenier, Elizabeth Kridl (1979) 959 "The Three Anticapitalistic Movements". ''European Socia ...
,
Georges Boulanger
Georges Ernest Jean-Marie Boulanger (29 April 1837 – 30 September 1891), nicknamed Général Revanche ("General Revenge"), was a French general and politician. An enormously popular public figure during the second decade of the Third Repub ...
, and
Léon Daudet
Léon Daudet (; 16 November 1867 – 2 July 1942) was a French journalist, writer, an active monarchist, and a member of the Académie Goncourt.
Move to the right
Daudet was born in Paris. His father was the novelist Alphonse Daudet, his moth ...
, to name a few. Attracted by the industrial opportunities, many workers moved in, first from the other
Belgian provinces (mainly rural residents from
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
) and France, then from
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern regions of Europe, region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countrie ...
an, and more recently from
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
an and
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n countries.
Nowadays, Brussels is home to a large number of immigrants and
émigré
An ''émigré'' () is a person who has emigrated, often with a connotation of political or social self-exile. The word is the past participle of the French ''émigrer'', "to emigrate".
French Huguenots
Many French Huguenots fled France followi ...
communities, as well as labour migrants, former foreign students or
expatriate
An expatriate (often shortened to expat) is a person who resides outside their native country. In common usage, the term often refers to educated professionals, skilled workers, or artists taking positions outside their home country, either ...
s, and many Belgian families in Brussels can claim at least one foreign grandparent. At the last Belgian census in 1991, 63.7% of inhabitants in Brussels-Capital Region answered that they were Belgian citizens, born as such in Belgium, indicating that more than a third of residents had not been born in the country.
[ – The linguistic situation in Belgium (and in particular various estimations of the population speaking French and Dutch in Brussels) is discussed in detail.] According to
Statbel (the Belgian Statistical Office), in 2020, taking into account the nationality of birth of the parents, 74.3% of the population of the Brussels-Capital Region was of foreign origin and 41.8% was of non-European origin (including 28.7% of African origin). Among those aged under 18, 88% were of foreign origin and 57% of non-European origin (including 42.4% of African origin).
[Michèle Tribalat]
Population d'origine étrangère en Belgique en 2020
, 8 February 2021
This large concentration of immigrants and their descendance includes many of
Moroccan (mainly
Riffian and other
Berbers
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg
, caption = The Berber ethnic flag
, population = 36 million
, region1 = Morocco
, pop1 = 14 million to 18 million
, region2 = Algeria
, pop2 ...
) and
Turkish ancestry, together with French-speaking black Africans from former
Belgian colonies, such as the
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
,
Rwanda
Rwanda (; rw, u Rwanda ), officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator ...
and
Burundi
Burundi (, ), officially the Republic of Burundi ( rn, Repuburika y’Uburundi ; Swahili language, Swahili: ''Jamuhuri ya Burundi''; French language, French: ''République du Burundi'' ), is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley at the ...
. People of foreign origin make up nearly 70%
of the population of Brussels, most of whom have been
naturalised
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the i ...
following the great 1991 reform of the naturalisation process. In 2012, about 32% of city residents were of non-Belgian
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an origin (mainly expatriates from France, Romania, Italy, Spain, Poland, and Portugal) and 36% were of another background, mostly from Morocco, Turkey and
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
. Among all major migrant groups from outside the EU, a majority of the permanent residents have acquired Belgian nationality.
Languages
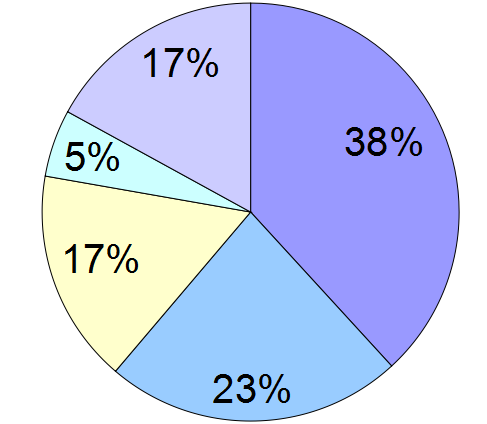
Brussels was historically
Dutch-speaking
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' i ...
, using the
Brabantian dialect
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic or Brabantine ( nl, Brabants, Standard Dutch pronunciation: , ), is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant, which corresponded mainly to the Dutch provi ...
,
but over the two past centuries
has become the predominant language of the city.
The main cause of this transition was the rapid
assimilation of the local
Flemish population,
amplified by immigration from
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
.
The
rise of French in public life gradually began by the end of the 18th century,
quickly accelerating after
Belgian independence.
Dutch — of which
standardisation
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ...
in Belgium was still very weak
— could not compete with French, which was the exclusive language of the judiciary, the administration, the army, education, cultural life and the media, and thus necessary for
social mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given society ...
.
The value and prestige of the French language was universally acknowledged
to such an extent that after 1880,
and more particularly after the turn of the 20th century,
proficiency in French among Dutch-speakers in Brussels increased spectacularly.
Although a majority of the population remained bilingual until the second half of the 20th century,
family transmission of the historic Brabantian dialect
declined,
leading to an increase of monolingual French-speakers from 1910 onwards.
From the mid-20th century, the number of monolingual French-speakers surpassed the number of mostly bilingual Flemish inhabitants.
This process of assimilation weakened after the 1960s,
as the
language border was fixed, the status of Dutch as an official language of Belgium was reinforced,
and the economic centre of gravity shifted northward to
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
.
However, with the continuing arrival of immigrants and the post-war emergence of Brussels as a
centre of international politics, the relative position of Dutch continued to decline.
Furthermore, as Brussels' urban area expanded,
a further number of Dutch-speaking municipalities in the
Brussels periphery
The Brussels Periphery (, i.e. the "Brussels Rim", or ''Vlaamse Rand'', i.e. the "Flemish Rim", or just ''De Rand'', "the Rim"; ) refers to 19 Flemish municipalities that encircle the Brussels-Capital Region. The Brussels Region is an enclave of ...
also became predominantly French-speaking.
This phenomenon of expanding Francisation — dubbed "oil slick" by its opponents
— is, together with the future of Brussels,
one of the most controversial topics in
Belgian politics
The politics of Belgium take place in the framework of a federal, representative democratic, constitutional monarchy. The King of the Belgians is the head of state, and the prime minister of Belgium is the head of government, in a multi-part ...
.

Today, the Brussels-Capital Region is legally bilingual, with both French and Dutch having official status,
as is the administration of the 19 municipalities.
The creation of this bilingual, full-fledged region, with its own competencies and jurisdiction, had long been hampered by different visions of Belgian federalism. Nevertheless, some communitarian issues remain.
Flemish political parties demanded, for decades, that the Flemish part of
Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde
The area within Belgium known as Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde encompasses the bilingual— French and Dutch—Brussels-Capital Region, which coincides with the arrondissement of Brussels-Capital and the surrounding Dutch-speaking area of Halle-Vilvo ...
(BHV) ''arrondissement'' be separated from the Brussels Region (which made Halle-Vilvoorde a monolingual Flemish electoral and judicial district). BHV was divided mid-2012. The French-speaking population regards the language border as artificial and demands the extension of the bilingual region to at least all six
municipalities with language facilities
There are 27 municipalities with language facilities ( nl, faciliteitengemeenten; french: communes à facilités; german: Fazilitäten-Gemeinden) in Belgium which must offer linguistic services to residents in Dutch, French, or German in additio ...
in the surroundings of Brussels. Flemish politicians have strongly rejected these proposals.
Owing to migration and to its international role, Brussels is home to a large number of native speakers of languages other than French or Dutch. Currently, about half of the population speaks a home language other than these two.
In 2013, academic research showed that approximately 17% of families spoke none of the official languages in the home, while in a further 23% a foreign language was used alongside French. The share of unilingual French-speaking families had fallen to 38% and that of Dutch-speaking families to 5%, while the percentage of bilingual Dutch-French families reached 17%. At the same time, French remains widely spoken: in 2013, French was spoken "well to perfectly" by 88% of the population, while for Dutch this percentage was only 23% (down from 33% in 2000);
the other most commonly known languages were English (30%), Arabic (18%), Spanish (9%), German (7%) and Italian and Turkish (5% each).
Despite the rise of English as a second language in Brussels, including as an unofficial compromise language between French and Dutch, as well as the working language for some of its international businesses and institutions, French remains the ''lingua franca'' and all public services are conducted exclusively in French or Dutch.
The original dialect of Brussels (known as
Brusselian, and also sometimes referred to as Marols or Marollien),
a form of
Brabantic
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic or Brabantine ( nl, Brabants, Standard Dutch pronunciation: , ), is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant, which corresponded mainly to the Dutch provi ...
(the variant of Dutch spoken in the ancient
Duchy of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Neth ...
) with a significant number of loanwords from French, still survives among a small minority of inhabitants called ''Brusseleers''
[Mary Anne Evans, ''Frommer's Brussels and Bruges Day by Day. First Edition'' (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2008), 71.] (or ''Brusseleirs''), many of them quite bi- and multilingual, or educated in French and not writing in Dutch.
The ethnic and national self-identification of Brussels' inhabitants is nonetheless sometimes quite distinct from the French and Dutch-speaking communities. For the French-speakers, it can vary from Francophone Belgian,
(French
demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
for an inhabitant of Brussels),
Walloon (for people who migrated from the Walloon Region at an adult age); for Flemings living in Brussels, it is mainly either Dutch-speaking Belgian, Flemish or (Dutch demonym for an inhabitant), and often both. For the ''Brusseleers'', many simply consider themselves as belonging to Brussels.
Religions

Historically, Brussels has been predominantly
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, especially since the expulsion of
Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
in the 16th century. This is clear from the large number of historical churches in the region, particularly in the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
. The pre-eminent Catholic
cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
in Brussels is the
Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula
nl, Kathedraal van Sint-Michiel en Sint-Goedele
, native_name_lang =
, image = Saints-Michel-et-Gudule Luc Viatour.jpg
, imagesize = 200px
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, landscape ...
, serving as the
co-cathedral of the
Archdiocese of Mechelen–Brussels. On the north-western side of the region, the
National Basilica of the Sacred Heart is a
Minor Basilica
In the Catholic Church, a basilica is a designation given by the Pope to a church building. Basilicas are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building need not be a basilica in the architectural sense (a rectangular ...
and
parish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in community activities, ...
, as well as the
14th largest church building in the world. The
Church of Our Lady of Laeken
nl, Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekerk van Laken
, native_name_lang =
, image = Église Notre-Dame de Laeken (DSCF1248-DSCF1251).jpg
, imagesize = 271
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, caption ...
holds the tombs of many members of the
Belgian Royal Family
Belgium is a constitutional, hereditary, and popular monarchy. The monarch is titled king or queen of the Belgians ( nl, Koning(in) der Belgen, french: Roi / Reine des Belges}, german: König(in) der Belgier) and serves as the country's he ...
, including all the former
Belgian monarchs
This is a list of Belgian monarchs from 1831 when the first Belgian king, Leopold I, ascended the throne, after Belgium seceded from the Kingdom of the Netherlands during the Belgian Revolution of 1830.
Under the Belgian Constitution, the Belg ...
, within the
Royal Crypt.
In reflection of its multicultural makeup, Brussels hosts a variety of religious communities, as well as large numbers of
atheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
and
agnostics
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
. Minority faiths include
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
,
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
,
Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first m ...
,
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, and
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
. According to a 2016 survey, approximately 40% of residents of Brussels declared themselves
Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
(12% were practising Catholics and 28% were non-practising Catholics), 30% were
non-religious
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and anti ...
, 23% were
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
(19% practising, 4% non-practising), 3% were
Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
and 4% were of another religion.
As guaranteed by Belgian law, recognised religions and non-religious philosophical organisations (french: organisations laïques, link=no, nl, vrijzinnige levensbeschouwelijke organisaties, link=no)
enjoy public funding and school courses. It was once the case that every pupil in an official school from 6 years old to 18 had to choose 2 hours per week of compulsory religious—or non-religious-inspired morals—courses. However, in 2015, the Belgian Constitutional court ruled religious studies could no longer be required in the
primary
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
* ...
and
secondary
Secondary may refer to: Science and nature
* Secondary emission, of particles
** Secondary electrons, electrons generated as ionization products
* The secondary winding, or the electrical or electronic circuit connected to the secondary winding i ...
educational systems.

Brussels has a large concentration of
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
, mostly of Moroccan, Turkish, Syrian and Guinean ancestry. The
Great Mosque of Brussels, located in the
Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark, is the oldest
mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
in Brussels. Belgium does not collect statistics by ethnic background or religious beliefs, so exact figures are unknown. It was estimated that, in 2005, people of Muslim background living in the Brussels Region numbered 256,220 and accounted for 25.5% of the city's population, a much higher concentration than those of the other regions of Belgium.
Culture
Architecture
The architecture in Brussels is diverse, and spans from the clashing combination of
Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
,
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
, and
Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
styles on the
Grand-Place
The Grand-Place (French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or Grote Markt (Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque guildhalls of the former Guilds of Brussels and two larger ...
to the
postmodern
Postmodernism is an intellectual stance or mode of discourseNuyen, A.T., 1992. The Role of Rhetorical Devices in Postmodernist Discourse. Philosophy & Rhetoric, pp.183–194. characterized by skepticism toward the " grand narratives" of moderni ...
buildings of the
EU institutions
The institutions of the European Union are the seven principal decision-making bodies of the European Union and the Euratom. They are, as listed in Article 13 of the Treaty on European Union:
* the European Parliament,
* the European Council ...
.

Very little
medieval architecture
Medieval architecture is architecture common in the Middle Ages, and includes religious, civil, and military buildings. Styles include pre-Romanesque, Romanesque, and Gothic. While most of the surviving medieval architecture is to be seen in c ...
is preserved in Brussels. Buildings from that period are mostly found in the historical centre (called ),
Saint Géry/Sint-Goriks and / neighbourhoods. The
Brabantine Gothic
Brabantine Gothic, occasionally called Brabantian Gothic, is a significant variant of Gothic architecture that is typical for the Low Countries. It surfaced in the first half of the 14th century at St. Rumbold's Cathedral in the City of Mechele ...
Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula
nl, Kathedraal van Sint-Michiel en Sint-Goedele
, native_name_lang =
, image = Saints-Michel-et-Gudule Luc Viatour.jpg
, imagesize = 200px
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, landscape ...
remains a prominent feature in the skyline of downtown Brussels. Isolated portions of the
first city walls were saved from destruction and can be seen to this day. One of the only remains of the
second walls is the
Halle Gate
The Halle Gate (french: Porte de Hal, ; nl, Hallepoort) is a former medieval city gate and the last vestige of the second walls of Brussels, Belgium. Built between 1381 and 1383, it was heavily restored in the 19th century in its current neo- ...
. The Grand-Place is the main attraction in the city centre and has been a
UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
since 1998. The square is dominated by the 15th century
Flamboyant
Flamboyant (from ) is a form of late Gothic architecture that developed in Europe in the Late Middle Ages and Renaissance, from around 1375 to the mid-16th century. It is characterized by double curves forming flame-like shapes in the bar-tr ...
Town Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
, the
neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
''
Breadhouse'' and the Baroque
guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a "guild hall" or "guild house", is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commonly become town halls and in som ...
s of the former
Guilds of Brussels
The Guilds of Brussels (french: Guildes de Bruxelles, nl, Gilden van Brussel), grouped in the Nine Nations of Brussels (french: Neuf Nations de Bruxelles, nl, Negen Naties van Brussel), were associations of craft guilds that dominated the ec ...
. ''
Manneken Pis
''Manneken Pis'' (; ) is a landmark bronze fountain sculpture in central Brussels, Belgium, depicting a puer mingens; a naked little boy urinating into the fountain's basin. Though its existence is attested as early as the 15th century, it wa ...
'', a fountain containing a small
bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
sculpture of a urinating youth, is a tourist attraction and
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
of the city.

The
neoclassical style of the 18th and 19th centuries is represented in the Royal Quarter/Coudenberg area, around
Brussels' Park and the
Place Royale/Koningsplein. Examples include the
Royal Palace
This is a list of royal palaces, sorted by continent.
Africa
* Abdin Palace, Cairo
* Al-Gawhara Palace, Cairo
* Koubbeh Palace, Cairo
* Tahra Palace, Cairo
* Menelik Palace
* Jubilee Palace
* Guenete Leul Palace
* Imperial Palace- Massa ...
, the
Church of St. James on Coudenberg, the
Palace of the Nation
The Federal Parliament is the bicameral parliament of Belgium. It consists of the Chamber of Representatives (Dutch: , french: Chambre des Représentants, german: Abgeordnetenkammer) and the Senate (Dutch: , french: Sénat, german: Senat). It s ...
(Parliament building), the
Academy Palace
The Academy Palace or Palace of the Academies (french: Palais des Académies, nl, Paleis der Academiën) is a neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally built between 1823 and 1828 for Prince William II of Orange. Today, it ...
, the
Palace of Charles of Lorraine
The Palace of Charles of Lorraine (french: Palais de Charles de Lorraine, nl, Paleis van Karel van Lotharingen) is a neoclassical palace in the Royal Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. Its construction started in 1757 to serve as the residence of ...
, the
Palace of the Count of Flanders
The Palace of the Count of Flanders (french: Palais du Comte de Flandre, nl, Paleis van de Graaf van Vlaanderen) is a neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally built between 1776 and 1781 for Countess Brigitte of Tirimont-Te ...
and the
Egmont Palace
The Egmont Palace (french: Palais d'Egmont, nl, Egmontpaleis), also sometimes known as the Arenberg Palace (french: Palais d'Arenberg, link=no, nl, Arenbergpaleis, link=no), is a neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally bu ...
. Other uniform neoclassical ensembles can be found around the
Place des Martyrs/Martelaarsplein and the /. Some additional landmarks in the centre are the
Royal Saint-Hubert Galleries (1847), one of the oldest covered shopping arcades in Europe, the
Congress Column
The Congress Column (french: Colonne du Congrès, nl, Congreskolom) is a monumental column in Brussels, Belgium, commemorating the creation of the Belgian Constitution by the National Congress of 1830–31. Inspired by Trajan's Column in Rome ...
(1859), the former
Brussels Stock Exchange
The Brussels Stock Exchange (french: Bourse de Bruxelles, nl, Beurs van Brussel), abbreviated to BSE, was founded in Brussels, Belgium, by decree of Napoleon in 1801. In 2002, the BSE merged with the Amsterdam, Lisbon and Paris stock exchang ...
building (1873) and the
Palace of Justice (1883). The latter, designed by
Joseph Poelaert
Joseph Poelaert (21 March 1817 – 3 November 1879) was a Belgian architect. He was entrusted with important projects in Brussels, such as Saint Catherine's Church, the Church of Our Lady of Laeken, the Congress Column, the Royal Theatre of la ...
, in
eclectic
Eclectic may refer to:
Music
* ''Eclectic'' (Eric Johnson and Mike Stern album), 2014
* ''Eclectic'' (Big Country album), 1996
* Eclectic Method, name of an audio-visual remix act
* Eclecticism in music, the conscious use of styles alien to th ...
style, is reputed to be the largest building constructed in the 19th century.
Located outside the historical centre, in a greener environment bordering the
European Quarter, are the
Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark with its
memorial arcade and nearby museums, and in
Laeken
() or () is a residential suburb in the north-western part of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It belongs to the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality of the City of Brussels and is mostly identified by the ...
, the
Royal Palace of Laeken
The Palace of Laeken or Castle of Laeken (french: Château de Laeken, nl, Kasteel van Laken, german: Schloss zu Laeken) is the official residence of the King of the Belgians and the Belgian Royal Family. It lies in the Brussels-Capital Regio ...
and the Royal Domain with its large
greenhouses
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These s ...
, as well as the
Museums of the Far East
The Museums of the Far East (french: Musées d'Extrême-Orient, nl, Musea van het Verre Oosten) is a complex of three museums in Laeken, City of Brussels, Belgium, dedicated to Oriental art and culture, specifically that of China and Japan. C ...
.
Also particularly striking are the buildings in the
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
style, most famously by the Belgian architects
Victor Horta
Victor Pierre Horta (; Victor, Baron Horta after 1932; 6 January 1861 – 8 September 1947) was a Belgian architect and designer, and one of the founders of the Art Nouveau movement. His Hôtel Tassel in Brussels, built in 1892–93, is often ...
,
Paul Hankar
Paul Hankar (11 December 1859 – 17 January 1901) was a Belgian architect and furniture designer, and an innovator in the Art Nouveau style.
Career
Hankar was born at Frameries, in Hainaut, Belgium, the son of a stonemason. He studied at the ...
and
Henry Van de Velde
Henry Clemens van de Velde (; 3 April 1863 – 15 October 1957) was a Belgian painter, architect, interior designer, and art theorist. Together with Victor Horta and Paul Hankar, he is considered one of the founders of Art Nouveau in Belgium.'' ...
. Some of Brussels' municipalities, such as
Schaerbeek
(French language, French and History of Dutch orthography, archaic Dutch, ) or (contemporary Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Re ...
,
Etterbeek
Etterbeek (French: ; Dutch: ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the municipalities of Auderghem, the City of Brussels, Ixelles, Schaerbeek, Wolu ...
,
Ixelles
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Brussels' city centre, it is geographically bisected by the City of Brussels. It is also bordered by the muni ...
, and
Saint-Gilles, were developed during the heyday of Art Nouveau and have many buildings in that style. The
Major Town Houses of the Architect Victor Horta—
Hôtel Tassel
The Hôtel Tassel (french: Hôtel Tassel, nl, Hotel Tassel) is a town house in Brussels, Belgium, designed by Victor Horta for the scientist and professor Emile Tassel, and built from 1892 to 1893. It is generally considered the first true Ar ...
(1893),
Hôtel Solvay
The Hôtel Solvay (french: Hôtel Solvay, nl, Hotel Solvay) is a large Art Nouveau town house designed by Victor Horta on the Avenue Louise/Louizalaan in Brussels, Belgium. The house was commissioned by Armand Solvay, the son of the chemist ...
(1894),
Hôtel van Eetvelde
The Hôtel van Eetvelde (french: Hôtel van Eetvelde, nl, Hotel van Eetvelde) is a town house designed in 1895 by Victor Horta for Edmond van Eetvelde, administrator of Congo Free State. It is located at 4, / in Brussels, Belgium.
Together ...
(1895) and the
Horta Museum
The Horta Museum (french: Musée Horta, nl, Hortamuseum) is a museum dedicated to the life and work of the Belgian Art Nouveau architect Victor Horta and his time. The museum is housed in Horta's former town house and workshop (french: Maison ...
(1901)—have been listed as a
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
since 2000.
Another example of Brussels' Art Nouveau is the
Stoclet Palace (1911), by the Viennese architect
Josef Hoffmann
Josef Hoffmann (15 December 1870 – 7 May 1956) was an Austrian- Moravian architect and designer. He was among the founders of Vienna Secession and co-establisher of the Wiener Werkstätte. His most famous architectural work is the Stoclet Pa ...
, designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in June 2009.
Art Nouveau in Brussels
The Art Nouveau movement of architecture and design first appeared in Brussels, Belgium, in the early 1890s, and quickly spread to France and to the rest of Europe. It began as a reaction against the formal vocabulary of European academic art, ...
">
File:Victor Horta Hotel Tassel.JPG,
Hôtel Tassel
The Hôtel Tassel (french: Hôtel Tassel, nl, Hotel Tassel) is a town house in Brussels, Belgium, designed by Victor Horta for the scientist and professor Emile Tassel, and built from 1892 to 1893. It is generally considered the first true Ar ...
by
Victor Horta
Victor Pierre Horta (; Victor, Baron Horta after 1932; 6 January 1861 – 8 September 1947) was a Belgian architect and designer, and one of the founders of the Art Nouveau movement. His Hôtel Tassel in Brussels, built in 1892–93, is often ...
(1893)
File:Tassel House stairway-00.JPG, Stairway in Hôtel Tassel
File:Hôtel Ciamberlani (DSCF7523).jpg, Hôtel Ciamberlani by
Paul Hankar
Paul Hankar (11 December 1859 – 17 January 1901) was a Belgian architect and furniture designer, and an innovator in the Art Nouveau style.
Career
Hankar was born at Frameries, in Hainaut, Belgium, the son of a stonemason. He studied at the ...
(1897)
File:Old England facade, Brussels (DSCF7544).jpg, Former
Old England department store by
Paul Saintenoy (1899)
File:Maison Saint-Cyr (DSCF7558).jpg,
Saint-Cyr House
The Saint-Cyr House (french: Maison Saint-Cyr, nl, Huis Saint-Cyr) is a town house in Brussels, Belgium. It was built by the architect Gustave Strauven, between 1901 and 1903, in Art Nouveau style. It is Strauven's most important building, and ...
by
Gustave Strauven
Gustave Strauven (23 June 1878 – 19 March 1919) was a Belgian architect of the Art Nouveau style. He created more than 30 buildings, using new technologies and incorporating wrought iron floral motifs.
Biography
Gustave Strauven was born in ...
(1903)
File:Maison Cauchie-445.jpg,
Cauchie House
The Cauchie House (french: Maison Cauchie, nl, Cauchiehuis) is a town house in Brussels, Belgium. It was built in 1905 by Art Nouveau architect, painter, and designer Paul Cauchie, in Etterbeek, next to the Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark. ...
by
Paul Cauchie (1905)
File:Maison Cauchie sgraffitopaneel.jpg,
Sgraffito
''Sgraffito'' (; plural: ''sgraffiti'') is a technique either of wall decor, produced by applying layers of plaster tinted in contrasting colours to a moistened surface, or in pottery, by applying to an unfired ceramic body two successive laye ...
panel in the Cauchie House
File:20120923 Brussels PalaisStoclet Hoffmann DSC06725 PtrQs.jpg,
Stoclet Palace by
Josef Hoffmann
Josef Hoffmann (15 December 1870 – 7 May 1956) was an Austrian- Moravian architect and designer. He was among the founders of Vienna Secession and co-establisher of the Wiener Werkstätte. His most famous architectural work is the Stoclet Pa ...
(1911)
Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unite ...
structures in Brussels include the Résidence Palace (1927) (now part of the
Europa building
The Europa building is the seat of the European Council and Council of the European Union, located on the Rue de la Loi/Wetstraat in the European Quarter of Brussels, Belgium. Its defining feature is the multi-storey "lantern-shaped" constr ...
), the
Centre for Fine Arts
The Centre for Fine Arts (french: Palais des Beaux-Arts, nl, Paleis voor Schone Kunsten) is a multi-purpose cultural venue in Brussels, Belgium. It is often referred to as BOZAR (a homophone of ''Beaux-arts'') in French or PSK in Dutch. The b ...
(1928), the
Villa Empain
The Villa Empain is a former private residence in Brussels, Belgium, which currently serves as a cultural centre and exhibition space. Built in 1930–1934 in Art Deco style by the Swiss-Belgian architect , the villa was commissioned by Baron L ...
(1934), the
Town Hall of Forest (1938), and the
Flagey Building
The Flagey Building (french: Bâtiment Flagey, nl, Flageygebouw) also known as Radio House (french: Maison de la Radio, nl, Radiohuis) is a building located in Ixelles, a municipality of Brussels, Belgium, housing the Flagey cultural centre. ...
(formerly known as the ''Maison de la Radio'') on the
Place Eugène Flagey/Eugène Flageyplein (1938) in Ixelles. Some religious buildings from the
interwar era
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relativel ...
were also constructed in that style, such as the
Church of St. John the Baptist (1932) in Molenbeek and the
Church of St. Augustine (1935) in Forest. Completed only in 1969, and combining Art Deco with
neo-Byzantine
Neo-Byzantine architecture (also referred to as Byzantine Revival) was a revival movement, most frequently seen in religious, institutional and public buildings. It incorporates elements of the Byzantine style associated with Eastern and Orth ...
elements, the
Basilica of the Sacred Heart in
Koekelberg
Koekelberg (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren, Jette and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean. In common with all ...
is one of the
largest churches by area in the world, and its
cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, from ...
provides a panoramic view of Brussels and its outskirts. Another example are the exhibition halls of the Centenary Palace, built for the
1935 World's Fair on the
Heysel/Heizel Plateau in northern Brussels, home to the Brussels Exhibition Centre (
Brussels Expo
The Brussels Exhibition Centre (french: Parc des Expositions de Bruxelles, nl, Tentoonstellingspark van Brussel), also known as Brussels Expo, is the most important event complex in Brussels, Belgium. Located on the Heysel Plateau, Heysel/Heiz ...
).

The
Atomium
The Atomium ( , , ) is a landmark building in Brussels, Belgium, originally constructed for the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (Expo '58). It is located on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Laeken (northern part of the City of Brussels), where the exh ...
is a symbolic
modernist
Modernism is both a philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new forms of art, philosophy, an ...
structure, located on the Heysel Plateau, which was originally built for the 1958 World's Fair (
Expo '58
Expo 58, also known as the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (french: Exposition Universelle et Internationale de Bruxelles de 1958, nl, Brusselse Wereldtentoonstelling van 1958), was a world's fair held on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Brussels, Bel ...
). It consists of nine steel spheres connected by tubes, and forms a model of an
iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
(specifically, a
unit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessaril ...
), magnified 165 billion times. The architect
André Waterkeyn
André Waterkeyn (23 August 1917 – 4 October 2005) was a Belgian engineer, born in Wimbledon, best known for creating the Atomium.
Waterkeyn was the economic director of Fabrimetal (now Agoria), a federation of metallurgical companies when i ...
devoted the building to science. It is now considered a
landmark
A landmark is a recognizable natural or artificial feature used for navigation, a feature that stands out from its near environment and is often visible from long distances.
In modern use, the term can also be applied to smaller structures or f ...
of Brussels. Next to the Atomium, is
Mini-Europe
Mini-Europe is a miniature park located in ''Bruparck'', at the foot of the Atomium, in Brussels, Belgium. Mini-Europe has reproductions of monuments in the European Union and other countries within the continent of Europe on display, at a scale o ...
miniature park
A miniature park is a display of miniature buildings and models, usually as a recreational and tourist attraction open to the public. A miniature park may contain a model of a single city or town, often called a miniature city or model village ...
, with 1:25 scale
maquette
A ''maquette'' (French word for scale model, sometimes referred to by the Italian names ''plastico'' or ''modello'') is a scale model or rough draft of an unfinished sculpture. An equivalent term is ''bozzetto'', from the Italian word for "sketc ...
s of famous buildings from across Europe.

Since the second half of the 20th century, modern office towers have been built in Brussels (
Madou Tower,
Rogier Tower
The Rogier Tower (french: Tour Rogier, nl, Rogiertoren) is a skyscraper located in the Northern Quarter central business district of Brussels, Belgium. It owes its name to the Place Charles Rogier/Karel Rogierplein on which it is situated. It ...
,
Proximus Towers
The Proximus Towers (french: Tours Proximus, nl, Proximus-torens, known as the Belgacom Towers before the company's name change) are twin skyscrapers on the / in the Northern Quarter central business district of Brussels, Belgium. The buildings ...
,
Finance Tower
The Finance Tower (french: Tour des Finances, nl, Financietoren) is a skyscraper in the Northern Quarter central business district of Brussels, Belgium. It was designed by the architects Hugo Van Kuyck, Marcel Lambrichs and Léon Stynen and buil ...
, the
World Trade Center
World Trade Centers are sites recognized by the World Trade Centers Association.
World Trade Center may refer to:
Buildings
* List of World Trade Centers
* World Trade Center (2001–present), a building complex that includes five skyscrapers, a ...
, among others). There are some thirty towers, mostly concentrated in the city's
main business district: the
Northern Quarter (also called ''Little Manhattan''), near
Brussels-North railway station
Brussels-North railway station (french: Gare de Bruxelles-Nord, nl, Station Brussel-Noord), officially Brussels-North (french: Bruxelles-Nord, link=no, nl, Brussel-Noord, link=no), is one of the three major railway stations in Brussels, Bel ...
. The
South Tower, standing adjacent to
Brussels-South railway station
Brussels-South railway station (french: Gare de Bruxelles-Midi, nl, Station Brussel-Zuid, IATA code: ZYR), officially Brussels-South (french: Bruxelles-Midi, link=no, nl, Brussel-Zuid, link=no), is a major railway station in Brussels, Belgium ...
, is the
tallest building in Belgium, at . Along the
North–South connection
The North–South connection (french: Jonction Nord-Midi, nl, Noord-Zuidverbinding) is a railway link of national and international importance through central Brussels, Belgium, that connects the major railway stations in the city. It is line ...
, is the State Administrative City, an administrative complex in the
International Style. The postmodern buildings of the
Espace Léopold
The Espace Léopold (French; commonly used in English) or Leopoldruimte (Dutch; ) is the complex of parliament buildings in Brussels, Belgium, housing the European Parliament, a legislative chamber of the European Union (EU). It consists of a ...
complete the picture.
The city's embrace of modern architecture translated into an ambivalent approach towards historic preservation, leading to the destruction of notable architectural landmarks, most famously the
Maison du Peuple/Volkshuis by Victor Horta, a process known as
Brusselisation
In urban planning, Brusselization ( UK and US) or Brusselisation ( UK variant) (french: bruxellisation, nl, verbrusseling) is "the indiscriminate and careless introduction of modern high-rise buildings into gentrified neighbourhoods" and has b ...
.
Arts

Brussels
contains over 80 museums. The
Royal Museums of Fine Arts has an extensive collection of various painters, such as
Flemish old masters like
Bruegel,
Rogier van der Weyden
Rogier van der Weyden () or Roger de la Pasture (1399 or 140018 June 1464) was an early Netherlandish painter whose surviving works consist mainly of religious triptychs, altarpieces, and commissioned single and diptych portraits. He was highly ...
,
Robert Campin
Robert Campin (c. 1375 – 26 April 1444), now usually identified with the Master of Flémalle (earlier the Master of the Merode Triptych, before the discovery of three other similar panels), was the first great master of Early Netherlandish paint ...
,
Anthony van Dyck
Sir Anthony van Dyck (, many variant spellings; 22 March 1599 – 9 December 1641) was a Brabantian Flemish Baroque artist who became the leading court painter in England after success in the Southern Netherlands and Italy.
The seventh c ...
,
Jacob Jordaens
Jacob (Jacques) Jordaens (19 May 1593 – 18 October 1678) was a Flemish painter, draughtsman and tapestry designer known for his history paintings, genre scenes and portraits. After Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck, he was the leading Fle ...
, and
Peter Paul Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque traditio ...
. The
Magritte Museum
The Magritte Museum (french: Musée Magritte, nl, Magritte Museum) is an art museum in central Brussels, Belgium, dedicated to the work of the Belgian surrealist artist, René Magritte. It is one of the constituent museums of the Royal Museu ...
houses the world's largest collection of the works of the
surrealist
Surrealism is a cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists depicted unnerving, illogical scenes and developed techniques to allow the unconscious mind to express itself. Its aim was, according to l ...
René Magritte
René François Ghislain Magritte (; 21 November 1898 – 15 August 1967) was a Belgian surrealist artist known for his depictions of familiar objects in unfamiliar, unexpected contexts, which often provoked questions about the nature and bounda ...
. Museums dedicated to the national history of Belgium include the
BELvue Museum
The BELvue Museum (french: Musée BELvue, nl, BELvue Museum) is a museum in central Brussels, Belgium, that focuses on the history of Belgium. It is managed by the King Baudouin Foundation (KBF).
The museum is located in the Hôtel Bellevue, ...
, the
Royal Museums of Art and History
The Royal Museums of Art and History (french: Musées royaux d'Art et d'Histoire, nl, Koninklijke Musea voor Kunst en Geschiedenis) or RMAH is a group of museums in Brussels, Belgium. It is part of the Belgian Federal government, federal insti ...
, and the
Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History
The Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History (french: Musée Royal de l'Armée et d'Histoire Militaire, often abbreviated to MRA, nl, Koninklijk Museum van het Leger en de Krijgsgeschiedenis, KLM) is a military museum that occupi ...
. The
Musical Instruments Museum (MIM), housed in the
Old England building, is part of the
Royal Museums of Art and History
The Royal Museums of Art and History (french: Musées royaux d'Art et d'Histoire, nl, Koninklijke Musea voor Kunst en Geschiedenis) or RMAH is a group of museums in Brussels, Belgium. It is part of the Belgian Federal government, federal insti ...
, and is internationally renowned for its collection of over 8,000 instruments.
The Brussels Museums Council is an independent body for all the museums in the Brussels-Capital Region, covering around 100 federal, private, municipal, and community museums. It promotes member museums through the Brussels Card (giving access to public transport and 30 of the 100 museums), the Brussels Museums Nocturnes (every Thursday from 5 p.m. to 10 p.m. from mid-September to mid-December) and the Museum Night Fever (an event for and by young people on a Saturday night in late February or early March).

Brussels has had a distinguished artist scene for many years. The famous Belgian surrealists
René Magritte
René François Ghislain Magritte (; 21 November 1898 – 15 August 1967) was a Belgian surrealist artist known for his depictions of familiar objects in unfamiliar, unexpected contexts, which often provoked questions about the nature and bounda ...
and
Paul Delvaux
Paul Delvaux (; 23 September 1897 – 20 July 1994) was a Belgian painter noted for his dream-like scenes of women, classical architecture, trains and train stations, and skeletons, often in combination. He is often considered a surrealist, alt ...
, for instance, studied and lived there, as did the
avant-garde
The avant-garde (; In 'advance guard' or ' vanguard', literally 'fore-guard') is a person or work that is experimental, radical, or unorthodox with respect to art, culture, or society.John Picchione, The New Avant-garde in Italy: Theoretical ...
dramatist
Michel de Ghelderode
Michel de Ghelderode (born Adémar Adolphe Louis Martens, 3 April 1898 – 1 April 1962) was an avant-garde Belgian dramatist, from Flanders, who spoke and wrote in French. His works often deal with the extremes of human experience, from death an ...
. The city was also home of the
impressionist
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passage ...
painter
Anna Boch from the artists' group
Les XX
''Les XX'' ( French; "''Les Vingt''"; ; ) was a group of twenty Belgian painters, designers and sculptors, formed in 1883 by the Brussels lawyer, publisher, and entrepreneur Octave Maus. For ten years, they held an annual exhibition of their ar ...
, and includes other famous Belgian painters such as
Léon Spilliaert
Léon Spilliaert (also Leon Spilliaert; 28 July 1881 – 23 November 1946) was a Belgian symbolist painter and graphic artist.
Biography
Spilliaert was born in Ostend, the oldest of seven children of Léonard-Hubert Spilliaert, a perfu ...
. Brussels is also a capital of the
comic strip
A comic strip is a sequence of drawings, often cartoons, arranged in interrelated panels to display brief humor or form a narrative, often serialized, with text in balloons and captions. Traditionally, throughout the 20th and into the 21st ...
;
some treasured Belgian characters are
Tintin
Tintin or Tin Tin may refer to:
''The Adventures of Tintin''
* ''The Adventures of Tintin'', a comics series by Belgian cartoonist Hergé
** Tintin (character), a fictional character in the series
** ''The Adventures of Tintin'' (film), 2011, ...
,
Lucky Luke
''Lucky Luke'' is a Western ''bande dessinée'' series created by Belgian cartoonist Morris in 1946. Morris wrote and drew the series single-handedly until 1955, after which he started collaborating with French writer René Goscinny. Their par ...
,
The Smurfs
''The Smurfs'' (french: Les Schtroumpfs; nl, De Smurfen) is a Belgian comic franchise centered on a fictional colony of small, blue, humanoid creatures who live in mushroom-shaped houses in the forest. ''The Smurfs'' was first created and in ...
,
Spirou,
Gaston
Gaston is a masculine given name of French origin and a surname. The name "Gaston" may refer to:
People
First name
*Gaston I, Count of Foix (1287–1315)
*Gaston II, Count of Foix (1308–1343)
*Gaston III, Count of Foix (1331–1391)
*Gaston ...
,
Marsupilami
''Marsupilami'' is a comic book character and fictional animal species created by André Franquin. Its first appearance was in the 31 January 1952 issue of the Franco-Belgian comics magazine '' Spirou''. Since then it appeared regularly in the ...
,
Blake and Mortimer
''Blake and Mortimer'' is a Belgian comics series created by the writer and comics artist Edgar P. Jacobs. It was one of the first series to appear in the Franco-Belgian comics magazine '' Tintin'' in 1946, and was subsequently published in boo ...
,
Boule et Bill ''Boule et Bill'' (known in English as ''Billy & Buddy'') is a popular comic, created in 1959 by Belgian writer-artist Jean Roba in collaboration with Maurice Rosy. In 2003, the artistic responsibility of the series was passed on to Roba's former a ...
and
Cubitus
''Cubitus'' is a Franco-Belgian comics series, and the basis for the ''Wowser'' cartoon series appearing in the United States. ''Cubitus'' was created by the Belgian cartoonist Dupa, and features Cubitus, a large anthropomorphic dog, who lives ...
(see
Belgian comics
Belgian comics are a distinct subgroup in the comics history, and played a major role in the development of European comics, alongside France with whom they share a long common history. While the comics in the two major language groups and regio ...
). Throughout the city, walls are painted with large motifs of comic book characters; these
mural
A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.
Word mural in art
The word ''mural'' is a Spani ...
s taken together are known as
Brussels' Comic Book Route.
Also, the interiors of some
Metro stations
A metro station or subway station is a station for a rapid transit system, which as a whole is usually called a "metro" or "subway". A station provides a means for passengers to purchase tickets, board trains, and evacuate the system in the ...
are designed by artists. The
Belgian Comic Strip Center
The Belgian Comic Strip Center (french: Centre belge de la Bande dessinée; nl, Belgisch Stripcentrum) is a museum in Brussels, Belgium, dedicated to Belgian comics. It is located at 20, /, in an Art Nouveau building designed by Victor Horta, ...
combines two artistic leitmotifs of Brussels, being a museum devoted to Belgian comic strips, housed in the former ''Magasins Waucquez'' textile department store, designed by
Victor Horta
Victor Pierre Horta (; Victor, Baron Horta after 1932; 6 January 1861 – 8 September 1947) was a Belgian architect and designer, and one of the founders of the Art Nouveau movement. His Hôtel Tassel in Brussels, built in 1892–93, is often ...
in the
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
style. In addition,
street art
Street art is visual art created in public locations for public visibility. It has been associated with the terms "independent art", "post-graffiti", "neo-graffiti" and guerrilla art.
Street art has evolved from the early forms of defiant graff ...
is changing the landscape of this multicultural city.
Brussels is well known for its performing arts scene, with the
Royal Theatre of La Monnaie and the Kaaitheater among the most notable institutions. The Kunstenfestivaldesarts, an international performing arts festival, is organised every year in May in about twenty different cultural houses and theatres throughout the city. The King Baudouin Stadium is a concert and competition facility with a 50,000 seat capacity, the largest in Belgium. The site was formerly occupied by the Heysel Stadium. The Centre for Fine Arts, Brussels, Center for Fine Arts (often referred to as BOZAR in French or PSK in Dutch), a multi-purpose centre for theatre, cinema, music, literature and art exhibitions, is home to the National Orchestra of Belgium and to the annual Queen Elisabeth Competition for Classical music, classical singers and instrumentalists, one of the most challenging and prestigious competitions of the kind. Studio 4 in Le Flagey cultural centre hosts the Brussels Philharmonic. Other concert venues include Forest National, Forest National/Vorst Nationaal, the Ancienne Belgique, the Cirque Royal, Cirque Royal/Koninklijk Circus, the Le Botanique, Botanique and Palais 12, Palais 12/Paleis 12. Furthermore, the Jazz Station in
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode () or Sint-Joost-ten-Node (), often simply called Saint-Josse or Sint-Joost, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the Ci ...
is a museum and archive on jazz, and a venue for jazz concerts.
Folklore

Brussels' identity owes much to its rich folklore and traditions, among the liveliest in the country.
* The Ommegang of Brussels, Ommegang, a folkloric costumed procession, commemorating the Joyous Entry of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Charles V and his son Philip II of Spain, Philip II in the city in 1549, takes place every year in July. The colourful parade includes floats, traditional processional giants, such as Michael (archangel), Saint Michael and
Saint Gudula
Saint Gudula was born in the pagus of Brabant (in present-day Belgium). According to her 11th-century biography ( Vita Gudilae), written by a monk of the abbey of Hautmont between 1048 and 1051, she was the daughter of a duke of Lotharingia call ...
, and scores of folkloric groups, either on foot or on horseback, dressed in medieval garb. The parade ends in a Medieval pageant, pageant on the
Grand-Place
The Grand-Place (French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or Grote Markt (Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque guildhalls of the former Guilds of Brussels and two larger ...
. Since 2019, it is recognised as a Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity, Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity by
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
.
* The Meyboom, an even-older folk tradition of Brussels (1308), celebrating the May tree—in fact, a bad translation of the Dutch ''tree of joy''—takes place paradoxically on 9 August. After parading a young beech in the city, it is planted in a joyful spirit with lots of music, ''Brusseleir'' songs, and processional giants. It was also recognised as an expression of intangible cultural heritage by UNESCO, as part of the bi-national inscription "Processional giants and dragons in Belgium and France". The celebration is reminiscent of the town's long-standing (folkloric) feud with
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic ...
, which dates back to the Middle Ages.
* Another good introduction to the ''Brusseleir'' Marols, local dialect and way of life can be obtained at the Royal Theatre Toone, a folkloric theatre of marionettes, located a stone's throw away from the Grand-Place.
* The St V, Saint-Verhaegen (often shortened to ''St V''), a folkloric student procession, celebrating the anniversary of the founding of the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) and the
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) () is a Dutch and English-speaking research university located in Brussels, Belgium.The Vrije Universiteit Brussel is one of the five universities officially recognised by the Flemish Community, Flemish gov ...
(VUB), is held on 20 November.
Cultural events and festivals

Many events are organised or hosted in Brussels throughout the year. In addition, many festivals animate the Brussels scene.
The Iris Festival is the official festival of the Brussels-Capital Region and is held annually in spring. The International Fantastic Film Festival of Brussels (BIFFF) is organised during the Easter holidays and the Magritte Awards in February. The Festival of Europe, an open day and activities in and around the institutions of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, is held on 9 May. On Belgian National Day, on 21 July, a military parade and celebrations take place on the / and in
Brussels' Park, ending with a display of fireworks in the evening.

Some summer festivities include Couleur Café, Couleur Café Festival, a festival of World music, world and Urban contemporary, urban music, around the end of June or early July, the Brussels Summer Festival (BSF), a music festival in August, the Brussels Fair, the most important yearly fair in Brussels, lasting more than a month, in July and August, and Brussels Beach, when the banks of the Brussels–Charleroi Canal, canal are turned into a temporary urban beach. Other biennial events are the Zinneke Parade, a colourful, multicultural parade through the city, which has been held since 2000 in May, as well as the popular Flower Carpet (Brussels), Flower Carpet at the
Grand-Place
The Grand-Place (French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or Grote Markt (Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque guildhalls of the former Guilds of Brussels and two larger ...
in August. European Heritage Days, Heritage Days are organised on the third weekend of September (sometimes coinciding with the car-free day) and are a good opportunity to discover the wealth of buildings, institutions and real estate in Brussels. The "Winter Wonders" animate the heart of Brussels in December; these winter activities were launched in Brussels in 2001.
Cuisine

Brussels is known for its local
waffle
A waffle is a dish made from leavened batter or dough that is cooked between two plates that are patterned to give a characteristic size, shape, and surface impression. There are many variations based on the type of waffle iron and recipe used ...
, its
chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civ ...
, its
French fries
French fries (North American English), chips (British English), finger chips ( Indian English), french-fried potatoes, or simply fries, are '' batonnet'' or ''allumette''-cut deep-fried potatoes of disputed origin from Belgium and France. Th ...
and its numerous types of
beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
s. The Brussels sprout, which has long been popular in Brussels, and may have originated there, is also named after the city.
The gastronomic offer includes approximately 1,800 restaurants (including three 2-starred and ten 1-starred Michelin Guide, Michelin restaurants), and a number of bars. In addition to the traditional restaurants, there are many Coffeehouse, cafés, bistros and the usual range of international Fast food restaurant, fast food chains. The cafés are similar to bars, and offer beer and light dishes; Coffeehouse, coffee houses are called (literally "tea salons"). Also widespread are brasseries, which usually offer a variety of beers and typical national dishes.
Belgian cuisine is known among connoisseurs as one of the best in Europe. It is characterised by the combination of French cuisine with the more hearty Flemish fare. Notable specialities include Brussels waffles (gaufres) and mussels (usually as moules frites, ''moules-frites'', served with fries). The city is a stronghold of
chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civ ...
and praline (Belgian chocolate), praline manufacturers with renowned companies like Côte d'Or (chocolate), Côte d'Or, Chocolatier Neuhaus, Neuhaus, Leonidas (chocolate maker), Leonidas and Godiva Chocolatier, Godiva. Pralines were first introduced in 1912 by Jean Neuhaus II, a Belgian chocolatier of Swiss origin, in the Royal Saint-Hubert Galleries. Numerous friteries are spread throughout the city, and in tourist areas, fresh hot waffles are also sold on the street.
As well as other Beer in Belgium, Belgian beers, the Spontaneous fermentation, spontaneously fermented lambic style, brewed in and around Brussels, is widely available there and in the nearby
Senne Senne may refer to:
Places
* Senne (Germany), a natural region of Germany
*Senne, a district of Bielefeld, Germany
* Senne (river), a river of Belgium
*Senné (disambiguation), places in Slovakia
People with the name
*Yōkō Senne, a 13th-centur ...
valley where the wild yeasts which ferment it have their origin. Kriek lambic, Kriek, a cherry lambic, is available in almost every bar or restaurant in Brussels.
Brussels is known as the birthplace of the Chicory, Belgian endive. The technique for growing Blanching (horticulture), blanched endives was accidentally discovered in the 1850s at the Botanical Garden of Brussels in
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode () or Sint-Joost-ten-Node (), often simply called Saint-Josse or Sint-Joost, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the Ci ...
.
Shopping

Famous shopping areas in Brussels include the pedestrian-only Rue Neuve (Brussels), Rue Neuve/Nieuwstraat, the second busiest shopping street in Belgium (after the Meir, Antwerp, Meir, in
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, ) with a weekly average of 230,000 visitors, home to popular international chains (H&M, C&A, Zara (retailer), Zara, Primark), as well as the City 2 and Anspach galleries.
The Royal Saint-Hubert Galleries hold a variety of luxury shops and some six million people stroll through them each year. The neighbourhood around the / has become, in recent years, a focal point for fashion and design; this main street and its side streets also feature Belgium's young and most happening artistic talent.
In Ixelles, the / and the Namur Gate area offer a blend of luxury shops, fast food restaurants and entertainment venues, and the /, in the mainly-Congolese ''Ixelles#Matongé, Matongé'' district, offers a great taste of African fashion and lifestyle. The nearby Avenue Louise, Avenue Louise/Louizalaan is lined with high-end fashion stores and boutiques, making it one of the most expensive streets in Belgium.
There are shopping centres outside the inner ring: Basilix, Woluwe Shopping Center, Westland Shopping Center, and Docks Bruxsel, which opened in October 2017.
In addition, Brussels ranks as one of Europe's best capital cities for flea market shopping. The ''Old Market'', on the Place du Jeu de Balle, Place du Jeu de Balle/Vossenplein, in the Marollen, Marolles/Marollen neighbourhood, is particularly renowned. The nearby
Sablon/Zavel area is home to many of Brussels' antique dealers. The ''Midi Market'' around Brussels-South railway station, Brussels-South station and the / is reputed to be one of the largest markets in Europe.
Sports

Sport in Brussels is under the responsibility of the Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, Communities. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
The King Baudouin Stadium (formerly the Heysel Stadium) is the largest in the country and home to the national teams in Belgium national football team, football and Belgium national rugby union team, rugby union. It hosted the final of the 1972 UEFA European Football Championship, and the opening game of Euro 2000, the 2000 edition. Several European club finals have been held at the ground, including the 1985 European Cup Final which saw 39 deaths due to hooliganism and structural collapse. The King Baudouin Stadium is also home of the annual Memorial Van Damme athletics event, Belgium's foremost track and field competition, which is part of the Diamond League. Other important athletics events are the Brussels Marathon and the 20 km of Brussels, an annual run with 30,000 participants.
Cycling
Brussels is home to notable cycling races. The city is the arrival location of the Brussels Cycling Classic, formerly known as Paris–Brussels, which is one of the oldest classic cycle races, semi classic Road bicycle racing, bicycle races on the international calendar. From World War I until the early 1970s, the Six Days of Brussels was organised regularly. In the last decades of the 20th century, the Grand Prix Eddy Merckx was also held in Brussels.
Association football

R.S.C. Anderlecht, based in the Constant Vanden Stock Stadium in
Anderlecht
Anderlecht (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the south-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Forest, Molenbeek-Saint-Jean, and Saint-Gilles, as well as the ...
, is the most successful Belgian football club in the Belgian Pro League, with 34 titles. It has also won the most major European tournaments for a Belgian side, with 6 European titles.
Brussels is also home to R. Union Saint-Gilloise, Union Saint-Gilloise, the most successful Belgian club before World War II, with 11 titles. The club was founded in
Saint-Gilles but is based in nearby
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
, and plays in the Belgian Pro League. R. White Star Bruxelles, White Star Bruxelles is another football club that plays in second division. R. White Daring Molenbeek, Racing White Daring Molenbeek, based in
Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, from which it is separated ...
, and often referred to as RWDM, was a very popular football club until it was dissolved in 2002. Since 2015, its reincarnation RWDM47 is back playing in the second division.
Other Brussels clubs that played in the national series over the years were Ixelles SC, K.V.V. Crossing Elewijt, Crossing Club de Schaerbeek (born from a merger between RCS de Schaerbeek and Crossing Club Molenbeek), Scup Jette, RUS de Laeken, Racing Jet de Bruxelles, AS Auderghem, KV Wosjot Woluwe and FC Ganshoren.
Economy
Serving as the centre of administration for Belgium and Europe, Brussels' economy is largely Tertiary sector of the economy, service-oriented. It is dominated by regional and world headquarters of Multinational corporation, multinationals, by European institutions, by various local and federal administrations, and by related services companies, though it does have a number of notable craft industries, such as the Cantillon Brewery, a lambic brewery founded in 1900.

Brussels has a robust economy. The region contributes to one fifth of Belgium's Gross domestic product, GDP, and its 550,000 jobs account for 17.7% of Belgium's employment. Its
GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
is nearly double that of Belgium as a whole,
and it has the highest GDP per capita of any Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics, NUTS 1 region in the EU, at ~$80,000 in 2016. That being said, the GDP is boosted by a massive inflow of Commuting, commuters from neighbouring regions; over half of those who work in Brussels live in Flanders or Wallonia, with 230,000 and 130,000 commuters per day respectively. Conversely, only 16.0% of people from Brussels work outside Brussels (68,827 (68.5%) of them in Flanders and 21,035 (31.5%) in Wallonia). Not all of the wealth generated in Brussels remains in Brussels itself, and , the unemployment among residents of Brussels is 20.4%.

There are approximately 50,000 businesses in Brussels, of which around 2,200 are foreign. This number is constantly increasing and can well explain the role of Brussels in Europe. The city's infrastructure is very favourable in terms of starting up a new business. House prices have also increased in recent years, especially with the increase of young professionals settling down in Brussels, making it the most expensive city to live in Belgium. In addition, Brussels holds more than 1,000 business conferences annually, making it the ninth most popular conference city in Europe.
Brussels is rated as the 34th most important financial centre in the world as of 2020, according to the Global Financial Centres Index. The
Brussels Stock Exchange
The Brussels Stock Exchange (french: Bourse de Bruxelles, nl, Beurs van Brussel), abbreviated to BSE, was founded in Brussels, Belgium, by decree of Napoleon in 1801. In 2002, the BSE merged with the Amsterdam, Lisbon and Paris stock exchang ...
, abbreviated to BSE, now called ''Euronext Brussels'', is part of the European stock exchange Euronext N.V., along with Paris Bourse, Lisbon Stock Exchange and Amsterdam Stock Exchange. Its benchmark stock market index is the BEL20.
Media
Brussels is a centre of both media and communications in Belgium, with many Belgian television stations, radio stations, newspapers and telephone companies having their headquarters in the region. The Belgian French-language Public broadcasting, public broadcaster RTBF, the Belgian Dutch-speaking public broadcaster Vlaamse Radio- en Televisieomroeporganisatie, VRT, the two regional channels BX1 (formerly Télé Bruxelles) and Bruzz (formerly TV Brussel), the encrypted BeTV (Belgium), BeTV channel and private channels RTL-TVI and VTM (TV channel), VTM are headquartered in Brussels. Some national newspapers such as Le Soir, La Libre Belgique, La Libre, De Morgen and the news agency Belga (news agency), Belga are based in or around Brussels. The Belgian Mail, postal company bpost, as well as the telecommunication companies and mobile operators Proximus, Orange Belgium and Telenet (Belgium), Telenet are all located there.
As English is spoken widely,
several English media organisations operate in Brussels. The most popular of these are the English-language daily news media platform and bi-monthly magazine ''The Brussels Times'' and the quarterly magazine and website ''The Bulletin (Brussels weekly), The Bulletin''. The Multilingualism, multilingual Pan-European identity, pan-European news channel Euronews also maintains an office in Brussels.
Education
Tertiary education

There are several University, universities in Brussels. Except for the Royal Military Academy (Belgium), Royal Military Academy, a federal military college established in 1834, all universities in Brussels are private and autonomous. The Royal Military Academy also the only Belgian university organised on the boarding school model.
The Université Libre de Bruxelles, Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), a French-speaking university, with about 20,000 students, has three campuses in the city, and the
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) () is a Dutch and English-speaking research university located in Brussels, Belgium.The Vrije Universiteit Brussel is one of the five universities officially recognised by the Flemish Community, Flemish gov ...
(VUB), its
Dutch-speaking
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' i ...
sister university, has about 10,000 students. Both universities originate from a single ancestor university, founded in 1834, namely the
Free University of Brussels University of Brussels may refer to several institutions in Brussels, Belgium: Current institutions
* Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), a French-speaking university established as a separate entity in 1970
*Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), a D ...
, which was split in 1970, at about the same time the Flemish and French Communities gained legislative power over the organisation of higher education.
Saint-Louis University, Brussels (also known as UCLouvain Saint-Louis – Bruxelles) was founded in 1858 and is specialised in social and human sciences, with 4,000 students, and located on two campuses in the
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
and
Ixelles
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Brussels' city centre, it is geographically bisected by the City of Brussels. It is also bordered by the muni ...
. From September 2018 on, the university uses the name ''UCLouvain'', together with the Université catholique de Louvain, Catholic University of Louvain, in the context of a merger between both universities.
Still other universities have campuses in Brussels, such as the French-speaking Catholic University of Louvain (UCLouvain), which has 10,000 students in the city with its medical faculties at UCLouvain Brussels Woluwe, UCLouvain Bruxelles Woluwe since 1973, in addition to its UCLouvain Faculty of Architecture, Architectural Engineering and Urban Planning, Faculty of Architecture, Architectural Engineering and Urban Planning and UCLouvain's Dutch-speaking sister KU Leuven, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (KU Leuven) (offering bachelor's and master's degrees in economics & business, law, arts, and architecture; 4,400 students). In addition, the University of Kent's Brussels School of International Studies is a specialised postgraduate school offering advanced international studies.
Also a dozen of university colleges are located in Brussels, including two drama schools, founded in 1832: the French-speaking Conservatoire royal de Bruxelles, Conservatoire Royal and its
Dutch-speaking
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' i ...
equivalent, the Koninklijk Conservatorium (Brussel), Koninklijk Conservatorium.
Primary and secondary education
Most of Brussels pupils between the ages of 3 and 18 go to schools organised by the French-speaking Community or the
Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
, with close to 80% going to French-speaking schools, and roughly 20% to Dutch-speaking schools. Due to the post-war international presence in the city, there are also a number of international schools, including the International School of Brussels, with 1,450 pupils, between the ages of and 18, the British School of Brussels, and the four European Schools, which provide free education for the children of those working in the
EU institutions
The institutions of the European Union are the seven principal decision-making bodies of the European Union and the Euratom. They are, as listed in Article 13 of the Treaty on European Union:
* the European Parliament,
* the European Council ...
. The combined student population of the four European Schools in Brussels is around 10,000.
Libraries

Brussels has a number of public or private-owned Library, libraries on its territory. Most public libraries in Brussels fall under the competence of the Communities and are usually separated between French-speaking and Dutch-speaking institutions, although some are mixed.
The Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) is the national library of Belgium and one of the most prestigious libraries in the world. It owns several collections of historical importance, like the famous Fétis archives, and is the depository for all books ever published in Belgium or abroad by Belgian authors. It is located on the Mont des Arts, Mont des Arts/Kunstberg in central Brussels, near the Brussels Central Station, Central Station.
There are several academic libraries and archives in Brussels. The libraries of the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) and the
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
The Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) () is a Dutch and English-speaking research university located in Brussels, Belgium.The Vrije Universiteit Brussel is one of the five universities officially recognised by the Flemish Community, Flemish gov ...
(VUB) constitute the largest ensemble of university libraries in the city. In addition to the ''Solbosch'' location, there are branches in ''La Plaine'' and ''Erasme''/''Erasmus''. Other academic libraries include those of Saint-Louis University, Brussels and the Université catholique de Louvain, Catholic University of Louvain (UCLouvain).
Science and technology

Science and technology in Brussels is well developed with the presence of several List of universities in Belgium, universities and research institutes. The Brussels-Capital Region is home to several national science and technology institutes including the National Fund for Scientific Research (NFSR), the Institute for the Encouragement of Scientific Research and Innovation of Brussels (ISRIB), the Royal Academies for Science and the Arts of Belgium (RASAB) and the Belgian Academy Council of Applied Sciences (BACAS). Several science parks associated with the universities are also spread over the region.
The Museum of Natural Sciences, Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, located in Leopold Park, houses the world's largest hall completely dedicated to dinosaurs, with its collection of 30 fossilised ''Iguanodon'' skeletons. In addition, the Planetarium (Belgium), Planetarium of the Royal Observatory of Belgium (part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office), on the Heysel Plateau in
Laeken
() or () is a residential suburb in the north-western part of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It belongs to the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality of the City of Brussels and is mostly identified by the ...
, is one of the largest in Europe.
Healthcare

Brussels is home to a thriving Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and health care industry which includes pioneering biotechnology research. The health sector employs 70,000 employees in 30,000 companies. There are 3,000 life sciences researchers in the city and two large science parks: Da Vinci Research Park and Erasmus Research Park. There are five Teaching hospital, university hospitals, a military hospital and more than 40 general hospitals and specialist clinics.
Due to Languages of Belgium, its bilingual nature, hospitals in the Brussels-Capital Region can be either monolingual French, monolingual Dutch, or bilingual, depending on their nature. University hospitals belong to one of the two Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, linguistic communities and are thus monolingual French or Dutch by law. Other hospitals managed by a public authority must be legally bilingual. Private hospitals are legally not bound to either language, but most cater to both. However, all hospital emergency services in the Capital Region (whether part of a public or private hospital) are required to be bilingual, since patients transported by emergency ambulance cannot choose the hospital they will be brought to.
Transport
Brussels has an extensive network of both private or public transportation means. Public transportation includes Brussels buses, Brussels trams, trams, and Brussels Metro, metro (all three operated by the Brussels Intercommunal Transport Company (STIB/MIVB)), as well as a set of railway lines (operated by Infrabel) and railway stations served by public trains (operated by the National Railway Company of Belgium (NMBS/SNCB)). Air transport is available via one of the city's two airports (
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport, nl, Luchthaven Brussel, vls, Vliegpling Brussel, german: Flughafen Brüssel is an international airport northeast of Brussels, the capital of Belgium. In 2019, more than 26 million passengers arrived or departed at Bruss ...
and Brussels South Charleroi Airport), and boat transport is available via the Port of Brussels. Bicycle-sharing and car-sharing public systems are also available.
The complexity of the Belgian political landscape makes some transportation issues difficult to solve. The Brussels-Capital Region is surrounded by the Flemish Region, Flemish and Wallonia, Walloon regions, which means that the airports, as well as many roads serving Brussels (most notably the Brussels Ring) are located in the other two Belgian regions. The city is relatively car-dependent by northern European standards and is considered to be the most congested city in the world according to the INRIX traffic survey.
Air
The Brussels-Capital Region is served by two airports which are located outside of the administrative territory of the region. The most notable is
Brussels Airport
Brussels Airport, nl, Luchthaven Brussel, vls, Vliegpling Brussel, german: Flughafen Brüssel is an international airport northeast of Brussels, the capital of Belgium. In 2019, more than 26 million passengers arrived or departed at Bruss ...
, located in the nearby Flemish municipality of
Zaventem
Zaventem () is a Belgian municipality in the province of Flemish Brabant. It is located in the Dijleland area, one of the three large recreational areas which together form the '' Groene Gordel'' ("Green Belt") around the Brussels-Capital Region. ...
, east of the capital. The secondary airport is Brussels South Charleroi Airport, located in Gosselies, a part of the city of
Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593. (
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
), some south-west of Brussels. There is also Melsbroek Air Base, located in Steenokkerzeel, a military airport which shares its infrastructure with Brussels Airport. The aforementioned airports are also the main airports of Belgium.
Water

Since the 16th century, Brussels has had its own harbour, the Port of Brussels. It has been enlarged throughout the centuries to become the second Belgian inland port. Historically situated near the /, it lies today to the north-west of the region, on the Brussels–Scheldt Maritime Canal (commonly called Willebroek Canal), which connects Brussels to
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, via the Scheldt. Ships and large barges up to can penetrate deep into the country, avoiding break-ups and load transfers between Antwerp and the centre of Brussels, hence reducing the cost for companies using the canal, and thus offering a competitive advantage.
Moreover, the connection of the Willebroek Canal with the
Brussels–Charleroi Canal, in the very heart of the capital, creates a north–south link, by means of waterways, between the Netherlands, Flanders and the industrial zone of Hainaut (province), Hainaut (
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
). There, navigation can access the network of French canals, thanks to the important Canal inclined plane, inclined plane of Ronquières inclined plane, Ronquières and the lifts of Strépy-Bracquegnies.
The importance of river traffic in Brussels makes it possible to avoid the road equivalent of 740,000 trucks per year—almost 2,000 per day—which, in addition to easing traffic problems, represents an estimated carbon dioxide saving of per year.
Train


The Brussels-Capital Region has three main train stations: Brussels-South railway station, Brussels-South, Brussels-Central railway station, Brussels-Central and Brussels-North railway station, Brussels-North, which are also the busiest of the country.
Brussels-South is also served by direct high-speed rail links: to
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
by Eurostar trains via the Channel Tunnel (1hr 51min); to Amsterdam by Thalys and ''InterCity'' connections; to Amsterdam,
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
(1hr 50min and 1hr 25min respectively ), and
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 m ...
by Thalys; and to Cologne (1hr 50min) and Frankfurt (2hr 57min) by the German Intercity Express, ICE.
The train rails in Brussels go underground, near the centre, through the
North–South connection
The North–South connection (french: Jonction Nord-Midi, nl, Noord-Zuidverbinding) is a railway link of national and international importance through central Brussels, Belgium, that connects the major railway stations in the city. It is line ...
, with Brussels Central Station also being largely underground. The tunnel itself is only six tracks wide at its narrowest point, which often causes congestion and delays due to heavy use of the route.
The
City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
has minor railway stations at Bockstael railway station, Bockstael, Brussels-Chapel railway station, Brussels-Chapel, Brussels-Congres railway station, Brussels-Congres, Brussels-Luxembourg railway station, Brussels-Luxembourg, Schuman station, Brussels-Schuman, Brussels-West station, Brussels-West, Haren railway station (Brussels), Haren, Haren-South railway station, Haren-South and Simonis metro station, Simonis. In the Brussels Region, there are also railways stations at Berchem-Sainte-Agathe railway station, Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Boitsfort railway station, Boitsfort, Boondael railway station, Boondael, Bordet railway station, Bordet (Evere), Etterbeek railway station, Etterbeek, Evere railway station, Evere, Forest-East railway station, Forest-East, Forest-South railway station, Forest-South, Jette railway station, Jette, Meiser railway station, Meiser (Schaerbeek), Moensberg railway station, Moensberg (Uccle), Saint-Job railway station, Saint-Job (Uccle), Schaerbeek railway station, Schaarbeek, Uccle-Calevoet railway station, Uccle-Calevoet, Uccle-Stalle railway station, Uccle-Stalle, Vivier d'Oie-Diesdelle (Uccle), Merode station, Merode and Watermael railway station, Watermael.
Public transport
The Brussels Intercommunal Transport Company (STIB/MIVB) is the local public transport operator in Brussels. It covers the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region and some surface routes extend to the near suburbs in the other two regions, linking with the De Lijn network in
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
and the TEC (transport), TEC network in
Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—alo ...
.
Metro, trams and buses


The
Brussels Metro
The Brussels Metro (french: Métro de Bruxelles, nl, Brusselse metro) is a rapid transit system serving a large part of the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It consists of four conventional metro lines and three ''premetro'' lines. The me ...
dates back to 1976, but underground lines known as the ''
premetro
A premetro is a tramway or light railway which includes segments built to rapid transit standards, generally as part of a process of conversion to a metro-standards railway usually by the construction of tunnels in the central city area.
Hist ...
'' have been serviced by tramways since 1968. It is the only
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
system in Belgium (Antwerp Pre-metro, Antwerp and Charleroi Metro, Charleroi both having light rail systems). The network consists of four conventional metro lines and three ''premetro'' lines. The metro-grade lines are M1, M2, M5, and M6, with some shared sections, covering a total of .
, the Metro network within the region has a total of List of Brussels Metro stations, 69 metro and ''premetro'' stations. The Metro is an important Transport in Brussels, means of transport, connecting with six railway stations of the National Railway Company of Belgium (NMBS/SNCB), and many tram and bus stops operated by STIB/MIVB, and with Flanders, Flemish De Lijn and Wallonia, Walloon TEC (transport), TEC bus stops.
A comprehensive Brussels buses, bus and Brussels trams, tram network covers the region. , the Brussels tram system consists of 17 tram lines (three of which – lines T3, T4 and T7 – qualify as ''premetro'' lines that partly travel over underground sections that were intended to be eventually converted into metro lines).
The total route length is ,
making it one of the largest tram networks in Europe. The Brussels bus network is complementary to the rail network. It consists of 50 bus routes and 11 night routes, spanning .
Since April 2007, STIB/MIVB has also been operating a night bus network called Noctis on Friday and Saturday nights from midnight until 3 a.m.
[ The service consists of 11 routes (N04, N05, N06, N08, N09, N10, N11, N12, N13, N16 and N18). The fare on these night buses is the same as during the day. All the lines leave from the Place de la Bourse, Brussels, Place de la Bourse/Beursplein in the city centre at 30 minutes intervals and cover all the main streets in the capital, as they radiate outwards to the suburbs. Noctis services returned from 2 July 2021 after over a year of disruption due to the COVID-19 pandemic in Belgium.]
Ticketing
MoBIB is the STIB/MIVB electronic smart card, introduced in 2007, replacing the discontinued paper tickets. The hourly travel fare includes all means of transport (metro, tram and bus) operated by STIB/MIVB. Each trip has a different cost depending on the type of support purchased. Passengers can purchase monthly passes, yearly passes, 1 and 10-trip tickets and daily and 3-day passes. These can be bought over the Internet, but require customers to have a smart card reader. GO vending machines accept coins, local and international chip and PIN credit and debit cards.
Moreover, a complimentary interticketing system means that a combined STIB/MIVB ticket holder can, depending on the option, also use the train network operated by NMBS/SNCB and/or long-distance buses and commuter services operated by De Lijn or TEC. With this ticket, a single journey can include multiple stages across the different modes of transport and networks.
Other public transport
 Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with STIB/MIVB and the local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a Community bicycle program, public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas.
Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with STIB/MIVB and the local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a Community bicycle program, public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas.
Road network
 In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north–south (the modern /) and east–west (/–/–/). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the
In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north–south (the modern /) and east–west (/–/–/). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the Grand-Place
The Grand-Place (French, ; "Grand Square"; also used in English) or Grote Markt (Dutch, ; "Big Market") is the central square of Brussels, Belgium. It is surrounded by opulent Baroque guildhalls of the former Guilds of Brussels and two larger ...
, in large part remains, but has been overlaid by boulevards built covering of the Senne, over the river Senne, Fortifications of Brussels#Construction of the Small Ring, over the city walls and over the railway connection between the North and South Stations. Today, Brussels has the most congested traffic in North America and Europe, according to US traffic information platform INRIX.
Brussels is the hub of a range of national roads, the main ones being clockwise: the N1 road (Belgium), N1 (N to Breda), N2 road (Belgium), N2 (E to Maastricht), N3 road (Belgium), N3 (E to Aachen), N4 road (Belgium), N4 (SE to Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
), N5 road (Belgium), N5 (S to Reims, Rheims), N6 (S to Maubeuge), N7 (SW to Lille), N8 road (Belgium), N8 (W to Koksijde) and N9 (NW to Ostend). Usually named /, these highways normally run in a straight line, but sometimes lose themselves in a maze of narrow shopping streets. The region is skirted by the European route E19 (N-S) and the European route E40, E40 (E-W), while the E411 leads away to the SE. Brussels has an beltway, orbital motorway, numbered R0 (R-zero) and commonly referred to as the Brussels Ring, Ring. It is pear-shaped, as the southern side was never built as originally conceived, owing to residents' objections.
The city centre, sometimes known as the Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon (from the Greek πέντε ''pente'' meaning ''five'' and γωνία ''gonia'' meaning ''angle'') is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simpl ...
, is surrounded by an inner ring road, the Small Ring
The Small Ring (french: Petite Ceinture, nl, Kleine Ring) inner ring road, formally R20 and N0 is a series of roadways in central Brussels, Belgium, surrounding the historic city centre. The city centre is usually defined as the area within t ...
(french: Petite Ceinture, link=no, nl, Kleine Ring, link=no), a sequence of boulevards formally numbered R20 or N0. These were built upon the site of the Second walls of Brussels, second set of city walls following their demolition. The Brussels Metro line 2, Metro line 2 runs under much of these. Since June 2015, a number of central boulevards inside the Pentagon have become car-free, limiting transit traffic through the old city.
On the eastern side of the region, the R21 or Greater ring (Brussels), Greater Ring (french: Grande Ceinture, link=no, nl, Grote Ring, link=no) is formed by a string of boulevards that curves round from Laeken
() or () is a residential suburb in the north-western part of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. It belongs to the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, municipality of the City of Brussels and is mostly identified by the ...
to Uccle
Uccle () or Ukkel () is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch). It is generally considered an affluent area of the city a ...
. Some ''premetro'' stations (see Brussels Metro
The Brussels Metro (french: Métro de Bruxelles, nl, Brusselse metro) is a rapid transit system serving a large part of the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It consists of four conventional metro lines and three ''premetro'' lines. The me ...
) were built on that route. A little further out, a stretch numbered R22 leads from Zaventem to Uccle, Saint-Job.
Security and emergency services
Police
 The Brussels local police, supported by the federal police, is responsible for law enforcement in Brussels. The 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region are divided into six police zones, all bilingual (French and Dutch):
*5339 Brussels Capital Ixelles: the
The Brussels local police, supported by the federal police, is responsible for law enforcement in Brussels. The 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region are divided into six police zones, all bilingual (French and Dutch):
*5339 Brussels Capital Ixelles: the City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
and Ixelles
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Brussels' city centre, it is geographically bisected by the City of Brussels. It is also bordered by the muni ...
*5340 Brussels West: Sint-Agatha-Berchem, Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren
Ganshoren (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Jette, Koekelberg, and Sint-Agatha-Berchem, as well as the Flemish municipality of As ...
, Jette
Jette (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Ganshoren, Koekelberg, and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean, as well as the Flemi ...
, Koekelberg
Koekelberg (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-western part of the region, it is bordered by Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Ganshoren, Jette and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean. In common with all ...
and Molenbeek-Saint-Jean
( French, ) or (Dutch, ), often simply called Molenbeek, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, from which it is separated ...
*5341 South: Anderlecht
Anderlecht (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the south-western part of the region, it is bordered by the City of Brussels, Forest, Molenbeek-Saint-Jean, and Saint-Gilles, as well as the ...
, Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
and Saint-Gilles
*5342 Uccle/Watermael-Boitsfort/Auderghem: Auderghem
Auderghem (former Dutch spelling, now used in French; pronounced ) or Oudergem () is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium).
Located to the southeast of the region, along the Woluwe valley and at the entrance to t ...
, Uccle
Uccle () or Ukkel () is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch). It is generally considered an affluent area of the city a ...
and Watermael-Boitsfort
Watermael-Boitsfort () or Watermaal-Bosvoorde () is a residential suburb of the city of Brussels in Belgium, and one of the 19 municipalities which form the Brussels-Capital Region.
The municipality has a total area of of which 58 percent is cov ...
*5343 Montgomery: Etterbeek
Etterbeek (French: ; Dutch: ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the municipalities of Auderghem, the City of Brussels, Ixelles, Schaerbeek, Wolu ...
, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert
Woluwe-Saint-Lambert () or Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe (Dutch, ) is one of the nineteen municipalities in the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It is a prosperous residential area, with a mixture of flats and detached, semi-detached and terraced hous ...
and Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
Woluwe-Saint-Pierre () or Sint-Pieters-Woluwe () is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the eastern part of the region, it is bordered by Etterbeek, Auderghem and Woluwe-Saint-Lambert, as well as th ...
*5344 Polbruno: Evere
Evere (, ) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium). On 1 January 2006, the municipality had a total population of 33,462. The total area is which gives a population density of . In common with all of Brussels' m ...
, Saint-Josse-ten-Noode
Saint-Josse-ten-Noode () or Sint-Joost-ten-Node (), often simply called Saint-Josse or Sint-Joost, is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located in the north-eastern part of the region, it is bordered by the Ci ...
and Schaerbeek
(French language, French and History of Dutch orthography, archaic Dutch, ) or (contemporary Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Re ...
Fire department
The Brussels Fire and Emergency Medical Care Service, commonly known by its acronym SIAMU (DBDMH), operates in the 19 municipalities of Brussels. It is a class X fire department and the largest Fire department, fire service in Belgium in terms of annual operations, equipment, and personnel. It has 9 fire stations, spread over the entire Brussels-Capital Region, and employs about 1,000 professional firefighters. As well as preventing and fighting fires, SIAMU also provides emergency medical care services in Brussels via its centralised 100 number (and the single 112 emergency number for the 27 countries of the European Union). It is bilingual (French–Dutch).
Parks and green spaces
Brussels is one of the greenest capitals in Europe, with over 8,000 hectares of green spaces. Vegetation cover and natural areas are higher in the outskirts, where they have limited the peri-urbanisation of the capital, but they decrease sharply towards the centre of Brussels; 10% in the central Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon (from the Greek πέντε ''pente'' meaning ''five'' and γωνία ''gonia'' meaning ''angle'') is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simpl ...
, 30% of the municipalities in the first ring, and 71% of the municipalities in the second ring are occupied by green spaces.
Many parks and gardens, both public and privately owned, are scattered throughout the city. In addition to this, the Sonian Forest
The Sonian Forest or Sonian Wood ( nl, Zoniënwoud, french: Forêt de Soignes, ) is a forest at the southeast edge of Brussels, Belgium.
The Sonian Forest was a favorite hunting ground of the Habsburg Imperial family, and as such features promi ...
is located in its southern part and stretches out over the three Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, Belgian regions. , it has been inscribed as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, the only Belgian component to the multinational inscription 'Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians and Other Regions of Europe'.
File:Brussels Park in summer 2007 1.JPG, Brussels Park
File:Brussels, Jardin du Mont des Arts foto5 2015-06-07 14.01.jpg, Mont des Arts, Mont des Arts / Kunstberg
File:Brussels Cinquantenaire R04.jpg, Cinquantenaire, Parc du Cinquantenaire / Jubelpark
File:Brusel, Bois de la Cambre, jezero.jpg, Bois de la Cambre, Bois de la Cambre / Ter Kamerenbos
File:Botanical Garden of Brussels during golden hour (DSCF8171).jpg, The Botanical Garden of Brussels
File:Ixelles Ponds.JPG, Ixelles Ponds
File:Parc de Forest - 20080325.JPG, Forest park, Brussels, Forest Park
File:Royal Greenhouses in Laeken (5704647112).jpg, The Royal Greenhouses of Laeken
File:Autumn light in the Sonian Forest.jpg, Sonian Forest
The Sonian Forest or Sonian Wood ( nl, Zoniënwoud, french: Forêt de Soignes, ) is a forest at the southeast edge of Brussels, Belgium.
The Sonian Forest was a favorite hunting ground of the Habsburg Imperial family, and as such features promi ...
Notable people
Twin towns – sister cities
Brussels is sister city, twinned with the following cities:Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, United States
See also
*Bourgeois of Brussels
*Brussels Regional Investment Company
*Outline of Belgium
*Seven Noble Houses of Brussels
*Statue of Europe
*List of urban areas in the European Union
References
Footnotes
Notes
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Brussels-Capital Region
Official tourism website
{{Authority control
Brussels,
Brabant
Regions of Belgium
Regions of Europe with multiple official languages
French-speaking countries and territories
Autonomous regions
NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union
Populated places established in the 1st millennium
 The history of Brussels is closely linked to that of
The history of Brussels is closely linked to that of  In the 15th century, the marriage between heiress
In the 15th century, the marriage between heiress  In the 16th and 17th centuries, Brussels was a centre for the
In the 16th and 17th centuries, Brussels was a centre for the  During the 19th century, the population of Brussels grew considerably; from about 80,000 to more than 625,000 people for the city and its surroundings. The Senne had become a serious
During the 19th century, the population of Brussels grew considerably; from about 80,000 to more than 625,000 people for the city and its surroundings. The Senne had become a serious  During the 20th century, the city hosted various fairs and conferences, including the
During the 20th century, the city hosted various fairs and conferences, including the  Brussels lies in the north-central part of Belgium, about from the Belgian coast and about from Belgium's southern tip. It is located in the heartland of the Brabantian Plateau, about south of
Brussels lies in the north-central part of Belgium, about from the Belgian coast and about from Belgium's southern tip. It is located in the heartland of the Brabantian Plateau, about south of 
 Brussels serves as ''
Brussels serves as '' Brussels, along with
Brussels, along with  The
The  The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol, is an
The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol, is an  Today, the Brussels-Capital Region is legally bilingual, with both French and Dutch having official status, as is the administration of the 19 municipalities. The creation of this bilingual, full-fledged region, with its own competencies and jurisdiction, had long been hampered by different visions of Belgian federalism. Nevertheless, some communitarian issues remain. Flemish political parties demanded, for decades, that the Flemish part of
Today, the Brussels-Capital Region is legally bilingual, with both French and Dutch having official status, as is the administration of the 19 municipalities. The creation of this bilingual, full-fledged region, with its own competencies and jurisdiction, had long been hampered by different visions of Belgian federalism. Nevertheless, some communitarian issues remain. Flemish political parties demanded, for decades, that the Flemish part of  Very little
Very little  The neoclassical style of the 18th and 19th centuries is represented in the Royal Quarter/Coudenberg area, around Brussels' Park and the Place Royale/Koningsplein. Examples include the
The neoclassical style of the 18th and 19th centuries is represented in the Royal Quarter/Coudenberg area, around Brussels' Park and the Place Royale/Koningsplein. Examples include the  Since the second half of the 20th century, modern office towers have been built in Brussels ( Madou Tower,
Since the second half of the 20th century, modern office towers have been built in Brussels ( Madou Tower,  Brussels contains over 80 museums. The Royal Museums of Fine Arts has an extensive collection of various painters, such as Flemish old masters like Bruegel,
Brussels contains over 80 museums. The Royal Museums of Fine Arts has an extensive collection of various painters, such as Flemish old masters like Bruegel,  Brussels' identity owes much to its rich folklore and traditions, among the liveliest in the country.
* The Ommegang of Brussels, Ommegang, a folkloric costumed procession, commemorating the Joyous Entry of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Charles V and his son Philip II of Spain, Philip II in the city in 1549, takes place every year in July. The colourful parade includes floats, traditional processional giants, such as Michael (archangel), Saint Michael and
Brussels' identity owes much to its rich folklore and traditions, among the liveliest in the country.
* The Ommegang of Brussels, Ommegang, a folkloric costumed procession, commemorating the Joyous Entry of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Charles V and his son Philip II of Spain, Philip II in the city in 1549, takes place every year in July. The colourful parade includes floats, traditional processional giants, such as Michael (archangel), Saint Michael and  Many events are organised or hosted in Brussels throughout the year. In addition, many festivals animate the Brussels scene.
The Iris Festival is the official festival of the Brussels-Capital Region and is held annually in spring. The International Fantastic Film Festival of Brussels (BIFFF) is organised during the Easter holidays and the Magritte Awards in February. The Festival of Europe, an open day and activities in and around the institutions of the
Many events are organised or hosted in Brussels throughout the year. In addition, many festivals animate the Brussels scene.
The Iris Festival is the official festival of the Brussels-Capital Region and is held annually in spring. The International Fantastic Film Festival of Brussels (BIFFF) is organised during the Easter holidays and the Magritte Awards in February. The Festival of Europe, an open day and activities in and around the institutions of the  Some summer festivities include Couleur Café, Couleur Café Festival, a festival of World music, world and Urban contemporary, urban music, around the end of June or early July, the Brussels Summer Festival (BSF), a music festival in August, the Brussels Fair, the most important yearly fair in Brussels, lasting more than a month, in July and August, and Brussels Beach, when the banks of the Brussels–Charleroi Canal, canal are turned into a temporary urban beach. Other biennial events are the Zinneke Parade, a colourful, multicultural parade through the city, which has been held since 2000 in May, as well as the popular Flower Carpet (Brussels), Flower Carpet at the
Some summer festivities include Couleur Café, Couleur Café Festival, a festival of World music, world and Urban contemporary, urban music, around the end of June or early July, the Brussels Summer Festival (BSF), a music festival in August, the Brussels Fair, the most important yearly fair in Brussels, lasting more than a month, in July and August, and Brussels Beach, when the banks of the Brussels–Charleroi Canal, canal are turned into a temporary urban beach. Other biennial events are the Zinneke Parade, a colourful, multicultural parade through the city, which has been held since 2000 in May, as well as the popular Flower Carpet (Brussels), Flower Carpet at the  Brussels is known for its local
Brussels is known for its local  Famous shopping areas in Brussels include the pedestrian-only Rue Neuve (Brussels), Rue Neuve/Nieuwstraat, the second busiest shopping street in Belgium (after the Meir, Antwerp, Meir, in
Famous shopping areas in Brussels include the pedestrian-only Rue Neuve (Brussels), Rue Neuve/Nieuwstraat, the second busiest shopping street in Belgium (after the Meir, Antwerp, Meir, in  Sport in Brussels is under the responsibility of the Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, Communities. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
The King Baudouin Stadium (formerly the Heysel Stadium) is the largest in the country and home to the national teams in Belgium national football team, football and Belgium national rugby union team, rugby union. It hosted the final of the 1972 UEFA European Football Championship, and the opening game of Euro 2000, the 2000 edition. Several European club finals have been held at the ground, including the 1985 European Cup Final which saw 39 deaths due to hooliganism and structural collapse. The King Baudouin Stadium is also home of the annual Memorial Van Damme athletics event, Belgium's foremost track and field competition, which is part of the Diamond League. Other important athletics events are the Brussels Marathon and the 20 km of Brussels, an annual run with 30,000 participants.
Sport in Brussels is under the responsibility of the Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, Communities. The (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region. Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is (formerly called Bloso, BLOSO).
The King Baudouin Stadium (formerly the Heysel Stadium) is the largest in the country and home to the national teams in Belgium national football team, football and Belgium national rugby union team, rugby union. It hosted the final of the 1972 UEFA European Football Championship, and the opening game of Euro 2000, the 2000 edition. Several European club finals have been held at the ground, including the 1985 European Cup Final which saw 39 deaths due to hooliganism and structural collapse. The King Baudouin Stadium is also home of the annual Memorial Van Damme athletics event, Belgium's foremost track and field competition, which is part of the Diamond League. Other important athletics events are the Brussels Marathon and the 20 km of Brussels, an annual run with 30,000 participants.
 R.S.C. Anderlecht, based in the Constant Vanden Stock Stadium in
R.S.C. Anderlecht, based in the Constant Vanden Stock Stadium in  There are several University, universities in Brussels. Except for the Royal Military Academy (Belgium), Royal Military Academy, a federal military college established in 1834, all universities in Brussels are private and autonomous. The Royal Military Academy also the only Belgian university organised on the boarding school model.
The Université Libre de Bruxelles, Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), a French-speaking university, with about 20,000 students, has three campuses in the city, and the
There are several University, universities in Brussels. Except for the Royal Military Academy (Belgium), Royal Military Academy, a federal military college established in 1834, all universities in Brussels are private and autonomous. The Royal Military Academy also the only Belgian university organised on the boarding school model.
The Université Libre de Bruxelles, Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), a French-speaking university, with about 20,000 students, has three campuses in the city, and the  Brussels has a number of public or private-owned Library, libraries on its territory. Most public libraries in Brussels fall under the competence of the Communities and are usually separated between French-speaking and Dutch-speaking institutions, although some are mixed.
The Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) is the national library of Belgium and one of the most prestigious libraries in the world. It owns several collections of historical importance, like the famous Fétis archives, and is the depository for all books ever published in Belgium or abroad by Belgian authors. It is located on the Mont des Arts, Mont des Arts/Kunstberg in central Brussels, near the Brussels Central Station, Central Station.
There are several academic libraries and archives in Brussels. The libraries of the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) and the
Brussels has a number of public or private-owned Library, libraries on its territory. Most public libraries in Brussels fall under the competence of the Communities and are usually separated between French-speaking and Dutch-speaking institutions, although some are mixed.
The Royal Library of Belgium (KBR) is the national library of Belgium and one of the most prestigious libraries in the world. It owns several collections of historical importance, like the famous Fétis archives, and is the depository for all books ever published in Belgium or abroad by Belgian authors. It is located on the Mont des Arts, Mont des Arts/Kunstberg in central Brussels, near the Brussels Central Station, Central Station.
There are several academic libraries and archives in Brussels. The libraries of the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB) and the  Science and technology in Brussels is well developed with the presence of several List of universities in Belgium, universities and research institutes. The Brussels-Capital Region is home to several national science and technology institutes including the National Fund for Scientific Research (NFSR), the Institute for the Encouragement of Scientific Research and Innovation of Brussels (ISRIB), the Royal Academies for Science and the Arts of Belgium (RASAB) and the Belgian Academy Council of Applied Sciences (BACAS). Several science parks associated with the universities are also spread over the region.
The Museum of Natural Sciences, Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, located in Leopold Park, houses the world's largest hall completely dedicated to dinosaurs, with its collection of 30 fossilised ''Iguanodon'' skeletons. In addition, the Planetarium (Belgium), Planetarium of the Royal Observatory of Belgium (part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office), on the Heysel Plateau in
Science and technology in Brussels is well developed with the presence of several List of universities in Belgium, universities and research institutes. The Brussels-Capital Region is home to several national science and technology institutes including the National Fund for Scientific Research (NFSR), the Institute for the Encouragement of Scientific Research and Innovation of Brussels (ISRIB), the Royal Academies for Science and the Arts of Belgium (RASAB) and the Belgian Academy Council of Applied Sciences (BACAS). Several science parks associated with the universities are also spread over the region.
The Museum of Natural Sciences, Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, located in Leopold Park, houses the world's largest hall completely dedicated to dinosaurs, with its collection of 30 fossilised ''Iguanodon'' skeletons. In addition, the Planetarium (Belgium), Planetarium of the Royal Observatory of Belgium (part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office), on the Heysel Plateau in  Brussels is home to a thriving Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and health care industry which includes pioneering biotechnology research. The health sector employs 70,000 employees in 30,000 companies. There are 3,000 life sciences researchers in the city and two large science parks: Da Vinci Research Park and Erasmus Research Park. There are five Teaching hospital, university hospitals, a military hospital and more than 40 general hospitals and specialist clinics.
Due to Languages of Belgium, its bilingual nature, hospitals in the Brussels-Capital Region can be either monolingual French, monolingual Dutch, or bilingual, depending on their nature. University hospitals belong to one of the two Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, linguistic communities and are thus monolingual French or Dutch by law. Other hospitals managed by a public authority must be legally bilingual. Private hospitals are legally not bound to either language, but most cater to both. However, all hospital emergency services in the Capital Region (whether part of a public or private hospital) are required to be bilingual, since patients transported by emergency ambulance cannot choose the hospital they will be brought to.
Brussels is home to a thriving Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and health care industry which includes pioneering biotechnology research. The health sector employs 70,000 employees in 30,000 companies. There are 3,000 life sciences researchers in the city and two large science parks: Da Vinci Research Park and Erasmus Research Park. There are five Teaching hospital, university hospitals, a military hospital and more than 40 general hospitals and specialist clinics.
Due to Languages of Belgium, its bilingual nature, hospitals in the Brussels-Capital Region can be either monolingual French, monolingual Dutch, or bilingual, depending on their nature. University hospitals belong to one of the two Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, linguistic communities and are thus monolingual French or Dutch by law. Other hospitals managed by a public authority must be legally bilingual. Private hospitals are legally not bound to either language, but most cater to both. However, all hospital emergency services in the Capital Region (whether part of a public or private hospital) are required to be bilingual, since patients transported by emergency ambulance cannot choose the hospital they will be brought to.
 Since the 16th century, Brussels has had its own harbour, the Port of Brussels. It has been enlarged throughout the centuries to become the second Belgian inland port. Historically situated near the /, it lies today to the north-west of the region, on the Brussels–Scheldt Maritime Canal (commonly called Willebroek Canal), which connects Brussels to
Since the 16th century, Brussels has had its own harbour, the Port of Brussels. It has been enlarged throughout the centuries to become the second Belgian inland port. Historically situated near the /, it lies today to the north-west of the region, on the Brussels–Scheldt Maritime Canal (commonly called Willebroek Canal), which connects Brussels to 

 Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with STIB/MIVB and the local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a Community bicycle program, public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas.
Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with STIB/MIVB and the local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a Community bicycle program, public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas.
 In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north–south (the modern /) and east–west (/–/–/). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the
In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north–south (the modern /) and east–west (/–/–/). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the  The Brussels local police, supported by the federal police, is responsible for law enforcement in Brussels. The 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region are divided into six police zones, all bilingual (French and Dutch):
*5339 Brussels Capital Ixelles: the
The Brussels local police, supported by the federal police, is responsible for law enforcement in Brussels. The 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region are divided into six police zones, all bilingual (French and Dutch):
*5339 Brussels Capital Ixelles: the