Brittones on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the 

 The Britons spoke an Insular Celtic language known as
The Britons spoke an Insular Celtic language known as
 Celtic Britain was made up of many territories controlled by Brittonic tribes. They are generally believed to have dwelt throughout the whole island of Great Britain, at least as far north as the Clyde–
Celtic Britain was made up of many territories controlled by Brittonic tribes. They are generally believed to have dwelt throughout the whole island of Great Britain, at least as far north as the Clyde–
 The La Tène style, which covers British Celtic art, was late arriving in Britain, but after 300 BC the ancient British seem to have had generally similar cultural practices to the Celtic cultures nearest to them on the continent. There are significant differences in artistic styles, and the greatest period of what is known as the "Insular La Tène" style, surviving mostly in metalwork, was in the century or so before the Roman conquest, and perhaps the decades after it.
The La Tène style, which covers British Celtic art, was late arriving in Britain, but after 300 BC the ancient British seem to have had generally similar cultural practices to the Celtic cultures nearest to them on the continent. There are significant differences in artistic styles, and the greatest period of what is known as the "Insular La Tène" style, surviving mostly in metalwork, was in the century or so before the Roman conquest, and perhaps the decades after it.
 The carnyx, a trumpet with an animal-headed bell, was used by Celtic Britons during war and ceremony.
The carnyx, a trumpet with an animal-headed bell, was used by Celtic Britons during war and ceremony.
 In 43 AD, the Roman Empire invaded Britain. The British tribes opposed the Roman legions for many decades, but by 84 AD the Romans had decisively conquered southern Britain and had pushed into Brittonic areas of what would later become northern England and southern Scotland. During the same period
In 43 AD, the Roman Empire invaded Britain. The British tribes opposed the Roman legions for many decades, but by 84 AD the Romans had decisively conquered southern Britain and had pushed into Brittonic areas of what would later become northern England and southern Scotland. During the same period
 Thirty years or so after the time of the Roman departure, the Germanic-speaking Anglo-Saxons began a migration to the south-eastern coast of Britain, where they began to establish their own kingdoms, and the
Thirty years or so after the time of the Roman departure, the Germanic-speaking Anglo-Saxons began a migration to the south-eastern coast of Britain, where they began to establish their own kingdoms, and the
 The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age
The British Iron Age is a conventional name used in the archaeology of Great Britain, referring to the prehistoric and protohistoric phases of the Iron Age culture of the main island and the smaller islands, typically excluding prehistoric Ire ...
and into the Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
, Cornish and Bretons (among others). They spoke the Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a ...
language, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages.
The earliest written evidence for the Britons is from Greco-Roman
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were di ...
writers and dates to the Iron Age.Koch, pp. 291–292. Celtic Britain was made up of many tribes and kingdoms, associated with various hillforts
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
. The Britons followed an Ancient Celtic religion overseen by druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. Whi ...
s. Some of the southern tribes had strong links with mainland Europe, especially Gaul and Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and German ...
, and minted their own coins. The Roman Empire conquered most of Britain in the 1st century, creating the province of Britannia. The Romans invaded northern Britain, but the Britons and Caledonians
The Caledonians (; la, Caledones or '; grc-gre, Καληδῶνες, ''Kalēdōnes'') or the Caledonian Confederacy were a Brittonic-speaking (Celtic) tribal confederacy in what is now Scotland during the Iron Age and Roman eras.
The Gree ...
in the north remained unconquered and Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. R ...
became the edge of the empire. A Romano-British culture
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a ...
emerged, mainly in the southeast, and British Latin
British Latin or British Vulgar Latin was the Vulgar Latin spoken in Great Britain in the Roman and sub-Roman periods. While Britain formed part of the Roman Empire, Latin became the principal language of the elite, especially in the more roma ...
coexisted with Brittonic. It is unclear what relationship the Britons had to the Picts, who lived outside the empire in northern Britain, though most scholars now accept that the Pictish language was closely related to Common Brittonic.
Following the end of Roman rule in Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances.
In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew tr ...
during the 5th century, Anglo-Saxon settlement of eastern and southern Britain began. The culture and language of the Britons fragmented, and much of their territory gradually became Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
, while small parts of the northwest became Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, and Ca ...
. The extent to which this cultural change was accompanied by wholesale population changes is still debated. During this time, Britons migrated to mainland Europe and established significant colonies in Brittany (now part of France), the Channel Islands, and Britonia (now part of Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
, Spain). By the 11th century, Brittonic-speaking populations had split into distinct groups: the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
in Wales, the Cornish in Cornwall, the Bretons in Brittany, the Cumbrians of the '' Hen Ogledd'' ("Old North") in southern Scotland and northern England, and the remnants of the Pictish people in northern Scotland. Common Brittonic developed into the distinct Brittonic languages: Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
, Cumbric, Cornish and Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
** Breton people
** Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Ga ...
.


Name
The earliest known reference to the inhabitants of Britain was byPytheas
Pytheas of Massalia (; Ancient Greek: Πυθέας ὁ Μασσαλιώτης ''Pythéas ho Massaliōtēs''; Latin: ''Pytheas Massiliensis''; born 350 BC, 320–306 BC) was a Greeks, Greek List of Graeco-Roman geographers, geographer, explor ...
, a Greek geographer who made a voyage of exploration around the British Isles between 330 and 320 BC. Although none of his own writings remain, writers during the time of the Roman Empire made much reference to them. Pytheas called the people of Britain the ''Pretanoí'' or ''Bretanoí''. Pliny's '' Natural History'' (77 AD) says the older name for the island was ''Albion
Albion is an alternative name for Great Britain. The oldest attestation of the toponym comes from the Greek language. It is sometimes used poetically and generally to refer to the island, but is less common than 'Britain' today. The name for Scot ...
'', and Avienius calls it ''insula Albionum'', "island of the Albions". The name could have reached Pytheas from the Gauls. The Latin name for the Britons was ''Britanni''.
The P-Celtic ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
has been reconstructed as *''Pritanī'', from Common Celtic *''kʷritu'', which became Old Irish ''cruth'' and Old Welsh
Old Welsh ( cy, Hen Gymraeg) is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic ...
''pryd''. This likely means "people of the forms", and could be linked to the Latin name ''Picti'' (the Picts), which is usually explained as meaning "painted people". The Old Welsh name for the Picts was ''Prydyn''. Linguist Kim McCone suggests the name became restricted to inhabitants of the far north after ''Cymry'' displaced it as the name for the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
and Cumbrians
Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the historical region which is now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages. Its population sp ...
. The Welsh ''prydydd'', "maker of forms", was also a term for the highest grade of bard
In Celtic cultures, a bard is a professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron (such as a monarch or chieftain) to commemorate one or more of the patron's ancestors and to praise t ...
.
The medieval Welsh form of Latin ''Britanni'' was ''Brython'' (singular and plural). ''Brython'' was introduced into English usage by John Rhys in 1884 as a term unambiguously referring to the P-Celtic speakers of Great Britain, to complement '' Goidel''; hence the adjective ''Brythonic'' referring to the group of languages. " Brittonic languages" is a more recent coinage (first attested 1923 according to the '' Oxford English Dictionary'') intended to refer to the ancient Britons specifically.
In English, the terms "Briton" and ''British'' for many centuries originally denoted only the ancient Celtic Britons and their descendants, most particularly the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
, Cornish and Bretons, who were seen as heirs to the ancient British people.
From the early 16th century, and especially after the Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union ( gd, Achd an Aonaidh) were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act 1707 passed by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the te ...
, the terms ''British'' and ''Briton'' could be applied to all inhabitants of the Kingdom of Great Britain, including the English, Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
and some Irish, or the subjects of the British Empire generally.
Language
 The Britons spoke an Insular Celtic language known as
The Britons spoke an Insular Celtic language known as Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a ...
. Brittonic was spoken throughout the island of Britain (in modern terms, England, Wales and Scotland), as well as offshore islands such as the Isle of Man, Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of the ...
, Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
, Hebrides, Isle of Wight and Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the no ...
. According to early medieval historical tradition, such as ''The Dream of Macsen Wledig
Magnus Maximus (; cy, Macsen Wledig ; died 8 August 388) was Roman emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian in 383 through negotiation with emperor Theodosius I.
He was made emperor in B ...
'', the post-Roman Celtic-speakers of Armorica were colonists from Britain, resulting in the Breton language
Breton (, ; or in Morbihan) is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family spoken in Brittany, part of modern-day France. It is the only Celtic language still widely in use on the European mainland, albeit as a member of t ...
, a language related to Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
and identical to Cornish in the early period and still used today. Thus the area today is called Brittany (Br. ''Breizh'', Fr. ''Bretagne'', derived from '' Britannia'').
Common Brittonic developed from the Insular branch of the Proto-Celtic language that developed in the British Isles after arriving from the continent in the 7th century BC. The language eventually began to diverge; some linguists have grouped subsequent developments as Western and Southwestern Brittonic languages. Western Brittonic developed into Welsh in Wales and the Cumbric language in the Hen Ogledd or "Old North" of Britain (modern northern England and southern Scotland), while the Southwestern dialect became Cornish in Cornwall and South West England and Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
** Breton people
** Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Ga ...
in Armorica. Pictish is now generally accepted to descend from Common Brittonic, rather than being a separate Celtic language. Welsh and Breton survive today; Cumbric and Pictish became extinct in the 12th century. Cornish had become extinct by the 19th century but has been the subject of language revitalization since the 20th century.
Tribal groups
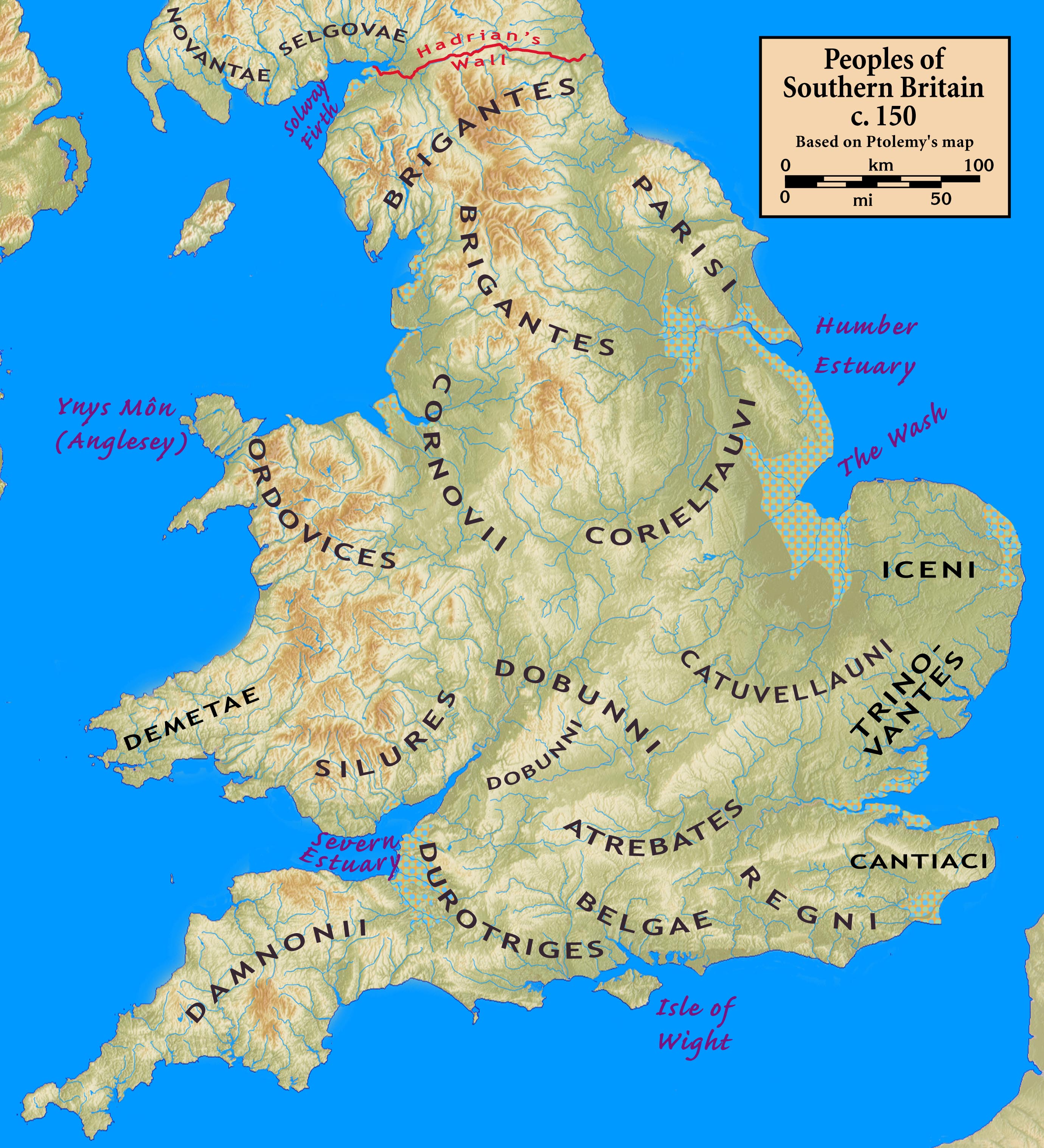
 Celtic Britain was made up of many territories controlled by Brittonic tribes. They are generally believed to have dwelt throughout the whole island of Great Britain, at least as far north as the Clyde–
Celtic Britain was made up of many territories controlled by Brittonic tribes. They are generally believed to have dwelt throughout the whole island of Great Britain, at least as far north as the Clyde–Forth
Forth or FORTH may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''forth'' magazine, an Internet magazine
* ''Forth'' (album), by The Verve, 2008
* ''Forth'', a 2011 album by Proto-Kaw
* Radio Forth, a group of independent local radio stations in Scotla ...
isthmus. The territory north of this was largely inhabited by the Picts; little direct evidence has been left of the Pictish language, but place names and Pictish personal names recorded in the later Irish annals
A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over t ...
suggest it was indeed related to the Common Brittonic language
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a ...
. Their Goidelic (Gaelic) name, '' Cruithne'', is cognate with ''Pritenī''.
The following is a list of the major Brittonic tribes, in both the Latin and Brittonic languages, as well as their capitals during the Roman period.
Art
 The La Tène style, which covers British Celtic art, was late arriving in Britain, but after 300 BC the ancient British seem to have had generally similar cultural practices to the Celtic cultures nearest to them on the continent. There are significant differences in artistic styles, and the greatest period of what is known as the "Insular La Tène" style, surviving mostly in metalwork, was in the century or so before the Roman conquest, and perhaps the decades after it.
The La Tène style, which covers British Celtic art, was late arriving in Britain, but after 300 BC the ancient British seem to have had generally similar cultural practices to the Celtic cultures nearest to them on the continent. There are significant differences in artistic styles, and the greatest period of what is known as the "Insular La Tène" style, surviving mostly in metalwork, was in the century or so before the Roman conquest, and perhaps the decades after it.
 The carnyx, a trumpet with an animal-headed bell, was used by Celtic Britons during war and ceremony.
The carnyx, a trumpet with an animal-headed bell, was used by Celtic Britons during war and ceremony.
History
Origins
There are competing hypotheses for when Celtic peoples, and the Celtic languages, first arrived in Britain, none of which have gained consensus. The traditional view during most of the twentieth century was that Celtic culture grew out of the central EuropeanHallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European Archaeological culture, culture of Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe ...
, from which the Celts and their languages reached Britain in the second half of the first millennium BC. More recently, John Koch
John Koch (August 18, 1909 — April 19, 1978), (pronounced "KŌK") was an American painter and teacher, and an important figure in 20th century Realism. He is best known for his light-filled paintings of urban interiors, often featuring classica ...
and Barry Cunliffe
Sir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe, (born 10 December 1939), known as Barry Cunliffe, is a British archaeologist and academic. He was Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford from 1972 to 2007. Since 2007, he has been an Emeri ...
have challenged that with their 'Celtic from the West' theory, which has the Celtic languages developing as a maritime trade language in the Atlantic Bronze Age cultural zone before it spread eastward. Alternatively, Patrick Sims-Williams criticises both of these hypotheses to propose 'Celtic from the Centre', which suggests Celtic originated in Gaul and spread during the first millennium BC, reaching Britain towards the end of this period.
In 2021, a major archaeogenetics study uncovered a migration into southern Britain during the Bronze Age, over a 500 year period from 1,300 BC to 800 BC. The migrants were "genetically most similar to ancient individuals from France" and had higher levels of Early European Farmers ancestry. From 1000 to 875 BC, their genetic marker swiftly spread through southern Britain, making up around half the ancestry of subsequent Iron Age people in this area, but not in northern Britain. The "evidence suggests that, rather than a violent invasion or a single migratory event, the genetic structure of the population changed through sustained contacts between mainland Britain and Europe over several centuries, such as the movement of traders, intermarriage, and small scale movements of family groups". The authors describe this as a "plausible vector for the spread of early Celtic languages into Britain". There was much less migration into Britain during the subsequent Iron Age, so it is more likely that Celtic reached Britain before then. Barry Cunliffe suggests that a branch of Celtic was already being spoken in Britain, and that the Bronze Age migration introduced the Brittonic branch.
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'', which was originally compiled by the orders of King Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bot ...
in approximately 890, starts with this sentence: "The island Britain is 800 miles long, and 200 miles broad. And there are in the island five nations; English, Welsh (or British), Scottish, Pictish, and Latin. The first inhabitants were the Britons, who came from Armenia, and first peopled Britain southward" ("Armenia" is possibly a mistaken transcription of Armorica, an area in northwestern Gaul including modern Brittany).
Roman conquest
 In 43 AD, the Roman Empire invaded Britain. The British tribes opposed the Roman legions for many decades, but by 84 AD the Romans had decisively conquered southern Britain and had pushed into Brittonic areas of what would later become northern England and southern Scotland. During the same period
In 43 AD, the Roman Empire invaded Britain. The British tribes opposed the Roman legions for many decades, but by 84 AD the Romans had decisively conquered southern Britain and had pushed into Brittonic areas of what would later become northern England and southern Scotland. During the same period Belgic Belgic may refer to:
* an adjective referring to the Belgae, an ancient confederation of tribes
* a rarer adjective referring to the Low Countries or to Belgium
* , several ships with the name
* Belgic ware
Aylesford-Swarling pottery is part of a ...
tribes from the Gaelic-Germanic borderlands settled in southern Britain. Caesar asserts the Belgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Ju ...
had first crossed the channel as raiders, only later establishing themselves on the island. 122 AD, the Romans fortified the northern border with Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall ( la, Vallum Aelium), also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Hadriani'' in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. R ...
, which spanned what is now Northern England. In 142 AD, Roman forces pushed north again and began construction of the Antonine Wall
The Antonine Wall, known to the Romans as ''Vallum Antonini'', was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some twe ...
, which ran between the Forth–Clyde isthmus, but they retreated back to Hadrian's Wall after only twenty years. Although the native Britons south of Hadrian's Wall mostly kept their land, they were subject to the Roman governors
A Roman governor was an official either elected or appointed to be the chief administrator of Roman law throughout one or more of the many provinces constituting the Roman Empire.
The generic term in Roman legal language was '' Rector provinciae ...
, whilst the Brittonic-Pictish Britons north of the wall probably remained fully independent and unconquered. The Roman Empire retained control of "Britannia" until its departure about AD 410, although parts of Britain had already effectively shrugged off Roman rule decades earlier.
An undercurrent of British influence is found in artefacts from the Roman period, such as the Staffordshire Moorlands Pan
The Staffordshire Moorlands Pan, sometimes known as the Ilam Pan, is a 2nd-century AD enamelled bronze ''trulla'' with an inscription relating to the forts of Hadrian's Wall. It was found in June 2003 in Ilam parish, Staffordshire, by met ...
, and it appears that it was from this, passing to Ireland in the late Roman and post-Roman period, that the "Celtic" element in Early Medieval Insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, was produced in the post-Roman era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term derives from ''insula'', the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style dif ...
derived.
Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain
 Thirty years or so after the time of the Roman departure, the Germanic-speaking Anglo-Saxons began a migration to the south-eastern coast of Britain, where they began to establish their own kingdoms, and the
Thirty years or so after the time of the Roman departure, the Germanic-speaking Anglo-Saxons began a migration to the south-eastern coast of Britain, where they began to establish their own kingdoms, and the Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, and Ca ...
-speaking Scots migrating from Dál nAraidi (modern Northern Ireland) did the same on the west coast of Scotland and the Isle of Man.
At the same time, Britons established themselves in what is now called Brittany and the Channel Islands. There they set up their own small kingdoms and the Breton language
Breton (, ; or in Morbihan) is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family spoken in Brittany, part of modern-day France. It is the only Celtic language still widely in use on the European mainland, albeit as a member of t ...
developed from Brittonic Insular Celtic
Insular Celtic languages are the group of Celtic languages of Brittany, Great Britain, Ireland, and the Isle of Man. All surviving Celtic languages are in the Insular group, including Breton, which is spoken on continental Europe in Brittany, ...
rather than Gaulish or Frankish. A further Brittonic colony, Britonia, was also set up at this time in Gallaecia in northwestern Spain.
Many of the old Brittonic kingdoms began to disappear in the centuries after the Anglo-Saxon and Scottish Gaelic invasions; Parts of the regions of modern East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
, East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, Li ...
, North East England
North East England is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. The region has three current administrative levels below the region level in the region; combined authority, unitary authorit ...
, Argyll and South East England were the first to fall to the Germanic and Gaelic Scots invasions.
The kingdom of Ceint (modern Kent) fell in 456 AD. Linnuis (which stood astride modern Lincolnshire and Nottinghamshire) was subsumed as early as 500 AD and became the English Kingdom of Lindsey.
Rhegin (essentially modern Sussex
Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the English ...
and eastern Hampshire) was likely fully conquered by 510 AD. Ynys Weith (Isle of Wight) fell in 530 AD, Caer Colun
Camulodunum (; la, ), the Ancient Roman
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. ...
(essentially modern Essex) by 540 AD. The Gaels arrived on the northwest coast of Britain from Ireland, dispossessed the native Britons, and founded Dal Riata
In Indian cuisine, ''dal'' (also spelled ''daal'' or ''dhal''; pronunciation: , Hindi: दाल, Urdu: ) are dried, split pulses (e.g., lentils, peas, and beans) that do not require soaking before cooking. India is the largest producer of pu ...
which encompassed modern Argyll, Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated b ...
and Iona
Iona (; gd, Ì Chaluim Chille (IPA: �iːˈxaɫ̪ɯimˈçiʎə, sometimes simply ''Ì''; sco, Iona) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there ...
between 500 and 560 AD. Deifr (Deira) which encompassed modern-day Teesside, Wearside, Tyneside, Humberside, Lindisfarne (Medcaut
Lindisfarne, also called Holy Island, is a tidal island off the northeast coast of England, which constitutes the civil parish of Holy Island in Northumberland. Holy Island has a recorded history from the 6th century AD; it was an important ...
) and the Farne Islands fell to the Anglo-Saxons in 559 AD and Deira became an Anglo-Saxon kingdom after this point. Caer Went had officially disappeared by 575 AD becoming the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of East Anglia. Gwent was only partly conquered; its capital Caer Gloui
Caer (; owl, cair or ') is a placename element in Welsh meaning "stronghold", "fortress", or "citadel", roughly equivalent to an Old English suffix (''-ceaster'') now variously written as , , and .Allen, Grant.