Boston University Terriers Men's Basketball Coaches on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the
Accessed October 7, 2018. professional and business services,
Lost Boston
', Amherst : University of Massachusetts Press, 2006. . Cf
p.4
/ref>Thurston, H. (1907). "St. Botulph." ''The Catholic Encyclopedia''. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved June 17, 2014 from New Advent: http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/02709a.htm
 Many crucial events of the
Many crucial events of the
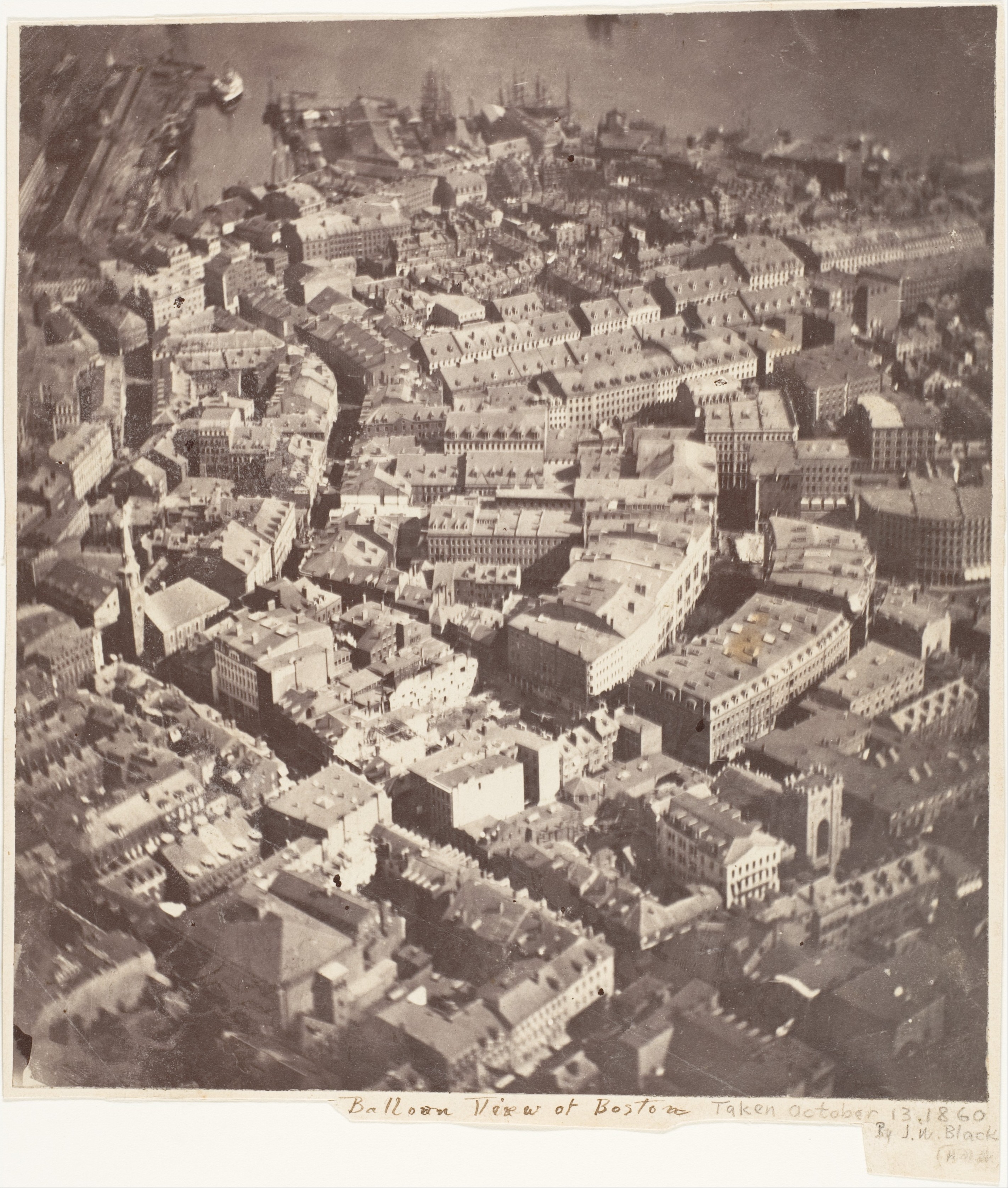 After the Revolution, Boston's long
After the Revolution, Boston's long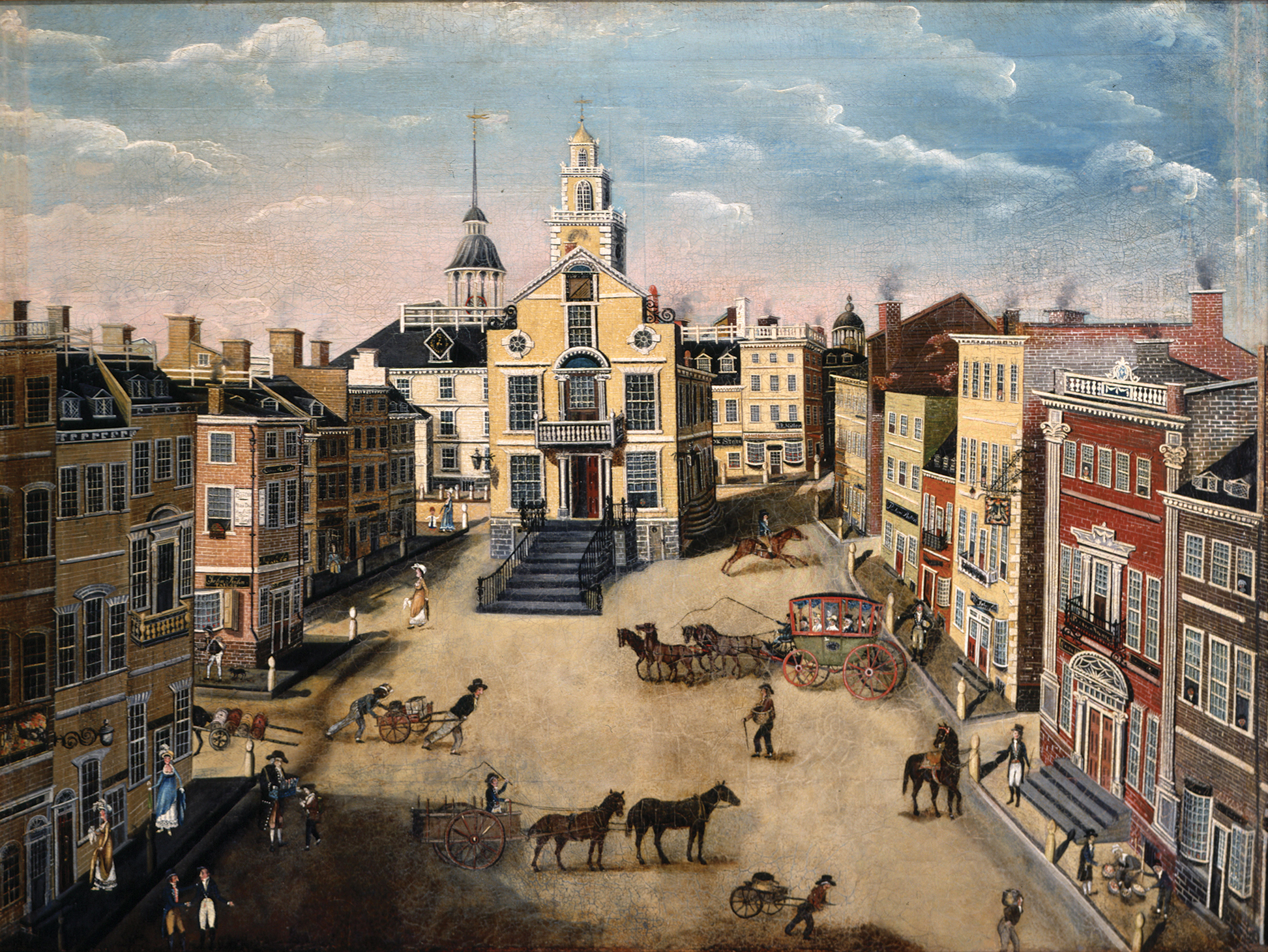  During this period, Boston flourished culturally, as well, admired for its rarefied literary life and generous artistic patronage, with members of old Boston families—eventually dubbed ''
During this period, Boston flourished culturally, as well, admired for its rarefied literary life and generous artistic patronage, with members of old Boston families—eventually dubbed ''

 In the 1820s, Boston's population grew rapidly, and the city's ethnic composition changed dramatically with the first wave of European
In the 1820s, Boston's population grew rapidly, and the city's ethnic composition changed dramatically with the first wave of European 
 After the Great Boston fire of 1872, workers used building rubble as landfill along the downtown waterfront. During the mid-to-late 19th century, workers filled almost of brackish Charles River marshlands west of
After the Great Boston fire of 1872, workers used building rubble as landfill along the downtown waterfront. During the mid-to-late 19th century, workers filled almost of brackish Charles River marshlands west of
 Boston is an intellectual, technological, and political center but has lost some important regional institutions, including the loss to mergers and acquisitions of local financial institutions such as FleetBoston Financial, which was acquired by Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte-based Bank of America in 2004. Boston-based department stores Jordan Marsh and Filene's have both merged into the New York City–based Macy's, Inc., Macy's.
The 1993 acquisition of ''The Boston Globe'' by ''The New York Times'' was reversed in 2013 when it was re-sold to Boston businessman John W. Henry. In 2016, it was announced General Electric would be moving its corporate headquarters from Connecticut to the Seaport District in Boston, joining many other companies in this rapidly developing neighborhood.
Boston has experienced gentrification in the latter half of the 20th century, with housing prices increasing sharply since the 1990s.
On April 15, 2013, two Chechen Islamist brothers Boston Marathon bombing, detonated a pair of bombs near the finish line of the 2013 Boston Marathon, Boston Marathon, killing three people and injuring roughly 264.
In 2016, Boston briefly Boston bid for the 2024 Summer Olympics, shouldered a bid as the US applicant for the 2024 Summer Olympics. The bid was supported by the mayor and a coalition of business leaders and local philanthropists, but was eventually dropped due to public opposition. The United States Olympic Committee, USOC then selected Los Angeles to be the American candidate with Los Angeles ultimately securing the right to host the 2028 Summer Olympics.
Boston is an intellectual, technological, and political center but has lost some important regional institutions, including the loss to mergers and acquisitions of local financial institutions such as FleetBoston Financial, which was acquired by Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte-based Bank of America in 2004. Boston-based department stores Jordan Marsh and Filene's have both merged into the New York City–based Macy's, Inc., Macy's.
The 1993 acquisition of ''The Boston Globe'' by ''The New York Times'' was reversed in 2013 when it was re-sold to Boston businessman John W. Henry. In 2016, it was announced General Electric would be moving its corporate headquarters from Connecticut to the Seaport District in Boston, joining many other companies in this rapidly developing neighborhood.
Boston has experienced gentrification in the latter half of the 20th century, with housing prices increasing sharply since the 1990s.
On April 15, 2013, two Chechen Islamist brothers Boston Marathon bombing, detonated a pair of bombs near the finish line of the 2013 Boston Marathon, Boston Marathon, killing three people and injuring roughly 264.
In 2016, Boston briefly Boston bid for the 2024 Summer Olympics, shouldered a bid as the US applicant for the 2024 Summer Olympics. The bid was supported by the mayor and a coalition of business leaders and local philanthropists, but was eventually dropped due to public opposition. The United States Olympic Committee, USOC then selected Los Angeles to be the American candidate with Los Angeles ultimately securing the right to host the 2028 Summer Olympics.
 Boston has an area of — (54%) of land and (46%) of water. The city's official elevation, as measured at Logan International Airport, is Above mean sea level, above sea level. The highest point in Boston is Bellevue Hill, Boston, Bellevue Hill at above sea level, and the lowest point is at sea level. Boston is situated on
Boston has an area of — (54%) of land and (46%) of water. The city's official elevation, as measured at Logan International Airport, is Above mean sea level, above sea level. The highest point in Boston is Bellevue Hill, Boston, Bellevue Hill at above sea level, and the lowest point is at sea level. Boston is situated on  Boston is surrounded by the
Boston is surrounded by the
 Boston is sometimes called a "city of neighborhoods" because of the profusion of diverse subsections; the city government's Office of Neighborhood Services has officially designated 23 neighborhoods. More than two-thirds of inner Boston's modern land area did not exist when the city was founded. Instead, it was created via the gradual filling in of the surrounding tidal areas over the centuries, with earth from leveling or lowering Boston's three original hills (the "Trimountain", after which Tremont Street is named) and with gravel brought by train from Needham to fill the Back Bay.
Downtown Boston, Downtown and its immediate surroundings consist largely of low-rise masonry buildings (often Federal architecture, Federal style and Greek Revival) interspersed with modern highrises, in the Financial District, Government Center, and South Boston. Back Bay includes many prominent landmarks, such as the
Boston is sometimes called a "city of neighborhoods" because of the profusion of diverse subsections; the city government's Office of Neighborhood Services has officially designated 23 neighborhoods. More than two-thirds of inner Boston's modern land area did not exist when the city was founded. Instead, it was created via the gradual filling in of the surrounding tidal areas over the centuries, with earth from leveling or lowering Boston's three original hills (the "Trimountain", after which Tremont Street is named) and with gravel brought by train from Needham to fill the Back Bay.
Downtown Boston, Downtown and its immediate surroundings consist largely of low-rise masonry buildings (often Federal architecture, Federal style and Greek Revival) interspersed with modern highrises, in the Financial District, Government Center, and South Boston. Back Bay includes many prominent landmarks, such as the
 Under the Köppen climate classification, depending on the isotherm used, Boston has either a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') under the isotherm or a humid continental climate under the 0 °C isotherm (Köppen ''Dfa''). The city is best described as being in a transitional zone between the two climates. Summers are typically warm and humid, while winters are cold and stormy, with occasional periods of heavy snow. Spring and fall are usually cool to mild, with varying conditions dependent on wind direction and jet stream positioning. Prevailing wind patterns that blow offshore minimize the influence of the Atlantic Ocean. However, in winter areas near the immediate coast will often see more rain than snow as warm air is drawn off the Atlantic at times. The city lies at the transition between USDA plant hardiness zones 6b (most of the city) and 7a (Downtown, South Boston, and East Boston neighborhoods).
The hottest month is July, with a mean temperature of . The coldest month is January, with a mean temperature of . Periods exceeding in summer and below freezing in winter are not uncommon but rarely extended, with about 13 and 25 days per year seeing each, respectively. The most recent sub- reading occurred on January 7, 2018, when the temperature dipped down to . In addition, several decades may pass between readings, with the most recent such occurrence on July 22, 2011, when the temperature reached . The city's average window for freezing temperatures is November 9 through April 5. Official temperature records have ranged from on February 9, 1934, up to on July 4, 1911. The record cold daily maximum is on December 30, 1917, while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum is on August 2, 1975, and July 21, 2019.
Under the Köppen climate classification, depending on the isotherm used, Boston has either a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') under the isotherm or a humid continental climate under the 0 °C isotherm (Köppen ''Dfa''). The city is best described as being in a transitional zone between the two climates. Summers are typically warm and humid, while winters are cold and stormy, with occasional periods of heavy snow. Spring and fall are usually cool to mild, with varying conditions dependent on wind direction and jet stream positioning. Prevailing wind patterns that blow offshore minimize the influence of the Atlantic Ocean. However, in winter areas near the immediate coast will often see more rain than snow as warm air is drawn off the Atlantic at times. The city lies at the transition between USDA plant hardiness zones 6b (most of the city) and 7a (Downtown, South Boston, and East Boston neighborhoods).
The hottest month is July, with a mean temperature of . The coldest month is January, with a mean temperature of . Periods exceeding in summer and below freezing in winter are not uncommon but rarely extended, with about 13 and 25 days per year seeing each, respectively. The most recent sub- reading occurred on January 7, 2018, when the temperature dipped down to . In addition, several decades may pass between readings, with the most recent such occurrence on July 22, 2011, when the temperature reached . The city's average window for freezing temperatures is November 9 through April 5. Official temperature records have ranged from on February 9, 1934, up to on July 4, 1911. The record cold daily maximum is on December 30, 1917, while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum is on August 2, 1975, and July 21, 2019.
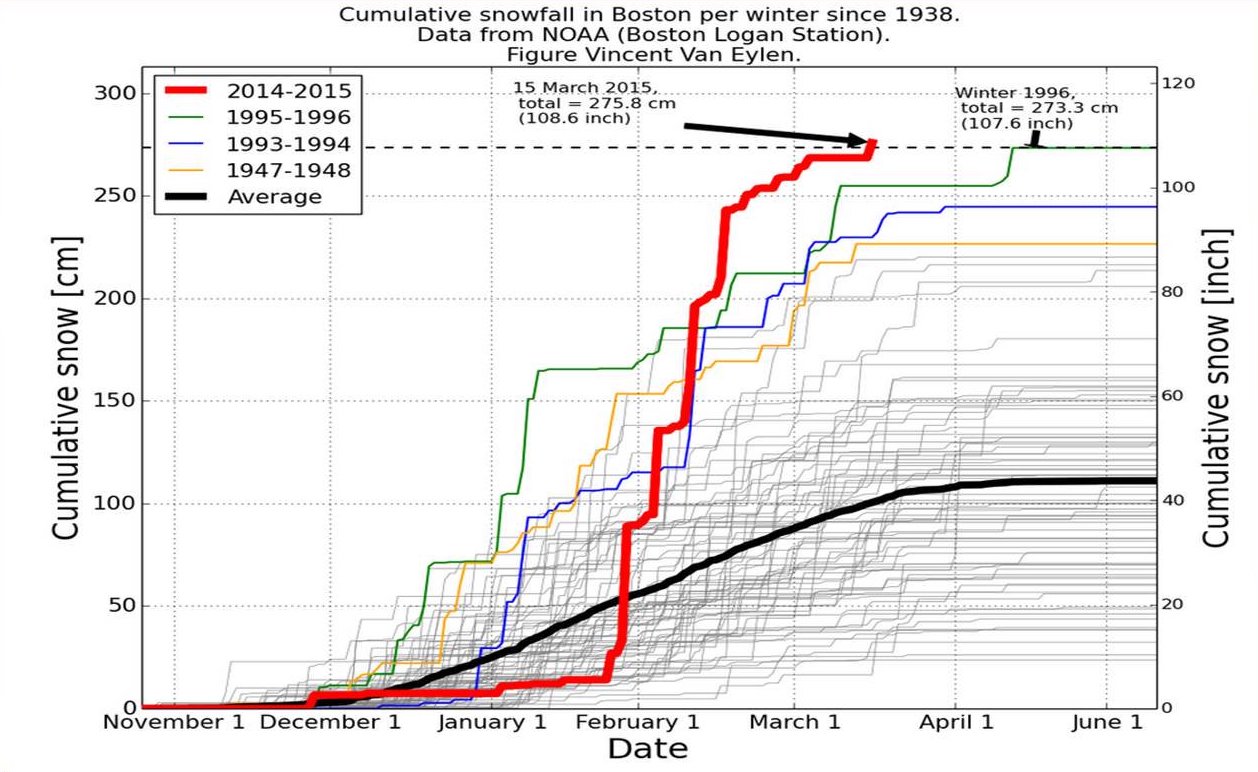 Boston's coastal location on the North Atlantic moderates its temperature but makes the city very prone to Nor'easter weather systems that can produce much snow and rain. The city averages of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation a year, with of snowfall per season. Most snowfall occurs from mid-November through early April, and snow is rare in May and October. There is also high year-to-year variability in snowfall; for instance, the winter of 2011–12 saw only of accumulating snow, but the previous winter, the corresponding figure was .
Fog is fairly common, particularly in spring and early summer. Due to its location along the North Atlantic, the city often receives sea breezes, especially in the late spring, when water temperatures are still quite cold and temperatures at the coast can be more than colder than a few miles inland, sometimes dropping by that amount near midday.
Thunderstorms occur from May to September, which are occasionally severe with large hail, damaging winds, and heavy downpours. Although downtown Boston has never been struck by a violent tornado, the city itself has experienced many tornado warnings. Damaging storms are more common to areas north, west, and northwest of the city. Boston has a relatively sunny climate for a coastal city at its latitude, averaging over 2,600 hours of sunshine per annum.
Boston's coastal location on the North Atlantic moderates its temperature but makes the city very prone to Nor'easter weather systems that can produce much snow and rain. The city averages of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation a year, with of snowfall per season. Most snowfall occurs from mid-November through early April, and snow is rare in May and October. There is also high year-to-year variability in snowfall; for instance, the winter of 2011–12 saw only of accumulating snow, but the previous winter, the corresponding figure was .
Fog is fairly common, particularly in spring and early summer. Due to its location along the North Atlantic, the city often receives sea breezes, especially in the late spring, when water temperatures are still quite cold and temperatures at the coast can be more than colder than a few miles inland, sometimes dropping by that amount near midday.
Thunderstorms occur from May to September, which are occasionally severe with large hail, damaging winds, and heavy downpours. Although downtown Boston has never been struck by a violent tornado, the city itself has experienced many tornado warnings. Damaging storms are more common to areas north, west, and northwest of the city. Boston has a relatively sunny climate for a coastal city at its latitude, averaging over 2,600 hours of sunshine per annum.
 In 2020, Boston was estimated to have 691,531 residents living in 266,724 households—a 12% population increase over 2010. The city is the List of United States cities by population density, third-most densely populated large U.S. city of over half a million residents, and the most densely populated state capital. Some 1.2 million persons may be within Boston's boundaries during work hours, and as many as 2 million during special events. This fluctuation of people is caused by hundreds of thousands of suburban residents who travel to the city for work, education, health care, and special events.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 21.9% at age 19 and under, 14.3% from 20 to 24, 33.2% from 25 to 44, 20.4% from 45 to 64, and 10.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 30.8 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.9 males. There were 252,699 households, of which 20.4% had children under the age of 18 living in them, 25.5% were married couples living together, 16.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 54.0% were non-families. 37.1% of all households were made up of individuals, and 9.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.26 and the average family size was 3.08. From an estimate in 2005, Boston has one of the LGBT demographics of the United States#By city, largest per capita LGBT populations in the United States.
The Median income, median household income in Boston was $51,739, while the median income for a family was $61,035. Full-time year-round male workers had a median income of $52,544 versus $46,540 for full-time year-round female workers. The per capita income for the city was $33,158. 21.4% of the population and 16.0% of families were below the poverty line. Of the total population, 28.8% of those under the age of 18 and 20.4% of those 65 and older were living below the poverty line. Boston has a significant racial wealth gap in the United States, racial wealth gap with White Bostonians having an median net worth of $247,500 compared to an $8 median net worth for non-immigrant Black residents and $0 for Dominican immigrant residents.
In 1950, Race (United States Census), Whites represented 94.7% of Boston's population. From the 1950s to the end of the 20th century, the proportion of non-Hispanic Whites in the city declined. In 2000, non-Hispanic Whites made up 49.5% of the city's population, making the city majority minority for the first time. However, in the 21st century, the city has experienced significant gentrification, during which affluent Whites have moved into formerly non-White areas. In 2006, the US Census Bureau estimated non-Hispanic Whites again formed a slight majority but , in part due to the housing crash, as well as increased efforts to make more affordable housing more available, the non-White population has rebounded. This may also have to do with increased Latin American and Asian Americans, Asian populations and more clarity surrounding US Census statistics, which indicate a non-Hispanic White population of 47 percent (some reports give slightly lower figures).
In 2020, Boston was estimated to have 691,531 residents living in 266,724 households—a 12% population increase over 2010. The city is the List of United States cities by population density, third-most densely populated large U.S. city of over half a million residents, and the most densely populated state capital. Some 1.2 million persons may be within Boston's boundaries during work hours, and as many as 2 million during special events. This fluctuation of people is caused by hundreds of thousands of suburban residents who travel to the city for work, education, health care, and special events.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 21.9% at age 19 and under, 14.3% from 20 to 24, 33.2% from 25 to 44, 20.4% from 45 to 64, and 10.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 30.8 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.9 males. There were 252,699 households, of which 20.4% had children under the age of 18 living in them, 25.5% were married couples living together, 16.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 54.0% were non-families. 37.1% of all households were made up of individuals, and 9.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.26 and the average family size was 3.08. From an estimate in 2005, Boston has one of the LGBT demographics of the United States#By city, largest per capita LGBT populations in the United States.
The Median income, median household income in Boston was $51,739, while the median income for a family was $61,035. Full-time year-round male workers had a median income of $52,544 versus $46,540 for full-time year-round female workers. The per capita income for the city was $33,158. 21.4% of the population and 16.0% of families were below the poverty line. Of the total population, 28.8% of those under the age of 18 and 20.4% of those 65 and older were living below the poverty line. Boston has a significant racial wealth gap in the United States, racial wealth gap with White Bostonians having an median net worth of $247,500 compared to an $8 median net worth for non-immigrant Black residents and $0 for Dominican immigrant residents.
In 1950, Race (United States Census), Whites represented 94.7% of Boston's population. From the 1950s to the end of the 20th century, the proportion of non-Hispanic Whites in the city declined. In 2000, non-Hispanic Whites made up 49.5% of the city's population, making the city majority minority for the first time. However, in the 21st century, the city has experienced significant gentrification, during which affluent Whites have moved into formerly non-White areas. In 2006, the US Census Bureau estimated non-Hispanic Whites again formed a slight majority but , in part due to the housing crash, as well as increased efforts to make more affordable housing more available, the non-White population has rebounded. This may also have to do with increased Latin American and Asian Americans, Asian populations and more clarity surrounding US Census statistics, which indicate a non-Hispanic White population of 47 percent (some reports give slightly lower figures).

 People of History of Irish Americans in Boston, Irish descent form the largest single American ancestry, ethnic group in the city, making up 15.8% of the population, followed by Italian Americans, Italians, accounting for 8.3% of the population. People of West Indies, West Indian and Caribbean ancestry are another sizable group, at over 15%.
In Greater Boston, these numbers grew significantly, with 150,000 Dominicans according to 2018 estimates, 134,000 Puerto Ricans, 57,500 Salvadorans, 39,000 Guatemalans, 36,000 Mexicans, and over 35,000 Colombians. East Boston has a diverse Hispanic/Latino population of Salvadorans, Colombians, Guatemalans, Mexicans, Dominicans, Puerto Ricans, and even Portuguese-speaking people from Portugal and Brazil. Hispanic populations in southwest Boston neighborhoods are mainly made up of Dominicans and Puerto Ricans, usually sharing neighborhoods in this section with African Americans and Blacks with origins from the Caribbean and Africa especially Cape Verdeans and Haitians. Neighborhoods such as Jamaica Plain, Boston, Jamaica Plain and Roslindale, Boston, Roslindale have experienced a growing number of Dominican-Americans in Boston, Dominican Americans.
Over 27,000 Chinese Americans in Boston, Chinese Americans made their home in Boston city proper in 2013.
People of History of Irish Americans in Boston, Irish descent form the largest single American ancestry, ethnic group in the city, making up 15.8% of the population, followed by Italian Americans, Italians, accounting for 8.3% of the population. People of West Indies, West Indian and Caribbean ancestry are another sizable group, at over 15%.
In Greater Boston, these numbers grew significantly, with 150,000 Dominicans according to 2018 estimates, 134,000 Puerto Ricans, 57,500 Salvadorans, 39,000 Guatemalans, 36,000 Mexicans, and over 35,000 Colombians. East Boston has a diverse Hispanic/Latino population of Salvadorans, Colombians, Guatemalans, Mexicans, Dominicans, Puerto Ricans, and even Portuguese-speaking people from Portugal and Brazil. Hispanic populations in southwest Boston neighborhoods are mainly made up of Dominicans and Puerto Ricans, usually sharing neighborhoods in this section with African Americans and Blacks with origins from the Caribbean and Africa especially Cape Verdeans and Haitians. Neighborhoods such as Jamaica Plain, Boston, Jamaica Plain and Roslindale, Boston, Roslindale have experienced a growing number of Dominican-Americans in Boston, Dominican Americans.
Over 27,000 Chinese Americans in Boston, Chinese Americans made their home in Boston city proper in 2013.
 According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, 57% of the population of the city identified themselves as Christians, with 25% attending a variety of Protestantism, Protestant churches and 29% professing Catholic Church, Roman Catholic beliefs; 33% claim Irreligion, no religious affiliation, while the remaining 10% are composed of adherents of Judaism, Buddhism, Islam, Hinduism, Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí and other faiths.
, the Catholic Church had the highest number of adherents as a single denomination in the
According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, 57% of the population of the city identified themselves as Christians, with 25% attending a variety of Protestantism, Protestant churches and 29% professing Catholic Church, Roman Catholic beliefs; 33% claim Irreligion, no religious affiliation, while the remaining 10% are composed of adherents of Judaism, Buddhism, Islam, Hinduism, Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí and other faiths.
, the Catholic Church had the highest number of adherents as a single denomination in the
 The Boston Public Schools enroll 57,000 students attending 145 schools, including the renowned Boston Latin Academy, John D. O'Bryant School of Mathematics & Science, John D. O'Bryant School of Math & Science, and
The Boston Public Schools enroll 57,000 students attending 145 schools, including the renowned Boston Latin Academy, John D. O'Bryant School of Mathematics & Science, John D. O'Bryant School of Math & Science, and
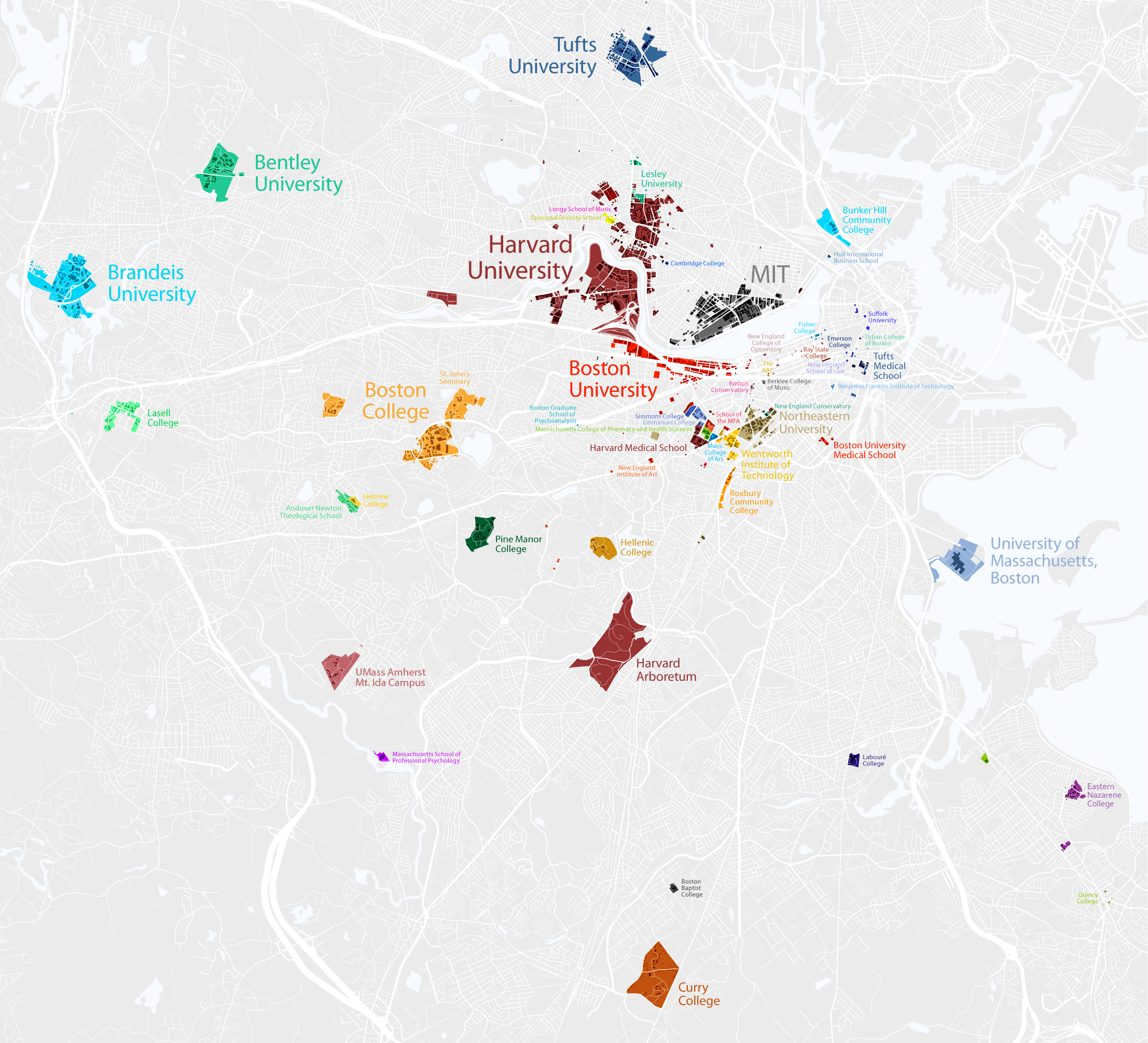 Some of the most renowned and highly ranked universities in the world are near Boston. Three universities with a major presence in the city,
Some of the most renowned and highly ranked universities in the world are near Boston. Three universities with a major presence in the city, 
 Greater Boston has more than 50 colleges and universities, with 250,000 students enrolled in Boston and Cambridge alone. The city's largest private universities include Boston University (also the city's fourth-largest employer), with its main campus along Commonwealth Avenue (Boston), Commonwealth Avenue and a medical campus in the South End, Boston, South End, Northeastern University in the Fenway–Kenmore, Fenway area, Suffolk University near Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill, which includes Suffolk University Law School, law school and Sawyer Business School, business school, and Boston College, which straddles the Boston (Brighton)–Newton border. Boston's only public university is the University of Massachusetts Boston on Columbia Point in Dorchester, Massachusetts, Dorchester. Roxbury Community College and Bunker Hill Community College are the city's two public community colleges. Altogether, Boston's colleges and universities employ more than 42,600 people, accounting for nearly seven percent of the city's workforce.
Smaller private colleges include Babson College, Bentley University, Boston Architectural College, Emmanuel College (Massachusetts), Emmanuel College, Fisher College, MGH Institute of Health Professions, MCPHS University, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Simmons University, Wellesley College, Wheelock College, Wentworth Institute of Technology, New England School of Law (originally established as America's first all female law school), and Emerson College.
Metropolitan Boston is home to several music school, conservatories and art schools, including Lesley University, Lesley University College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art, the School of the Museum of Fine Arts at Tufts, School of the Museum of Fine Arts, New England Institute of Art, New England School of Art and Design (Suffolk University), Longy School of Music of Bard College, and the New England Conservatory of Music, New England Conservatory (the oldest independent conservatory in the United States). Other conservatories include the Boston Conservatory and Berklee College of Music, which has made Boston an important city for jazz music.
Greater Boston has more than 50 colleges and universities, with 250,000 students enrolled in Boston and Cambridge alone. The city's largest private universities include Boston University (also the city's fourth-largest employer), with its main campus along Commonwealth Avenue (Boston), Commonwealth Avenue and a medical campus in the South End, Boston, South End, Northeastern University in the Fenway–Kenmore, Fenway area, Suffolk University near Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill, which includes Suffolk University Law School, law school and Sawyer Business School, business school, and Boston College, which straddles the Boston (Brighton)–Newton border. Boston's only public university is the University of Massachusetts Boston on Columbia Point in Dorchester, Massachusetts, Dorchester. Roxbury Community College and Bunker Hill Community College are the city's two public community colleges. Altogether, Boston's colleges and universities employ more than 42,600 people, accounting for nearly seven percent of the city's workforce.
Smaller private colleges include Babson College, Bentley University, Boston Architectural College, Emmanuel College (Massachusetts), Emmanuel College, Fisher College, MGH Institute of Health Professions, MCPHS University, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Simmons University, Wellesley College, Wheelock College, Wentworth Institute of Technology, New England School of Law (originally established as America's first all female law school), and Emerson College.
Metropolitan Boston is home to several music school, conservatories and art schools, including Lesley University, Lesley University College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art, the School of the Museum of Fine Arts at Tufts, School of the Museum of Fine Arts, New England Institute of Art, New England School of Art and Design (Suffolk University), Longy School of Music of Bard College, and the New England Conservatory of Music, New England Conservatory (the oldest independent conservatory in the United States). Other conservatories include the Boston Conservatory and Berklee College of Music, which has made Boston an important city for jazz music.
 The Longwood Medical and Academic Area, adjacent to the Fenway, district, is home to a large number of medical and research facilities, including Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston Children's Hospital, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Joslin Diabetes Center, and the MCPHS University, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences.
Prominent medical facilities, including Massachusetts General Hospital, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital are in the Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill area. St. Elizabeth's Medical Center (Boston), St. Elizabeth's Medical Center is in Brighton Center of the city's Brighton, Boston, Brighton neighborhood. New England Baptist Hospital is in Mission Hill. VA Boston Healthcare System, The city has Veterans Affairs medical centers in the Jamaica Plain, Boston, Jamaica Plain and West Roxbury, Boston, West Roxbury neighborhoods. The Boston Public Health Commission, an agency of the Massachusetts government, oversees health concerns for city residents. Boston EMS provides pre-hospital emergency medical services to residents and visitors.
Many of Boston's medical facilities are associated with universities. The facilities in the Longwood Medical and Academic Area and in Massachusetts General Hospital are affiliated with Harvard Medical School. Tufts Medical Center (formerly Tufts-New England Medical Center), in the southern portion of the Chinatown, Boston, Chinatown neighborhood, is affiliated with Tufts University School of Medicine. Boston Medical Center, in the South End, Boston, South End neighborhood, is the primary teaching facility for the Boston University School of Medicine as well as the largest trauma center in the Boston area; it was formed by the merger of Boston University Hospital and Boston City Hospital, which was the first municipal hospital in the United States.
The Longwood Medical and Academic Area, adjacent to the Fenway, district, is home to a large number of medical and research facilities, including Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston Children's Hospital, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Joslin Diabetes Center, and the MCPHS University, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences.
Prominent medical facilities, including Massachusetts General Hospital, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital are in the Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill area. St. Elizabeth's Medical Center (Boston), St. Elizabeth's Medical Center is in Brighton Center of the city's Brighton, Boston, Brighton neighborhood. New England Baptist Hospital is in Mission Hill. VA Boston Healthcare System, The city has Veterans Affairs medical centers in the Jamaica Plain, Boston, Jamaica Plain and West Roxbury, Boston, West Roxbury neighborhoods. The Boston Public Health Commission, an agency of the Massachusetts government, oversees health concerns for city residents. Boston EMS provides pre-hospital emergency medical services to residents and visitors.
Many of Boston's medical facilities are associated with universities. The facilities in the Longwood Medical and Academic Area and in Massachusetts General Hospital are affiliated with Harvard Medical School. Tufts Medical Center (formerly Tufts-New England Medical Center), in the southern portion of the Chinatown, Boston, Chinatown neighborhood, is affiliated with Tufts University School of Medicine. Boston Medical Center, in the South End, Boston, South End neighborhood, is the primary teaching facility for the Boston University School of Medicine as well as the largest trauma center in the Boston area; it was formed by the merger of Boston University Hospital and Boston City Hospital, which was the first municipal hospital in the United States.
 Boston included $414 million in spending on the Boston Police Department in the fiscal 2021 budget. This is the second largest allocation of funding by the city after the allocation to Boston Public Schools.
Like many major American cities, Boston has experienced a great reduction in violent crime since the early 1990s. Boston's low crime rate since the 1990s has been credited to the Boston Police Department's collaboration with neighborhood groups and church parishes to prevent youths from joining gangs, as well as involvement from the United States Attorney, United States Attorney and District Attorney's offices. This helped lead in part to what has been touted as the "Boston Miracle". Murders in the city dropped from 152 in 1990 (for a murder rate of 26.5 per 100,000 people) to just 31—not one of them a juvenile—in 1999 (for a murder rate of 5.26 per 100,000).
In 2008, there were 62 reported homicides. Through December 30, 2016, major crime was down seven percent and there were 46 homicides compared to 40 in 2015.
Boston included $414 million in spending on the Boston Police Department in the fiscal 2021 budget. This is the second largest allocation of funding by the city after the allocation to Boston Public Schools.
Like many major American cities, Boston has experienced a great reduction in violent crime since the early 1990s. Boston's low crime rate since the 1990s has been credited to the Boston Police Department's collaboration with neighborhood groups and church parishes to prevent youths from joining gangs, as well as involvement from the United States Attorney, United States Attorney and District Attorney's offices. This helped lead in part to what has been touted as the "Boston Miracle". Murders in the city dropped from 152 in 1990 (for a murder rate of 26.5 per 100,000 people) to just 31—not one of them a juvenile—in 1999 (for a murder rate of 5.26 per 100,000).
In 2008, there were 62 reported homicides. Through December 30, 2016, major crime was down seven percent and there were 46 homicides compared to 40 in 2015.

 Boston shares many cultural roots with greater New England, including a dialect of the non-Rhoticity in English, rhotic Eastern New England English, New England accent known as the Boston accent and a New England cuisine, regional cuisine with a large emphasis on seafood, salt, and dairy products. Boston also has its own collection of neologisms known as ''Boston slang'' and sardonic humor.
In the early 1800s, William Tudor (1779–1830), William Tudor wrote that Boston was "'perhaps the most perfect and certainly the best-regulated democracy that ever existed. There is something so impossible in the immortal fame of Athens, that the very name makes everything modern shrink from comparison; but since the days of that glorious city I know of none that has approached so near in some points, distant as it may still be from that illustrious model.' From this, Boston has been called the "Athens of America" (also a nickname of
Boston shares many cultural roots with greater New England, including a dialect of the non-Rhoticity in English, rhotic Eastern New England English, New England accent known as the Boston accent and a New England cuisine, regional cuisine with a large emphasis on seafood, salt, and dairy products. Boston also has its own collection of neologisms known as ''Boston slang'' and sardonic humor.
In the early 1800s, William Tudor (1779–1830), William Tudor wrote that Boston was "'perhaps the most perfect and certainly the best-regulated democracy that ever existed. There is something so impossible in the immortal fame of Athens, that the very name makes everything modern shrink from comparison; but since the days of that glorious city I know of none that has approached so near in some points, distant as it may still be from that illustrious model.' From this, Boston has been called the "Athens of America" (also a nickname of 
 There are several major annual events, such as First Night which occurs on New Year's Eve, the Boston Early Music Festival, the annual Boston Arts Festival at Christopher Columbus Waterfront Park, the annual Boston gay pride parade and festival held in June, and Italian summer feasts in the North End honoring Catholic saints. The city is the site of several events during the Independence Day (United States), Fourth of July period. They include the week-long Harborfest festivities and a Boston Pops concert accompanied by fireworks on the banks of the
There are several major annual events, such as First Night which occurs on New Year's Eve, the Boston Early Music Festival, the annual Boston Arts Festival at Christopher Columbus Waterfront Park, the annual Boston gay pride parade and festival held in June, and Italian summer feasts in the North End honoring Catholic saints. The city is the site of several events during the Independence Day (United States), Fourth of July period. They include the week-long Harborfest festivities and a Boston Pops concert accompanied by fireworks on the banks of the
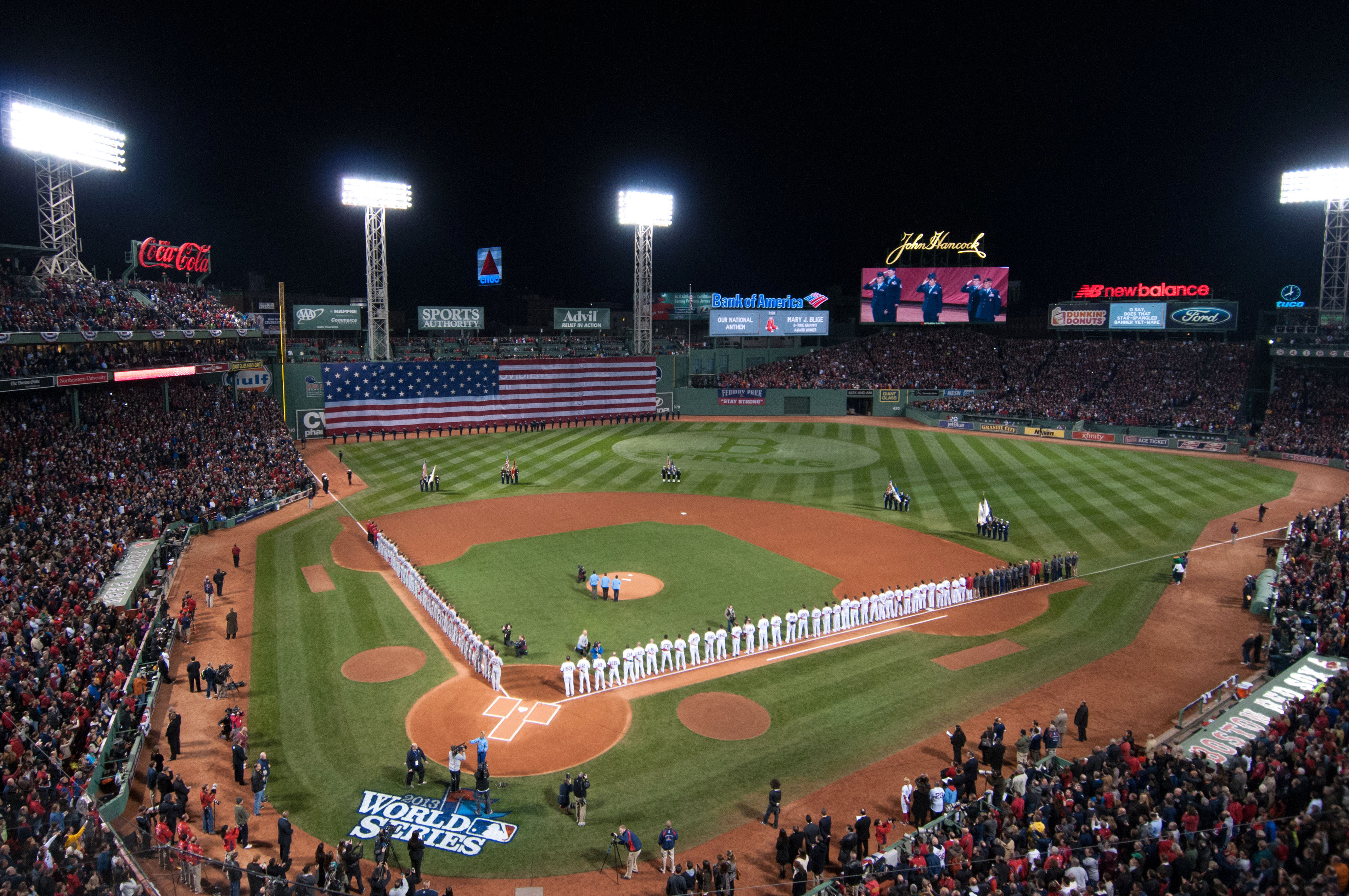 Boston has teams in Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, the four major North American men's professional sports leagues plus Major League Soccer, and, as of List of U.S. cities by number of professional sports championships, 2019, has won 39 championships in these leagues. It is one of eight cities (along with Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, New York, Philadelphia, St. Louis and Washington) to have won championships in all four major American sports leagues. It has been suggested that Boston is the new "TitleTown, USA", as the city's professional sports teams have won twelve championships since 2001: Patriots (2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, 2016 and 2018), Red Sox (2004, 2007, 2013, and 2018), Celtics (2008), and Bruins (2011). This love of sports made Boston the United States Olympic Committee's choice to Bids for Olympic Games, bid to hold the 2024 Summer Olympic Games, but the city cited financial concerns when it withdrew its bid on July 27, 2015.
The Boston Red Sox, a founding member of the American League of Major League Baseball in 1901, play their home games at Fenway Park, near Kenmore Square, in the city's Fenway-Kenmore, Fenway section. Built in 1912, it is the oldest sports arena or stadium in active use in the United States among the four major professional American sports leagues, Major League Baseball, the National Football League, National Basketball Association, and the National Hockey League. Boston was the site of the first game of the first modern World Series, in 1903. The series was played between the AL Champion Boston Americans and the NL champion Pittsburgh Pirates. Persistent reports that the team was known in 1903 as the "Boston Pilgrims" appear to be unfounded. Boston's first professional baseball team was the Red Stockings, one of the charter members of the National Association of Professional Base Ball Players, National Association in 1871, and of the National League in 1876. The team played under that name until 1883, under the name Beaneaters until 1911, and under the name Braves from 1912 until they moved to Milwaukee after the 1952 season. Since 1966 they have played in Atlanta as the Atlanta Braves.
Boston has teams in Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, the four major North American men's professional sports leagues plus Major League Soccer, and, as of List of U.S. cities by number of professional sports championships, 2019, has won 39 championships in these leagues. It is one of eight cities (along with Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, New York, Philadelphia, St. Louis and Washington) to have won championships in all four major American sports leagues. It has been suggested that Boston is the new "TitleTown, USA", as the city's professional sports teams have won twelve championships since 2001: Patriots (2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, 2016 and 2018), Red Sox (2004, 2007, 2013, and 2018), Celtics (2008), and Bruins (2011). This love of sports made Boston the United States Olympic Committee's choice to Bids for Olympic Games, bid to hold the 2024 Summer Olympic Games, but the city cited financial concerns when it withdrew its bid on July 27, 2015.
The Boston Red Sox, a founding member of the American League of Major League Baseball in 1901, play their home games at Fenway Park, near Kenmore Square, in the city's Fenway-Kenmore, Fenway section. Built in 1912, it is the oldest sports arena or stadium in active use in the United States among the four major professional American sports leagues, Major League Baseball, the National Football League, National Basketball Association, and the National Hockey League. Boston was the site of the first game of the first modern World Series, in 1903. The series was played between the AL Champion Boston Americans and the NL champion Pittsburgh Pirates. Persistent reports that the team was known in 1903 as the "Boston Pilgrims" appear to be unfounded. Boston's first professional baseball team was the Red Stockings, one of the charter members of the National Association of Professional Base Ball Players, National Association in 1871, and of the National League in 1876. The team played under that name until 1883, under the name Beaneaters until 1911, and under the name Braves from 1912 until they moved to Milwaukee after the 1952 season. Since 1966 they have played in Atlanta as the Atlanta Braves.
 The TD Garden, formerly called the FleetCenter and built to replace the old, since-demolished Boston Garden, is adjoined to North Station and is the home of two major league teams: the Boston Bruins of the National Hockey League and the Boston Celtics of the National Basketball Association. The arena seats 18,624 for basketball games and 17,565 for ice hockey games. The Bruins were the first American member of the National Hockey League and an Original Six franchise. The Boston Celtics were founding members of the Basketball Association of America, one of the two leagues that merged to form the NBA. The Celtics, along with the Los Angeles Lakers, have the distinction of having won more championships than any other NBA team, both with seventeen. The venue is also set to host the 2020 Laver Cup, an international men's tennis tournament consisting of two teams: Team Europe and Team World, the latter of which consisting of non-European players. This will be the fourth edition of the tournament, and the first time Boston has hosted an ATP tournament since 1999, where Marat Safin defeated Greg Rusedski.
While they have played in suburban Foxborough, Massachusetts, Foxborough since 1971, the New England Patriots of the National Football League were founded in 1960 as the Boston Patriots, changing their name after relocating. The team won the Super Bowl after the 2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, 2016 and 2018 seasons. They share Gillette Stadium with the New England Revolution of Major League Soccer. The Boston Breakers (WPS), Boston Breakers of Women's Professional Soccer, which formed in 2009, played their home games at Dilboy Stadium in Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville. The Boston Storm (UWLX), Boston Storm of the United Women's Lacrosse League was formed in 2015.
The TD Garden, formerly called the FleetCenter and built to replace the old, since-demolished Boston Garden, is adjoined to North Station and is the home of two major league teams: the Boston Bruins of the National Hockey League and the Boston Celtics of the National Basketball Association. The arena seats 18,624 for basketball games and 17,565 for ice hockey games. The Bruins were the first American member of the National Hockey League and an Original Six franchise. The Boston Celtics were founding members of the Basketball Association of America, one of the two leagues that merged to form the NBA. The Celtics, along with the Los Angeles Lakers, have the distinction of having won more championships than any other NBA team, both with seventeen. The venue is also set to host the 2020 Laver Cup, an international men's tennis tournament consisting of two teams: Team Europe and Team World, the latter of which consisting of non-European players. This will be the fourth edition of the tournament, and the first time Boston has hosted an ATP tournament since 1999, where Marat Safin defeated Greg Rusedski.
While they have played in suburban Foxborough, Massachusetts, Foxborough since 1971, the New England Patriots of the National Football League were founded in 1960 as the Boston Patriots, changing their name after relocating. The team won the Super Bowl after the 2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, 2016 and 2018 seasons. They share Gillette Stadium with the New England Revolution of Major League Soccer. The Boston Breakers (WPS), Boston Breakers of Women's Professional Soccer, which formed in 2009, played their home games at Dilboy Stadium in Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville. The Boston Storm (UWLX), Boston Storm of the United Women's Lacrosse League was formed in 2015.
 The area's many colleges and universities are active in college athletics. Four National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA Division I members play in the area—Boston College, Boston University,
The area's many colleges and universities are active in college athletics. Four National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA Division I members play in the area—Boston College, Boston University,

 Boston has a Mayor–council government, strong mayor–council government system in which the mayor (elected every fourth year) has extensive executive power. Michelle Wu, a city councilor, became mayor in November 2021, succeeding Kim Janey, a former City Council President, who became the Acting Mayor in March 2021 following Marty Walsh's confirmation to the position of United States Secretary of Labor, Secretary of Labor in the Presidency of Joe Biden, Biden/Harris Administration. Walsh's predecessor Thomas Menino's twenty-year tenure was the longest in the city's history.
The Boston City Council is elected every two years; there are nine district seats, and four citywide "at-large" seats. The School Committee, which oversees the Boston Public Schools, is appointed by the mayor.
Boston has a Mayor–council government, strong mayor–council government system in which the mayor (elected every fourth year) has extensive executive power. Michelle Wu, a city councilor, became mayor in November 2021, succeeding Kim Janey, a former City Council President, who became the Acting Mayor in March 2021 following Marty Walsh's confirmation to the position of United States Secretary of Labor, Secretary of Labor in the Presidency of Joe Biden, Biden/Harris Administration. Walsh's predecessor Thomas Menino's twenty-year tenure was the longest in the city's history.
The Boston City Council is elected every two years; there are nine district seats, and four citywide "at-large" seats. The School Committee, which oversees the Boston Public Schools, is appointed by the mayor.
 In addition to city government, numerous commissions and state authorities—including the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation, the Boston Public Health Commission, the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority, Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA), and the Massachusetts Port Authority, Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport)—play a role in the life of Bostonians. As the capital of Massachusetts, Boston plays a major role in Massachusetts#Politics, state politics.
In addition to city government, numerous commissions and state authorities—including the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation, the Boston Public Health Commission, the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority, Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA), and the Massachusetts Port Authority, Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport)—play a role in the life of Bostonians. As the capital of Massachusetts, Boston plays a major role in Massachusetts#Politics, state politics.
 The city has several federal facilities, including the John F. Kennedy Federal Office Building, the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building (Boston), Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building, the John W. McCormack Post Office and Courthouse, the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston, the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit, and the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. Both courts are housed in the John Joseph Moakley United States Courthouse.
The city has several federal facilities, including the John F. Kennedy Federal Office Building, the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building (Boston), Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building, the John W. McCormack Post Office and Courthouse, the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston, the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit, and the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. Both courts are housed in the John Joseph Moakley United States Courthouse.
 Federally, Boston is split between two congressional districts. Three-fourths of the city is in the Massachusetts's 7th congressional district, 7th district and is represented by Ayanna Pressley while the remaining southern fourth is in the Massachusetts's 8th congressional district, 8th district and is represented by Stephen Lynch (politician), Stephen Lynch, both of whom are Democrats; a Republican has not represented a significant portion of Boston in over a century. The state's senior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Elizabeth Warren, first elected in 2012. The state's junior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Ed Markey, who was elected in 2013 to succeed John Kerry after Kerry's appointment and confirmation as the United States Secretary of State.
The city uses an algorithm created by the Walsh administration, called CityScore, to measure the effectiveness of various city services. This score is available on a public online dashboard and allows city managers in police, fire, schools, emergency management services, and 3-1-1 to take action and make adjustments in areas of concern.
Boston has an ordinance, enacted in 2014, that bars the Boston Police Department "from detaining anyone based on their immigration status unless they have a criminal warrant".
Federally, Boston is split between two congressional districts. Three-fourths of the city is in the Massachusetts's 7th congressional district, 7th district and is represented by Ayanna Pressley while the remaining southern fourth is in the Massachusetts's 8th congressional district, 8th district and is represented by Stephen Lynch (politician), Stephen Lynch, both of whom are Democrats; a Republican has not represented a significant portion of Boston in over a century. The state's senior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Elizabeth Warren, first elected in 2012. The state's junior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Ed Markey, who was elected in 2013 to succeed John Kerry after Kerry's appointment and confirmation as the United States Secretary of State.
The city uses an algorithm created by the Walsh administration, called CityScore, to measure the effectiveness of various city services. This score is available on a public online dashboard and allows city managers in police, fire, schools, emergency management services, and 3-1-1 to take action and make adjustments in areas of concern.
Boston has an ordinance, enacted in 2014, that bars the Boston Police Department "from detaining anyone based on their immigration status unless they have a criminal warrant".
 Logan International Airport, in East Boston and operated by the Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport), is Boston's principal airport. Nearby general aviation airports are Beverly Municipal Airport to the north, Hanscom Field to the west, and Norwood Memorial Airport to the south. Massport also operates several major facilities within the Port of Boston, including a cruise ship terminal and facilities to handle bulk and container cargo in South Boston, and other facilities in Charlestown and East Boston.
Downtown Boston's streets grew organically, so they do not form a Grid plan, planned grid, unlike those in later-developed
Logan International Airport, in East Boston and operated by the Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport), is Boston's principal airport. Nearby general aviation airports are Beverly Municipal Airport to the north, Hanscom Field to the west, and Norwood Memorial Airport to the south. Massport also operates several major facilities within the Port of Boston, including a cruise ship terminal and facilities to handle bulk and container cargo in South Boston, and other facilities in Charlestown and East Boston.
Downtown Boston's streets grew organically, so they do not form a Grid plan, planned grid, unlike those in later-developed 
 Amtrak intercity rail to Boston is provided through four stations: South Station, North Station, Back Bay station, Back Bay, and Route 128 station, Route 128. South Station is a major Intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transportation hub and is the terminus of Amtrak's ''Northeast Regional'', ''Acela Express'', and ''Lake Shore Limited'' routes, in addition to multiple MBTA services. Back Bay is also served by MBTA and those three Amtrak routes, while Route 128, in the southwestern suburbs of Boston, is only served by the ''Acela Express'' and ''Northeast Regional''. Meanwhile, Amtrak's ''Downeaster (train), Downeaster'' to Brunswick, Maine, Brunswick, Maine terminates in North Station, and is the only Amtrak route to do so.
Nicknamed "The Walking City", Boston hosts more pedestrian commuters than do other comparably populated cities. Owing to factors such as necessity, the compactness of the city and large student population, 13 percent of the population commutes by foot, making it the List of U.S. cities with most pedestrian commuters, highest percentage of pedestrian commuters in the country out of the major American cities. In 2011, Walk Score ranked Boston the third-most walkable city in the United States. , Walk Score still ranks Boston as the third most walkable US city, with a Walk Score of 80, a Transit Score of 75, and a Bike Score of 70.
Between 1999 and 2006, ''Bicycling (magazine), Bicycling'' magazine named Boston three times as one of the worst cities in the US for cycling; regardless, it has one of the highest rates of bicycle commuting. In 2008, as a consequence of improvements made to bicycling conditions within the city, the same magazine put Boston on its "Five for the Future" list as a "Future Best City" for biking, and Boston's bicycle commuting percentage increased from 1% in 2000 to 2.1% in 2009. The bikeshare program Bluebikes, originally called Hubway, launched in late July 2011, logging more than 140,000 rides before the close of its first season. The neighboring municipalities of Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville, and Brookline, Massachusetts, Brookline joined the Hubway program in the summer of 2012. In 2016, there were 1,461 bikes and 158 docking stations across the city, which in 2022 has increased to 400 stations with a total of 4,000 bikes. PBSC Urban Solutions provides bicycles and technology for this Bicycle-sharing system, bike-sharing system.
In 2013, the Boston-Cambridge-Newton metropolitan statistical area (Boston MSA) had the seventh-lowest percentage of workers who commuted by private automobile (75.6 percent), with 6.2 percent of area workers traveling via rail transit. During the period starting in 2006 and ending in 2013, the Boston MSA had the greatest percentage decline of workers commuting by automobile (3.3 percent) among MSAs with more than a half-million residents.
Amtrak intercity rail to Boston is provided through four stations: South Station, North Station, Back Bay station, Back Bay, and Route 128 station, Route 128. South Station is a major Intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transportation hub and is the terminus of Amtrak's ''Northeast Regional'', ''Acela Express'', and ''Lake Shore Limited'' routes, in addition to multiple MBTA services. Back Bay is also served by MBTA and those three Amtrak routes, while Route 128, in the southwestern suburbs of Boston, is only served by the ''Acela Express'' and ''Northeast Regional''. Meanwhile, Amtrak's ''Downeaster (train), Downeaster'' to Brunswick, Maine, Brunswick, Maine terminates in North Station, and is the only Amtrak route to do so.
Nicknamed "The Walking City", Boston hosts more pedestrian commuters than do other comparably populated cities. Owing to factors such as necessity, the compactness of the city and large student population, 13 percent of the population commutes by foot, making it the List of U.S. cities with most pedestrian commuters, highest percentage of pedestrian commuters in the country out of the major American cities. In 2011, Walk Score ranked Boston the third-most walkable city in the United States. , Walk Score still ranks Boston as the third most walkable US city, with a Walk Score of 80, a Transit Score of 75, and a Bike Score of 70.
Between 1999 and 2006, ''Bicycling (magazine), Bicycling'' magazine named Boston three times as one of the worst cities in the US for cycling; regardless, it has one of the highest rates of bicycle commuting. In 2008, as a consequence of improvements made to bicycling conditions within the city, the same magazine put Boston on its "Five for the Future" list as a "Future Best City" for biking, and Boston's bicycle commuting percentage increased from 1% in 2000 to 2.1% in 2009. The bikeshare program Bluebikes, originally called Hubway, launched in late July 2011, logging more than 140,000 rides before the close of its first season. The neighboring municipalities of Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville, and Brookline, Massachusetts, Brookline joined the Hubway program in the summer of 2012. In 2016, there were 1,461 bikes and 158 docking stations across the city, which in 2022 has increased to 400 stations with a total of 4,000 bikes. PBSC Urban Solutions provides bicycles and technology for this Bicycle-sharing system, bike-sharing system.
In 2013, the Boston-Cambridge-Newton metropolitan statistical area (Boston MSA) had the seventh-lowest percentage of workers who commuted by private automobile (75.6 percent), with 6.2 percent of area workers traveling via rail transit. During the period starting in 2006 and ending in 2013, the Boston MSA had the greatest percentage decline of workers commuting by automobile (3.3 percent) among MSAs with more than a half-million residents.
Visit Boston
official tourism website * * *
Historical Maps of Boston
from the Norman B. Leventhal Map Center at the
state capital
Below is an index of pages containing lists of capital cities.
National capitals
*List of national capitals
*List of national capitals by latitude
*List of national capitals by population
*List of national capitals by area
*List of capital citie ...
and most populous city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the city proper, cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or th ...
of the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
of Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, as well as the cultural and financial center
A financial centre ( BE), financial center ( AE), or financial hub, is a location with a concentration of participants in banking, asset management, insurance or financial markets with venues and supporting services for these activities to t ...
of the New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
region of the United States. It is the 24th- most populous city in the country. The city boundaries encompass an area of about and a population of 675,647 as of 2020. It is the seat of Suffolk County (although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999). The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
, a metropolitan statistical area
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally Incorporated town, incorporate ...
(MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country. A broader combined statistical area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and the territory of Puerto Ric ...
(CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area and including Providence, Rhode Island
Providence is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Rhode Island. One of the oldest cities in New England, it was founded in 1636 by Roger Williams, a Reformed Baptist theologian and religious exile from the Massachusetts Bay ...
, is home to approximately 8.2 million people, making it the sixth most populous in the United States.
Boston is one of the oldest municipalities in America, founded on the Shawmut Peninsula
Shawmut Peninsula is the promontory of land on which Boston, Massachusetts was built. The peninsula, originally a mere in area,Miller, Bradford A., "Digging up Boston: The Big Dig Builds on Centuries of Geological Engineering", GeoTimes, Octobe ...
in 1630 by Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Catholic Church, Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become m ...
settlers from the English town of the same name. It was the scene of several key events of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
and the nation's founding, such as the Boston Massacre
The Boston Massacre (known in Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain as the Incident on King Street) was a confrontation in Boston on March 5, 1770, in which a group of nine British soldiers shot five people out of a crowd of three or four hu ...
, the Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was an American political and mercantile protest by the Sons of Liberty in Boston, Massachusetts, on December 16, 1773. The target was the Tea Act of May 10, 1773, which allowed the British East India Company to sell tea ...
, the Battle of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill was fought on June 17, 1775, during the Siege of Boston in the first stage of the American Revolutionary War. The battle is named after Bunker Hill in Charlestown, Massachusetts, which was peripherally involved in ...
, and the siege of Boston
The siege of Boston (April 19, 1775 – March 17, 1776) was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War. New England militiamen prevented the movement by land of the British Army, which was garrisoned in what was then the peninsular town ...
. Upon American independence
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, the city continued to be an important port and manufacturing hub as well as a center for education and culture. The city has expanded beyond the original peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all ...
through land reclamation and municipal annexation. Its rich history attracts many tourists, with Faneuil Hall
Faneuil Hall ( or ; previously ) is a marketplace and meeting hall located near the waterfront and today's Government Center, in Boston, Massachusetts. Opened in 1742, it was the site of several speeches by Samuel Adams, James Otis, and others ...
alone drawing more than 20 million visitors per year. Boston's many firsts include the United States' first public park (Boston Common
The Boston Common (also known as the Common) is a public park in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It is the oldest city park in the United States. Boston Common consists of of land bounded by Tremont Street (139 Tremont St.), Park Street, Beacon ...
, 1634), first public or state school
State schools (in England, Wales, Australia and New Zealand) or public schools (Scottish English and North American English) are generally primary or secondary educational institution, schools that educate all students without charge. They are ...
(Boston Latin School
The Boston Latin School is a public exam school in Boston, Massachusetts. It was established on April 23, 1635, making it both the oldest public school in the British America and the oldest existing school in the United States. Its curriculum f ...
, 1635) first subway system (Tremont Street subway
The Tremont Street subway in Boston's MBTA subway system is the oldest subway tunnel in North America and the third oldest still in use worldwide to exclusively use electric traction (after the City and South London Railway in 1890, and the Bud ...
, 1897), and first large public library (Boston Public Library
The Boston Public Library is a municipal public library system in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, founded in 1848. The Boston Public Library is also the Library for the Commonwealth (formerly ''library of last recourse'') of the Commonweal ...
, 1848).
Today, Boston is a center of scientific research; the area's many colleges and universities, notably Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
and MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the mo ...
, make it a world leader in higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completi ...
, including law, medicine, engineering and business, and the city is considered to be a global pioneer in innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity ...
and entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value. With this definition, entrepreneurship is viewed as change, generally entailing risk beyond what is normally encountered in starting a business, which may include other values th ...
, with nearly 5,000 startups. Boston's economic base also includes finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fina ...
,Accessed October 7, 2018. professional and business services,
biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
, information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system (I ...
, and government activities. Boston is a hub for LGBT culture
LGBT culture is a culture shared by lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer individuals. It is sometimes referred to as queer culture (indicating people who are queer), while the term gay culture may be used to mean "LGBT culture" o ...
and LGBT activism
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) movements are social movements that advocate for LGBT people in society. Some focus on equal rights, such as the ongoing movement for same-sex marriage, while others focus on liberation, as in the ...
in the United States. Households in the city claim the highest average rate of philanthropy
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the Public good (economics), public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private goo ...
in the United States. Boston businesses and institutions rank among the top in the country for environmental sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livi ...
and new investment.
History
Indigenous era
Prior toEuropean colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense began ...
, the region around modern-day Boston was inhabited by the indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
Massachusett
The Massachusett were a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills ...
. Their habitation consisted of small, seasonal communities. The people who lived in the area most likely moved between inland winter homes along the Charles River
The Charles River ( Massachusett: ''Quinobequin)'' (sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles) is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton to Boston along a highly meandering route, that doubles b ...
(called Quinobequin, meaning "meandering," by the Native people) and summer communities on the coast. Game was more easily hunted inland during bare-tree seasons and fishing shoals and shellfish beds were most easily exploited during the summer months.
Being surrounded by foul-smelling mudflat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal fl ...
s during the temperate part of the year, the Shawmut Peninsula
Shawmut Peninsula is the promontory of land on which Boston, Massachusetts was built. The peninsula, originally a mere in area,Miller, Bradford A., "Digging up Boston: The Big Dig Builds on Centuries of Geological Engineering", GeoTimes, Octobe ...
itself was more sparsely occupied than its surroundings before the arrival of Europeans. Nevertheless, archeological excavations have revealed one of the oldest fishweirs in New England on Boylston Street. Native people constructed this weir to trap fish as early as 7,000 years before European arrival in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the term We ...
.
Founding by Europeans
The first European to live in what would become Boston was aCambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
-educated Episcopalian
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the l ...
cleric named William Blaxton
Reverend William Blaxton (also spelled William Blackstone) (1595 – 26 May 1675) was an early English settler in New England and the first European settler of Boston and Rhode Island.
Biography
William Blaxton was born in Horncastle, Lincolns ...
. He was the person most directly responsible for the foundation of Boston by Puritan colonizers in 1630. This occurred after Blaxton invited one of their leaders, Isaac Johnson
Isaac Johnson (November 1, 1803 – March 15, 1853) was a US politician and the 12th Governor of the state of Louisiana.
Born on his father's plantation "Troy" near St. Francisville in West Feliciana Parish, Johnson was the fourth son of J ...
to cross Back Bay
Back Bay is an officially recognized neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, built on reclaimed land in the Charles River basin. Construction began in 1859, as the demand for luxury housing exceeded the availability in the city at the time, and t ...
from the failing colony of Charlestown and share the peninsula. This the Puritans did in September 1630.
The name "Boston"
Before dying on 30 September 1630, one of Johnson's last official acts as the leader of the Charlestown community was to name their new settlement across the river "Boston." He named the settlement after hishometown
Hometown, HomeTown, or Home Town may refer to:
*A hometown, the town where someone lives or the town that they come from, typically their place of birth.
*In developing nations particularly: native place, village of origin in newly urbanized soci ...
in Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire (abbreviated Lincs.) is a county in the East Midlands of England, with a long coastline on the North Sea to the east. It borders Norfolk to the south-east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south-west, Leicestershire ...
, the place from which he, his wife (namesake of the ''Arbella
''Arbella'' or ''Arabella'' was the flagship of the Winthrop Fleet on which Governor John Winthrop, other members of the Company (including William Gager), and Puritan emigrants transported themselves and the Charter of the Massachusetts Bay Comp ...
'') and John Cotton (grandfather of Cotton Mather
Cotton Mather (; February 12, 1663 – February 13, 1728) was a New England Puritan clergyman and a prolific writer. Educated at Harvard College, in 1685 he joined his father Increase as minister of the Congregationalist Old North Meeting H ...
) had emigrated
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
to New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
. The name of the English city ultimately derives from that town's patron saint, St. Botolph
Botolph of Thorney (also called Botolph, Botulph or Botulf; later known as Saint Botolph; died around 680) was an English abbot and saint. He is regarded as the patron saint of boundaries, and by extension, of trade and travel, as well as vario ...
, in whose church John Cotton served as the rector until his emigration with Johnson. In early sources the Lincolnshire Boston was known as "St. Botolph's town", later contracted to "Boston". Before this renaming the settlement on the peninsula had been known as "Shawmut" by Blaxton and "Trimountain" by the Puritan settlers he had invited.Weston, George F. ''Boston Ways: High, By & Folk'', Beacon Press: Beacon Hill, Boston, p.11–15 (1957).Kay, Jane Holtz, Lost Boston
', Amherst : University of Massachusetts Press, 2006. . Cf
p.4
/ref>Thurston, H. (1907). "St. Botulph." ''The Catholic Encyclopedia''. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved June 17, 2014 from New Advent: http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/02709a.htm
Puritan occupation
The Puritan influence on Boston began even before its foundation, with the 1629Cambridge Agreement The Cambridge Agreement''T ...
. This document created the Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
and was signed by its first governor John Winthrop
John Winthrop (January 12, 1587/88 – March 26, 1649) was an English Puritan lawyer and one of the leading figures in founding the Massachusetts Bay Colony, the second major settlement in New England following Plymouth Colony. Winthrop led t ...
. Puritan ethics and their focus on education influenced the early history of the city. America's first public school, Boston Latin School
The Boston Latin School is a public exam school in Boston, Massachusetts. It was established on April 23, 1635, making it both the oldest public school in the British America and the oldest existing school in the United States. Its curriculum f ...
, was founded in Boston in 1635.
John Hull and the pine tree shilling
The pine tree shilling was a type of coin minted and circulated in the thirteen colonies.
The Massachusetts Bay Colony established a mint in Boston in 1652. John Hull was Treasurer and mintmaster; Hull's partner at the "Hull Mint" was Robert S ...
played a central role in the establishment of the Massachusetts Bay Colony and the Old South Church
Old South Church in Boston, Massachusetts, (also known as New Old South Church or Third Church) is a historic United Church of Christ congregation first organized in 1669. Its present building was designed in the Gothic Revival style by Charles ...
in the 1600s. In 1652 the Massachusetts legislature
The Massachusetts General Court (formally styled the General Court of Massachusetts) is the state legislature of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name "General Court" is a hold-over from the earliest days of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, w ...
authorized John Hull to produce coinage. "The Hull Mint produced several denominations of silver coinage, including the pine tree shilling, for over 30 years until the political and economic situation made operating the mint no longer practical." King Charles II for reasons which were mostly political deemed the "Hull Mint" high treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
which had a punishment of being hanged, drawn and quartered
To be hanged, drawn and quartered became a statutory penalty for men convicted of high treason in the Kingdom of England from 1352 under Edward III of England, King Edward III (1327–1377), although similar rituals are recorded during the rei ...
. "On April 6, 1681, Edward Randolph
Edward Randolph (~October 1690 – after 1756), sometimes referred to as Edward Randolph of Bremo, was a ship captain, a London tobacco merchant, and the seventh and youngest son of William Randolph and Mary Isham.
Biography
In 1713, Randolph ...
petitioned the king, informing him the colony was still pressing their own coins which he saw as high treason and believed it was enough to void the charter. He asked that a writ of Quo warranto
In law, especially English and American common law, ''quo warranto'' (Medieval Latin for "by what warrant?") is a prerogative writ requiring the person to whom it is directed to show what authority they have for exercising some right, power, or ...
(a legal action requiring the defendant to show what authority they have for exercising some right, power, or franchise they claim to hold) be issued against Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
for the violations."
Boston was the largest town in the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
until Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
outgrew it in the mid-18th century. Boston's oceanfront location made it a lively port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
, and the city primarily engaged in shipping
Freight transport, also referred as ''Freight Forwarding'', is the physical process of transporting Commodity, commodities and merchandise goods and cargo. The term shipping originally referred to transport by sea but in American English, it h ...
and fishing during its colonial days. However, Boston stagnated in the decades prior to the Revolution. By the mid-18th century, New York City and Philadelphia surpassed Boston in wealth. During this period, Boston encountered financial difficulties even as other cities in New England grew rapidly.
Revolution and the siege of Boston
 Many crucial events of the
Many crucial events of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
occurred in or near Boston. The city's mob presence along with the colonists' growing lack of faith in either Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
or its Parliament fostered a revolutionary spirit in the city. When the British parliament passed the Stamp Act in 1765, a Boston mob ravaged the homes of Andrew Oliver, the official tasked with enforcing the Act, and Thomas Hutchinson, then the Lieutenant Governor of Massachusetts. The British sent two regiments to Boston in 1768 in an attempt to quell the angry colonists. This did not sit well with the colonists. In 1770, during the Boston Massacre
The Boston Massacre (known in Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain as the Incident on King Street) was a confrontation in Boston on March 5, 1770, in which a group of nine British soldiers shot five people out of a crowd of three or four hu ...
, British troops shot into a crowd that had started to violently harass them. The colonists compelled the British to withdraw their troops. The event was widely publicized and fueled a revolutionary movement in America.
In 1773, Parliament passed the Tea Act
The Tea Act 1773 (13 Geo 3 c 44) was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain. The principal objective was to reduce the massive amount of tea held by the financially troubled British East India Company in its London warehouses and to help th ...
. Many of the colonists saw the act as an attempt to force them to accept the taxes established by the Townshend Acts
The Townshend Acts () or Townshend Duties, were a series of British acts of Parliament passed during 1767 and 1768 introducing a series of taxes and regulations to fund administration of the British colonies in America. They are named after the ...
. The act prompted the Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was an American political and mercantile protest by the Sons of Liberty in Boston, Massachusetts, on December 16, 1773. The target was the Tea Act of May 10, 1773, which allowed the British East India Company to sell tea ...
, where a group of angered Bostonian citizens threw an entire shipment of tea sent by the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
into Boston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, and is located adjacent to the city of Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the northeastern United States.
History
Since ...
. The Boston Tea Party was a key event leading up to the revolution, as the British government responded furiously with the Coercive Acts
The Intolerable Acts were a series of punitive laws passed by the British Parliament in 1774 after the Boston Tea Party. The laws aimed to punish Massachusetts colonists for their defiance in the Tea Party protest of the Tea Act, a tax measure ...
, demanding compensation for the destroyed tea from the Bostonians. This angered the colonists further and led to the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. The war began in the area surrounding Boston with the Battles of Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord ...
.
Boston itself was besieged for almost a year during the siege of Boston
The siege of Boston (April 19, 1775 – March 17, 1776) was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War. New England militiamen prevented the movement by land of the British Army, which was garrisoned in what was then the peninsular town ...
, which began on April 19, 1775. The New England militia impeded the movement of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
. Sir William Howe
William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe, KB PC (10 August 172912 July 1814) was a British Army officer who rose to become Commander-in-Chief of British land forces in the Colonies during the American War of Independence. Howe was one of three brot ...
, then the commander-in-chief of the British forces in North America, led the British army in the siege. On June 17, the British captured the Charlestown peninsula
Charlestown is the oldest neighborhood in Boston, Massachusetts, in the United States. Originally called Mishawum by the Massachusett tribe, it is located on a peninsula north of the Charles River, across from downtown Boston, and also adjoins t ...
in Boston, during the Battle of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill was fought on June 17, 1775, during the Siege of Boston in the first stage of the American Revolutionary War. The battle is named after Bunker Hill in Charlestown, Massachusetts, which was peripherally involved in ...
. The British army outnumbered the militia stationed there, but it was a pyrrhic victory
A Pyrrhic victory ( ) is a victory that inflicts such a devastating toll on the victor that it is tantamount to defeat. Such a victory negates any true sense of achievement or damages long-term progress.
The phrase originates from a quote from P ...
for the British because their army suffered irreplaceable casualties. It was also a testament to the skill and training of the militia, as their stubborn defence made it difficult for the British to capture Charlestown without suffering further irreplaceable casualties.
Several weeks later, George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
took over the militia after the Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. ...
established the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
to unify the revolutionary effort. Both sides faced difficulties and supply shortages in the siege, and the fighting was limited to small-scale raids and skirmishes. The narrow Boston Neck, which at that time was only about a hundred feet wide, impeded Washington's ability to invade Boston, and a long stalemate ensued. A young officer, Rufus Putnam
Brigadier-General Rufus Putnam (April 9, 1738 – May 4, 1824) was an American military officer who fought during the French and Indian War and the American Revolutionary War. As an organizer of the Ohio Company of Associates, he was instrumental ...
, came up with a plan to make portable fortifications out of wood that could be erected on the frozen ground under cover of darkness. Putnam supervised this effort, which successfully installed both the fortifications and dozens of cannon on Dorchester Heights that Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806), a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the ...
had laboriously brought through the snow from Fort Ticonderoga. The astonished British awoke the next morning to see a large array of cannons bearing down on them. General Howe is believed to have said that the Americans had done more in one night than his army could have done in six months. The British Army attempted a cannon barrage for two hours, but their shot could not reach the colonists' cannons at such a height. The British gave up, boarded their ships and sailed away. Boston still celebrates " Evacuation Day" each year. Washington was so impressed, he made Rufus Putnam his chief engineer.
Post-revolution and the War of 1812
 After the Revolution, Boston's long
After the Revolution, Boston's long seafaring
Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."
It involves topics a ...
tradition helped make it one of the nation's busiest ports for both domestic and international trade. Boston's harbor activity was significantly curtailed by the Embargo Act of 1807
The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations that was enacted by the United States Congress. As a successor or replacement law for the 1806 Non-importation Act and passed as the Napoleonic Wars continued, it repr ...
(adopted during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
) and the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
. Foreign trade returned after these hostilities, but Boston's merchants had found alternatives for their capital investments in the interim. Manufacturing became an important component of the city's economy, and the city's industrial manufacturing overtook international trade in economic importance by the mid-19th century. A network of small rivers bordering the city and connecting it to the surrounding region facilitated shipment of goods and led to a proliferation of mills and factories. Later, a dense network of railroads furthered the region's industry and commerce.
 During this period, Boston flourished culturally, as well, admired for its rarefied literary life and generous artistic patronage, with members of old Boston families—eventually dubbed ''
During this period, Boston flourished culturally, as well, admired for its rarefied literary life and generous artistic patronage, with members of old Boston families—eventually dubbed ''Boston Brahmin
The Boston Brahmins or Boston elite are members of Boston's traditional upper class. They are often associated with Harvard University; Anglicanism; and traditional Anglo-American customs and clothing. Descendants of the earliest English colonis ...
s''—coming to be regarded as the nation's social and cultural elites. They are often associated with the American upper class
The American upper class is a social group within the United States consisting of people who have the highest social rank, primarily due to economic wealth. The American upper class is distinguished from the rest of the population due to the fa ...
, Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
; and the Episcopal Church.
Boston was an early port of the Atlantic triangular slave trade in the New England colonies, but was soon overtaken by Salem, Massachusetts and Newport, Rhode Island. Boston eventually became a center of the abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
movement. The city reacted strongly to the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850
The Fugitive Slave Act or Fugitive Slave Law was passed by the United States Congress on September 18, 1850, as part of the Compromise of 1850 between Southern interests in slavery and Northern Free-Soilers.
The Act was one of the most co ...
, contributing to President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
Franklin Pierce
Franklin Pierce (November 23, 1804October 8, 1869) was the 14th president of the United States, serving from 1853 to 1857. He was a northern Democrat who believed that the abolitionist movement was a fundamental threat to the nation's unity ...
's attempt to make an example of Boston after the Anthony Burns
Anthony Burns (May 31, 1834 – July 17, 1862) was an African-American man who escaped from slavery in Virginia in 1854. His capture and trial in Boston, and transport back to Virginia, generated wide-scale public outrage in the North and ...
Fugitive Slave Case.
In 1822, the citizens of Boston voted to change the official name from the "Town of Boston" to the "City of Boston", and on March 19, 1822, the people of Boston accepted the charter incorporating the city. At the time Boston was chartered as a city, the population was about 46,226, while the area of the city was only.
19th century

 In the 1820s, Boston's population grew rapidly, and the city's ethnic composition changed dramatically with the first wave of European
In the 1820s, Boston's population grew rapidly, and the city's ethnic composition changed dramatically with the first wave of European immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
. Irish immigrants dominated the first wave of newcomers during this period, especially following the Great Famine; by 1850, about 35,000 Irish lived in Boston. In the latter half of the 19th century, the city saw increasing numbers of Irish, Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, Lebanese, Syrians, French Canadians
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fren ...
, and Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
and Polish Jews
The history of the Jews in Poland dates back at least 1,000 years. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Ashkenazi Jewish community in the world. Poland was a principal center of Jewish culture, because of the lo ...
settling in the city. By the end of the 19th century, Boston's core neighborhoods had become enclaves of ethnically distinct immigrants with their residence yielding lasting cultural change. Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
became the largest inhabitants of the North End, Boston, North End, Irish Americans, Irish dominated South Boston and Charlestown, and Russians, Russian Jews lived in the West End, Boston, West End. Irish Americans, Irish and Italian Americans, Italian immigrants brought with them Roman Catholicism. Currently, Catholics make up Boston's largest religious community, and the Irish have played a major role in Boston politics since the early 20th century; prominent figures include the Kennedy family, Kennedys, Tip O'Neill, and John F. Fitzgerald.
Between 1631 and 1890, the city tripled its area through land reclamation by filling in marshes, mud flats, and gaps between wharves along the waterfront.. Also see The largest reclamation efforts took place during the 19th century; beginning in 1807, the crown of Beacon Hill was used to fill in a mill pond that later became the Bulfinch Triangle Historic District, Bulfinch Triangle and Haymarket Square (Boston), Haymarket Square. The present-day Massachusetts State House, State House sits atop this lowered Beacon Hill. Reclamation projects in the middle of the century created significant parts of the South End, Boston, South End, the West End, Boston, West End, the Financial District, Boston, Financial District, and Chinatown, Boston, Chinatown.


Boston Common
The Boston Common (also known as the Common) is a public park in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It is the oldest city park in the United States. Boston Common consists of of land bounded by Tremont Street (139 Tremont St.), Park Street, Beacon ...
with gravel brought by rail from the hills of Needham Heights. The city annexed the adjacent towns of South Boston (1804), East Boston (1836), Roxbury, Boston, Roxbury (1868), Dorchester, Boston, Dorchester (including present-day Mattapan and a portion of South Boston) (1870), Brighton, Boston, Brighton (including present-day Allston) (1874), West Roxbury (including present-day Jamaica Plain and Roslindale) (1874), Charlestown (1874), and Hyde Park, Boston, Hyde Park (1912). Other proposals were unsuccessful for the annexation of Boston–Brookline annexation debate of 1873, Brookline, Cambridge, and Chelsea, Massachusetts, Chelsea.
20th century
Fenway Park, home of the Boston Red Sox, opened in 1912. Many architecturally significant buildings were built during these early years of the 20th century: Horticultural Hall, Boston, Massachusetts, Horticultural Hall, the Tennis and Racquet Club, Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum, Fenway Studios, Jordan Hall, and the Boston Opera House (1909), Boston Opera House. The Longfellow Bridge, built in 1906, was mentioned by Robert McCloskey in ''Make Way for Ducklings'', describing its "salt and pepper shakers" feature. Logan International Airport opened on September 8, 1923. The Boston Bruins were founded in 1924 and played their first game at Boston Garden in November 1928. Boston went into decline by the early to mid-20th century, as factories became old and obsolete and businesses moved out of the region for cheaper labor elsewhere. Boston responded by initiating various urban renewal projects, under the direction of the Boston Planning and Development Agency, Boston Redevelopment Authority (BRA) established in 1957. In 1958, BRA initiated a project to improve the historic West End neighborhood. Extensive demolition was met with strong public opposition, and thousands of families were displaced. The BRA continued implementing eminent domain projects, including the clearance of the vibrant Scollay Square area for construction of the modernist style Government Center, Boston, Government Center. In 1965, the Columbia Point Health Center opened in the Dorchester, Boston, Dorchester neighborhood, the first Community health centers in the United States, Community Health Center in the United States. It mostly served the massive Columbia Point (Boston), Columbia Point public housing complex adjoining it, which was built in 1953. The health center is still in operation and was rededicated in 1990 as the Geiger-Gibson Community Health Center. The Columbia Point complex itself was redeveloped and revitalized from 1984 to 1990 into a mixed-income residential development called Harbor Point Apartments.Cf. Roessner, p.293. "The HOPE VI housing program, inspired in part by the success of Harbor Point, was created by legislation passed by Congress in 1992." By the 1970s, the city's economy had begun to recover after 30 years of economic downturn. A large number of high-rises were constructed in the Financial District, Boston, Financial District and in Boston'sBack Bay
Back Bay is an officially recognized neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, built on reclaimed land in the Charles River basin. Construction began in 1859, as the demand for luxury housing exceeded the availability in the city at the time, and t ...
during this period. This boom continued into the mid-1980s and resumed after a few pauses. Hospitals such as Massachusetts General Hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and Brigham and Women's Hospital lead the nation in medical innovation and patient care. Schools such as the Boston Architectural College, Boston College, Boston University, the Harvard Medical School, Tufts University School of Medicine, Northeastern University, Massachusetts College of Art and Design, Wentworth Institute of Technology, Berklee College of Music, the Boston Conservatory, and many others attract students to the area. Nevertheless, the city experienced conflict starting in 1974 over desegregation busing, which resulted in unrest and violence around public schools throughout the mid-1970s.
21st century
 Boston is an intellectual, technological, and political center but has lost some important regional institutions, including the loss to mergers and acquisitions of local financial institutions such as FleetBoston Financial, which was acquired by Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte-based Bank of America in 2004. Boston-based department stores Jordan Marsh and Filene's have both merged into the New York City–based Macy's, Inc., Macy's.
The 1993 acquisition of ''The Boston Globe'' by ''The New York Times'' was reversed in 2013 when it was re-sold to Boston businessman John W. Henry. In 2016, it was announced General Electric would be moving its corporate headquarters from Connecticut to the Seaport District in Boston, joining many other companies in this rapidly developing neighborhood.
Boston has experienced gentrification in the latter half of the 20th century, with housing prices increasing sharply since the 1990s.
On April 15, 2013, two Chechen Islamist brothers Boston Marathon bombing, detonated a pair of bombs near the finish line of the 2013 Boston Marathon, Boston Marathon, killing three people and injuring roughly 264.
In 2016, Boston briefly Boston bid for the 2024 Summer Olympics, shouldered a bid as the US applicant for the 2024 Summer Olympics. The bid was supported by the mayor and a coalition of business leaders and local philanthropists, but was eventually dropped due to public opposition. The United States Olympic Committee, USOC then selected Los Angeles to be the American candidate with Los Angeles ultimately securing the right to host the 2028 Summer Olympics.
Boston is an intellectual, technological, and political center but has lost some important regional institutions, including the loss to mergers and acquisitions of local financial institutions such as FleetBoston Financial, which was acquired by Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte-based Bank of America in 2004. Boston-based department stores Jordan Marsh and Filene's have both merged into the New York City–based Macy's, Inc., Macy's.
The 1993 acquisition of ''The Boston Globe'' by ''The New York Times'' was reversed in 2013 when it was re-sold to Boston businessman John W. Henry. In 2016, it was announced General Electric would be moving its corporate headquarters from Connecticut to the Seaport District in Boston, joining many other companies in this rapidly developing neighborhood.
Boston has experienced gentrification in the latter half of the 20th century, with housing prices increasing sharply since the 1990s.
On April 15, 2013, two Chechen Islamist brothers Boston Marathon bombing, detonated a pair of bombs near the finish line of the 2013 Boston Marathon, Boston Marathon, killing three people and injuring roughly 264.
In 2016, Boston briefly Boston bid for the 2024 Summer Olympics, shouldered a bid as the US applicant for the 2024 Summer Olympics. The bid was supported by the mayor and a coalition of business leaders and local philanthropists, but was eventually dropped due to public opposition. The United States Olympic Committee, USOC then selected Los Angeles to be the American candidate with Los Angeles ultimately securing the right to host the 2028 Summer Olympics.
Geography
 Boston has an area of — (54%) of land and (46%) of water. The city's official elevation, as measured at Logan International Airport, is Above mean sea level, above sea level. The highest point in Boston is Bellevue Hill, Boston, Bellevue Hill at above sea level, and the lowest point is at sea level. Boston is situated on
Boston has an area of — (54%) of land and (46%) of water. The city's official elevation, as measured at Logan International Airport, is Above mean sea level, above sea level. The highest point in Boston is Bellevue Hill, Boston, Bellevue Hill at above sea level, and the lowest point is at sea level. Boston is situated on Boston Harbor
Boston Harbor is a natural harbor and estuary of Massachusetts Bay, and is located adjacent to the city of Boston, Massachusetts. It is home to the Port of Boston, a major shipping facility in the northeastern United States.
History
Since ...
, an arm of Massachusetts Bay, itself an arm of the Atlantic Ocean.
 Boston is surrounded by the
Boston is surrounded by the Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
metropolitan region. It is bordered to the east by the town of Winthrop, Massachusetts, Winthrop and the Boston Harbor Islands, to the northeast by the cities of Revere, Massachusetts, Revere, Chelsea, Massachusetts, Chelsea and Everett, Massachusetts, Everett, to the north by the cities of Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville and Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, to the northwest by Watertown, Massachusetts, Watertown, to the west by the city of Newton, Massachusetts, Newton and town of Brookline, Massachusetts, Brookline, to the southwest by the town of Dedham, Massachusetts, Dedham and small portions of Needham, Massachusetts, Needham and Canton, Massachusetts, Canton, and to the southeast by the town of Milton, Massachusetts, Milton, and the city of Quincy, Massachusetts, Quincy. The Charles River
The Charles River ( Massachusett: ''Quinobequin)'' (sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles) is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton to Boston along a highly meandering route, that doubles b ...
separates Boston's Allston-Brighton, Fenway-Kenmore and Back Bay neighborhoods from Watertown, Massachusetts, Watertown and the majority of Cambridge, and the mass of Boston from its own Charlestown neighborhood. The Neponset River forms the boundary between Boston's southern neighborhoods and Quincy, Massachusetts, Quincy and Milton, Massachusetts, Milton. The Mystic River separates Charlestown from Chelsea and Everett, and Chelsea Creek and Boston Harbor separate East Boston from Downtown, the North End, and the Seaport.
Neighborhoods
 Boston is sometimes called a "city of neighborhoods" because of the profusion of diverse subsections; the city government's Office of Neighborhood Services has officially designated 23 neighborhoods. More than two-thirds of inner Boston's modern land area did not exist when the city was founded. Instead, it was created via the gradual filling in of the surrounding tidal areas over the centuries, with earth from leveling or lowering Boston's three original hills (the "Trimountain", after which Tremont Street is named) and with gravel brought by train from Needham to fill the Back Bay.
Downtown Boston, Downtown and its immediate surroundings consist largely of low-rise masonry buildings (often Federal architecture, Federal style and Greek Revival) interspersed with modern highrises, in the Financial District, Government Center, and South Boston. Back Bay includes many prominent landmarks, such as the
Boston is sometimes called a "city of neighborhoods" because of the profusion of diverse subsections; the city government's Office of Neighborhood Services has officially designated 23 neighborhoods. More than two-thirds of inner Boston's modern land area did not exist when the city was founded. Instead, it was created via the gradual filling in of the surrounding tidal areas over the centuries, with earth from leveling or lowering Boston's three original hills (the "Trimountain", after which Tremont Street is named) and with gravel brought by train from Needham to fill the Back Bay.
Downtown Boston, Downtown and its immediate surroundings consist largely of low-rise masonry buildings (often Federal architecture, Federal style and Greek Revival) interspersed with modern highrises, in the Financial District, Government Center, and South Boston. Back Bay includes many prominent landmarks, such as the Boston Public Library
The Boston Public Library is a municipal public library system in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, founded in 1848. The Boston Public Library is also the Library for the Commonwealth (formerly ''library of last recourse'') of the Commonweal ...
, The First Church of Christ, Scientist, Christian Science Center, Copley Square, Newbury Street, and New England's two tallest buildings: the 200 Clarendon Street, John Hancock Tower and the Prudential Tower, Prudential Center.
Near the John Hancock Tower is the Berkeley Building, old John Hancock Building with its prominent weather beacon, illuminated beacon, the color of which forecasts the weather. Smaller commercial areas are interspersed among areas of single-family homes and wooden/brick multi-family row houses. The South End Historic District is the largest surviving contiguous Victorian-era neighborhood in the US. The geography of downtown and South Boston was particularly affected by the Central Artery/Tunnel Project (known unofficially as the "Big Dig") which removed the elevated Central Artery and incorporated new green spaces and open areas.
Climate
 Under the Köppen climate classification, depending on the isotherm used, Boston has either a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') under the isotherm or a humid continental climate under the 0 °C isotherm (Köppen ''Dfa''). The city is best described as being in a transitional zone between the two climates. Summers are typically warm and humid, while winters are cold and stormy, with occasional periods of heavy snow. Spring and fall are usually cool to mild, with varying conditions dependent on wind direction and jet stream positioning. Prevailing wind patterns that blow offshore minimize the influence of the Atlantic Ocean. However, in winter areas near the immediate coast will often see more rain than snow as warm air is drawn off the Atlantic at times. The city lies at the transition between USDA plant hardiness zones 6b (most of the city) and 7a (Downtown, South Boston, and East Boston neighborhoods).
The hottest month is July, with a mean temperature of . The coldest month is January, with a mean temperature of . Periods exceeding in summer and below freezing in winter are not uncommon but rarely extended, with about 13 and 25 days per year seeing each, respectively. The most recent sub- reading occurred on January 7, 2018, when the temperature dipped down to . In addition, several decades may pass between readings, with the most recent such occurrence on July 22, 2011, when the temperature reached . The city's average window for freezing temperatures is November 9 through April 5. Official temperature records have ranged from on February 9, 1934, up to on July 4, 1911. The record cold daily maximum is on December 30, 1917, while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum is on August 2, 1975, and July 21, 2019.
Under the Köppen climate classification, depending on the isotherm used, Boston has either a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') under the isotherm or a humid continental climate under the 0 °C isotherm (Köppen ''Dfa''). The city is best described as being in a transitional zone between the two climates. Summers are typically warm and humid, while winters are cold and stormy, with occasional periods of heavy snow. Spring and fall are usually cool to mild, with varying conditions dependent on wind direction and jet stream positioning. Prevailing wind patterns that blow offshore minimize the influence of the Atlantic Ocean. However, in winter areas near the immediate coast will often see more rain than snow as warm air is drawn off the Atlantic at times. The city lies at the transition between USDA plant hardiness zones 6b (most of the city) and 7a (Downtown, South Boston, and East Boston neighborhoods).
The hottest month is July, with a mean temperature of . The coldest month is January, with a mean temperature of . Periods exceeding in summer and below freezing in winter are not uncommon but rarely extended, with about 13 and 25 days per year seeing each, respectively. The most recent sub- reading occurred on January 7, 2018, when the temperature dipped down to . In addition, several decades may pass between readings, with the most recent such occurrence on July 22, 2011, when the temperature reached . The city's average window for freezing temperatures is November 9 through April 5. Official temperature records have ranged from on February 9, 1934, up to on July 4, 1911. The record cold daily maximum is on December 30, 1917, while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum is on August 2, 1975, and July 21, 2019.
 Boston's coastal location on the North Atlantic moderates its temperature but makes the city very prone to Nor'easter weather systems that can produce much snow and rain. The city averages of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation a year, with of snowfall per season. Most snowfall occurs from mid-November through early April, and snow is rare in May and October. There is also high year-to-year variability in snowfall; for instance, the winter of 2011–12 saw only of accumulating snow, but the previous winter, the corresponding figure was .
Fog is fairly common, particularly in spring and early summer. Due to its location along the North Atlantic, the city often receives sea breezes, especially in the late spring, when water temperatures are still quite cold and temperatures at the coast can be more than colder than a few miles inland, sometimes dropping by that amount near midday.
Thunderstorms occur from May to September, which are occasionally severe with large hail, damaging winds, and heavy downpours. Although downtown Boston has never been struck by a violent tornado, the city itself has experienced many tornado warnings. Damaging storms are more common to areas north, west, and northwest of the city. Boston has a relatively sunny climate for a coastal city at its latitude, averaging over 2,600 hours of sunshine per annum.
Boston's coastal location on the North Atlantic moderates its temperature but makes the city very prone to Nor'easter weather systems that can produce much snow and rain. The city averages of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation a year, with of snowfall per season. Most snowfall occurs from mid-November through early April, and snow is rare in May and October. There is also high year-to-year variability in snowfall; for instance, the winter of 2011–12 saw only of accumulating snow, but the previous winter, the corresponding figure was .
Fog is fairly common, particularly in spring and early summer. Due to its location along the North Atlantic, the city often receives sea breezes, especially in the late spring, when water temperatures are still quite cold and temperatures at the coast can be more than colder than a few miles inland, sometimes dropping by that amount near midday.
Thunderstorms occur from May to September, which are occasionally severe with large hail, damaging winds, and heavy downpours. Although downtown Boston has never been struck by a violent tornado, the city itself has experienced many tornado warnings. Damaging storms are more common to areas north, west, and northwest of the city. Boston has a relatively sunny climate for a coastal city at its latitude, averaging over 2,600 hours of sunshine per annum.
Cityscapes
Demographics
 In 2020, Boston was estimated to have 691,531 residents living in 266,724 households—a 12% population increase over 2010. The city is the List of United States cities by population density, third-most densely populated large U.S. city of over half a million residents, and the most densely populated state capital. Some 1.2 million persons may be within Boston's boundaries during work hours, and as many as 2 million during special events. This fluctuation of people is caused by hundreds of thousands of suburban residents who travel to the city for work, education, health care, and special events.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 21.9% at age 19 and under, 14.3% from 20 to 24, 33.2% from 25 to 44, 20.4% from 45 to 64, and 10.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 30.8 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.9 males. There were 252,699 households, of which 20.4% had children under the age of 18 living in them, 25.5% were married couples living together, 16.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 54.0% were non-families. 37.1% of all households were made up of individuals, and 9.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.26 and the average family size was 3.08. From an estimate in 2005, Boston has one of the LGBT demographics of the United States#By city, largest per capita LGBT populations in the United States.
The Median income, median household income in Boston was $51,739, while the median income for a family was $61,035. Full-time year-round male workers had a median income of $52,544 versus $46,540 for full-time year-round female workers. The per capita income for the city was $33,158. 21.4% of the population and 16.0% of families were below the poverty line. Of the total population, 28.8% of those under the age of 18 and 20.4% of those 65 and older were living below the poverty line. Boston has a significant racial wealth gap in the United States, racial wealth gap with White Bostonians having an median net worth of $247,500 compared to an $8 median net worth for non-immigrant Black residents and $0 for Dominican immigrant residents.
In 1950, Race (United States Census), Whites represented 94.7% of Boston's population. From the 1950s to the end of the 20th century, the proportion of non-Hispanic Whites in the city declined. In 2000, non-Hispanic Whites made up 49.5% of the city's population, making the city majority minority for the first time. However, in the 21st century, the city has experienced significant gentrification, during which affluent Whites have moved into formerly non-White areas. In 2006, the US Census Bureau estimated non-Hispanic Whites again formed a slight majority but , in part due to the housing crash, as well as increased efforts to make more affordable housing more available, the non-White population has rebounded. This may also have to do with increased Latin American and Asian Americans, Asian populations and more clarity surrounding US Census statistics, which indicate a non-Hispanic White population of 47 percent (some reports give slightly lower figures).
In 2020, Boston was estimated to have 691,531 residents living in 266,724 households—a 12% population increase over 2010. The city is the List of United States cities by population density, third-most densely populated large U.S. city of over half a million residents, and the most densely populated state capital. Some 1.2 million persons may be within Boston's boundaries during work hours, and as many as 2 million during special events. This fluctuation of people is caused by hundreds of thousands of suburban residents who travel to the city for work, education, health care, and special events.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 21.9% at age 19 and under, 14.3% from 20 to 24, 33.2% from 25 to 44, 20.4% from 45 to 64, and 10.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 30.8 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.9 males. There were 252,699 households, of which 20.4% had children under the age of 18 living in them, 25.5% were married couples living together, 16.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 54.0% were non-families. 37.1% of all households were made up of individuals, and 9.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.26 and the average family size was 3.08. From an estimate in 2005, Boston has one of the LGBT demographics of the United States#By city, largest per capita LGBT populations in the United States.
The Median income, median household income in Boston was $51,739, while the median income for a family was $61,035. Full-time year-round male workers had a median income of $52,544 versus $46,540 for full-time year-round female workers. The per capita income for the city was $33,158. 21.4% of the population and 16.0% of families were below the poverty line. Of the total population, 28.8% of those under the age of 18 and 20.4% of those 65 and older were living below the poverty line. Boston has a significant racial wealth gap in the United States, racial wealth gap with White Bostonians having an median net worth of $247,500 compared to an $8 median net worth for non-immigrant Black residents and $0 for Dominican immigrant residents.
In 1950, Race (United States Census), Whites represented 94.7% of Boston's population. From the 1950s to the end of the 20th century, the proportion of non-Hispanic Whites in the city declined. In 2000, non-Hispanic Whites made up 49.5% of the city's population, making the city majority minority for the first time. However, in the 21st century, the city has experienced significant gentrification, during which affluent Whites have moved into formerly non-White areas. In 2006, the US Census Bureau estimated non-Hispanic Whites again formed a slight majority but , in part due to the housing crash, as well as increased efforts to make more affordable housing more available, the non-White population has rebounded. This may also have to do with increased Latin American and Asian Americans, Asian populations and more clarity surrounding US Census statistics, which indicate a non-Hispanic White population of 47 percent (some reports give slightly lower figures).

 People of History of Irish Americans in Boston, Irish descent form the largest single American ancestry, ethnic group in the city, making up 15.8% of the population, followed by Italian Americans, Italians, accounting for 8.3% of the population. People of West Indies, West Indian and Caribbean ancestry are another sizable group, at over 15%.
In Greater Boston, these numbers grew significantly, with 150,000 Dominicans according to 2018 estimates, 134,000 Puerto Ricans, 57,500 Salvadorans, 39,000 Guatemalans, 36,000 Mexicans, and over 35,000 Colombians. East Boston has a diverse Hispanic/Latino population of Salvadorans, Colombians, Guatemalans, Mexicans, Dominicans, Puerto Ricans, and even Portuguese-speaking people from Portugal and Brazil. Hispanic populations in southwest Boston neighborhoods are mainly made up of Dominicans and Puerto Ricans, usually sharing neighborhoods in this section with African Americans and Blacks with origins from the Caribbean and Africa especially Cape Verdeans and Haitians. Neighborhoods such as Jamaica Plain, Boston, Jamaica Plain and Roslindale, Boston, Roslindale have experienced a growing number of Dominican-Americans in Boston, Dominican Americans.
Over 27,000 Chinese Americans in Boston, Chinese Americans made their home in Boston city proper in 2013.
People of History of Irish Americans in Boston, Irish descent form the largest single American ancestry, ethnic group in the city, making up 15.8% of the population, followed by Italian Americans, Italians, accounting for 8.3% of the population. People of West Indies, West Indian and Caribbean ancestry are another sizable group, at over 15%.
In Greater Boston, these numbers grew significantly, with 150,000 Dominicans according to 2018 estimates, 134,000 Puerto Ricans, 57,500 Salvadorans, 39,000 Guatemalans, 36,000 Mexicans, and over 35,000 Colombians. East Boston has a diverse Hispanic/Latino population of Salvadorans, Colombians, Guatemalans, Mexicans, Dominicans, Puerto Ricans, and even Portuguese-speaking people from Portugal and Brazil. Hispanic populations in southwest Boston neighborhoods are mainly made up of Dominicans and Puerto Ricans, usually sharing neighborhoods in this section with African Americans and Blacks with origins from the Caribbean and Africa especially Cape Verdeans and Haitians. Neighborhoods such as Jamaica Plain, Boston, Jamaica Plain and Roslindale, Boston, Roslindale have experienced a growing number of Dominican-Americans in Boston, Dominican Americans.
Over 27,000 Chinese Americans in Boston, Chinese Americans made their home in Boston city proper in 2013.
Ancestry
According to the 2012–2016 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates, the largest ancestry groups in Boston, Massachusetts are:Demographic breakdown by ZIP Code
Income
Data is from the 2008–2012 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates.Religion
Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
area, with more than two million members and 339 churches, followed by the Episcopal Church with 58,000 adherents in 160 churches. The United Church of Christ had 55,000 members and 213 churches.
The city has a American Jews, Jewish population of an estimated 248,000 Jews within the Boston metro area. More than half of Jewish households in the Greater Boston area reside in the city itself, Brookline, Massachusetts, Brookline, Newton, Massachusetts, Newton, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville, or adjacent towns.
Economy
A global city, Boston is placed among the top 30 most economically powerful cities in the world. Encompassing $363 billion, theGreater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
metropolitan area has the List of cities by GDP, sixth-largest economy in the country and 12th-largest in the world.
Boston's colleges and universities exert a significant impact on the regional economy. Boston attracts more than 350,000 college students from around the world, who contribute more than US$4.8 billion annually to the city's economy. The area's schools are major employers and attract industries to the city and surrounding region. The city is home to a number of technology companies and is a hub for biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
, with the Milken Institute rating Boston as the top List of life sciences, life sciences cluster in the country. Boston receives the highest absolute amount of annual funding from the National Institutes of Health of all cities in the United States.
The city is considered highly innovative for a variety of reasons, including the presence of academia, access to venture capital, and the presence of many high-tech companies. The Massachusetts Route 128, Route 128 corridor and Greater Boston continue to be a major center for venture capital investment, and high technology remains an important sector.
Tourism also composes a large part of Boston's economy, with 21.2 million domestic and international visitors spending $8.3 billion in 2011. Excluding visitors from Canada and Mexico, over 1.4 million international tourists visited Boston in 2014, with those from China and the United Kingdom leading the list. Boston's status as a state capital as well as the regional home of federal agencies has rendered law and government to be another major component of the city's economy. The city is a major Port of Boston, seaport along the East Coast of the United States and the oldest continuously operated industrial and fishing port in the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the term We ...
.
In the 2018 Global Financial Centres Index, Boston was ranked as having the thirteenth most competitive financial services center in the world and the second most competitive in the United States. Boston-based Fidelity Investments helped popularize the mutual fund in the 1980s and has made Boston one of the top financial centers in the United States. The city is home to the headquarters of Santander Bank, and Boston is a center for venture capital firms. State Street Corporation, which specializes in asset management and custody services, is based in the city. Boston is a printing and publishing center—Houghton Mifflin Harcourt is headquartered within the city, along with Bedford-St. Martin's, Bedford-St. Martin's Press and Beacon Press. Pearson PLC publishing units also employ several hundred people in Boston. The city is home to three major convention centers—the Hynes Convention Center in the Back Bay, and the Seaport Hotel and Seaport World Trade Center, Seaport World Trade Center and Boston Convention and Exhibition Center on the South Boston waterfront. The General Electric Corporation announced in January 2016 its decision to move the company's global headquarters to the Seaport District in Boston, from Fairfield, Connecticut, Fairfield, Connecticut, citing factors including Boston's preeminence in the realm of higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completi ...
. Boston is home to the headquarters of several major athletic and footwear companies including Converse (shoe company), Converse, New Balance, and Reebok. Rockport (company), Rockport, Puma (brand), Puma and Wolverine World Wide, Wolverine World Wide, Inc. headquarters or regional offices are just outside the city.
In 2019, a yearly ranking of time wasted in traffic listed Boston area drivers lost approximately 164 hours a year in lost productivity due to the area's traffic congestion. This amounted to $2,300 a year per driver in costs.
Education
Primary and secondary education
 The Boston Public Schools enroll 57,000 students attending 145 schools, including the renowned Boston Latin Academy, John D. O'Bryant School of Mathematics & Science, John D. O'Bryant School of Math & Science, and
The Boston Public Schools enroll 57,000 students attending 145 schools, including the renowned Boston Latin Academy, John D. O'Bryant School of Mathematics & Science, John D. O'Bryant School of Math & Science, and Boston Latin School
The Boston Latin School is a public exam school in Boston, Massachusetts. It was established on April 23, 1635, making it both the oldest public school in the British America and the oldest existing school in the United States. Its curriculum f ...
. The Boston Latin School was established in 1635 and is the oldest public high school in the US. Boston also operates the United States' second-oldest public high school and its oldest public elementary school. The system's students are 40% Hispanic or Latino, 35% Black or African American, 13% White, and 9% Asian. There are private, parochial, and charter schools as well, and approximately 3,300 minority students attend participating suburban schools through the METCO, Metropolitan Educational Opportunity Council. In September 2019, the city formally inaugurated Boston Saves, a program that provides every child enrolled in the city's kindergarten system a savings account containing $50 to be used toward college or career training.
Higher education
 Some of the most renowned and highly ranked universities in the world are near Boston. Three universities with a major presence in the city,
Some of the most renowned and highly ranked universities in the world are near Boston. Three universities with a major presence in the city, Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the mo ...
, and Tufts University, Tufts, are just outside of Boston in the cities of Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge and Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville, known as the ''Brainpower Triangle''. Harvard is the nation's oldest institute of higher education and is centered across the Charles River in Cambridge, though the majority of its land holdings and a substantial amount of its educational activities are in Boston. Its Harvard Business School, business school and athletics facilities are in Boston's Allston neighborhood, and its Harvard Medical School, medical, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, dental, and Harvard School of Public Health, public health schools are located in the Longwood Medical and Academic Area, Longwood area.
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) originated in Boston and was long known as "History of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology#Boston Tech (1865–1916), Boston Tech"; it moved across the river to Cambridge in 1916. Tufts University's main campus is north of the city in Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville and Medford, Massachusetts, Medford, though it locates its medical and dental schools in Boston's Chinatown at Tufts Medical Center, a 451-bed academic medical institution that is home to a full-service hospital for adults and the Floating Hospital for Children.
Five members of the Association of American Universities are in Greater Boston (more than any other metropolitan area): Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Tufts University, Boston University, and Brandeis University. Furthermore, Greater Boston contains seven List of research universities in the United States#Universities classified as "R1: Doctoral Universities – Highest Research Activity", Highest Research Activity (R1) Universities as per the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, Carnegie Classification. This includes, in addition to the aforementioned five, Boston College, and Northeastern University. This is, by a large margin, the highest concentration of such institutions in a single metropolitan area.
Hospitals, universities, and research institutions in Greater Boston received more than $1.77 billion in National Institutes of Health grants in 2013, more money than any other American metropolitan area. This high density of research institutes also contributes to Boston's Boston Postdoctoral Association, high density of early career researchers, which, due to high housing costs in the region, have been shown to face Boston Postdoctoral Association#Advocacy, housing stress.

 Greater Boston has more than 50 colleges and universities, with 250,000 students enrolled in Boston and Cambridge alone. The city's largest private universities include Boston University (also the city's fourth-largest employer), with its main campus along Commonwealth Avenue (Boston), Commonwealth Avenue and a medical campus in the South End, Boston, South End, Northeastern University in the Fenway–Kenmore, Fenway area, Suffolk University near Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill, which includes Suffolk University Law School, law school and Sawyer Business School, business school, and Boston College, which straddles the Boston (Brighton)–Newton border. Boston's only public university is the University of Massachusetts Boston on Columbia Point in Dorchester, Massachusetts, Dorchester. Roxbury Community College and Bunker Hill Community College are the city's two public community colleges. Altogether, Boston's colleges and universities employ more than 42,600 people, accounting for nearly seven percent of the city's workforce.
Smaller private colleges include Babson College, Bentley University, Boston Architectural College, Emmanuel College (Massachusetts), Emmanuel College, Fisher College, MGH Institute of Health Professions, MCPHS University, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Simmons University, Wellesley College, Wheelock College, Wentworth Institute of Technology, New England School of Law (originally established as America's first all female law school), and Emerson College.
Metropolitan Boston is home to several music school, conservatories and art schools, including Lesley University, Lesley University College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art, the School of the Museum of Fine Arts at Tufts, School of the Museum of Fine Arts, New England Institute of Art, New England School of Art and Design (Suffolk University), Longy School of Music of Bard College, and the New England Conservatory of Music, New England Conservatory (the oldest independent conservatory in the United States). Other conservatories include the Boston Conservatory and Berklee College of Music, which has made Boston an important city for jazz music.
Greater Boston has more than 50 colleges and universities, with 250,000 students enrolled in Boston and Cambridge alone. The city's largest private universities include Boston University (also the city's fourth-largest employer), with its main campus along Commonwealth Avenue (Boston), Commonwealth Avenue and a medical campus in the South End, Boston, South End, Northeastern University in the Fenway–Kenmore, Fenway area, Suffolk University near Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill, which includes Suffolk University Law School, law school and Sawyer Business School, business school, and Boston College, which straddles the Boston (Brighton)–Newton border. Boston's only public university is the University of Massachusetts Boston on Columbia Point in Dorchester, Massachusetts, Dorchester. Roxbury Community College and Bunker Hill Community College are the city's two public community colleges. Altogether, Boston's colleges and universities employ more than 42,600 people, accounting for nearly seven percent of the city's workforce.
Smaller private colleges include Babson College, Bentley University, Boston Architectural College, Emmanuel College (Massachusetts), Emmanuel College, Fisher College, MGH Institute of Health Professions, MCPHS University, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Simmons University, Wellesley College, Wheelock College, Wentworth Institute of Technology, New England School of Law (originally established as America's first all female law school), and Emerson College.
Metropolitan Boston is home to several music school, conservatories and art schools, including Lesley University, Lesley University College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art and Design, Massachusetts College of Art, the School of the Museum of Fine Arts at Tufts, School of the Museum of Fine Arts, New England Institute of Art, New England School of Art and Design (Suffolk University), Longy School of Music of Bard College, and the New England Conservatory of Music, New England Conservatory (the oldest independent conservatory in the United States). Other conservatories include the Boston Conservatory and Berklee College of Music, which has made Boston an important city for jazz music.
Healthcare
 The Longwood Medical and Academic Area, adjacent to the Fenway, district, is home to a large number of medical and research facilities, including Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston Children's Hospital, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Joslin Diabetes Center, and the MCPHS University, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences.
Prominent medical facilities, including Massachusetts General Hospital, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital are in the Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill area. St. Elizabeth's Medical Center (Boston), St. Elizabeth's Medical Center is in Brighton Center of the city's Brighton, Boston, Brighton neighborhood. New England Baptist Hospital is in Mission Hill. VA Boston Healthcare System, The city has Veterans Affairs medical centers in the Jamaica Plain, Boston, Jamaica Plain and West Roxbury, Boston, West Roxbury neighborhoods. The Boston Public Health Commission, an agency of the Massachusetts government, oversees health concerns for city residents. Boston EMS provides pre-hospital emergency medical services to residents and visitors.
Many of Boston's medical facilities are associated with universities. The facilities in the Longwood Medical and Academic Area and in Massachusetts General Hospital are affiliated with Harvard Medical School. Tufts Medical Center (formerly Tufts-New England Medical Center), in the southern portion of the Chinatown, Boston, Chinatown neighborhood, is affiliated with Tufts University School of Medicine. Boston Medical Center, in the South End, Boston, South End neighborhood, is the primary teaching facility for the Boston University School of Medicine as well as the largest trauma center in the Boston area; it was formed by the merger of Boston University Hospital and Boston City Hospital, which was the first municipal hospital in the United States.
The Longwood Medical and Academic Area, adjacent to the Fenway, district, is home to a large number of medical and research facilities, including Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston Children's Hospital, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Joslin Diabetes Center, and the MCPHS University, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences.
Prominent medical facilities, including Massachusetts General Hospital, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital are in the Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill area. St. Elizabeth's Medical Center (Boston), St. Elizabeth's Medical Center is in Brighton Center of the city's Brighton, Boston, Brighton neighborhood. New England Baptist Hospital is in Mission Hill. VA Boston Healthcare System, The city has Veterans Affairs medical centers in the Jamaica Plain, Boston, Jamaica Plain and West Roxbury, Boston, West Roxbury neighborhoods. The Boston Public Health Commission, an agency of the Massachusetts government, oversees health concerns for city residents. Boston EMS provides pre-hospital emergency medical services to residents and visitors.
Many of Boston's medical facilities are associated with universities. The facilities in the Longwood Medical and Academic Area and in Massachusetts General Hospital are affiliated with Harvard Medical School. Tufts Medical Center (formerly Tufts-New England Medical Center), in the southern portion of the Chinatown, Boston, Chinatown neighborhood, is affiliated with Tufts University School of Medicine. Boston Medical Center, in the South End, Boston, South End neighborhood, is the primary teaching facility for the Boston University School of Medicine as well as the largest trauma center in the Boston area; it was formed by the merger of Boston University Hospital and Boston City Hospital, which was the first municipal hospital in the United States.
Public safety
Culture

 Boston shares many cultural roots with greater New England, including a dialect of the non-Rhoticity in English, rhotic Eastern New England English, New England accent known as the Boston accent and a New England cuisine, regional cuisine with a large emphasis on seafood, salt, and dairy products. Boston also has its own collection of neologisms known as ''Boston slang'' and sardonic humor.
In the early 1800s, William Tudor (1779–1830), William Tudor wrote that Boston was "'perhaps the most perfect and certainly the best-regulated democracy that ever existed. There is something so impossible in the immortal fame of Athens, that the very name makes everything modern shrink from comparison; but since the days of that glorious city I know of none that has approached so near in some points, distant as it may still be from that illustrious model.' From this, Boston has been called the "Athens of America" (also a nickname of
Boston shares many cultural roots with greater New England, including a dialect of the non-Rhoticity in English, rhotic Eastern New England English, New England accent known as the Boston accent and a New England cuisine, regional cuisine with a large emphasis on seafood, salt, and dairy products. Boston also has its own collection of neologisms known as ''Boston slang'' and sardonic humor.
In the early 1800s, William Tudor (1779–1830), William Tudor wrote that Boston was "'perhaps the most perfect and certainly the best-regulated democracy that ever existed. There is something so impossible in the immortal fame of Athens, that the very name makes everything modern shrink from comparison; but since the days of that glorious city I know of none that has approached so near in some points, distant as it may still be from that illustrious model.' From this, Boston has been called the "Athens of America" (also a nickname of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
) for its literary genre, literary culture, earning a reputation as "the intellectual capital of the United States".
In the nineteenth century, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Henry David Thoreau, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Margaret Fuller, James Russell Lowell, and Henry Wadsworth Longfellow wrote in Boston. Some consider the Old Corner Bookstore to be the "cradle of American literature", the place where these writers met and where ''The Atlantic Monthly'' was first published. In 1852, the Boston Public Library
The Boston Public Library is a municipal public library system in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, founded in 1848. The Boston Public Library is also the Library for the Commonwealth (formerly ''library of last recourse'') of the Commonweal ...
was founded as the first free library in the United States. Boston's literary culture continues today thanks to the city's many universities and the Boston Book Festival.
Music is afforded a high degree of civic engagement, civic support in Boston. The Boston Symphony Orchestra is one of the "Big Five (orchestras), Big Five", a group of the greatest American orchestras, and the classical music magazine ''Gramophone (magazine), Gramophone'' called it one of the "world's best" orchestras. Symphony Hall, Boston, Symphony Hall (west of Back Bay) is home to the Boston Symphony Orchestra and the related Boston Youth Symphony Orchestras, Boston Youth Symphony Orchestra, which is the largest youth orchestra in the nation, and to the Boston Pops Orchestra. The British newspaper ''The Guardian'' called Boston Symphony Hall "one of the top venues for classical music in the world", adding "Symphony Hall in Boston was where science became an essential part of concert hall design". Other concerts are held at the New England Conservatory of Music, New England Conservatory's Jordan Hall. The Boston Ballet performs at the Boston Opera House (1980), Boston Opera House. Other performing-arts organizations in the city include the Boston Lyric Opera, Boston Lyric Opera Company, Opera Boston, Boston Baroque (the first permanent Baroque orchestra in the US), and the Handel and Haydn Society (one of the oldest choral companies in the United States). The city is a center for contemporary classical music with a number of performing groups, several of which are associated with the city's conservatories and universities. These include the Boston Modern Orchestra Project and Boston Musica Viva. Several theaters are in or near the Washington Street Theatre District, Theater District south of Boston Common, including the Cutler Majestic Theatre, Citi Performing Arts Center, the Colonial Theatre (Boston), Colonial Theater, and the Orpheum Theatre (Boston), Orpheum Theatre.

 There are several major annual events, such as First Night which occurs on New Year's Eve, the Boston Early Music Festival, the annual Boston Arts Festival at Christopher Columbus Waterfront Park, the annual Boston gay pride parade and festival held in June, and Italian summer feasts in the North End honoring Catholic saints. The city is the site of several events during the Independence Day (United States), Fourth of July period. They include the week-long Harborfest festivities and a Boston Pops concert accompanied by fireworks on the banks of the
There are several major annual events, such as First Night which occurs on New Year's Eve, the Boston Early Music Festival, the annual Boston Arts Festival at Christopher Columbus Waterfront Park, the annual Boston gay pride parade and festival held in June, and Italian summer feasts in the North End honoring Catholic saints. The city is the site of several events during the Independence Day (United States), Fourth of July period. They include the week-long Harborfest festivities and a Boston Pops concert accompanied by fireworks on the banks of the Charles River
The Charles River ( Massachusett: ''Quinobequin)'' (sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles) is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton to Boston along a highly meandering route, that doubles b ...
.
Several historic sites relating to the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
period are preserved as part of the Boston National Historical Park because of the city's prominent role. Many are found along the Freedom Trail, which is marked by a red line of bricks embedded in the ground.
The city is also home to several art museums and galleries, including the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, Museum of Fine Arts and the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum. The Institute of Contemporary Art, Boston, Institute of Contemporary Art is housed in a contemporary building designed by Diller Scofidio + Renfro in the Seaport District. Boston's South End Art and Design District (SoWa) and Newbury St. are both art gallery destinations. Columbia Point is the location of the University of Massachusetts Boston, the Edward M. Kennedy Institute for the United States Senate, the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum, and the Massachusetts Archives, Massachusetts Archives and Commonwealth Museum. The Boston Athenæum (one of the oldest independent libraries in the United States), Boston Children's Museum, Bull & Finch Pub (whose building is known from the television show ''Cheers''), Museum of Science (Boston), Museum of Science, and the New England Aquarium are within the city.
Boston has been a noted religious center from its earliest days. The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Boston serves nearly 300 parishes and is based in the Cathedral of the Holy Cross (Boston), Cathedral of the Holy Cross (1875) in the South End, while the Episcopal Diocese of Massachusetts serves just under 200 congregations, with the Cathedral Church of St. Paul, Boston, Cathedral Church of St. Paul (1819) as its episcopal seat. Unitarian Universalist Association, Unitarian Universalism has its headquarters in the Fort Point neighborhood. The Church of Christ, Scientist, Christian Scientists are headquartered in Back Bay at the The First Church of Christ, Scientist, Mother Church (1894). The oldest church in Boston is First Church in Boston, founded in 1630. King's Chapel was the city's first Anglican church, founded in 1686 and converted to Unitarianism in 1785. Other churches include Christ Church (better known as Old North Church, 1723), the oldest church building in the city, Trinity Church, Boston, Trinity Church (1733), Park Street Church (1809), Old South Church
Old South Church in Boston, Massachusetts, (also known as New Old South Church or Third Church) is a historic United Church of Christ congregation first organized in 1669. Its present building was designed in the Gothic Revival style by Charles ...
(1874), Jubilee Christian Church, and Basilica and Shrine of Our Lady of Perpetual Help on Mission Hill, Boston, Mission Hill (1878).
Environment
Pollution control
Air quality in Boston is generally very good. Between 2004 and 2013, there were only four days in which the air was unhealthy for the general public, according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA. Some of the cleaner energy facilities in Boston include the Allston green district, with three ecologically compatible housing facilities. Boston is also breaking ground on multiple green affordable housing facilities to help reduce the carbon impact of the city while simultaneously making these initiatives financially available to a greater population. Boston's climate plan is updated every three years and was most recently modified in 2013. This legislature includes the Building Energy Reporting and Disclosure Ordinance, which requires the city's larger buildings to disclose their yearly energy and water use statistics and to partake in an energy assessment every five years. These statistics are made public by the city, thereby increasing incentives for buildings to be more environmentally conscious. Mayor Thomas Menino introduced the Renew Boston Whole Building Incentive which reduces the cost of living in buildings that are deemed energy efficient. This gives people an opportunity to find housing in neighborhoods that support the environment. The ultimate goal of this initiative is to enlist 500 Bostonians to participate in a free, in-home energy assessment.Water purity and availability
Many older buildings in certain areas of Boston are supported by wooden piles driven into the area's fill; these piles remain sound if submerged in water, but are subject to dry rot if exposed to air for long periods. Ground water levels have been dropping in many areas of the city, due in part to an increase in the amount of rainwater discharged directly into sewers rather than absorbed by the ground. The Boston Groundwater Trust coordinates monitoring ground water levels throughout the city via a network of public and private monitoring wells. However, Boston's drinking water supply from the Quabbin Reservoir, Quabbin and Wachusett Reservoirs is one of the very few in the country so pure as to satisfy the Federal Clean Water Act without filtration.Climate change and sea level rise
The City of Boston has developed a climate action plan covering carbon reduction in buildings, transportation, and energy use. Mayor Thomas Menino commissioned the city's first Climate Action Plan in 2007, with an update released in 2011. Since then, Mayor Marty Walsh has built upon these plans with further updates released in 2014 and 2019. As a coastal city built largely on Land reclamation, fill, Sea level rise, sea-level rise is of major concern to the city government. The latest version of the climate action plan anticipates between two and seven feet of sea-level rise in Boston by the end of the century. A separate initiative, Resilient Boston Harbor, lays out neighborhood-specific recommendations for coastal resilience.Sports
 Boston has teams in Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, the four major North American men's professional sports leagues plus Major League Soccer, and, as of List of U.S. cities by number of professional sports championships, 2019, has won 39 championships in these leagues. It is one of eight cities (along with Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, New York, Philadelphia, St. Louis and Washington) to have won championships in all four major American sports leagues. It has been suggested that Boston is the new "TitleTown, USA", as the city's professional sports teams have won twelve championships since 2001: Patriots (2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, 2016 and 2018), Red Sox (2004, 2007, 2013, and 2018), Celtics (2008), and Bruins (2011). This love of sports made Boston the United States Olympic Committee's choice to Bids for Olympic Games, bid to hold the 2024 Summer Olympic Games, but the city cited financial concerns when it withdrew its bid on July 27, 2015.
The Boston Red Sox, a founding member of the American League of Major League Baseball in 1901, play their home games at Fenway Park, near Kenmore Square, in the city's Fenway-Kenmore, Fenway section. Built in 1912, it is the oldest sports arena or stadium in active use in the United States among the four major professional American sports leagues, Major League Baseball, the National Football League, National Basketball Association, and the National Hockey League. Boston was the site of the first game of the first modern World Series, in 1903. The series was played between the AL Champion Boston Americans and the NL champion Pittsburgh Pirates. Persistent reports that the team was known in 1903 as the "Boston Pilgrims" appear to be unfounded. Boston's first professional baseball team was the Red Stockings, one of the charter members of the National Association of Professional Base Ball Players, National Association in 1871, and of the National League in 1876. The team played under that name until 1883, under the name Beaneaters until 1911, and under the name Braves from 1912 until they moved to Milwaukee after the 1952 season. Since 1966 they have played in Atlanta as the Atlanta Braves.
Boston has teams in Major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada, the four major North American men's professional sports leagues plus Major League Soccer, and, as of List of U.S. cities by number of professional sports championships, 2019, has won 39 championships in these leagues. It is one of eight cities (along with Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, New York, Philadelphia, St. Louis and Washington) to have won championships in all four major American sports leagues. It has been suggested that Boston is the new "TitleTown, USA", as the city's professional sports teams have won twelve championships since 2001: Patriots (2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, 2016 and 2018), Red Sox (2004, 2007, 2013, and 2018), Celtics (2008), and Bruins (2011). This love of sports made Boston the United States Olympic Committee's choice to Bids for Olympic Games, bid to hold the 2024 Summer Olympic Games, but the city cited financial concerns when it withdrew its bid on July 27, 2015.
The Boston Red Sox, a founding member of the American League of Major League Baseball in 1901, play their home games at Fenway Park, near Kenmore Square, in the city's Fenway-Kenmore, Fenway section. Built in 1912, it is the oldest sports arena or stadium in active use in the United States among the four major professional American sports leagues, Major League Baseball, the National Football League, National Basketball Association, and the National Hockey League. Boston was the site of the first game of the first modern World Series, in 1903. The series was played between the AL Champion Boston Americans and the NL champion Pittsburgh Pirates. Persistent reports that the team was known in 1903 as the "Boston Pilgrims" appear to be unfounded. Boston's first professional baseball team was the Red Stockings, one of the charter members of the National Association of Professional Base Ball Players, National Association in 1871, and of the National League in 1876. The team played under that name until 1883, under the name Beaneaters until 1911, and under the name Braves from 1912 until they moved to Milwaukee after the 1952 season. Since 1966 they have played in Atlanta as the Atlanta Braves.
 The TD Garden, formerly called the FleetCenter and built to replace the old, since-demolished Boston Garden, is adjoined to North Station and is the home of two major league teams: the Boston Bruins of the National Hockey League and the Boston Celtics of the National Basketball Association. The arena seats 18,624 for basketball games and 17,565 for ice hockey games. The Bruins were the first American member of the National Hockey League and an Original Six franchise. The Boston Celtics were founding members of the Basketball Association of America, one of the two leagues that merged to form the NBA. The Celtics, along with the Los Angeles Lakers, have the distinction of having won more championships than any other NBA team, both with seventeen. The venue is also set to host the 2020 Laver Cup, an international men's tennis tournament consisting of two teams: Team Europe and Team World, the latter of which consisting of non-European players. This will be the fourth edition of the tournament, and the first time Boston has hosted an ATP tournament since 1999, where Marat Safin defeated Greg Rusedski.
While they have played in suburban Foxborough, Massachusetts, Foxborough since 1971, the New England Patriots of the National Football League were founded in 1960 as the Boston Patriots, changing their name after relocating. The team won the Super Bowl after the 2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, 2016 and 2018 seasons. They share Gillette Stadium with the New England Revolution of Major League Soccer. The Boston Breakers (WPS), Boston Breakers of Women's Professional Soccer, which formed in 2009, played their home games at Dilboy Stadium in Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville. The Boston Storm (UWLX), Boston Storm of the United Women's Lacrosse League was formed in 2015.
The TD Garden, formerly called the FleetCenter and built to replace the old, since-demolished Boston Garden, is adjoined to North Station and is the home of two major league teams: the Boston Bruins of the National Hockey League and the Boston Celtics of the National Basketball Association. The arena seats 18,624 for basketball games and 17,565 for ice hockey games. The Bruins were the first American member of the National Hockey League and an Original Six franchise. The Boston Celtics were founding members of the Basketball Association of America, one of the two leagues that merged to form the NBA. The Celtics, along with the Los Angeles Lakers, have the distinction of having won more championships than any other NBA team, both with seventeen. The venue is also set to host the 2020 Laver Cup, an international men's tennis tournament consisting of two teams: Team Europe and Team World, the latter of which consisting of non-European players. This will be the fourth edition of the tournament, and the first time Boston has hosted an ATP tournament since 1999, where Marat Safin defeated Greg Rusedski.
While they have played in suburban Foxborough, Massachusetts, Foxborough since 1971, the New England Patriots of the National Football League were founded in 1960 as the Boston Patriots, changing their name after relocating. The team won the Super Bowl after the 2001, 2003, 2004, 2014, 2016 and 2018 seasons. They share Gillette Stadium with the New England Revolution of Major League Soccer. The Boston Breakers (WPS), Boston Breakers of Women's Professional Soccer, which formed in 2009, played their home games at Dilboy Stadium in Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville. The Boston Storm (UWLX), Boston Storm of the United Women's Lacrosse League was formed in 2015.
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, and Northeastern University. Of the four, only Boston College participates in college football at the highest level, the NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, Football Bowl Subdivision. Harvard participates in the second-highest level, the Football Championship Subdivision. The Boston Cannons of the Major League Lacrosse, MLL play at Harvard Stadium.
Boston has Esports teams as well, such as the Overwatch League's Boston Uprising. Established in 2017, they were the first team to complete a perfect stage with 0 losses. The Boston Breach is another esports team in the Call of Duty League (CDL).
One of the best known sporting events in the city is the Boston Marathon, the race which is the world's oldest annual marathon, run on Patriots' Day in April. On April 15, 2013, Boston Marathon bombing, two explosions killed three people and injured hundreds at the marathon.
Another major annual event is the Head of the Charles Regatta, held in October.
Boston is one of eleven US cities which will host matches during the 2026 FIFA World Cup.
Parks and recreation

Boston Common
The Boston Common (also known as the Common) is a public park in downtown Boston, Massachusetts. It is the oldest city park in the United States. Boston Common consists of of land bounded by Tremont Street (139 Tremont St.), Park Street, Beacon ...
, near the Financial District and Beacon Hill, is the oldest public park in the United States. Along with the adjacent Public Garden (Boston), Boston Public Garden, it is part of the Emerald Necklace, a string of parks designed by Frederick Law Olmsted to encircle the city. The Emerald Necklace includes the Back Bay Fens, Arnold Arboretum, Jamaica Pond, Boston's largest body of freshwater, and Franklin Park (Boston), Franklin Park, the city's largest park and home of the Franklin Park Zoo. Another major park is the Charles River Esplanade, Esplanade, along the banks of the Charles River. The Hatch Shell, an outdoor concert venue, is adjacent to the Charles River Esplanade. Other parks are scattered throughout the city, with major parks and beaches near Castle Island (Massachusetts), Castle Island, in Charlestown and along the Dorchester, South Boston, and East Boston shorelines.
Boston's park system is well-reputed nationally. In its 2013 ParkScore ranking, Trust for Public Land, The Trust for Public Land reported Boston was tied with Sacramento, California, Sacramento and San Francisco for having the third-best park system among the 50 most populous US cities. ParkScore ranks city park systems by a formula that analyzes the city's median park size, park acres as percent of city area, the percent of residents within a half-mile of a park, spending of park services per resident, and the number of playgrounds per 10,000 residents.
Government and politics
 Boston has a Mayor–council government, strong mayor–council government system in which the mayor (elected every fourth year) has extensive executive power. Michelle Wu, a city councilor, became mayor in November 2021, succeeding Kim Janey, a former City Council President, who became the Acting Mayor in March 2021 following Marty Walsh's confirmation to the position of United States Secretary of Labor, Secretary of Labor in the Presidency of Joe Biden, Biden/Harris Administration. Walsh's predecessor Thomas Menino's twenty-year tenure was the longest in the city's history.
The Boston City Council is elected every two years; there are nine district seats, and four citywide "at-large" seats. The School Committee, which oversees the Boston Public Schools, is appointed by the mayor.
Boston has a Mayor–council government, strong mayor–council government system in which the mayor (elected every fourth year) has extensive executive power. Michelle Wu, a city councilor, became mayor in November 2021, succeeding Kim Janey, a former City Council President, who became the Acting Mayor in March 2021 following Marty Walsh's confirmation to the position of United States Secretary of Labor, Secretary of Labor in the Presidency of Joe Biden, Biden/Harris Administration. Walsh's predecessor Thomas Menino's twenty-year tenure was the longest in the city's history.
The Boston City Council is elected every two years; there are nine district seats, and four citywide "at-large" seats. The School Committee, which oversees the Boston Public Schools, is appointed by the mayor.
 In addition to city government, numerous commissions and state authorities—including the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation, the Boston Public Health Commission, the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority, Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA), and the Massachusetts Port Authority, Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport)—play a role in the life of Bostonians. As the capital of Massachusetts, Boston plays a major role in Massachusetts#Politics, state politics.
In addition to city government, numerous commissions and state authorities—including the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation, the Boston Public Health Commission, the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority, Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA), and the Massachusetts Port Authority, Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport)—play a role in the life of Bostonians. As the capital of Massachusetts, Boston plays a major role in Massachusetts#Politics, state politics.
 The city has several federal facilities, including the John F. Kennedy Federal Office Building, the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building (Boston), Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building, the John W. McCormack Post Office and Courthouse, the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston, the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit, and the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. Both courts are housed in the John Joseph Moakley United States Courthouse.
The city has several federal facilities, including the John F. Kennedy Federal Office Building, the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building (Boston), Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Federal Building, the John W. McCormack Post Office and Courthouse, the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston, the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit, and the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. Both courts are housed in the John Joseph Moakley United States Courthouse.
 Federally, Boston is split between two congressional districts. Three-fourths of the city is in the Massachusetts's 7th congressional district, 7th district and is represented by Ayanna Pressley while the remaining southern fourth is in the Massachusetts's 8th congressional district, 8th district and is represented by Stephen Lynch (politician), Stephen Lynch, both of whom are Democrats; a Republican has not represented a significant portion of Boston in over a century. The state's senior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Elizabeth Warren, first elected in 2012. The state's junior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Ed Markey, who was elected in 2013 to succeed John Kerry after Kerry's appointment and confirmation as the United States Secretary of State.
The city uses an algorithm created by the Walsh administration, called CityScore, to measure the effectiveness of various city services. This score is available on a public online dashboard and allows city managers in police, fire, schools, emergency management services, and 3-1-1 to take action and make adjustments in areas of concern.
Boston has an ordinance, enacted in 2014, that bars the Boston Police Department "from detaining anyone based on their immigration status unless they have a criminal warrant".
Federally, Boston is split between two congressional districts. Three-fourths of the city is in the Massachusetts's 7th congressional district, 7th district and is represented by Ayanna Pressley while the remaining southern fourth is in the Massachusetts's 8th congressional district, 8th district and is represented by Stephen Lynch (politician), Stephen Lynch, both of whom are Democrats; a Republican has not represented a significant portion of Boston in over a century. The state's senior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Elizabeth Warren, first elected in 2012. The state's junior member of the United States Senate is Democrat Ed Markey, who was elected in 2013 to succeed John Kerry after Kerry's appointment and confirmation as the United States Secretary of State.
The city uses an algorithm created by the Walsh administration, called CityScore, to measure the effectiveness of various city services. This score is available on a public online dashboard and allows city managers in police, fire, schools, emergency management services, and 3-1-1 to take action and make adjustments in areas of concern.
Boston has an ordinance, enacted in 2014, that bars the Boston Police Department "from detaining anyone based on their immigration status unless they have a criminal warrant".
Media
Newspapers
''The Boston Globe'' is the oldest and largest daily newspaper in the city and is generally acknowledged as its paper of record. The city is also served by other publications such as the ''Boston Herald'', ''Boston (magazine), Boston magazine'', ''DigBoston'', and the Boston edition of ''Metro International, Metro''. ''The Christian Science Monitor'', headquartered in Boston, was formerly a worldwide daily newspaper but ended publication of daily print editions in 2009, switching to continuous online and weekly magazine format publications. ''The Boston Globe'' also releases a teen publication to the city's public high schools, called ''Teens in Print'' or ''T.i.P.'', which is written by the city's teens and delivered quarterly within the school year. ''The Improper Bostonian'', a glossy lifestyle magazine, was published from 1991 through April 2019. The city's growing Hispanic and Latino Americans, Latino population has given rise to a number of local and regional Spanish language, Spanish-language newspapers. These include ''El Planeta'' (owned by the former publisher of ''The Phoenix (newspaper), The Boston Phoenix''), ''El Mundo'', and ''La Semana''. ''Siglo21'', with its main offices in nearby Lawrence, Massachusetts, Lawrence, is also widely distributed. Various LGBT publications serve the city's large LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender) population such as ''The Rainbow Times'', the only minority and lesbian-owned LGBT news magazine. Founded in 2006, ''The Rainbow Times'' is now based out of Boston, but serves all of New England.Radio and television
Boston is the largest broadcasting market in New England, with the radio market being the ninth largest in the United States. Several major AM broadcasting, AM stations include talk radio WRKO, sports radio, sports/talk station WEEI (AM), WEEI, and iHeartMedia WBZ (AM), WBZ. WBZ (AM) broadcasts a all-news radio, news radio format and is a 50,000 watt "clear channel" station, whose nighttime broadcasts are heard hundreds of miles from Boston. A variety of commercial FM broadcasting, FM radio formats serve the area, as do National Public Radio, NPR stations WBUR and WGBH (FM), WGBH. College and university radio stations include WERS (Emerson), WHRB (Harvard), WUMB (UMass Boston), WMBR (MIT), WZBC (Boston College), WMFO (Tufts University), WBRS (Brandeis University), WTBU (college radio), WTBU (Boston University, campus and web only), WRBB (Northeastern University) and WMLN-FM (Curry College). The Boston television Designated market area, DMA, which also includes Manchester, New Hampshire, Manchester, New Hampshire, is the eighth largest in the United States. The city is served by stations representing every major List of United States broadcast television networks, American network, including WBZ-TV 4 and its sister station WSBK-TV 38 (the former a CBS Owned-and-operated station, O&O, the latter an Independent station (North America), independent station), WCVB-TV 5 and its sister station WMUR-TV 9 (both American Broadcasting Company, ABC), WHDH (TV), WHDH 7 and its sister station WLVI 56 (the former an independent station, the latter a The CW, CW affiliate), WBTS-CD 15 (an NBC O&O), and WFXT-TV, WFXT 25 (Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox). The city is also home to PBS member station WGBH-TV 2, a major producer of PBS programs, which also operates WGBX 44. Spanish-language television networks, including UniMás (WUTF-TV 27), Telemundo (WNEU 60, a sister station to WBTS-CD), and Univisión (WUNI 66), have a presence in the region, with WNEU serving as network owned-and-operated station. Most of the area's television stations have their transmitters in nearby Needham, Massachusetts, Needham and Newton, Massachusetts, Newton along the Massachusetts Route 128, Route 128 corridor. Six Boston television stations are carried by Canadian satellite television provider Bell TV and by cable television providers in Canada.Film
Films have been made in Boston since as early as 1903, and it continues to be both a popular setting and a popular filming location. Notable movies like ''The Fighter'' and ''The Town (2010 film), The Town'' were filmed in Boston.Video games
Video games have used Boston as a backdrop and setting, such as Assassin's Creed III published in 2012 and Fallout 4 in 2015. Some characters from video games are from Boston, such as the Scout from Team Fortress 2. The gaming convention PAX (event), PAX East is held in Boston, which many gaming companies like Microsoft, Ubisoft, and Wizards of the Coast have previously attended.Infrastructure
Transportation
 Logan International Airport, in East Boston and operated by the Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport), is Boston's principal airport. Nearby general aviation airports are Beverly Municipal Airport to the north, Hanscom Field to the west, and Norwood Memorial Airport to the south. Massport also operates several major facilities within the Port of Boston, including a cruise ship terminal and facilities to handle bulk and container cargo in South Boston, and other facilities in Charlestown and East Boston.
Downtown Boston's streets grew organically, so they do not form a Grid plan, planned grid, unlike those in later-developed
Logan International Airport, in East Boston and operated by the Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport), is Boston's principal airport. Nearby general aviation airports are Beverly Municipal Airport to the north, Hanscom Field to the west, and Norwood Memorial Airport to the south. Massport also operates several major facilities within the Port of Boston, including a cruise ship terminal and facilities to handle bulk and container cargo in South Boston, and other facilities in Charlestown and East Boston.
Downtown Boston's streets grew organically, so they do not form a Grid plan, planned grid, unlike those in later-developed Back Bay
Back Bay is an officially recognized neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, built on reclaimed land in the Charles River basin. Construction began in 1859, as the demand for luxury housing exceeded the availability in the city at the time, and t ...
, East Boston, the South End, Boston, South End, and South Boston, Boston, South Boston. Boston is the eastern terminus of Interstate 90, I-90, which in Massachusetts runs along the Massachusetts Turnpike. The elevated portion of the Central Artery, which carried most of the through traffic in downtown Boston, was replaced with the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Tunnel, O'Neill Tunnel during the Big Dig, Construction management#Post-Construction, substantially completed in early 2006. The former and current Central Artery follow Interstate 93, I-93 as the primary north–south artery from the city. Other major highways include U.S. Route 1 in Massachusetts, US 1, which carries traffic to the North Shore (Massachusetts), North Shore and areas south of Boston, U.S. Route 3, US 3, which connects to the northwestern suburbs, Massachusetts Route 3, which connects to the South Shore (Massachusetts), South Shore and Cape Cod, and Massachusetts Route 2 which connects to the western suburbs. Surrounding the city is Massachusetts Route 128, a partial beltway which has been largely subsumed by other routes (mostly Interstate 95 in Massachusetts, I-95 and I-93).
With nearly a third of Bostonians using public transit for their commute to work, Boston has the List of U.S. cities with high transit ridership, fourth-highest rate of public transit usage in the country. The city of Boston has a higher than average percentage of households without a car. In 2015, 35.4 percent of Boston households lacked a car, which decreased slightly to 33.8 percent in 2016. The national average was 8.7 percent in 2016. Boston averaged 0.94 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8. Boston's public transportation agency, the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) operates the oldest underground rapid transit system in the Americas, and is the List of United States rapid transit systems by ridership, fourth-busiest rapid transit system in the country, with of track on four lines. The MBTA also operates busy bus and commuter rail networks, and water shuttles.

 Amtrak intercity rail to Boston is provided through four stations: South Station, North Station, Back Bay station, Back Bay, and Route 128 station, Route 128. South Station is a major Intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transportation hub and is the terminus of Amtrak's ''Northeast Regional'', ''Acela Express'', and ''Lake Shore Limited'' routes, in addition to multiple MBTA services. Back Bay is also served by MBTA and those three Amtrak routes, while Route 128, in the southwestern suburbs of Boston, is only served by the ''Acela Express'' and ''Northeast Regional''. Meanwhile, Amtrak's ''Downeaster (train), Downeaster'' to Brunswick, Maine, Brunswick, Maine terminates in North Station, and is the only Amtrak route to do so.
Nicknamed "The Walking City", Boston hosts more pedestrian commuters than do other comparably populated cities. Owing to factors such as necessity, the compactness of the city and large student population, 13 percent of the population commutes by foot, making it the List of U.S. cities with most pedestrian commuters, highest percentage of pedestrian commuters in the country out of the major American cities. In 2011, Walk Score ranked Boston the third-most walkable city in the United States. , Walk Score still ranks Boston as the third most walkable US city, with a Walk Score of 80, a Transit Score of 75, and a Bike Score of 70.
Between 1999 and 2006, ''Bicycling (magazine), Bicycling'' magazine named Boston three times as one of the worst cities in the US for cycling; regardless, it has one of the highest rates of bicycle commuting. In 2008, as a consequence of improvements made to bicycling conditions within the city, the same magazine put Boston on its "Five for the Future" list as a "Future Best City" for biking, and Boston's bicycle commuting percentage increased from 1% in 2000 to 2.1% in 2009. The bikeshare program Bluebikes, originally called Hubway, launched in late July 2011, logging more than 140,000 rides before the close of its first season. The neighboring municipalities of Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville, and Brookline, Massachusetts, Brookline joined the Hubway program in the summer of 2012. In 2016, there were 1,461 bikes and 158 docking stations across the city, which in 2022 has increased to 400 stations with a total of 4,000 bikes. PBSC Urban Solutions provides bicycles and technology for this Bicycle-sharing system, bike-sharing system.
In 2013, the Boston-Cambridge-Newton metropolitan statistical area (Boston MSA) had the seventh-lowest percentage of workers who commuted by private automobile (75.6 percent), with 6.2 percent of area workers traveling via rail transit. During the period starting in 2006 and ending in 2013, the Boston MSA had the greatest percentage decline of workers commuting by automobile (3.3 percent) among MSAs with more than a half-million residents.
Amtrak intercity rail to Boston is provided through four stations: South Station, North Station, Back Bay station, Back Bay, and Route 128 station, Route 128. South Station is a major Intermodal passenger transport, intermodal transportation hub and is the terminus of Amtrak's ''Northeast Regional'', ''Acela Express'', and ''Lake Shore Limited'' routes, in addition to multiple MBTA services. Back Bay is also served by MBTA and those three Amtrak routes, while Route 128, in the southwestern suburbs of Boston, is only served by the ''Acela Express'' and ''Northeast Regional''. Meanwhile, Amtrak's ''Downeaster (train), Downeaster'' to Brunswick, Maine, Brunswick, Maine terminates in North Station, and is the only Amtrak route to do so.
Nicknamed "The Walking City", Boston hosts more pedestrian commuters than do other comparably populated cities. Owing to factors such as necessity, the compactness of the city and large student population, 13 percent of the population commutes by foot, making it the List of U.S. cities with most pedestrian commuters, highest percentage of pedestrian commuters in the country out of the major American cities. In 2011, Walk Score ranked Boston the third-most walkable city in the United States. , Walk Score still ranks Boston as the third most walkable US city, with a Walk Score of 80, a Transit Score of 75, and a Bike Score of 70.
Between 1999 and 2006, ''Bicycling (magazine), Bicycling'' magazine named Boston three times as one of the worst cities in the US for cycling; regardless, it has one of the highest rates of bicycle commuting. In 2008, as a consequence of improvements made to bicycling conditions within the city, the same magazine put Boston on its "Five for the Future" list as a "Future Best City" for biking, and Boston's bicycle commuting percentage increased from 1% in 2000 to 2.1% in 2009. The bikeshare program Bluebikes, originally called Hubway, launched in late July 2011, logging more than 140,000 rides before the close of its first season. The neighboring municipalities of Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, Somerville, Massachusetts, Somerville, and Brookline, Massachusetts, Brookline joined the Hubway program in the summer of 2012. In 2016, there were 1,461 bikes and 158 docking stations across the city, which in 2022 has increased to 400 stations with a total of 4,000 bikes. PBSC Urban Solutions provides bicycles and technology for this Bicycle-sharing system, bike-sharing system.
In 2013, the Boston-Cambridge-Newton metropolitan statistical area (Boston MSA) had the seventh-lowest percentage of workers who commuted by private automobile (75.6 percent), with 6.2 percent of area workers traveling via rail transit. During the period starting in 2006 and ending in 2013, the Boston MSA had the greatest percentage decline of workers commuting by automobile (3.3 percent) among MSAs with more than a half-million residents.
International relations
The City of Boston has twelve official Twin towns and sister cities, sister cities: * Kyoto, Japan (1959) * Strasbourg, France (1960) * Barcelona, Spain (1980) * Hangzhou, China (1982) * Padua, Italy (1983) * City of Melbourne, Australia (1985) * Beira, Mozambique, Beira, Mozambique (1990) * Taipei, Taiwan (1996) * Sekondi-Takoradi, Ghana (2001) * Belfast, Northern Ireland (2014) * Praia, Cape Verde (2015) * Boston, Lincolnshire, UK (2015) Boston has formal partnership relationships through a Memorandum Of Understanding (MOU) with five additional cities or regions: * Guangzhou, China (2014) * Lyon, France (2016) * Copenhagen, Denmark (2017) * Mexico City, Mexico (2017) * North West of Ireland, Ireland (2017)See also
*Outline of Boston *Boston City League (high-school athletic conference) *Boston Citgo Sign *Boston nicknames *Boston–Halifax relations *List of diplomatic missions in Boston *List of people from Boston *National Register of Historic Places listings in BostonNotes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Visit Boston
official tourism website * * *
Historical Maps of Boston
from the Norman B. Leventhal Map Center at the
Boston Public Library
The Boston Public Library is a municipal public library system in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, founded in 1848. The Boston Public Library is also the Library for the Commonwealth (formerly ''library of last recourse'') of the Commonweal ...
*
{{Authority control
Boston,
1630 establishments in Massachusetts
Cities in Massachusetts
Cities in Suffolk County, Massachusetts
County seats in Massachusetts
Greater Boston, *
Irish-American culture in Boston
Populated coastal places in Massachusetts
Populated places established in 1630
Port cities and towns in Massachusetts
Geographical articles missing image alternative text