Borabenzene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Borabenzene is a hypothetical
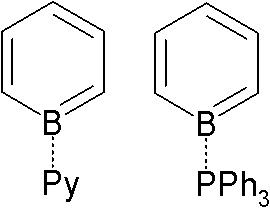 The borabenzene-pyridine adduct behaves like a
The borabenzene-pyridine adduct behaves like a 
organoboron compound
Organoborane or organoboron compounds are chemical compounds of boron and carbon that are organic derivatives of BH3, for example trialkyl boranes. Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry is the chemistry of these compounds.
Organoboron ...
with the formula C5H5B. Unlike the related but highly stable benzene molecule, borabenzene would be electron-deficient. Related derivatives are the boratabenzene
Boratabenzene is the heteroaromatic anion with the formula 5H5BHsup>−. Derivatives of boratabenzene are ligands akin to cyclopentadienyl anion. sandwich or half-sandwich type complexes of many transition metals have been reported.{{cite journa ...
anions, including the parent 5H5BHsup>−.
Adducts
Adducts of borabenzene with Lewis bases are isolatable. Since borabenzene is unavailable, these adducts require indirect methods. 4-Silyl-1-methoxyboracyclohexadiene is used as a precursor to the borabenzene: : + → + MeOSiMe3 The pyridine adduct is structurally related tobiphenyl
Biphenyl (also known as diphenyl, phenylbenzene, 1,1′-biphenyl, lemonene or BP) is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. Particularly in older literature, compounds containing the functional group consisting of biphenyl less one ...
. It is a yellow whereas biphenyl is colorless, indicating distinct electronic structures. The pyridine ligand is tightly bound: no exchange is observed with free pyridine, even at elevated temperatures.
: The borabenzene-pyridine adduct behaves like a
The borabenzene-pyridine adduct behaves like a diene
In organic chemistry a diene ( ) (diolefin ( ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nomenclature. ...
, not an analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog ...
of biphenyl
Biphenyl (also known as diphenyl, phenylbenzene, 1,1′-biphenyl, lemonene or BP) is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. Particularly in older literature, compounds containing the functional group consisting of biphenyl less one ...
, and will undergo Diels-Alder reactions.{{cite journal , doi=10.1021/ol061201w , title=1-Borabarrelene Derivatives via Diels−Alder Additions to Borabenzenes , year=2006 , last1=Wood , first1=Thomas K. , last2=Piers , first2=Warren E. , last3=Keay , first3=Brian A. , last4=Parvez , first4=Masood , journal=Organic Letters , volume=8 , issue=13 , pages=2875–2878 , pmid=16774279
:
See also
* 6-membered aromatic rings with one carbon replaced by another group:silabenzene
A silabenzene is a heteroaromatic compound containing one or more silicon atoms instead of carbon atoms in benzene. A single substitution gives silabenzene proper; additional substitutions give a disilabenzene (3 theoretical isomers), trisilabenz ...
, germabenzene
Germabenzene (C5H6Ge) is the parent representative of a group of chemical compounds containing in their molecular structure a benzene ring with a carbon atom replaced by a germanium atom. Germabenzene itself has been studied theoretically, and syn ...
, stannabenzene
Stannabenzene (C5H6Sn) is the parent representative of a group of organotin compounds that are related to benzene with a carbon atom replaced by a tin atom. Stannabenzene itself has been studied by computational chemistry, but has not been isolat ...
, pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a d ...
, phosphorine
Phosphorine (IUPAC name: phosphinine) is a heavier element analog of pyridine, containing a phosphorus atom instead of an aza- moiety. It is also called phosphabenzene and belongs to the phosphaalkene class. It is a colorless liquid that is m ...
, arsabenzene
Arsabenzene (IUPAC name: arsinine) is an organoarsenic heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C5H5As. It belongs to a group of compounds called heteroarenes that have the general formula C5H5E (E= N, P, As, Sb, Bi).
This air sensitive li ...
, stibabenzene
Stibinin, also known as stibabenzene, is an organic chemical compound. Stibinin has the chemical formula . The molecule, stibinin, is a derivative of benzene, with one of the carbon atoms in the 6-membered ring replaced by an antimony (Sb) atom. ...
, bismabenzene, pyrylium
Pyrylium is a cation (positive ion) with formula , consisting of a six-membered ring of five carbon atoms, each with one hydrogen atom, and one positively charged oxygen atom. The bonds in the ring are conjugated as in benzene, giving it an aroma ...
, thiopyrylium
Thiopyrylium is a cation with the chemical formula C5H5S+. It is analogous to the pyrylium cation with the oxygen atom replaced by a sulfur atom.
Thiopyrylium salts are less reactive than the analogous pyrylium salts due to the higher polarizab ...
, selenopyrylium
Selenopyrylium is an aromatic heterocyclic compound consisting of a six-membered ring with five carbon atoms and a positively charged selenium atom.
Naming and numbering
Formerly it was named selenapyrylium. However, this is misleading as "selena ...
, telluropyrylium
Telluropyrylium is an aromatic heterocyclic compound consisting of a six member ring with five carbon atoms, and a positively charged tellurium atom. Derivatives of telluropyrylium are important in research of infrared dyes.
Naming and numbering ...
* Borazine
Borazine, also known as borazole, is a non-polar inorganic compound with the chemical formula B3H6N3. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. For thi ...
References