Boeing P2B Superfortress on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the
 In response, Boeing began work on pressurized long-range bombers in 1938. Boeing's design study for the Model 334 was a pressurized derivative of the
In response, Boeing began work on pressurized long-range bombers in 1938. Boeing's design study for the Model 334 was a pressurized derivative of the
''National Museum of the United States Air Force''. Retrieved: 15 November 2010. and Douglas (the Douglas XB-31).Francillon 1979, p. 713. Douglas and Lockheed soon abandoned work on their projects, but Boeing received an order for two flying prototypes, which were given the designation XB-29, and an airframe for static testing on 24 August 1940, with the order being revised to add a third flying aircraft on 14 December. Consolidated continued to work on its Model 33, as it was seen by the Air Corps as a backup if there were problems with Boeing's design.Willis 2007, p. 138. Boeing received an initial production order for 14 service test aircraft and 250 production bombers in May 1941,Knaack 1988, p. 480. this being increased to 500 aircraft in January 1942. The B-29 featured a fuselage design with circular cross-section for strength. The need for pressurization in the cockpit area also led to the B-29 being one of very few American combat aircraft of World War II to have a stepless cockpit design, without a separate windscreen for the pilots. Manufacturing the B-29 was a complex task that involved four main-assembly factories. There were two Boeing operated plants at
"A Year in the B-29 Superfortress."
''Fred Carl Gardner's website'', updated 1 May 2005. Retrieved: 11 April 2009.
 In wartime, the B-29 was capable of flight at altitudes up to ,
In wartime, the B-29 was capable of flight at altitudes up to ,
''Boeing''. Retrieved: 22 March 2012. at speeds of up to ( true airspeed). This was its best defense because Japanese fighters could barely reach that altitude, and few could catch the B-29 even if they did attain that altitude.
 The General Electric Central Fire Control system on the B-29 directed four remotely controlled turrets armed with two .50 Browning M2 machine guns each. All weapons were aimed optically, with targeting computed by analog electrical instrumentation. There were five interconnected sighting stations located in the nose and tail positions and three Plexiglas blisters in the central fuselage. Five General Electric analog computers (one dedicated to each sight) increased the weapons' accuracy by compensating for factors such as airspeed, lead, gravity, temperature and humidity. The computers also allowed a single gunner to operate two or more turrets (including tail guns) simultaneously. The gunner in the upper position acted as fire control officer, managing the distribution of turrets among the other gunners during combat.Brown 1977, pp. 80–83.Williams and Gustin 2003, pp. 164–166. The tail position initially had two .50 Browning machine guns and a single M2 20 mm cannon. Later aircraft had the 20 mm cannon removed,Willis 2007, p. 140. sometimes replaced by a third machine gun.Pace 2003, p. 53.
In early 1945, Major General Curtis Lemay, commander of XXI Bomber Command—the Marianas-based B-29-equipped bombing force—ordered most of the defensive armament and remote-controlled sighting equipment removed from the B-29s under his command. The affected aircraft had the same reduced defensive firepower as the nuclear weapons-delivery intended ''Silverplate'' B-29 airframes and could carry greater fuel and bomb loads as a result of the change. The lighter defensive armament was made possible by a change in mission from high-altitude, daylight bombing with high explosive bombs to low-altitude night raids using incendiary bombs. As a consequence of that requirement, Bell Atlanta (BA) produced a series of 311 B-29Bs that had turrets and sighting equipment omitted, except for the tail position, which was fitted with AN/APG-15 fire-control radar.Willis 2007, pp. 140, 144. That version could also have an improved APQ-7 "Eagle" bombing-through-overcast radar fitted in an airfoil-shaped radome under the fuselage. Most of those aircraft were assigned to the 315th Bomb Wing, Northwest Field, Guam.
The General Electric Central Fire Control system on the B-29 directed four remotely controlled turrets armed with two .50 Browning M2 machine guns each. All weapons were aimed optically, with targeting computed by analog electrical instrumentation. There were five interconnected sighting stations located in the nose and tail positions and three Plexiglas blisters in the central fuselage. Five General Electric analog computers (one dedicated to each sight) increased the weapons' accuracy by compensating for factors such as airspeed, lead, gravity, temperature and humidity. The computers also allowed a single gunner to operate two or more turrets (including tail guns) simultaneously. The gunner in the upper position acted as fire control officer, managing the distribution of turrets among the other gunners during combat.Brown 1977, pp. 80–83.Williams and Gustin 2003, pp. 164–166. The tail position initially had two .50 Browning machine guns and a single M2 20 mm cannon. Later aircraft had the 20 mm cannon removed,Willis 2007, p. 140. sometimes replaced by a third machine gun.Pace 2003, p. 53.
In early 1945, Major General Curtis Lemay, commander of XXI Bomber Command—the Marianas-based B-29-equipped bombing force—ordered most of the defensive armament and remote-controlled sighting equipment removed from the B-29s under his command. The affected aircraft had the same reduced defensive firepower as the nuclear weapons-delivery intended ''Silverplate'' B-29 airframes and could carry greater fuel and bomb loads as a result of the change. The lighter defensive armament was made possible by a change in mission from high-altitude, daylight bombing with high explosive bombs to low-altitude night raids using incendiary bombs. As a consequence of that requirement, Bell Atlanta (BA) produced a series of 311 B-29Bs that had turrets and sighting equipment omitted, except for the tail position, which was fitted with AN/APG-15 fire-control radar.Willis 2007, pp. 140, 144. That version could also have an improved APQ-7 "Eagle" bombing-through-overcast radar fitted in an airfoil-shaped radome under the fuselage. Most of those aircraft were assigned to the 315th Bomb Wing, Northwest Field, Guam.
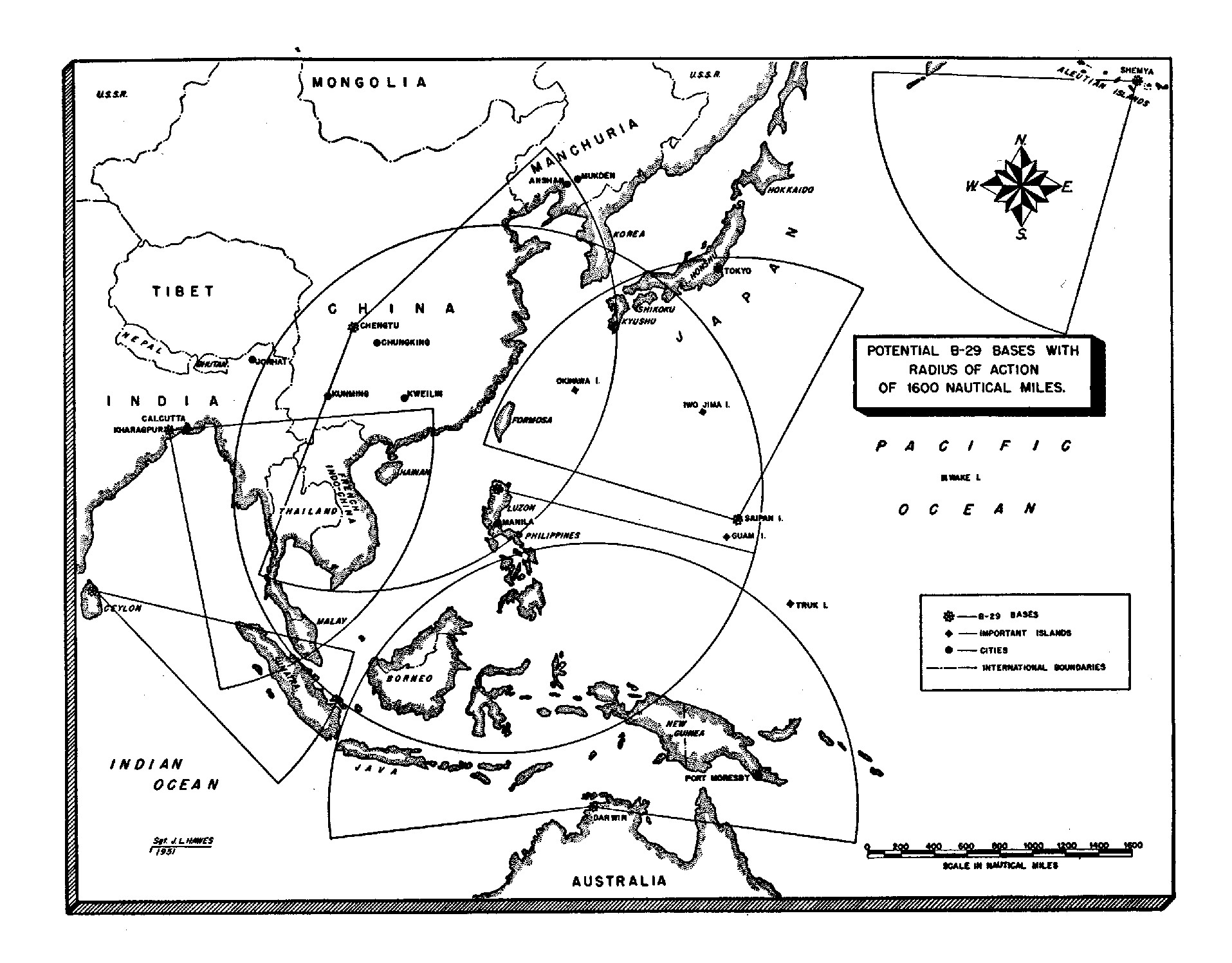


 In September 1941, the United States Army Air Forces' plans for war against Germany and Japan proposed basing the B-29 in Egypt for operations against Germany, as British airbases were likely to be overcrowded.Craven and Cate Vol. 1 1983, pp. 145–149.Craven and Cate Vol. 2 1983, p. 6. Air Force planning throughout 1942 and early 1943 continued to have the B-29 deployed initially against Germany, only transferring to the Pacific after the end of the war in Europe. By the end of 1943, plans had changed, partly due to production delays, and the B-29 was dedicated to the Pacific Theater.Craven and Cate Vol. 5 1983, pp. 11–12. A new plan implemented at the direction of President Franklin D. Roosevelt as a promise to China, called Operation Matterhorn, deployed the B-29 units to attack Japan from four forward bases in southern China, with five main bases in India, and to attack other targets in the region from China and India as needed.Willis 2007, pp. 144–145. The
In September 1941, the United States Army Air Forces' plans for war against Germany and Japan proposed basing the B-29 in Egypt for operations against Germany, as British airbases were likely to be overcrowded.Craven and Cate Vol. 1 1983, pp. 145–149.Craven and Cate Vol. 2 1983, p. 6. Air Force planning throughout 1942 and early 1943 continued to have the B-29 deployed initially against Germany, only transferring to the Pacific after the end of the war in Europe. By the end of 1943, plans had changed, partly due to production delays, and the B-29 was dedicated to the Pacific Theater.Craven and Cate Vol. 5 1983, pp. 11–12. A new plan implemented at the direction of President Franklin D. Roosevelt as a promise to China, called Operation Matterhorn, deployed the B-29 units to attack Japan from four forward bases in southern China, with five main bases in India, and to attack other targets in the region from China and India as needed.Willis 2007, pp. 144–145. The
"The air war over Thailand, 1941–1945; Part Two, The Allies attack Thailand, 1942–1945."
''Pattaya Mail,'' Volume XI, Issue 21, 30 May – 5 June 2003. Retrieved: 18 February 2012. On 15 June 1944, 68 B-29s took off from bases around Chengdu, 47 B-29s bombed the Imperial Iron and Steel Works at Yawata, Fukuoka Prefecture,
"Chapter: The Japan to Washington Flight."''Remembrance of War: The Experiences of a B-29 Pilot in World War II.''
Shelbyville, Tennessee: J.I. Potts & Associates, 1995. Retrieved: 8 June 2009. Two months later, Colonel Clarence S. Irvine commanded another modified B-29, ''Pacusan Dreamboat'', in a world-record-breaking long-distance flight from Guam to Washington, D.C., traveling in 35 hours,"Monday, January 01, 1940 – Saturday, December 31, 1949."
''History Milestones (US Air Force).'' Retrieved: 21 October 2010. with a gross takeoff weight of .Mayo, Weyland
''b-29s-over-korea.com.'' Retrieved: 21 October 2010. Almost a year later, in October 1946, the same B-29 flew 9,422 miles nonstop from Oahu, Hawaii, to Cairo, Egypt, in less than 40 hours, demonstrating the possibility of routing airlines over the polar ice cap.
 Although considered for other theaters, and briefly evaluated in the UK, the B-29 was exclusively used in World War II in the Pacific Theatre. The use of YB-29-BW ''41-36393'', the so-named ''Hobo Queen'', one of the service test aircraft flown around several British airfields in early 1944, was part of a "disinformation" program from its mention in an American-published ''Sternenbanner'' German-language propaganda leaflet from Leap Year Day in 1944, meant to be circulated within the Reich, with the intent to deceive the Germans into believing that the B-29 would be deployed to Europe.
American post-war military assistance programs loaned the RAF enough Superfortresses to equip several
Although considered for other theaters, and briefly evaluated in the UK, the B-29 was exclusively used in World War II in the Pacific Theatre. The use of YB-29-BW ''41-36393'', the so-named ''Hobo Queen'', one of the service test aircraft flown around several British airfields in early 1944, was part of a "disinformation" program from its mention in an American-published ''Sternenbanner'' German-language propaganda leaflet from Leap Year Day in 1944, meant to be circulated within the Reich, with the intent to deceive the Germans into believing that the B-29 would be deployed to Europe.
American post-war military assistance programs loaned the RAF enough Superfortresses to equip several
''RAAF Museum.'' Retrieved: 28 January 2012.
 At the end of WWII, Soviet development of modern four-engined heavy bombers lagged behind the west. The Petlyakov Pe-8—the sole heavy bomber operated by the
At the end of WWII, Soviet development of modern four-engined heavy bombers lagged behind the west. The Petlyakov Pe-8—the sole heavy bomber operated by the
''Monino Aviation''. Retrieved: 1 November 2009. On 20 August 1944, ''Cait Paomat'' (42-93829), flying from Chengdu, was damaged by anti-aircraft gunfire during a raid on the Yawata Iron Works. Due to the damage it sustained, the crew elected to divert to the Soviet Union. The aircraft crashed in the foothills of
"Intrusions, Overflights, Shootdowns and Defections During the Cold War and Thereafter".
David Lednicer, 16 April 2011. Retrieved: 31 July 2011. Because aluminum in the USSR was supplied in different gauges from that available in the US (metric vs imperial), the entire aircraft had to be extensively re-engineered. In addition, Tupolev substituted his own favored airfoil sections for those used by Boeing, with the Soviets themselves already having their own Wright R-1820-derived 18 cylinder radial engine, the Shvetsov ASh-73 of comparable power and displacement to the B-29's Duplex Cyclone radials available to power their design. In 1947, the Soviets debuted both the Tupolev Tu-4 ( NATO ASCC code named Bull), and the Tupolev Tu-70 transport variant. The Soviets used tail-gunner positions similar to the B-29 in many later bombers and transports.
 The B-29 was used in 1950–53 in the Korean War. At first, the bomber was used in normal strategic day-bombing missions, though North Korea's few strategic targets and industries were quickly destroyed. More importantly, in 1950 numbers of Soviet MiG-15 jet fighters appeared over Korea, and after the loss of 28 aircraft, future B-29 raids were restricted to night missions, largely in a supply-interdiction role.
The B-29 dropped the 1,000-lb VB-3 "Razon" (a range-controllable version of the earlier
The B-29 was used in 1950–53 in the Korean War. At first, the bomber was used in normal strategic day-bombing missions, though North Korea's few strategic targets and industries were quickly destroyed. More importantly, in 1950 numbers of Soviet MiG-15 jet fighters appeared over Korea, and after the loss of 28 aircraft, future B-29 raids were restricted to night missions, largely in a supply-interdiction role.
The B-29 dropped the 1,000-lb VB-3 "Razon" (a range-controllable version of the earlier
 The variants of the B-29 were outwardly similar in appearance but were built around different wing center sections that affected the wingspan dimensions. The wing of the Renton-built B-29A-BN used a different subassembly process and was a foot longer in span. The Georgia-built B-29B-BA weighed less through armament reduction. A planned C series with more reliable R-3350s was not built.
Moreover, engine packages changed, including the type of propellers and range of the variable pitch. A notable example was the eventual 65 airframes (up to 1947's end) for the Silverplate and successor-name "Saddletree" specifications built for the Manhattan Project with Curtiss Electric reversible pitch propellers.
The other differences came through added equipment for varied mission roles. These roles included cargo carriers (CB); rescue aircraft (SB); weather ships (WB); and trainers (TB); and aerial tankers (KB).
Some were used for odd purposes such as flying relay television transmitters under the name of Stratovision.
The variants of the B-29 were outwardly similar in appearance but were built around different wing center sections that affected the wingspan dimensions. The wing of the Renton-built B-29A-BN used a different subassembly process and was a foot longer in span. The Georgia-built B-29B-BA weighed less through armament reduction. A planned C series with more reliable R-3350s was not built.
Moreover, engine packages changed, including the type of propellers and range of the variable pitch. A notable example was the eventual 65 airframes (up to 1947's end) for the Silverplate and successor-name "Saddletree" specifications built for the Manhattan Project with Curtiss Electric reversible pitch propellers.
The other differences came through added equipment for varied mission roles. These roles included cargo carriers (CB); rescue aircraft (SB); weather ships (WB); and trainers (TB); and aerial tankers (KB).
Some were used for odd purposes such as flying relay television transmitters under the name of Stratovision.
 The B-29D led progressively to the XB-44, and the family of B-50 Superfortress (which was powered by four Pratt & Whitney R-4360-35 Wasp Major engines).
Another role was as a mothership. This included being rigged for carrying the experimental parasite fighter aircraft, such as the McDonnell XF-85 Goblin and Republic F-84 Thunderjets as in flight lock on and offs. It was also used to develop the Airborne Early Warning program; it was the ancestor of various modern radar picket aircraft. A B-29 with the original Wright Duplex Cyclone powerplants was used to air-launch the
The B-29D led progressively to the XB-44, and the family of B-50 Superfortress (which was powered by four Pratt & Whitney R-4360-35 Wasp Major engines).
Another role was as a mothership. This included being rigged for carrying the experimental parasite fighter aircraft, such as the McDonnell XF-85 Goblin and Republic F-84 Thunderjets as in flight lock on and offs. It was also used to develop the Airborne Early Warning program; it was the ancestor of various modern radar picket aircraft. A B-29 with the original Wright Duplex Cyclone powerplants was used to air-launch the
"Whoosh failures were 'instructive'."
''
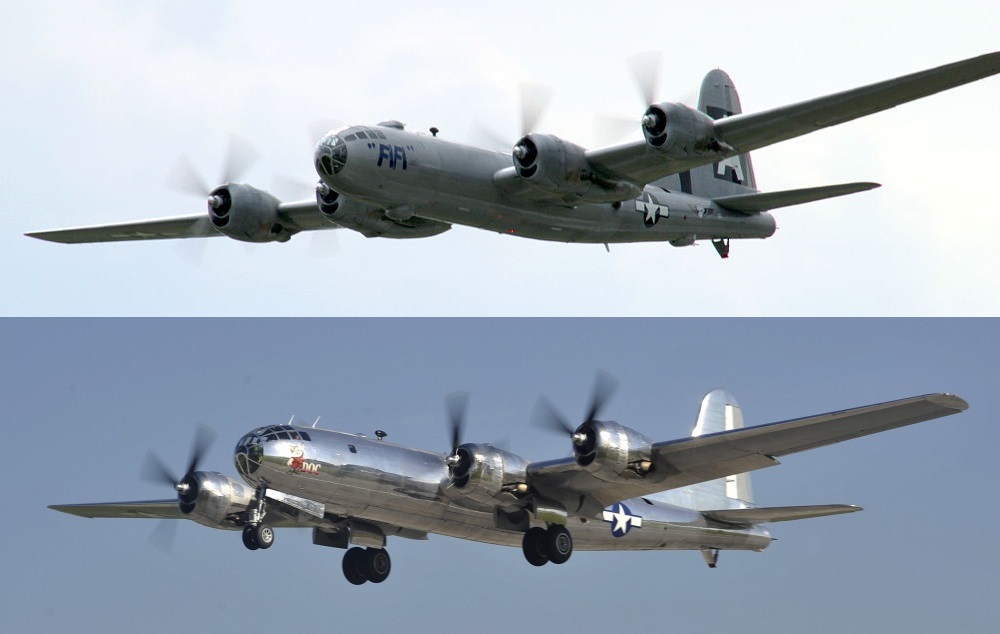 Twenty-two B-29s are preserved at various museums worldwide, including two flying examples; ''FIFI'', which belongs to the Commemorative Air Force, and ''Doc'', which belongs to Doc's Friends. Doc made its first flight in 60 years from Wichita, Kansas, on 17 July 2016. There are also four complete airframes either in storage or under restoration, eight partial airframes in storage or under restoration, and four known wreck sites.
Three of the Silverplate B-29s modified to drop nuclear bombs survive. The ''
Twenty-two B-29s are preserved at various museums worldwide, including two flying examples; ''FIFI'', which belongs to the Commemorative Air Force, and ''Doc'', which belongs to Doc's Friends. Doc made its first flight in 60 years from Wichita, Kansas, on 17 July 2016. There are also four complete airframes either in storage or under restoration, eight partial airframes in storage or under restoration, and four known wreck sites.
Three of the Silverplate B-29s modified to drop nuclear bombs survive. The '' Only two of the 22 museum aircraft are outside the United States: ''It's Hawg Wild'' at the Imperial War Museum Duxford and another at the
Only two of the 22 museum aircraft are outside the United States: ''It's Hawg Wild'' at the Imperial War Museum Duxford and another at the
 Accidents and incidents involving B-29s include:
* The Friday evening of 10 November 1944 crash of a B-29 near Clovis, New Mexico. All 15 members of the crew were killed.
* 12 June 1946 a B-29 crashed into
Accidents and incidents involving B-29s include:
* The Friday evening of 10 November 1944 crash of a B-29 near Clovis, New Mexico. All 15 members of the crew were killed.
* 12 June 1946 a B-29 crashed into



"The Cannons on the B-29 Bomber Were a Mid-Century Engineering Masterpiece"
'' Popular Mechanics'', 30 November 2015. * Craven, Wesley Frank and James Lea Cate, eds
''The Army Air Forces In World War II: Volume One: Plans and Early Operations: January 1939 to August 1942''
. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1983. * Craven, Wesley Frank and James Lea Cate, eds
''The Army Air Forces In World War II: Volume Two: Europe: Torch to Pointblank August 1942 to December 1943''
. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1983. * Craven, Wesley Frank and James Lea Cate, eds
''The Army Air Forces In World War II: Volume Five: The Pacific: Matterhorn to Nagasaki June 1944 to August 1945''
Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1983. * Davis, Larry. ''B-29 Superfortress in Action (Aircraft in Action 165)''. Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, 1997. . * Dear, I.C.B. and M.R.D. Foo, eds. ''The Oxford Companion of World War II''. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 1995. . * Dorr, Robert F. ''B-29 Superfortress Units in World War Two''. Combat Aircraft 33. Botley, Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2002. . * Dorr, Robert F. ''B-29 Superfortress Units of the Korean War''. Botley, Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2003. . * Fopp, Michael A. ''The Washington File''. Tonbridge, Kent, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd., 1983. . * Francillon, René J. ''McDonnell Douglas Aircraft since 1920''. London: Putnam, 1979. . * Futrell R.F. et al. ''Aces and Aerial Victories: The United States Air Force in Southeast Asia, 1965–1973''. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1976. . * Grant, R.G. and John R. Dailey. ''Flight: 100 Years of Aviation''. Harlow, Essex, UK: DK Adult, 2007. . * Herbert, Kevin B. ''Maximum Effort: The B-29s Against Japan''. Manhattan, Kansas: Sunflower University Press, 1983. . * Herman, Arthur. ''Freedom's Forge: How American Business Produced Victory in World War II''. New York: Random House, 2012. . * Hess, William N. ''Great American Bombers of WW II''. St. Paul, Minnesota: Motorbooks International, 1999. . * Higham, Robin and Carol Williams, eds. ''Flying Combat Aircraft of USAAF-USAF''. Volume 1. Washington, D.C.: Air Force Historical Foundation, 1975. . * Howlett, Chris. "Washington Times"
The history of the Washington
* ''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft'' (Part Work 1982–1985). London: Orbis Publishing, 1985. * Johnsen, Frederick A. ''The B-29 Book''. Tacoma, Washington: Bomber Books, 1978. , . * Johnson, Robert E. "Why the Boeing B-29 Bomber, and Why the Wright R-3350 Engine?" ''American Aviation Historical Society Journal,'' 33(3), 1988, pp. 174–189. ISSN 0002-7553. * Knaack, Marcelle Size. ''Post-World War II Bombers, 1945–1973''. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1988. . * LeMay, Curtis and Bill Yenne. ''Super Fortress''. London:
B-29 Combat Crew Manual
"Meet the B-29"
''
Pelican's Perch #56:Superfortress!
Article wrote by John Deakin, one of the pilots who regularly fly the world's first restored-to-flight B-29
Listing of surviving B-29s
* {{Authority control Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki B-29 Superfortress Four-engined tractor aircraft Boeing B-29 World War II bombers of the United States Mid-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1942 Four-engined piston aircraft
 The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater ...
, the Superfortress was designed for high-altitude strategic bombing, but also excelled in low-altitude night incendiary bombing, and in dropping naval mines to blockade Japan. B-29s dropped the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the only aircraft ever to drop nuclear weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
in combat
Combat ( French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or ...
.
One of the largest aircraft of World War II, the B-29 was designed with state-of-the-art
The state of the art (sometimes cutting edge or leading edge) refers to the highest level of general development, as of a device, technique, or scientific field achieved at a particular time. However, in some contexts it can also refer to a level ...
technology, which included a pressurized cabin, dual-wheeled tricycle landing gear, and an analog computer-controlled fire-control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a ...
that allowed one gunner and a fire-control officer to direct four remote machine gun turrets. The $3 billion cost of design and production (equivalent to $ billion today), far exceeding the $1.9 billion cost of the Manhattan Project, made the B-29 program the most expensive of the war. The B-29 remained in service in various roles throughout the 1950s, being retired in the early 1960s after 3,970 had been built. A few were also used as flying television transmitters by the Stratovision company. The Royal Air Force flew the B-29 as the ''Washington'' until 1954.
The B-29 was the progenitor of a series of Boeing-built bombers, transports, tankers, reconnaissance aircraft, and trainers. For example, the re-engined B-50 Superfortress '' Lucky Lady II'' became the first aircraft to fly around the world non-stop, during a 94-hour flight in 1949. The Boeing C-97 Stratofreighter airlifter, which was first flown in 1944, was followed in 1947 by its commercial airliner variant, the Boeing Model 377 Stratocruiser. This bomber-to-airliner derivation was similar to the B-17/ Model 307 evolution. In 1948, Boeing introduced the KB-29 tanker, followed in 1950 by the Model 377-derivative KC-97. A line of outsized-cargo variants of the Stratocruiser is the Guppy Mini GuppySuper Guppy
Super may refer to:
Computing
* SUPER (computer program), or Simplified Universal Player Encoder & Renderer, a video converter / player
* Super (computer science), a keyword in object-oriented programming languages
* Super key (keyboard butt ...
, which remain in service with NASA and other operators. The Soviet Union produced 847 Tupolev Tu-4s, an unlicensed reverse-engineered copy of the B-29. Twenty B-29s remain as static displays, but only two, ''FIFI'' and ''Doc'', still fly.
Design and development
Before World War II, the United States Army Air Corps concluded that the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, which would be the Americans' primary strategic bomber during the war, would be inadequate for thePacific Theater
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
, which required a bomber that could carry a larger payload more than 3,000 miles.
 In response, Boeing began work on pressurized long-range bombers in 1938. Boeing's design study for the Model 334 was a pressurized derivative of the
In response, Boeing began work on pressurized long-range bombers in 1938. Boeing's design study for the Model 334 was a pressurized derivative of the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater ...
with nosewheel undercarriage. Although the Air Corps lacked funds to pursue the design, Boeing continued development with its own funds as a private venture.Bowers 1989, p. 318. In April 1939, Charles Lindbergh convinced General Henry H. Arnold to produce a new bomber in large numbers to counter the Germans' bomber production. In December 1939, the Air Corps issued a formal specification for a so-called "superbomber" that could deliver of bombs to a target away, and at a speed of . Boeing's previous private venture studies formed the starting point for its response to the Air Corps formal specification.Willis 2007, pp. 136–137.
Boeing submitted its Model 345 on 11 May 1940,Bowers 1989, p. 319. in competition with designs from Consolidated Aircraft (the Model 33, which later became the B-32),Wegg 1990, p. 91. Lockheed (the Lockheed XB-30),"Factsheet: Lockheed XB-30."''National Museum of the United States Air Force''. Retrieved: 15 November 2010. and Douglas (the Douglas XB-31).Francillon 1979, p. 713. Douglas and Lockheed soon abandoned work on their projects, but Boeing received an order for two flying prototypes, which were given the designation XB-29, and an airframe for static testing on 24 August 1940, with the order being revised to add a third flying aircraft on 14 December. Consolidated continued to work on its Model 33, as it was seen by the Air Corps as a backup if there were problems with Boeing's design.Willis 2007, p. 138. Boeing received an initial production order for 14 service test aircraft and 250 production bombers in May 1941,Knaack 1988, p. 480. this being increased to 500 aircraft in January 1942. The B-29 featured a fuselage design with circular cross-section for strength. The need for pressurization in the cockpit area also led to the B-29 being one of very few American combat aircraft of World War II to have a stepless cockpit design, without a separate windscreen for the pilots. Manufacturing the B-29 was a complex task that involved four main-assembly factories. There were two Boeing operated plants at
Renton, Washington
Renton is a city in King County, Washington, and an inner-ring suburb of Seattle. Situated southeast of downtown Seattle, Renton straddles the southeast shore of Lake Washington, at the mouth of the Cedar River. As of the 2020 census, the ...
( Boeing Renton Factory), and one in Wichita, Kansas (now Spirit AeroSystems), a Bell plant at Marietta, Georgia, near Atlanta ("Bell-Atlanta"), and a Martin plant at Omaha, Nebraska ("Martin-Omaha" – Offutt Field Offutt may refer to:
*Offutt (surname)
*Offutt, Kentucky
*Offutt Air Force Base, United States Air Force airbase in Sarpy County, Nebraska
*Offutt Field (Greensburg)
Offutt Field is a multi-purpose athletic field, located in Greensburg, Pennsylv ...
).Bowers 1989, p. 322. Thousands of subcontractors were also involved in the project.Willis 2007, pp. 138–139. The first prototype made its maiden flight from Boeing Field, Seattle, on 21 September 1942. The combined effects of the aircraft's highly advanced design, challenging requirements, immense pressure for production, and hurried development caused setbacks. Unlike the unarmed first prototype,Brown 1977, p. 80. the second was fitted with a Sperry defensive armament system using remote-controlled gun turrets sighted by periscopes and first flew on 30 December 1942, although the flight was terminated due to a serious engine fire.Peacock ''Air International'' August 1989, pp. 70–71.
On 18 February 1943, the second prototype, flying out of Boeing Field in Seattle, experienced an engine fire and crashed. The crash killed Boeing test pilot Edmund T. Allen and his 10-man crew, 20 workers at the Frye Meat Packing Plant and a Seattle firefighter. Changes to the production craft came so often and so fast that, in early 1944, B-29s flew from the production lines directly to modification depots for extensive rebuilds to incorporate the latest changes. AAF-contracted modification centers and its own air depot system struggled to handle the scope of the requirements. Some facilities lacked hangars capable of housing the giant B-29, requiring outdoor work in freezing weather, further delaying necessary modification. By the end of 1943, although almost 100 aircraft had been delivered, only 15 were airworthy.Willis 2007, p. 144.Peacock ''Air International'' August 1989, p. 76. This prompted an intervention by General Hap Arnold to resolve the problem, with production personnel being sent from the factories to the modification centers to speed availability of sufficient aircraft to equip the first bomb groups in what became known as the " Battle of Kansas". This resulted in 150 aircraft being modified in the five weeks, between 10 March and 15 April 1944.Knaack 1988, p. 484.Bowers 1989, p. 323.
The most common cause of maintenance headaches and catastrophic failures was the engines. Although the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone radial engines later became a trustworthy workhorse in large piston-engined aircraft, early models were beset with dangerous reliability problems. This problem was not fully cured until the aircraft was fitted with the more powerful Pratt & Whitney R-4360 "Wasp Major" in the B-29D/B-50 program, which arrived too late for World War II. Interim measures included cuffs placed on propeller blades to divert a greater flow of cooling air into the intakes, which had baffles installed to direct a stream of air onto the exhaust valves. Oil flow to the valves was also increased, asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
baffles were installed around rubber push rod fittings to prevent oil loss, thorough pre-flight inspections were made to detect unseated valves, and mechanics frequently replaced the uppermost five cylinders (every 25 hours of engine time) and the entire engines (every 75 hours).
Pilots, including the present-day pilots of the Commemorative Air Force's ''Fifi
Fifi may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Fifi (''Better Call Saul''), an episode of the TV show
* Fifi, a ''Beverly Hills Teens'' character
* Fifi (Peanuts), a love interest of Snoopy
* Fifi La Fume, in ''Tiny Toon Adventures''
* Fifi the ...
'', one of the last two remaining flying B-29s, describe flight after takeoff as being an urgent struggle for airspeed (generally, flight after takeoff should consist of striving for altitude). Radial engines need airflow to keep them cool, and failure to get up to speed as soon as possible could result in an engine failure and risk of fire. One useful technique was to check the magnetos while already on takeoff roll rather than during a conventional static engine-runup before takeoff.Gardner, Fred Car"A Year in the B-29 Superfortress."
''Fred Carl Gardner's website'', updated 1 May 2005. Retrieved: 11 April 2009.

 In wartime, the B-29 was capable of flight at altitudes up to ,
In wartime, the B-29 was capable of flight at altitudes up to ,''Boeing''. Retrieved: 22 March 2012. at speeds of up to ( true airspeed). This was its best defense because Japanese fighters could barely reach that altitude, and few could catch the B-29 even if they did attain that altitude.
Defensive gun turret emplacements
 The General Electric Central Fire Control system on the B-29 directed four remotely controlled turrets armed with two .50 Browning M2 machine guns each. All weapons were aimed optically, with targeting computed by analog electrical instrumentation. There were five interconnected sighting stations located in the nose and tail positions and three Plexiglas blisters in the central fuselage. Five General Electric analog computers (one dedicated to each sight) increased the weapons' accuracy by compensating for factors such as airspeed, lead, gravity, temperature and humidity. The computers also allowed a single gunner to operate two or more turrets (including tail guns) simultaneously. The gunner in the upper position acted as fire control officer, managing the distribution of turrets among the other gunners during combat.Brown 1977, pp. 80–83.Williams and Gustin 2003, pp. 164–166. The tail position initially had two .50 Browning machine guns and a single M2 20 mm cannon. Later aircraft had the 20 mm cannon removed,Willis 2007, p. 140. sometimes replaced by a third machine gun.Pace 2003, p. 53.
In early 1945, Major General Curtis Lemay, commander of XXI Bomber Command—the Marianas-based B-29-equipped bombing force—ordered most of the defensive armament and remote-controlled sighting equipment removed from the B-29s under his command. The affected aircraft had the same reduced defensive firepower as the nuclear weapons-delivery intended ''Silverplate'' B-29 airframes and could carry greater fuel and bomb loads as a result of the change. The lighter defensive armament was made possible by a change in mission from high-altitude, daylight bombing with high explosive bombs to low-altitude night raids using incendiary bombs. As a consequence of that requirement, Bell Atlanta (BA) produced a series of 311 B-29Bs that had turrets and sighting equipment omitted, except for the tail position, which was fitted with AN/APG-15 fire-control radar.Willis 2007, pp. 140, 144. That version could also have an improved APQ-7 "Eagle" bombing-through-overcast radar fitted in an airfoil-shaped radome under the fuselage. Most of those aircraft were assigned to the 315th Bomb Wing, Northwest Field, Guam.
The General Electric Central Fire Control system on the B-29 directed four remotely controlled turrets armed with two .50 Browning M2 machine guns each. All weapons were aimed optically, with targeting computed by analog electrical instrumentation. There were five interconnected sighting stations located in the nose and tail positions and three Plexiglas blisters in the central fuselage. Five General Electric analog computers (one dedicated to each sight) increased the weapons' accuracy by compensating for factors such as airspeed, lead, gravity, temperature and humidity. The computers also allowed a single gunner to operate two or more turrets (including tail guns) simultaneously. The gunner in the upper position acted as fire control officer, managing the distribution of turrets among the other gunners during combat.Brown 1977, pp. 80–83.Williams and Gustin 2003, pp. 164–166. The tail position initially had two .50 Browning machine guns and a single M2 20 mm cannon. Later aircraft had the 20 mm cannon removed,Willis 2007, p. 140. sometimes replaced by a third machine gun.Pace 2003, p. 53.
In early 1945, Major General Curtis Lemay, commander of XXI Bomber Command—the Marianas-based B-29-equipped bombing force—ordered most of the defensive armament and remote-controlled sighting equipment removed from the B-29s under his command. The affected aircraft had the same reduced defensive firepower as the nuclear weapons-delivery intended ''Silverplate'' B-29 airframes and could carry greater fuel and bomb loads as a result of the change. The lighter defensive armament was made possible by a change in mission from high-altitude, daylight bombing with high explosive bombs to low-altitude night raids using incendiary bombs. As a consequence of that requirement, Bell Atlanta (BA) produced a series of 311 B-29Bs that had turrets and sighting equipment omitted, except for the tail position, which was fitted with AN/APG-15 fire-control radar.Willis 2007, pp. 140, 144. That version could also have an improved APQ-7 "Eagle" bombing-through-overcast radar fitted in an airfoil-shaped radome under the fuselage. Most of those aircraft were assigned to the 315th Bomb Wing, Northwest Field, Guam.
Pressurization
The crew would enjoy, for the first time in a bomber, full-pressurization comfort. This first-ever cabin pressure system for an Allied production bomber was developed for the B-29 by Garrett AiResearch. Both the forward and rear crew compartments were to be pressurized, but the designers had to decide whether to have bomb bays that were not pressurized or a fully pressurized fuselage that would have to be de-pressurized prior to opening the bomb bay doors. The solution was to have bomb bays that were not pressurized and a long tunnel joining the forward and rear crew compartments. Crews could use the tunnel if necessary to crawl from one pressurized compartment to the other.Operational history
World War II



 In September 1941, the United States Army Air Forces' plans for war against Germany and Japan proposed basing the B-29 in Egypt for operations against Germany, as British airbases were likely to be overcrowded.Craven and Cate Vol. 1 1983, pp. 145–149.Craven and Cate Vol. 2 1983, p. 6. Air Force planning throughout 1942 and early 1943 continued to have the B-29 deployed initially against Germany, only transferring to the Pacific after the end of the war in Europe. By the end of 1943, plans had changed, partly due to production delays, and the B-29 was dedicated to the Pacific Theater.Craven and Cate Vol. 5 1983, pp. 11–12. A new plan implemented at the direction of President Franklin D. Roosevelt as a promise to China, called Operation Matterhorn, deployed the B-29 units to attack Japan from four forward bases in southern China, with five main bases in India, and to attack other targets in the region from China and India as needed.Willis 2007, pp. 144–145. The
In September 1941, the United States Army Air Forces' plans for war against Germany and Japan proposed basing the B-29 in Egypt for operations against Germany, as British airbases were likely to be overcrowded.Craven and Cate Vol. 1 1983, pp. 145–149.Craven and Cate Vol. 2 1983, p. 6. Air Force planning throughout 1942 and early 1943 continued to have the B-29 deployed initially against Germany, only transferring to the Pacific after the end of the war in Europe. By the end of 1943, plans had changed, partly due to production delays, and the B-29 was dedicated to the Pacific Theater.Craven and Cate Vol. 5 1983, pp. 11–12. A new plan implemented at the direction of President Franklin D. Roosevelt as a promise to China, called Operation Matterhorn, deployed the B-29 units to attack Japan from four forward bases in southern China, with five main bases in India, and to attack other targets in the region from China and India as needed.Willis 2007, pp. 144–145. The Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively Romanization of Chi ...
region was eventually chosen over the Guilin region to avoid having to raise, equip, and train 50 Chinese divisions to protect the advanced bases from Japanese ground attack.Craven and Cate Vol. 5 1983, pp. 18–22. The XX Bomber Command, initially intended to be two combat wings of four groups each, was reduced to a single wing of four groups because of the lack of availability of aircraft, automatically limiting the effectiveness of any attacks from China.
This was an extremely costly scheme, as there was no overland connection available between India and China, and all supplies had to be flown over the Himalayas, either by transport aircraft or by B-29s themselves, with some aircraft being stripped of armor and guns and used to deliver fuel. B-29s started to arrive in India in early April 1944. The first B-29 flight to airfields in China (over the Himalayas, or " The Hump") took place on 24 April 1944. The first B-29 combat mission was flown on 5 June 1944, with 77 out of 98 B-29s launched from India bombing the railroad shops in Bangkok and elsewhere in Thailand. Five B-29s were lost during the mission, none to hostile fire.Peacock ''Air International'' August 1989, p. 87.
Forward base in China
On 5 June 1944, B-29s raided Bangkok, in what is reported as a test before being deployed against the Japanese home islands. Sources do not report from where they launched and vary as to the numbers involved—77, 98, and 114 being claimed. Targets were Bangkok's Memorial Bridge and a major power plant. Bombs fell over two kilometers away, damaged no civilian structures, but destroyed some tram lines, and destroyed both a Japanese military hospital and theJapanese secret police
The , also known as Kempeitai, was the military police arm of the Imperial Japanese Army from 1881 to 1945 that also served as a secret police force. In addition, in Japanese-occupied territories, the Kenpeitai arrested or killed those suspecte ...
headquarters.Stearn, Duncan"The air war over Thailand, 1941–1945; Part Two, The Allies attack Thailand, 1942–1945."
''Pattaya Mail,'' Volume XI, Issue 21, 30 May – 5 June 2003. Retrieved: 18 February 2012. On 15 June 1944, 68 B-29s took off from bases around Chengdu, 47 B-29s bombed the Imperial Iron and Steel Works at Yawata, Fukuoka Prefecture,
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. This was the first attack on Japanese islands since the Doolittle raid in April 1942.Craven and Cate Vol. 5 1983, p. 100. The first B-29 combat losses occurred during this raid, with one B-29 destroyed on the ground by Japanese fighters after an emergency landing in China,Craven and Cate Vol. 5 1983, p. 101. one lost to anti-aircraft fire over Yawata, and another, the ''Stockett's Rocket'' (after Capt. Marvin M. Stockett, Aircraft Commander) B-29-1-BW 42-6261, disappeared after takeoff from Chakulia, India, over the Himalayas (12 KIA, 11 crew and one passenger). This raid, which did little damage to the target, with only one bomb striking the target factory complex,Willis 2007, p. 145. nearly exhausted fuel stocks at the Chengdu B-29 bases, resulting in a slow-down of operations until the fuel stockpiles could be replenished.Craven and Cate Vol. 5 1983, pp. 101, 103. Starting in July, the raids against Japan from Chinese airfields continued at relatively low intensity. Japan was bombed on:
* 7 July 1944 (14 B-29s)
* 29 July (70+)
* 10 August (24)
* 20 August (61)
* 8 September (90)
* 26 September (83)
* 25 October (59)
* 12 November (29)
* 21 November (61)
* 19 December (36)
* 6 January 1945 (49)
B-29s were withdrawn from airfields in China by the end of January 1945. Throughout the prior period, B-29 raids were also launched from China and India against many other targets throughout Southeast Asia, including a series of raids on Singapore and Thailand. On 2 November 1944, 55 B-29s raided Bangkok's Bang Sue marshaling yards in the largest raid of the war. Seven RTAF Nakajima Ki-43 ''Hayabusa''s from Foong Bin (Air Group) 16 and 14 IJAAF Ki-43s attempted intercept. RTAF Flt Lt Therdsak Worrasap attacked a B-29, damaging it, but was shot down by return fire. One B-29 was lost, possibly the one damaged by Flt Lt Therdsak. On 14 April 1945, a second B-29 raid on Bangkok destroyed two key power plants and was the last major attack conducted against Thai targets. The B-29 effort was gradually shifted to the new bases in the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
in the Central Pacific, with the last B-29 combat mission from India flown on 29 March 1945.

New Mariana Islands air bases
In addition to the logistical problems associated with operations from China, the B-29 could only reach a limited part of Japan while flying from Chinese bases. The solution to this problem was to capture the Mariana Islands, which would bring targets such as Tokyo, about north of the Marianas within range of B-29 attacks. The Joint Chiefs of Staff agreed in December 1943 to seize the Marianas.Willis 2007, pp. 145–146. US forces invaded Saipan on 15 June 1944. Despite a Japanese naval counterattack which led to the Battle of the Philippine Sea and heavy fighting on land, Saipan was secured by 9 July.Willis 2007, p. 146. Operations followed against Guam and Tinian, with all three islands secured by August.Dear and Foot 1995, p. 718. Naval construction battalions (Seabees
United States Naval Construction Battalions, better known as the Navy Seabees, form the U.S. Naval Construction Force (NCF). The Seabee nickname is a heterograph of the initial letters "CB" from the words "Construction Battalion". Depending upon ...
) began at once to construct air bases suitable for the B-29, commencing even before the end of ground fighting. In all, five major airfields were built: two on the flat island of Tinian, one on Saipan
Saipan ( ch, Sa’ipan, cal, Seipél, formerly in es, Saipán, and in ja, 彩帆島, Saipan-tō) is the largest island of the Northern Mariana Islands, a Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States in the western Pa ...
, and two on Guam. Each was large enough to eventually accommodate a bomb wing consisting of four bomb groups, giving a total of 180 B-29s per airfield. These bases could be supplied by ship and, unlike the bases in China, were not vulnerable to attack by Japanese ground forces.
The bases became the launch sites for the large B-29 raids against Japan in the final year of the war. The first B-29 arrived on Saipan on 12 October 1944, and the first combat mission was launched from there on 28 October 1944, with 14 B-29s attacking the Truk atoll. The 73rd Bomb Wing launched the first mission against Japan from bases in the Marianas, on 24 November 1944, sending 111 B-29s to attack Tokyo. For this first attack on the Japanese capital since the Doolittle Raid in April 1942, 73rd Bomb Wing wing commander Brigadier General Emmett O'Donnell Jr. acted as mission command pilot in B-29 ''Dauntless Dotty
''Dauntless Dotty'' is the nickname of a Boeing B-29-40-BW Superfortress during the Second World War that led the first B-29 raid on Tokyo on 24 November 1944, the first bombing attack of the Japanese capital since the Doolittle Raid on 18 April ...
''.
The campaign of incendiary raids started with the bombardment of Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, whic ...
on 4 February 1945, then peaked early with the most destructive bombing raid in history (even when the later ''Silverplate''-flown nuclear attacks on Hiroshima and Nagasaki are considered) on the night of 9–10 March 1945 on Tokyo. From then on, the raids intensified, being launched regularly until the end of the war. The attacks succeeded in devastating most large Japanese cities (with the exception of Kyoto and four that were reserved for nuclear attacks), and gravely damaged Japan's war industries. Although less publicly appreciated, the mining of Japanese ports and shipping routes ( Operation Starvation) carried out by B-29s from April 1945 reduced Japan's ability to support its population and move its troops.
The nuclear weapons
The most famous B-29s were the Silverplate series. These aircraft were extensively modified to carry nuclear weapons. Serious consideration was given to using the British Lancaster bomber, as this would require less modification. The most significant modification was the enlargement of the bomb bay enabling each aircraft to carry either the Thinman or Fatman weapons. These Silverplate bombers differed from other B-29s then in service by havingfuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
and reversible props. Also, to make a lighter aircraft, the Silverplate B-29s were stripped of all guns, except for those on the tail. Pilot Charles Sweeney credits the reversible props for saving ''Bockscar'' after making an emergency landing on Okinawa following the Nagasaki bombing.
''Enola Gay
The ''Enola Gay'' () is a Boeing B-29 Superfortress bomber, named after Enola Gay Tibbets, the mother of the pilot, Colonel Paul Tibbets. On 6 August 1945, piloted by Tibbets and Robert A. Lewis during the final stages of World War II, it be ...
'', flown by Tibbets, dropped the first bomb, called Little Boy, on Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui h ...
on 6 August 1945. ''Enola Gay'' is fully restored and on display at the Smithsonian's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, outside Dulles Airport near Washington, D.C. ''Bockscar
''Bockscar'', sometimes called Bock's Car, is the name of the United States Army Air Forces B-29 bomber that dropped a Fat Man nuclear weapon over the Japanese city of Nagasaki during World War II in the secondand most recent nuclear attack in ...
'', piloted by Major
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
Charles W. Sweeney
Charles William Sweeney (December 27, 1919 – July 16, 2004) was an officer in the United States Army Air Forces during World War II and the pilot who flew ''Bockscar'' carrying the Fat Man atomic bomb to the Japanese city of Nagasaki on Augus ...
, dropped the second bomb, called Fat Man, on Nagasaki three days later. ''Bockscar'' is on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force.
Following the surrender of Japan, called V-J Day, B-29s were used for other purposes. A number supplied POWs with food and other necessities by dropping barrels of rations on Japanese POW camps. In September 1945, a long-distance flight was undertaken for public relations purposes: Generals Barney M. Giles, Curtis LeMay, and Emmett O'Donnell Jr. piloted three specially modified B-29s from Chitose Air Base in Hokkaidō
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel.
The la ...
to Chicago Municipal Airport, continuing to Washington, D.C., the farthest nonstop distance (c.6400 miles) to that date flown by U.S. Army Air Forces aircraft and the first-ever nonstop flight from Japan to Chicago.Potts, J. Ivan, Jr"Chapter: The Japan to Washington Flight."
Shelbyville, Tennessee: J.I. Potts & Associates, 1995. Retrieved: 8 June 2009.
''History Milestones (US Air Force).'' Retrieved: 21 October 2010. with a gross takeoff weight of .Mayo, Weyland
''b-29s-over-korea.com.'' Retrieved: 21 October 2010. Almost a year later, in October 1946, the same B-29 flew 9,422 miles nonstop from Oahu, Hawaii, to Cairo, Egypt, in less than 40 hours, demonstrating the possibility of routing airlines over the polar ice cap.
B-29s in Europe and Australia
 Although considered for other theaters, and briefly evaluated in the UK, the B-29 was exclusively used in World War II in the Pacific Theatre. The use of YB-29-BW ''41-36393'', the so-named ''Hobo Queen'', one of the service test aircraft flown around several British airfields in early 1944, was part of a "disinformation" program from its mention in an American-published ''Sternenbanner'' German-language propaganda leaflet from Leap Year Day in 1944, meant to be circulated within the Reich, with the intent to deceive the Germans into believing that the B-29 would be deployed to Europe.
American post-war military assistance programs loaned the RAF enough Superfortresses to equip several
Although considered for other theaters, and briefly evaluated in the UK, the B-29 was exclusively used in World War II in the Pacific Theatre. The use of YB-29-BW ''41-36393'', the so-named ''Hobo Queen'', one of the service test aircraft flown around several British airfields in early 1944, was part of a "disinformation" program from its mention in an American-published ''Sternenbanner'' German-language propaganda leaflet from Leap Year Day in 1944, meant to be circulated within the Reich, with the intent to deceive the Germans into believing that the B-29 would be deployed to Europe.
American post-war military assistance programs loaned the RAF enough Superfortresses to equip several RAF Bomber Command
RAF Bomber Command controlled the Royal Air Force's bomber forces from 1936 to 1968. Along with the United States Army Air Forces, it played the central role in the strategic bombing of Germany in World War II. From 1942 onward, the British bo ...
squadrons. The aircraft was known as the Washington B.1 in RAF service and served from March 1950 until the last bombers were returned in early 1954. The phase-out was occasioned by deliveries of the English Electric Canberra bombers. Three Washingtons modified for ELINT duties and a standard bomber version used for support by No. 192 Squadron RAF were decommissioned in 1958, being replaced by de Havilland Comet aircraft.
Two British Washington B.1 aircraft were transferred to the Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
(RAAF) in 1952. They were attached to the Aircraft Research and Development Unit and used in trials conducted on behalf of the British Ministry of Supply
The Ministry of Supply (MoS) was a department of the UK government formed in 1939 to co-ordinate the supply of equipment to all three British armed forces, headed by the Minister of Supply. A separate ministry, however, was responsible for aircr ...
. Both aircraft were placed in storage in 1956 and were sold for scrap in 1957."A76: Boeing Washington."''RAAF Museum.'' Retrieved: 28 January 2012.
Soviet Tupolev Tu-4
 At the end of WWII, Soviet development of modern four-engined heavy bombers lagged behind the west. The Petlyakov Pe-8—the sole heavy bomber operated by the
At the end of WWII, Soviet development of modern four-engined heavy bombers lagged behind the west. The Petlyakov Pe-8—the sole heavy bomber operated by the Soviet Air Forces
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
—first flew in 1936. Intended to replace the obsolete Tupolev TB-3, only 93 Pe-8s were built by the end of WWII. During 1944 and 1945, four B-29s made emergency landings in Soviet territory after bombing raids on Japanese Manchuria and Japan. In accordance with Soviet neutrality in the Pacific War, the bombers were interned by the Soviets despite American requests for their return. Rather than return the aircraft, the Soviets reverse engineered the American B-29s and used them as a pattern for the Tupolev Tu-4.
On 31 July 1944, ''Ramp Tramp'' (serial number
A serial number is a unique identifier assigned incrementally or sequentially to an item, to ''uniquely'' identify it.
Serial numbers need not be strictly numerical. They may contain letters and other typographical symbols, or may consist enti ...
42-6256), of the United States Army Air Forces 462nd (Very Heavy) Bomb Group was diverted to Vladivostok, Russia, after an engine failed and the propeller could not be feathered. This B-29 was part of a 100-aircraft raid against the Japanese Showa steel mill in Anshan, Manchuria."Tu-4 "Bull" and ''Ramp Tramp''."''Monino Aviation''. Retrieved: 1 November 2009. On 20 August 1944, ''Cait Paomat'' (42-93829), flying from Chengdu, was damaged by anti-aircraft gunfire during a raid on the Yawata Iron Works. Due to the damage it sustained, the crew elected to divert to the Soviet Union. The aircraft crashed in the foothills of
Sikhote-Alin
The Sikhote-Alin (russian: Сихотэ́-Али́нь, , , ) is a mountain range in Primorsky and Khabarovsk Krais, Russia, extending about to the northeast of the Russian Pacific seaport of Vladivostok. The highest summits are Tordoki Yani at ...
mountain range east of Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( rus, Хабaровск, a=Хабаровск.ogg, r=Habárovsk, p=xɐˈbarəfsk) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China ...
after the crew bailed out.
On 11 November 1944, during a night raid on Omura in Kyushu, Japan, the ''General H. H. Arnold Special'' (42-6365) was damaged and forced to divert to Vladivostok in the Soviet Union. The crew was interned. On 21 November 1944, ''Ding Hao'' (42-6358) was damaged during a raid on an aircraft factory at Omura and was also forced to divert to Vladivostok.
The interned crews of these four B-29s were allowed to escape into American-occupied Iran in January 1945, but none of the B-29s were returned after Stalin ordered the Tupolev OKB to examine and copy the B-29 and produce a design ready for quantity production as soon as possible.Lednicer, David"Intrusions, Overflights, Shootdowns and Defections During the Cold War and Thereafter".
David Lednicer, 16 April 2011. Retrieved: 31 July 2011. Because aluminum in the USSR was supplied in different gauges from that available in the US (metric vs imperial), the entire aircraft had to be extensively re-engineered. In addition, Tupolev substituted his own favored airfoil sections for those used by Boeing, with the Soviets themselves already having their own Wright R-1820-derived 18 cylinder radial engine, the Shvetsov ASh-73 of comparable power and displacement to the B-29's Duplex Cyclone radials available to power their design. In 1947, the Soviets debuted both the Tupolev Tu-4 ( NATO ASCC code named Bull), and the Tupolev Tu-70 transport variant. The Soviets used tail-gunner positions similar to the B-29 in many later bombers and transports.
Transition to USAF
Production of the B-29 was phased out after WWII, with the last example completed by Boeing's Renton factory on 28 May 1946. Many aircraft went into storage, being declared excess inventory, and were ultimately scrapped as surplus. Others remained in the active inventory and equipped theStrategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
when it formed on 21 March 1946.Peacock ''Air International'' September 1989, p. 141. In particular, the "Silverplate" modified aircraft of the 509th Composite Group remained the only aircraft capable of delivering the atomic bomb, and so the unit was involved in the Operation Crossroads series of tests, with B-29 ''Dave's Dream'' dropping a "Fat Man"-type bomb in Test ''Able'' on 1 July 1946.
Some B-29s, fitted with filtered air sampling scoops, were used to monitor above-ground nuclear weapons testing by the US and the USSR by sampling airborne radioactive contamination. The USAF also used the aircraft for long-range weather reconnaissance (WB-29), for signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ( ...
gathering (EB-29) and photographic reconnaissance (RB-29).
Korean War and postwar service
 The B-29 was used in 1950–53 in the Korean War. At first, the bomber was used in normal strategic day-bombing missions, though North Korea's few strategic targets and industries were quickly destroyed. More importantly, in 1950 numbers of Soviet MiG-15 jet fighters appeared over Korea, and after the loss of 28 aircraft, future B-29 raids were restricted to night missions, largely in a supply-interdiction role.
The B-29 dropped the 1,000-lb VB-3 "Razon" (a range-controllable version of the earlier
The B-29 was used in 1950–53 in the Korean War. At first, the bomber was used in normal strategic day-bombing missions, though North Korea's few strategic targets and industries were quickly destroyed. More importantly, in 1950 numbers of Soviet MiG-15 jet fighters appeared over Korea, and after the loss of 28 aircraft, future B-29 raids were restricted to night missions, largely in a supply-interdiction role.
The B-29 dropped the 1,000-lb VB-3 "Razon" (a range-controllable version of the earlier Azon
AZON (or Azon), from "azimuth only", was one of the world's first guided weapons, deployed by the Allies and contemporary with the German Fritz X.
Officially designated VB-1 ("Vertical Bomb 1"), it was invented by Major Henry J. Rand and Thoma ...
guided ordnance device) and the 12,000 lb. VB-13 " Tarzon" MCLOS radio-controlled bombs in Korea, mostly for demolishing major bridges, like the ones across the Yalu River, and for attacks on dams. The aircraft also was used for numerous leaflet drops in North Korea, such as those for Operation Moolah.
A Superfortress of the 91st Strategic Reconnaissance Squadron flew the last B-29 mission of the war on 27 July 1953.
Over the course of the war, B-29s flew 20,000 sorties and dropped 200,000 tonnes (180,000 tons) of bombs. B-29 gunners were credited with shooting down 27 enemy aircraft.Futrell et al. 1976. In turn 78 B-29s were lost; 57 B-29 and reconnaissance variants were lost in action and 21 were non-combat losses.
Soviet records show that one MiG-15 jet fighter was shot down by a B-29 during the war. This occurred on 6 December 1950, when a B-29 shot down Lieutenant N. Serikov.
With the arrival of the mammoth Convair B-36, the B-29 was reclassified as a medium bomber by the Air Force. The later B-50 Superfortress variant (initially designated B-29D) was able to handle auxiliary roles such as air-sea rescue, electronic intelligence gathering, air-to-air refueling, and weather reconnaissance.
The B-50D was replaced in its primary role during the early 1950s by the Boeing B-47 Stratojet, which in turn was replaced by the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air ...
. The final active-duty KB-50 and WB-50 variants were phased out in the mid-1960s, with the final example retired in 1965. A total of 3,970 B-29s were built.
Variants
 The variants of the B-29 were outwardly similar in appearance but were built around different wing center sections that affected the wingspan dimensions. The wing of the Renton-built B-29A-BN used a different subassembly process and was a foot longer in span. The Georgia-built B-29B-BA weighed less through armament reduction. A planned C series with more reliable R-3350s was not built.
Moreover, engine packages changed, including the type of propellers and range of the variable pitch. A notable example was the eventual 65 airframes (up to 1947's end) for the Silverplate and successor-name "Saddletree" specifications built for the Manhattan Project with Curtiss Electric reversible pitch propellers.
The other differences came through added equipment for varied mission roles. These roles included cargo carriers (CB); rescue aircraft (SB); weather ships (WB); and trainers (TB); and aerial tankers (KB).
Some were used for odd purposes such as flying relay television transmitters under the name of Stratovision.
The variants of the B-29 were outwardly similar in appearance but were built around different wing center sections that affected the wingspan dimensions. The wing of the Renton-built B-29A-BN used a different subassembly process and was a foot longer in span. The Georgia-built B-29B-BA weighed less through armament reduction. A planned C series with more reliable R-3350s was not built.
Moreover, engine packages changed, including the type of propellers and range of the variable pitch. A notable example was the eventual 65 airframes (up to 1947's end) for the Silverplate and successor-name "Saddletree" specifications built for the Manhattan Project with Curtiss Electric reversible pitch propellers.
The other differences came through added equipment for varied mission roles. These roles included cargo carriers (CB); rescue aircraft (SB); weather ships (WB); and trainers (TB); and aerial tankers (KB).
Some were used for odd purposes such as flying relay television transmitters under the name of Stratovision.
 The B-29D led progressively to the XB-44, and the family of B-50 Superfortress (which was powered by four Pratt & Whitney R-4360-35 Wasp Major engines).
Another role was as a mothership. This included being rigged for carrying the experimental parasite fighter aircraft, such as the McDonnell XF-85 Goblin and Republic F-84 Thunderjets as in flight lock on and offs. It was also used to develop the Airborne Early Warning program; it was the ancestor of various modern radar picket aircraft. A B-29 with the original Wright Duplex Cyclone powerplants was used to air-launch the
The B-29D led progressively to the XB-44, and the family of B-50 Superfortress (which was powered by four Pratt & Whitney R-4360-35 Wasp Major engines).
Another role was as a mothership. This included being rigged for carrying the experimental parasite fighter aircraft, such as the McDonnell XF-85 Goblin and Republic F-84 Thunderjets as in flight lock on and offs. It was also used to develop the Airborne Early Warning program; it was the ancestor of various modern radar picket aircraft. A B-29 with the original Wright Duplex Cyclone powerplants was used to air-launch the Bell X-1
The Bell X-1 (Bell Model 44) is a rocket engine–powered aircraft, designated originally as the XS-1, and was a joint National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics– U.S. Army Air Forces–U.S. Air Force supersonic research project built by Be ...
supersonic research rocket aircraft, as well as Cherokee rockets for the testing of ejection seats.Shinabery, Michael"Whoosh failures were 'instructive'."
''
Alamogordo Daily News
''Alamogordo Daily News'', founded in 1898, is a daily newspaper published in Alamogordo, New Mexico. It carries local news as well as syndicated content from Associated Press and others.
History
''Alamogordo Daily News'' claims 1898 as its f ...
'', 26 October 2008. Retrieved: 17 May 2014.
Some B-29s were modified to act as testbeds for various new systems or special conditions, including fire-control systems, cold-weather operations, and various armament configurations. Several converted B-29s were used to experiment with aerial refueling
Aerial refueling, also referred to as air refueling, in-flight refueling (IFR), air-to-air refueling (AAR), and tanking, is the process of transferring aviation fuel from one aircraft (the tanker) to another (the receiver) while both aircraft a ...
and re-designated as KB-29s. Perhaps the most important tests were conducted by the XB-29G. It carried prototype jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term ...
s in its bomb bay, and lowered them into the air stream to conduct measurements.
Operators
; *Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
(two former RAF aircraft for trials)
;
* Royal Air Force (87 loaned from the USAF as the Washington B.1)
;
* United States Army Air Forces
* United States Air Force
* United States Navy (four former USAF aircraft designated as P2B patrol bombers)
;
* Soviet Air Forces
The Soviet Air Forces ( rus, Военно-воздушные силы, r=Voyenno-vozdushnyye sily, VVS; literally "Military Air Forces") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces. The Air Forces ...
(three USAAF B-29s made emergency landings in the USSR during WWII, and were never returned; they were reverse-engineered to make the Soviet Tupolev Tu-4 "Bull" bomber.)
Surviving aircraft
 Twenty-two B-29s are preserved at various museums worldwide, including two flying examples; ''FIFI'', which belongs to the Commemorative Air Force, and ''Doc'', which belongs to Doc's Friends. Doc made its first flight in 60 years from Wichita, Kansas, on 17 July 2016. There are also four complete airframes either in storage or under restoration, eight partial airframes in storage or under restoration, and four known wreck sites.
Three of the Silverplate B-29s modified to drop nuclear bombs survive. The ''
Twenty-two B-29s are preserved at various museums worldwide, including two flying examples; ''FIFI'', which belongs to the Commemorative Air Force, and ''Doc'', which belongs to Doc's Friends. Doc made its first flight in 60 years from Wichita, Kansas, on 17 July 2016. There are also four complete airframes either in storage or under restoration, eight partial airframes in storage or under restoration, and four known wreck sites.
Three of the Silverplate B-29s modified to drop nuclear bombs survive. The ''Enola Gay
The ''Enola Gay'' () is a Boeing B-29 Superfortress bomber, named after Enola Gay Tibbets, the mother of the pilot, Colonel Paul Tibbets. On 6 August 1945, piloted by Tibbets and Robert A. Lewis during the final stages of World War II, it be ...
'' (nose number 82), which dropped the first atomic bomb, was fully restored and placed on display at the Smithsonian's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center of the National Air & Space Museum near Washington Dulles International Airport in 2003. The B-29 that dropped Fat Man on Nagasaki, ''Bockscar
''Bockscar'', sometimes called Bock's Car, is the name of the United States Army Air Forces B-29 bomber that dropped a Fat Man nuclear weapon over the Japanese city of Nagasaki during World War II in the secondand most recent nuclear attack in ...
'' (nose number 77), is restored and on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force at Wright-Patterson AFB
Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB) is a United States Air Force base and census-designated place just east of Dayton, Ohio, in Greene and Montgomery counties. It includes both Wright and Patterson Fields, which were originally Wilbur Wri ...
in Dayton, Ohio. The third is the 15th Silverplate to be delivered, on the last day of the war in the Pacific. It is on display at the National Museum of Nuclear Science & History in Albuquerque, New Mexico, posed with a replica of the Mark-3 "Fat Man" nuclear bomb.
 Only two of the 22 museum aircraft are outside the United States: ''It's Hawg Wild'' at the Imperial War Museum Duxford and another at the
Only two of the 22 museum aircraft are outside the United States: ''It's Hawg Wild'' at the Imperial War Museum Duxford and another at the KAI Aerospace Museum
The KAI Aerospace Museum is an aerospace museum in Sacheon, South Korea located at adjacent to Sacheon Airport.
Aircraft on display
Helicopters
* Bell UH-1B-BF 64-14003 (Construction Number 1127). This helicopter was purchased by the United Sta ...
in Sachon, South Korea.
Accidents and incidents
 Accidents and incidents involving B-29s include:
* The Friday evening of 10 November 1944 crash of a B-29 near Clovis, New Mexico. All 15 members of the crew were killed.
* 12 June 1946 a B-29 crashed into
Accidents and incidents involving B-29s include:
* The Friday evening of 10 November 1944 crash of a B-29 near Clovis, New Mexico. All 15 members of the crew were killed.
* 12 June 1946 a B-29 crashed into Clingmans Dome
Clingmans Dome (or Clingman's Dome) is a mountain in the Great Smoky Mountains of Tennessee and North Carolina in the southeastern United States. Its name in Cherokee is Kuwahi or Kuwohi (ᎫᏩᎯ or ᎫᏬᎯ), meaning "mulberry place." At an to ...
in Tennessee killing the entire crew of twelve.
* The 1947 crash of the Kee Bird
The ''Kee Bird'' was a United States Army Air Forces Boeing B-29 Superfortress, serial ''45-21768'', of the 46th Reconnaissance Squadron, that became marooned after making an emergency landing in northwest Greenland during a secret Cold War sp ...
in Greenland during a flight to the geographic North Pole, and its subsequent destruction in 1995 during a recovery attempt.
* The 1948 Waycross B-29 crash
The 1948 Waycross B-29 crash occurred on 6 October 1948 when an engine fire contributed to the crash of a Boeing B-29-100-BW Superfortress bomber in Waycross, Georgia. The plane was from the 3150th Electronics Squadron, United States Air Force a ...
, which resulted in the '' United States v. Reynolds'' lawsuit regarding state secrets privilege The state secrets privilege is an evidentiary rule created by United States legal precedent. Application of the privilege results in exclusion of evidence from a legal case based solely on affidavits submitted by the government stating that court ...
* The 1948 Lake Mead Boeing B-29 crash
The 1948 Lake Mead Boeing B-29 crash occurred 21 July 1948 when a Boeing B-29 Superfortress, Boeing B-29-100-BW Superfortress, modified into an Boeing B-29 Superfortress variants#RB-29J (RB-29, FB-29J, F-13, F-13A), F-13 reconnaissance platform an ...
.
* The 3 November 1948 crash at Bleaklow moor near Glossop
Glossop is a market town in the Borough of High Peak, Derbyshire, England. It is located east of Manchester, north-west of Sheffield and north of the county town, Matlock. Glossop lies near Derbyshire's borders with Cheshire, Greater Manches ...
, Derbyshire, England. All 13 crew onboard were killed. Much of the wreckage is still exposed and can be reached by a 2 mile walk from the summit of Snake Pass, starting along the Pennine Way footpath through Devil's Dyke.
* On 11 April 1950 a B-29 departed Kirtland Air Force Base
Kirtland Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in the southeast quadrant of the Albuquerque, New Mexico urban area, adjacent to the Albuquerque International Sunport. The base was named for the early Army aviator Col. Roy ...
at 9:38 PM and crashed into a mountain on Manzano Base approximately three minutes later, killing the crew. Detonators were installed in the nuclear bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
on the aircraft. The bomb case was demolished and some high-explosive (HE) material burned in the gasoline fire. Other pieces of unburned HE were scattered throughout the wreckage. Four spare detonators in their carrying case were recovered undamaged. There were no contamination or recovery problems. The recovered components were returned to the Atomic Energy Commission. Both the weapon and the capsule of nuclear material were on board the aircraft but the capsule was not inserted in the bomb for safety reasons, so a nuclear detonation was not possible.
*On 5 August 1950 a bomb-laden B-29 Superfortress crashed into a residential area in California; 17 were killed and 68 injured
* The 1953 "Tip Tow" crash, Peconic Bay, New York State.
Specifications


Notable appearances in media
See also
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * Anderton, David A. ''B-29 Superfortress at War''. Shepperton, Surrey, UK: Ian Allan Ltd., 1978. . * Berger, Carl. ''B29: The Superfortress''. New York: Ballantine Books, 1970. . * Birdsall, Steve. ''B-29 Superfortress in Action (Aircraft in Action 31)''. Carrolton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 1977. . * Birdsall, Steve. ''Saga of the Superfortress: The Dramatic Story of the B-29 and the Twentieth Air Force''. London: Sidgewick & Jackson Limited, 1991. . * Birdsall, Steve. ''Superfortress: The Boeing B-29''. Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, Inc., 1980. . * Bowers, Peter M. ''Boeing Aircraft since 1916''. London: Putnam, 1989. . * Bowers, Peter M. ''Boeing B-29 Superfortress''. Stillwater, Minnesota: Voyageur Press, 1999. . * Brown, J. "RCT Armament in the Boeing B-29". '' Air Enthusiast'', Number Three, 1977, pp. 80–83. * Campbell, Richard H., ''The Silverplate Bombers: A History and Registry of the Enola Gay and Other B-29s Configured to Carry Atomic Bombs''. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company, Inc., 2005. . * Chant, Christopher. ''Superprofile: B-29 Superfortress''. Sparkford, Yeovil, Somerset, UK: Haynes Publishing Group, 1983. . * Clarke, Chris"The Cannons on the B-29 Bomber Were a Mid-Century Engineering Masterpiece"
'' Popular Mechanics'', 30 November 2015. * Craven, Wesley Frank and James Lea Cate, eds
''The Army Air Forces In World War II: Volume One: Plans and Early Operations: January 1939 to August 1942''
. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1983. * Craven, Wesley Frank and James Lea Cate, eds
''The Army Air Forces In World War II: Volume Two: Europe: Torch to Pointblank August 1942 to December 1943''
. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1983. * Craven, Wesley Frank and James Lea Cate, eds
''The Army Air Forces In World War II: Volume Five: The Pacific: Matterhorn to Nagasaki June 1944 to August 1945''
Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1983. * Davis, Larry. ''B-29 Superfortress in Action (Aircraft in Action 165)''. Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, 1997. . * Dear, I.C.B. and M.R.D. Foo, eds. ''The Oxford Companion of World War II''. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 1995. . * Dorr, Robert F. ''B-29 Superfortress Units in World War Two''. Combat Aircraft 33. Botley, Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2002. . * Dorr, Robert F. ''B-29 Superfortress Units of the Korean War''. Botley, Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2003. . * Fopp, Michael A. ''The Washington File''. Tonbridge, Kent, UK: Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd., 1983. . * Francillon, René J. ''McDonnell Douglas Aircraft since 1920''. London: Putnam, 1979. . * Futrell R.F. et al. ''Aces and Aerial Victories: The United States Air Force in Southeast Asia, 1965–1973''. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1976. . * Grant, R.G. and John R. Dailey. ''Flight: 100 Years of Aviation''. Harlow, Essex, UK: DK Adult, 2007. . * Herbert, Kevin B. ''Maximum Effort: The B-29s Against Japan''. Manhattan, Kansas: Sunflower University Press, 1983. . * Herman, Arthur. ''Freedom's Forge: How American Business Produced Victory in World War II''. New York: Random House, 2012. . * Hess, William N. ''Great American Bombers of WW II''. St. Paul, Minnesota: Motorbooks International, 1999. . * Higham, Robin and Carol Williams, eds. ''Flying Combat Aircraft of USAAF-USAF''. Volume 1. Washington, D.C.: Air Force Historical Foundation, 1975. . * Howlett, Chris. "Washington Times"
The history of the Washington
* ''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft'' (Part Work 1982–1985). London: Orbis Publishing, 1985. * Johnsen, Frederick A. ''The B-29 Book''. Tacoma, Washington: Bomber Books, 1978. , . * Johnson, Robert E. "Why the Boeing B-29 Bomber, and Why the Wright R-3350 Engine?" ''American Aviation Historical Society Journal,'' 33(3), 1988, pp. 174–189. ISSN 0002-7553. * Knaack, Marcelle Size. ''Post-World War II Bombers, 1945–1973''. Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1988. . * LeMay, Curtis and Bill Yenne. ''Super Fortress''. London:
Berkley Books
Berkley Books is an imprint of the Penguin Group.
History
Berkley Books began as an independent company in 1955. It was founded as "Chic News Company" by Charles Byrne and Frederick Klein, who had worked for Avon; they quickly renamed it Berk ...
, 1988. .
* Lewis, Peter M. H., ed. "B-29 Superfortress". ''Academic American Encyclopedia''. Volume 10. Chicago: Grolier Incorporated, 1994. .
* Lloyd, Alwyn T. ''B-29 Superfortress, Part 1. Production Versions (Detail & Scale 10)''. Fallbrook, California/London: Aero Publishers/Arms & Armour Press, Ltd., 1983. .
* Lloyd, Alwyn T. ''B-29 Superfortress. Part 2. Derivatives (Detail & Scale 25)''. Blue Ridge Summit, Pennsylvania/London: TAB Books/Arms & Armour Press, Ltd., 1987.
* Mann, Robert A. ''The B-29 Superfortress: A Comprehensive Registry of the Planes and Their Missions''. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company, 2004. .
* Mann, Robert A. ''The B-29 Superfortress Chronology, 1934–1960''. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company, 2009. .
* Marshall, Chester. ''Warbird History: B-29 Superfortress''. St. Paul, Minnesota: Motorbooks International, 1993. .
* Mayborn, Mitch. ''The Boeing B-29 Superfortress (Aircraft in Profile 101)''. Windsor, Berkshire, UK: Profile Publications Ltd., 1971 (reprint).
* Miller, Jay. "Tip Tow & Tom-Tom". '' Air Enthusiast'', No. 9, February–May 1979, pp. 40–42. .
* Nijboer, Donald. ''B-29 Superfortress vs Ki-44 "Tojo": Pacific Theater 1944–45'' (Bloomsbury Publishing, 2017).
* Nijboer, Donald, and Steve Pace. ''B-29 Combat Missions: First-hand Accounts of Superfortress Operations Over the Pacific and Korea'' (Metro Books, 2011).
* Nowicki, Jacek. ''B-29 Superfortress (Monografie Lotnicze 13)'' (in Polish). Gdańsk, Poland: AJ-Press, 1994. .
* Pace, Steve. ''Boeing B-29 Superfortress''. Ramsbury, Marlborough, Wiltshire, United Kingdom: Crowood Press, 2003. .
* Peacock, Lindsay. "Boeing B-29... First of the Superbombers, Part One." ''Air International
''AIR International'' is a British aviation magazine covering current defence aerospace and civil aviation topics. It has been in publication since 1971 and is currently published by Key Publishing Ltd.
History and profile
The magazine was fir ...
'', August 1989, Vol. 37, No. 2, pp. 68–76, 87.
* Peacock, Lindsay. "Boeing B-29... First of the Superbombers, Part Two." ''Air International'', September 1989, Vol. 37, No. 3, pp. 141–144, 150–151.
* Pimlott, John. ''B-29 Superfortress''. London: Bison Books Ltd., 1980. .
* Rigmant, Vladimir. ''B-29, Tу-4 – стратегические близнецы – как это было (Авиация и космонавтика 17 �рылья 4 (in Russian)''. Moscow: 1996.
* Toh, Boon Kwan. "Black and Silver: Perceptions and Memories of the B-29 Bomber, American Strategic Bombing and the Longest Bombing Missions of the Second World War on Singapore" '' War & Society'' 39#2 (2020) pp. 109–125
* Vander Meulen, Jacob. ''Building the B-29''. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Books, 1995. .
* Wegg, John. ''General Dynamics Aircraft and their Predecessors''. London: Putnam, 1990. .
* Wheeler, Barry C. ''The Hamlyn Guide to Military Aircraft Markings.'' London: Chancellor Press, 1992. .
* Wheeler, Keith. ''Bombers over Japan''. Virginia Beach, Virginia: Time-Life Books, 1982. .
* White, Jerry. ''Combat Crew and Unit Training in the AAF 1939–1945''. USAF Historical Study No. 61. Washington, D.C.: Center for Air Force History, 1949.
* Williams, Anthony G. and Emmanuel Gustin. ''Flying Guns World War II: Development of Aircraft Guns, Ammunition and Installations 1933–45''. Shrewsbury, UK: Airlife, 2003. .
* Willis, David. "Boeing B-29 and B-50 Superfortress". ''International Air Power Review'', Volume 22, 2007, pp. 136–169. Westport, Connecticut: AIRtime Publishing. . .
* Wolf, William. ''Boeing B-29 Superfortress: The Ultimate Look''. Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing, 2005. .
External links
B-29 Combat Crew Manual
"Meet the B-29"
''
Popular Science
''Popular Science'' (also known as ''PopSci'') is an American digital magazine carrying popular science content, which refers to articles for the general reader on science and technology subjects. ''Popular Science'' has won over 58 awards, incl ...
'', August 1944—the first large and detailed public article printed on the B-29 in the US
Pelican's Perch #56:Superfortress!
Article wrote by John Deakin, one of the pilots who regularly fly the world's first restored-to-flight B-29
Listing of surviving B-29s
* {{Authority control Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki B-29 Superfortress Four-engined tractor aircraft Boeing B-29 World War II bombers of the United States Mid-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1942 Four-engined piston aircraft