Boars Head 1873 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to
 MtDNA studies indicate that the wild boar originated from islands in Southeast Asia such as Indonesia and the Philippines, and subsequently spread onto mainland Eurasia and North Africa. The earliest fossil finds of the species come from both Europe and Asia, and date back to the
MtDNA studies indicate that the wild boar originated from islands in Southeast Asia such as Indonesia and the Philippines, and subsequently spread onto mainland Eurasia and North Africa. The earliest fossil finds of the species come from both Europe and Asia, and date back to the
 , 16 subspecies are recognised, which are divided into four regional groupings:
* Western: Includes ''S. s. scrofa'', ''S. s. meridionalis'', ''S. s. algira'', ''S. s. attila'', ''S. s. lybicus'' and ''S. s. nigripes''. These subspecies are typically high-skulled (though ''lybicus'' and some ''scrofa'' are low-skulled), with thick underwool and (excepting ''scrofa'' and ''attila'') poorly developed manes.Groves, C. P. et al. 1993. The Eurasian Suids ''Sus'' and ''Babyrousa''. In Oliver, W. L. R., ed., ''Pigs, Peccaries, and Hippos – 1993 Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan'', 107–108. IUCN/SSC Pigs and Peccaries Specialist Group,
* Indian: Includes ''S. s. davidi'' and ''S. s. cristatus''. These subspecies have sparse or absent underwool, with long manes and prominent bands on the snout and mouth. While ''S. s. cristatus'' is high-skulled, ''S. s. davidi'' is low-skulled.
* Eastern: Includes ''S. s. sibiricus'', ''S. s. ussuricus'', ''S. s. leucomystax'', ''S. s. riukiuanus'', ''S. s. taivanus'' and ''S. s. moupinensis''. These subspecies are characterised by a whitish streak extending from the corners of the mouth to the lower jaw. With the exception of ''S. s. ussuricus'', most are high-skulled. The underwool is thick, except in ''S. s. moupinensis'', and the mane is largely absent.
* Indonesian: Represented solely by ''S. s. vittatus'', it is characterised by its sparse body hair, lack of underwool, fairly long mane, a broad reddish band extending from the muzzle to the sides of the neck. It is the most
, 16 subspecies are recognised, which are divided into four regional groupings:
* Western: Includes ''S. s. scrofa'', ''S. s. meridionalis'', ''S. s. algira'', ''S. s. attila'', ''S. s. lybicus'' and ''S. s. nigripes''. These subspecies are typically high-skulled (though ''lybicus'' and some ''scrofa'' are low-skulled), with thick underwool and (excepting ''scrofa'' and ''attila'') poorly developed manes.Groves, C. P. et al. 1993. The Eurasian Suids ''Sus'' and ''Babyrousa''. In Oliver, W. L. R., ed., ''Pigs, Peccaries, and Hippos – 1993 Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan'', 107–108. IUCN/SSC Pigs and Peccaries Specialist Group,
* Indian: Includes ''S. s. davidi'' and ''S. s. cristatus''. These subspecies have sparse or absent underwool, with long manes and prominent bands on the snout and mouth. While ''S. s. cristatus'' is high-skulled, ''S. s. davidi'' is low-skulled.
* Eastern: Includes ''S. s. sibiricus'', ''S. s. ussuricus'', ''S. s. leucomystax'', ''S. s. riukiuanus'', ''S. s. taivanus'' and ''S. s. moupinensis''. These subspecies are characterised by a whitish streak extending from the corners of the mouth to the lower jaw. With the exception of ''S. s. ussuricus'', most are high-skulled. The underwool is thick, except in ''S. s. moupinensis'', and the mane is largely absent.
* Indonesian: Represented solely by ''S. s. vittatus'', it is characterised by its sparse body hair, lack of underwool, fairly long mane, a broad reddish band extending from the muzzle to the sides of the neck. It is the most
 With the exception of domestic pigs in Timor and Papua New Guinea (which appear to be of
With the exception of domestic pigs in Timor and Papua New Guinea (which appear to be of

 The wild boar is a bulky, massively built suid with short and relatively thin legs. The trunk is short and robust, while the hindquarters are comparatively underdeveloped. The region behind the shoulder blades rises into a hump and the neck is short and thick to the point of being nearly immobile. The animal's head is very large, taking up to one-third of the body's entire length. The structure of the head is well suited for digging. The head acts as a plough, while the powerful neck muscles allow the animal to upturn considerable amounts of soil: it is capable of digging into frozen ground and can upturn rocks weighing . The eyes are small and deep-set and the ears long and broad. The species has well developed canine teeth, which protrude from the mouths of adult males. The medial hooves are larger and more elongated than the lateral ones and are capable of quick movements. The animal can run at a maximum speed of 40 km/h (25 mph) and jump at a height of .
Sexual dimorphism is very pronounced in the species, with males being typically 5–10% larger and 20–30% heavier than females. Males also sport a mane running down the back, which is particularly apparent during autumn and winter. The canine teeth are also much more prominent in males and grow throughout life. The upper canines are relatively short and grow sideways early in life, though they gradually curve upwards. The lower canines are much sharper and longer, with the exposed parts measuring in length. In the breeding period, males develop a coating of
The wild boar is a bulky, massively built suid with short and relatively thin legs. The trunk is short and robust, while the hindquarters are comparatively underdeveloped. The region behind the shoulder blades rises into a hump and the neck is short and thick to the point of being nearly immobile. The animal's head is very large, taking up to one-third of the body's entire length. The structure of the head is well suited for digging. The head acts as a plough, while the powerful neck muscles allow the animal to upturn considerable amounts of soil: it is capable of digging into frozen ground and can upturn rocks weighing . The eyes are small and deep-set and the ears long and broad. The species has well developed canine teeth, which protrude from the mouths of adult males. The medial hooves are larger and more elongated than the lateral ones and are capable of quick movements. The animal can run at a maximum speed of 40 km/h (25 mph) and jump at a height of .
Sexual dimorphism is very pronounced in the species, with males being typically 5–10% larger and 20–30% heavier than females. Males also sport a mane running down the back, which is particularly apparent during autumn and winter. The canine teeth are also much more prominent in males and grow throughout life. The upper canines are relatively short and grow sideways early in life, though they gradually curve upwards. The lower canines are much sharper and longer, with the exposed parts measuring in length. In the breeding period, males develop a coating of 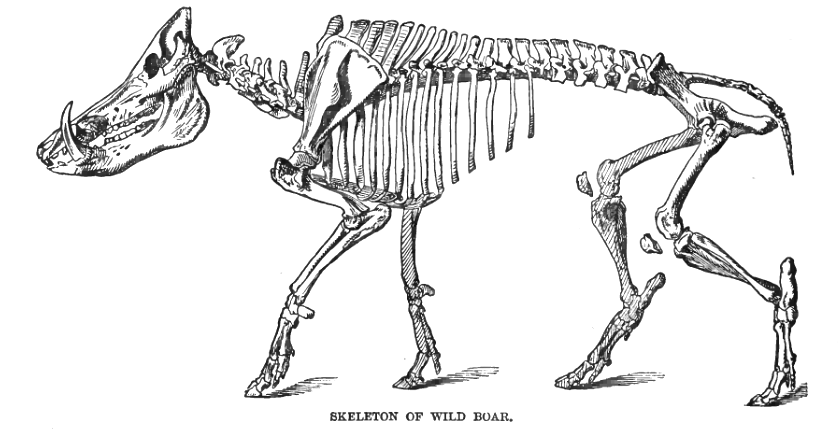
 Adult size and weight is largely determined by environmental factors; boars living in arid areas with little productivity tend to attain smaller sizes than their counterparts inhabiting areas with abundant food and water. In most of Europe, males average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length, whereas females average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length. In Europe's Mediterranean regions, males may reach average weights as low as and females , with shoulder heights of . In the more productive areas of Eastern Europe, males average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length, while females weigh , reach in shoulder height, and reach in body length. In Western and Central Europe, the largest males weigh and females . In Northeastern Asia, large males can reach brown bear-like sizes, weighing and measuring in shoulder height. Some adult males in Ussuriland and Manchuria have been recorded to weigh and measure in shoulder height. Adults of this size are generally immune from wolf predation. Such giants are rare in modern times, due to past overhunting preventing animals from attaining their full growth.
The winter coat consists of long, coarse bristles underlaid with short brown downy fur. The length of these bristles varies along the body, with the shortest being around the face and limbs and the longest running along the back. These back bristles form the aforementioned mane prominent in males and stand erect when the animal is agitated. Colour is highly variable; specimens around Lake Balkhash are very lightly coloured, and can even be white, while some boars from Belarus and Ussuriland can be black. Some subspecies sport a light-coloured patch running backward from the corners of the mouth. Coat colour also varies with age, with piglets having light brown or rusty-brown fur with pale bands extending from the flanks and back.
The wild boar produces a number of different sounds which are divided into three categories:
* Contact calls: Grunting noises which differ in intensity according to the situation. Adult males are usually silent, while females frequently grunt and piglets whine. When feeding, boars express their contentment through purring. Studies have shown that piglets imitate the sounds of their mother, thus different litters may have unique vocalisations.
* Alarm calls: Warning cries emitted in response to threats. When frightened, boars make loud huffing ''ukh! ukh!'' sounds or emit screeches transcribed as ''gu-gu-gu''.
* Combat calls: High-pitched, piercing cries.
Its sense of
Adult size and weight is largely determined by environmental factors; boars living in arid areas with little productivity tend to attain smaller sizes than their counterparts inhabiting areas with abundant food and water. In most of Europe, males average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length, whereas females average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length. In Europe's Mediterranean regions, males may reach average weights as low as and females , with shoulder heights of . In the more productive areas of Eastern Europe, males average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length, while females weigh , reach in shoulder height, and reach in body length. In Western and Central Europe, the largest males weigh and females . In Northeastern Asia, large males can reach brown bear-like sizes, weighing and measuring in shoulder height. Some adult males in Ussuriland and Manchuria have been recorded to weigh and measure in shoulder height. Adults of this size are generally immune from wolf predation. Such giants are rare in modern times, due to past overhunting preventing animals from attaining their full growth.
The winter coat consists of long, coarse bristles underlaid with short brown downy fur. The length of these bristles varies along the body, with the shortest being around the face and limbs and the longest running along the back. These back bristles form the aforementioned mane prominent in males and stand erect when the animal is agitated. Colour is highly variable; specimens around Lake Balkhash are very lightly coloured, and can even be white, while some boars from Belarus and Ussuriland can be black. Some subspecies sport a light-coloured patch running backward from the corners of the mouth. Coat colour also varies with age, with piglets having light brown or rusty-brown fur with pale bands extending from the flanks and back.
The wild boar produces a number of different sounds which are divided into three categories:
* Contact calls: Grunting noises which differ in intensity according to the situation. Adult males are usually silent, while females frequently grunt and piglets whine. When feeding, boars express their contentment through purring. Studies have shown that piglets imitate the sounds of their mother, thus different litters may have unique vocalisations.
* Alarm calls: Warning cries emitted in response to threats. When frightened, boars make loud huffing ''ukh! ukh!'' sounds or emit screeches transcribed as ''gu-gu-gu''.
* Combat calls: High-pitched, piercing cries.
Its sense of
 The period in most areas lasts from November to January, though most mating only lasts a month and a half. Prior to mating, the males develop their subcutaneous armour in preparation for confronting rivals. The testicles double in size and the glands secrete a foamy yellowish liquid. Once ready to reproduce, males travel long distances in search of a sounder of sows, eating little on the way. Once a sounder has been located, the male drives off all young animals and persistently chases the sows. At this point, the male fiercely fights potential rivals. A single male can mate with 5–10 sows. By the end of the rut, males are often badly mauled and have lost 20% of their body weight, with bite-induced injuries to the penis being common. The
The period in most areas lasts from November to January, though most mating only lasts a month and a half. Prior to mating, the males develop their subcutaneous armour in preparation for confronting rivals. The testicles double in size and the glands secrete a foamy yellowish liquid. Once ready to reproduce, males travel long distances in search of a sounder of sows, eating little on the way. Once a sounder has been located, the male drives off all young animals and persistently chases the sows. At this point, the male fiercely fights potential rivals. A single male can mate with 5–10 sows. By the end of the rut, males are often badly mauled and have lost 20% of their body weight, with bite-induced injuries to the penis being common. The  Newborn piglets weigh around 600–1,000 grams, lacking underfur and bearing a single milk incisor and canine on each half of the jaw. There is intense competition between the piglets over the most milk-rich nipples, as the best-fed young grow faster and have stronger constitutions. The piglets do not leave the lair for their first week of life. Should the mother be absent, the piglets lie closely pressed to each other. By two weeks of age, the piglets begin accompanying their mother on her journeys. Should danger be detected, the piglets take cover or stand immobile, relying on their camouflage to keep them hidden. The neonatal coat fades after three months, with adult colouration being attained at eight months. Although the lactation period lasts 2.5–3.5 months, the piglets begin displaying adult feeding behaviours at the age of 2–3 weeks. The permanent dentition is fully formed by 1–2 years. With the exception of the canines in males, the teeth stop growing during the middle of the fourth year. The canines in old males continue to grow throughout their lives, curving strongly as they age. Sows attain sexual maturity at the age of one year, with males attaining it a year later. However, estrus usually first occurs after two years in sows, while males begin participating in the rut after 4–5 years, as they are not permitted to mate by the older males. The maximum lifespan in the wild is 10–14 years, though few specimens survive past 4–5 years. Boars in captivity have lived for 20 years.
Newborn piglets weigh around 600–1,000 grams, lacking underfur and bearing a single milk incisor and canine on each half of the jaw. There is intense competition between the piglets over the most milk-rich nipples, as the best-fed young grow faster and have stronger constitutions. The piglets do not leave the lair for their first week of life. Should the mother be absent, the piglets lie closely pressed to each other. By two weeks of age, the piglets begin accompanying their mother on her journeys. Should danger be detected, the piglets take cover or stand immobile, relying on their camouflage to keep them hidden. The neonatal coat fades after three months, with adult colouration being attained at eight months. Although the lactation period lasts 2.5–3.5 months, the piglets begin displaying adult feeding behaviours at the age of 2–3 weeks. The permanent dentition is fully formed by 1–2 years. With the exception of the canines in males, the teeth stop growing during the middle of the fourth year. The canines in old males continue to grow throughout their lives, curving strongly as they age. Sows attain sexual maturity at the age of one year, with males attaining it a year later. However, estrus usually first occurs after two years in sows, while males begin participating in the rut after 4–5 years, as they are not permitted to mate by the older males. The maximum lifespan in the wild is 10–14 years, though few specimens survive past 4–5 years. Boars in captivity have lived for 20 years.

 The wild boar inhabits a diverse array of habitats from boreal taigas to
The wild boar inhabits a diverse array of habitats from boreal taigas to
 The wild boar is a highly versatile
The wild boar is a highly versatile
 Piglets are vulnerable to attack from medium-sized felids like Eurasian lynx (''Lynx lynx''), jungle cats (''Felis chaus''), and snow leopards (''Panthera uncia''), as well as other carnivorans like brown bears (''Ursus arctos'') and yellow-throated martens (''Martes flavigula'').
The wolf (''Canis lupus'') is the main predator of wild boar throughout most of its range. A single wolf can kill around 50 to 80 boars of differing ages in one year. In Italy and Belarus' Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park, boars are the wolf's primary prey, despite an abundance of alternative, less powerful ungulates. Wolves are particularly threatening during the winter, when deep snow impedes the boars' movements. In the Baltic regions, heavy snowfall can allow wolves to eliminate boars from an area almost completely. Wolves primarily target piglets and subadults and only rarely attack adult sows. Adult males are usually avoided entirely. Dholes (''Cuon alpinus'') may also prey on boars, to the point of keeping their numbers down in northwestern Bhutan, despite there being many more cattle in the area.
Piglets are vulnerable to attack from medium-sized felids like Eurasian lynx (''Lynx lynx''), jungle cats (''Felis chaus''), and snow leopards (''Panthera uncia''), as well as other carnivorans like brown bears (''Ursus arctos'') and yellow-throated martens (''Martes flavigula'').
The wolf (''Canis lupus'') is the main predator of wild boar throughout most of its range. A single wolf can kill around 50 to 80 boars of differing ages in one year. In Italy and Belarus' Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park, boars are the wolf's primary prey, despite an abundance of alternative, less powerful ungulates. Wolves are particularly threatening during the winter, when deep snow impedes the boars' movements. In the Baltic regions, heavy snowfall can allow wolves to eliminate boars from an area almost completely. Wolves primarily target piglets and subadults and only rarely attack adult sows. Adult males are usually avoided entirely. Dholes (''Cuon alpinus'') may also prey on boars, to the point of keeping their numbers down in northwestern Bhutan, despite there being many more cattle in the area.

 Wild boars were apparently already becoming rare by the 11th century; a 1087 forestry law enacted by William the Conqueror punished through blinding the unlawful killing of a boar. Charles I attempted to reintroduce the species into the New Forest, though this population was exterminated during the Civil War. Between their medieval extinction and the 1980s, when wild boar farming began, only a handful of captive wild boar, imported from the continent, were present in Britain. Occasional escapes of wild boar from wildlife parks have occurred as early as the 1970s, but since the early 1990s significant populations have re-established themselves after escapes from farms, the number of which has increased as the demand for meat from the species has grown. A 1998 MAFF (now DEFRA) study on wild boar living wild in Britain confirmed the presence of two populations of wild boar living in Britain; one in Kent/
Wild boars were apparently already becoming rare by the 11th century; a 1087 forestry law enacted by William the Conqueror punished through blinding the unlawful killing of a boar. Charles I attempted to reintroduce the species into the New Forest, though this population was exterminated during the Civil War. Between their medieval extinction and the 1980s, when wild boar farming began, only a handful of captive wild boar, imported from the continent, were present in Britain. Occasional escapes of wild boar from wildlife parks have occurred as early as the 1970s, but since the early 1990s significant populations have re-established themselves after escapes from farms, the number of which has increased as the demand for meat from the species has grown. A 1998 MAFF (now DEFRA) study on wild boar living wild in Britain confirmed the presence of two populations of wild boar living in Britain; one in Kent/
 Wild boars are an
Wild boars are an
Wild Pigs: Biology, Damage, Control Techniques and Management
'', Savannah River National Laboratory Aiken, South Carolina, SRNL-RP-2009-00869 In 1902, 15–20 wild boar from Germany were released into a estate in Hamilton County, New York. Several specimens escaped six years later, dispersing into the William C. Whitney Wilderness Area, with their descendants surviving for at least 20 years. The most extensive boar introduction in the US took place in western North Carolina in 1912, when 13 boars of undetermined European origin were released into two fenced enclosures in a game preserve in
 In South America, the European boar is believed to have been introduced for the first time in Argentina and Uruguay around the 20th century for breeding purposes. In Brazil, the creation of wild boar and hybrids started on a large scale in the mid-1990s. With the invasion of wild boar that crossed the border and entered
In South America, the European boar is believed to have been introduced for the first time in Argentina and Uruguay around the 20th century for breeding purposes. In Brazil, the creation of wild boar and hybrids started on a large scale in the mid-1990s. With the invasion of wild boar that crossed the border and entered
 Wild boars are known to host at least 20 different parasitic worm species, with maximum infections occurring in summer. Young animals are vulnerable to
Wild boars are known to host at least 20 different parasitic worm species, with maximum infections occurring in summer. Young animals are vulnerable to

 The wild boar features prominently in the cultures of Indo-European people, many of which saw the animal as embodying warrior virtues. Cultures throughout Europe and Asia Minor saw the killing of a boar as proof of one's valor and strength. Neolithic hunter gatherers depicted reliefs of ferocious wild boars on their temple pillars at Göbekli Tepe some 11,600 years ago. Virtually all heroes in Greek mythology fight or kill a boar at one point. The demigod Herakles' third labour involves the capture of the Erymanthian Boar, Theseus slays the wild sow
The wild boar features prominently in the cultures of Indo-European people, many of which saw the animal as embodying warrior virtues. Cultures throughout Europe and Asia Minor saw the killing of a boar as proof of one's valor and strength. Neolithic hunter gatherers depicted reliefs of ferocious wild boars on their temple pillars at Göbekli Tepe some 11,600 years ago. Virtually all heroes in Greek mythology fight or kill a boar at one point. The demigod Herakles' third labour involves the capture of the Erymanthian Boar, Theseus slays the wild sow 
 The boar as a warrior also appears in
The boar as a warrior also appears in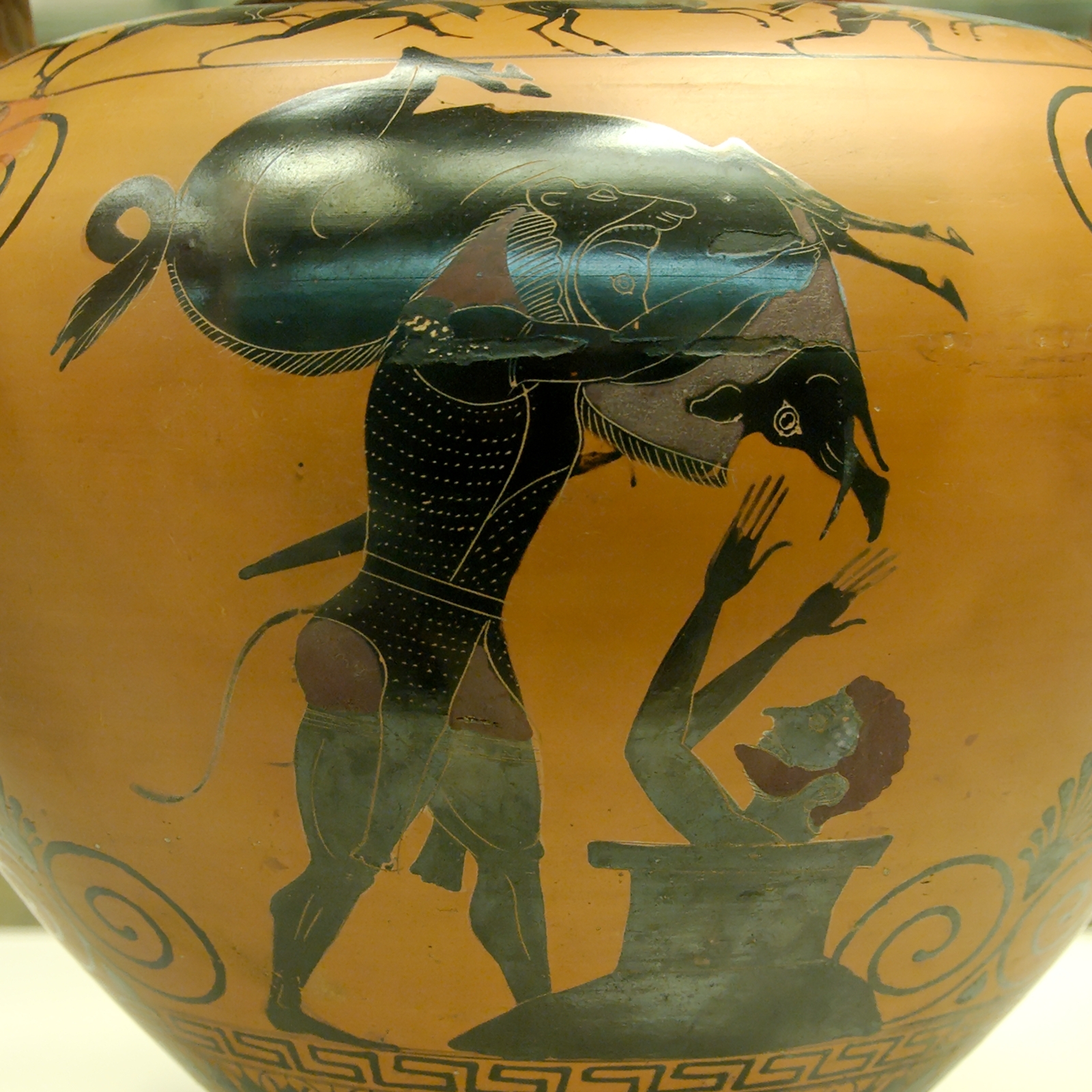  In
In

 Humans have been hunting boar for millennia, the earliest artistic depictions of such activities dating back to the Upper Paleolithic. The animal was seen as a source of food among the Ancient Greeks, as well as a sporting challenge and source of epic narratives. The Romans inherited this tradition, with one of its first practitioners being Scipio Aemilianus. Boar hunting became particularly popular among the young nobility during the 3rd century BC as preparation for manhood and battle. A typical Roman boar hunting tactic involved surrounding a given area with large nets, then flushing the boar with dogs and immobilizing it with smaller nets. The animal would then be dispatched with a ''venabulum'', a short spear with a crossguard at the base of the blade. More than their Greek predecessors, the Romans extensively took inspiration from boar hunting in their art and sculpture. With the ascension of
Humans have been hunting boar for millennia, the earliest artistic depictions of such activities dating back to the Upper Paleolithic. The animal was seen as a source of food among the Ancient Greeks, as well as a sporting challenge and source of epic narratives. The Romans inherited this tradition, with one of its first practitioners being Scipio Aemilianus. Boar hunting became particularly popular among the young nobility during the 3rd century BC as preparation for manhood and battle. A typical Roman boar hunting tactic involved surrounding a given area with large nets, then flushing the boar with dogs and immobilizing it with smaller nets. The animal would then be dispatched with a ''venabulum'', a short spear with a crossguard at the base of the blade. More than their Greek predecessors, the Romans extensively took inspiration from boar hunting in their art and sculpture. With the ascension of
A Guide to Traditional Pig Keeping
', Good Life Press, pp. 26–27, being of higher nutritional value and having a much higher concentration of essential amino acids. Most meat-dressing organizations agree that a boar carcass should yield of meat on average. Large specimens can yield of fat, with some giants yielding or more. A boar hide can measure and can yield of bristle and of underwool.
File:EberreliefmitHund-3Jhrnchr-FOKoeln2.jpg, Roman relief of a dog confronting a boar, Cologne
File:Südindischer Meister um 1540 002.jpg, Southern Indian depiction of boar hunt, c. 1540
File:Modern Pig-Sticking (1914) A. E. Wardrop I.png, Pig-sticking in British India
File:Регулирование численности кабана (1).jpg, Boar shot in
 Boars can be damaging to agriculture in situations where their natural habitat is sparse. Populations living on the outskirts of towns or farms can dig up potatoes and damage melons, watermelons and maize. However, they generally only encroach upon farms when natural food is scarce. In the Belovezh forest for example, 34–47% of the local boar population will enter fields in years of moderate availability of natural foods. While the role of boars in damaging crops is often exaggerated, cases are known of boar depredations causing
Boars can be damaging to agriculture in situations where their natural habitat is sparse. Populations living on the outskirts of towns or farms can dig up potatoes and damage melons, watermelons and maize. However, they generally only encroach upon farms when natural food is scarce. In the Belovezh forest for example, 34–47% of the local boar population will enter fields in years of moderate availability of natural foods. While the role of boars in damaging crops is often exaggerated, cases are known of boar depredations causing
"Wild Pig Attacks on Humans"
Wildlife Damage Management Conferences – Proceedings. Paper 151.
 Defining the limits of proper management is difficult, but the exclusion of wild boar from rare environments is generally agreed upon, as when not properly managed, they can damage agricultural ventures and harm vulnerable plant life. These damages are estimated at $800 million yearly in environmental and financial costs for the United States alone. The breadth of this damage is due to prior inattention and lack of management tactics for extended lengths of time. Managing wild boar is a complex task, as it involves coordinating a combination of crop harvest techniques, fencing, toxic bait, corrals, and hunting. The most common tactic employed by private land owners in the United States is recreational hunting, however, this is generally not as effective on its own. Management strategies are most successful when they take into account reproduction, dispersion, and the differences between ideal resources for males and females.
Defining the limits of proper management is difficult, but the exclusion of wild boar from rare environments is generally agreed upon, as when not properly managed, they can damage agricultural ventures and harm vulnerable plant life. These damages are estimated at $800 million yearly in environmental and financial costs for the United States alone. The breadth of this damage is due to prior inattention and lack of management tactics for extended lengths of time. Managing wild boar is a complex task, as it involves coordinating a combination of crop harvest techniques, fencing, toxic bait, corrals, and hunting. The most common tactic employed by private land owners in the United States is recreational hunting, however, this is generally not as effective on its own. Management strategies are most successful when they take into account reproduction, dispersion, and the differences between ideal resources for males and females.
"The systematics of the wild boar (''Sus scrofa'' L.) in Italy"
''Bolletino di Zoologia''a, 3:213–221 * Carden, R.F. (2012
"Review of the Natural History of Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) on the island of Ireland"
Report prepared by Ruth Carden for the Northern Ireland Environment Agency, Northern Ireland, UK, National Parks & Wildlife Service, Department of Arts, Heritage and the Gaeltacht, Dublin, Ireland and the National Museum of Ireland – Education & Outreach Department. * Durantel, P. (2007), ''Le sanglier et ses chasses'', Editions Artemis, * Greene, J. (2011), ''The Golden-Bristled Boar: Last Ferocious Beast of the Forest'', University of Virginia Press, * Hatto, A. T. (1957) "Snake‐swords and Boar‐helms in Beowulf". In: ''English Studies'', 38:1–6, 145–160. DOI: 10.1080/00138385708596994 * Marillier, B. (2003), ''Le sanglier héraldique'', Editions Cheminements, * Mayer, J. J. & Shedrow, C. B. (2007),
Annotated Bibliography of the Wild Pig (Sus scrofa): Environmental Information Document
', Washington Savannah River Company * Padiglione, V. (1989), ''Il cinghiale cacciatore: Antropologia simbolica della caccia in Sardegna'', Armando Editore (collana Antropologia culturale) *
BBC profile
* *
Species Profile- Wild Boar (''Sus scrofa'')
National Invasive Species Information Center, United States National Agricultural Library. Lists general information and resources for wild boar. *
A sounder of wild boars
Wild pigs with piglets – white piglets with black spots
Sow feeding piglets, Lodz (Poland)
A wild boar struggling with plastic film, Lodz (Poland
{{Authority control Extant Pleistocene first appearances Palearctic fauna Introduced mammals of Australia wild boar Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Sus (genus)
the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
and Oceania. The species is now one of the widest-ranging mammals in the world, as well as the most widespread suiform. It has been assessed as least concern on the IUCN Red List due to its wide range, high numbers, and adaptability to a diversity of habitats. It has become an invasive species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species ad ...
in part of its introduced range. Wild boars probably originated in Southeast Asia during the Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
and outcompeted other suid species as they spread throughout the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by the ...
.
, up to 16 subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
are recognized, which are divided into four regional groupings based on skull height and lacrimal bone length. The species lives in matriarchal societies consisting of interrelated females and their young (both male and female). Fully grown males are usually solitary outside the breeding season
Seasonal breeders are animal species that successfully mate only during certain times of the year. These times of year allow for the optimization of survival of young due to factors such as ambient temperature, food and water availability, and cha ...
. The wolf is the wild boar's main predator in most of its natural range except in the Far East and the Lesser Sunda Islands
The Lesser Sunda Islands or nowadays known as Nusa Tenggara Islands ( id, Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, formerly ) are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up t ...
, where it is replaced by the tiger and Komodo dragon respectively. The wild boar has a long history of association with humans, having been the ancestor of most domestic pig breeds and a big-game animal for millennia. Boars have also re- hybridized in recent decades with feral pigs; these boar–pig hybrids have become a serious pest wild animal in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
.
Terminology
As true wild boars became extinct in Great Britain before the development of Modern English, the same terms are often used for both true wild boar and pigs, especially large or semi-wild ones. The English ''boar'' stems from theOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
, which is thought to be derived from the West Germanic ''bairaz'', of unknown origin. Boar is sometimes used specifically to refer to males, and may also be used to refer to male domesticated pigs, especially breeding males that have not been castrated.
''Sow'', the traditional name for a female, again comes from Old English and Germanic; it stems from Proto-Indo-European, and is related to the lat, sus and Greek ''hus'', and more closely to the New High German . The young may be called ''piglets'' or ''boarlets''.
The animals' specific name ''scrofa'' is Latin for 'sow'.
Hunting
In hunting terminology, boars are given different designations according to their age:Taxonomy and evolution
Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
.Ruvinsky, A. et al. (2011). "Systematics and evolution of the pig". In: Ruvinsky A, Rothschild MF (eds), ''The Genetics of the Pig''. 2nd ed. CAB International, Oxon. pp. 1–13. By the late Villafranchian, ''S. scrofa'' largely displaced the related '' S. strozzii'', a large, possibly swamp-adapted suid ancestral to the modern '' S. verrucosus'' throughout the Eurasian mainland, restricting it to insular Asia.Kurtén, Björn (1968). Pleistocene mammals of Europe. Weidenfeld and Nicolson. pp. 153–155 Its closest wild relative is the bearded pig of Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
and surrounding islands.
Subspecies
 , 16 subspecies are recognised, which are divided into four regional groupings:
* Western: Includes ''S. s. scrofa'', ''S. s. meridionalis'', ''S. s. algira'', ''S. s. attila'', ''S. s. lybicus'' and ''S. s. nigripes''. These subspecies are typically high-skulled (though ''lybicus'' and some ''scrofa'' are low-skulled), with thick underwool and (excepting ''scrofa'' and ''attila'') poorly developed manes.Groves, C. P. et al. 1993. The Eurasian Suids ''Sus'' and ''Babyrousa''. In Oliver, W. L. R., ed., ''Pigs, Peccaries, and Hippos – 1993 Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan'', 107–108. IUCN/SSC Pigs and Peccaries Specialist Group,
* Indian: Includes ''S. s. davidi'' and ''S. s. cristatus''. These subspecies have sparse or absent underwool, with long manes and prominent bands on the snout and mouth. While ''S. s. cristatus'' is high-skulled, ''S. s. davidi'' is low-skulled.
* Eastern: Includes ''S. s. sibiricus'', ''S. s. ussuricus'', ''S. s. leucomystax'', ''S. s. riukiuanus'', ''S. s. taivanus'' and ''S. s. moupinensis''. These subspecies are characterised by a whitish streak extending from the corners of the mouth to the lower jaw. With the exception of ''S. s. ussuricus'', most are high-skulled. The underwool is thick, except in ''S. s. moupinensis'', and the mane is largely absent.
* Indonesian: Represented solely by ''S. s. vittatus'', it is characterised by its sparse body hair, lack of underwool, fairly long mane, a broad reddish band extending from the muzzle to the sides of the neck. It is the most
, 16 subspecies are recognised, which are divided into four regional groupings:
* Western: Includes ''S. s. scrofa'', ''S. s. meridionalis'', ''S. s. algira'', ''S. s. attila'', ''S. s. lybicus'' and ''S. s. nigripes''. These subspecies are typically high-skulled (though ''lybicus'' and some ''scrofa'' are low-skulled), with thick underwool and (excepting ''scrofa'' and ''attila'') poorly developed manes.Groves, C. P. et al. 1993. The Eurasian Suids ''Sus'' and ''Babyrousa''. In Oliver, W. L. R., ed., ''Pigs, Peccaries, and Hippos – 1993 Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan'', 107–108. IUCN/SSC Pigs and Peccaries Specialist Group,
* Indian: Includes ''S. s. davidi'' and ''S. s. cristatus''. These subspecies have sparse or absent underwool, with long manes and prominent bands on the snout and mouth. While ''S. s. cristatus'' is high-skulled, ''S. s. davidi'' is low-skulled.
* Eastern: Includes ''S. s. sibiricus'', ''S. s. ussuricus'', ''S. s. leucomystax'', ''S. s. riukiuanus'', ''S. s. taivanus'' and ''S. s. moupinensis''. These subspecies are characterised by a whitish streak extending from the corners of the mouth to the lower jaw. With the exception of ''S. s. ussuricus'', most are high-skulled. The underwool is thick, except in ''S. s. moupinensis'', and the mane is largely absent.
* Indonesian: Represented solely by ''S. s. vittatus'', it is characterised by its sparse body hair, lack of underwool, fairly long mane, a broad reddish band extending from the muzzle to the sides of the neck. It is the most basal
Basal or basilar is a term meaning ''base'', ''bottom'', or ''minimum''.
Science
* Basal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location for features associated with the base of an organism or structure
* Basal (medicine), a minimal level that is nec ...
of the four groups, having the smallest relative brain size, more primitive dentition and unspecialised cranial structure.Hemmer, H. (1990), ''Domestication: The Decline of Environmental Appreciation'', Cambridge University Press, pp. 55–59,
Domestication
 With the exception of domestic pigs in Timor and Papua New Guinea (which appear to be of
With the exception of domestic pigs in Timor and Papua New Guinea (which appear to be of Sulawesi warty pig
The Celebes warty pig (''Sus celebensis''), also called Sulawesi warty pig or Sulawesi pig, is a species in the pig genus ('' Sus'') that lives on Sulawesi in Indonesia. It survives in most habitats and can live in altitudes of up to . It has bee ...
stock), the wild boar is the ancestor of most pig breeds. Archaeological evidence suggests that pigs were domesticated from wild boar as early as 13,000–12,700 BCE in the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
in the Tigris Basin, being managed in the wild in a way similar to the way they are managed by some modern New Guineans. Remains of pigs have been dated to earlier than 11,400 BCE in Cyprus. Those animals must have been introduced from the mainland, which suggests domestication in the adjacent mainland by then. There was also a separate domestication in China, which took place about 8,000 years ago.
DNA evidence from sub-fossil remains of teeth and jawbones of Neolithic pigs shows that the first domestic pigs in Europe had been brought from the Near East. This stimulated the domestication of local European wild boars, resulting in a third domestication event with the Near Eastern genes dying out in European pig stock. Modern domesticated pigs have involved complex exchanges, with European domesticated lines being exported in turn to the ancient Near East. Historical records indicate that Asian pigs were introduced into Europe during the 18th and early 19th centuries. Domestic pigs tend to have much more developed hindquarters than their wild boar ancestors, to the point where 70% of their body weight is concentrated in the posterior, which is the opposite of wild boar, where most of the muscles are concentrated on the head and shoulders.
Synonymous species
The Heude's pig (''Sus bucculentus''), also known as the Indochinese warty pig or Vietnam warty pig, was an alleged pig species found inLaos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist ...
and Vietnam. It was virtually unknown and was feared extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
, until the discovery of a skull from a recently killed individual in the Annamite Range, Laos, in 1995. Subsequent studies indicated that ''Sus bucculentus'' was not a valid taxon. As of 2022 the Mammal Diversity Database included it in ''Sus scrofa''.
Description
 The wild boar is a bulky, massively built suid with short and relatively thin legs. The trunk is short and robust, while the hindquarters are comparatively underdeveloped. The region behind the shoulder blades rises into a hump and the neck is short and thick to the point of being nearly immobile. The animal's head is very large, taking up to one-third of the body's entire length. The structure of the head is well suited for digging. The head acts as a plough, while the powerful neck muscles allow the animal to upturn considerable amounts of soil: it is capable of digging into frozen ground and can upturn rocks weighing . The eyes are small and deep-set and the ears long and broad. The species has well developed canine teeth, which protrude from the mouths of adult males. The medial hooves are larger and more elongated than the lateral ones and are capable of quick movements. The animal can run at a maximum speed of 40 km/h (25 mph) and jump at a height of .
Sexual dimorphism is very pronounced in the species, with males being typically 5–10% larger and 20–30% heavier than females. Males also sport a mane running down the back, which is particularly apparent during autumn and winter. The canine teeth are also much more prominent in males and grow throughout life. The upper canines are relatively short and grow sideways early in life, though they gradually curve upwards. The lower canines are much sharper and longer, with the exposed parts measuring in length. In the breeding period, males develop a coating of
The wild boar is a bulky, massively built suid with short and relatively thin legs. The trunk is short and robust, while the hindquarters are comparatively underdeveloped. The region behind the shoulder blades rises into a hump and the neck is short and thick to the point of being nearly immobile. The animal's head is very large, taking up to one-third of the body's entire length. The structure of the head is well suited for digging. The head acts as a plough, while the powerful neck muscles allow the animal to upturn considerable amounts of soil: it is capable of digging into frozen ground and can upturn rocks weighing . The eyes are small and deep-set and the ears long and broad. The species has well developed canine teeth, which protrude from the mouths of adult males. The medial hooves are larger and more elongated than the lateral ones and are capable of quick movements. The animal can run at a maximum speed of 40 km/h (25 mph) and jump at a height of .
Sexual dimorphism is very pronounced in the species, with males being typically 5–10% larger and 20–30% heavier than females. Males also sport a mane running down the back, which is particularly apparent during autumn and winter. The canine teeth are also much more prominent in males and grow throughout life. The upper canines are relatively short and grow sideways early in life, though they gradually curve upwards. The lower canines are much sharper and longer, with the exposed parts measuring in length. In the breeding period, males develop a coating of subcutaneous tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macr ...
, which may be thick, extending from the shoulder blades to the rump, thus protecting vital organs during fights. Males sport a roughly egg-sized sack near the opening of the penis, which collects urine and emits a sharp odour. The function of this sack is not fully understood.

 Adult size and weight is largely determined by environmental factors; boars living in arid areas with little productivity tend to attain smaller sizes than their counterparts inhabiting areas with abundant food and water. In most of Europe, males average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length, whereas females average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length. In Europe's Mediterranean regions, males may reach average weights as low as and females , with shoulder heights of . In the more productive areas of Eastern Europe, males average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length, while females weigh , reach in shoulder height, and reach in body length. In Western and Central Europe, the largest males weigh and females . In Northeastern Asia, large males can reach brown bear-like sizes, weighing and measuring in shoulder height. Some adult males in Ussuriland and Manchuria have been recorded to weigh and measure in shoulder height. Adults of this size are generally immune from wolf predation. Such giants are rare in modern times, due to past overhunting preventing animals from attaining their full growth.
The winter coat consists of long, coarse bristles underlaid with short brown downy fur. The length of these bristles varies along the body, with the shortest being around the face and limbs and the longest running along the back. These back bristles form the aforementioned mane prominent in males and stand erect when the animal is agitated. Colour is highly variable; specimens around Lake Balkhash are very lightly coloured, and can even be white, while some boars from Belarus and Ussuriland can be black. Some subspecies sport a light-coloured patch running backward from the corners of the mouth. Coat colour also varies with age, with piglets having light brown or rusty-brown fur with pale bands extending from the flanks and back.
The wild boar produces a number of different sounds which are divided into three categories:
* Contact calls: Grunting noises which differ in intensity according to the situation. Adult males are usually silent, while females frequently grunt and piglets whine. When feeding, boars express their contentment through purring. Studies have shown that piglets imitate the sounds of their mother, thus different litters may have unique vocalisations.
* Alarm calls: Warning cries emitted in response to threats. When frightened, boars make loud huffing ''ukh! ukh!'' sounds or emit screeches transcribed as ''gu-gu-gu''.
* Combat calls: High-pitched, piercing cries.
Its sense of
Adult size and weight is largely determined by environmental factors; boars living in arid areas with little productivity tend to attain smaller sizes than their counterparts inhabiting areas with abundant food and water. In most of Europe, males average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length, whereas females average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length. In Europe's Mediterranean regions, males may reach average weights as low as and females , with shoulder heights of . In the more productive areas of Eastern Europe, males average in weight, in shoulder height and in body length, while females weigh , reach in shoulder height, and reach in body length. In Western and Central Europe, the largest males weigh and females . In Northeastern Asia, large males can reach brown bear-like sizes, weighing and measuring in shoulder height. Some adult males in Ussuriland and Manchuria have been recorded to weigh and measure in shoulder height. Adults of this size are generally immune from wolf predation. Such giants are rare in modern times, due to past overhunting preventing animals from attaining their full growth.
The winter coat consists of long, coarse bristles underlaid with short brown downy fur. The length of these bristles varies along the body, with the shortest being around the face and limbs and the longest running along the back. These back bristles form the aforementioned mane prominent in males and stand erect when the animal is agitated. Colour is highly variable; specimens around Lake Balkhash are very lightly coloured, and can even be white, while some boars from Belarus and Ussuriland can be black. Some subspecies sport a light-coloured patch running backward from the corners of the mouth. Coat colour also varies with age, with piglets having light brown or rusty-brown fur with pale bands extending from the flanks and back.
The wild boar produces a number of different sounds which are divided into three categories:
* Contact calls: Grunting noises which differ in intensity according to the situation. Adult males are usually silent, while females frequently grunt and piglets whine. When feeding, boars express their contentment through purring. Studies have shown that piglets imitate the sounds of their mother, thus different litters may have unique vocalisations.
* Alarm calls: Warning cries emitted in response to threats. When frightened, boars make loud huffing ''ukh! ukh!'' sounds or emit screeches transcribed as ''gu-gu-gu''.
* Combat calls: High-pitched, piercing cries.
Its sense of smell
Smell may refer to;
* Odor, airborne molecules perceived as a scent or aroma
* Sense of smell, the scent also known scientifically as olfaction
* "Smells" (''Bottom''), an episode of ''Bottom''
* The Smell, a music venue in Los Angeles, Californ ...
is very well developed to the point that the animal is used for drug detection in Germany. Its hearing is also acute, though its eyesight is comparatively weak, lacking color vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
and being unable to recognise a standing human away.
Pigs are one of four known mammalian taxa which possess mutations in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor that protect against snake venom. Mongooses, honey badgers, hedgehogs, and pigs all have modifications to the receptor pocket which prevents the snake venom
Snake venom is a highly toxic saliva containing zootoxins that facilitates in the immobilization and digestion of prey. This also provides defense against threats. Snake venom is injected by unique fangs during a bite, whereas some species are a ...
α-neurotoxin from binding. These represent four separate, independent mutations.
Social behaviour and life cycle
Boars are typically social animals, living in female-dominated sounders consisting of barren sows and mothers with young led by an old matriarch. Male boars leave their sounder at the age of 8–15 months, while females either remain with their mothers or establish new territories nearby. Subadult males may live in loosely knit groups, while adult and elderly males tend to be solitary outside the breeding season.gestation period
In mammals, pregnancy is the period of reproduction during which a female carries one or more live offspring from implantation in the uterus through gestation. It begins when a fertilized zygote implants in the female's uterus, and ends once it ...
varies according to the age of the expecting mother. For first-time breeders, it lasts 114–130 days, while it lasts 133–140 days in older sows. Farrowing occurs between March and May, with litter sizes depending on the age and nutrition of the mother. The average litter consists of 4–6 piglets, with the maximum being 10–12. The piglets are whelped in a nest constructed from twigs, grasses and leaves. Should the mother die prematurely, the piglets are adopted by the other sows in the sounder.
 Newborn piglets weigh around 600–1,000 grams, lacking underfur and bearing a single milk incisor and canine on each half of the jaw. There is intense competition between the piglets over the most milk-rich nipples, as the best-fed young grow faster and have stronger constitutions. The piglets do not leave the lair for their first week of life. Should the mother be absent, the piglets lie closely pressed to each other. By two weeks of age, the piglets begin accompanying their mother on her journeys. Should danger be detected, the piglets take cover or stand immobile, relying on their camouflage to keep them hidden. The neonatal coat fades after three months, with adult colouration being attained at eight months. Although the lactation period lasts 2.5–3.5 months, the piglets begin displaying adult feeding behaviours at the age of 2–3 weeks. The permanent dentition is fully formed by 1–2 years. With the exception of the canines in males, the teeth stop growing during the middle of the fourth year. The canines in old males continue to grow throughout their lives, curving strongly as they age. Sows attain sexual maturity at the age of one year, with males attaining it a year later. However, estrus usually first occurs after two years in sows, while males begin participating in the rut after 4–5 years, as they are not permitted to mate by the older males. The maximum lifespan in the wild is 10–14 years, though few specimens survive past 4–5 years. Boars in captivity have lived for 20 years.
Newborn piglets weigh around 600–1,000 grams, lacking underfur and bearing a single milk incisor and canine on each half of the jaw. There is intense competition between the piglets over the most milk-rich nipples, as the best-fed young grow faster and have stronger constitutions. The piglets do not leave the lair for their first week of life. Should the mother be absent, the piglets lie closely pressed to each other. By two weeks of age, the piglets begin accompanying their mother on her journeys. Should danger be detected, the piglets take cover or stand immobile, relying on their camouflage to keep them hidden. The neonatal coat fades after three months, with adult colouration being attained at eight months. Although the lactation period lasts 2.5–3.5 months, the piglets begin displaying adult feeding behaviours at the age of 2–3 weeks. The permanent dentition is fully formed by 1–2 years. With the exception of the canines in males, the teeth stop growing during the middle of the fourth year. The canines in old males continue to grow throughout their lives, curving strongly as they age. Sows attain sexual maturity at the age of one year, with males attaining it a year later. However, estrus usually first occurs after two years in sows, while males begin participating in the rut after 4–5 years, as they are not permitted to mate by the older males. The maximum lifespan in the wild is 10–14 years, though few specimens survive past 4–5 years. Boars in captivity have lived for 20 years.
Behaviour and ecology
Habitat and sheltering

 The wild boar inhabits a diverse array of habitats from boreal taigas to
The wild boar inhabits a diverse array of habitats from boreal taigas to desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
s. In mountainous regions, it can even occupy alpine zones, occurring up to in the Carpathians, in the Caucasus and up to in the mountains in Central Asia and Kazakhstan. In order to survive in a given area, wild boars require a habitat fulfilling three conditions: heavily brushed areas providing shelter from predators, water for drinking and bathing purposes and an absence of regular snowfall.
The main habitats favored by boars in Europe are deciduous and mixed forests, with the most favorable areas consisting of forest composed of oak and beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
enclosing marshes and meadows. In the Białowieża Forest, the animal's primary habitat consists of well-developed broad-leaved and mixed forests, along with marshy mixed forests, with coniferous
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant ...
forests and undergrowths being of secondary importance. Forests made up entirely of oak groves and beeches are used only during the fruit-bearing season. This is in contrast to the Caucasian and Transcaucasian mountain areas, where boars will occupy such fruit-bearing forests year-round. In the mountainous areas of the Russian Far East, the species inhabits nutpine groves, hilly mixed forests where Mongolian oak and Korean pine are present, swampy mixed taiga and coastal oak forests. In Transbaikalia, boars are restricted to river valleys with nut pine and shrubs. Boars are regularly encountered in pistachio
The pistachio (, ''Pistacia vera''), a member of the cashew family, is a small tree originating from Central Asia and the Middle East. The tree produces seeds that are widely consumed as food.
''Pistacia vera'' is often confused with other sp ...
groves in winter in some areas of Tajikistan and Turkmenistan, while in spring they migrate to open deserts; boar have also colonized deserts in several areas they have been introduced to.
On the islands of Komodo and Rinca, the boar mostly inhabits savanna or open monsoon forests, avoiding heavily forested areas unless pursued by humans. Wild boar are known to be competent swimmers, capable of covering long distances. In 2013, one boar was reported to have completed the swim from France to Alderney
Alderney (; french: Aurigny ; Auregnais: ) is the northernmost of the inhabited Channel Islands. It is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown dependency. It is long and wide.
The island's area is , making it the third-largest ...
in the Channel Islands. Due to concerns about disease, it was shot and incinerated.
Wild boar rest in shelters, which contain insulating material like spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfami ...
branches and dry hay. These resting places are occupied by whole families (though males lie separately) and are often located in the vicinity of streams, in swamp forests and in tall grass or shrub thickets. Boars never defecate in their shelters and will cover themselves with soil and pine needles when irritated by insects.
Diet
 The wild boar is a highly versatile
The wild boar is a highly versatile omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutr ...
, whose diversity in choice of food is comparable to that of humans. Their foods can be divided into four categories:
* Rhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome (; , ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and shoots from its nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from axillary buds and grow hori ...
s, roots, tubers and bulb
In botany, a bulb is structurally a short stem with fleshy leaves or leaf basesBell, A.D. 1997. ''Plant form: an illustrated guide to flowering plant morphology''. Oxford University Press, Oxford, U.K. that function as food storage organs duri ...
s, all of which are dug up throughout the year in the animal's whole range.
* Nuts
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Com ...
, berries and seeds, which are consumed when ripened and are dug up from the snow when necessary.
* Leaves
A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", wh ...
, bark
Bark may refer to:
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Places
* Bark, Germany
* Bark, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland
Arts, ...
, twigs and shoots, along with garbage
Garbage, trash, rubbish, or refuse is waste material that is discarded by humans, usually due to a perceived lack of utility. The term generally does not encompass bodily waste products, purely liquid or gaseous wastes, or toxic waste produc ...
.
* Earthworms, insects, mollusks, fish, rodents, insectivores, bird eggs, lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia alt ...
s, snakes, frogs and carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
. Most of these prey items are taken in warm periods.
A boar needs around 4,000–4,500 calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of on ...
s of food per day, though this required amount increases during winter and pregnancy, with the majority of its diet consisting of food items dug from the ground, like underground plant material and burrowing animals. Acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and borne ...
s and beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
nuts are invariably its most important food items in temperate zones, as they are rich in the carbohydrates necessary for the buildup of fat reserves needed to survive lean periods. In Western Europe, underground plant material favoured by boars includes bracken, willow herb, bulbs, meadow herb roots and bulbs and the bulbs of cultivated crops. Such food is favoured in early spring and summer, but may also be eaten in autumn and winter during beechnut and acorn crop failures. Should regular wild foods become scarce, boars will eat tree bark and fungi, as well as visit cultivated potato and artichoke fields. Boar soil disturbance and foraging have been shown to facilitate invasive
Invasive may refer to:
*Invasive (medical) procedure
*Invasive species
*Invasive observation, especially in reference to surveillance
*Invasively progressive spread of disease from one organ in the body to another, especially in reference to cancer ...
plants. Boars of the ''vittatus'' subspecies in Ujung Kulon National Park in Java differ from most other populations by their primarily frugivorous diet, which consists of 50 different fruit species, especially figs, thus making them important seed dispersers. The wild boar can consume numerous genera of poisonous plants without ill effect, including ''Aconitum
''Aconitum'' (), also known as aconite, monkshood, wolf's-bane, leopard's bane, mousebane, women's bane, devil's helmet, queen of poisons, or blue rocket, is a genus of over 250 species of flowering plants belonging to the family Ranunculaceae. ...
'', '' Anemone'', '' Calla'', '' Caltha'', '' Ferula'' and '' Pteridium''.
Boars may occasionally prey on small vertebrates like newborn deer fawns, leporids
Leporidae is the family of rabbits and hares, containing over 60 species of extant mammals in all. The Latin word ''Leporidae'' means "those that resemble ''lepus''" (hare). Together with the pikas, the Leporidae constitute the mammalian order ...
and galliform chicks. Boars inhabiting the Volga Delta and near some lakes and rivers of Kazakhstan have been recorded to feed extensively on fish like carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
and Caspian roach. Boars in the former area will also feed on cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the IOC adopted a consensus taxonomy of seven ge ...
and heron
The herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera ''Botaurus'' and ''Ixobrychus ...
chicks, bivalved molluscs, trapped muskrat
The muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America. The muskrat is found in wetlands over a wide range of climates and habitat ...
s and mice. There is at least one record of a boar killing and eating a bonnet macaque in southern India's Bandipur National Park
Bandipur National Park is a national park covering in Chamarajnagar district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It was established as a tiger reserve under Project Tiger in 1973.
It is part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve since 1986.
History
...
, though this may have been a case of intraguild predation, brought on by interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of ''different'' species compete for the same resources in an ecosystem (e.g. food or living space). This can be contrasted with mutualism, a type of symbiosis. ...
for human handouts. There is also at least one recorded case of a group of wild boar attacking, killing, and eating an adult, healthy female axis deer (''Axis axis
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also known as the spotted deer, chital deer, and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described and given a binomial name by German naturalist Johann Christian Po ...
'') as a pack.
Predators
 Piglets are vulnerable to attack from medium-sized felids like Eurasian lynx (''Lynx lynx''), jungle cats (''Felis chaus''), and snow leopards (''Panthera uncia''), as well as other carnivorans like brown bears (''Ursus arctos'') and yellow-throated martens (''Martes flavigula'').
The wolf (''Canis lupus'') is the main predator of wild boar throughout most of its range. A single wolf can kill around 50 to 80 boars of differing ages in one year. In Italy and Belarus' Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park, boars are the wolf's primary prey, despite an abundance of alternative, less powerful ungulates. Wolves are particularly threatening during the winter, when deep snow impedes the boars' movements. In the Baltic regions, heavy snowfall can allow wolves to eliminate boars from an area almost completely. Wolves primarily target piglets and subadults and only rarely attack adult sows. Adult males are usually avoided entirely. Dholes (''Cuon alpinus'') may also prey on boars, to the point of keeping their numbers down in northwestern Bhutan, despite there being many more cattle in the area.
Piglets are vulnerable to attack from medium-sized felids like Eurasian lynx (''Lynx lynx''), jungle cats (''Felis chaus''), and snow leopards (''Panthera uncia''), as well as other carnivorans like brown bears (''Ursus arctos'') and yellow-throated martens (''Martes flavigula'').
The wolf (''Canis lupus'') is the main predator of wild boar throughout most of its range. A single wolf can kill around 50 to 80 boars of differing ages in one year. In Italy and Belarus' Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park, boars are the wolf's primary prey, despite an abundance of alternative, less powerful ungulates. Wolves are particularly threatening during the winter, when deep snow impedes the boars' movements. In the Baltic regions, heavy snowfall can allow wolves to eliminate boars from an area almost completely. Wolves primarily target piglets and subadults and only rarely attack adult sows. Adult males are usually avoided entirely. Dholes (''Cuon alpinus'') may also prey on boars, to the point of keeping their numbers down in northwestern Bhutan, despite there being many more cattle in the area.

Leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
s (''Panthera pardus'') are predators of wild boar in the Caucasus (particularly Transcaucasia), the Russian Far East, India, China and Iran. In most areas, boars constitute only a small part of the leopard's diet. However, in Iran's Sarigol National Park, boars are the second most frequently targeted prey species after mouflon (''Ovis gmelini''), though adult individuals are generally avoided, as they are above the leopard's preferred weight range of . This dependence on wild boar is largely due in part to the local leopard subspecies' large size.
Boars of all ages were once the primary prey of the tiger (''Panthera tigris'') in Transcaucasia, Kazakhstan, Middle Asia and the Far East up until the late 19th century. In modern times, tiger numbers are too low to have a limiting effect on boar populations. A single tiger can systematically destroy an entire sounder by preying on its members one by one, before moving on to another sounder. Tigers have been noted to chase boars for longer distances than with other prey. In two rare cases, boars were reported to gore a small tiger and a tigress to death in self-defense. A "large male tiger" died of wounds inflicted by an old wild boar it had killed in "a battle royal" between the two animals.
In the Amur region, wild boars are one of the two most important prey species for Siberian tigers, alongside the Manchurian wapiti (''Cervus canadensis xanthopygus''), with the two species collectively comprising roughly 80% of the felid's prey. In Sikhote Alin, a tiger can kill 30–34 boars a year. Studies of tigers in India indicate that boars are usually secondary in preference to various cervids
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer ...
and bovids, though when boars are targeted, healthy adults are caught more frequently than young and sick specimens.
On the islands of Komodo, Rinca and Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and th ...
, the boar's main predator is the Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis'').
Distribution and habitat
Reconstructed range
The species originally occurred in North Africa and much of Eurasia; from the British Isles to Korea and theSunda Islands
The Sunda Islands ( id, Kepulauan Sunda) are a group of islands in the Malay Archipelago.Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Sunda Islands" . ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 26 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. They consist of the Greater Sunda ...
. The northern limit of its range extended from southern Scandinavia to southern Siberia and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. Within this range, it was only absent in extremely dry deserts and alpine zones. It was once found in North Africa along the Nile valley up to Khartoum and north of the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
. The species occurs on a few Ionian
Ionic or Ionian may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Ionic meter, a poetic metre in ancient Greek and Latin poetry
* Ionian mode, a musical mode or a diatonic scale
Places and peoples
* Ionian, of or from Ionia, an ancient region in western ...
and Aegean Islands, sometimes swimming between islands.Masseti, M. (2012), ''Atlas of terrestrial mammals of the Ionian and Aegean islands'', Walter de Gruyter, pp. 139–141, The reconstructed northern boundary of the animal's Asian range ran from Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga (; rus, Ла́дожское о́зеро, r=Ladozhskoye ozero, p=ˈladəʂskəjə ˈozʲɪrə or rus, Ла́дога, r=Ladoga, p=ˈladəɡə, fi, Laatokka arlier in Finnish ''Nevajärvi'' ; vep, Ladog, Ladoganjärv) is a fresh ...
(at 60°N) through the area of Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ol ...
and Moscow into the southern Urals, where it reached 52°N. From there, the boundary passed Ishim
Ishim may refer to:
*Ishim (river), a river in Kazakhstan and Russia
*Ishim, Tyumen Oblast, a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia
*Ishim (angel), a rank of angels in the Jewish angelic hierarchy
See also
*Ishimsky (disambiguation)
*Ishimbay
Ishimbay ...
and farther east the Irtysh at 56°N. In the eastern Baraba steppe (near Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk (, also ; rus, Новосиби́рск, p=nəvəsʲɪˈbʲirsk, a=ru-Новосибирск.ogg) is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the Russian Census ...
) the boundary turned steep south, encircled the Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The m ...
and went again eastward including the Tannu-Ola Mountains and Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
. From here, the boundary went slightly north of the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
eastward to its lower reaches at the Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands ...
. On Sakhalin, there are only fossil reports of wild boar. The southern boundaries in Europe and Asia were almost invariably identical to the seashores of these continents. It is absent in the dry regions of Mongolia from 44 to 46°N southward, in China westward of Sichuan and in India north of the Himalayas. It is absent in the higher elevations of the Pamir and the Tian Shan, though they do occur in the Tarim basin and on the lower slopes of the Tien Shan.
Present range
In recent centuries, the range of wild boar has changed dramatically, largely due to hunting by humans and more recently because of captive wild boar escaping into the wild. Prior to the 20th century, boar populations had declined in numerous areas, with British populations probably becoming extinct during the 13th century. In the warm period after the ice age, wild boar lived in the southern parts ofSweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
and Norway and north of Lake Ladoga in Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, Каре́лия, links=y, r=Karélija, p=kɐˈrʲelʲɪjə, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for ...
. It was previously thought that the species did not live in Finland during prehistory because no prehistoric wild boar bones had been found within the borders of the country. It was not until 2013, when a wild boar bone was found in Askola, that the species was found to have lived in Finland more than 8,000 years ago. It is believed, however, that man prevented its establishment by hunting. In Denmark, the last boar was shot at the beginning of the 19th century, and by 1900 they were absent in Tunisia and Sudan and large areas of Germany, Austria and Italy. In Russia, they were extirpated in wide areas by the 1930s. The last boar in Egypt reportedly died on 20 December 1912 in the Giza Zoo, with wild populations having disappeared by 1894–1902. Prince Kamal el Dine Hussein attempted to repopulate Wadi El Natrun with boars of Hungarian stock, but they were quickly exterminated by poachers.
A revival of boar populations began in the middle of the 20th century. By 1950, wild boar had once again reached their original northern boundary in many parts of their Asiatic range. By 1960, they reached Leningrad and Moscow and by 1975, they were to be found in Archangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ; rus, Арха́нгельск, p=ɐrˈxanɡʲɪlʲsk), also known in English as Archangel and Archangelsk, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near i ...
and Astrakhan. In the 1970s they again occurred in Denmark and Sweden, where captive animals escaped and now survive in the wild. In England, wild boar populations re-established themselves in the 1990s, after escaping from specialist farms that had imported European stock.
Status in Great Britain
 Wild boars were apparently already becoming rare by the 11th century; a 1087 forestry law enacted by William the Conqueror punished through blinding the unlawful killing of a boar. Charles I attempted to reintroduce the species into the New Forest, though this population was exterminated during the Civil War. Between their medieval extinction and the 1980s, when wild boar farming began, only a handful of captive wild boar, imported from the continent, were present in Britain. Occasional escapes of wild boar from wildlife parks have occurred as early as the 1970s, but since the early 1990s significant populations have re-established themselves after escapes from farms, the number of which has increased as the demand for meat from the species has grown. A 1998 MAFF (now DEFRA) study on wild boar living wild in Britain confirmed the presence of two populations of wild boar living in Britain; one in Kent/
Wild boars were apparently already becoming rare by the 11th century; a 1087 forestry law enacted by William the Conqueror punished through blinding the unlawful killing of a boar. Charles I attempted to reintroduce the species into the New Forest, though this population was exterminated during the Civil War. Between their medieval extinction and the 1980s, when wild boar farming began, only a handful of captive wild boar, imported from the continent, were present in Britain. Occasional escapes of wild boar from wildlife parks have occurred as early as the 1970s, but since the early 1990s significant populations have re-established themselves after escapes from farms, the number of which has increased as the demand for meat from the species has grown. A 1998 MAFF (now DEFRA) study on wild boar living wild in Britain confirmed the presence of two populations of wild boar living in Britain; one in Kent/East Sussex
East Sussex is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England on the English Channel coast. It is bordered by Kent to the north and east, West Sussex to the west, and Surrey to the north-west. The largest settlement in East Su ...
and another in Dorset.
Another DEFRA report, in February 2008, confirmed the existence of these two sites as 'established breeding areas' and identified a third in Gloucestershire/ Herefordshire; in the Forest of Dean/Ross on Wye
Ross-on-Wye (Welsh: ''Rhosan ar Wy'') is a market town in England, near the border with Wales. It had a population of 10,582 according to the 2011 census, estimated at 11,309 in 2019. It lies in south-eastern Herefordshire, on the River Wye and ...
area. A 'new breeding population' was also identified in Devon. There is another significant population in Dumfries
Dumfries ( ; sco, Dumfries; from gd, Dùn Phris ) is a market town and former royal burgh within the Dumfries and Galloway council area of Scotland. It is located near the mouth of the River Nith into the Solway Firth about by road from the ...
and Galloway. Populations estimates were as follows:
* The largest population, in Kent/East Sussex, was then estimated at 200 animals in the core distribution area.
* The smallest, in west Dorset, was estimated to be fewer than 50 animals.
* Since winter 2005–2006 significant escapes/releases have also resulted in animals colonizing areas around the fringes of Dartmoor, in Devon. These are considered as an additional single 'new breeding population' and currently estimated to be up to 100 animals.
Population estimates for the Forest of Dean are disputed as, at the time that the DEFRA population estimate was 100, a photo of a boar sounder in the forest near Staunton with over 33 animals visible was published and at about the same time over 30 boar were seen in a field near the original escape location of Weston under Penyard many kilometres or miles away. In early 2010 the Forestry Commission embarked on a cull, with the aim of reducing the boar population from an estimated 150 animals to 100. By August it was stated that efforts were being made to reduce the population from 200 to 90, but that only 25 had been killed. The failure to meet cull targets was confirmed in February 2011.
Wild boars have crossed the River Wye
The River Wye (; cy, Afon Gwy ) is the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn estuary. For much of its length the river forms part of Wal ...
into Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire ( cy, Sir Fynwy) is a county in the south-east of Wales. The name derives from the historic county of the same name; the modern county covers the eastern three-fifths of the historic county. The largest town is Abergavenny, with ...
, Wales. Iolo Williams, the BBC Wales wildlife expert, attempted to film Welsh boar in late 2012. Many other sightings, across the UK, have also been reported. The effects of wild boar on the U.K.'s woodlands were discussed with Ralph Harmer of the Forestry Commission on the 's '' Farming Today'' radio programme in 2011. The programme prompted activist writer George Monbiot to propose a thorough population study, followed by the introduction of permit-controlled culling.
In Scotland wild boar can be killed legally without a license and are culled by land managers as wild populations appear occasionally.
Introduction to North America
invasive species
An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species ad ...
in the Americas and cause problems including out-competing native species for food, destroying the nests of ground-nesting species, killing fawns and young domestic livestock, destroying agricultural crops, eating tree seeds and seedlings, destroying native vegetation and wetlands through wallowing, damaging water quality, coming into violent conflict with humans and pets and carrying pig and human diseases including brucellosis, trichinosis and pseudorabies. In some jurisdictions, it is illegal to import, breed, release, possess, sell, distribute, trade, transport, hunt, or trap Eurasian boars. Hunting and trapping is done systematically, to increase the chance of eradication and to remove the incentive to illegally release boars, which have mostly been spread deliberately by sport hunters.
History
While domestic pigs, both captive and feral (popularly termed "razorbacks"), have been in North America since the earliest days of European colonization, pure wild boars were not introduced into the New World until the 19th century. The suids were released into the wild by wealthy landowners as big game animals. The initial introductions took place in fenced enclosures, though several escapes occurred, with the escapees sometimes intermixing with already established feral pig populations. The first of these introductions occurred in New Hampshire in 1890. Thirteen wild boars from Germany were purchased by Austin Corbin fromCarl Hagenbeck
Carl Hagenbeck (10 June 1844 – 14 April 1913) was a Germans, German merchant of wild animals who supplied many European zoos, as well as P. T. Barnum. He created the modern zoo with animal enclosures without bars that were closer to their natu ...
and released into a game preserve in Sullivan County. Several of these boars escaped, though they were quickly hunted down by locals. Two further introductions were made from the original stocking, with several escapes taking place due to breaches in the game preserve's fencing. These escapees have ranged widely, with some specimens having been observed crossing into Vermont.Mayer, J. J. et al. (2009), Wild Pigs: Biology, Damage, Control Techniques and Management
'', Savannah River National Laboratory Aiken, South Carolina, SRNL-RP-2009-00869 In 1902, 15–20 wild boar from Germany were released into a estate in Hamilton County, New York. Several specimens escaped six years later, dispersing into the William C. Whitney Wilderness Area, with their descendants surviving for at least 20 years. The most extensive boar introduction in the US took place in western North Carolina in 1912, when 13 boars of undetermined European origin were released into two fenced enclosures in a game preserve in
Hooper Bald
Hooper Bald is a grassy bald mountain in the Unicoi Mountain Range located in the Cheoah Ranger District (northwestern district) of Nantahala National Forest in Graham County, North Carolina, United States. The summit is 5,429 ft/1,655 ...
, Graham County. Most of the specimens remained in the preserve for the next decade, until a large-scale hunt caused the remaining animals to break through their confines and escape. Some of the boars migrated to Tennessee, where they intermixed with both free-ranging and feral pigs in the area. In 1924, a dozen Hooper Bald wild pigs were shipped to California and released in a property between Carmel Valley and the Los Padres National Forest. These hybrid boar were later used as breeding stock on various private and public lands throughout the state, as well as in other states like Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, West Virginia and Mississippi.
Several wild boars from Leon Springs
Leon Springs is an unincorporated community in Bexar County, Texas, now partially within the city limits of San Antonio. According to the Handbook of Texas, the community had a population of 137 in 2000. It is located within the San Antonio Met ...
and the San Antonio, Saint Louis and San Diego Zoos were released in the Powder Horn Ranch in Calhoun County, Texas, in 1939. These specimens escaped and established themselves in surrounding ranchlands and coastal areas, with some crossing the Espiritu Santo Bay Espiritu Santo Bay is a northeastern extension of San Antonio Bay in Calhoun County, Texas. It is separated from Matagorda Bay by a line of barrier islands that run south from Port O'Connor to Matagorda Island.
History
''Espiritu Santo'' is Spani ...
and colonizing Matagorda Island. Descendants of the Powder Horn Ranch boars were later released onto San José Island and the coast of Chalmette, Louisiana.
Wild boar of unknown origin were stocked in a ranch in the Edwards Plateau in the 1940s, only to escape during a storm and hybridize with local feral pig populations, later spreading into neighboring counties.
Starting in the mid-1980s, several boars purchased from the San Diego Zoo and Tierpark Berlin were released into the United States. A decade later, more specimens from farms in Canada and Białowieża Forest were let loose. In recent years, wild pig populations have been reported in 44 states within the US, most of which are likely wild boar–feral hog hybrids. Pure wild boar populations may still be present, but are extremely localized.
Introduction and lack of control in South America
 In South America, the European boar is believed to have been introduced for the first time in Argentina and Uruguay around the 20th century for breeding purposes. In Brazil, the creation of wild boar and hybrids started on a large scale in the mid-1990s. With the invasion of wild boar that crossed the border and entered
In South America, the European boar is believed to have been introduced for the first time in Argentina and Uruguay around the 20th century for breeding purposes. In Brazil, the creation of wild boar and hybrids started on a large scale in the mid-1990s. With the invasion of wild boar that crossed the border and entered Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, , ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative_units_of_Brazil#List, fifth-most-populous state and the List of Brazilian st ...
around 1989, and the escape and intentional release by several Brazilian breeders in the late 1990s – in response to a IBAMA decision against the import and breeding of wild boar in 1998 – numerous feral species formed a growing population, which progressively advances in Brazilian territory. The species has no natural predators in Brazil, as it is an exotic species, in addition to breeding with the domestic pig, generating the so-called "javaporco" (neologism created to define this hybrid), factors that contribute to the exaggerated increase in the population. With its population in continuous and uncontrolled growth, without predators, the wild boar causes environmental damage, contributing to the aggradation of river and stream springs, attacking native species feeding on eggs and puppies, causing damage to fauna, flora and to agriculture and livestock, since it also attacks farm animals and can carry various diseases, including zoonosis.
Pest control in Brazil
As a form of control for the wild boar population (which is considered a pest and harmful species), hunting and killing are allowed forCollectors, Shooters and Hunters
Collectors, Shooters and Hunters (in Portuguese: "Colecionadores, Atiradores desportivos e Caçadores" - CACs), in Brazilian law, is the designation given to those citizens, who, fulfilling the imposed demands, in relation to criminal records and ...
(CACs) duly registered by the environmental control agency, IBAMA, which, on the other hand, seeks to encourage the preservation of similar species of native peccaries, such as the ''" queixada"'' and the ''" caititu"''.
Effect on other habitats
Wild boars negatively impact other habitats through the destruction of the environment, or homes of wildlife. When wild boars invade new areas, they adapt to the new area by trampling and rooting, as well as displacing many saplings/nutrients. This causes a decrease in growing of many plants and trees. Water is also affected negatively by wild boars. When wild boars are active in streams, or small pools of water, it causes increased turbidity (excessive silt and particle suspension). In some cases, the fecal coliform concentration increases to dangerous levels because of wild boars. Aquatic wildlife is affected, more prominently fish, and amphibians. Wild boars have caused a great decrease in over 300 animal or plant species, 250 being endangered or threatened. The boars cause many habitats to become less diverse because of their feeding behaviors and predation. Wild boars will dig up eggs of species and eat them, as well as killing other wildlife for food. When these boars compete with other species for resources, they usually come out successful. A study published in the Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology was conducted on the results of Feral Swine control. Only two years after the control started, the amount of turtle nests jumped from 57 to 143, and the turtle nest predation percent dropped from 74 to 15. They kill and eat deers, lizards, birds, snakes, and more. These boars are called "opportunist omnivores," which means they eat almost anything. This means they can survive almost anywhere. A big surplus of food and the ability to adapt to any new place causes lots of breeding. All of these factors make it difficult to get rid of wild boars. Wild boars also tend to carry diseases and numerous pathogens. This also adds to the decrease in diversity among species.Diseases and parasites
 Wild boars are known to host at least 20 different parasitic worm species, with maximum infections occurring in summer. Young animals are vulnerable to
Wild boars are known to host at least 20 different parasitic worm species, with maximum infections occurring in summer. Young animals are vulnerable to helminth
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schi ...
s like '' Metastrongylus'', which are consumed by boars through earthworms and cause death by parasitising the lungs. Wild boar also carry parasites known to infect humans, including ''Gastrodiscoides
''Gastrodiscoides'' is genus of zoonotic trematode under the class Trematoda. It has only one species, ''Gastrodiscoides hominis''. It is a parasite of a variety of vertebrates, including humans. The first definitive specimen was described from ...
'', '' Trichinella spiralis'', '' Taenia solium'', ''Balantidium coli
''Balantidium coli'' is a parasitic species of ciliate alveolates that causes the disease balantidiasis. It is the only member of the ciliate phylum known to be pathogenic to humans.
Morphology
''Balantidium coli'' has two developmental stage ...
'' and '' Toxoplasma gondii''. Wild boar in southern regions are frequently infested with ticks ('' Dermacentor'', '' Rhipicephalus'', and '' Hyalomma'') and hog lice. The species also suffers from blood-sucking flies, which it escapes by bathing frequently or hiding in dense shrubs.
Swine plague spreads very quickly in wild boar, with epizootics being recorded in Germany, Poland, Hungary, Belarus, the Caucasus, the Far East, Kazakhstan and other regions. Foot-and-mouth disease
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious and sometimes fatal viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including domestic and wild bovids. The virus causes a high fever lasting two to six days, followe ...
can also take on epidemic proportions in boar populations. The species occasionally, but rarely contracts '' Pasteurellosis'', hemorrhagic sepsis
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagi ...
, tularemia, and anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium ''Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The sk ...
. Wild boar may on occasion contract swine erysipelas through rodents or hog lice and ticks.
Relationships with humans
In culture

Phaea
The Crommyonian Sow ( grc, Ὕς Κρομμύων ''Hus Krommúōn'', also called (Phaia "Grey") after the woman who owned it) is a pig in Greek mythology.
Mythology
The Crommyonian Sow was a wild pig that ravaged the region around the villag ...
, and a disguised Odysseus
Odysseus ( ; grc-gre, Ὀδυσσεύς, Ὀδυσεύς, OdysseúsOdyseús, ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; lat, UlyssesUlixes), is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. Odysse ...
is recognised by his handmaiden Eurycleia by the scars inflicted on him by a boar during a hunt in his youth.Mallory, J. P. & Adams, D. Q. (1997), ''Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture'', Taylor & Francis, pp. 426–428, To the mythical Hyperboreans, the boar represented spiritual authority. Several Greek myths use the boar as a symbol of darkness, death and winter. One example is the story of the youthful Adonis, who is killed by a boar and is permitted by Zeus to depart from Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
only during the spring and summer period. This theme also occurs in Irish and Egyptian mythology, where the animal is explicitly linked to the month of October, therefore autumn. This association likely arose from aspects of the boar's actual nature. Its dark colour was linked to the night, while its solitary habits, proclivity to consume crops and nocturnal nature were associated with evil. The foundation myth of Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in t ...
has the city being built over the site where Prince Androklos of Athens killed a boar. Boars were frequently depicted on Greek funerary monuments alongside lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
s, representing gallant losers who have finally met their match, as opposed to victorious hunters as lions are. The theme of the doomed, yet valorous boar warrior also occurred in Hittite culture, where it was traditional to sacrifice a boar alongside a dog and a prisoner of war after a military defeat.
Germanic cultures
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
, with its image having been frequently engraved on shields and swords. They also feature on Germanic boar helmets, such as the Benty Grange helmet, where it was believed to offer protection to the wearer and has been theorised to have been used in spiritual transformations into swine, similar to berserkers. The boar features heavily in religious practice in Germanic paganism where it is closely associated with Freyr and has also been suggested to have been a totemic animal to the Swedes, especially to the Yngling royal dynasty who claimed descent from the god.
According to Tacitus, the Baltic Aesti featured boars on their helmets and may have also worn boar masks. The boar and pig were held in particularly high esteem by the Celts, who considered them to be their most important sacred animal. Some Celtic deities linked to boars include Moccus and Veteris
Veteris (commonly spelled ''Vitiris, Vheteris, Huetiris'', and ''Hueteris'') was a Celtic god attested from many inscriptions in Roman Britain. The dedicants were usually private individuals and were exclusively male. During the 3rd Century AD the ...
. It has been suggested that some early myths surrounding the Welsh hero Culhwch involved the character being the son of a boar god. Nevertheless, the importance of the boar as a culinary item among Celtic tribes may have been exaggerated in popular culture by the '' Asterix'' series, as wild boar bones are rare among Celtic archaeological sites and the few that do occur show no signs of butchery, having probably been used in sacrificial rituals.Green, M. (2002), ''Animals in Celtic Life and Myth'', Routledge, p. 46,
The boar also appears in Vedic mythology and Hindu mythology
Hindu mythology is the body of myths and literature attributed to, and espoused by, the adherents of the Hindu religion, found in Hindu texts such as the Vedic literature, epics like ''Mahabharata'' and ''Ramayana'', the Puranas, and reg ...
. A story present in the Brahmanas
The Brahmanas (; Sanskrit: , ''Brāhmaṇam'') are Vedic śruti works attached to the Samhitas (hymns and mantras) of the Rig, Sama, Yajur, and Atharva Vedas. They are a secondary layer or classification of Sanskrit texts embedded within ea ...
has the god Indra
Indra (; Sanskrit: इन्द्र) is the king of the devas (god-like deities) and Svarga (heaven) in Hindu mythology. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. volumes/ref> I ...
slaying an avaricious boar, who has stolen the treasure of the asuras
Asuras (Sanskrit: असुर) are a class of beings in Indic religions. They are described as power-seeking clans related to the more benevolent Devas (also known as Suras) in Hinduism. In its Buddhist context, the word is sometimes translated ...
, then giving its carcass to the god Vishnu, who offered it as a sacrifice to the gods. In the story's retelling in the Charaka Samhita
The ''Charaka Samhita'' (, “Compendium of ''Charaka''”) is a Sanskrit text on Ayurveda (Indian traditional medicine). Along with the ''Sushruta Samhita'', it is one of the two foundational texts of this field that have survived from ancien ...
, the boar is described as a form of Prajapati
Prajapati ( sa, प्रजापति, Prajāpati, lord and protector of creation) is a Vedic deity of Hinduism. In later literature, Prajapati is identified with the creator god Brahma, but the term also connotes many different gods, depe ...
and is credited with having raised the Earth from the primeval waters. In the Ramayana and the Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
, the same boar is portrayed as Varaha, an avatar of Vishnu.
 In
In Japanese culture
The culture of Japan has changed greatly over the millennia, from the country's prehistoric Jōmon period, to its contemporary modern culture, which absorbs influences from Asia and other regions of the world.
Historical overview
The ance ...
, the boar is widely seen as a fearsome and reckless animal, to the point that several words and expressions in Japanese referring to recklessness include references to boars. The boar is the last animal of the Oriental zodiac, with people born during the year of the Pig being said to embody the boar-like traits of determination and impetuosity. Among Japanese hunters, the boar's courage and defiance is a source of admiration and it is not uncommon for hunters and mountain people to name their sons after the animal ''inoshishi'' (猪). Boars are also seen as symbols of fertility and prosperity; in some regions, it is thought that boars are drawn to fields owned by families including pregnant women, and hunters with pregnant wives are thought to have greater chances of success when boar hunting. The animal's link to prosperity was illustrated by its inclusion on the ¥10 note during the Meiji period and it was once believed that a man could become wealthy by keeping a clump of boar hair in his wallet.Knight, J. (2003), ''Waiting for Wolves in Japan: An Anthropological Study of People-wildlife Relations'', Oxford University Press, pp. 49–73,
In the folklore of the Mongol Altai Uriankhai tribe, the wild boar was associated with the watery underworld, as it was thought that the spirits of the dead entered the animal's head, to be ultimately transported to the water.Pegg, C. (2001), ''Mongolian Music, Dance, & Oral Narrative: Performing Diverse Identities'', University of Washington Press, p. 140, Prior to the conversion to Islam, the Kyrgyz people
The Kyrgyz people (also spelled Kyrghyz, Kirgiz, and Kirghiz; ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is the nation state of the Kyrgyz people and significant diaspora can be found in China, Russia, and Uzbekistan. ...
believed that they were descended from boars and thus did not eat pork. In Buryat mythology, the forefathers of the Buryats descended from heaven and were nourished by a boar.Holmberg, U. (1927), '' The Mythology of All Races volume 4: Finno-Ugric, Siberian'', New York, Cooper Square Publishing Inc. pp. 502–503 In China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, the boar is the emblem of the Miao people
The Miao are a group of linguistically-related peoples living in Southern China and Southeast Asia, who are recognized by the government of China as one of the 56 List of ethnic groups in China, official ethnic groups. The Miao live primarily in ...
.
The boar ( sanglier) is frequently displayed in English, Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
and Welsh heraldry. As with the lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
, the boar is often shown as armed and langued
In heraldry, the term attitude describes the ''position'' in which a figure (animal or human) is emblazoned as a Charge (heraldry), charge, a Supporter (heraldry), supporter, or as a Crest (heraldry), crest. The attitude of an heraldic figure al ...
. As with the bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
, Scottish and Welsh heraldry displays the boar's head with the neck cropped, unlike the English version, which retains the neck. The white boar served as the badge of King Richard III of England, who distributed it among his northern retainers during his tenure as Duke of Gloucester
Duke of Gloucester () is a British royal title (after Gloucester), often conferred on one of the sons of the reigning monarch. The first four creations were in the Peerage of England and the last in the Peerage of the United Kingdom; the curren ...
.
As a game animal and food source

 Humans have been hunting boar for millennia, the earliest artistic depictions of such activities dating back to the Upper Paleolithic. The animal was seen as a source of food among the Ancient Greeks, as well as a sporting challenge and source of epic narratives. The Romans inherited this tradition, with one of its first practitioners being Scipio Aemilianus. Boar hunting became particularly popular among the young nobility during the 3rd century BC as preparation for manhood and battle. A typical Roman boar hunting tactic involved surrounding a given area with large nets, then flushing the boar with dogs and immobilizing it with smaller nets. The animal would then be dispatched with a ''venabulum'', a short spear with a crossguard at the base of the blade. More than their Greek predecessors, the Romans extensively took inspiration from boar hunting in their art and sculpture. With the ascension of
Humans have been hunting boar for millennia, the earliest artistic depictions of such activities dating back to the Upper Paleolithic. The animal was seen as a source of food among the Ancient Greeks, as well as a sporting challenge and source of epic narratives. The Romans inherited this tradition, with one of its first practitioners being Scipio Aemilianus. Boar hunting became particularly popular among the young nobility during the 3rd century BC as preparation for manhood and battle. A typical Roman boar hunting tactic involved surrounding a given area with large nets, then flushing the boar with dogs and immobilizing it with smaller nets. The animal would then be dispatched with a ''venabulum'', a short spear with a crossguard at the base of the blade. More than their Greek predecessors, the Romans extensively took inspiration from boar hunting in their art and sculpture. With the ascension of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
, boar hunting took on Christian allegorical themes, with the animal being portrayed as a "black beast" analogous to the dragon of Saint George.
Boar hunting continued after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, though the Germanic tribes considered the red deer to be a more noble and worthy quarry. The post-Roman nobility hunted boar as their predecessors did, but primarily as training for battle rather than sport. It was not uncommon for medieval hunters to deliberately hunt boars during the breeding season when the animals were more aggressive. During the Renaissance, when deforestation and the introduction of firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s reduced boar numbers, boar hunting became the sole prerogative of the nobility, one of many charges brought up against the rich during the German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense oppositio ...
and the French Revolution.
During the mid-20th century, 7,000–8,000 boars were caught in the Caucasus, 6,000–7,000 in Kazakhstan and about 5,000 in Central Asia during the Soviet period, primarily through the use of dogs and beats. In Nepal, farmers and poachers eliminate boars by baiting balls of wheat flour containing explosives with kerosene oil, with the animals' chewing motions triggering the devices.
Wild boar can thrive in captivity, though piglets grow slowly and poorly without their mothers. Products derived from wild boar include meat, hide and bristles. '' Apicius'' devotes a whole chapter to the cooking of boar meat, providing 10 recipes involving roasting, boiling and what sauces to use. The Romans usually served boar meat with garum. Boar's head was the centrepiece of most medieval Christmas celebrations among the nobility. Although growing in popularity as a captive-bred source of food, the wild boar takes longer to mature than most domestic pigs and it is usually smaller and produces less meat. Nevertheless, wild boar meat is leaner and healthier than pork,Harris, C. (2009), A Guide to Traditional Pig Keeping
', Good Life Press, pp. 26–27, being of higher nutritional value and having a much higher concentration of essential amino acids. Most meat-dressing organizations agree that a boar carcass should yield of meat on average. Large specimens can yield of fat, with some giants yielding or more. A boar hide can measure and can yield of bristle and of underwool.
Volgograd Oblast
Volgograd Oblast (russian: Волгогра́дская о́бласть, ''Volgogradskaya oblast'') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (an oblast) of Russia, located in the Volga region, Volga region of Southern Russia. Its adminis ...
, Russia
File:Brooklyn Museum - The Boar Hunt - Hans Wertinger.jpg, The Boar Hunt – Hans Wertinger, c. 1530, the Danube Valley
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
Crop and garbage raiding
 Boars can be damaging to agriculture in situations where their natural habitat is sparse. Populations living on the outskirts of towns or farms can dig up potatoes and damage melons, watermelons and maize. However, they generally only encroach upon farms when natural food is scarce. In the Belovezh forest for example, 34–47% of the local boar population will enter fields in years of moderate availability of natural foods. While the role of boars in damaging crops is often exaggerated, cases are known of boar depredations causing
Boars can be damaging to agriculture in situations where their natural habitat is sparse. Populations living on the outskirts of towns or farms can dig up potatoes and damage melons, watermelons and maize. However, they generally only encroach upon farms when natural food is scarce. In the Belovezh forest for example, 34–47% of the local boar population will enter fields in years of moderate availability of natural foods. While the role of boars in damaging crops is often exaggerated, cases are known of boar depredations causing famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
s, as was the case in Hachinohe, Japan in 1749, where 3,000 people died of what became known as the "wild boar famine". Still, within Japanese culture, the boar's status as vermin is expressed through its title as "king of pests" and the popular saying (addressed to young men in rural areas) "When you get married, choose a place with no wild boar."
In Central Europe, farmers typically repel boars through distraction or fright, while in Kazakhstan it is usual to employ guard dogs in plantations. However, research shows that when compared with other mitigation tactics, hunting is the only strategy to significantly reduce crop damage by boars. Although large boar populations can play an important role in limiting forest growth, they are also useful in keeping pest populations such as June bugs under control. The growth of urban areas and the corresponding decline in natural boar habitats has led to some sounders entering human habitations in search of food. As in natural conditions, sounders in peri-urban areas are matriarchal, though males tend to be much less represented and adults of both sexes can be up to 35% heavier than their forest-dwelling counterparts. As of 2010, at least 44 cities in 15 countries have experienced problems of some kind relating to the presence of habituated wild boar.
Attacks on humans
Actual attacks on humans are rare, but can be serious, resulting in penetrating injuries to the lower part of the body. They generally occur during the boars' rutting season from November to January, in agricultural areas bordering forests or on paths leading through forests. The animal typically attacks by charging and pointing its tusks towards the intended victim, with most injuries occurring on the thigh region. Once the initial attack is over, the boar steps back, takes position and attacks again if the victim is still moving, only ending once the victim is completely incapacitated. Boar attacks on humans have been documented throughout history. The Romans and Ancient Greeks wrote of these attacks (Odysseus
Odysseus ( ; grc-gre, Ὀδυσσεύς, Ὀδυσεύς, OdysseúsOdyseús, ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; lat, UlyssesUlixes), is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. Odysse ...
was wounded by a boar and Adonis was killed by one). A 2012 study compiling recorded attacks from 1825 to 2012 found accounts of 665 human victims of both wild boars and feral pigs, with the majority (19%) of attacks in the animal's native range occurring in India. Most of the attacks occurred in rural areas during the winter months in non-hunting contexts and were committed by solitary males.Mayer, John J. (2013"Wild Pig Attacks on Humans"
Wildlife Damage Management Conferences – Proceedings. Paper 151.
Management
Managing wild boar is a pressing task in both native and invasive contexts as they can be disrupting to other systems when not addressed. Wild boar find their success through adaptation of daily patterns to circumvent threats. They avoid human contact through nocturnal lifestyles, despite the fact that they are not evolutionarily predisposed, and alter their diets substantially based on what is available. These "adaptive generalists", can survive in a variety of landscapes, making the prediction of their movement patterns and any potential close contact areas crucial to limiting damage. All of these qualities make them equally difficult to manage or limit. Within Central Europe, the native habitat of the wild boar, there has been a push to re-evaluate interactions between wild boar and humans, with the priority of fostering positive engagement. Negative media and public perception of wild boar as "crop raiders" have made those living alongside them less willing to accept the economic damages of their behaviors, as wild boar are seen as pests. This media tone impacts management policy, with every 10 negative articles increasing wild boar policy activity by 6.7%. Contrary to this portrayal, wild boar, when managed well within their natural environments, can be a crucial part of forest ecosystems. Defining the limits of proper management is difficult, but the exclusion of wild boar from rare environments is generally agreed upon, as when not properly managed, they can damage agricultural ventures and harm vulnerable plant life. These damages are estimated at $800 million yearly in environmental and financial costs for the United States alone. The breadth of this damage is due to prior inattention and lack of management tactics for extended lengths of time. Managing wild boar is a complex task, as it involves coordinating a combination of crop harvest techniques, fencing, toxic bait, corrals, and hunting. The most common tactic employed by private land owners in the United States is recreational hunting, however, this is generally not as effective on its own. Management strategies are most successful when they take into account reproduction, dispersion, and the differences between ideal resources for males and females.
Defining the limits of proper management is difficult, but the exclusion of wild boar from rare environments is generally agreed upon, as when not properly managed, they can damage agricultural ventures and harm vulnerable plant life. These damages are estimated at $800 million yearly in environmental and financial costs for the United States alone. The breadth of this damage is due to prior inattention and lack of management tactics for extended lengths of time. Managing wild boar is a complex task, as it involves coordinating a combination of crop harvest techniques, fencing, toxic bait, corrals, and hunting. The most common tactic employed by private land owners in the United States is recreational hunting, however, this is generally not as effective on its own. Management strategies are most successful when they take into account reproduction, dispersion, and the differences between ideal resources for males and females.
See also
* Babirusa *Boar-baiting Boar-baiting is a blood sport involving the baiting of wild boars against dogs.
Villagers in Indonesia call the event "adu bagong" translated as boar fighting. Boar-baiting began in the 1960s, to test hunting dogs against wild boars. In 2017, an ...
* Boars in heraldry
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * *Further reading
* Apollonio, M. et al. (1988)"The systematics of the wild boar (''Sus scrofa'' L.) in Italy"
''Bolletino di Zoologia''a, 3:213–221 * Carden, R.F. (2012
"Review of the Natural History of Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) on the island of Ireland"
Report prepared by Ruth Carden for the Northern Ireland Environment Agency, Northern Ireland, UK, National Parks & Wildlife Service, Department of Arts, Heritage and the Gaeltacht, Dublin, Ireland and the National Museum of Ireland – Education & Outreach Department. * Durantel, P. (2007), ''Le sanglier et ses chasses'', Editions Artemis, * Greene, J. (2011), ''The Golden-Bristled Boar: Last Ferocious Beast of the Forest'', University of Virginia Press, * Hatto, A. T. (1957) "Snake‐swords and Boar‐helms in Beowulf". In: ''English Studies'', 38:1–6, 145–160. DOI: 10.1080/00138385708596994 * Marillier, B. (2003), ''Le sanglier héraldique'', Editions Cheminements, * Mayer, J. J. & Shedrow, C. B. (2007),
Annotated Bibliography of the Wild Pig (Sus scrofa): Environmental Information Document
', Washington Savannah River Company * Padiglione, V. (1989), ''Il cinghiale cacciatore: Antropologia simbolica della caccia in Sardegna'', Armando Editore (collana Antropologia culturale) *
External links
BBC profile
* *
Species Profile- Wild Boar (''Sus scrofa'')
National Invasive Species Information Center, United States National Agricultural Library. Lists general information and resources for wild boar. *
A sounder of wild boars
Wild pigs with piglets – white piglets with black spots
Sow feeding piglets, Lodz (Poland)
A wild boar struggling with plastic film, Lodz (Poland
{{Authority control Extant Pleistocene first appearances Palearctic fauna Introduced mammals of Australia wild boar Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Sus (genus)