Blade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
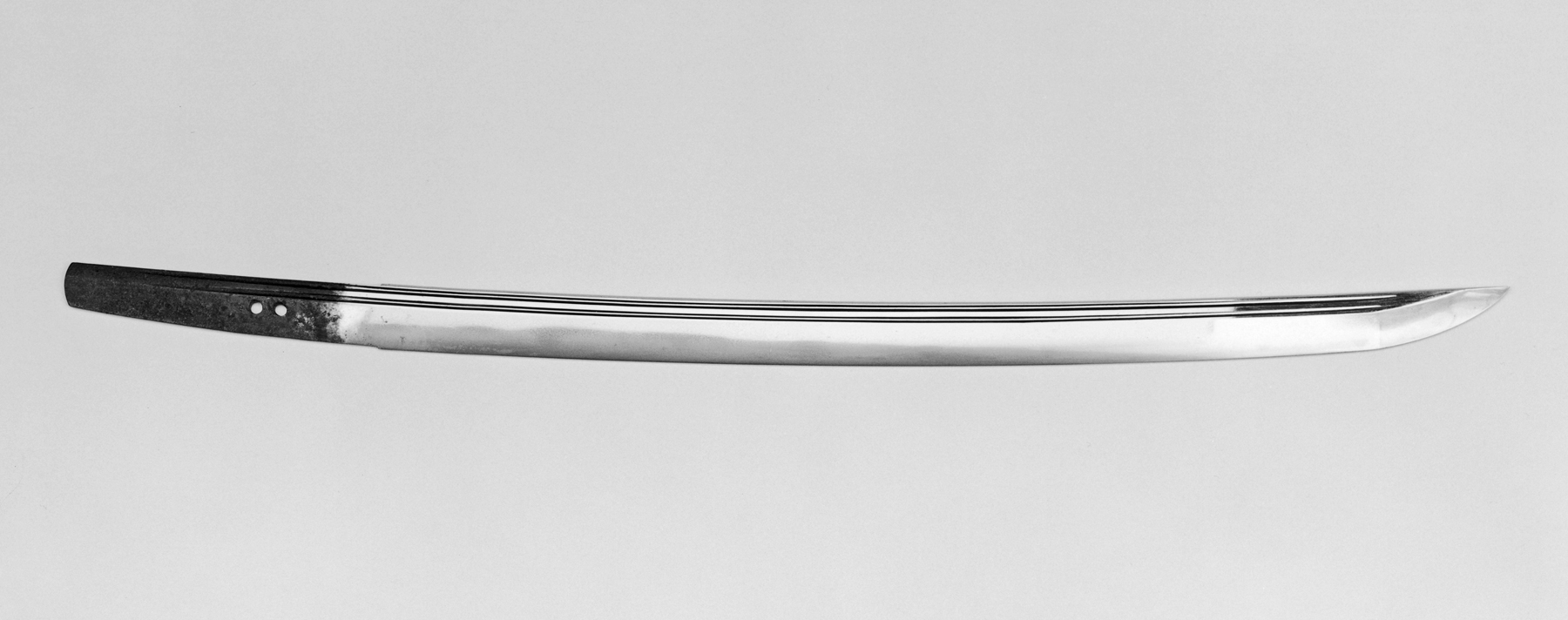 A blade is the sharp, cutting portion of a
A blade is the sharp, cutting portion of a
 The more acute the blade, the more easily it will dull. As the blade near the edge is thinner, there is little material to remove before the edge is worn away to a thicker section. Thin edges can also roll over when force is applied it them, forming a section like the bottom part of a letter "J". For this reason, straight edge razors are frequently stropped to straighten the edge.
Drawing a blade across any material tends to abrade both the blade, usually making it duller, and the cut material. Though softer than glass or many types of stone used in the kitchen, steel edges can still scratch these surfaces. The resulting scratch is full of very fine particles of ground glass or stone which will very quickly abrade the blade's edge and so dull it.
In times when swords were regularly used in warfare, they required frequent sharpening because of dulling from contact with rigid armor, mail, metal rimmed shields, or other swords, for example. Particularly, hitting the edge of another sword by accident or in an emergency could chip away metal and even cause cracks through the blade. Soft-cored blades are more resistant to fracturing on impact.
The more acute the blade, the more easily it will dull. As the blade near the edge is thinner, there is little material to remove before the edge is worn away to a thicker section. Thin edges can also roll over when force is applied it them, forming a section like the bottom part of a letter "J". For this reason, straight edge razors are frequently stropped to straighten the edge.
Drawing a blade across any material tends to abrade both the blade, usually making it duller, and the cut material. Though softer than glass or many types of stone used in the kitchen, steel edges can still scratch these surfaces. The resulting scratch is full of very fine particles of ground glass or stone which will very quickly abrade the blade's edge and so dull it.
In times when swords were regularly used in warfare, they required frequent sharpening because of dulling from contact with rigid armor, mail, metal rimmed shields, or other swords, for example. Particularly, hitting the edge of another sword by accident or in an emergency could chip away metal and even cause cracks through the blade. Soft-cored blades are more resistant to fracturing on impact.
 ;C1: ''Leaf blade'' with a distinctive recurved "waist" adding some curved "belly" to the knife facilitating slicing as well as shifting weight towards the tip meaning that it is commonly used for throwing knives as well as improving chopping ability.
;C1: ''Leaf blade'' with a distinctive recurved "waist" adding some curved "belly" to the knife facilitating slicing as well as shifting weight towards the tip meaning that it is commonly used for throwing knives as well as improving chopping ability.
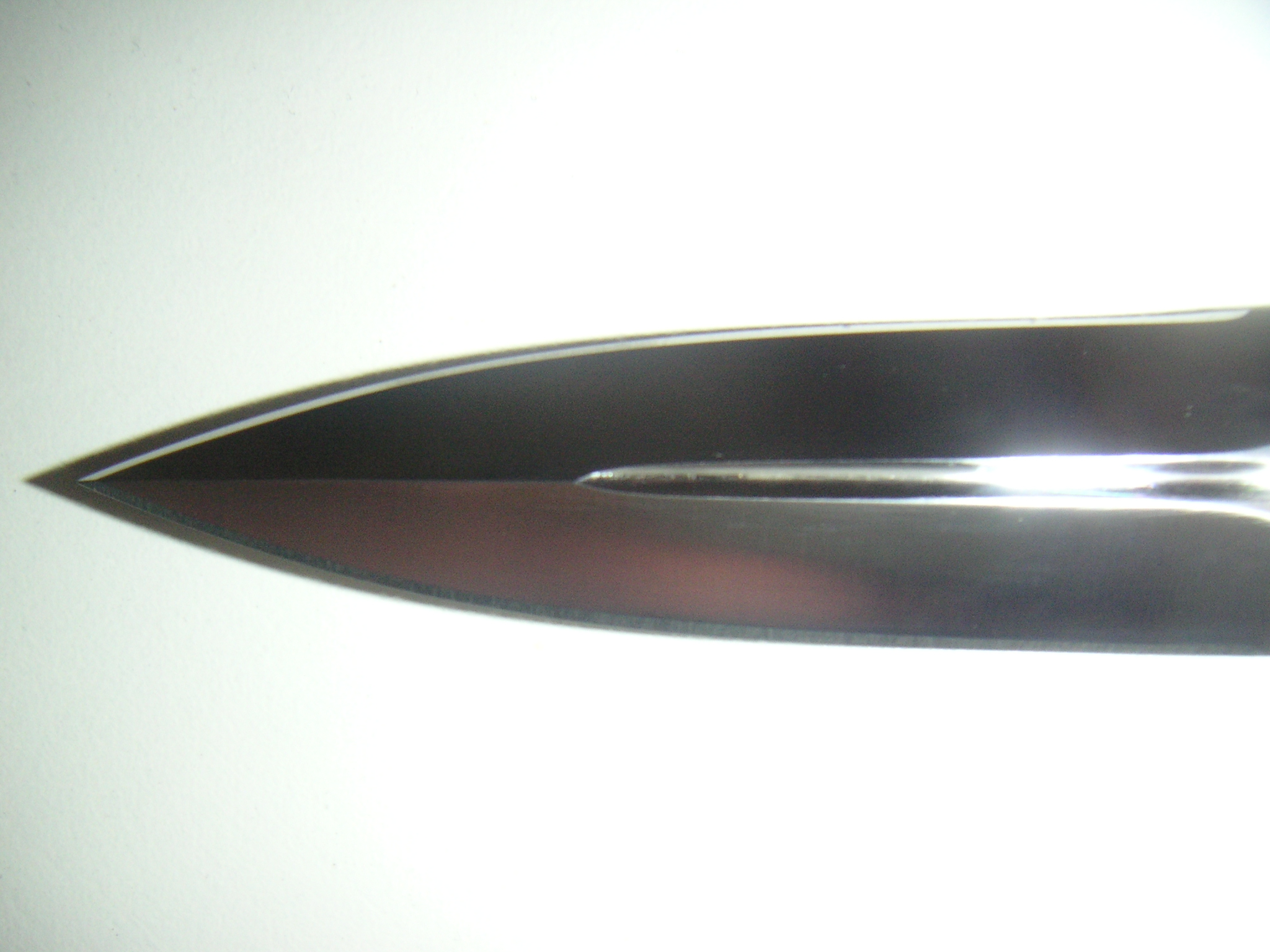 ;C2: A ''spear point'' blade is a symmetrically-shaped blade with a point aligned with the centerline of the blade's long axis. True spear-point blades are double-edged with a central spine, like a dagger or
;C2: A ''spear point'' blade is a symmetrically-shaped blade with a point aligned with the centerline of the blade's long axis. True spear-point blades are double-edged with a central spine, like a dagger or
 The sharp edges of a
The sharp edges of a
 Blades are sometimes marked or inscribed, for decorative purposes, or with the mark of either the maker or the owner. Blade decorations are often realized in
Blades are sometimes marked or inscribed, for decorative purposes, or with the mark of either the maker or the owner. Blade decorations are often realized in
HROARR – Robert Geißler, Concerning the Sharpness of Blades
{{Use dmy dates, date=August 2016 Edged and bladed weapons Cutting tools
 A blade is the sharp, cutting portion of a
A blade is the sharp, cutting portion of a tool
A tool is an Physical object, object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many Tool use by animals, animals use simple tools, only human bei ...
, weapon
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime (e.g., murder), law ...
, or machine
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromol ...
, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are intended to cut. This includes early examples made from flaked stones like flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
or obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
, evolving through the ages into metal forms like copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
, and iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, and culminating in modern versions made from steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
or ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porce ...
. Serving as one of humanity's oldest tools, blades continue to have wide-ranging applications, including in combat, cooking
Cooking, also known as cookery or professionally as the culinary arts, is the art, science and craft of using heat to make food more palatable, digestible, nutritious, or Food safety, safe. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from ...
, and various other everyday and specialized tasks.
Blades function by concentrating force at the cutting edge. Design variations, such as serrated edge
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pr ...
s found on bread knives and saws
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard toothed edge used to cut through material. Various terms are used to describe toothed and abrasive saws.
Saws began as serrated materials, and when mankind learned how to ...
, serve to enhance this force concentration, adapting blades for specific functions and materials. Blades thus hold a significant place both historically and in contemporary society, reflecting an evolution in material technology and utility.
Uses
During food preparation, knives are mainly used for slicing, chopping, and piercing. In combat, a blade may be used to slash or puncture, and may also be thrown or otherwise propelled. The function is to sever a nerve, muscle or tendon fibers, or blood vessel to disable or kill the adversary. Severing a major blood vessel typically leads to death due toexsanguination
Exsanguination is the loss of blood from the circulatory system of a vertebrate, usually leading to death. The word comes from the Latin 'sanguis', meaning blood, and the prefix 'ex-', meaning 'out of'.
Exsanguination has long been used as a met ...
.
Blades may be used to scrape, moving the blade ''sideways'' across a surface, as in an ink eraser
An ink eraser is an instrument used to scrape away or chemically bleach ink from a writing surface. This is a more involved process than removing pencil markings. Pencil marks can be gradually adhered to natural rubber fragments by rubbing the ma ...
, rather than along or through a surface. For construction equipment such as a grader
A grader, also commonly referred to as a road grader, motor grader, or simply blade, is a form of heavy equipment with a long blade used to create a flat surface during Grading (engineering), grading. Although the earliest models were towed b ...
, the ground-working implement is also referred to as the blade, typically with a replaceable cutting edge.
Physics
A simple blade intended for cutting has two faces that meet at an edge. Ideally, this edge would have no roundness but in practice, all edges can be seen to be rounded to some degree under magnification either optically or with an electron microscope. Force is applied to the blade, either from the handle or pressing on the back of the blade. The handle or back of the blade has a largearea
Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while '' surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-di ...
compared to the fine edge. This concentration of applied force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitu ...
onto the small edge area increases the pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
exerted by the edge. It is this high pressure that allows a blade to cut through a material by breaking the bonds between the molecules, crystals, fibers, etc. in the material. This necessitates the blade being strong enough to resist breaking before the other material gives way.
Geometry
The angle at which the faces meet is important as a larger angle will make for a duller blade while making the edge stronger. A stronger edge is less likely to dull from fracture or have the edge roll out of shape. The shape of the blade is also important. A thicker blade will be heavier and stronger and stiffer than a thinner one of similar design while also making it experience more drag while slicing or piercing. A filleting knife will be thin enough to be very flexible while a carving knife will be thicker and stiffer; a dagger will be thin so it can pierce, while a camping knife will be thicker so it can be stronger and more durable. A strongly curved edge, like atalwar
The talwar (), also spelled talwaar and tulwar, is a type of curved sword or sabre from the Indian subcontinent.
Etymology and classification
The word ''talwar'' originated from the Sanskrit Language, Sanskrit word ''taravāri'' () which means ...
, will allow the user to draw the edge of the blade against an opponent even while close to the opponent where a straight sword would be more difficult to pull in the same fashion. The curved edge of an axe means that only a small length of the edge will initially strike the tree, concentrating force as does a thinner edge, whereas a straight edge could potentially land with the full length of its edge against a flat section of the tree. A splitting maul has a convex section to avoid getting stuck in the wood where chopping axes can be flat or even concave. A khopesh
The ''khopesh'' ('; also vocalized khepesh) is an Egyptian sickle-shaped sword that developed from battle axes. The sword style originated in Western Asia during the Bronze Age and was introduced in the Second Intermediate Period.Lloyd, Alan B. ...
, falchion
A falchion (; Old French: ''fauchon''; Latin: ''falx'', "sickle") is a one-handed, backsword, single-edged sword of European origin. Falchions are found in different forms from around the 13th century up to and including the 16th century. In so ...
, or kukri
The kukri () or khukuri (, ) is a type of knife or short sword with a distinct recurve in its blade that originated in the Indian subcontinent. It serves multiple purposes as a melee weapon and also as a regular cutting/chopping tool throughout ...
is angled and/or weighted at the distal end so that force is concentrated at the faster moving, heavier part of the blade maximizing cutting power and making it largely unsuitable for thrusting, whereas a rapier
A rapier () is a type of sword originally used in Spain (known as ' -) and Italy (known as '' spada da lato a striscia''). The name designates a sword with a straight, slender and sharply pointed two-edged long blade wielded in one hand. It wa ...
is thin and tapered allowing it to pierce and be moved with more agility while reducing its chopping power compared to a similarly sized sword.
A serrated edge, such as on a saw
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, Wire saw, wire, or Chainsaw, chain with a hard toothed edge used to cut through material. Various terms are used to describe toothed and abrasive saws.
Saws began as serrated materials, and when man ...
or a bread knife
Bread knives are used for cutting bread and are one of many kitchen knife, kitchen knives used by cooks. The serrated blades of bread knives are able to cut soft bread without crushing it.
History
One such knife was exhibited at the World's Co ...
, concentrates force onto the tips of the serrations which increases pressure as well as allowing soft or fibrous material (like wood, rope, bread, and vegetables) to expand into the spaces between serrations. Whereas pushing any knife, even a bread knife, down onto a bread loaf will just squash the loaf as bread has a low elastic modulus
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity (MOE)) is a quantity that describes an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it.
Definition
The elastic modu ...
(is soft) but high yield strain (loosely, can be stretched or squashed by a large proportion without breaking), drawing serrations across the loaf with little downward force will allow each serration to simultaneously cut the bread with much less deformation of the loaf. Similarly, pushing on a rope tends to squash the rope while drawing serrations across it sheers the rope fibers. Drawing a smooth blade is less effective as the blade is parallel to the direction draw but the serrations of a serrated blade are at an angle to the fibers. Serrations on knives are often symmetric allowing the blade to cut on both the forward and reverse strokes of a cut, a notable exception being Veff serration
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pr ...
s which are designed to maximize cutting power while moving the blade away from the user. Saw blade serrations, for both wood and metal, are typically asymmetrical so that they cut while moving in only one direction. (Saws act by abrading a material into dust along a narrow channel, the kerf
A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard toothed edge used to cut through material. Various terms are used to describe toothed and abrasive saws.
Saws began as serrated materials, and when mankind learned how t ...
, whereas knives and similar act by forcing the material apart. This means that saws result in a loss of material and the serrations of a saw also serve to carry metal swarf
Swarf, also known as chips or by other process-specific names (such as turnings, filings, or shavings), are pieces of metal, wood, or plastic that are the debris or waste resulting from machining, woodworking, or similar subtractive (material-r ...
and sawdust
Sawdust (or wood dust) is a by-product or waste product of woodworking operations such as sawing, sanding, milling and routing. It is composed of very small chips of wood. These operations can be performed by woodworking machinery, portable p ...
out of the cut channel.)
Fullers are longitudinal channels either forged into the blade or later machined/milled out of the blade though the latter process is less desirable. This loss of material necessarily weakens the blade but serves to make the blade lighter without sacrificing stiffness. The same principle is applied in the manufacture of beams such as I-beam
An I-beam is any of various structural members with an - (serif capital letter 'I') or H-shaped cross section (geometry), cross-section. Technical terms for similar items include H-beam, I-profile, universal column (UC), w-beam (for "wide flang ...
s. Fullers are only of significant utility in swords. In most knives there is so little material removed by the fuller that it makes little difference to the weight of the blade and they are largely cosmetic.
Materials
Typically blades are made from a material that is about as hard, though usually harder, than the material to be cut. Insufficiently hard blades will be unable to cut a material or will wear away quickly as hardness is related to a material's ability to resist abrasion. However, blades must also be tough enough to resist the dynamic load of impact and as a general rule the harder a blade the less tough (the more brittle) a material. For example, a steel axehead is much harder than the wood it is intended to cut and is sufficiently tough to resist the impact resulting when swung against a tree while a ceramic kitchen knife, harder than steel, is very brittle (has low toughness) and can easily shatter if dropped onto the floor or twisted while inside the food it is cutting or carelessly stored under other kitchen utensils. This creates a tension between the intended use of the blade, the material it is to be made from, and any manufacturing processes (such asheat treatment
Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are a ...
in the case of steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
blades that will affect a blade's hardness and toughness). A balance must be found between the sharpness and how well it can last. Methods that can circumvent this include differential hardening
Differential heat treatment (also called selective heat treatment or local heat treatment) is a technique used during heat treating of steel to harden or soften certain areas of an object, creating a difference in hardness between these areas. Ther ...
. This method yields an edge that can hold its sharpness as well as a body that is tough.
Non-metals
Prehistorically, and in less technologically advanced cultures even into modern times, tool and weapon blades have been made from wood, bone, and stone. Most woods are exceptionally poor at holding edges and bone and stone suffer from brittleness making them suffer from fracture when striking or struck. In modern times stone, in the form of obsidian, is used in some medical scalpels as it is capable of being formed into an exceedingly fine edge. Ceramic knives are non-metallic and non-magnetic. As non-metals do not corrode they remain rust and corrosion free but they suffer from similar faults as stone and bone, being rather brittle and almost entirely inflexible. They are harder than metal knives and so more difficult to sharpen, and some ceramic knives may be as hard or harder than some sharpening stones. For example, synthetic sapphire is harder than natural sharpening stones and is as hard as alumina sharpening stones.Zirconium dioxide
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zirconium silicate or zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral bad ...
is also harder than garnet sharpening stones and is nearly as hard as alumina. Both require diamond stones or silicon carbide stones to sharpen and care has to be taken to avoid chipping the blade. As such ceramic knives are seldom used outside of a kitchen and they are still quite uncommon. Plastic knives are difficult to make sharp and poorly retain an edge. They are largely used as low cost, disposable utensils or as children's utensils or in environments such as air travel where metal blades are prohibited. They are often serrated to compensate for their general lack of sharpness but, as evidenced by the fact they can cut food, they are still capable of inflicting injury. Plastic blades of designs other than disposable cutlery are prohibited or restricted in some jurisdictions as they are undetectable by metal detectors.
Metals
Nativecopper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
was used to make blades by ancient civilizations due to its availability. Copper's comparative softness causes it to deform easily; it does not hold an edge well and is poorly suited for working stone. Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
is superior in this regard, and was taken up by later
Later may refer to:
* Future
The future is the time after the past and present. Its arrival is considered inevitable due to the existence of time and the laws of physics. Due to the apparent nature of reality and the unavoidability of the futur ...
civilizations. Both bronze and copper can be work hardened by hitting the metal with a hammer. With technological advancement in smelting, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
came to be used in the manufacturing of blades. Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
, a range of alloys made from iron, has become the metal of choice for the modern age.
Various alloys of steel can be made which offer a wide range of physical and chemical properties desirable for blades. For example, surgical scalpels are often made of stainless steel so that they remain free of rust and largely chemically inert; tool steels are hard and impact resistant (and often expensive as retaining toughness and hardness requires expensive alloying materials, and, being hard, they are difficult to make into their finished shape) and some are designed to resist changes to their physical properties at high temperatures. Steels can be further heat treated to optimize their toughness, which is important for impact blades, or their hardness, which allows them to retain an edge well with use (although harder metals require more effort to sharpen).
Combined materials and heat-treatments
It is possible to combine different materials, or different heat treatments, to produce desirable qualities in a blade. For example, the finest Japanese swords were routinely made of up to seven sections of metals and even poorer quality swords were often made of two. These would include soft irons that could absorb the energy of impact without fracturing but which would bend and poorly retain an edge, and hard steels more liable to shatter on impact but which retained an edge well. The combination provided a sword that would resist impact while remaining sharp, even though the edge could chip if abused. Pattern welding involvedforging
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compression (physics), compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die (manufacturing), die. Forging is often classif ...
together twisted bars of soft (bendable) low carbon and hard (brittle) higher carbon iron. This was done because furnaces of the time were typically able to produce only one grade or the other, and neither was well suited for more than a very limited use blade. The ability of modern steelmakers to produce very high-quality steels of various compositions has largely relegated this technique to either historical recreations or to artistic works. Acid etching and polishing blades made of different grades of steel can be used to produce decorative or artistic effects.
Japanese sword makers developed the technique of differential hardening by covering their sword blades in different thicknesses of clay before quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, gas, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, suc ...
. Thinner clay allowed the heated metal to cool faster, particularly along the edge. Faster cooling resulted in a finer crystal structure, resulting in a blade with a hard edge but a more flexible body. European sword makers produced similar results using differential tempering.
Dulling
Blades dull with use and abuse. This is particularly true of acute blades and those made of soft materials. Dulling usually occurs due to contact between the blade and a hard substance such as ceramic, stone, bone, glass, or metal. The more acute the blade, the more easily it will dull. As the blade near the edge is thinner, there is little material to remove before the edge is worn away to a thicker section. Thin edges can also roll over when force is applied it them, forming a section like the bottom part of a letter "J". For this reason, straight edge razors are frequently stropped to straighten the edge.
Drawing a blade across any material tends to abrade both the blade, usually making it duller, and the cut material. Though softer than glass or many types of stone used in the kitchen, steel edges can still scratch these surfaces. The resulting scratch is full of very fine particles of ground glass or stone which will very quickly abrade the blade's edge and so dull it.
In times when swords were regularly used in warfare, they required frequent sharpening because of dulling from contact with rigid armor, mail, metal rimmed shields, or other swords, for example. Particularly, hitting the edge of another sword by accident or in an emergency could chip away metal and even cause cracks through the blade. Soft-cored blades are more resistant to fracturing on impact.
The more acute the blade, the more easily it will dull. As the blade near the edge is thinner, there is little material to remove before the edge is worn away to a thicker section. Thin edges can also roll over when force is applied it them, forming a section like the bottom part of a letter "J". For this reason, straight edge razors are frequently stropped to straighten the edge.
Drawing a blade across any material tends to abrade both the blade, usually making it duller, and the cut material. Though softer than glass or many types of stone used in the kitchen, steel edges can still scratch these surfaces. The resulting scratch is full of very fine particles of ground glass or stone which will very quickly abrade the blade's edge and so dull it.
In times when swords were regularly used in warfare, they required frequent sharpening because of dulling from contact with rigid armor, mail, metal rimmed shields, or other swords, for example. Particularly, hitting the edge of another sword by accident or in an emergency could chip away metal and even cause cracks through the blade. Soft-cored blades are more resistant to fracturing on impact.
Nail pulls
Folding pocket knives often have a groove cut in the side of the blade near the spine. This is called a nail pull and allows the fingernail to be inserted to swing the blade out of the holder.Knife patterns
Some of the most common shapes are listed below. ;S1: A ''straight back'' blade, also called ''standard'' or ''normal'', has a curving edge and a straight back. A dull back lets the wielder use fingers to concentrate force; it also makes the knife heavy and strong for its size. The curve concentrates force on a smaller area, making cutting easier. This knife can chop as well as pick and slice. This is also the best single-edged blade shape for thrusting, as the edge cuts a swath that the entire width of the knife can pass through without the spine having to push aside any material on its path, as a sheepsfoot or drop-point knife would. ;S2: A ''trailing-point'' knife has a back edge that curves upward to end above the spine. This lets a lightweight knife have a larger curve on its edge and indeed the whole of the knife may be curved. Such a knife is optimized for slicing or slashing. Trailing point blades provide a larger cutting area, or belly, and are common on skinning knives. ;S3: A ''drop point
Drop point is a style of knife blade that slopes on the spine of the blade from the handle of the knife to the tip of the blade. This allows the spine of the blade (where the blade is thicker, and thus stronger) to continue forward to the tip of ...
'' blade has a convex curve of the back towards the point. It handles much like the ''clip-point'', though with a stronger point typically less suitable for piercing. Swiss army pocket knives often have drop-points on their larger blades.
;S4: A '' clip-point'' blade is like a normal blade with the back "clipped". This clip can be either straight or concave. The back edge of the clip may have a false edge that could be sharpened to make a second edge. The sharp tip is useful as a pick, or for cutting in tight places. If the false edge is sharpened it increases the knife's effectiveness in piercing. As well, having the tip closer to the center of the blade allows greater control in piercing. The Bowie knife
A Bowie knife ( ) is a pattern of fixed-blade fighting knives created by Rezin Bowie in the early 19th century for his brother James Bowie, who had become famous for his use of a large knife at a duel known as the Sandbar Fight.
Since its fir ...
has a clip point blade and clip-points are common on pocket knives and other folding knives.
;S5: A ' blade has a straightedge and a straight dull back that curves towards the edge at the end. It gives the most control because the dull back edge is made to be held by fingers. Sheepsfoot blades were originally made to trim the hooves of sheep; their shape bears no similarity to the foot of a sheep.
;S6: A ''Wharncliffe'' blade is similar in profile to a sheep's foot but the curve of the back edge starts closer to the handle and is more gradual. Its blade is much thicker than a knife of comparable size. Wharncliffes were used by sailors, as the shape of the tip prevented accidental penetration of the work or the user's hand with the sudden motion of a ship.
;S7: A ''spey point'' blade (once used for neutering livestock) has a single, sharp, straight edge that curves strongly upwards at the end to meet a short, dull, straight point from the dull back. With the curved end of the blade being closer to perpendicular to the blade's axis than other knives and lacking a point, making penetration unlikely, spey blades are common on Trapper style pocket knives for skinning fur-bearing animals.
 ;C2: A ''spear point'' blade is a symmetrically-shaped blade with a point aligned with the centerline of the blade's long axis. True spear-point blades are double-edged with a central spine, like a dagger or
;C2: A ''spear point'' blade is a symmetrically-shaped blade with a point aligned with the centerline of the blade's long axis. True spear-point blades are double-edged with a central spine, like a dagger or spear
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with Fire hardening, fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable materia ...
head. The spear point is one of the stronger blade point designs in terms of penetration stress, and is found on many thrusting knives such as the dagger. The term spear point is occasionally and confusingly used to describe small single-edged blades without a central spine, such as that of the '' pen knife'', a small folding-blade pocket knife formerly used in sharpening quills for writing. Pen-knife may also nowadays refer to a knifelike weapon blade pattern of some of larger pocket knife blades that would otherwise be termed drop-point designs.
;C3: A ''needle point'' blade has a sharply-tapered acuminated point. It is frequently found on dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually one or two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a cutting or stabbing, thrusting weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or ...
s such as the stiletto
A stiletto (plural stilettos) is a specialized dagger with a long slender blade and needle-like point, primarily intended as a thrusting and stabbing weapon.Limburg, Peter R., ''What's In The Names Of Antique Weapons'', Coward, McCann & Geoghega ...
(which had no sharpened edges) and the Fairbairn–Sykes fighting knife. Its long, narrow point reduces friction and increases the blade's penetrative capabilities, but is liable to stick in bone and can break if abused. When the needle point is combined with a reinforced 'T' section running the length of the blade's spine, it is called a ''reinforced tip''. One example of a knife with a reinforced tip is the ''pesh-kabz
The pesh-kabz or peshkabz (, ) is a type of Indo-Persian knife designed to penetrate mail armour and other types of armour.Lexicon of Medieval Knives and Daggers', retrieved 5 July 2011Shackleford, Steve, (ed.), ''Blade's Guide To Knives And Th ...
''.
;C4: Kris
The kris or is a Javanese culture, Javanese asymmetrical dagger with a distinctive blade-patterning achieved through alternating laminations of iron and nickelous iron (''pamor''). The kris is famous for its distinctive wavy blade, although ma ...
or flame-bladed sword
A flame-bladed sword or wave-bladed sword has a characteristically undulating style of blade. The wave in the blade is often considered to contribute a flame-like quality to the appearance of a sword. The dents on the blade can appear parallel o ...
. These blades have a distinct recurved blade form and are sharpened on both sides, typically tapering to (or approximating) a symmetrical point.
;C5: Referred to in English speaking countries as a "tanto" or "tanto a corruption of the Japanese word ''tantō
A is a traditionally made Japanese knife () that was worn by the samurai class of feudal Japan. The dates to the Heian period, when it was mainly used as a weapon but evolved in design over the years to become more ornate. were used in tradit ...
'', despite the tip bearing no resemblance to a or as a ''chisel
A chisel is a hand tool with a characteristic Wedge, wedge-shaped cutting edge on the end of its blade. A chisel is useful for carving or cutting a hard material such as woodworking, wood, lapidary, stone, or metalworking, metal.
Using a chi ...
point'', referring to the straightness of the edge that comprises the end of the blade (and not to be confused with a blade said to have a "chisel grind", which would refer to a blade ground on only one side, even though chisels can be ground on one or both sides). It is similar to, but not the same as, some early Japanese swords that had ''kamasu kissaki'' ("barracuda tip"), a ''nearly'' straight edge at the tip whereas the typical "tanto point" as found in the west has a straight edge. The barracuda tip sword was sharp but also fragile whereas modern tanto points are often advertised as being stronger at the tip for having nearly the whole thickness of the blade present until quite close to the end of the knife. The geometry of the angle under the point gives tanto blades excellent penetration capabilities. For this reason, tanto blades are often found on knives designed for combat or fighting applications, where the user may need to pierce heavy clothing or low-level soft body armor. With a ''modified tanto'', the end is clipped and often sharpened. This brings the tip closer to the center of the blade increasing control of the blade and improves penetration potential by having a finer point and a sharpened back edge.
;C6: A ''hawkbill'' blade is sharpened on the inside edge and is similar to carpet and linoleum knives. The point will tear even if the rest of the knife is comparatively dull. The karambit from Far South-East Asia is a hawkbill knife which is held with the blade extending from the bottom of the fist and the tip facing forward. The outside edge of a karambit may be sharp and if so may also feature a backward-facing point.
;C7: An '' ulu'' (lit. 'woman's knife' in Inuktitut
Inuktitut ( ; , Inuktitut syllabics, syllabics ), also known as Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the North American tree line, including parts of the provinces of ...
) knife is a sharpened segment of a circle. This blade type has no point, and has a handle in the middle. It is good for scraping and sometimes chopping. The semi-circular version appears elsewhere in the world and is called a ''head knife''. It is used in leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning (leather), tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffal ...
working both to scrape down leather (reducing thickness, i.e. skiving), and to make precise, rolling cuts for shapes other than straight lines. The circular version is a popular tool for slicing pizza
Pizza is an Italian cuisine, Italian, specifically Neapolitan cuisine, Neapolitan, dish typically consisting of a flat base of Leavening agent, leavened wheat-based dough topped with tomato, cheese, and other ingredients, baked at a high t ...
s. One corner is placed at the edge of the pizza and the blade is rolled across in a diameter cut.
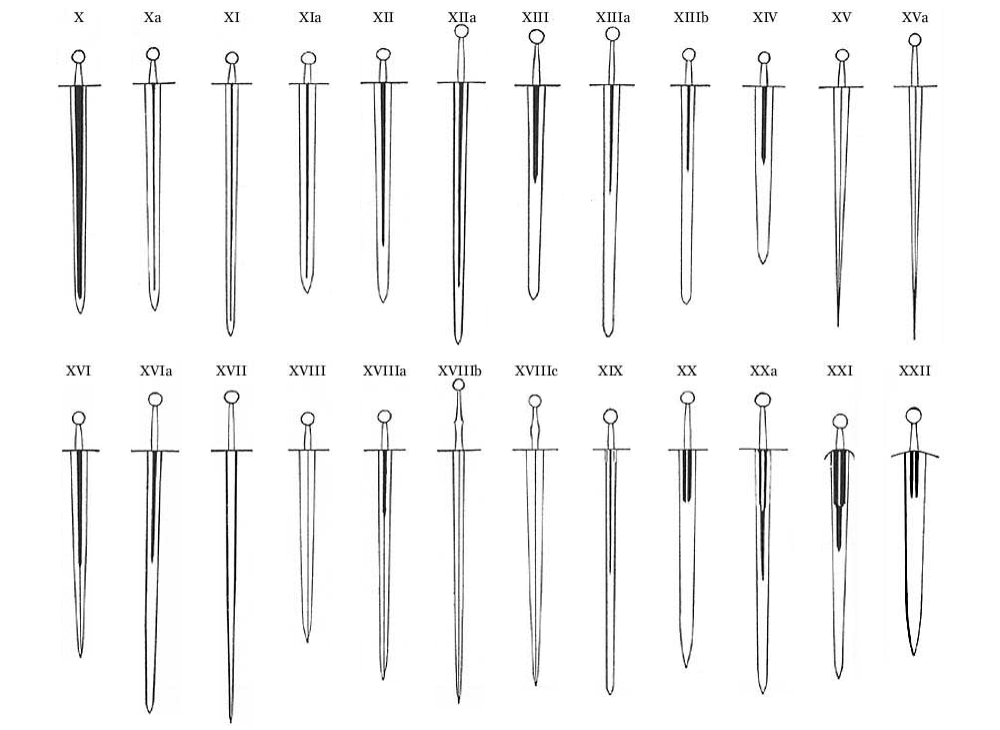
Sword patterns
 The sharp edges of a
The sharp edges of a sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
may be either curved or straight. Curved blades tend to glide more easily through soft materials, making these weapons more ideal for slicing. Techniques for such weapons feature drawing the blade across the opponent's body and back. For straight-edged weapons, many recorded techniques feature cleaving cuts, which deliver the power out to a point, striking directly in at the target's body, done to split flesh and bone rather than slice it. That being said, there also exist many historical slicing techniques for straight-edged weapons. Hacking cuts can be followed by a drawing action to maximize the cut's effectiveness. For more information see Western Martial Arts or kenjutsu
is an umbrella term for all ('' ko-budō'') schools of Japanese swordsmanship, in particular those that predate the Meiji Restoration. Some modern styles of kendo and iaido that were established in the 20th century also included modern forms o ...
.
Some weapons are made with only a single leading edge, such as the sabre
A sabre or saber ( ) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the Early Modern warfare, early modern and Napoleonic period, Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such a ...
or dusack. The dusack has a 'false edge' near the tip, which only extends down a portion of the blade's backside. Other weapons have a blade that is entirely dull except for a sharpened point, like the épée
The (, ; ), also rendered as epee in English, is the largest and heaviest of the three weapons used in the sport of fencing. The modern derives from the 19th-century , a weapon which itself derives from the French small sword. This contains a ...
or foil
Foil may refer to:
Materials
* Foil (metal), a quite thin sheet of metal, usually manufactured with a rolling mill machine
* Metal leaf, a very thin sheet of decorative metal
* Aluminium foil, a type of wrapping for food
* Tin foil, metal foil ma ...
, which prefer thrusts over cuts. A blade cannot perform a proper cut without an edge, and so in competitive fencing such attacks reward no points.
Some variations include:
* The flame blade (an undulated blade, for both psychological effect and some tactical advantage of using a non-standard blade: vibrations and easier parry)
* The colichemarde, found in smallsword
Marks and decoration
 Blades are sometimes marked or inscribed, for decorative purposes, or with the mark of either the maker or the owner. Blade decorations are often realized in
Blades are sometimes marked or inscribed, for decorative purposes, or with the mark of either the maker or the owner. Blade decorations are often realized in inlay
Inlay covers a range of techniques in sculpture and the decorative arts for inserting pieces of contrasting, often colored materials into depressions in a base object to form Ornament (art), ornament or pictures that normally are flush with the ...
in some precious metal (gold or silver).
Early blade inscriptions are known from the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, a Hittite sword found at Hattusa
Hattusa, also Hattuşa, Ḫattuša, Hattusas, or Hattusha, was the capital of the Hittites, Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age during two distinct periods. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey (originally Boğazköy) within the great ...
bears an inscription chiseled into the bronze, stating that the blade was deposited as an offering to the storm-god by king Tuthaliya.
Blade inscriptions become particularly popular in the 12th century knightly sword
In the European High Middle Ages, the typical sword (sometimes academically categorized as the knightly sword, arming sword, or in full, knightly arming sword) was a straight, double-edged weapon with a single-handed, cruciform (i.e., cross-shape ...
, based on the earlier, 9th to 11th century, the tradition of the so-called Ulfberht swords.Geibig, A. (1991), Beiträge zur morphologischen Entwicklung des Schwertes im Mittelalter.
See also
* Athamé *List of premodern combat weapons
This is a list of notable types of weapons that were used in warfare, and more broadly in combat, prior to the advent of the early modern period, i.e., approximately prior to the start of the 16th century. It therefore excludes objects that may b ...
References
External links
HROARR – Robert Geißler, Concerning the Sharpness of Blades
{{Use dmy dates, date=August 2016 Edged and bladed weapons Cutting tools