Birendra Singh Rana With Cabinet Minister Ashutosh Tondon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Birendra Bir Bikram Shah Dev ( ne, ÓżČÓźŹÓż░ÓźĆ Óź½ Óż«Óż╣ÓżŠÓż░ÓżŠÓż£ÓżŠÓż¦Óż┐Óż░ÓżŠÓż£ ÓżĄÓźĆÓż░ÓźćÓż©ÓźŹÓż”ÓźŹÓż░ ÓżĄÓźĆÓż░ ÓżĄÓż┐ÓżĢÓźŹÓż░Óż« ÓżČÓżŠÓż╣ Óż”ÓźćÓżĄ ) (28 December 1945 ŌĆō 1 June 2001) was the tenth Shah Ruler and the King of Nepal from 1972 until his
 In 1990, a series of strikes and pro-democracy riots broke out in Nepal. Due to the riots, Birendra lifted the ban on political parties and agreed to become a constitutional monarch in April 1990. He appointed an independent Constitution Recommendation Commission to represent the main opposition factions and to prepare a new constitution to accommodate their demands for political reform. The commission presented him with the draft of the proposed constitution on 10 September 1990. The new constitution would make Birendra head of state of a constitutional monarchy with a system of multiparty democracy. The draft constitution was approved by the Prime Minister Krishna Prasad Bhattarai and his cabinet and so, on 9 November 1990, Birendra promulgated the new constitution transformed Nepal into a constitutional monarchy. As a constitutional monarchy, Birendra became more popular than he was as a autocratic ruler attributing to his democratic views and behaviors as well as the inability of the political parties. Birendra, however, could not prevent the Nepalese Civil War, a conflict between Maoist rebels and government forces, which lasted from 1996 until 2006.Sharma, S. (2019). ''The Nepal Nexus: An Inside Account of the Maoists, the Durbar and New Delhi''. Penguin Random House India Private Limited.
In 1990, a series of strikes and pro-democracy riots broke out in Nepal. Due to the riots, Birendra lifted the ban on political parties and agreed to become a constitutional monarch in April 1990. He appointed an independent Constitution Recommendation Commission to represent the main opposition factions and to prepare a new constitution to accommodate their demands for political reform. The commission presented him with the draft of the proposed constitution on 10 September 1990. The new constitution would make Birendra head of state of a constitutional monarchy with a system of multiparty democracy. The draft constitution was approved by the Prime Minister Krishna Prasad Bhattarai and his cabinet and so, on 9 November 1990, Birendra promulgated the new constitution transformed Nepal into a constitutional monarchy. As a constitutional monarchy, Birendra became more popular than he was as a autocratic ruler attributing to his democratic views and behaviors as well as the inability of the political parties. Birendra, however, could not prevent the Nepalese Civil War, a conflict between Maoist rebels and government forces, which lasted from 1996 until 2006.Sharma, S. (2019). ''The Nepal Nexus: An Inside Account of the Maoists, the Durbar and New Delhi''. Penguin Random House India Private Limited.
 He managed to maintain NepalŌĆÖs independence despite encroaching influences by India, China, and the Soviet Union. His first trips abroad as king were to India in October 1973 and
He managed to maintain NepalŌĆÖs independence despite encroaching influences by India, China, and the Soviet Union. His first trips abroad as king were to India in October 1973 and
 King Birendra was regarded as a lover of nature and a great supporter of nature conservation. The trend of nature conservation from the government started during his reign. The dramatic decline of the rhinoceros population due to massive Terai migration and the extent of poaching prompted the government to institute the Rhino Patrol force (Nepali: ''ÓżŚÓźłÓżĪÓżŠ ÓżŚÓżĖÓźŹÓżżÓźĆ'' ) of 130 armed men and a network of guard posts all over Chitwan. To prevent the extinction of rhinos through a legal system, National park law was introduced which gazetted the Chitwan National Park in December 1970, with borders delineated the following year and established in 1973.Gurung, K. K. (1983). ''Heart of the Jungle: the Wildlife of Chitwan, Nepal''. Andr├® Deutsch, London.Adhikari, T. R. (2002)
King Birendra was regarded as a lover of nature and a great supporter of nature conservation. The trend of nature conservation from the government started during his reign. The dramatic decline of the rhinoceros population due to massive Terai migration and the extent of poaching prompted the government to institute the Rhino Patrol force (Nepali: ''ÓżŚÓźłÓżĪÓżŠ ÓżŚÓżĖÓźŹÓżżÓźĆ'' ) of 130 armed men and a network of guard posts all over Chitwan. To prevent the extinction of rhinos through a legal system, National park law was introduced which gazetted the Chitwan National Park in December 1970, with borders delineated the following year and established in 1973.Gurung, K. K. (1983). ''Heart of the Jungle: the Wildlife of Chitwan, Nepal''. Andr├® Deutsch, London.Adhikari, T. R. (2002)
''The curse of success''.
Habitat Himalaya - A Resources Himalaya Factfile, Volume IX, Number 3. For the purpose of conservation of Tigers in the nation, an area of 368 km2 was gazetted as ''Royal Karnali Wildlife Reserve'' in 1976 which was later proclaimed as Royal Bardiya Wildlife Reserve in 1982. The Babai River Valley was further added to this reserved area in 1984. A flourishing ecosystem in the reserve later led to the proclamation of the area as national park in 1988.Majupuria, T. C., Kumar, R. (1998). ''Wildlife, National Parks and Reserves of Nepal.'' S. Devi, Saharanpur and Tecpress Books, Bangkok. The country's fourth protected area was established in 1976 from the Himalayan area of Langtang and named as Langtang National Park. For this purpose, an area of 1,710 km2 was reserved in the district of Nuwakot,
For the purpose of conservation of Tigers in the nation, an area of 368 km2 was gazetted as ''Royal Karnali Wildlife Reserve'' in 1976 which was later proclaimed as Royal Bardiya Wildlife Reserve in 1982. The Babai River Valley was further added to this reserved area in 1984. A flourishing ecosystem in the reserve later led to the proclamation of the area as national park in 1988.Majupuria, T. C., Kumar, R. (1998). ''Wildlife, National Parks and Reserves of Nepal.'' S. Devi, Saharanpur and Tecpress Books, Bangkok. The country's fourth protected area was established in 1976 from the Himalayan area of Langtang and named as Langtang National Park. For this purpose, an area of 1,710 km2 was reserved in the district of Nuwakot,
 Focusing on sustainability and environmental conservation, on , trolley bus system was established in Nepal from the aid of People's Republic of China. He followed in the path of his father to establish industrial estates by establishing Nepalgunj Industrial Area(1973), Pokhara Industrial Area(1974), Butwal Industrial Area(1976), Bhaktapur Industrial Area(1979), Dhankuta Industrial Area(1980), Birendranagar Industrial Area(1981), Gajendranarayan Industrial Area(1986) respectively.
Birendra is initially credited for devising the plan of Melamchi water project to Kathmandu. Gorakhali Tires Industries, Udayapur Cement Industries Limited, Nepal Metal company, Nepal Pharmaceuticals were all established during his time. King Birendra, was the patron of Pashupati Area Development Trust. In April 1979, Nepal Oriental Magnesite factory was established with a joint investment of Nepal government and Orissa Industries, India at Lakuri Danda in Dolakha District with the objective of producing dead burnt magnesite and talc powder. In 1983 he was able to establish a Nepal-Pakistan Joint Economic Commission bringing in significant foreign investments in the country.
A 60 Megawatt hydropower project at Kulekhani began operation in 1982 with economic aid from the World Bank, Kuwait, and
Focusing on sustainability and environmental conservation, on , trolley bus system was established in Nepal from the aid of People's Republic of China. He followed in the path of his father to establish industrial estates by establishing Nepalgunj Industrial Area(1973), Pokhara Industrial Area(1974), Butwal Industrial Area(1976), Bhaktapur Industrial Area(1979), Dhankuta Industrial Area(1980), Birendranagar Industrial Area(1981), Gajendranarayan Industrial Area(1986) respectively.
Birendra is initially credited for devising the plan of Melamchi water project to Kathmandu. Gorakhali Tires Industries, Udayapur Cement Industries Limited, Nepal Metal company, Nepal Pharmaceuticals were all established during his time. King Birendra, was the patron of Pashupati Area Development Trust. In April 1979, Nepal Oriental Magnesite factory was established with a joint investment of Nepal government and Orissa Industries, India at Lakuri Danda in Dolakha District with the objective of producing dead burnt magnesite and talc powder. In 1983 he was able to establish a Nepal-Pakistan Joint Economic Commission bringing in significant foreign investments in the country.
A 60 Megawatt hydropower project at Kulekhani began operation in 1982 with economic aid from the World Bank, Kuwait, and
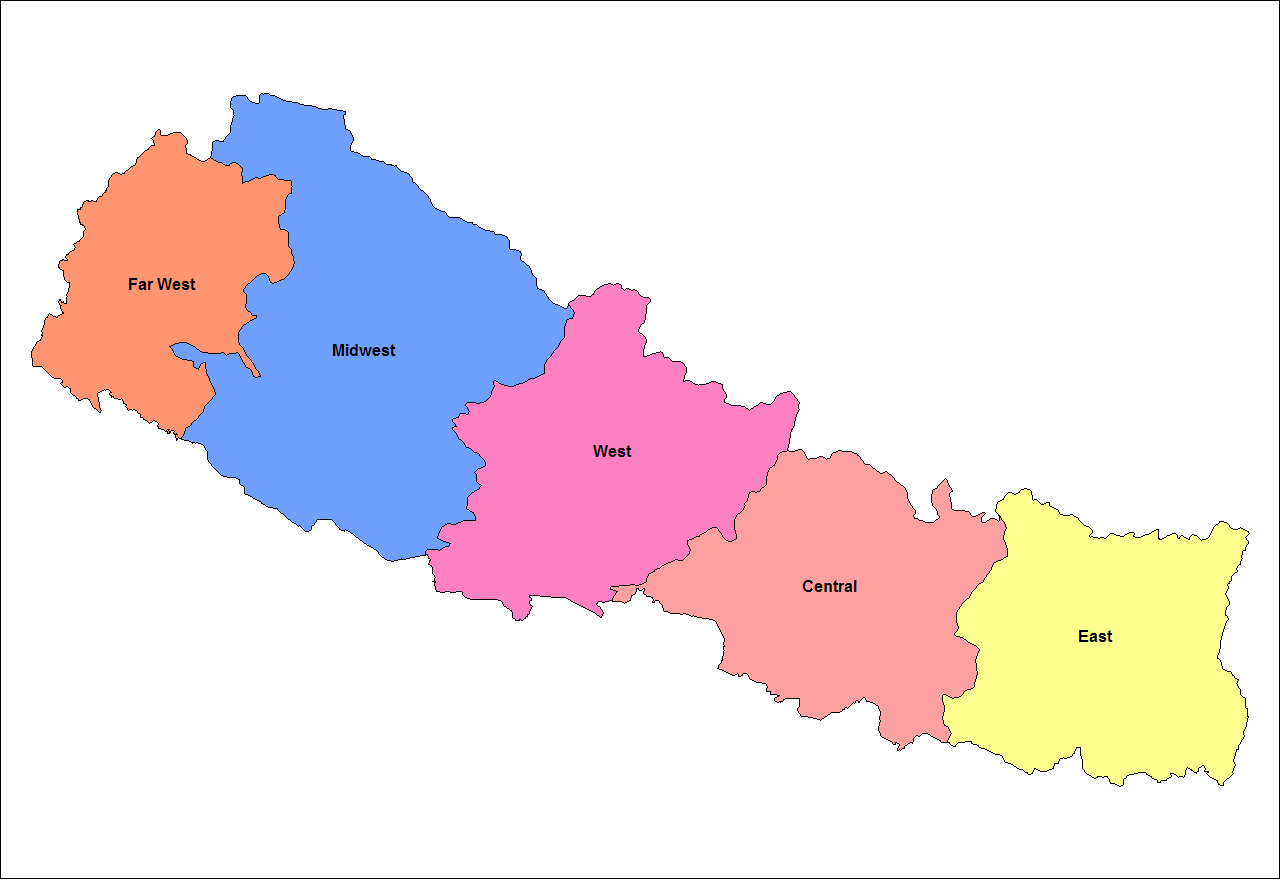 During the reign of King Birendra, referendum was held in 2037 BS for democracy wherein options were a multi-party system or a Panchayati system. During the Panchayat era and after the national referendum, he divided the nation into 5 development regions in order to create balanced development, and visited each division once a year; the visits were discontinued after 1990 democracy movement.
Despite previously being an autocratic rule and constant pressure from the supporters and royal members, the king always played the role of constitutional monarch by the book and never overstepped his boundaries. King Birendra was always there when there was some political crisis in the nation. Mid-term elections, 2051 and General Election, 2056 can be attributed to his good governance. The King regularly asked the Supreme Court for its advice on any political matters that could concern the constitution so that he would never overstep the boundaries of the constitution. He created a culture where the king and prime minister would meet every Thursday at his palace to discuss matters of state.
During the reign of King Birendra, referendum was held in 2037 BS for democracy wherein options were a multi-party system or a Panchayati system. During the Panchayat era and after the national referendum, he divided the nation into 5 development regions in order to create balanced development, and visited each division once a year; the visits were discontinued after 1990 democracy movement.
Despite previously being an autocratic rule and constant pressure from the supporters and royal members, the king always played the role of constitutional monarch by the book and never overstepped his boundaries. King Birendra was always there when there was some political crisis in the nation. Mid-term elections, 2051 and General Election, 2056 can be attributed to his good governance. The King regularly asked the Supreme Court for its advice on any political matters that could concern the constitution so that he would never overstep the boundaries of the constitution. He created a culture where the king and prime minister would meet every Thursday at his palace to discuss matters of state.


 Sovereign of the Order of Nepal Pratap Bhaskara
*
Sovereign of the Order of Nepal Pratap Bhaskara
*  Sovereign of the Order of Ojaswi Rajanya
*
Sovereign of the Order of Ojaswi Rajanya
*  Sovereign of the Order of Nepal Taradisha
*
Sovereign of the Order of Nepal Taradisha
*  Sovereign of the Order of Tri Shakti Patta
*
Sovereign of the Order of Tri Shakti Patta
*  Sovereign of the Order of Gorkha Dakshina Bahu
* Most Glorious Mahendra Chain
*
Sovereign of the Order of Gorkha Dakshina Bahu
* Most Glorious Mahendra Chain
*  Recipient of the King Mahendra Investiture Medal (02/05/1956)
; Foreign orders
* :
**
Recipient of the King Mahendra Investiture Medal (02/05/1956)
; Foreign orders
* :
** Knight of the Order of the Rajamitrabhorn, (1979)
* :
**
Knight of the Order of the Rajamitrabhorn, (1979)
* :
** Knight of the
Knight of the  Knight Grand Cordon with Collar of the Order of the Chrysanthemum, (1975)
* :
**
Knight Grand Cordon with Collar of the Order of the Chrysanthemum, (1975)
* :
** Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Makarios III of Cyprus, (1980)
* :
**
Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Makarios III of Cyprus, (1980)
* :
** Knight Grand Cordon with Collar of the Order of the Million Elephants and the White Parasol, (1970)
* :
**
Knight Grand Cordon with Collar of the Order of the Million Elephants and the White Parasol, (1970)
* :
** Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Gold Lion of the House of Nassau, (22 March 1975)
* :
**
Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Gold Lion of the House of Nassau, (22 March 1975)
* :
** Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour, Order of the Legion of Honour, (02/05/1983)
* :
**
Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour, Order of the Legion of Honour, (02/05/1983)
* :
** Grand Cross Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany, (1986)
* :
**
Grand Cross Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany, (1986)
* :
** Knight Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Charles III, Order of Carlos III, (19 September 1983)
* :
**
Knight Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Charles III, Order of Carlos III, (19 September 1983)
* :
** Nishan-e-Pakistan, (1983)
* :
**
Nishan-e-Pakistan, (1983)
* :
** Grand Cross of the Order of the Star of Romania, (1975)
* :
**
Grand Cross of the Order of the Star of Romania, (1975)
* :
** Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Merit (Chile), Order of Merit of Chile (1989)
* :
**
Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Merit (Chile), Order of Merit of Chile (1989)
* :
** Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of the White Rose of Finland, Order of the White Rose, (1988)
* :
**
Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of the White Rose of Finland, Order of the White Rose, (1988)
* :
** Collar of the Order of the Nile, (1974)
* :
**
Collar of the Order of the Nile, (1974)
* :
** Great Star of the Order of the Yugoslav Star, (2 February 1974)
* Socialist Republic of Romania, Romania:
**
Great Star of the Order of the Yugoslav Star, (2 February 1974)
* Socialist Republic of Romania, Romania:
** Knight Grand Cross of the Order of 23 August (1987)
* :
**
Knight Grand Cross of the Order of 23 August (1987)
* :
** Recipient of the Royal Victorian Chain (23 February 1975)
; Association honours
* :
**
Recipient of the Royal Victorian Chain (23 February 1975)
; Association honours
* :
** Golden Pheasant Award of the Scout Association of Japan, (1978)
Golden Pheasant Award of the Scout Association of Japan, (1978)
Election
, - {{DEFAULTSORT:Birendra Bir Bikram Shah Dev 2001 murders in Asia Nepalese monarchs British field marshals 21st-century murdered monarchs Nepalese Hindus Nepalese murder victims Deaths by firearm in Nepal People educated at Eton College University of Tokyo alumni Harvard University alumni 1945 births 2001 deaths People murdered in Nepal Male murder victims Grand Croix of the L├®gion d'honneur Grand Crosses Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany Grand Crosses of the Order of the Star of Romania Recipients of Nishan-e-Imtiaz Shah dynasty MurderŌĆōsuicides in Asia Assassinated people Assassinated heads of state People of the Nepalese Civil War Hindu monarchs
assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
in 2001. He was the eldest son of King Mahendra
Mahendra is a Sanskrit compound word deriving from Maha (Highest position) and Indra Deva (the King of Gods) from Hindu mythology.{{Citation needed, date=April 2022 It has been used in compound royal styles.
History and politics
Royalty
* M ...
.
Early life and education
Birendra was born at theNarayanhiti Royal Palace
The Narayanhiti Palace Museum ( Nepali: Óż©ÓżŠÓż░ÓżŠÓż»ÓżŻÓż╣Óż┐Óż¤ÓźĆ Óż”Óż░ÓżĄÓżŠÓż░) is a public museum in Kathmandu, Nepal located east of the Kaiser Mahal and next to Thamel. The museum was created in 2008 from the complex of the former Nar ...
in Kathmandu as the eldest son of the then Crown Prince Mahendra Bir Bikram Shah Dev and his first wife, Crown Princess Indra Rajya Lakshmi Devi.
Birendra spent eight years studying at St Joseph's School, a Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
school in Darjeeling, with his brother Gyanendra. On 13 March 1955, their grandfather King Tribhuvan died and their father succeeded the Nepalese throne. With his father's ascension, Birendra became the crown prince of Nepal.
In 1959, Birendra was enrolled at Eton College in the United Kingdom. After studying at Eton until 1964, he returned to Nepal where he began to explore the country by traveling on foot to the remote parts of the country where he lived humbly with what was available in the villages. He later completed his education by spending some time at the University of Tokyo, before studying political theory at Harvard University from 1967 to 1968. Birendra enjoyed travelling in his youth, and went on trips to Canada, Latin America, Africa, many parts of India, and a number of other Asian countries. He was also an art collector and supporter of Nepalese craftspeople and artists and learned to fly helicopters.
Birendra was married to Aishwarya Rajya Lakshmi Devi from the Rana family, his second cousin, on 27 February 1970. The wedding, which was billed as one of the most lavish Hindu nuptial ceremonies in history, cost $9.5 million to stage.
Early reign
Birendra ascended to the Nepalese throne on 31 January 1972, at the age of 27, after the death of his father, King Mahendra. However, his coronation was delayed until February 24, 1975, when he was 29, since the first year was considered to be a mourning period for death of king's father and the second year was deemed to be inauspicious by religious astrologers. As a Hindu monarch, he had to follow Nepalese tradition.Panchayat era (1972-1980)
On his ascension to the throne, Birendra was effectively an absolute monarch, as he inherited a country where political parties were banned and he ruled through a system of local and regional councils known as panchayats.Panchayat era (1980-1990)
In an attempt to maintain the '' panchayat'' system of government prominent leaders of theNepali Congress Party
The Nepali Congress ( ne, Óż©ÓźćÓż¬ÓżŠÓż▓ÓźĆ ÓżĢÓżŠÓżéÓżŚÓźŹÓż░ÓźćÓżĖ ; abbr. NC) is the largest social democratic political party in Nepal. As per the results of recent local election, ''Nepali Congress'' stands as the single largest party of ...
were arrested frequently. During the 1980s the restraints that had been imposed on political organizations were eased, and liberal student-led groups started to demand constitutional change in Nepal. Because of the growing pro-democracy movement Birendra announced that a referendum to decide between a party-less or a multi-party system would be held. During, referendum options were given for a multi-party system or a Panchayati system. The referendum was held in May 1980 with the party-less system winning by a margin of 55% to 45%. The result of the election led the king to make mass restructuring of country both economically and politically. After the national referendum, he divided the nation into 5 development regions in order to create balanced development and visited each division once a year; the visits were discontinued after his status as a constitutional monarchy in 1990.
Democratic era
 In 1990, a series of strikes and pro-democracy riots broke out in Nepal. Due to the riots, Birendra lifted the ban on political parties and agreed to become a constitutional monarch in April 1990. He appointed an independent Constitution Recommendation Commission to represent the main opposition factions and to prepare a new constitution to accommodate their demands for political reform. The commission presented him with the draft of the proposed constitution on 10 September 1990. The new constitution would make Birendra head of state of a constitutional monarchy with a system of multiparty democracy. The draft constitution was approved by the Prime Minister Krishna Prasad Bhattarai and his cabinet and so, on 9 November 1990, Birendra promulgated the new constitution transformed Nepal into a constitutional monarchy. As a constitutional monarchy, Birendra became more popular than he was as a autocratic ruler attributing to his democratic views and behaviors as well as the inability of the political parties. Birendra, however, could not prevent the Nepalese Civil War, a conflict between Maoist rebels and government forces, which lasted from 1996 until 2006.Sharma, S. (2019). ''The Nepal Nexus: An Inside Account of the Maoists, the Durbar and New Delhi''. Penguin Random House India Private Limited.
In 1990, a series of strikes and pro-democracy riots broke out in Nepal. Due to the riots, Birendra lifted the ban on political parties and agreed to become a constitutional monarch in April 1990. He appointed an independent Constitution Recommendation Commission to represent the main opposition factions and to prepare a new constitution to accommodate their demands for political reform. The commission presented him with the draft of the proposed constitution on 10 September 1990. The new constitution would make Birendra head of state of a constitutional monarchy with a system of multiparty democracy. The draft constitution was approved by the Prime Minister Krishna Prasad Bhattarai and his cabinet and so, on 9 November 1990, Birendra promulgated the new constitution transformed Nepal into a constitutional monarchy. As a constitutional monarchy, Birendra became more popular than he was as a autocratic ruler attributing to his democratic views and behaviors as well as the inability of the political parties. Birendra, however, could not prevent the Nepalese Civil War, a conflict between Maoist rebels and government forces, which lasted from 1996 until 2006.Sharma, S. (2019). ''The Nepal Nexus: An Inside Account of the Maoists, the Durbar and New Delhi''. Penguin Random House India Private Limited.
Notable works and improvements
Diplomatic campaign
 He managed to maintain NepalŌĆÖs independence despite encroaching influences by India, China, and the Soviet Union. His first trips abroad as king were to India in October 1973 and
He managed to maintain NepalŌĆÖs independence despite encroaching influences by India, China, and the Soviet Union. His first trips abroad as king were to India in October 1973 and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
two months later. He prevented the breaking up of Mustang from Nepal and Tibet from China during the Mustang revolution. The disarmament of Khampas rebellions working against China brought Nepal-China relations to a new height. His compatriots remember him for his extensive campaign and contribution for the establishment of South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation and South Asian food reserve. During his reign, he was also able to set up the SAARC Secretariat in Kathmandu. He was able to establish diplomatic relations with additional 46 countries taking the total number of countries for diplomatic relations from 49 to 96. He further strengthened Nepal's policy of neutrality by promoting Nepal as zone of Peace in the UN. He believed that Nepal, sandwiched between the two Asian powers, should have good relationship with both.
Promotion of peace
He proposed Nepal to be declared a zone of Peace in the United Nations meeting, taking into consideration Nepal's historic peace status, birth of Gautam Buddha and its historical policy of Non-alignment to any foreign powers. This proposal was supported by 116 countries in the UNO. He later established a "Peace Keeping Training Camp" in 1986. This was later restructured into a training institute in 2001 for training peace keeping forces . It was later renamed as Birendra Peace Operations Training Centre. This institute, was later restructured as the training organization through which Nepal started sending trained, peace-keeping forces in cooperation with the UN and became an active member of it. In 1974, King Birendra was successful in peacefully disarming theKham
Kham (; )
is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham ...
pas rebellions, settled in the northern Himalayan region, by giving land, money and citizenship to those who surrendered their arms, and by confiscating weapons as well. Thus who did not surrender would be prohibited from moving toward the Tibetan region. Birendra is also credited with blocking the use of the army for suppressing the Maoist revolution in the country, which would've further aggravated the situation and disturbed the peace in the nation.
Environmental protection
 King Birendra was regarded as a lover of nature and a great supporter of nature conservation. The trend of nature conservation from the government started during his reign. The dramatic decline of the rhinoceros population due to massive Terai migration and the extent of poaching prompted the government to institute the Rhino Patrol force (Nepali: ''ÓżŚÓźłÓżĪÓżŠ ÓżŚÓżĖÓźŹÓżżÓźĆ'' ) of 130 armed men and a network of guard posts all over Chitwan. To prevent the extinction of rhinos through a legal system, National park law was introduced which gazetted the Chitwan National Park in December 1970, with borders delineated the following year and established in 1973.Gurung, K. K. (1983). ''Heart of the Jungle: the Wildlife of Chitwan, Nepal''. Andr├® Deutsch, London.Adhikari, T. R. (2002)
King Birendra was regarded as a lover of nature and a great supporter of nature conservation. The trend of nature conservation from the government started during his reign. The dramatic decline of the rhinoceros population due to massive Terai migration and the extent of poaching prompted the government to institute the Rhino Patrol force (Nepali: ''ÓżŚÓźłÓżĪÓżŠ ÓżŚÓżĖÓźŹÓżżÓźĆ'' ) of 130 armed men and a network of guard posts all over Chitwan. To prevent the extinction of rhinos through a legal system, National park law was introduced which gazetted the Chitwan National Park in December 1970, with borders delineated the following year and established in 1973.Gurung, K. K. (1983). ''Heart of the Jungle: the Wildlife of Chitwan, Nepal''. Andr├® Deutsch, London.Adhikari, T. R. (2002)''The curse of success''.
Habitat Himalaya - A Resources Himalaya Factfile, Volume IX, Number 3.
 For the purpose of conservation of Tigers in the nation, an area of 368 km2 was gazetted as ''Royal Karnali Wildlife Reserve'' in 1976 which was later proclaimed as Royal Bardiya Wildlife Reserve in 1982. The Babai River Valley was further added to this reserved area in 1984. A flourishing ecosystem in the reserve later led to the proclamation of the area as national park in 1988.Majupuria, T. C., Kumar, R. (1998). ''Wildlife, National Parks and Reserves of Nepal.'' S. Devi, Saharanpur and Tecpress Books, Bangkok. The country's fourth protected area was established in 1976 from the Himalayan area of Langtang and named as Langtang National Park. For this purpose, an area of 1,710 km2 was reserved in the district of Nuwakot,
For the purpose of conservation of Tigers in the nation, an area of 368 km2 was gazetted as ''Royal Karnali Wildlife Reserve'' in 1976 which was later proclaimed as Royal Bardiya Wildlife Reserve in 1982. The Babai River Valley was further added to this reserved area in 1984. A flourishing ecosystem in the reserve later led to the proclamation of the area as national park in 1988.Majupuria, T. C., Kumar, R. (1998). ''Wildlife, National Parks and Reserves of Nepal.'' S. Devi, Saharanpur and Tecpress Books, Bangkok. The country's fourth protected area was established in 1976 from the Himalayan area of Langtang and named as Langtang National Park. For this purpose, an area of 1,710 km2 was reserved in the district of Nuwakot, Rasuwa
Rasuwa District ( ne, Óż░ÓżĖÓźüÓżĄÓżŠ Óż£Óż┐Óż▓ÓźŹÓż▓ÓżŠ is one of 13 districts of Bagmati Province and one of seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Dhunche as its district headquarters, covers an area of and has a population (20 ...
and Sindhulpalchok
Sindhupalchowk District ( ne, ÓżĖÓż┐Óż©ÓźŹÓż¦ÓźüÓż¬ÓżŠÓż▓ÓźŹÓżÜÓźŗÓżĢ Óż£Óż┐Óż▓ÓźŹÓż▓ÓżŠ ) is a part of Bagmati Province and one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal, with an area of . The district's headquarters is in Chautara. In 2006, 33 ...
. He also gazetted another wildlife reserve in 1976 as Koshi Tappu Wildlife Reserve. In the same year, he also established Royal Shuklaphanta Wildlife Reserve in the Terai region of far-western provinc''e'' which was later enlarged and converted to national park in the late 1980s. Also, another protected area, Rara National Park was established in the same year in order to protect the unique flora and fauna of Humla, Mugu and Jumla regions and to fulfil his father, King Mahendra's dream of creating a pristine nature reserve with a reserved area of 106 km2 in the Mugu and Jumla districts which also includes the famous Rara Lake. The last National Park to be established as part of the Sacred Himalayan Landscape in the same year was Sagarmatha National Park in with reservation of area of 1,148 km2 in the Solukhumbu District
Solukhumbu District ( ne, ÓżĖÓźŗÓż▓ÓźüÓż¢ÓźüÓż«ÓźŹÓż¼Óźü Óż£Óż┐Óż▓ÓźŹÓż▓ÓżŠ , Sherpa: , Wylie: shar khum bu dzong) is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of eastern Nepal. As the name suggests, it consists of the subregions Solu and Khumb ...
.
In 1984, a 225 km2 area of Bajhang, Bajura, Achham
Achham ( ne, ÓżģÓżøÓżŠÓż« Óż£Óż┐Óż▓ÓźŹÓż▓ÓżŠ ) is a district located in Sudurpashchim province of Nepal. It is one of the nine districts of the province. The district, with Mangalsen as its district headquarters, covers an area of 1,692 km ...
and Doti was set aside as a protected area in the Far-Western Region, Nepal and was named Khaptad National Park. In the same year, he also established Parsa Wildlife Reserve
Parsa National Park is a protected area in the Inner Terai lowlands of south-central Nepal. It covers an area of in the Parsa, Makwanpur and Bara districts and ranges in altitude from to in the Siwalik Hills. It was established as a wild ...
which was later extended to a National Park. Similarly, the nation's only trans- Himalayan national park, Shey Phoksundo National Park, was established in 1984 with an area of 3,555 square Kilometers in the districts of Dolpa and Mugu in the Karnali Province which also included the famous Phoksundo Lake.
In order to preserve the royal tradition of hunting as a hobby, but also to prevent the depleting wild life resource he established Dhorpatan Hunting Reserve in 1987 AD. King Mahendra Trust for Nature Conservation
The National Trust for Nature Conservation (NTNC), () previously known as King Mahendra Trust for Nature Conservation is a Nepalese non-governmental organization working in the field of nature conservation.
History
It was established in 1982 as ...
as a memorial to his father, with the then prince Gyanendra as the chairman, was also established in 1990. With the establishment of Mahendra trust, he declared Annapurna Conservation Area
Moreover, with his efforts, Nepal was able to enlist Sagarmatha National Park in 1979 and Chitwan National Park in 1984 into the UNESCO World heritage sites. Similarly, monument zones such as the Durbar squares of Kathmandu, Lalitpur and Bhaktapur and religious sites such as Swayambhunath, Boudhanath, Pashupatinath Temple and Changu Narayan was also enlisted in 1979.
Economic reforms
 Focusing on sustainability and environmental conservation, on , trolley bus system was established in Nepal from the aid of People's Republic of China. He followed in the path of his father to establish industrial estates by establishing Nepalgunj Industrial Area(1973), Pokhara Industrial Area(1974), Butwal Industrial Area(1976), Bhaktapur Industrial Area(1979), Dhankuta Industrial Area(1980), Birendranagar Industrial Area(1981), Gajendranarayan Industrial Area(1986) respectively.
Birendra is initially credited for devising the plan of Melamchi water project to Kathmandu. Gorakhali Tires Industries, Udayapur Cement Industries Limited, Nepal Metal company, Nepal Pharmaceuticals were all established during his time. King Birendra, was the patron of Pashupati Area Development Trust. In April 1979, Nepal Oriental Magnesite factory was established with a joint investment of Nepal government and Orissa Industries, India at Lakuri Danda in Dolakha District with the objective of producing dead burnt magnesite and talc powder. In 1983 he was able to establish a Nepal-Pakistan Joint Economic Commission bringing in significant foreign investments in the country.
A 60 Megawatt hydropower project at Kulekhani began operation in 1982 with economic aid from the World Bank, Kuwait, and
Focusing on sustainability and environmental conservation, on , trolley bus system was established in Nepal from the aid of People's Republic of China. He followed in the path of his father to establish industrial estates by establishing Nepalgunj Industrial Area(1973), Pokhara Industrial Area(1974), Butwal Industrial Area(1976), Bhaktapur Industrial Area(1979), Dhankuta Industrial Area(1980), Birendranagar Industrial Area(1981), Gajendranarayan Industrial Area(1986) respectively.
Birendra is initially credited for devising the plan of Melamchi water project to Kathmandu. Gorakhali Tires Industries, Udayapur Cement Industries Limited, Nepal Metal company, Nepal Pharmaceuticals were all established during his time. King Birendra, was the patron of Pashupati Area Development Trust. In April 1979, Nepal Oriental Magnesite factory was established with a joint investment of Nepal government and Orissa Industries, India at Lakuri Danda in Dolakha District with the objective of producing dead burnt magnesite and talc powder. In 1983 he was able to establish a Nepal-Pakistan Joint Economic Commission bringing in significant foreign investments in the country.
A 60 Megawatt hydropower project at Kulekhani began operation in 1982 with economic aid from the World Bank, Kuwait, and Japan
Japan ( ja, µŚźµ£¼, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
.
TU Teaching Hospital
Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital is well known public hospital in Nepal.This was established in 1982. Initially it had 300 bed facility which is now increased and now it has 700 bed facility.
this hospital is the site of Under Tribhuvan Un ...
was established in 1982 with the economic support from Japan International Cooperation Agency. Nardevi Ayurvedic Hospital was established in 1974. Nepal Police Hospital was established by the king on the 27th of Chaitra, 2040 BS with an intention to provide free health services to in- service policemen and, their families.
He established Securities Exchange Center Ltd in 1976 to manage, promote and support the growth of trade of stocks and capitals in the nation. This center was later developed to what we know today as Nepal Stock Exchange.
He is also credited for establishing the first television channel of Nepal Nepal Television in 1984 which started its first channel in 1985 with French aid. Due to these economic reforms, by 1986, there were 2,054 industrial establishments employing about 125 thousand workers in the nation. By 1990, reach of people for television meant that video rental services and satellite dishes were commonly available.
King Birendra in the advice and consent of Rastriya Panchayat in 1986 established Mahendra Sanskrit University to manage Sanskrit education in Nepal in Dang which at the time of its commencement was the second university of the country .
Roads and transportation
Various Studies in 1972 showed that building road connectivity in hilly and rural areas were more expensive than air connectivity. So, the then government took the policy of connecting rural areas with airports and build roads only when there was a high amount of traffic flow. Under this policy, Baglung Airport (Balewa Airport
Sir Abubakar Tafawa Balewa (December 1912 ŌĆō 15 January 1966) was a Nigerian politician who served as the first and only Prime Minister of Nigeria upon independence.
Early life
Abubakar Tafawa Balewa was born in December 1912 in modern-day B ...
), Dhorpatan Airport, Mahendranagar Airport
Mahendranagar Airport is a domestic airport located in Mahendranagar serving Kanchanpur District, a district in Sudurpashchim Province in Nepal. It is the main tourist gateway to Shuklaphanta National Park.
History
The airport started opera ...
and Rukum Chaurjahari Airport
Rukum Chaurjahari Airport is a domestic airport located in Chaurjahari serving Western Rukum District, a district in Karnali Province in Nepal.
History
The airport started operations on 24 September 1973.
The airport was renovated and the ru ...
was established in the year 1973. Sanphebagar airport was established in 1975. Simikot Airport was established on 18th March 1977, Dolpa Airport, was established in 1978 and Ramechhap airport
Ramechhap Airport is a domestic airport serving the municipality of Manthali, the district headquarters of Ramechhap District located in the Tamakoshi River valley in Bagmati Province in Nepal. As of October 2022, most flights to Lukla Airpor ...
in 1979. Doti Airport
Doti Airport , also known as Silgadhi Airport, is a domestic airport located in Dipayal Silgadhi serving Doti District, a district in Sudurpashchim Province in Nepal.
History
The airport started operations on 24 September 1973, but the runway ...
, also known as Silgadhi Airport was established in 1973 with the blacktopped runway. Talcha Airport, also known as Rara Airport
Rara Airport , also known as Talcha Airport, is a domestic airport located in Chhayanath Rara serving Rara National Park in Karnali Province in Nepal.
History
The airport was constructed in 1975 but was only blacktopped in 2015.
Airlines and ...
was built in 1975. Taplejung Airport located in Phungling, also called Suketar Airport
Taplejung Airport , also known as Suketar Airport, is a domestic airport located in Phungling serving Taplejung District, a district in Province No. 1 in Nepal. It is the main tourist gateway on the Kangchenjunga mountainous area and Pathibhar ...
, Jiri Airport and Phaplu Airport and Bajhang Airport
Bajhang Airport is a domestic airport located in Jayaprithvi serving Bajhang District, a district in Sudurpashchim Province in Nepal.
History
The airport was originally opened in October 1976 but ceased to operate after road access to the di ...
was built in 1976. Rolpa Airport
Rolpa Airport is an airport in Rolpa District, Lumbini Province, Nepal.
The ICAO code is VNRP and the IATA code is RPA. It is currently not in operation.
See also
* List of airports in Nepal
This is a list of airports in Nepal, sorted by l ...
in 1980, Manang Airport in 1981, Bajura airport in 1984 and Darchula Airport in 1986.
Similarly, The Lamosangu-Jiri road leading to Solukhumbu was commissioned in 1985 with Swiss government aid.
Promotion of agriculture
The government, during Birendra's reign, focused highly on agriculture promotion. As a result, almost 90% of the population was directly or indirectly involved in agriculture by 1990. Bhrikuti Pulp and Paper was established in 1985 under the Companies Act 2021 ( Bikram Sambat) with support from the People's Republic of China. Increase in agricultural lands and agricultural workforce provided increased supplies of food, resulting in better nutrition. Corn production was increased to over 1 million tons in 1991 from 500,000 tons in 1961. Lumbini Sugar Mills at Sunwal, Nawalparasi was built with the technical assistance from China in 1982. The establishment of Gorakhali rubber Industries led to the cultivation of rubber for the first time in Jhapa, Illam and many other places of eastern Nepal. Similarly. establishment of agriculture based industries such as Bhrikuti Pulp and Paper, Hetauda Textile and huge number of carpet and garment industry were established to convert raw agricultural produce which contributed greatly to the economy.Political achievements
 During the reign of King Birendra, referendum was held in 2037 BS for democracy wherein options were a multi-party system or a Panchayati system. During the Panchayat era and after the national referendum, he divided the nation into 5 development regions in order to create balanced development, and visited each division once a year; the visits were discontinued after 1990 democracy movement.
Despite previously being an autocratic rule and constant pressure from the supporters and royal members, the king always played the role of constitutional monarch by the book and never overstepped his boundaries. King Birendra was always there when there was some political crisis in the nation. Mid-term elections, 2051 and General Election, 2056 can be attributed to his good governance. The King regularly asked the Supreme Court for its advice on any political matters that could concern the constitution so that he would never overstep the boundaries of the constitution. He created a culture where the king and prime minister would meet every Thursday at his palace to discuss matters of state.
During the reign of King Birendra, referendum was held in 2037 BS for democracy wherein options were a multi-party system or a Panchayati system. During the Panchayat era and after the national referendum, he divided the nation into 5 development regions in order to create balanced development, and visited each division once a year; the visits were discontinued after 1990 democracy movement.
Despite previously being an autocratic rule and constant pressure from the supporters and royal members, the king always played the role of constitutional monarch by the book and never overstepped his boundaries. King Birendra was always there when there was some political crisis in the nation. Mid-term elections, 2051 and General Election, 2056 can be attributed to his good governance. The King regularly asked the Supreme Court for its advice on any political matters that could concern the constitution so that he would never overstep the boundaries of the constitution. He created a culture where the king and prime minister would meet every Thursday at his palace to discuss matters of state.
Social reforms
Recognizing low literacy levels as the main hindrance to national progress, King Birendra made development of education system his national priority. The five year plan starting from 1971 was mainly focused in building new educational institutions and upgrading the efficiency of the current education system. On the auspicious occasion of his coronation, King Birendra declared primary education to be free for all Nepalese citizens. Similarly, in 1978 with a royal approval all educational material started to be distributed free of costs to educational institutions. King Birendra became the patron of Royal Nepal Academy of Science and Technology which worked in the field of developing science and technology in the nation. He established Mahendra Sanskrit University in 1986 to preserve the language and culture in the region. Dowry system was criminalized in Nepal in 1976 under the Social Practices Reform Act (2033 B.S). Under the five year plan, King Birendra started the policy of National Service which required the post-graduate students to contribute their one-year of service to the development works in the rural areas. He initiated the process of preserving the history by establishing Natural History Museum in 1975.On 22 September 1976 he enacted Narcotic Drugs (Control) Act, 2033 prohibiting the trade, smuggling or any kind of drug trafficking in the country.Development policy
Birendra took the policy of road development according to the population and daily road traffic and connecting the rural areas with airports. He restructured many governmental organization for the purpose of achieving developmental goals. He stressed roadbuilding, sanitation and scientific as well as technical trainings. A comprehensive study performed regarding the central planning agency triggered the restructuring of the National Planning Commission in 1972 and minor changes in 1987. The government policy focused mainly on environment conservation, agriculture and education.Criticism
Stagnant economy
Though King Birendra is remembered as a development-friendly king, he is also criticized for his inability to drive the country towards rapid development efforts like his father King Mahendra. He had the political will but simply not the skill through which development efforts could be rapidly gained. His policy of sustainable development, shown by his nature conservation efforts, culture, and history became hindrances for economic development. The Panchayat regime created a stagnant economy during his reign as an autocratic ruler.Administrative failure
Historians point out that the Panchayat Regime under King Birendra was a failure. He was not able to bring in much direct foreign investment during his reign, and all the programs he brought, or all the reforms he made were the continuation of his father's legacy. He restructured various organization previously established by his father, and implemented various development plan envisioned by his father. However, he was not able to bring about radical change in the country. Moreover, some historians also claim that making cannabis trade illegal, implemented during this era, created mass unemployment which eventually became one of the causes of the Maoist revolution.Failed development efforts
Birendra restructured various organization and brought many development plans, but his development efforts were mostly a failure; which hindered any radical change in the country. Many airports and roads built during his era were rarely used, and eventually had to be closed down. Moreover, the reason the newly-built roads were rarely used was due to very low vehicle ownership or access to vehicles; so rarely contributing to economic development.Killer of the Panchayat system
Some historians and anti-democrats blame Birendra solely for the fall of Panchayat regime. During the 1980s, the restraints that he had eased against political organizations provided a breeding ground for political parties which had previously been powerless and virtually non-existent until then.Personality
From a very young age, Birendra was described by his Eton teachers as a kind prince. He was remembered by his Eton classmates as a "very, very nice bloke who was embarrassed when his full title was read out at the school assembly." Very famous Nepalese media personality, Neer Shah describe Birendra as kind and development loving king. Royalist around the king and various scholars define him as a simple king who was able to listen to others view. They also criticize him for his weakness of not being able to deny the requests of people around him and his habit to act like a clerk and work himself rather than order others. Birendra allowed the 2036 B.S. ''Janmat Sangraha'' (1980 Referendum) which was considered a move towards democracy. However, the leaders advocating for democracy and historians have claimed that the referendum was rigged. After People's Movement I that resulted in few hundred deaths, he established a constitutional monarchy in Nepal. Some historians have speculated that Birendra's democratic views and simple nature may have led to the success of the People's Movement I (1990). He is credited for introducingSAARC
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, ...
in Asia in order to strengthen the foreign relations of Nepal with the other South Asian countries.
Memorial
Many structures, institutions and honors have been built in the memory of King Birendra. Monuments erected in his name were renamed after the restoration of the parliament in 2063 BS and the end of the monarchy in 2065 BS. After the political changes of 2063 BS, an attempt was made to rename the highway built in the name of the king as Lok Marg.
Statues
# Birendra statue, Dhamboji Chowk, ( Nepalgunj) # Birendra statue ( Dang ) # Birendra statue, Birendranagar (Surkhet
Surkhet District ( ne, ÓżĖÓźüÓż░ÓźŹÓż¢ÓźćÓżż Óż£Óż┐Óż▓ÓźŹÓż▓ÓżŠ, ) is a district in Karnali Province of mid-western Nepal. Surkhet is the one of the ten districts of Karnali located about west of the national capital Kathmandu. The district's are ...
)
# Birendra statue, Swargapuri ( Shivapuri )
# Birendra statue, Jawalakhel
J─üwal─ükhel ( ne, Óż£ÓżŠÓżĄÓż▓ÓżŠÓż¢ÓźćÓż▓) is a subdivision of Lalitpur in Nepal. It is located 2 km from the ancient city centre P─ütan, one of the three great capitals of Nepal until the 18th century. It derives its name from Jaulakhel ...
( Lalitpur )
# Birendra statue, Bindhyabasini Temple (Pokhara
Pokhara ( ne, Óż¬ÓźŗÓż¢Óż░ÓżŠ, ) is a metropolis, metropolitan city in Nepal, which serves as the capital of Gandaki Province. It is the List of cities in Nepal, second most populous city of Nepal after Kathmandu, with 518,452 inhabitants living ...
)
# Birendra statue, Pashupatinath temple ( Kathmandu)
School
# Shree Birendra Higher Secondary School, Bhadrapur, Jhapa # Shree Birendra Higher Secondary School, Charghare, Nuwakot # Shree Birendra Sarwajanik Higher Secondary School, Morang # Shree Birendra secondary school,Lakhantari
Lakhantari is a village development committee in Morang District in the Kosi Zone of south-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census
The 1991 Nepal census was a widespread national census conducted by the Nepal Central Bureau of Stati ...
, Morang
# Shree Birendra secondary school, Belbari, Morang
# Shree Birendra Madhyamik Bidhyalaya, Jhorahat, Morang
# Birendra Secondary School, Katahari, Morang
# Birendra Secondary School, Argakhanchi
# Birendra Secondary School, Dasharathchand
Dasharathchand is a municipality and the district headquarter of Baitadi District in Sudurpashchim Province of Nepal. It is a hill station above Mahakali River close to the Indian border. At the time of the 2011 Nepal census it had a population ...
a, Baitadi
# Birendra secondary school, Badikedar
Badikedar ( ne, Óż¼ÓżĪÓźŹÓżĪÓźĆ ÓżĢÓźćÓż”ÓżŠÓż░) is a Gaupalika( Nepali: ÓżŚÓżŠÓżēÓż¬ÓżŠÓż▓Óż┐ÓżĢÓżŠ ; ''gaupalika'') in Doti District in the Sudurpashchim Province of far-western Nepal. Badikedar has a population of 16720.The land area is 332.55& ...
, Doti
# Birendra Secondary School, Syangja
# Birendra Secondary School, Nuwakot
# Birendra Secondary School, Parbat
# Birendra Sainik Awasiya Mahavidyalaya, Bhaktapur
College
# Birendara Bidhya Mandir Campus,Tikapur
Tikapur ( ne, Óż¤Óż┐ÓżĢÓżŠÓż¬ÓźüÓż░) is a Municipality in Kailali District in Sudurpashchim Province of Nepal that was established in January 1997. Tikapur Municipality was further expanded on 10 March 2017 through merger with the two former V ...
, Kailali
# Birendra Multiple Campus
Birendra Multiple Campus ( ne, ÓżĄÓźĆÓż░ÓźćÓż©ÓźŹÓż”ÓźŹÓż░ Óż¼Óż╣ÓźüÓż«ÓźüÓż¢ÓźĆ ÓżĢÓźŹÓż»ÓżŠÓż«ÓźŹÓż¬ÓżĖ) is one of the constituent campuses of Tribhuvan University in Bharatpur, Chitwan district in Nepal. The campus was established in 1st Bi ...
, Bharatpur
# Birendra Memorial College , Dharan
# Birendra Multiple Campus
Birendra Multiple Campus ( ne, ÓżĄÓźĆÓż░ÓźćÓż©ÓźŹÓż”ÓźŹÓż░ Óż¼Óż╣ÓźüÓż«ÓźüÓż¢ÓźĆ ÓżĢÓźŹÓż»ÓżŠÓż«ÓźŹÓż¬ÓżĖ) is one of the constituent campuses of Tribhuvan University in Bharatpur, Chitwan district in Nepal. The campus was established in 1st Bi ...
Location
# Birendranagar,Surkhet
Surkhet District ( ne, ÓżĖÓźüÓż░ÓźŹÓż¢ÓźćÓżż Óż£Óż┐Óż▓ÓźŹÓż▓ÓżŠ, ) is a district in Karnali Province of mid-western Nepal. Surkhet is the one of the ten districts of Karnali located about west of the national capital Kathmandu. The district's are ...
# Birendranagar, Chitwan
Birendranagar is a village development committee (VDC) in Chitwan District in the Narayani Zone of southern Nepal. At the time of the 2011 Nepal census it had a population of 14,934 people (6,909 male; 8,025 female) living in 3,374 individual ho ...
# Birendra Chowk , ( Birendranagar)
# Birendra chowk, Kageshwari-Manohara Municipality
# Birendra chowk , Phungling Municipality
Phungling Municipality (previously also ''Taplejung Municipality'') is a municipality located in Taplejung District in the Province No. 1 of Nepal.
The municipality was formed merging the then two Village Development Committees of Phungling and ...
# Birendra Chowk, Dharan
# Birendra Chowk, Tulsipur, ( Dang)
# Birendra Chowk , ( Nepalgunj)
# Birendra Chowk , ( Itahari)
# Birendra Lake
Birendra Lake (Birendra Tal), is a freshwater lake located in Manaslu Glacier in Gorkha District
Gorkha District ( ne, ÓżŚÓźŗÓż░Óż¢ÓżŠ Óż£Óż┐Óż▓ÓźŹÓż▓ÓżŠ ), a part of Gandaki Province, is one of the 77 districts of Nepal, which is the fourt ...
(Birendra Tal), Gorkha
# Birendra Aishwarya Park, Dhangadi
Dhangadhi ( ne, Óż¦Óż©ÓżŚÓżóÓźĆ ) is a sub-metropolitan city and the district headquarters of Kailali District in Sudurpashchim Province of Nepal.Dhangadhi is also the temporary capital of Sudurpashchim Province. It shares a border with Uttar ...
# Birendra Aishwarya Park, Baglung
Structure
#Birendra Museum
The Birendra Museum is a museum located in Kathmandu Durbar Square, Kathmandu, Nepal. It is located alongside Tribhuvan Museum and Mahendra Museum. It contains personal artefacts that belonged to King Birendra Bir Bikram Shah, who is internationa ...
, Kathmandu Durbar Square
# Birendra Army Hospital
# Birendranagar Airport
Others
# Birendra Beer, Z├╝rich #Birendra Memorial Cup The Birthday Cup (also referred to as the Birendra Memorial Cup in the 2002 edition) was an association football competition organised to mark the birthday of King Birendra of Nepal
Nepal (; ne, Óż©ÓźćÓż¬ÓżŠÓż▓ ), formerly the Federal Demo ...
# Birendra Peace Operations Training Centre
# Birendranagar Jaycees
Nepalese royal massacre
Birendra and his whole family were gunned down on 1 June 2001. Almost all of the royal family were killed in the massacre exceptGyanendra Shah
Gyanendra Shah ( ne, Óż£ÓźŹÓż×ÓżŠÓż©ÓźćÓż©ÓźŹÓż”ÓźŹÓż░ ÓżČÓżŠÓż╣, born 7 July 1947) is a former monarch who was the last King of Nepal, reigning from 2001 to 2008. As a child, he was briefly king from 1950 to 1951, when his grandfather, Tribhuva ...
, Birendra's younger brother. Dipendra was proclaimed King but could not be crowned since he was in coma in hospital. He died a few days later of self-inflicted gunshot wounds sustained in the massacre. Consequently, Gyanendra was made the king.
Titles and honours
; National orders * Sovereign of the Order of Ojaswi Rajanya
*
Sovereign of the Order of Ojaswi Rajanya
*  Sovereign of the Order of Tri Shakti Patta
*
Sovereign of the Order of Tri Shakti Patta
*  Recipient of the King Mahendra Investiture Medal (02/05/1956)
; Foreign orders
* :
**
Recipient of the King Mahendra Investiture Medal (02/05/1956)
; Foreign orders
* :
**Order of the Elephant
The Order of the Elephant ( da, Elefantordenen) is a Danish order of chivalry and is Denmark's highest-ranked honour. It has origins in the 15th century, but has officially existed since 1693, and since the establishment of constitutional ...
, (17 October 1989)
* :
** Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Makarios III of Cyprus, (1980)
* :
**
Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Makarios III of Cyprus, (1980)
* :
** Nishan-e-Pakistan, (1983)
* :
**
Nishan-e-Pakistan, (1983)
* :
** Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of the White Rose of Finland, Order of the White Rose, (1988)
* :
**
Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of the White Rose of Finland, Order of the White Rose, (1988)
* :
** Collar of the Order of the Nile, (1974)
* :
**
Collar of the Order of the Nile, (1974)
* :
** Great Star of the Order of the Yugoslav Star, (2 February 1974)
* Socialist Republic of Romania, Romania:
**
Great Star of the Order of the Yugoslav Star, (2 February 1974)
* Socialist Republic of Romania, Romania:
** Knight Grand Cross of the Order of 23 August (1987)
* :
**
Knight Grand Cross of the Order of 23 August (1987)
* :
** Recipient of the Royal Victorian Chain (23 February 1975)
; Association honours
* :
**
Recipient of the Royal Victorian Chain (23 February 1975)
; Association honours
* :
**Ancestry
See also
*List of state visits by Birendra *Wedding of Birendra and Aishwarya *Coronation of BirendraReferences
*Album of late King Birendra Bir Bikram Shah Dev by Narayan Prasad Shiwakoti: Published in 1995 ŌĆElection
, - {{DEFAULTSORT:Birendra Bir Bikram Shah Dev 2001 murders in Asia Nepalese monarchs British field marshals 21st-century murdered monarchs Nepalese Hindus Nepalese murder victims Deaths by firearm in Nepal People educated at Eton College University of Tokyo alumni Harvard University alumni 1945 births 2001 deaths People murdered in Nepal Male murder victims Grand Croix of the L├®gion d'honneur Grand Crosses Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany Grand Crosses of the Order of the Star of Romania Recipients of Nishan-e-Imtiaz Shah dynasty MurderŌĆōsuicides in Asia Assassinated people Assassinated heads of state People of the Nepalese Civil War Hindu monarchs