Bioluminescent Fish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
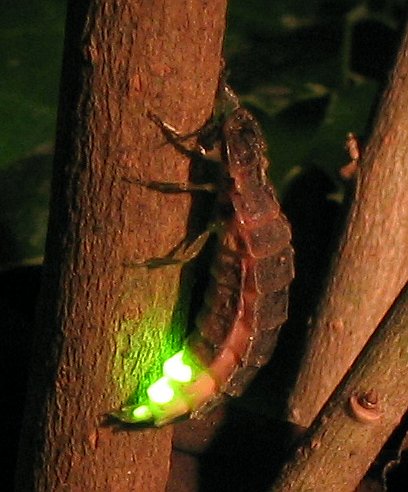


 Bioluminescence is the production and emission of
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of
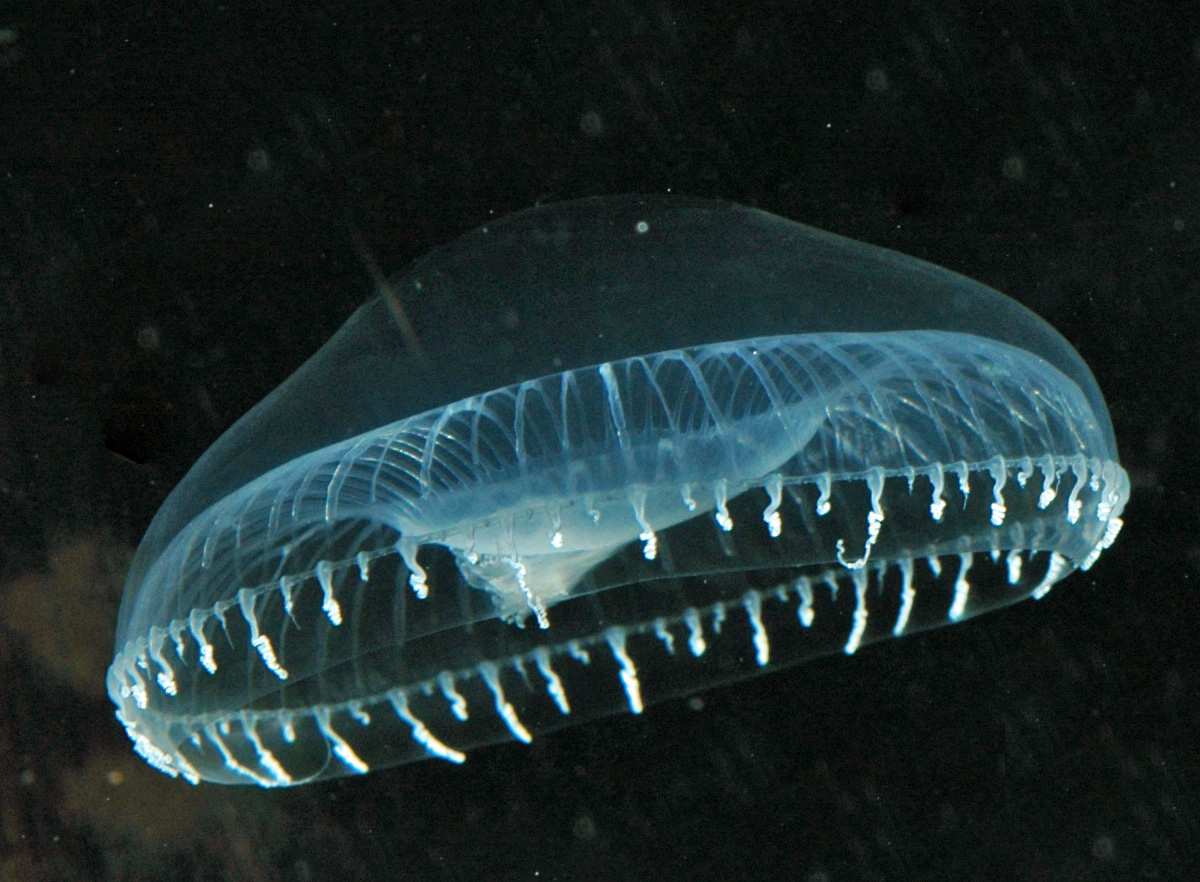 Bioluminescence attracted the attention of the
Bioluminescence attracted the attention of the
 Bioluminescence is a form of
Bioluminescence is a form of -> Oxyluciferin + light energy
Instead of a luciferase, the jellyfish ''
 Bioluminescence has several functions in different taxa.
Bioluminescence has several functions in different taxa.
 In many animals of the deep sea, including several
In many animals of the deep sea, including several
 Bioluminescence is used in a variety of ways and for different purposes. The cirrate octopod ''Stauroteuthis syrtensis'' uses emits bioluminescence from its sucker like structures. These structures are believed to have evolved from what are more commonly known as octopus suckers. They do not have the same function as the normal suckers because they no longer have any handling or grappling ability due its evolution of
Bioluminescence is used in a variety of ways and for different purposes. The cirrate octopod ''Stauroteuthis syrtensis'' uses emits bioluminescence from its sucker like structures. These structures are believed to have evolved from what are more commonly known as octopus suckers. They do not have the same function as the normal suckers because they no longer have any handling or grappling ability due its evolution of
 Communication in the form of quorum sensing plays a role in the regulation of luminescence in many species of bacteria. Small extracellularly secreted molecules stimulate the bacteria to turn on genes for light production when cell density, measured by concentration of the secreted molecules, is high.
Pyrosomes are colonial Tunicata, tunicates and each zooid has a pair of luminescent organs on either side of the inlet siphon. When stimulated by light, these turn on and off, causing rhythmic flashing. No neural pathway runs between the zooids, but each responds to the light produced by other individuals, and even to light from other nearby colonies. Communication by light emission between the zooids enables coordination of colony effort, for example in swimming where each zooid provides part of the propulsive force.
Some bioluminous bacteria infect nematodes that parasitize Lepidoptera larvae. When these caterpillars die, their luminosity may attract predators to the dead insect thus assisting in the dispersal of both bacteria and nematodes. A similar reason may account for the many species of fungi that emit light. Species in the genera ''Armillaria'', ''Mycena'', ''Omphalotus'', ''Panellus'', ''Pleurotus'' and others do this, emitting usually greenish light from the mycelium, Pileus (mycology), cap and Lamella (mycology), gills. This may attract night-flying insects and aid in spore dispersal, but other functions may also be involved.
''Quantula striata'' is the only known bioluminescent terrestrial mollusc. Pulses of light are emitted from a gland near the front of the foot and may have a communicative function, although the adaptive significance is not fully understood.
Communication in the form of quorum sensing plays a role in the regulation of luminescence in many species of bacteria. Small extracellularly secreted molecules stimulate the bacteria to turn on genes for light production when cell density, measured by concentration of the secreted molecules, is high.
Pyrosomes are colonial Tunicata, tunicates and each zooid has a pair of luminescent organs on either side of the inlet siphon. When stimulated by light, these turn on and off, causing rhythmic flashing. No neural pathway runs between the zooids, but each responds to the light produced by other individuals, and even to light from other nearby colonies. Communication by light emission between the zooids enables coordination of colony effort, for example in swimming where each zooid provides part of the propulsive force.
Some bioluminous bacteria infect nematodes that parasitize Lepidoptera larvae. When these caterpillars die, their luminosity may attract predators to the dead insect thus assisting in the dispersal of both bacteria and nematodes. A similar reason may account for the many species of fungi that emit light. Species in the genera ''Armillaria'', ''Mycena'', ''Omphalotus'', ''Panellus'', ''Pleurotus'' and others do this, emitting usually greenish light from the mycelium, Pileus (mycology), cap and Lamella (mycology), gills. This may attract night-flying insects and aid in spore dispersal, but other functions may also be involved.
''Quantula striata'' is the only known bioluminescent terrestrial mollusc. Pulses of light are emitted from a gland near the front of the foot and may have a communicative function, although the adaptive significance is not fully understood.
 Bioluminescence is used by a variety of animals to mimicry, mimic other species. Many species of deep sea fish such as the anglerfish and Stomiidae, dragonfish make use of aggressive mimicry to attract prey. They have an appendage on their heads called an esca that contains bioluminescent bacteria able to produce a long-lasting glow which the fish can control. The glowing esca is dangled or waved about to lure small animals to within striking distance of the fish.
The cookiecutter shark uses bioluminescence to camouflage its underside by counterillumination, but a small patch near its pectoral fins remains dark, appearing as a small fish to large predatory fish like tuna and mackerel swimming beneath it. When such fish approach the lure, they are bitten by the shark.
Female ''Photuris'' fireflies sometimes mimic the light pattern of another firefly, ''Photinus'', to attract its males as prey. In this way they obtain both food and the defensive chemicals named lucibufagins, which ''Photuris'' cannot synthesize.
South American giant cockroaches of the genus ''Lucihormetica'' were believed to be the first known example of defensive mimicry, emitting light in imitation of bioluminescent, poisonous click beetles. However, doubt has been cast on this assertion, and there is no conclusive evidence that the cockroaches are bioluminescent.
Bioluminescence is used by a variety of animals to mimicry, mimic other species. Many species of deep sea fish such as the anglerfish and Stomiidae, dragonfish make use of aggressive mimicry to attract prey. They have an appendage on their heads called an esca that contains bioluminescent bacteria able to produce a long-lasting glow which the fish can control. The glowing esca is dangled or waved about to lure small animals to within striking distance of the fish.
The cookiecutter shark uses bioluminescence to camouflage its underside by counterillumination, but a small patch near its pectoral fins remains dark, appearing as a small fish to large predatory fish like tuna and mackerel swimming beneath it. When such fish approach the lure, they are bitten by the shark.
Female ''Photuris'' fireflies sometimes mimic the light pattern of another firefly, ''Photinus'', to attract its males as prey. In this way they obtain both food and the defensive chemicals named lucibufagins, which ''Photuris'' cannot synthesize.
South American giant cockroaches of the genus ''Lucihormetica'' were believed to be the first known example of defensive mimicry, emitting light in imitation of bioluminescent, poisonous click beetles. However, doubt has been cast on this assertion, and there is no conclusive evidence that the cockroaches are bioluminescent.

Siobiolum.ucsd.edu. Retrieved on 20 October 2011. The gene that makes the tails of
BBC: Red tide: Electric blue waves wash California shore
(video)
Smithsonian Ocean Portal: Bioluminescent animals photo gallery
National Geographic: Bioluminescence
Annual Review of Marine Science: Bioluminescence in the Sea
Canon Australia – Tips on How to Photograph Bioluminescence
* The New York City American Natural History Museum's "Creatures of Light: Nature's Bioluminescence" 2022 Featured Exhibit (in concert with the Ottawa, Canada-based Canadian Museum of Nature and Chicago's Field Museum of Natural History) webpage
{{good article Bioluminescence, Fisheries science Light sources Camouflage Mimicry Bioelectromagnetics


 Bioluminescence is the production and emission of
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
by living organism
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
s. It is a form of chemiluminescence
Chemiluminescence (also chemoluminescence) is the emission of light ( luminescence) as the result of a chemical reaction. There may also be limited emission of heat. Given reactants A and B, with an excited intermediate ◊,
: + -> lozenge - ...
. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s and invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s, as well as in some fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria
Bioluminescent bacteria are light-producing bacteria that are predominantly present in sea water, marine sediments, the surface of decomposing fish and in the gut of marine animals. While not as common, bacterial bioluminescence is also found in t ...
, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies
The Lampyridae are a family of elateroid beetles with more than 2,000 described species, many of which are light-emitting. They are soft-bodied beetles commonly called fireflies, lightning bugs, or glowworms for their conspicuous production ...
. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus ''Vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive ...
''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves.
In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
, generally called luciferin
Luciferin (from the Latin ''lucifer'', "light-bearer") is a generic term for the light-emitting compound found in organisms that generate bioluminescence. Luciferins typically undergo an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with molecular oxygen. The resu ...
and luciferase
Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words '' luciferin'' and ''luciferase'' ...
, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin
Firefly luciferin (also known as beetle luciferin) is the luciferin, or light-emitting compound, used for the firefly (Lampyridae), railroad worm (Phengodidae), starworm (Rhagophthalmidae), and click-beetle ( Pyrophorini) bioluminescent systems. ...
. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycl ...
the oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
of the luciferin.
In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to:
* Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed
* A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the orde ...
, such as calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
or magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
ions, and sometimes also the energy-carrying molecule adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms ...
(ATP). In evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
, luciferins vary little: one in particular, coelenterazine
Coelenterazine is a luciferin, a molecule that emits light after reaction with oxygen, found in many aquatic organisms across eight phyla. It is the substrate of many luciferases such as ''Renilla reniformis'' luciferase (Rluc), ''Gaussia'' lucif ...
, is found in 11 different animal phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phyl ...
, though in some of these, the animals obtain it through their diet. Conversely, luciferases vary widely between different species, which is evidence that bioluminescence has arisen over 40 times in evolutionary history
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', for '' gigaannum'') and e ...
.
Both Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
and Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
mentioned that damp wood sometimes gives off a glow. Many centuries later Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of ...
showed that oxygen was involved in the process, in both wood and glowworms. It was not until the late nineteenth century that bioluminescence was properly investigated. The phenomenon is widely distributed among animal groups, especially in marine environments. On land it occurs in fungi, bacteria and some groups of invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s, including insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
s.
The uses of bioluminescence by animals include counterillumination
Counter-illumination is a method of active camouflage seen in marine animals such as firefly squid and midshipman fish, and in military prototypes, producing light to match their backgrounds in both brightness and wavelength.
Marine animals of ...
camouflage, mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry ...
of other animals, for example to lure prey, and signaling
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing' ...
to other individuals of the same species, such as to attract mates. In the laboratory, luciferase-based systems are used in genetic engineering and biomedical research. Researchers are also investigating the possibility of using bioluminescent systems for street and decorative lighting, and a bioluminescent plant has been created.
History
Before the development of thesafety lamp
A safety lamp is any of several types of lamp that provides illumination in coal mines and is designed to operate in air that may contain coal dust or gases, both of which are potentially flammable or explosive. Until the development of effecti ...
for use in coal mines, dried fish skins were used in Britain and Europe as a weak source of light. This experimental form of illumination avoided the necessity of using candles which risked sparking explosions of firedamp
Firedamp is any flammable gas found in coal mines, typically coalbed methane. It is particularly found in areas where the coal is bituminous. The gas accumulates in pockets in the coal and adjacent strata and when they are penetrated the relea ...
. Another safe source of illumination in mines was bottles containing fireflies. In 1920, the American zoologist E. Newton Harvey
Edmund Newton Harvey (November 25, 1887 – July 21, 1959) was an American zoologist. He was acknowledged as one of the leading authorities on bioluminescence. He won the Rumford Prize in 1947 and was a member of the National Academy of Science ...
published a monograph, ''The Nature of Animal Light'', summarizing early work on bioluminescence. Harvey notes that Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
mentions light produced by dead fish and flesh, and that both Aristotle and Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
(in his '' Natural History'') mention light from damp wood. He also records that Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of ...
experimented on these light sources, and showed that both they and the glowworm require air for light to be produced. Harvey notes that in 1753, J. Baker identified the flagellate ''Noctiluca
''Noctiluca scintillans'' is a marine species of dinoflagellate that can exist in a green or red form, depending on the pigmentation in its vacuoles. It can be found worldwide, but its geographical distribution varies depending on whether it is ...
'' "as a luminous animal" "just visible to the naked eye", and in 1854 Johann Florian Heller
Johann Florian Heller (4 May 1813 – 21 November 1871) was an Austrian chemist who was one of the founders of clinical chemistry.
Heller was born in Vienna, Austria. He studied chemistry in Prague and later with Liebig and Wöhler at Giessen.
...
(1813–1871) identified strands (hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one o ...
e) of fungi as the source of light in dead wood.
Tuckey, in his posthumous 1818 ''Narrative of the Expedition to the Zaire'', described catching the animals responsible for luminescence. He mentions pellucids, crustaceans (to which he ascribes the milky whiteness of the water), and cancers (shrimps and crabs). Under the microscope he described the "luminous property" to be in the brain, resembling "a most brilliant amethyst about the size of a large pin's head".
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
noticed bioluminescence in the sea, describing it in his ''Journal'':
While sailing in these latitudes on one very dark night, the sea presented a wonderful and most beautiful spectacle. There was a fresh breeze, and every part of the surface, which during the day is seen as foam, now glowed with a pale light. The vessel drove before her bows two billows of liquid phosphorus, and in her wake she was followed by a milky train. As far as the eye reached, the crest of every wave was bright, and the sky above the horizon, from the reflected glare of these livid flames, was not so utterly obscure, as over the rest of the heavens.Darwin also observed a luminous "jelly-fish of the genus Dianaea", noting that: "When the waves scintillate with bright green sparks, I believe it is generally owing to minute crustacea. But there can be no doubt that very many other pelagic animals, when alive, are phosphorescent." He guessed that "a disturbed electrical condition of the atmosphere" was probably responsible. Daniel Pauly comments that Darwin "was lucky with most of his guesses, but not here", noting that biochemistry was too little known, and that the complex evolution of the marine animals involved "would have been too much for comfort".
 Bioluminescence attracted the attention of the
Bioluminescence attracted the attention of the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
in the Cold War, since submarines in some waters can create a bright enough wake to be detected; a German submarine was sunk in the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
, having been detected in this way. The navy was interested in predicting when such detection would be possible, and hence guiding their own submarines to avoid detection.
Among the anecdotes of navigation by bioluminescence is one recounted by the Apollo 13
Apollo 13 (April 1117, 1970) was the seventh crewed mission in the Apollo space program and the third meant to land on the Moon. The craft was launched from Kennedy Space Center on April 11, 1970, but the lunar landing was aborted af ...
astronaut Jim Lovell
James Arthur Lovell Jr. (; born March 25, 1928) is an American retired astronaut, naval aviator, test pilot and mechanical engineer. In 1968, as command module pilot of Apollo 8, he became, with Frank Borman and William Anders, one of th ...
, who as a navy pilot had found his way back to his aircraft carrier USS ''Shangri-La'' when his navigation systems failed. Turning off his cabin lights, he saw the glowing wake of the ship, and was able to fly to it and land safely.
The French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ...
pharmacologist Raphaël Dubois
Raphaël Horace Dubois (20 June 1849, Le Mans – 21 January 1929) was a French pharmacologist known for his work on bioluminescence and anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is indu ...
carried out work on bioluminescence in the late nineteenth century. He studied click beetles
Elateridae or click beetles (or "typical click beetles" to distinguish them from the related families Cerophytidae and Eucnemidae, which are also capable of clicking) are a family of beetles. Other names include elaters, snapping beetles, s ...
(''Pyrophorus'') and the marine bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, biv ...
mollusc ''Pholas dactylus
''Pholas dactylus'', or common piddock, is a bioluminescent clam-like species of marine mollusc found on the coasts of the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea. It bores into gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of ...
''. He refuted the old idea that bioluminescence came from phosphorus, and demonstrated that the process was related to the oxidation of a specific compound, which he named luciferin
Luciferin (from the Latin ''lucifer'', "light-bearer") is a generic term for the light-emitting compound found in organisms that generate bioluminescence. Luciferins typically undergo an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with molecular oxygen. The resu ...
, by an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
. He sent Harvey siphons
A siphon (from grc, σίφων, síphōn, "pipe, tube", also spelled nonetymologically syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in a ...
from the mollusc preserved in sugar. Harvey had become interested in bioluminescence as a result of visiting the South Pacific and Japan and observing phosphorescent organisms there. He studied the phenomenon for many years. His research aimed to demonstrate that luciferin, and the enzymes that act on it to produce light, were interchangeable between species, showing that all bioluminescent organisms had a common ancestor. However, he found this hypothesis to be false, with different organisms having major differences in the composition of their light-producing proteins. He spent the next 30 years purifying and studying the components, but it fell to the young Japanese chemist Osamu Shimomura
was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist, and Professor Emeritus at Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) in Woods Hole, Massachusetts and Boston University School of Medicine. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2008 for ...
to be the first to obtain crystalline luciferin. He used the sea firefly ''Vargula hilgendorfii'', but it was another ten years before he discovered the chemical's structure and published his 1957 paper ''Crystalline Cypridina Luciferin''. Shimomura, Martin Chalfie
Martin Lee Chalfie (born January 15, 1947) is an American scientist. He is List of university professors at Columbia University, University Professor at Columbia University. He shared the 2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry along with Osamu Shimomura ...
, and Roger Y. Tsien
Roger Yonchien Tsien (pronounced , "'' CHEN''"'';'' February 1, 1952 – August 24, 2016) was an American biochemist. He was a professor of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of California, San Diego and was awarded the Nobel Prize in ...
won the 2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
for their 1961 discovery and development of green fluorescent protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish '' Aeq ...
as a tool for biological research.
Harvey wrote a detailed historical account on all forms of luminescence in 1957. An updated book on bioluminescence covering also the twentieth and early twenty-first century was published recently.
Evolution
In 1932 E. N. Harvey was among the first to propose how bioluminescence could have evolved. In this early paper, he suggested that proto-bioluminescence could have arisen from respiratory chain proteins that hold fluorescent groups. This hypothesis has since been disproven, but it did lead to considerable interest in the origins of the phenomenon. Today, the two prevailing hypotheses (both concerning marine bioluminescence) are those put forth by Howard Seliger in 1993 and Rees et al. in 1998. Seliger's theory identifies luciferase enzymes as the catalyst for the evolution of bioluminescent systems. It suggests that the original purpose of luciferases was as mixed-function oxygenases. As the early ancestors of many species moved into deeper and darker waters natural selection favored the development of increased eye sensitivity and enhanced visual signals. If selection were to favor a mutation in the oxygenase enzyme required for the breakdown of pigment molecules (molecules often associated with spots used to attract a mate or distract a predator) it could have eventually resulted in external luminescence in tissues. Rees et al. use evidence gathered from the marine luciferin coelenterazine to suggest that selection acting on luciferins may have arisen from pressures to protect oceanic organisms from potentially deleterious reactive oxygen species (e.g. H2O2 and O2− ). The functional shift from antioxidation to bioluminescence probably occurred when the strength of selection for antioxidation defense decreased as early species moved further down the water column. At greater depths exposure to ROS is significantly lower, as is the endogenous production of ROS through metabolism. While popular at first, Seliger's theory has been challenged, particularly on the biochemical and genetic evidence that Rees examines. What remains clear, however, is that bioluminescence has evolved independently at least 40 times. Bioluminescence in fish began at least by theCretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
period. About 1,500 fish species are known to be bioluminescent; the capability evolved independently at least 27 times. Of these, 17 involved the taking up of bioluminous bacteria from the surrounding water while in the others, the intrinsic light evolved through chemical synthesis. These fish have become surprisingly diverse in the deep ocean and control their light with the help of their nervous system, using it not just to lure prey or hide from predators, but also for communication.
All bioluminescent organisms have in common that the reaction of a "luciferin" and oxygen is catalyzed by a luciferase to produce light. McElroy and Seliger proposed in 1962 that the bioluminescent reaction evolved to detoxify oxygen, in parallel with photosynthesis.
Thuesen, Davis et al. showed in 2016 that bioluminescence has evolved independently 27 times within 14 fish clades across ray-finned fishes.
Chemical mechanism
 Bioluminescence is a form of
Bioluminescence is a form of chemiluminescence
Chemiluminescence (also chemoluminescence) is the emission of light ( luminescence) as the result of a chemical reaction. There may also be limited emission of heat. Given reactants A and B, with an excited intermediate ◊,
: + -> lozenge - ...
where light energy is released by a chemical reaction. This reaction involves a light-emitting pigment, the luciferin
Luciferin (from the Latin ''lucifer'', "light-bearer") is a generic term for the light-emitting compound found in organisms that generate bioluminescence. Luciferins typically undergo an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with molecular oxygen. The resu ...
, and a luciferase
Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words '' luciferin'' and ''luciferase'' ...
, the enzyme component. Because of the diversity of luciferin/luciferase combinations, there are very few commonalities in the chemical mechanism. From currently studied systems, the only unifying mechanism is the role of molecular oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
; often there is a concurrent release of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
(CO2). For example, the firefly luciferin/luciferase reaction requires magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
and ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
and produces CO2, adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine; it is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. As a substitu ...
(AMP) and pyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among o ...
(PP) as waste products. Other cofactors may be required, such as calcium (Ca2+) for the photoprotein Photoproteins are a type of enzyme, made of protein, from bioluminescent organisms. They add to the function of the luciferins whose usual light-producing reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme luciferase.
History
The term photoprotein was first use ...
aequorin
Aequorin is a calcium-activated photoprotein isolated from the hydrozoan ''Aequorea victoria''. Its bioluminescence was studied decades before the protein was isolated from the animal by Osamu Shimomura in 1962. In the animal, the protein occurs ...
, or magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
(Mg2+) ions and ATP for the firefly luciferase
Firefly luciferase is the light-emitting enzyme responsible for the bioluminescence of fireflies and click beetles. The enzyme catalyses the oxidation of firefly luciferin, requiring oxygen and ATP. Because of the requirement of ATP, firefly lu ...
. Generically, this reaction can be described as:
:Luciferin + O2text
Text may refer to:
Written word
* Text (literary theory), any object that can be read, including:
**Religious text, a writing that a religious tradition considers to be sacred
**Text, a verse or passage from scripture used in expository preachin ...
\text]Aequorea victoria
''Aequorea victoria'', also sometimes called the crystal jelly, is a bioluminescent hydrozoan jellyfish, or hydromedusa, that is found off the west coast of North America.
The species is best known as the source of two proteins involved in biolu ...
'' makes use of another type of protein called a photoprotein Photoproteins are a type of enzyme, made of protein, from bioluminescent organisms. They add to the function of the luciferins whose usual light-producing reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme luciferase.
History
The term photoprotein was first use ...
, in this case specifically aequorin
Aequorin is a calcium-activated photoprotein isolated from the hydrozoan ''Aequorea victoria''. Its bioluminescence was studied decades before the protein was isolated from the animal by Osamu Shimomura in 1962. In the animal, the protein occurs ...
. When calcium ions are added, rapid catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycl ...
creates a brief flash quite unlike the prolonged glow produced by luciferase. In a second, much slower step, luciferin is regenerated from the oxidized (oxyluciferin) form, allowing it to recombine with aequorin, in preparation for a subsequent flash. Photoproteins are thus enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s, but with unusual reaction kinetics. Furthermore, some of the blue light released by aequorin in contact with calcium ions is absorbed by a green fluorescent protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish '' Aeq ...
, which in turn releases green light in a process called resonant energy transfer.
Overall, bioluminescence has arisen over 40 times in evolutionary history. In evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
, luciferins tend to vary little: one in particular, coelenterazine
Coelenterazine is a luciferin, a molecule that emits light after reaction with oxygen, found in many aquatic organisms across eight phyla. It is the substrate of many luciferases such as ''Renilla reniformis'' luciferase (Rluc), ''Gaussia'' lucif ...
, is the light emitting pigment for nine phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phyl ...
(groups of very different organisms), including polycystine radiolaria
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elab ...
, Cercozoa
Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead defined by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major ...
(Phaeodaria
Phaeodarea, or Phaeodaria, is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They ...
), protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histor ...
, comb jellies
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...
, cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in Fresh water, freshwater and Marine habitats, marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocyt ...
including jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
and coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secre ...
s, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
s, molluscs
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is esti ...
, arrow worms
The Chaetognatha or chaetognaths (meaning ''bristle-jaws'') are a phylum of predatory marine worms that are a major component of plankton worldwide. Commonly known as arrow worms, about 20% of the known Chaetognatha species are benthic, and can ...
and vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s (ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species.
The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or h ...
). Not all these organisms synthesise coelenterazine: some of them obtain it through their diet. Conversely, luciferase enzymes vary widely and tend to be different in each species.
Distribution
Bioluminescence occurs widely among animals, especially in the open sea, includingfish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
, jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
, comb jellies
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...
, crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
s, and cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda ( Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, ...
molluscs; in some fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
and bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
; and in various terrestrial invertebrates including insects. In marine coastal habitats, about 2.5% of organisms are estimated to be bioluminescent, whereas in pelagic habitats in the eastern Pacific, about 76% of the main taxa of deep-sea animals have been found to be capable of producing light. Most marine light-emission is in the blue and green light spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from ...
. However, some loose-jawed fish emit red and infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from aroun ...
light, and the genus ''Tomopteris
The gossamer worm (''Tomopteris'', Neo-Latin from Greek meaning "a cut" + "wing" but taken to mean "fin") is a genus of marine planktonic polychaetes.
All described species are known to be holoplanktic, meaning that they spend their entire lif ...
'' emits yellow light.
The most frequently encountered bioluminescent organisms may be the dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s in the surface layers of the sea, which are responsible for the sparkling phosphorescence sometimes seen at night in disturbed water. At least 18 genera exhibit luminosity. A different effect is the thousands of square miles of the ocean which shine with the light produced by bioluminescent bacteria, known as mareel or the milky seas effect.
Pelagic zone
Bioluminescence is abundant in the pelagic zone, with the most concentration at depths devoid of light and surface waters at night. These organisms participate in diurnal vertical migration from the dark depths to the surface at night, dispersing the population of bioluminescent organisms across the pelagic water column. The dispersal of bioluminescence across different depths in the pelagic zone has been attributed to the selection pressures imposed by predation and the lack of places to hide in the open sea. In depths where sunlight never penetrates, often below 200m, the significance of bioluminescent is evident in the retainment of functional eyes for organisms to detect bioluminescence.Bacterial symbioses
Organisms often produce bioluminescence themselves, rarely do they generate it from outside phenomena. However, there are occasions where bioluminescence is produced by bacterial symbionts that have a symbiotic relationship with the host organism. Although many luminous bacteria in the marine environment are free-living, a majority are found in symbiotic relationships that involve fish, squids, crustaceans etc. as hosts. Most luminous bacterial inhabit the marine sea, with ''Photobacterium
''Photobacterium'' is a genus of gram-negative, oxidase positive and catalase positive bacteria in the family ''Vibrionaceae''. Members of the genus are bioluminescent, that is they have the ability to emit light.
Many species, including '' Phot ...
'' and ''Vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive ...
'' genera dominating the marine environment.
In the symbiotic relationship, bacterium benefit from having a source of nourishment and a refuge to grow. Hosts obtain these bacterial symbionts either from the environment, spawning
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, and the act of both sexes is called spawning. Most aquatic animals, except for aqua ...
, or the luminous bacterium is evolving with their host. Coevolutionary interactions are suggested as host organisms’ anatomical adaptations have become specific to only certain luminous bacteria, to suffice ecological dependence of bioluminescence.
Benthic zone
Bioluminescence is widely studied amongst species located in the mesopelagic zone, but the benthic zone at mesopelagic depths has remained widely unknown. Benthic habitats at depths beyond the mesopelagic are also poorly understood due to the same constraints. Unlike the pelagic zone where the emission of light is undisturbed in the open sea, the occurrence of bioluminescence in the benthic zone is less common. It has been attributed to the blockage of emitted light by a number of sources such as the sea floor, and inorganic and organic structures. Visual signals and communication that is prevalent in the pelagic zone such as counterillumination may not be functional or relevant in the benthic realm. Bioluminescence in bathyal benthic species still remains poorly studied due to difficulties of the collection of species at these depths.Uses in nature
 Bioluminescence has several functions in different taxa.
Bioluminescence has several functions in different taxa. Steven Haddock Steven H. D. Haddock is a marine biologist known for his work on bioluminescence of the jellylike animals of the open ocean and the deep sea, and the photoproteins and fluorescent proteins of these animals.
Life
Haddock was educated at Harvey Mud ...
et al. (2010) list as more or less definite functions in marine organisms the following: defensive functions of startle, counterillumination (camouflage), misdirection (smoke screen), distractive body parts, burglar alarm (making predators easier for higher predators to see), and warning to deter settlers; offensive functions of lure, stun or confuse prey, illuminate prey, and mate attraction/recognition. It is much easier for researchers to detect that a species is able to produce light than to analyze the chemical mechanisms or to prove what function the light serves. In some cases the function is unknown, as with species in three families of earthworm (Oligochaeta
Oligochaeta () is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworm ...
), such as ''Diplocardia longa
''Diplocardia longa'' is a species of earthworm native to North America. It was first described by the American zoologist John Percy Moore in 1904. The type locality is Hawkinsville, Georgia. This worm has bioluminescent properties; its body f ...
'' where the coelomic fluid
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, ...
produces light when the animal moves. The following functions are reasonably well established in the named organisms.
Counterillumination camouflage
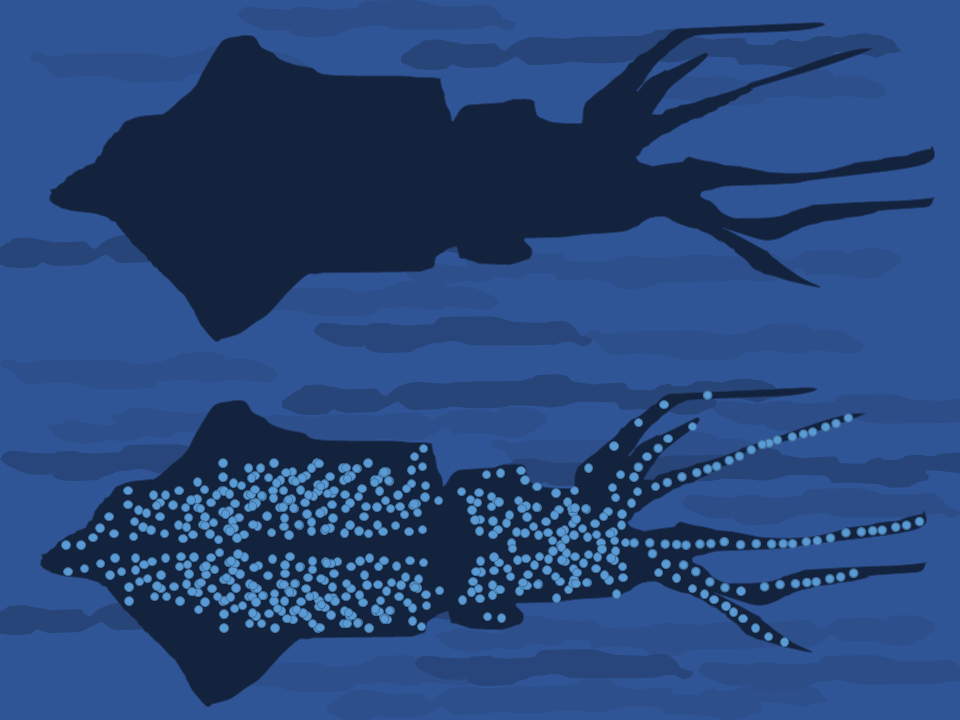
 In many animals of the deep sea, including several
In many animals of the deep sea, including several squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting ...
species, bacterial bioluminescence is used for camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
by counterillumination
Counter-illumination is a method of active camouflage seen in marine animals such as firefly squid and midshipman fish, and in military prototypes, producing light to match their backgrounds in both brightness and wavelength.
Marine animals of ...
, in which the animal matches the overhead environmental light as seen from below. In these animals, photoreceptors control the illumination to match the brightness of the background. These light organs are usually separate from the tissue containing the bioluminescent bacteria. However, in one species, ''Euprymna scolopes
__NOTOC__
''Euprymna scolopes'', also known as the Hawaiian bobtail squid, is a species of bobtail squid in the family Sepiolidae native to the central Pacific Ocean, where it occurs in shallow coastal waters off the Hawaiian Islands and Midway Is ...
'', the bacteria are an integral component of the animal's light organ.
Attraction
 Bioluminescence is used in a variety of ways and for different purposes. The cirrate octopod ''Stauroteuthis syrtensis'' uses emits bioluminescence from its sucker like structures. These structures are believed to have evolved from what are more commonly known as octopus suckers. They do not have the same function as the normal suckers because they no longer have any handling or grappling ability due its evolution of
Bioluminescence is used in a variety of ways and for different purposes. The cirrate octopod ''Stauroteuthis syrtensis'' uses emits bioluminescence from its sucker like structures. These structures are believed to have evolved from what are more commonly known as octopus suckers. They do not have the same function as the normal suckers because they no longer have any handling or grappling ability due its evolution of photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, h ...
s. The placement of the photophores are within the animals oral reach, which leads researchers to suggest that it uses it bioluminescence to capture and lure prey.
Fireflies
The Lampyridae are a family of elateroid beetles with more than 2,000 described species, many of which are light-emitting. They are soft-bodied beetles commonly called fireflies, lightning bugs, or glowworms for their conspicuous production ...
use light to attract mates
Mates is an English surname, and may refer to:
* Mates (born 1964), British newsreader and journalist
* Michael Mates (born 1934), British politician
* Frederick S. Mates, founded the Mates Investment Fund in 1967 that crashed in the bear market ...
. Two systems are involved according to species; in one, females emit light from their abdomens to attract males; in the other, flying males emit signals to which the sometimes sedentary females respond. Click beetle
Elateridae or click beetles (or "typical click beetles" to distinguish them from the related families Cerophytidae and Eucnemidae, which are also capable of clicking) are a family of beetles. Other names include elaters, snapping beetles, ...
s emit an orange light from the abdomen when flying and a green light from the thorax when they are disturbed or moving about on the ground. The former is probably a sexual attractant but the latter may be defensive. Larvae of the click beetle ''Pyrophorus nyctophanus
''Pyrophorus nyctophanus'' (=''fire-bearing night-shiner''), aka headlight beetle or carbunco, is a species of click beetle that occurs on the cerrado of Brazil. Its luminescent larvae are either soil-dwelling or found in tunnels in the outer la ...
'' live in the surface layers of termite mounds in Brazil. They light up the mounds by emitting a bright greenish glow which attracts the flying insects on which they feed.
In the marine environment, use of luminescence for mate attraction is chiefly known among ostracod
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 70,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant) have been identified, grouped into several orders. They are small crustaceans, typic ...
s, small shrimplike crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
s, especially in the family Cyprididae
Cyprididae is "the most diverse group of freshwater ostracods". It contains over 1000 species, which represents 50% of the known species of freshwater ostracods (other speciose families include Candonidae, with 25%, and Limnocytheridae, with 1 ...
. Pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s may be used for long-distance communication, with bioluminescence used at close range to enable mates to "home in". A polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are ...
worm, the Bermuda fireworm creates a brief display, a few nights after the full moon, when the female lights up to attract males.
Defense
The defense mechanisms for bioluminescent organisms can come in multiple forms; startling prey, counterillumination, smoke screen or misdirection, distractive body parts, burglar alarm, sacrificial tag or warning coloration. The shrimp family Oplophoridae Dana use their bioluminescence as a way of startling the predator that is after them. ''Acanthephyra purpurea'', within the Oplophoridae family, uses its photophores to emit light, and can secrete a bioluminescent substance when in the presence of a predator. This secretory mechanism is common among prey fish. Manycephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda ( Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, ...
s, including at least 70 genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial ...
of squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting ...
, are bioluminescent. Some squid and small crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
s use bioluminescent chemical mixtures or bacterial slurries in the same way as many squid use ink
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. ...
. A cloud of luminescent material is expelled, distracting or repelling a potential predator, while the animal escapes to safety. The deep sea squid ''Octopoteuthis deletron
''Octopoteuthis deletron'' is a species of squid in the genus ''Octopoteuthis'' of the family Octopoteuthidae. They belong to the pelagic squids of order Oegopsida. Found at depths of in the Pacific Ocean, they have been known to grow to .
''O. ...
'' may autotomise portions of its arms which are luminous and continue to twitch and flash, thus distracting a predator while the animal flees.
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s may use bioluminescence for defense against predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
s. They shine when they detect a predator, possibly making the predator itself more vulnerable by attracting the attention of predators from higher trophic levels. Grazing copepods release any phytoplankton cells that flash, unharmed; if they were eaten they would make the copepods glow, attracting predators, so the phytoplankton's bioluminescence is defensive. The problem of shining stomach contents is solved (and the explanation corroborated) in predatory deep-sea fishes: their stomachs have a black lining able to keep the light from any bioluminescent fish prey which they have swallowed from attracting larger predators.
The sea-firefly is a small crustacean living in sediment. At rest it emits a dull glow but when disturbed it darts away leaving a cloud of shimmering blue light to confuse the predator. During World War II it was gathered and dried for use by the Japanese army as a source of light during clandestine operations.
The larvae of railroad worm
A railroad worm is a larva or larviform female adult of a beetle of the genus ''Phrixothrix'' in the family Phengodidae, characterized by the possession of two different colors of bioluminescence. It has the appearance of a caterpillar. The ...
s (''Phrixothrix'') have paired photic organs on each body segment, able to glow with green light; these are thought to have a defensive purpose. They also have organs on the head which produce red light; they are the only terrestrial organisms to emit light of this color.
Warning
Aposematism
Aposematism is the Advertising in biology, advertising by an animal to potential predation, predators that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defences which make the prey difficult to kill and eat, suc ...
is a widely used function of bioluminescence, providing a warning that the creature concerned is unpalatable. It is suggested that many firefly larvae glow to repel predators; some millipede
Millipedes are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a re ...
s glow for the same purpose. Some marine organisms are believed to emit light for a similar reason. These include scale worms, jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella- ...
and brittle star
Brittle stars, serpent stars, or ophiuroids (; ; referring to the serpent-like arms of the brittle star) are echinoderms in the class Ophiuroidea, closely related to starfish. They crawl across the sea floor using their flexible arms for locom ...
s but further research is needed to fully establish the function of the luminescence. Such a mechanism would be of particular advantage to soft-bodied cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in Fresh water, freshwater and Marine habitats, marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocyt ...
ns if they were able to deter predation in this way. The limpet ''Latia neritoides'' is the only known freshwater Gastropoda, gastropod that emits light. It produces greenish luminescent mucus which may have an anti-predator function. The marine snail ''Hinea brasiliana'' uses flashes of light, probably to deter predators. The blue-green light is emitted through the translucent shell, which functions as an efficient diffuser of light.
Communication
 Communication in the form of quorum sensing plays a role in the regulation of luminescence in many species of bacteria. Small extracellularly secreted molecules stimulate the bacteria to turn on genes for light production when cell density, measured by concentration of the secreted molecules, is high.
Pyrosomes are colonial Tunicata, tunicates and each zooid has a pair of luminescent organs on either side of the inlet siphon. When stimulated by light, these turn on and off, causing rhythmic flashing. No neural pathway runs between the zooids, but each responds to the light produced by other individuals, and even to light from other nearby colonies. Communication by light emission between the zooids enables coordination of colony effort, for example in swimming where each zooid provides part of the propulsive force.
Some bioluminous bacteria infect nematodes that parasitize Lepidoptera larvae. When these caterpillars die, their luminosity may attract predators to the dead insect thus assisting in the dispersal of both bacteria and nematodes. A similar reason may account for the many species of fungi that emit light. Species in the genera ''Armillaria'', ''Mycena'', ''Omphalotus'', ''Panellus'', ''Pleurotus'' and others do this, emitting usually greenish light from the mycelium, Pileus (mycology), cap and Lamella (mycology), gills. This may attract night-flying insects and aid in spore dispersal, but other functions may also be involved.
''Quantula striata'' is the only known bioluminescent terrestrial mollusc. Pulses of light are emitted from a gland near the front of the foot and may have a communicative function, although the adaptive significance is not fully understood.
Communication in the form of quorum sensing plays a role in the regulation of luminescence in many species of bacteria. Small extracellularly secreted molecules stimulate the bacteria to turn on genes for light production when cell density, measured by concentration of the secreted molecules, is high.
Pyrosomes are colonial Tunicata, tunicates and each zooid has a pair of luminescent organs on either side of the inlet siphon. When stimulated by light, these turn on and off, causing rhythmic flashing. No neural pathway runs between the zooids, but each responds to the light produced by other individuals, and even to light from other nearby colonies. Communication by light emission between the zooids enables coordination of colony effort, for example in swimming where each zooid provides part of the propulsive force.
Some bioluminous bacteria infect nematodes that parasitize Lepidoptera larvae. When these caterpillars die, their luminosity may attract predators to the dead insect thus assisting in the dispersal of both bacteria and nematodes. A similar reason may account for the many species of fungi that emit light. Species in the genera ''Armillaria'', ''Mycena'', ''Omphalotus'', ''Panellus'', ''Pleurotus'' and others do this, emitting usually greenish light from the mycelium, Pileus (mycology), cap and Lamella (mycology), gills. This may attract night-flying insects and aid in spore dispersal, but other functions may also be involved.
''Quantula striata'' is the only known bioluminescent terrestrial mollusc. Pulses of light are emitted from a gland near the front of the foot and may have a communicative function, although the adaptive significance is not fully understood.
Mimicry
 Bioluminescence is used by a variety of animals to mimicry, mimic other species. Many species of deep sea fish such as the anglerfish and Stomiidae, dragonfish make use of aggressive mimicry to attract prey. They have an appendage on their heads called an esca that contains bioluminescent bacteria able to produce a long-lasting glow which the fish can control. The glowing esca is dangled or waved about to lure small animals to within striking distance of the fish.
The cookiecutter shark uses bioluminescence to camouflage its underside by counterillumination, but a small patch near its pectoral fins remains dark, appearing as a small fish to large predatory fish like tuna and mackerel swimming beneath it. When such fish approach the lure, they are bitten by the shark.
Female ''Photuris'' fireflies sometimes mimic the light pattern of another firefly, ''Photinus'', to attract its males as prey. In this way they obtain both food and the defensive chemicals named lucibufagins, which ''Photuris'' cannot synthesize.
South American giant cockroaches of the genus ''Lucihormetica'' were believed to be the first known example of defensive mimicry, emitting light in imitation of bioluminescent, poisonous click beetles. However, doubt has been cast on this assertion, and there is no conclusive evidence that the cockroaches are bioluminescent.
Bioluminescence is used by a variety of animals to mimicry, mimic other species. Many species of deep sea fish such as the anglerfish and Stomiidae, dragonfish make use of aggressive mimicry to attract prey. They have an appendage on their heads called an esca that contains bioluminescent bacteria able to produce a long-lasting glow which the fish can control. The glowing esca is dangled or waved about to lure small animals to within striking distance of the fish.
The cookiecutter shark uses bioluminescence to camouflage its underside by counterillumination, but a small patch near its pectoral fins remains dark, appearing as a small fish to large predatory fish like tuna and mackerel swimming beneath it. When such fish approach the lure, they are bitten by the shark.
Female ''Photuris'' fireflies sometimes mimic the light pattern of another firefly, ''Photinus'', to attract its males as prey. In this way they obtain both food and the defensive chemicals named lucibufagins, which ''Photuris'' cannot synthesize.
South American giant cockroaches of the genus ''Lucihormetica'' were believed to be the first known example of defensive mimicry, emitting light in imitation of bioluminescent, poisonous click beetles. However, doubt has been cast on this assertion, and there is no conclusive evidence that the cockroaches are bioluminescent.

Illumination
While most marine bioluminescence is green to blue, some deep sea Stomiidae, barbeled dragonfishes in the genera ''Aristostomias'', ''Pachystomias'' and ''Malacosteus'' emit a red glow. This adaptation allows the fish to see red-pigmented prey, which are normally invisible to other organisms in the deep ocean environment where red light has been filtered out by the water column. The fish is able to utilize the longer wavelength to act as a spotlight for its prey that only it is able to see. In addition to the utilization of the light for predation, it has been hypothesized that the fish use this to communicate with each other to find potential mates. The ability of the fish to see this light is explained by the presence of specialized rhodopsin pigment. The angler siphonophore (Erenna), also utilizes red bioluminescence in appendages to lure fish. The mechanism of light creation is through a suborbital photophore that utilizes gland cells which produce exergonic chemical reactions that produce light with a longer, red wavelength. The dragonfish species which produce the red light also produce blue light in photophore on the dorsal area. The main function of this is to alert the fish to the presence of its prey. The additional pigment is thought to be assimilated from chlorophyll derivatives found in the copepods which form part of its diet.Biotechnology
Biology and medicine
Bioluminescent organisms are a target for many areas of research. Luciferase systems are widely used in genetic engineering as reporter genes, each producing a different color by fluorescence, and for biomedical research using bioluminescence imaging. For example, the firefly luciferase gene was used as early as 1986 for research using transgenic tobacco plants. ''Vibrio'' bacteria symbiose with marine invertebrates such as the Euprymna scolopes, Hawaiian bobtail squid (''Euprymna scolopes''), are key model organism, experimental models for bioluminescence. Bioluminescent activated destruction is an experimental cancer treatment. ''In Vivo'' luminescence cell and animal imaging uses dyes and fluorescent proteins as chromophores. The characteristics of each chromophore determine which cell area(s) will be targeted and illuminated.Light production
The structures ofphotophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, h ...
s, the light producing organs in bioluminescent organisms, are being investigated by industrial designers. Engineered bioluminescence could perhaps one day be used to reduce the need for street lighting, or for decorative purposes if it becomes possible to produce light that is both bright enough and can be sustained for long periods at a workable price.Bioluminescence Questions and AnswersSiobiolum.ucsd.edu. Retrieved on 20 October 2011. The gene that makes the tails of
fireflies
The Lampyridae are a family of elateroid beetles with more than 2,000 described species, many of which are light-emitting. They are soft-bodied beetles commonly called fireflies, lightning bugs, or glowworms for their conspicuous production ...
glow has been added to mustard plants. The plants glow faintly for an hour when touched, but a sensitive camera is needed to see the glow. University of Wisconsin–Madison is researching the use of genetically engineered bioluminescent Escherichia coli, E. coli bacteria, for use as bioluminescent bacteria
Bioluminescent bacteria are light-producing bacteria that are predominantly present in sea water, marine sediments, the surface of decomposing fish and in the gut of marine animals. While not as common, bacterial bioluminescence is also found in t ...
in a light bulb.
In 2011, Philips launched a microbial system for ambience lighting in the home.
An International Genetically Engineered Machine, iGEM team from Cambridge (England) has started to address the problem that luciferin is consumed in the light-producing reaction by developing a genetic biotechnology part that codes for a luciferin regenerating enzyme from the North American firefly.
In 2016, Glowee, a French company started selling bioluminescent lights for shop fronts and street signs, for use between 1 and 7 in the morning when the law forbids use of electricity for this purpose. They used the bioluminescent bacterium ''Aliivibrio fischeri'', but the maximum lifetime of their product was three days.
In April 2020, plants were genetically engineered to glow more brightly using genes from the bioluminescent mushroom ''Neonothopanus nambi'' to convert caffeic acid into luciferin.
ATP bioluminescence
ATP bioluminescence is the process in which ATP is used to generate luminescence in an organism. It proves to be a very good biosensor to test cell viability. Optical biosensors include process of measurement of ''luminescence, fluorescence absorbance or emission''. Through these measurements, quantitative measurement of ATP bioluminescence is applied to detect existence of living microbes only. Since the method is quick and convenient, it results in real-time data. It is faster, economical and easier to work with. Optical biosensors sense the observed optical signal based on measuring the photons involved in the phenomenon (''spiking'') It depends on the interaction of microbes with analytes. Thus, it is correlated with the concentration of the microbial population which is determined through this method.Differentiation between living and non living cells
In ATP bioluminescence, it is assumed that all living cells in the same have the same amount of ATP over time during the chemical reaction between luciferin, luciferase to produce ATP, This is done in order to measure the viability of the cell and allows the researcher to measure the amount of living and dead cells in the sample on basis of presence or absence of ATP. Living cells that contain ATP produce a bioluminescent flash due to the ''luciferin-luciferase reaction'' in presence of ATP. Dead cells do not produce any bioluminescence due to absence of ATP The amount of the intensity of the signal is constant for each living cell in a healthy sample. In this way, the overall number of living cells within a sample is determined.= Process of measurement of microbial population
= ATP, which is a fundamental compound in the luciferase reaction, is utilized and in the second step, oxyluciferin is produced. The oxyluciferin is produced in an excited state, which produces light when it goes back to ground state. The light emitted is detected by a luminometer. Concentration of the ATP is directly proportional to the expressed light measured as Relative Light Units (RLU). A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) is used to calculate the sensitivity and specificity of the measurements. There is direct correlation between luminescence intensity and concentration of standard ATP. There is a direct correlation between bioluminescence and colony forming unit (CFU). Thus, concentration of standard ATP and CFU gives a standard correlation. In this way, ATP is measured and microbial population is determined through bioluminescence. However, it is important to keep in mind that different types of microbial populations are determined through different sets of ATP assays using other substrates and reagents. ''Renilla'' and ''Gaussia'' based cell viability assays use the substrate coelenterazine.See also
*Animal coloration *Biophoton *''Life That Glows'', 2016 full-length documentaryNotes
References
Further reading
* Victor Benno Meyer-Rochow (2009) Bioluminescence in Focus – a collection of illuminating essays Research Signpost: * Osamu Shimomura, Shimomura, Osamu (2006). ''Bioluminescence: Chemical Principles and Methods.'' Word Scientific Publishing. . * Lee, John (2016). "Bioluminescence, the Nature of the Light." The University of Georgia Libraries. http://hdl.handle.net/10724/20031 * *Anctil, Michel (2018). ''Luminous Creatures: The History and Science of Light Production in Living Organisms''. McGill-Queen's University Press.External links
BBC: Red tide: Electric blue waves wash California shore
(video)
Smithsonian Ocean Portal: Bioluminescent animals photo gallery
National Geographic: Bioluminescence
Annual Review of Marine Science: Bioluminescence in the Sea
Canon Australia – Tips on How to Photograph Bioluminescence
* The New York City American Natural History Museum's "Creatures of Light: Nature's Bioluminescence" 2022 Featured Exhibit (in concert with the Ottawa, Canada-based Canadian Museum of Nature and Chicago's Field Museum of Natural History) webpage
{{good article Bioluminescence, Fisheries science Light sources Camouflage Mimicry Bioelectromagnetics