Beta Canis Majoris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beta Canis Majoris (β Canis Majoris, abbreviated Beta CMa, β CMa), also named Mirzam , is a
 This star has a mass of about 13–14 times the
This star has a mass of about 13–14 times the
star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
in the southern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
of Canis Major
Canis Major is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin fo ...
, the "Great Dog", located at a distance of about 500 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s (150 parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and ...
s) from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. In the modern constellation it lies at the position of the dog's front leg.
Nomenclature
''Beta Canis Majoris'' is the star'sBayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. ...
. The traditional names ''Mirzam'', ''Al-Murzim'' or ''Murzim'', derive from the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
(مرزم) for 'The Herald', and probably refers to its position, heralding (i.e., rising before) Sirius
Sirius is the list of brightest stars, brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek language, Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinisation ...
in the night sky. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
organized a Working Group on Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education ...
(WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Mirzam'' for this star.
In Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, (), meaning ' Market for Soldiers', refers to an asterism consisting of β Canis Majoris, Nu3 Canis Majoris
Nu3 Canis Majoris, Latinized from ν3 Canis Majoris, is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Canis Major.
Characteristics
The star system, appearing as one star, is deemed visible to the naked eye with its combined app ...
, 15 Canis Majoris
15 Canis Majoris is a variable star in the southern constellation of Canis Major, located roughly 1,200 light years away from the Sun. It has the variable star designation EY Canis Majoris; ''15 Canis Majoris'' is the Flamsteed desig ...
, Pi Canis Majoris
Pi Canis Majoris (π Canis Majoris; Latin for 'Greater Dog') is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Canis Major. It is visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of +4.69. Based upon an annual parallax ...
, Omicron1 Canis Majoris
Omicron1 Canis Majoris (ο1 CMa, ο1 Canis Majoris) is a red supergiant star in the constellation Canis Major. It is also a variable star.
Name
Johann Bayer gave two adjacent stars the Bayer designation of ο Canis Majoris in 1603, b ...
and Xi1 Canis Majoris
Xi1 Canis Majoris, Latinized from ξ1 Canis Majoris, is a Beta Cephei variable star in the constellation Canis Major. It is approximately 1,400 light years from Earth.
ξ1 Canis Majoris is a blue-white B-type star. It has generally ...
. Consequently, β Canis Majoris itself is known as (, en, the First Star of Market for Soldiers). From this Chinese name arose the name ''Kuen She''.
The Dunhuang Star Chart
The Dunhuang map or Dunhuang Star map is one of the first known graphical representations of stars from ancient Chinese astronomy, dated to the Tang Dynasty (618–907). Before this map, much of the star information mentioned in historical ...
noted β Canis Majoris as Yeji "Pheasant Cock", though was located about 10 degrees too far north of its correct position.
Beta Canis Majoris was called ''Oupo'' by the people of the Tuamotus
The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands (french: Îles Tuamotu, officially ) are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extendin ...
.
Properties
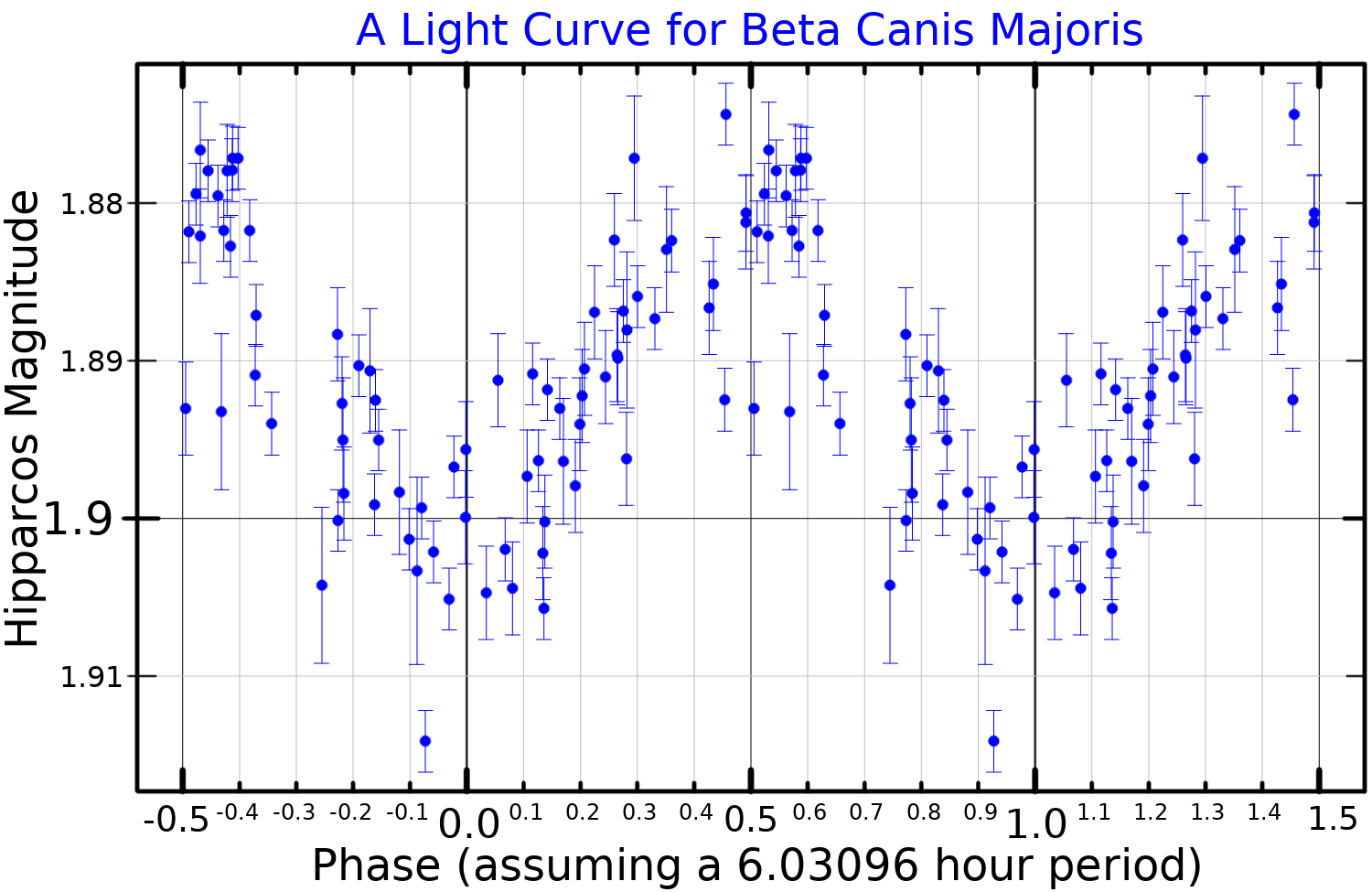
Mirzam is aBeta Cephei variable Beta Cephei variables, also known as Beta Canis Majoris stars, are variable stars that exhibit small rapid variations in their brightness due to pulsations of the stars' surfaces, thought due to the unusual properties of iron at temperatures of 200, ...
that varies in apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
between +1.97 and +2.01 over a six-hour period, a change in brightness that is too small to be discerned with the naked eye. It exhibits this variation in luminosity because of periodic pulsations in its outer envelope, which follow a complex pattern with three different cycles; all about six hours in length. The two dominant pulsation frequencies have a combined beat period of roughly 50 days. The strongest pulsation mode is a radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Mathematics and Direction
* Vector (geometric)
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector or spatial vector) ...
first overtone
An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. (An overtone may or may not be a harmonic) In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental i ...
, while the second is non-radial.
 This star has a mass of about 13–14 times the
This star has a mass of about 13–14 times the mass of the Sun
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass ...
with 8–11 times the Sun's radius. The effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
of the star's outer envelope is about 23,150 K, which is much higher than the Sun's at 5,778 K. The energy emitted at the high temperature of the former is what gives this star a blue-white hue characteristic of a B-type star
A B-type main-sequence star (B V) is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type B and luminosity class V. These stars have from 2 to 16 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 10,000 and 30,000 K. B-type star ...
. The estimated age of Mirzam is , which is long enough for a star of this mass to have evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
into a giant star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main sequence, main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same effective temperature, surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moo ...
. The stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grati ...
of B1 II-III indicates that the spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors i ...
matches a star part way between a giant star and a bright giant
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press ...
.
Beta Canis Majoris is located near the far end of the Local Bubble
The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbours and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud (which contains the Sola ...
, a cavity in the local interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
through which the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
is traveling. Beta Canis Majoris was the brightest star in the night sky around four million years ago, peaking with an apparent magnitude of -3.65. – based on computations from HIPPARCOS
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial obj ...
data. (The calculations exclude stars whose distance or proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more dista ...
is uncertain.) tp://tlgleonid.asuscomm.com/HITACHI/BOOK_ASTRO/S&T/SkyandTelescope_1998%20-%20astronomy/04/199804059063.pdf PDF/ref>
In culture
Mirzam appears on theflag of Brazil
The national flag of Brazil ( pt, bandeira do Brasil), is a blue disc depicting a starry sky (which includes the Southern Cross) spanned by a curved band inscribed with the national motto "''Ordem e Progresso''" ("Order and Progress"), within a y ...
, symbolising the state of Amapá
Amapá () is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is in the northern region of Brazil. It is the second least populous state and the eighteenth largest by area. Located in the far northern part of the country, Amapá is bordered clockwise by Fr ...
.
''Murzim'' (AK-95) was a United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
Crater class cargo ship
The ''Crater''-class cargo ship were converted EC2-S-C1 type, Liberty ship, Liberty cargo ships, constructed by the United States Maritime Commission (USMC) for use by the United States Navy, US Navy during World War II. The designation 'EC2-S-C1' ...
named after one of the star's alternative traditional names.
A small Dutch lamp company used the star in one of their commercials.
References
Sources
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Beta Canis Majoris Canis Majoris, Beta B-type bright giants B-type giants Canis Major Beta Cephei variables Local BubbleMirzam
Beta Canis Majoris (β Canis Majoris, abbreviated Beta CMa, β CMa), also named Mirzam , is a star in the southern constellation of Canis Major, the "Great Dog", located at a distance of about 500 light-years (150 parsecs) from ...
Canis Majoris, 02
044743
2294
BD-17 1467
030324