|
Beat (acoustics)
In acoustics, a beat is an interference pattern between two sounds of slightly different frequencies, ''perceived'' as a periodic variation in volume whose rate is the difference of the two frequencies. With tuning instruments that can produce sustained tones, beats can be readily recognized. Tuning two tones to a unison will present a peculiar effect: when the two tones are close in pitch but not identical, the difference in frequency generates the beating. The volume varies like in a tremolo as the sounds alternately interfere constructively and destructively. As the two tones gradually approach unison, the beating slows down and may become so slow as to be imperceptible. As the two tones get further apart, their beat frequency starts to approach the range of human pitch perception, the beating starts to sound like a note, and a combination tone is produced. This combination tone can also be referred to as a missing fundamental, as the beat frequency of any two tones is equivalen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beating Frequency
Beat, beats or beating may refer to: Common uses * Patrol, or beat, a group of personnel assigned to monitor a specific area ** Beat (police), the territory that a police officer patrols ** Gay beat, an area frequented by gay men * Battery (crime), a criminal offense involving unlawful physical contact * Assault, inflicting physical harm or unwanted physical contact * Corporal punishment, punishment intended to cause physical pain * Strike (attack), repeatedly and violently striking a person or object * Victory, success achieved in personal combat, military operations or in any competition People * Beat (name), a German male given name * Jackie Beat, drag persona of Kent Fuher (born 1963) * Aone Beats (born 1984) Nigerian record producer * Billy Beats (1871-1936) British footballer * Cohen Beats (Michael Cohen, born 1986), Israeli record producer * Eno Beats (Enock Kisakye, born 1991), Ugandan record producer * Laxio Beats (Bernard Antwi-Darko, born 1987), Ghanaian record pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Trigonometric Identities
In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. Geometrically, these are identities involving certain functions of one or more angles. They are distinct from triangle identities, which are identities potentially involving angles but also involving side lengths or other lengths of a triangle. These identities are useful whenever expressions involving trigonometric functions need to be simplified. An important application is the integration of non-trigonometric functions: a common technique involves first using the substitution rule with a trigonometric function, and then simplifying the resulting integral with a trigonometric identity. Pythagorean identities The basic relationship between the sine and cosine is given by the Pythagorean identity: :\sin^2\theta + \cos^2\theta = 1, where \sin^2 \theta means (\sin \theta)^2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Series (music)
A harmonic series (also overtone series) is the sequence of harmonics, musical tones, or pure tones whose frequency is an integer multiple of a ''fundamental frequency''. Pitched musical instruments are often based on an acoustic resonator such as a string or a column of air, which oscillates at numerous modes simultaneously. At the frequencies of each vibrating mode, waves travel in both directions along the string or air column, reinforcing and canceling each other to form standing waves. Interaction with the surrounding air causes audible sound waves, which travel away from the instrument. Because of the typical spacing of the resonances, these frequencies are mostly limited to integer multiples, or harmonics, of the lowest frequency, and such multiples form the harmonic series. The musical pitch of a note is usually perceived as the lowest partial present (the fundamental frequency), which may be the one created by vibration over the full length of the string or air co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
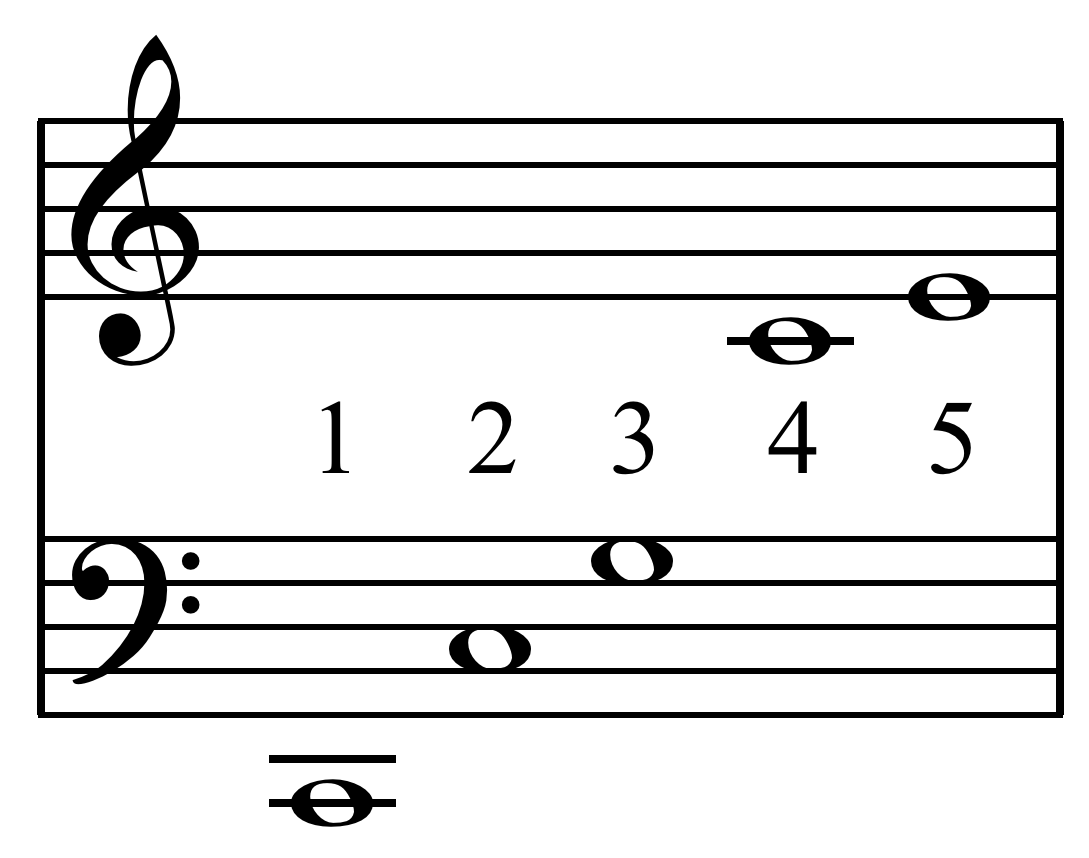
Just Intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals Interval may refer to: Mathematics and physics * Interval (mathematics), a range of numbers ** Partially ordered set#Intervals, its generalization from numbers to arbitrary partially ordered sets * A statistical level of measurement * Interval e ... as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of Frequency, frequencies. An interval (music), interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series (music), harmonic series of an implied fundamental frequency, fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth (music), fourth. In Western musical practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, which gives an equal perceived step size as pitch is perceived roughly as the logarithm of frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been twelve-tone equal temperament (also known as 12 equal temperament, 12-TET or 12-ET; informally abbreviated to twelve equal), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the 12th root of 2 ( ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western countries the term ''equal temperament'', without qualification, generally means 12-TET. In modern times, 12-TET is usually tuned relative to a standard pitch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |