Benin City, on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in
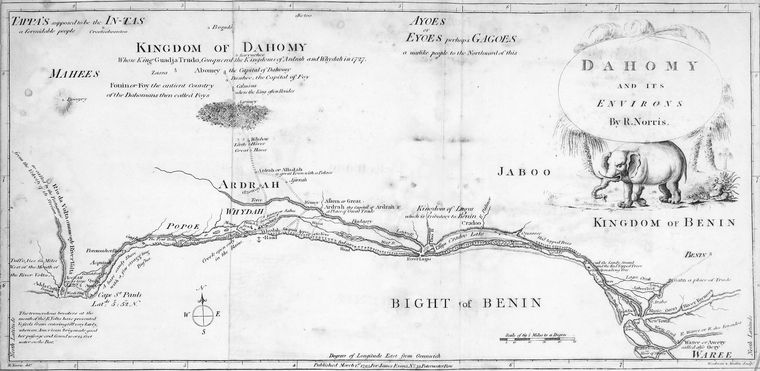 Prior to 1600, present-day Benin comprised a variety of areas with different political systems and ethnicities. These included city-states along the coast (primarily of the Aja ethnic group, and also including
Prior to 1600, present-day Benin comprised a variety of areas with different political systems and ethnicities. These included city-states along the coast (primarily of the Aja ethnic group, and also including  The kings of Dahomey sold their war captives into transatlantic slavery or killed them ritually in a ceremony known as the Annual Customs. By about 1750, the King of Dahomey was earning an estimated £250,000 per year by selling African captives to European slave-traders. The area was named the "Slave Coast" because of a flourishing slave trade. Court protocols which demanded that a portion of war captives from the kingdom's battles be decapitated, decreased the number of enslaved people exported from the area. The number went from 102,000 people per decade in the 1780s to 24,000 per decade by the 1860s. The decline was partly due to the
The kings of Dahomey sold their war captives into transatlantic slavery or killed them ritually in a ceremony known as the Annual Customs. By about 1750, the King of Dahomey was earning an estimated £250,000 per year by selling African captives to European slave-traders. The area was named the "Slave Coast" because of a flourishing slave trade. Court protocols which demanded that a portion of war captives from the kingdom's battles be decapitated, decreased the number of enslaved people exported from the area. The number went from 102,000 people per decade in the 1780s to 24,000 per decade by the 1860s. The decline was partly due to the  Among the goods the Portuguese sought were carved items of ivory made by Benin's artisans in the form of carved saltcellars, spoons, and hunting horns - pieces of African art produced for sale abroad as exotic objects.
Among the goods the Portuguese sought were carved items of ivory made by Benin's artisans in the form of carved saltcellars, spoons, and hunting horns - pieces of African art produced for sale abroad as exotic objects.
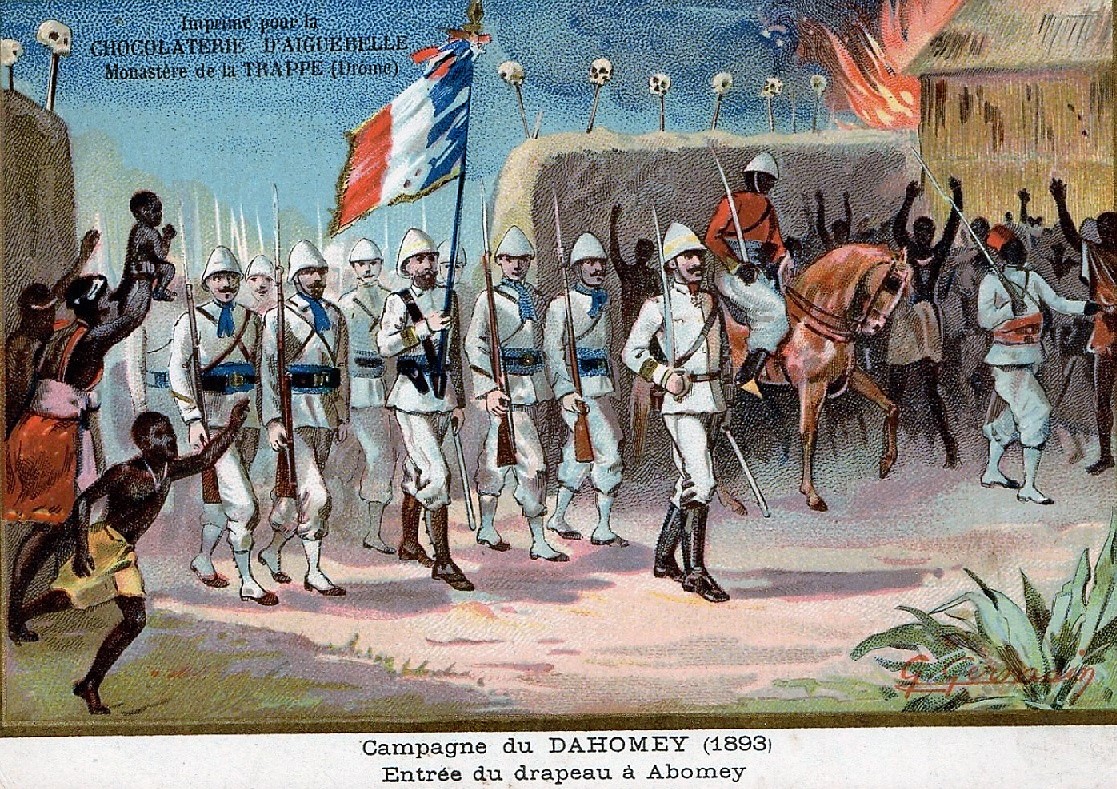 By the middle of the 19th century, Dahomey had "begun to weaken and lose its status as the regional power". The French took over the area in 1892. In 1899, the French included the land called
By the middle of the 19th century, Dahomey had "begun to weaken and lose its status as the regional power". The French took over the area in 1892. In 1899, the French included the land called
 Kérékou lost to
Kérékou lost to
File:Benin departments named.png, Departments of Benin.
poly 452.13 201.00 432.37 175.00 432.37 175.00 429.41 171.04 424.48 166.29 425.49 161.00 425.49 161.00 430.99 145.17 430.99 145.17 430.99 145.17 434.73 139.91 434.73 139.91 434.73 139.91 437.47 133.00 437.47 133.00 438.73 130.04 441.97 126.19 440.84 123.09 440.84 123.09 437.00 117.84 437.00 117.84 437.00 117.84 435.46 114.25 435.46 114.25 435.46 114.25 427.78 103.48 427.78 103.48 423.94 99.85 421.52 100.59 418.00 99.08 418.00 99.08 412.00 95.94 412.00 95.94 407.56 94.53 403.87 97.80 399.21 93.69 393.54 88.68 389.49 74.63 388.41 73.22 386.74 71.06 384.29 70.27 382.33 68.51 382.33 68.51 376.63 61.45 376.63 61.45 376.63 61.45 367.91 53.63 367.91 53.63 367.91 53.63 361.27 49.37 361.27 49.37 358.02 46.48 356.56 40.31 353.39 37.60 350.60 35.21 347.18 36.57 343.28 33.20 338.92 29.44 339.95 23.09 331.00 19.63 323.94 16.91 317.88 24.78 310.00 24.00 310.00 24.00 305.70 33.03 305.70 33.03 305.70 33.03 294.00 34.21 294.00 34.21 294.00 34.21 286.00 36.09 286.00 36.09 286.00 36.09 281.00 36.67 281.00 36.67 281.00 36.67 274.00 39.28 274.00 39.28 274.00 39.28 261.00 42.00 261.00 42.00 264.45 68.19 264.13 56.05 268.00 73.00 275.10 74.53 277.32 79.66 270.00 82.00 268.11 85.35 267.76 85.37 264.00 86.00 264.82 97.35 264.58 93.94 261.00 104.00 259.83 107.27 259.88 108.74 257.86 112.00 257.86 112.00 251.03 121.00 251.03 121.00 248.70 125.78 252.41 127.54 246.93 131.96 232.52 143.59 230.29 142.17 216.58 158.00 214.22 160.72 209.02 165.50 208.65 169.00 208.26 172.72 216.24 185.20 218.42 189.00 218.42 189.00 235.30 219.00 235.30 219.00 240.56 228.57 243.98 230.73 244.00 242.00 244.00 242.00 244.00 291.00 244.00 291.00 244.00 292.99 243.77 296.81 245.02 298.40 246.38 300.12 260.71 301.03 263.00 300.38 266.22 299.47 267.09 297.41 272.00 297.06 280.71 296.45 282.90 301.51 287.17 303.70 289.24 304.76 293.61 305.42 296.00 305.53 298.65 306.04 301.42 306.13 304.00 305.53 308.54 303.99 312.26 300.21 316.00 298.52 319.81 296.63 330.39 296.04 333.86 298.52 335.71 299.95 336.06 301.09 337.00 303.00 337.00 303.00 355.00 303.00 355.00 303.00 355.00 303.00 373.00 301.00 373.00 301.00 373.00 301.00 404.00 292.44 404.00 292.44 404.00 292.44 431.00 290.00 431.00 290.00 431.00 290.00 445.00 288.21 445.00 288.21 445.00 288.21 460.00 288.82 460.00 288.82 460.00 288.82 474.00 284.78 474.00 284.78 474.00 284.78 483.00 283.00 483.00 283.00 482.50 274.60 480.55 277.64 476.39 273.57 474.00 271.25 473.50 268.53 471.93 266.37 470.45 264.35 468.05 263.00 467.11 260.90 465.21 256.64 470.40 249.79 470.70 245.00 470.84 242.80 468.02 232.09 467.01 230.00 465.75 227.38 464.06 226.13 463.31 223.00 462.41 219.20 463.69 215.50 465.00 212.00 458.09 210.88 456.07 206.26 452.13 201.00
Benin is divided into 12
 In the 2013 census, 48.5% of the population of Benin were
In the 2013 census, 48.5% of the population of Benin were
. United States
 The
The
 The north–south strip of land in West Africa lies between latitudes 6° and 13°N, and longitudes 0° and 4°E. It is bounded by Togo to the west,
The north–south strip of land in West Africa lies between latitudes 6° and 13°N, and longitudes 0° and 4°E. It is bounded by Togo to the west, 
 Benin shows some variation in elevation and can be divided into 4 areas from the south to the north, starting with the lower-lying, sandy, coastal plain (highest elevation ) which is, at most, wide. It is marshy and dotted with lakes and lagoons communicating with the ocean. Behind the coast lies the
Benin shows some variation in elevation and can be divided into 4 areas from the south to the north, starting with the lower-lying, sandy, coastal plain (highest elevation ) which is, at most, wide. It is marshy and dotted with lakes and lagoons communicating with the ocean. Behind the coast lies the


 The economy is dependent on
The economy is dependent on  In order to raise growth still further, Benin plans to attract more foreign investment, place more emphasis on
In order to raise growth still further, Benin plans to attract more foreign investment, place more emphasis on
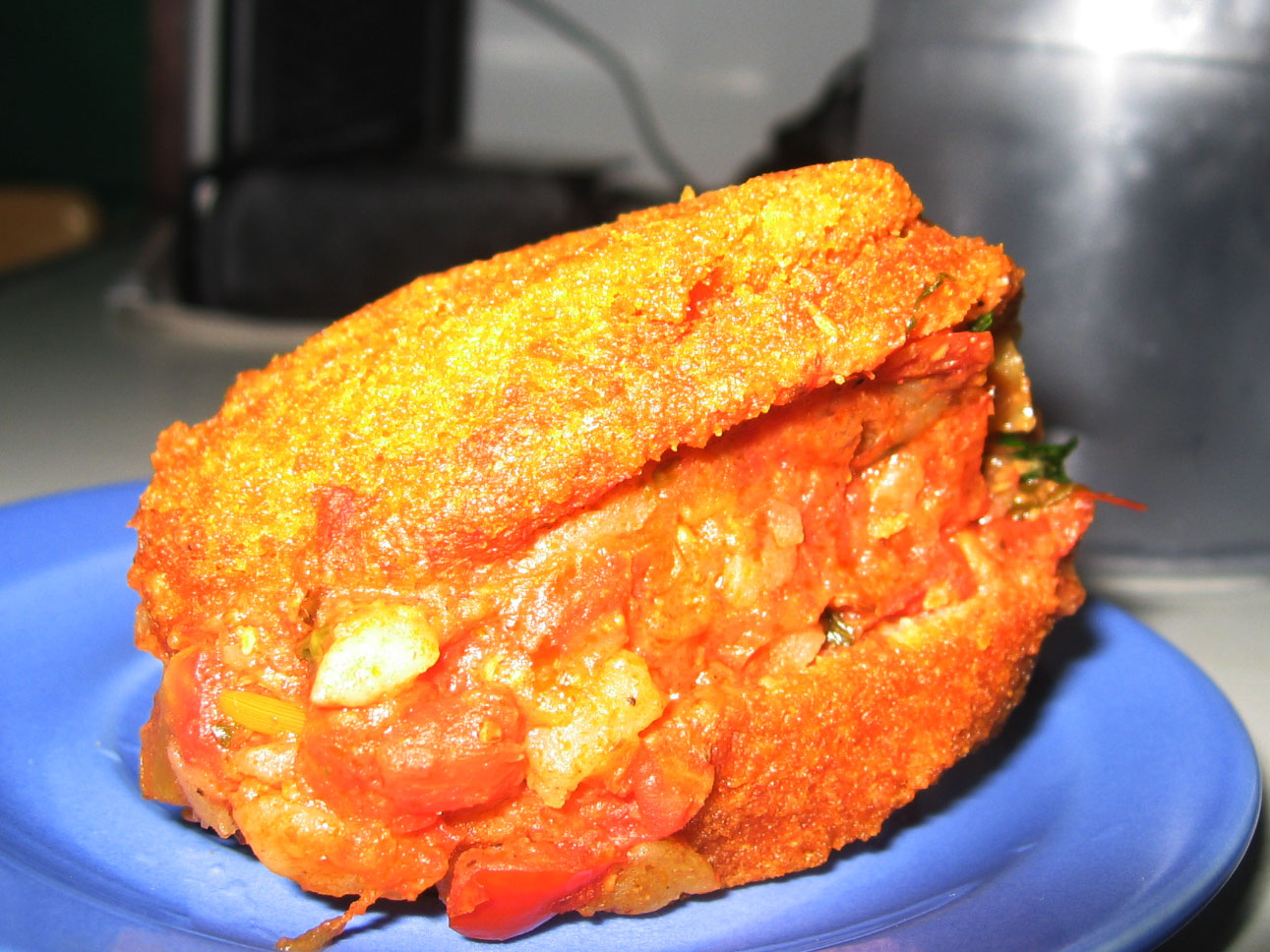
 The cuisine involves fresh meals served with a variety of key sauces. In southern Benin cuisine, an ingredient is
The cuisine involves fresh meals served with a variety of key sauces. In southern Benin cuisine, an ingredient is
Country Profile
from
Benin
''
Benin
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Benin Exports
Forecasts for Benin Development
Government
Government of Benin
(official website)
Global Integrity Report: Benin
News media
from Stanford University Trade
World Bank Benin 2010 Summary Trade Statistics
Sports
Baseball
{{Authority control Countries in Africa Economic Community of West African States Former Portuguese colonies French-speaking countries and territories Least developed countries Member states of the African Union Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Republics States and territories established in 1960 West African countries 1960 establishments in Africa
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
. It is bordered by Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
to the west, Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
to the east, Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
to the north-west, and Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesBight of Benin
The Bight of Benin or Bay of Benin is a bight in the Gulf of Guinea area on the western African coast that derives its name from the historical Kingdom of Benin.
Geography
It extends eastward for about from Cape St. Paul to the Nun outlet of t ...
, part of the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is in the ...
in the northernmost tropical portion of the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
. The capital is Porto-Novo
Porto-Novo (Portuguese: "New Port", , ; yo, Àjàṣẹ́, ), also known as Hogbonu and Ajashe, is the capital of Benin. The commune covers an area of and as of 2002 had a population of 223,552 people.
Situated on an inlet of the Gulf of Gu ...
, and the seat of government
The seat of government is (as defined by ''Brewer's Politics'') "the building, complex of buildings or the city from which a government exercises its authority".
In most countries, the nation’s capital is also seat of its government, thus that ...
is in Cotonou
Cotonou (; fon, Kútɔ̀nú) is a city in Benin. Its official population count was 679,012 inhabitants in 2012; however, over two million people live in the larger urban area.
The urban area continues to expand, notably toward the west. The ci ...
, the most populous city and economic capital. Benin covers an area of and its population in was estimated to be approximately million. It is a tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
nation, dependent on agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, and is an exporter of palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 33% of global oils produced from ...
and cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
. Some employment and income arise from subsistence farming
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no su ...
.
The official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
of Benin is French, with indigenous languages such as Fon, Bariba, Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
and Dendi also spoken. The largest religious group in Benin is Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
(27.7%), followed by Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
(25.5%), Vodun
Vodun (meaning ''spirit'' in the Fon, Gun and Ewe languages, with a nasal high-tone ''u''; also spelled Vodon, Vodoun, Vodou, Vudu, Voudou, Voodoo, etc.) is a religion practiced by the Aja, Ewe, and Fon peoples of Benin, Togo, Ghana, and ...
(11.6%), and Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
. Benin is a member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
, the Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
, the South Atlantic Peace and Cooperation Zone
The South Atlantic Peace and Cooperation Zone (abbreviations: ZPCAS or ZOPACAS; es, Zona de Paz y Cooperación del Atlántico Sur; pt, Zona de Paz e Cooperação do Atlântico Sul; also called the ''Zone of Peace and Cooperation of the South A ...
, Francophonie
Francophonie is the quality of speaking French. The term designates the ensemble of people, organisations and governments that share the use of French on a daily basis and as administrative language, teaching language or chosen language. The ...
, the Community of Sahel–Saharan States
The Community of Sahel–Saharan States (CEN-SAD; Arabic: ; French: ''Communauté des Etats Sahélo-Sahariens''; Portuguese: ''Comunidade dos Estados Sahelo-Saarianos'') aims to create a free trade area within a region of Africa. There are ques ...
, the African Petroleum Producers Association African Petroleum Producers Organization (APPO) (''Organisation Africaine des Producteurs Pétroliers'' in French language, French, ''Organização dos Produtores Africanos de Petróleo'' in Portuguese language, Portuguese and ''المنظمة ال� ...
and the Niger Basin Authority
The Niger Basin Authority (french: Autorité du Bassin du Niger) is an intergovernmental organization in West Africa aiming to foster co-operation in managing and developing the resources of the basin of the Niger River. The group is referred to ...
.
From the 17th to the 19th century, political entities in the area included the Kingdom of Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a region ...
, the city-state of Porto-Novo, and other states to the north. This region was referred to as the Slave Coast Slave Coast can mean:
* the Slave Coast of West Africa
* the Dutch Slave Coast
The Dutch Slave Coast ( Dutch: ''Slavenkust'') refers to the trading posts of the Dutch West India Company on the Slave Coast, which lie in contemporary Ghana, Ben ...
from the early 17th century due to the high number of people who were sold and trafficked during the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
to the New World. France took over the territory in 1894, incorporating it into French West Africa
French West Africa (french: Afrique-Occidentale française, ) was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Ivory Coast, Upper Volta (now Burki ...
as French Dahomey
French Dahomey was a French colony and part of French West Africa from 1894 to 1958. After World War II, by the establishment of the French Fourth Republic in 1947, Dahomey became part of the French Union with an increased autonomy. On 4 Octob ...
. In 1960, Dahomey gained full independence from France. As a sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
, Benin has had democratic governments, military coups, and military governments. A self-described Marxist–Leninist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state that is administered and governed by a communist party guided by Marxism–Leninism. Marxism–Leninism was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, the Comint ...
called the People's Republic of Benin
The People's Republic of Benin (french: République populaire du Bénin; sometimes translated as Benin Popular Republic or Popular Republic of Benin) was a socialist state located in the Gulf of Guinea on the African continent, which would becom ...
existed between 1975 and 1990. In 1991, it was replaced by the multi-party
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in c ...
Republic of Benin.
Name
During French colonial rule and after independence on 1 August 1960, the country was named Dahomey, after theKingdom of Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a region ...
. On 30 November 1975, the country was renamed Benin following a Marxist-Leninist military coup. The Bight of Benin
The Bight of Benin or Bay of Benin is a bight in the Gulf of Guinea area on the western African coast that derives its name from the historical Kingdom of Benin.
Geography
It extends eastward for about from Cape St. Paul to the Nun outlet of t ...
borders the country, and the bight takes its name from the Kingdom of Benin
The Kingdom of Benin, also known as the Edo Kingdom, or the Benin Empire ( Bini: ') was a kingdom within what is now southern Nigeria. It has no historical relation to the modern republic of Benin, which was known as Dahomey from the 17th c ...
, located in present-day Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
.History
Pre-colonial
 Prior to 1600, present-day Benin comprised a variety of areas with different political systems and ethnicities. These included city-states along the coast (primarily of the Aja ethnic group, and also including
Prior to 1600, present-day Benin comprised a variety of areas with different political systems and ethnicities. These included city-states along the coast (primarily of the Aja ethnic group, and also including Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
and Gbe peoples) and tribal regions inland (composed of Bariba, Mahi, Gedevi, and Kabye peoples). The Oyo Empire
The Oyo Empire was a powerful Yoruba empire of West Africa made up of parts of present-day eastern Benin and western Nigeria (including Southwest zone and the western half of Northcentral zone). It grew to become the largest Yoruba language, ...
, located primarily to the east of Benin, was a military force in the region, conducting raids and exacting tribute from the coastal kingdoms and tribal regions. The situation changed in the 17th and 18th centuries as the Kingdom of Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a region ...
, consisting mostly of Fon people
The Fon people, also called Fon nu, Agadja or Dahomey, are a Gbe ethnic group.Fon people
Encyclopædia Britan ...
, was founded on the Encyclopædia Britan ...
Abomey
Abomey is the capital of the Zou Department of Benin. The commune of Abomey covers an area of 142 square kilometres and, as of 2012, had a population of 90,195 people.
Abomey houses the Royal Palaces of Abomey, a collection of small traditional ...
plateau and began taking over areas along the coast. By 1727, King Agaja
Agaja (also spelled Agadja and also known as Trudo Agaja or Trudo Audati) was a king of the Kingdom of Dahomey, in present-day Benin, who ruled from 1718 until 1740. He came to the throne after his brother King Akaba. During his reign, Dahomey e ...
of the Kingdom of Dahomey had conquered the coastal cities of Allada
Allada is a town, arrondissement, and commune, located in the Atlantique Department of Benin.
The current town of Allada corresponds to Great Ardra (also called Grand Ardra, or Arda), which was the capital of a Fon kingdom also called Allada (t ...
and Whydah. Dahomey had become a tributary of the Oyo Empire, and rivaled but did not directly attack the Oyo-allied city-state of Porto-Novo
Porto-Novo (Portuguese: "New Port", , ; yo, Àjàṣẹ́, ), also known as Hogbonu and Ajashe, is the capital of Benin. The commune covers an area of and as of 2002 had a population of 223,552 people.
Situated on an inlet of the Gulf of Gu ...
. The rise of Dahomey, its rivalry with Porto-Novo, and tribal politics in the northern region persisted into the colonial and post-colonial periods.
In the Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a region ...
, some younger people were apprenticed to older soldiers and taught the kingdom's military customs until they were old enough to join the army. Dahomey instituted an elite female soldier corps variously called Ahosi
The Dahomey Mino ( Fon: Agojie, Agoji, Mino, or Minon) were a Fon all-female military regiment of the Kingdom of Dahomey (in today's Benin, West Africa) that existed from the 17th century until the late 19th century. They are one of the few do ...
(the king's wives), Mino ("our mothers" in Fongbe
Fon (, ) is spoken in Benin, Nigeria, Togo, Ghana and Gabon by approximately 1.7 million speakers, and is the language of the Fon people. Like the other Gbe languages, Fon is an isolating language with an SVO basic word order.
Cultural and le ...
), or the "Dahomean Amazons
In Greek mythology, the Amazons (Ancient Greek: Ἀμαζόνες ''Amazónes'', singular Ἀμαζών ''Amazōn'', via Latin ''Amāzon, -ŏnis'') are portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercules, ...
". This emphasis on military preparation and achievement earned Dahomey the nickname of "Black Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
" from European observers and 19th-century explorers such as Sir Richard Burton
Sir Richard Francis Burton (; 19 March 1821 – 20 October 1890) was a British explorer, writer, orientalist scholar,and soldier. He was famed for his travels and explorations in Asia, Africa, and the Americas, as well as his extraordinary kn ...
.
 The kings of Dahomey sold their war captives into transatlantic slavery or killed them ritually in a ceremony known as the Annual Customs. By about 1750, the King of Dahomey was earning an estimated £250,000 per year by selling African captives to European slave-traders. The area was named the "Slave Coast" because of a flourishing slave trade. Court protocols which demanded that a portion of war captives from the kingdom's battles be decapitated, decreased the number of enslaved people exported from the area. The number went from 102,000 people per decade in the 1780s to 24,000 per decade by the 1860s. The decline was partly due to the
The kings of Dahomey sold their war captives into transatlantic slavery or killed them ritually in a ceremony known as the Annual Customs. By about 1750, the King of Dahomey was earning an estimated £250,000 per year by selling African captives to European slave-traders. The area was named the "Slave Coast" because of a flourishing slave trade. Court protocols which demanded that a portion of war captives from the kingdom's battles be decapitated, decreased the number of enslaved people exported from the area. The number went from 102,000 people per decade in the 1780s to 24,000 per decade by the 1860s. The decline was partly due to the Slave Trade Act 1807
The Slave Trade Act 1807, officially An Act for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom prohibiting the slave trade in the British Empire. Although it did not abolish the practice of slavery, it ...
banning the trans-Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
by Britain in 1808, followed by other countries. This decline continued until 1885 when the last slave ship departed the modern Benin Republic for Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, which had yet to abolish slavery. The capital Porto-Novo
Porto-Novo (Portuguese: "New Port", , ; yo, Àjàṣẹ́, ), also known as Hogbonu and Ajashe, is the capital of Benin. The commune covers an area of and as of 2002 had a population of 223,552 people.
Situated on an inlet of the Gulf of Gu ...
("New Port" in Portuguese) was originally developed as a port for the slave trade.
 Among the goods the Portuguese sought were carved items of ivory made by Benin's artisans in the form of carved saltcellars, spoons, and hunting horns - pieces of African art produced for sale abroad as exotic objects.
Among the goods the Portuguese sought were carved items of ivory made by Benin's artisans in the form of carved saltcellars, spoons, and hunting horns - pieces of African art produced for sale abroad as exotic objects.
Colonial
 By the middle of the 19th century, Dahomey had "begun to weaken and lose its status as the regional power". The French took over the area in 1892. In 1899, the French included the land called
By the middle of the 19th century, Dahomey had "begun to weaken and lose its status as the regional power". The French took over the area in 1892. In 1899, the French included the land called French Dahomey
French Dahomey was a French colony and part of French West Africa from 1894 to 1958. After World War II, by the establishment of the French Fourth Republic in 1947, Dahomey became part of the French Union with an increased autonomy. On 4 Octob ...
within the larger French West Africa
French West Africa (french: Afrique-Occidentale française, ) was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Ivory Coast, Upper Volta (now Burki ...
colonial region.
France sought to benefit from Dahomey and the region "appeared to lack the necessary agricultural or mineral resources for large-scale capitalist development". As a result, France treated Dahomey as a sort of preserve in case future discoveries revealed resources worth developing.
The French government outlawed the capture and sale of slaves. Previous slaveowners sought to redefine their control over slaves as control over land, tenants, and lineage members. This provoked a struggle among Dahomeans, "concentrated in the period from 1895 to 1920, for the redistribution of control over land and labor. Villages sought to redefine boundaries of lands and fishing preserves. Religious disputes scarcely veiled the factional struggles over control of land and commerce which underlay them. Factions struggled for the leadership of great families".
In 1958, France granted autonomy to the Republic of Dahomey
The Republic of Dahomey (french: République du Dahomey; ), simply known as Dahomey, was established on 4 December 1958, as a self-governing colony within the French Community. Prior to attaining autonomy, it had been French Dahomey, part of ...
, and full independence on 1 August 1960 which is celebrated each year as Independence Day, a national holiday National holiday may refer to:
* National day, a day when a nation celebrates a very important event in its history, such as its establishment
*Public holiday, a holiday established by law, usually a day off for at least a portion of the workforce, ...
. The president who led the country to independence was Hubert Maga
Coutoucou Hubert Maga (August 10, 1916 – May 8, 2000) was a politician from Dahomey (now known as Benin).Dahomey was renamed Benin in 1975. Se''New York Times'' obituary He arose on a political scene where one's power was dictated by what regi ...
.
Post-colonial
After 1960, there were coups and regime changes, with the figures ofHubert Maga
Coutoucou Hubert Maga (August 10, 1916 – May 8, 2000) was a politician from Dahomey (now known as Benin).Dahomey was renamed Benin in 1975. Se''New York Times'' obituary He arose on a political scene where one's power was dictated by what regi ...
, Sourou Apithy, Justin Ahomadégbé
Justin may refer to: People
* Justin (name), including a list of persons with the given name Justin
* Justin (historian), a Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527), or ''Flavius Iustinius Augustus'', Eastern Ro ...
, and Émile Derlin Zinsou
Émile Derlin Zinsou (23 March 1918 – 28 July 2016) was a Beninese politician and physician who was the President of Dahomey (now Benin) from 17 July 1968 until 10 December 1969, supported by the military regime that took power in 1967. Zinso ...
dominating; the first 3 each represented a different area and ethnicity of the country. These 3 agreed to form a Presidential Council after violence marred the 1970 elections.
On 7 May 1972, Maga ceded power to Ahomadégbé. On 26 October 1972, Lt. Col. Mathieu Kérékou
Mathieu Kérékou (; 2 September 1933 – 14 October 2015) was a Beninese politician who served as President of Benin from 1972 to 1991 and again from 1996 to 2006.
After seizing power in a military coup, he ruled the country for 19 years, for ...
overthrew the ruling triumvirate, becoming president and stating that the country would not "burden itself by copying foreign ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied pri ...
, and wants neither Capitalism, Communism, nor Socialism". On 30 November 1974, he announced that the country was officially Marxist
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
, under control of the Military Council of the Revolution (CMR), which nationalized the petroleum industry and banks. On 30 November 1975, he renamed the country the People's Republic of Benin
The People's Republic of Benin (french: République populaire du Bénin; sometimes translated as Benin Popular Republic or Popular Republic of Benin) was a socialist state located in the Gulf of Guinea on the African continent, which would becom ...
. The regime of the People's Republic of Benin underwent changes over the course of its existence: a nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
period (1972-1974); a socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
phase (1974-1982); and a phase involving an opening to Western countries and economic liberalism
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism ...
(1982-1990).
In 1974, under the influence of young revolutionaries - the "Ligueurs" - the government embarked on a socialist program: nationalization of strategic sectors of the economy, reform of the education system, establishment of agricultural cooperatives and new local government structures, and a campaign to eradicate "feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a wa ...
forces" including tribalism
Tribalism is the state of being organized by, or advocating for, tribes or tribal lifestyles. Human evolution has primarily occurred in small hunter-gatherer groups, as opposed to in larger and more recently settled agricultural societies or civ ...
. The regime banned opposition activities. Mathieu Kérékou was elected president by the National Revolutionary Assembly in 1980, re-elected in 1984. Establishing relations with China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
, and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
, he put "nearly all" businesses and economic activities under state control, causing foreign investment in Benin to dry up. Kérékou attempted to reorganize education, pushing his own aphorisms such as "Poverty is not a fatality". The regime financed itself by contracting to take nuclear waste, first from the Soviet Union and later from France.
In the 1980s, Benin experienced higher economic growth rates (15.6% in 1982, 4.6% in 1983 and 8.2% in 1984), and the closure of the Nigerian border with Benin led to a drop in customs and tax revenues. The government was no longer able to pay civil servants' salaries. In 1989, riots broke out when the regime did not have enough money to pay its army. The banking system collapsed. Eventually, Kérékou renounced Marxism
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
, and a convention forced Kérékou to release political prisoners and arrange elections. Marxism–Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a communist ideology which was the main communist movement throughout the 20th century. Developed by the Bolsheviks, it was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, its satellite states in the Eastern Bloc, and various co ...
was abolished as the nation's form of government.
The country's name was officially changed to the'' Republic of Benin'' on 1 March 1990, after the newly formed government's constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
was completed.
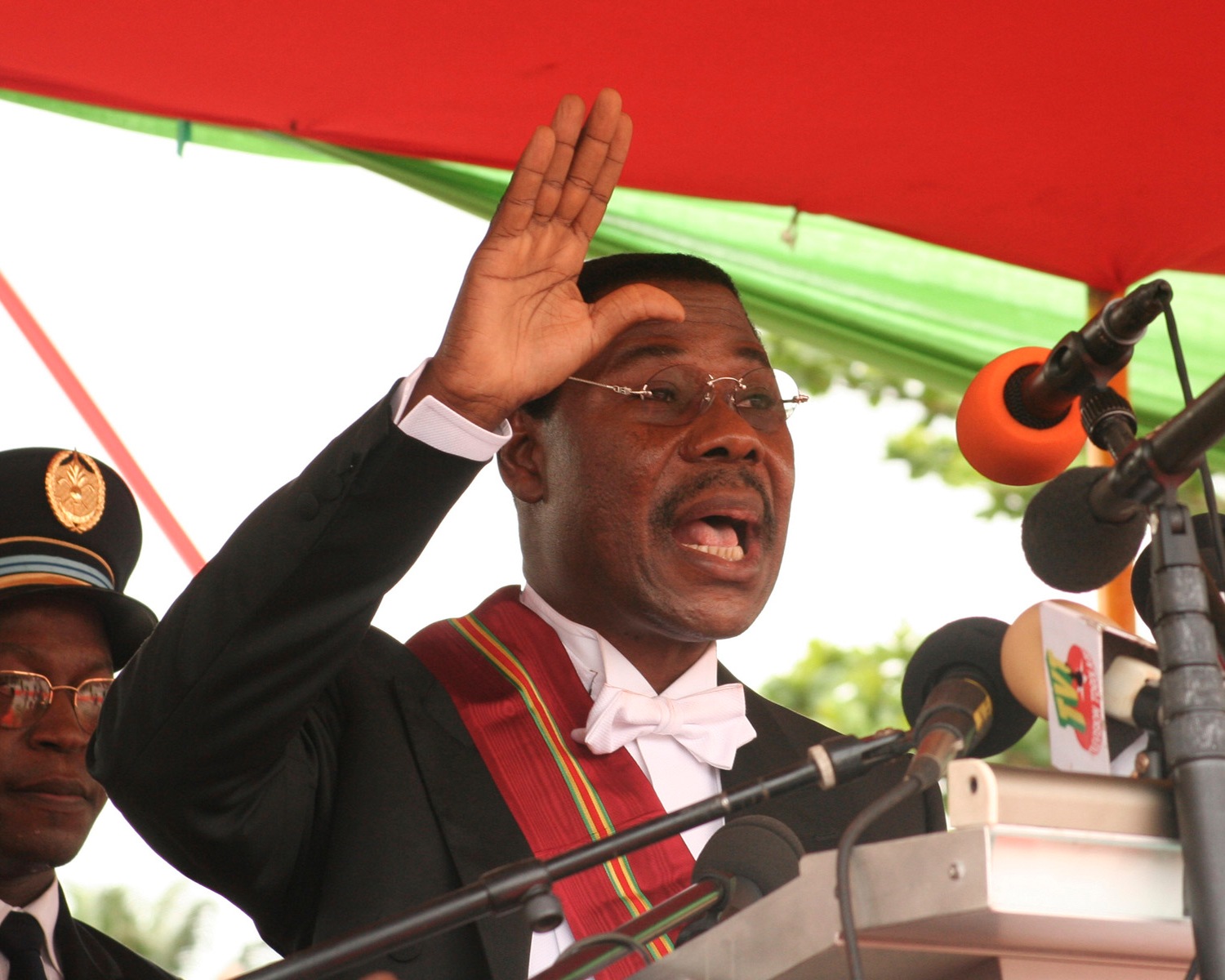
 Kérékou lost to
Kérékou lost to Nicéphore Soglo
Nicéphore Dieudonné Soglo (born November 29, 1934) is a Beninese politician who was Prime Minister of Benin from 1990 to 1991 and President from 1991 to 1996. He was Mayor of Cotonou from 2003 to 2015. Soglo was married to Rosine Vieyra Soglo, ...
in a 1991 election and became the first President on the African mainland to lose power through an election. Kérékou returned to power after winning the 1996 vote. In 2001, an election resulted in Kérékou winning another term, after which his opponents claimed election irregularities. In 1999, Kérékou issued a national apology for the substantial role that Africans had played in the Atlantic slave trade.
Kérékou and former president Soglo did not run in the 2006 elections, as both were barred by the constitution's restrictions on age and total terms of candidates. On 5 March 2006, an election resulted in a runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock market ...
between Yayi Boni Yayi may refer to
* China-Taiwan Yayi Cup, a Go competition
*Thomas Boni Yayi
Thomas Boni Yayi (born 1 July 1951) is a Beninese banker and politician who was President of Benin from 2006 to 2016. He took office after winning the March 2006 presi ...
and Adrien Houngbédji
Adrien Houngbédji (born 5 March 1942) is a Beninese politician and the leader of the Democratic Renewal Party (''Parti du renouveau démocratique'', PRD), one of Benin's main political parties. He was President of the National Assembly of Benin ...
. The runoff election was held on 19 March and was won by Boni, who assumed office on 6 April. Boni was reelected in 2011, taking 53.18% of the vote in the first round—enough to avoid a runoff election. He was the first president to win an election without a runoff since the restoration of democracy in 1991.
In the March 2016 presidential elections in which Boni Yayi was barred by the constitution from running for a third term, businessman Patrice Talon
Patrice Guillaume Athanase Talon (born 1 May 1958) is a Beninese politician and businessman who has been President of Benin since 6 April 2016.
Early life and career
Talon is of Fon origin and was born in Ouidah. He descends from slave trader ...
won the second round with 65.37% of the vote, defeating investment banker and former Prime Minister Lionel Zinsou
Lionel Zinsou (born 23 October 1953) is a French–Beninese economist and investment banker who was Prime Minister of Benin from 2015 to 2016. Since June 2017, he has been the president of Terra Nova, a centre-left French think tank.
Early ...
. Talon was sworn in on 6 April 2016. Speaking on the same day that the Constitutional Court confirmed the results, Talon said that he would "first and foremost tackle constitutional reform", discussing his plan to limit presidents to a single term of 5 years in order to combat "complacency". He said that he planned to slash the size of the government from 28 to 16 members. In April 2021, President Patrice Talon was re-elected, with more than 86.3% of the votes cast, in Benin's presidential election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has opera ...
. The change in election laws resulted in total control of parliament by president Talon's supporters.
In February 2022, Benin saw its largest terrorist attack in history.
On 20 February 2022, President Patrice Talon
Patrice Guillaume Athanase Talon (born 1 May 1958) is a Beninese politician and businessman who has been President of Benin since 6 April 2016.
Early life and career
Talon is of Fon origin and was born in Ouidah. He descends from slave trader ...
inaugurated an exhibition with 26 pieces of sacred art returned to Benin by France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, 129 years after they were looted by colonial forces.
Politics
Its politics take place in a framework of apresidential
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese fu ...
representative democratic
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
in which the President of Benin
The president of Benin () is both head of state and head of government in Benin. The Cabinet of Benin is under the authority of the President, and serves to advise and help formulate strategies. It also liaises with ministries and other governme ...
is both head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
and head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a gro ...
, within a multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in coal ...
. Executive power
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a state.
In political systems ba ...
is exercised by the government. Legislative power
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as p ...
is vested in the government and the legislature. The judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
is officially independent of the executive and the legislature, while in practice its independence has been gradually hollowed out by Talon, and the Constitutional Court is headed by his former personal lawyer. The political system is derived from the 1990 Constitution of Benin
The Constitution of Benin was adopted by referendum on 23 December 1956. The constitution is made up of a preamble, twelve titles, and 160 articles.
Preamble
(Preamble text comes from thEnglish translationof the Beninese Constitution via the Const ...
and the subsequent transition to democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose gov ...
in 1991.
It was ranked 18th out of 52 African countries and scored best in the categories of Safety & Rule of Law and Participation & Human Rights. In its 2007 Worldwide Press Freedom Index, Reporters Without Borders
Reporters Without Borders (RWB; french: Reporters sans frontières; RSF) is an international non-profit and non-governmental organization with the stated aim of safeguarding the right to freedom of information. It describes its advocacy as found ...
ranked Benin 53rd out of 169 countries. That place had fallen to 78th by 2016, when Talon took office, and has fallen further to 113th. Benin has been rated equal-88th out of 159 countries in a 2005 analysis of police, business, and political corruption.
Its democratic system "has eroded" since President Talon took office. In 2018 his government introduced new rules for fielding candidates and raised the cost of registering. The electoral commission, packed with Talon's allies, barred all opposition parties from the parliamentary election in 2019, resulting in a parliament made up entirely of supporters of Talon. That parliament subsequently changed election laws such that presidential candidates need to have the approval of at least 10% of Benin's MPs and mayors. As parliament and most mayors' offices are controlled by Talon, he has control over who can run for president. These changes have drawn condemnation from international observers and led to the United States government partially terminating development assistance to the country.
Administrative divisions
Alibori
Alibori is the largest and northernmost department (French: ''département'') of Benin. Externally the department borders the countries of Burkina Faso, Niger, and Nigeria, and internally the departments of Atakora and Borgou. The department of ...
poly 37.46 246.00 37.46 252.00 37.46 252.00 37.46 252.00 35.31 258.00 35.31 258.00 35.31 258.00 34.40 265.00 34.40 265.00 32.65 269.76 26.21 273.58 24.01 278.00 22.52 281.03 24.08 291.52 24.01 296.00 23.82 305.84 20.15 302.44 20.00 313.00 20.00 313.00 20.00 323.00 20.00 323.00 20.00 325.41 19.78 328.58 21.02 330.70 22.40 333.07 26.70 335.76 29.00 337.42 29.00 337.42 45.00 349.37 45.00 349.37 45.00 349.37 82.00 373.20 82.00 373.20 82.00 373.20 107.00 388.27 107.00 388.27 111.81 390.32 114.39 389.60 118.00 390.63 130.19 394.14 122.76 395.20 140.00 395.00 145.96 394.93 151.03 393.89 156.00 390.36 160.95 386.85 170.76 377.10 176.00 375.13 180.62 373.39 183.60 376.89 194.00 376.76 194.00 376.76 214.00 376.76 214.00 376.76 219.13 375.48 220.35 373.34 230.00 371.40 233.97 370.60 241.83 370.30 243.98 366.77 245.17 364.82 245.08 361.23 244.82 359.00 244.34 354.97 239.47 338.13 237.30 335.17 234.48 331.32 229.02 329.01 229.16 323.00 229.33 316.13 237.71 311.47 240.40 307.72 242.31 305.05 241.99 302.12 241.84 299.00 241.84 299.00 241.84 241.00 241.84 241.00 242.00 238.76 242.09 236.16 241.83 234.00 240.65 230.85 237.02 225.12 235.30 222.00 235.30 222.00 222.42 199.00 222.42 199.00 222.42 199.00 211.72 180.00 211.72 180.00 210.41 177.70 207.70 172.35 205.61 171.02 203.63 169.77 200.33 170.06 198.00 169.83 198.00 169.83 179.00 168.01 179.00 168.01 172.75 168.17 171.85 169.55 167.00 170.24 167.00 170.24 159.00 170.24 159.00 170.24 154.87 170.68 148.54 174.29 145.00 173.97 140.61 173.58 139.06 169.50 137.20 167.84 135.56 166.35 130.21 164.35 128.00 163.80 124.03 162.80 116.29 163.66 113.75 167.22 112.30 169.25 112.92 171.08 110.65 173.37 108.55 175.49 104.72 176.40 103.92 180.04 103.92 180.04 105.00 189.00 105.00 189.00 105.00 189.00 95.00 188.00 95.00 188.00 95.20 190.02 95.78 192.77 94.31 194.45 91.55 197.61 77.91 193.83 74.00 193.00 74.12 200.87 77.74 199.74 75.00 211.00 69.72 208.52 68.74 210.16 64.00 213.00 66.47 221.45 72.00 221.45 70.00 232.00 70.00 232.00 63.00 228.56 63.00 228.56 63.00 228.56 57.00 226.73 57.00 226.73 57.00 226.73 49.00 223.00 49.00 223.00 46.19 229.10 45.52 230.06 49.00 236.00 49.00 236.00 40.00 237.00 40.00 237.00 40.00 237.00 37.46 246.00 37.46 246.00 Atakora
poly 457.00 290.83 444.00 290.06 444.00 290.06 444.00 290.06 435.00 291.86 435.00 291.86 435.00 291.86 425.00 291.21 425.00 291.21 425.00 291.21 410.00 293.79 410.00 293.79 410.00 293.79 402.00 294.46 402.00 294.46 390.01 296.62 381.24 303.72 369.00 302.73 362.03 302.17 363.46 303.89 358.00 304.89 358.00 304.89 344.00 304.89 344.00 304.89 338.12 304.96 336.10 304.95 334.00 299.00 330.07 299.00 319.10 298.57 316.00 299.74 311.61 301.39 307.49 307.15 301.00 307.70 297.78 307.97 288.94 306.59 286.17 304.93 282.96 303.00 281.61 300.23 277.00 299.28 267.48 297.31 266.77 302.05 261.99 302.66 261.99 302.66 244.00 302.00 244.00 302.00 243.08 313.35 229.57 314.00 231.24 325.00 232.04 330.24 236.64 331.99 239.44 336.01 241.19 338.53 242.02 342.05 242.86 345.00 244.32 350.15 247.94 360.01 246.57 364.98 244.30 373.20 230.96 372.34 224.00 374.25 215.51 376.59 216.42 381.17 221.00 387.00 215.50 390.69 219.79 394.05 219.41 399.00 219.07 403.42 213.76 408.39 216.95 418.00 221.36 431.25 229.17 432.89 228.89 442.00 228.89 442.00 225.42 471.00 225.42 471.00 224.95 474.53 225.04 479.91 223.07 482.85 220.31 486.96 210.88 486.90 206.10 489.56 200.51 492.67 199.71 502.20 200.09 508.00 200.34 511.83 201.45 517.74 203.85 520.78 206.80 524.50 211.02 524.42 212.39 530.00 213.73 535.43 206.59 553.24 211.74 560.95 217.97 570.28 236.41 563.79 236.00 577.00 236.00 577.00 310.00 577.00 310.00 577.00 312.73 576.99 316.25 577.33 318.43 575.40 320.92 573.20 320.80 569.99 321.32 567.00 322.73 558.85 321.71 561.34 322.24 556.00 322.24 556.00 323.91 547.00 323.91 547.00 324.35 540.98 322.25 532.46 331.00 531.69 332.81 531.53 334.28 532.10 336.00 532.28 341.27 532.85 343.12 529.82 349.00 529.06 353.86 528.43 354.56 530.23 358.00 530.54 361.32 530.83 370.70 528.20 372.73 525.49 374.30 523.40 376.92 513.91 377.58 511.00 377.58 511.00 381.66 497.83 381.66 497.83 381.66 497.83 380.98 486.00 380.98 486.00 380.68 476.61 375.81 477.30 379.29 470.00 383.12 461.98 385.40 466.33 391.98 456.00 396.68 448.63 393.76 447.02 397.31 443.39 401.48 439.14 406.55 441.71 408.94 436.93 410.67 433.46 407.81 429.38 406.94 426.00 405.90 421.94 407.23 418.17 410.22 415.27 412.84 412.73 424.28 408.25 428.00 407.56 433.00 406.65 435.16 409.44 439.24 404.85 441.02 402.86 448.74 392.17 449.44 390.00 452.26 381.29 445.08 373.83 458.00 370.00 458.00 366.84 458.47 359.88 456.98 357.32 455.80 355.29 446.60 348.06 445.26 343.00 444.26 339.23 447.43 333.31 449.10 330.00 452.77 322.74 449.55 322.09 458.00 317.29 459.54 316.42 461.17 315.40 463.00 315.34 465.90 315.25 472.14 319.47 475.00 321.00 475.00 321.00 477.68 312.00 477.68 312.00 477.68 312.00 478.63 305.00 478.63 305.00 478.63 305.00 483.05 295.00 483.05 295.00 483.05 295.00 483.05 285.00 483.05 285.00 483.05 285.00 457.00 290.83 457.00 290.83 Borgou
Borgou is one of the twelve departments of Benin. Borgou borders the country of Nigeria and the departments of Alibori Department, Alibori, Atakora Department, Atakora, Collines Department, Collines and Donga Department, Donga. The capital of Bo ...
poly 204.00 378.09 198.00 378.82 198.00 378.82 195.22 379.01 189.99 378.26 187.00 377.91 183.64 377.52 180.15 375.88 177.00 376.43 168.76 377.87 159.89 391.57 150.00 395.14 145.58 396.38 131.55 396.56 127.00 395.14 119.22 393.40 119.53 391.49 109.00 391.00 109.00 391.00 109.00 409.00 109.00 409.00 109.00 409.00 110.00 424.00 110.00 424.00 110.00 424.00 110.00 444.00 110.00 444.00 109.87 453.63 106.71 453.36 105.91 458.00 105.45 460.61 107.25 464.32 108.00 467.00 114.17 468.97 113.93 474.31 114.00 480.00 114.03 482.98 113.74 487.26 114.72 490.00 116.12 493.90 128.70 508.73 132.09 511.78 135.10 514.48 137.49 514.98 139.44 517.27 139.44 517.27 145.51 528.00 145.51 528.00 147.02 531.73 147.68 545.12 148.17 550.00 148.17 550.00 149.00 608.00 149.00 608.00 152.74 607.83 162.55 606.68 166.00 605.70 170.07 604.54 173.60 601.66 178.00 602.89 181.90 603.99 184.73 607.28 188.00 608.84 191.81 610.65 193.97 609.29 198.00 611.73 201.82 614.05 205.90 619.16 213.00 621.59 221.08 624.36 228.08 622.78 236.00 621.00 236.00 621.00 236.86 599.00 236.86 599.00 236.86 599.00 234.51 587.04 234.51 587.04 234.51 587.04 233.07 582.58 233.07 582.58 232.54 579.04 234.93 575.89 233.77 573.14 232.45 570.01 227.92 569.43 225.00 568.79 219.30 567.55 214.40 566.93 210.64 561.96 202.86 551.69 211.67 541.18 209.85 530.04 208.90 524.19 203.33 524.76 199.99 517.00 196.43 508.71 197.14 494.28 205.04 488.70 209.60 485.47 216.59 484.97 222.00 484.00 222.00 484.00 225.28 454.00 225.28 454.00 225.75 450.23 227.35 441.23 226.58 438.00 224.89 430.85 215.61 424.73 214.21 414.00 213.33 407.25 216.93 404.33 217.52 400.00 217.95 396.84 216.60 394.67 216.66 392.00 216.29 389.21 217.38 387.80 216.66 385.00 216.46 382.76 215.64 382.31 215.00 378.09 208.25 379.58 209.49 378.17 204.00 378.09 Donga
poly 318.42 730.00 311.02 715.00 311.02 715.00 311.02 715.00 313.71 704.00 313.71 704.00 313.71 704.00 314.30 696.00 314.30 696.00 314.30 696.00 315.83 688.00 315.83 688.00 315.83 688.00 316.39 680.00 316.39 680.00 316.39 680.00 319.72 668.00 319.72 668.00 319.72 668.00 313.56 646.00 313.56 646.00 313.56 646.00 315.37 640.00 315.37 640.00 315.37 640.00 316.64 633.00 316.64 633.00 316.64 633.00 320.82 619.00 320.82 619.00 320.82 619.00 320.00 612.00 320.00 612.00 320.00 612.00 320.00 603.00 320.00 603.00 320.00 603.00 319.00 591.00 319.00 591.00 319.00 591.00 317.98 580.60 317.98 580.60 317.98 580.60 310.00 579.00 310.00 579.00 310.00 579.00 235.00 579.00 235.00 579.00 235.26 586.63 236.56 584.73 237.67 590.00 239.34 597.46 238.85 605.57 237.67 613.00 237.01 616.76 238.31 618.16 237.10 620.07 234.94 623.47 229.59 623.95 226.00 624.00 221.06 624.06 215.54 624.49 211.00 622.33 205.31 619.62 201.44 614.89 198.00 613.17 194.55 611.45 192.14 612.51 188.00 610.16 184.89 608.40 182.82 605.80 179.00 604.65 173.86 603.11 169.76 606.21 165.00 607.51 158.90 609.18 155.15 609.00 149.00 609.00 149.00 609.00 153.66 623.42 153.66 623.42 153.66 623.42 148.64 636.00 148.64 636.00 148.64 636.00 151.00 649.00 151.00 649.00 151.00 649.00 151.00 722.00 151.00 722.00 151.00 722.00 152.00 735.00 152.00 735.00 152.00 735.00 152.00 755.94 152.00 755.94 166.40 753.42 176.18 756.23 181.00 755.94 187.22 755.43 189.92 751.17 198.00 754.13 201.28 755.33 204.30 757.44 206.59 760.08 208.54 762.34 209.03 764.62 212.12 765.57 217.89 767.35 223.35 763.69 226.00 763.61 228.52 763.53 229.97 765.05 233.00 765.70 235.57 766.25 238.37 765.71 240.90 766.73 240.90 766.73 255.70 777.45 255.70 777.45 257.51 779.06 259.10 781.50 261.30 782.43 263.15 783.21 267.83 783.00 270.00 783.00 272.03 774.71 276.57 773.19 278.40 768.00 279.76 764.17 277.20 755.85 284.10 752.02 286.30 750.80 289.53 751.00 292.00 751.00 292.00 751.00 319.00 751.00 319.00 751.00 319.00 751.00 318.42 730.00 318.42 730.00 Collines
poly 292.30 753.00 286.57 752.61 284.39 754.02 281.46 755.92 281.10 759.84 281.08 763.00 281.04 774.80 270.91 774.76 272.27 785.00 272.27 785.00 273.76 791.00 273.76 791.00 275.77 801.74 275.37 806.88 280.47 817.96 283.01 823.47 285.98 822.81 287.98 826.21 288.89 827.76 289.44 832.73 290.00 835.00 292.46 844.84 293.99 846.60 294.00 857.00 294.00 857.00 286.00 857.00 286.00 857.00 286.23 859.87 287.62 869.61 289.01 871.72 290.95 874.68 294.33 874.42 296.69 876.56 298.98 878.65 298.94 881.14 299.00 884.00 299.00 884.00 299.00 913.00 299.00 913.00 299.00 913.00 315.00 912.00 315.00 912.00 315.76 917.70 316.21 927.45 321.00 931.00 321.00 931.00 322.37 924.00 322.37 924.00 322.93 917.23 320.61 905.79 329.00 903.00 329.00 903.00 328.00 894.00 328.00 894.00 318.78 891.20 322.04 885.32 322.64 880.00 322.64 880.00 322.64 872.01 322.64 872.01 322.64 866.54 319.80 866.88 319.03 862.96 317.84 856.92 322.79 851.79 328.00 850.00 326.01 846.41 321.84 843.26 321.74 840.00 321.64 836.40 325.42 834.71 325.69 830.00 325.69 830.00 323.14 814.00 323.14 814.00 323.14 814.00 323.14 796.00 323.14 796.00 323.04 790.35 322.85 788.03 329.00 787.00 329.00 787.00 328.02 776.51 328.02 776.51 328.02 776.51 319.58 765.91 319.58 765.91 319.58 765.91 319.00 753.00 319.00 753.00 319.00 753.00 295.00 753.00 295.00 753.00 Plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ha ...
poly 206.34 763.93 205.43 757.98 198.00 755.65 191.50 753.61 187.31 756.49 184.00 757.05 184.00 757.05 174.00 757.05 174.00 757.05 174.00 757.05 169.00 757.05 169.00 757.05 164.61 756.98 153.74 754.41 152.33 760.22 151.73 762.72 153.77 772.55 154.89 775.00 154.89 775.00 158.36 781.00 158.36 781.00 158.36 781.00 166.66 799.00 166.66 799.00 167.87 801.99 168.54 806.16 170.20 808.63 170.20 808.63 174.52 813.21 174.52 813.21 174.52 813.21 183.37 825.01 183.37 825.01 187.45 831.76 184.90 833.76 187.92 839.99 187.92 839.99 197.31 852.00 197.31 852.00 198.71 854.11 208.31 865.01 210.09 865.98 211.94 866.98 213.96 866.99 216.00 866.83 216.00 866.83 238.00 863.41 238.00 863.41 240.99 862.91 246.45 862.26 249.00 861.03 251.65 859.76 254.75 856.94 257.00 855.00 261.30 861.61 263.82 856.19 272.00 851.00 272.00 851.00 272.00 855.00 272.00 855.00 272.00 855.00 292.00 855.00 292.00 855.00 292.00 855.00 288.00 835.00 288.00 835.00 288.00 835.00 286.41 827.21 286.41 827.21 286.41 827.21 279.70 819.96 279.70 819.96 279.70 819.96 274.37 806.00 274.37 806.00 274.37 806.00 269.43 786.60 269.43 786.60 269.43 786.60 260.30 783.98 260.30 783.98 260.30 783.98 253.83 777.87 253.83 777.87 253.83 777.87 241.55 769.00 241.55 769.00 241.55 769.00 233.00 767.69 233.00 767.69 233.00 767.69 226.00 764.00 226.00 764.00 221.54 767.25 214.37 769.95 209.30 766.15 Zou
poly 153.00 804.00 153.00 859.00 153.00 859.00 153.00 859.00 139.00 859.00 139.00 859.00 140.12 869.52 144.79 869.08 146.70 874.04 146.70 874.04 148.00 891.00 148.00 891.00 148.00 891.00 167.00 887.01 167.00 887.01 173.25 884.66 179.78 879.51 187.00 881.43 192.57 882.92 192.27 886.99 195.43 890.37 199.86 895.12 204.70 896.92 211.00 897.00 211.10 886.84 212.56 890.16 215.29 883.00 215.29 883.00 217.11 877.00 217.11 877.00 218.73 873.21 219.32 873.47 220.00 869.07 220.00 869.07 213.00 869.07 213.00 869.07 206.74 868.26 197.27 854.10 193.37 849.09 190.23 845.06 187.66 844.48 185.56 839.00 183.47 833.53 184.76 830.30 182.35 826.01 182.35 826.01 168.00 807.99 168.00 807.99 168.00 807.99 160.57 789.00 160.57 789.00 160.57 789.00 155.00 778.00 155.00 778.00 151.88 784.13 153.00 796.83 153.00 804.00 Couffo
Kouffo or Couffo is one of the twelve departments of Benin. Kouffo borders the country of Togo and the departments of Mono, Zou and Atlantique. Since 2008, the department's capital has been Aplahoué. The department of Kouffo was created in 199 ...
poly 257.00 858.00 248.00 863.30 248.00 863.30 248.00 863.30 222.00 868.00 222.00 868.00 221.30 877.09 214.05 887.68 213.30 891.00 213.30 891.00 212.78 897.00 212.78 897.00 212.78 897.00 210.56 904.00 210.56 904.00 210.56 904.00 210.03 909.00 210.03 909.00 209.27 912.47 207.53 913.55 207.11 918.00 206.62 923.23 208.88 928.13 207.61 934.00 206.40 939.60 201.12 945.73 201.38 952.00 201.38 952.00 206.00 968.00 206.00 968.00 222.41 965.82 240.46 961.05 257.00 961.00 262.31 950.04 272.23 953.79 277.61 950.02 281.43 947.33 282.20 940.30 281.95 936.00 281.83 933.85 281.57 933.02 281.00 931.00 274.36 932.39 273.12 930.44 273.00 924.00 273.00 924.00 273.00 901.00 273.00 901.00 273.00 901.00 271.88 889.00 271.88 889.00 271.88 889.00 271.88 880.00 271.88 880.00 270.65 874.76 266.10 871.72 265.57 868.00 265.10 864.74 268.71 860.40 270.00 855.00 262.76 858.36 261.92 862.80 257.00 858.00 Atlantique
poly 265.94 871.63 272.70 873.14 274.03 882.00 274.03 882.00 276.00 930.06 276.00 930.06 277.77 929.74 280.02 929.17 281.69 930.06 286.93 933.10 282.45 945.82 281.00 950.00 290.46 952.22 290.49 955.31 294.09 956.25 296.22 956.80 307.99 954.73 311.00 954.27 312.59 954.03 315.15 953.84 316.43 952.83 318.46 951.21 317.93 947.36 318.04 945.00 318.18 941.90 319.74 936.26 319.27 934.17 318.66 931.45 316.47 930.61 315.04 925.00 314.39 922.44 314.16 916.52 312.26 915.00 309.68 912.91 300.38 914.73 297.00 915.00 297.00 915.00 297.00 885.00 297.00 885.00 297.00 885.00 295.98 878.56 295.98 878.56 295.98 878.56 286.74 871.95 286.74 871.95 286.74 871.95 284.00 857.00 284.00 857.00 276.19 857.00 270.53 855.71 267.85 865.00 Ouémé
poly 190.28 887.88 191.51 885.48 187.86 884.18 179.49 881.23 172.19 887.47 165.00 890.03 161.26 891.37 159.48 890.71 156.00 891.21 156.00 891.21 149.00 893.00 149.00 893.00 149.00 893.00 144.00 907.00 144.00 907.00 150.92 912.00 146.25 912.89 149.18 917.78 150.76 920.42 153.53 920.93 155.83 922.69 160.20 926.05 161.69 929.71 162.00 935.00 172.27 940.14 174.95 959.54 178.00 970.00 178.00 970.00 161.00 974.00 161.00 974.00 157.16 974.77 154.35 974.62 152.00 978.00 152.00 978.00 204.00 968.00 204.00 968.00 204.00 968.00 199.26 951.00 199.26 951.00 199.26 951.00 205.79 933.00 205.79 933.00 205.79 933.00 205.06 919.00 205.06 919.00 205.06 919.00 210.00 900.00 210.00 900.00 204.65 899.12 198.01 895.52 194.14 891.70 Mono
Mono may refer to:
Common meanings
* Infectious mononucleosis, "the kissing disease"
* Monaural, monophonic sound reproduction, often shortened to mono
* Mono-, a numerical prefix representing anything single
Music Performers
* Mono (Japanese b ...
poly 278.09 952.30 265.26 954.83 262.14 957.00 260.19 958.36 260.03 959.06 259.00 961.00 259.00 961.00 274.00 960.00 274.00 960.00 274.00 960.00 275.00 956.00 275.00 956.00 275.00 956.00 275.00 960.00 275.00 960.00 275.00 960.00 290.00 957.00 290.00 957.00 290.00 957.00 290.00 955.00 290.00 955.00 287.42 953.90 284.83 952.87 282.00 952.63 Littoral
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal areas ...
department
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
s (French: ''départements'') which are subdivided into 77 communes
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, religious, ...
. In 1999, the previous 6 departments were each split into 2 halves, forming the later 12.
Demographics
The majority of Benin's 11,485,000 inhabitants live in the south of the country. Thelife expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
is 62 years. About 42 African ethnic groups live in this country, including the Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
in the southeast (migrated from Nigeria in the 12th century); the Dendi in the north-central area (who came from Mali in the 16th century); the Bariba and the Fula
Fula may refer to:
*Fula people (or Fulani, Fulɓe)
*Fula language (or Pulaar, Fulfulde, Fulani)
**The Fula variety known as the Pulaar language
**The Fula variety known as the Pular language
**The Fula variety known as Maasina Fulfulde
*Al-Fula
...
in the northeast; the Betammaribe
The Tammari people, or Batammariba, also known as Otamari or Ottamari, are an Oti–Volta languages, Oti–Volta-speaking people of the Atakora Department of Benin where they are also known as Somba people, Somba and neighboring areas of Togo, w ...
and the Somba in the Atakora Mountains
The Togo Mountains is a mountain range which stretches across the central region of the West African country of Togo and across the eastern and western borders of that country into Ghana and Benin. In Ghana, the range is also known as the Akwapim ...
; the Fon in the area around Abomey
Abomey is the capital of the Zou Department of Benin. The commune of Abomey covers an area of 142 square kilometres and, as of 2012, had a population of 90,195 people.
Abomey houses the Royal Palaces of Abomey, a collection of small traditional ...
in the South Central and the Mina, Xueda, and Aja (who came from Togo) on the coast.
Migrations have brought other African nationals to Benin that include Nigerians, Togolese, and Malians. The foreign community includes Lebanese and Indians involved in trade and commerce. The personnel of European embassies and foreign aid missions and of nongovernmental organisations and missionary groups account for a part of the 5,500 European population. A part of the European population consists of Beninese citizens of French ancestry.
Religion
 In the 2013 census, 48.5% of the population of Benin were
In the 2013 census, 48.5% of the population of Benin were Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
(25.5% Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, 6.7% Celestial Church of Christ
The Celestial Church of Christ (CCC) is a church founded in Africa by Samuel Oshoffa on 29 September 1947 in Porto-Novo, Benin. It is located in most countries worldwide including the United States and various countries in Africa.
History
Osho ...
, 3.4% Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
, 12.9% other Christian denominations), 27.7% were Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, 11.6% practiced Vodun
Vodun (meaning ''spirit'' in the Fon, Gun and Ewe languages, with a nasal high-tone ''u''; also spelled Vodon, Vodoun, Vodou, Vudu, Voudou, Voodoo, etc.) is a religion practiced by the Aja, Ewe, and Fon peoples of Benin, Togo, Ghana, and ...
, 2.6% practiced other local traditional religions, 2.6% practiced other religions, and 5.8% claimed no religious affiliation.International Religious Freedom Report 2007: Benin. United States
Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor
The Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor Affairs (DRL) is a bureau within the United States Department of State. The bureau is under the purview of the Under Secretary of State for Civilian Security, Democracy, and Human Rights.
DRL's resp ...
(14 September 2007). ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work
A creative work is a manifestation of creative effort including fine artwork (sculpture, paintings, drawing, sketching, performance art), dance, writing (literature), filmmaking, ...
.'' A government survey conducted by the Demographic and Health Surveys The Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) Program is responsible for collecting and disseminating accurate, nationally representative data on health and population in developing countries. The project is implemented by ICF International and is funded ...
Program in 2011-2012 indicated that followers of Christianity were 57.5% of the population (with Catholics making up 33.9%, Methodists 3.0%, Celestials 6.2% and other Christians 14.5%), while Muslims were 22.8%.
Traditional religions include local animistic
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, hum ...
religions in the Atakora (Atakora and Donga provinces), and Vodun
Vodun (meaning ''spirit'' in the Fon, Gun and Ewe languages, with a nasal high-tone ''u''; also spelled Vodon, Vodoun, Vodou, Vudu, Voudou, Voodoo, etc.) is a religion practiced by the Aja, Ewe, and Fon peoples of Benin, Togo, Ghana, and ...
and Orisha
Orishas (singular: orisha) are spirits that play a key role in the Yoruba religion of West Africa and several religions of the African diaspora that derive from it, such as Cuban, Dominican and Puerto Rican Santería and Brazilian Candomblé. T ...
veneration among the Yoruba and Tado peoples in the center and south of the nation. The town of Ouidah
Ouidah () or Whydah (; ''Ouidah'', ''Juida'', and ''Juda'' by the French; ''Ajudá'' by the Portuguese; and ''Fida'' by the Dutch) and known locally as Glexwe, formerly the chief port of the Kingdom of Whydah, is a city on the coast of the Repub ...
on the central coast is the spiritual center of Beninese Vodun.
The 2 largest religions are Christianity, followed throughout the south and center of Benin and in Otammari
The Tammari people, or Batammariba, also known as Otamari or Ottamari, are an Oti–Volta-speaking people of the Atakora Department of Benin where they are also known as Somba and neighboring areas of Togo, where they are officially known as ' ...
country in the Atakora, and Islam, introduced by the Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire (also transliterated as Songhay) was a state that dominated the western Sahel/Sudan in the 15th and 16th century. At its peak, it was one of the largest states in African history. The state is known by its historiographical ...
and Hausa merchants, and followed throughout Alibori
Alibori is the largest and northernmost department (French: ''département'') of Benin. Externally the department borders the countries of Burkina Faso, Niger, and Nigeria, and internally the departments of Atakora and Borgou. The department of ...
, Borgou
Borgou is one of the twelve departments of Benin. Borgou borders the country of Nigeria and the departments of Alibori Department, Alibori, Atakora Department, Atakora, Collines Department, Collines and Donga Department, Donga. The capital of Bo ...
and Donga provinces, and among the Yoruba (who also follow Christianity). Some continue to hold Vodun and Orisha beliefs and have incorporated the pantheon of Vodun and Orisha into Christianity. The Ahmadiyya Muslim Community
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, الجماعة الإسلامية الأحمدية, al-Jamāʿah al-Islāmīyah al-Aḥmadīyah; ur, , translit=Jamā'at Aḥmadiyyah Musl ...
, a Muslim sect originating in the 19th century, has a presence in the country.
Education
 The
The literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, huma ...
rate: in 2015 it was estimated to be 38.4% (49.9% for males and 27.3% for females). Benin has achieved universal primary education and half of the children (54%) were enrolled in secondary education in 2013, according to the UNESCO Institute for Statistics
The UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) is the statistical office of UNESCO and is the UN depository for cross-nationally comparable statistics on education, science and technology, culture, and communication.
The UIS was established in 1999. ...
.
While at a time the education system was not free, Benin has abolished school fees and is carrying out the recommendations of its 2007 Educational Forum. The government has devoted more than 4% of GDP to education since 2009. In 2015, public expenditure on education (all levels) amounted to 4.4% of GDP, according to the UNESCO Institute for Statistics
The UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) is the statistical office of UNESCO and is the UN depository for cross-nationally comparable statistics on education, science and technology, culture, and communication.
The UIS was established in 1999. ...
. Within this expenditure, Benin devoted a share to tertiary education: 0.97% of GDP.
Between 2009 and 2011, the share of people enrolled at university rose from 10% to 12% of the 18''–''25 year age cohort. Student enrollment in tertiary education more than doubled between 2006 and 2011 from 50,225 to 110,181. These statistics encompass not only bachelor's, master's and Ph.D. programmes but also students enrolled in non-degree post-secondary diplomas.
Health
TheHIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
rate in Benin was estimated in 2013 at 1.13% of adults aged 15–49 years. Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
is a problem in Benin, being a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among children younger than 5 years.
During the 1980s, less than 30% of the country's population had access to primary health care services. Benin's infant mortality rate
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
stood at 203 deaths for every live births. 1 in 3 mothers had access to child health care services. The Bamako Initiative
The Bamako Initiative was a formal statement adopted by African health ministers in 1987 in Bamako, Mali, to implement strategies designed to increase the availability of essential drugs and other healthcare services for Sub-Saharan Africans.
The ...
changed that by introducing community-based healthcare reform, resulting in "more efficient and equitable" provision of services. , Benin had the 26th highest rate of maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
in the world. According to a 2013 UNICEF report, 13% of women had undergone female genital mutilation
Female genital mutilation (FGM), also known as female genital cutting, female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) and female circumcision, is the ritual cutting or removal of some or all of the external female genitalia. The practice is found ...
. An approach strategy was extended to all areas of healthcare, with subsequent improvement in the health care indicators and improvement in health care efficiency and cost. Demographic and Health Surveys The Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) Program is responsible for collecting and disseminating accurate, nationally representative data on health and population in developing countries. The project is implemented by ICF International and is funded ...
has surveyed the issue in Benin since 1996.
Geography
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
and Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesNigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
to the east, and the Bight of Benin
The Bight of Benin or Bay of Benin is a bight in the Gulf of Guinea area on the western African coast that derives its name from the historical Kingdom of Benin.
Geography
It extends eastward for about from Cape St. Paul to the Nun outlet of t ...
to the south. The distance from the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through ...
in the north to the Atlantic Ocean in the south is about . Although the coastline measures , the country measures about at its widest point. 4 terrestrial ecoregions lie within Benin's borders: Eastern Guinean forests
The Eastern Guinean forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of West Africa.
Geography
The ecoregion includes the lowland forests extending from the Gulf of Guinea a few hundred kilometres inland, from western Côte d'Ivoire to ...
, Nigerian lowland forests
The Nigerian lowland forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in southwestern Nigeria and southeastern Benin. The ecoregion is densely populated, and home to several large cities including Lagos, Ibadan, and Benin City. There is still signifi ...
, Guinean forest-savanna mosaic
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
, and West Sudanian savanna
The West Sudanian savanna is a tropical savanna ecoregion that extends across West Africa.
Geography
The ecoregion stretches east and west across West Africa, from the Atlantic coast of Senegal to the Mandara Mountains on Nigeria's eastern borde ...
. It had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 5.86/10, ranking it 93rd globally out of 172 countries.

 Benin shows some variation in elevation and can be divided into 4 areas from the south to the north, starting with the lower-lying, sandy, coastal plain (highest elevation ) which is, at most, wide. It is marshy and dotted with lakes and lagoons communicating with the ocean. Behind the coast lies the
Benin shows some variation in elevation and can be divided into 4 areas from the south to the north, starting with the lower-lying, sandy, coastal plain (highest elevation ) which is, at most, wide. It is marshy and dotted with lakes and lagoons communicating with the ocean. Behind the coast lies the Guinean forest-savanna mosaic
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
-covered plateaus of southern Benin (altitude between ), which are split by valleys running north to south along the Couffo
Kouffo or Couffo is one of the twelve departments of Benin. Kouffo borders the country of Togo and the departments of Mono, Zou and Atlantique. Since 2008, the department's capital has been Aplahoué. The department of Kouffo was created in 199 ...
, Zou, and Ouémé River
The Ouémé River, also known as the Weme River, is a river in Benin. It rises in the Atakora Mountains, and is about long. It flows past the towns of Carnotville and Ouémé to a large delta on the Gulf of Guinea near the seaport city of Coto ...
s.
This geography makes it vulnerable to climate change. With the majority of the country living near the coast in lower-lying areas sea level rise could have effects on the economy and population. Northern areas will see additional regions become deserts.
An area of flatter land dotted with rocky hills whose altitude reaches extends around Nikki and Save.
A range of mountains extends along the northwest border and into Togo; these are the Atacora
Atakora is the northwesternmost department of Benin. Externally it borders Togo to the west and Burkina Faso to the north; internally it borders the departments of Alibori, Borgou and Donga. Major towns in the Atakora include Natitingou and Tan ...
. The highest point, Mont Sokbaro
Mont Sokbaro (also spelled as SagbaraoTchaboue, B.I. (2015) ''Tourisme et developpement socio-economique dans la commune de Bassila (Benin)''. Université d'Abomey-Calavi) is a hill that is mostly cited as the highest point of Benin, with an eleva ...
, is at . Benin has fields, mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evoluti ...
s, and remnants of forests. In the rest of the country, the savanna is covered with thorny scrub and dotted with baobab
''Adansonia'' is a genus made up of eight species of medium-to-large deciduous trees known as baobabs ( or ). They are placed in the Malvaceae family, subfamily Bombacoideae. They are native to Madagascar, mainland Africa, and Australia.Tropic ...
trees. Some forests line the banks of rivers. In the north and the northwest of Benin, the Reserve du W du Niger and Pendjari National Park
The Pendjari National Park (french: Parc National de la Pendjari) lies in north western Benin, adjoining the Arli National Park in Burkina Faso. Named for the Pendjari River, the national park is known for its wildlife and is home to some of the ...
has elephants, lions, antelopes, hippos, and monkeys.. Pendjari National Park together with the bordering Parks Arli and W in Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
and Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesWest African lion
''Panthera leo leo'' is a lion subspecies, which is present in West Africa, northern Central Africa and India. In West and Central Africa it is restricted to fragmented and isolated populations with a declining trajectory. It has been referred to ...
. With an estimated 356 (range: 246–466) lions, W-Arli-Pendjari harbors the largest remaining population of lions in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
. Historically Benin has served as habitat for the endangered painted hunting dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called the painted dog or Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine which is a native species to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Lyc ...
, ''Lycaon pictus''; this canid is thought to have been locally extirpated
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
.
Annual rainfall in the coastal area averages 1300 mm or about 51 inches. Benin has 2 rainy and 2 dry seasons per year. The principal rainy season is from April to late July, with a shorter less intense rainy period from September to November. The main dry season is from December to April, with a cooler dry season from July to September. Temperatures and humidity are higher along the tropical coast. In Cotonou
Cotonou (; fon, Kútɔ̀nú) is a city in Benin. Its official population count was 679,012 inhabitants in 2012; however, over two million people live in the larger urban area.
The urban area continues to expand, notably toward the west. The ci ...
, the average maximum temperature is ; the minimum is .
Variations in temperature increase when moving north through savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
and plateau toward the Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
. A dry wind from the Sahara called the Harmattan
The Harmattan is a season in West Africa that occurs between the end of November and the middle of March. It is characterized by the dry and dusty northeasterly trade wind, of the same name, which blows from the Sahara over West Africa into the ...
blows from December to March, when grass dries up, other vegetation turns reddish brown, and a veil of fine dust hangs over the country, causing the skies to be "overcast". It is also the season when farmers burn brush in the fields.
Economy

subsistence agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no su ...
, cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
production, and regional trade. Cotton accounts for 40% of the GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often ...
and roughly 80% of official export
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is an ...
receipts.
Real GDP growth was estimated at 5.1 and 5.7% in 2008 and 2009, respectively. The main driver of growth is the agricultural sector, with cotton being the main export, while services continue to contribute the largest part of GDP mostly because of Benin's geographical location, enabling trade, transportation, transit and tourism activities with its neighboring states. Benin's overall macroeconomic conditions were "positive" in 2017, with a growth rate of around 5.6%. Economic growth was mostly driven by the cotton industry and other cash crops, the Port of Cotonou, and telecommunications. A source of revenue is the Port of Cotonou, and the government is seeking to expand its revenue base. In 2017, Benin imported about $2.8 billion in goods such as rice, meat and poultry, alcoholic beverages, fuel plastic materials, specialized mining and excavating machinery, telecommunications equipment, passenger vehicles, and toiletries and cosmetics. Principal exports are ginned cotton, cotton cake and cotton seeds, cashew, shea butter, cooking oil, and lumber.
Access to biocapacity
The biocapacity or biological capacity of an ecosystem is an estimate of its production of certain biological materials such as natural resources, and its absorption and filtering of other materials such as carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chem ...
is lower than world average. In 2016, Benin had 0.9 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016 Benin used 1.4 global hectares of biocapacity per person - their ecological footprint
The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounti ...
of consumption. This means they use "slightly under double" as much biocapacity as Benin contains. As a result, Benin is running a biocapacity deficit.
tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
, facilitate the development of new food processing systems and agricultural products, and encourage new information and communication technology. Projects to improve the business climate by reforms to the land tenure system, the commercial justice system, and the financial sector were included in Benin's US$307 million Millennium Challenge Account
The Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) is a bilateral United States foreign aid agency established by the U.S. Congress in 2004. It is an independent agency separate from the State Department and USAID. It provides grants to countries that ...
grant signed in February 2006.
The Paris Club
The Paris Club (french: Club de Paris) is a group of officials from major creditor countries whose role is to find co-ordinated and sustainable solutions to the payment difficulties experienced by debtor countries. As debtor countries undertake ...
and bilateral creditors have eased the external debt situation, with Benin benefiting from a G8 debt reduction announced in July 2005, while pressing for more rapid structural reforms. An "insufficient" electrical supply continues to "adversely affect" Benin's economic growth and the government has taken steps to increase domestic power production.
While trade unions in Benin
Trade unions in Benin operate in relative freedom, with approximately 75% of the formal sector being unionized. There are, however, concerns expressed by the International Labour Organization (ILO) and the International Trade Union Confederation ( ...
represent up to 75% of the formal workforce, the informal economy has been noted by the International Trade Union Confederation
The International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC); german: Internationaler Gewerkschaftsbund (IGB), link=no; es, Confederación Sindical Internacional (CSI), link=no. is the world's largest trade union federation.
History
The federation w ...
(ITCU) to contain ongoing problems, including a lack of women's wage equality, the use of child labor
Child labour refers to the exploitation of children through any form of work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular school, and is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such e ...
, and the continuing issue of forced labor
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
. Benin is a member of the Organization for the Harmonization of Business Law in Africa OHADA is a system of corporate law and implementing institutions adopted by seventeen West Africa, West and Central African nations in 1993 in Port Louis, Mauritius before it was revised in 2008 in Quebec, Canada. OHADA is the acronym for the French ...
(OHADA OHADA is a system of corporate law and implementing institutions adopted by seventeen West and Central African nations in 1993 in Port Louis, Mauritius before it was revised in 2008 in Quebec, Canada. OHADA is the acronym for the French "''Organisa ...
).
Cotonou has the country's only seaport and international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
. Benin is connected by 2-lane asphalted roads to its neighboring countries (Togo, Burkina Faso, Niger, and Nigeria). Mobile telephone service is available across the country through operators
Operator may refer to:
Mathematics
* A symbol indicating a mathematical operation
* Logical operator or logical connective in mathematical logic
* Operator (mathematics), mapping that acts on elements of a space to produce elements of another sp ...
. ADSL connections are available in some areas. Benin is connected to the Internet by way of satellite connections (since 1998) and a single submarine cable SAT-3/WASC
SAT-3/WASC or South Atlantic 3/West Africa Submarine Cable is a submarine communications cable linking Portugal and Spain to South Africa, with connections to several West African countries along the route. It forms part of the SAT-3/WASC/SAFE cabl ...
(since 2001). Relief of "high price" is expected with the initiation of the Africa Coast to Europe cable in 2011.
With the GDP growth rate of 4-5% remaining consistent over 2 decades, poverty has been increasing. According to the National Institute of Statistics and Economic Analysis in Benin, those living under the poverty line have increased from 36.2% in 2011 to 40.1% in 2015.
Science and technology
National policy framework
TheMinistry of Higher Education and Scientific Research
{{Unreferenced, date=March 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
A Ministry of Higher Education is a government department that focuses on the provision or regulation of institutions of higher education. In some countries these exist as ministries compounde ...
is responsible for implementing science policy. The National Directorate of Scientific and Technological Research
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
handles planning and coordination whereas the National Council for Scientific and Technical Research and National Academy of Sciences, Arts, and Letters each play an advisory role. Financial support comes from Benin's National Fund for Scientific Research and Technological Innovation. The Benin Agency for the Promotion of Research Results and Technological Innovation
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
carries out technology transfer through the development and dissemination of research results. Benin was ranked 128th in the Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization. It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British maga ...
in 2021, down from 123rd in 2019.
The regulatory framework has evolved since 2006 when the a science policy was prepared. This has been updated and complemented by new texts on science and innovation (the year of adoption is between brackets):
* a manual for monitoring and evaluating research structures and organizations (2013);
* a manual on how to select research programmes and projects and apply to the National Fund for Scientific Research and Technological Innovation (2013) for competitive grants;
* a draft act for funding scientific research and innovation and a draft code of ethics for scientific research and innovation were both submitted to the Supreme Court in 2014;
* a strategic plan for scientific research and innovation (under development in 2015).
Equally important are Benin's efforts to integrate science into existing policy documents:
* ''Benin Development Strategies 2025'': ''Benin 2025 Alafia'' (2000);
* Growt''h Strategy for Poverty Reduction 2011–2016'' (2011);
* Phase 3 of the ''Ten-year Development Plan for the Education Sector'', covering 2013–2015;
* ''Development Plan for Higher Education and Scientific Research 2013–2017'' (2014).
In 2015, Benin's priority areas for scientific research were: health, education, construction and building materials, transportation and trade, culture, tourism and handicrafts, cotton/textiles, food, energy and climate change.
Some so-called challenges facing research and development in Benin are:
* the unfavorable organizational framework for research: weak governance, a lack of co-operation between research structures and the absence of an official document on the status of researchers;
* the inadequate use of human resources and the lack of any motivational policy for researchers; and
* the mismatch between research and development needs.
Human and financial investment in research
In 2007, Benin counted 1,000 researchers (in headcounts). This corresponds to 115 researchers per million inhabitants. The "main research structures" are the Centre for Scientific and Technical Research, National Institute of Agricultural Research, National Institute for Training and Research in Education, Office of Geological and Mining Research and the Centre for Entomological Research. The University of Abomey-Calavi was selected by theWorld Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
in 2014 to participate in its Centres of Excellence project, owing to its expertise in applied mathematics. Within this project, the World Bank has loaned $8 million to Benin. The Association of African Universities has received funds to enable it to co-ordinate knowledge-sharing among the 19 universities in West Africa involved in the project.
There are "no available data" on Benin's level of investment in research and development.
In 2013, the government devoted 2.5% of GDP to public health. In December 2014, 150 volunteer health professionals travelled to Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone from Benin, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Mali, Niger, and Nigeria, as part of a joint initiative by the Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
(ECOWAS) and its specialized agency, the West African Health Organisation, to help combat the epidemic. The Ebola epidemic has been a reminder of the underinvestment in West African health systems.
The Government of Benin devoted less than 5% of GDP to agricultural development in 2010, while the members of the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
had agreed to commit at least 10% of GDP to this area in the ''Maputo Declaration'' of 2003. They reiterated this goal in the ''Malabo Declaration'' adopted in Equatorial Guinea in 2014. In the latter declaration, they reaffirmed their 'intention to devote 10% of their national budgets to agricultural development and agreed to targets such as doubling agricultural productivity, halving post-harvest loss and bringing stunting down to 10% across Africa'. African leaders meeting in Equatorial Guinea failed to resolve the debate on establishing a common standard of measurement for the 10% target.
Research output
Benin has the third-highest publication intensity for scientific journals in West Africa, according to Thomson Reuters' Web of Science, Science Citation Index Expanded. There were 25.5 scientific articles per million inhabitants cataloged in this database in 2014. This compares with 65.0 for the Gambia, 49.6 for Cape Verde, 23.2 for Senegal and 21.9 for Ghana. The volume of publications in this database tripled in Benin between 2005 and 2014 from 86 to 270. Between 2008 and 2014, Benin's "main scientific collaborators" were based in France (529 articles), United States (261), United Kingdom (254), Belgium (198) and Germany (156).Transportation
Transport in Benin Benin possesses railway and road infrastructure, as well as two seaports. Benin currently does not have rail connections to other countries, but new proposals seek to change this.
Railways
Benin has a total of of single track, railway. Ben ...
includes road, rail, water and air transportation. Benin possesses a total of 6,787 km of highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access ...
, of which 1,357 km are paved. Of the paved highways in the country, there are 10 expressways
Expressway may refer to:
*Controlled-access highway, the highest-grade type of highway with access ramps, lane markings, etc., for high-speed traffic.
*Limited-access road, a lower grade of highway or arterial road.
*Expressway, the fictional slide ...
. This leaves 5,430 km of unpaved road. The Trans-West African Coastal Highway crosses Benin, connecting it to Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
to the east, and Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
, Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
and Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
to the west. When construction in Liberia
Liberia (), officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to its north, Ivory Coast to its east, and the Atlantic Ocean ...
and Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra ...
is finished, the highway will continue west to 7 other Economic Community of West African States
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as in French and Portuguese) is a regional political union, political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an ...
(ECOWAS) nations. A paved highway connects Benin northwards to Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesBurkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the ...
and Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
to the north-west.
Rail transport in Benin
Benin has a total of of Single track (rail), single track, (metre gauge) railway. Rail construction began around 1900, with regular services commencing in 1906; rail operation was taken into government control (from private companies) in 1930.
...
consists of of single track
Single may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Single (music), a song release
Songs
* "Single" (Natasha Bedingfield song), 2004
* "Single" (New Kids on the Block and Ne-Yo song), 2008
* "Single" (William Wei song), 2016
* "Single", by ...
, railway. Construction work has commenced on international lines connecting Benin with Niger and Nigeria, with outline plans announced for further connections to Togo and Burkina Faso. Benin will be a participant in the AfricaRail
AfricaRail is a project to link the railway systems of Ivory Coast, Burkina Faso, Niger, Benin and Togo. These are all gauge.
A future stage is proposed to link Mali, Senegal, which are also gauge; Nigeria and Ghana have a different narrow ga ...
project.
Cadjehoun Airport
Cotonou Cadjehoun Airport is an airport in the Cadjehoun neighborhood of Cotonou, the largest city in Benin, in West Africa. The airport is the largest in the country, and as such, is the primary entry point into the country by air, with fligh ...
, located at Cotonou, has direct international jet service to Accra
Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , ...
, Niamey, Monrovia
Monrovia () is the capital city of the West African country of Liberia. Founded in 1822, it is located on Cape Mesurado on the Atlantic coast and as of the 2008 census had 1,010,970 residents, home to 29% of Liberia’s total population. As the ...
, Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
, Ouagadougou
Ouagadougou ( , , ) is the capital and largest city of Burkina Faso and the administrative, communications, cultural, and economic centre of the nation. It is also the country's largest city, with a population of 2,415,266 in 2019. The city's n ...
, Lomé
Lomé is the capital and largest city of Togo. It has an urban population of 837,437
, and Douala
Douala is the largest city in Cameroon and its economic capital. It is also the capital of Cameroon's Littoral Region (Cameroon), Littoral Region. Home to Central Africa's largest port and its major international airport, Douala International Ai ...
, and other cities in Africa. Direct services link Cotonou to Paris, Brussels, and Istanbul.
Culture

Arts
Beninese literature had an oral tradition before French became the dominant language.Félix Couchoro
Félix Couchoro (30 January 1900 – 5 April 1968) was a Togolese writer and educator.
Biography
Couchoro was born on 30 January 1900 in Ouidah, Dahomey, to Dahomeyan parents. He attended primary school and secondary school respectively at the C ...
wrote the first Beninese novel, '' L'Esclave'' (The Slave), in 1929.
Post-independence, native folk music was combined with Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
ian highlife
Highlife is a music genre that started in present-day Ghana in the 19th century, during its Gold Coast (British colony), history as a colony of the British Empire and through its trade routes in coastal areas. It describes multiple local fusions ...
, French cabaret
Cabaret is a form of theatrical entertainment featuring music, song, dance, recitation, or drama. The performance venue might be a pub, a casino, a hotel, a restaurant, or a nightclub with a stage for performances. The audience, often dining or d ...
, American rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
, funk
Funk is a music genre that originated in African American communities in the mid-1960s when musicians created a rhythmic, danceable new form of music through a mixture of various music genres that were popular among African Americans in the m ...
and soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun ''soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest attes ...
, and Congolese rumba
The term rumba may refer to a variety of unrelated music styles. Originally, "rumba" was used as a synonym for "party" in northern Cuba, and by the late 19th century it was used to denote the complex of secular music styles known as Cuban rumba ...
.
Biennale Benin, continuing the projects of some organizations and artists, started in the country in 2010 as a collaborative event called "Regard Benin". In 2012, the project became a Biennial coordinated by the Consortium, a federation of local associations. The international exhibition and artistic program of the 2012 Biennale Benin are curated by Abdellah Karroum and the Curatorial Delegation.
Customary names
Some Beninese in the south of the country have Akan-based names indicating the day of the week on which they were born. This is due to influence of theAkan people
The Akan () people live primarily in present-day Ghana and Ivory Coast in West Africa. The Akan language (also known as ''Twi/Fante'') are a group of dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo ...
such as the Akwamu
Akwamu was a state set up by the Akwamu people in present-day Ghana. After migrating from Bono state, the Akan founders of Akwamu settled in Twifo-Heman. The Akwamu led an expansionist empire in the 17th and 18th centuries. At the peak of their ...
and others.
Language
Local languages are used as the languages of instruction in elementary schools, with French introduced after years. At the secondary school level, French is the sole language of instruction. Beninese languages are "generally transcribed" with a separate letter for each speech sound (phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-west o ...
), rather than using diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacriti ...
s as in French or digraphs as in English. This includes Beninese Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
, which in Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
is written with both diacritics and digraphs. For instance, the mid vowel
A mid vowel (or a true-mid vowel) is any in a class of vowel sounds used in some spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a mid vowel is that the tongue is positioned midway between an open vowel and a close vowel.
Other names for a mid ...
s written ''é, è, ô, o'' in French are written ' in Beninese languages, whereas the consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced wit ...
s are written ''ng'' and ''sh'' or ''ch'' in English are written ''ŋ'' and ''c.'' Digraphs are used for nasal vowel
A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the soft palate (or velum) so that the air flow escapes through the nose and the mouth simultaneously, as in the French vowel or Amoy []. By contrast, oral vowels are produced wit ...
s and the labial-velar consonants ''kp'' and ''gb,'' as in the name of the Fon language ''Fon gbe'' , and diacritics are used as tone marks
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning – that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All verbal languages use pitch to express emotional and other paralinguistic information and to convey emph ...
. In French-language publications, a mixture of French and Beninese orthographies may be seen.
Cuisine
 The cuisine involves fresh meals served with a variety of key sauces. In southern Benin cuisine, an ingredient is
The cuisine involves fresh meals served with a variety of key sauces. In southern Benin cuisine, an ingredient is corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
which has been used to prepare dough
Dough is a thick, malleable, sometimes elastic paste made from grains or from leguminous or chestnut crops. Dough is typically made by mixing flour with a small amount of water or other liquid and sometimes includes yeast or other leavening ag ...
which has been served with peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible Seed, seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small ...
- or tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
-based sauce
In cooking, a sauce is a liquid, cream, or semi-solid food, served on or used in preparing other foods. Most sauces are not normally consumed by themselves; they add flavor, moisture, and visual appeal to a dish. ''Sauce'' is a French word t ...
s. Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
and chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adult m ...
, beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quantity ...
, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
, and bush rat
The bush rat or Australian bush rat (''Rattus fuscipes'') is a small Australian Nocturnality, nocturnal animal. It is an omnivore and one of the most common indigenous species of rat on the continent, found in many heathland areas of Victoria ...
are consumed. A staple in northern Benin is yams which has been served with sauces mentioned above. The population in the northern provinces use beef and pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the domestic pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig husbandry dating back to 5000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooked and preserved; ...
meat which is fried in palm or peanut oil or cooked in sauces. Cheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During production, ...
is used in some dishes. Couscous
Couscous ( '; ber, ⵙⴽⵙⵓ, translit=Seksu) – sometimes called kusksi or kseksu – is a Maghrebi dish of small steamed granules of rolled durum wheat semolina that is often served with a stew spooned on top. Pearl millet, sorghum, ...
, rice, and bean
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes th ...
s are eaten, along with fruits such as mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree ''Mangifera indica''. It is believed to have originated in the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South a ...
es, oranges, avocados, bananas, kiwi fruit, and pineapples.
Meals are said to be generally light on meat and generous on vegetable fat
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or fats ...
. Frying in palm or peanut oil is a meat preparation, and smoked fish
Smoked fish is fish that has been cured by smoking. Foods have been smoked by humans throughout history. Originally this was done as a preservative. In more recent times fish is readily preserved by refrigeration and freezing and the smoking of ...
is prepared in Benin. Grinders are used to prepare corn flour
Cornflour may refer to:
* Cornflour (in the UK), corn starch, from the endosperm of the kernel of the corn (maize) grain
* Corn flour (in the US and elsewhere), very finely ground cornmeal, ground from dried maize
See also
* Flour
* Starch
* Gl ...
, which is made into a dough and served with sauces. " Chicken on the spit" is a recipe in which chicken is roasted over a fire on wooden sticks. Palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
**List of Arecaceae genera
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music
* Palm (ba ...
roots are sometimes soaked in a jar with salt water and sliced garlic to tenderize them, then used in dishes. Some people have outdoor mud stoves for cooking.
Sports
In the 21st century,baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding tea ...
was introduced to the country.
Traditional authorities
Benin has numerous non-sovereign monarchies within the country, many of them derivative of pre-colonial kingdoms (such asArda
Arda or ARDA may refer to:
Places
*Arda (Maritsa), a river in Bulgaria and Greece
* Arda (Italy), a river in Italy
*Arda (Douro), a river in Portugal
* Arda, Bulgaria, a village in southern Bulgaria
* Arda, County Fermanagh, a townland in County ...
). Non-sovereign monarchs do not have an official, constitutional role, and are largely ceremonial and subservient to political and civil authorities. Despite this, they play an influential role in local political matters within their particular realms and are often courted by Beninese politicians for electoral support. Advocacy groups such as the High Council of Kings of Benin
The High Council of Kings of Benin (French language, French: Haut Conseil des rois du Bénin), sometimes simply referred to as the High Council of Kings (French: Haut Conseil des Rois) or HCRB, is a Non-governmental organization, non-governmental o ...
represent the monarchs nationally.
See also
*Index of Benin-related articles
Benin , officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in Western Africa. It borders Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east and Burkina Faso and Niger to the north; its short coastline to the south leads to the Bight of Benin. Its size is just ov ...
* Outline of Benin
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Benin:
Benin – country in West Africa. Benin borders Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east and Burkina Faso and Niger to the north; its short coastline to the so ...
* Telephone numbers in Benin
Country Code: +229
International Call Prefix: 00
Trunk Prefix:
Calling formats
* yyxx xxxx Calls within Benin
* +229 yyxx xxxx Calls from outside Benin
The NSN length is eight digits.
List of area codes in Benin
Mobile phone numbers
Mob ...
References
Further reading
* Butler, S., ''Benin (Bradt Travel Guides)'' (Bradt Travel Guides, 2019) * Caulfield, Annie, ''Show Me the Magic: Travels Round Benin by Taxi'' (Penguin Books Ltd, 2003) * Kraus, Erika and Reid, Felice, ''Benin (Other Places Travel Guide)'' (Other Places Publishing, 2010) * Seely, Jennifer, ''The Legacies of Transition Governments in Africa: The Cases of Benin and Togo'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2009)External links
Country Profile
from
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadca ...
Benin
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
Benin
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board ex ...
, , Apr 10, 2018.
*
* commons:Atlas of Benin
Benin Exports
Forecasts for Benin Development
Government
Government of Benin
(official website)
Global Integrity Report: Benin
News media
from Stanford University Trade
World Bank Benin 2010 Summary Trade Statistics
Sports
Baseball
{{Authority control Countries in Africa Economic Community of West African States Former Portuguese colonies French-speaking countries and territories Least developed countries Member states of the African Union Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Republics States and territories established in 1960 West African countries 1960 establishments in Africa