Benelux B on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
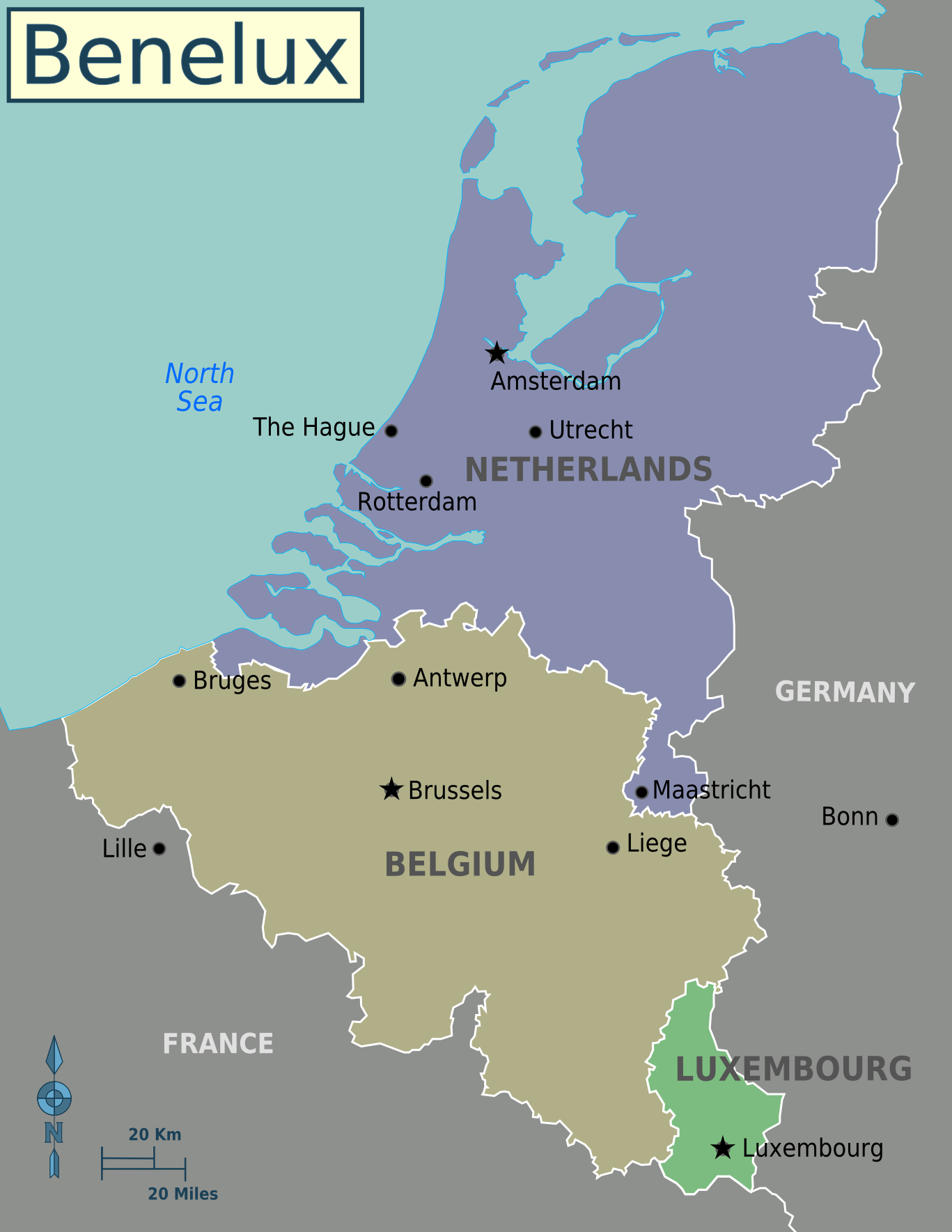
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a
politico
''Politico'' (stylized in all caps), known originally as ''The Politico'', is an American, German-owned political journalism newspaper company based in Arlington County, Virginia, that covers politics and policy in the United States and intern ...
-economic union
An economic union is a type of trade bloc which is composed of a common market with a customs union. The participant countries have both common policies on product regulation, freedom of movement of goods, services and the factors of production ...
and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in western Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
: Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, and Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
. The name is a portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsEU. Currently 37% of the total number of EU frontier workers work in the Benelux and surrounding areas. 35,000 Belgian citizens work in Luxembourg, while 37,000 Belgian citizens cross the border to work in the Netherlands each day. In addition, 12,000 Dutch and close to a thousand Luxembourg residents work in Belgium.
The main institutions of the Union are the Committee of Ministers, the Council of the Union, the General Secretariat, the Interparliamentary Consultative Council and the Benelux Court of Justice while the
 The Benelux countries also work together in the so-called Pentalateral Energy Forum, a regional cooperation group formed of five members—the Benelux states,
The Benelux countries also work together in the so-called Pentalateral Energy Forum, a regional cooperation group formed of five members—the Benelux states,
Benelux Court of Justice
Benelux Office for Intellectual Property
{{Authority control Regions of Europe History of the Low Countries Economic history of Belgium Economic history of Luxembourg Economic history of the Netherlands 1944 establishments in the Netherlands 1944 establishments in Belgium 1944 establishments in Luxembourg International economic organizations Supranational unions Organizations established in 1944 Northwestern Europe Bottom-up regional groups within the European Union
Benelux Office for Intellectual Property
(BBIE)french: Office Benelux de la Propriété intellectuelle
, image = Boip.logo.115x100.gif
, image_border =
, size = 115
, alt =
, caption =
, map =
, msize =
, malt =
, mcaption =
, abbr ...
covers the same land but is not part of the Benelux Union.
The Benelux General Secretariat is located in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
. It is the central platform of the Benelux Union cooperation. It handles the secretariat of the Committee of Ministers, the Council of Benelux Union and the sundry committees and working parties. The General Secretariat provides day-to-day support for the Benelux cooperation on the substantive, procedural, diplomatic and logistical levels. The Secretary-General is Alain de Muyser from Luxembourg and there are two deputies: Deputy Secretary-General Frank Weekers from the Netherlands and Deputy Secretary-General Michel-Etienne Tilemans from Belgium.
The presidency of the Benelux is held in turn by the three countries for a period of one year. Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
holds the presidency for 2022.
History
In 1944, exiled representatives of the three countries signed theLondon Customs Convention
Officially titled the ''Netherlands–Belgium–Luxembourg Customs Convention'', the London Customs Convention was the treaty that established the Benelux Customs Union on 5 September 1944. The word "Benelux" comes from an acronym of the countrie ...
, the treaty that established the Benelux Customs Union. Ratified in 1947, the treaty was in force from 1948 until it was superseded by the Benelux Economic Union. The initial form of economic cooperation expanded steadily over time, leading to the signing of the treaty establishing the Benelux Economic Union (''Benelux Economische Unie'', ''Union Économique Benelux'') on 3 February 1958 in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
, which came into force on 1 November 1960. Initially, the purpose of cooperation among the three partners was to put an end to customs barriers at their borders and ensure free movement of persons, capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
, services
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a pu ...
, and goods
In economics, goods are items that satisfy human wants
and provide utility, for example, to a consumer making a purchase of a satisfying product. A common distinction is made between goods which are transferable, and services, which are not tran ...
between the three countries. This treaty was the first example of international economic integration in Europe since the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
The three countries therefore foreshadowed and provided the model for future European integration, such as the European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was a European organization created after World War II to regulate the coal and steel industries. It was formally established in 1951 by the Treaty of Paris, signed by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembo ...
, the European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
(EEC), and the European Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisbo ...
–European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
(EC–EU). The three partners also launched the Schengen
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
process, which came into operation in 1985. Benelux cooperation has been constantly adapted and now goes much further than mere economic cooperation, extending to new and topical policy areas connected with security, sustainable development, and the economy.
In 1965, the treaty establishing a Benelux Court of Justice was signed. It entered into force in 1974. The court, composed of judges from the highest courts of the three states, has to guarantee the uniform interpretation of common legal rules. This international judicial institution
International judicial institutions can be divided into courts, arbitral tribunals and quasi-judicial institutions. Courts are permanent bodies, with near the same composition for each case. Arbitral tribunals, by contrast, are constituted anew fo ...
is located in Luxembourg.
Renewal of the agreement
The 1958 Treaty between the Benelux countries establishing the Benelux Economic Union was limited to a period of 50 years. During the following years, and even more so after the creation of the European Union, the Benelux cooperation focused on developing other fields of activity within a constantly changing international context. At the end of the 50 years, the governments of the three Benelux countries decided to renew the agreement, taking into account the new aspects of the Benelux-cooperation – such as security – and the newfederal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
structure of Belgium. The original establishing treaty, set to expire in 2010, was replaced by a new legal framework (called the Treaty revising the Treaty establishing the Benelux Economic Union), which was signed on 17 June 2008.
The new treaty has no set time limit and the name of the ''Benelux Economic Union'' changed to ''Benelux Union'' to reflect the broad scope on the union. The main objectives of the treaty are the continuation and enlargement of the cooperation between the three member states within a larger European context. The renewed treaty explicitly foresees the possibility that the Benelux countries will cooperate with other European member states or with regional cooperation structures. The new Benelux cooperation focuses on three main topics: internal market and economic union, sustainability, justice and internal affairs. The number of structures in the renewed Treaty has been reduced and thus simplified.
Activities since 2008
Benelux seeks region-to-region cooperation, be it with France and Germany (North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a States of Germany, state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more tha ...
) or beyond with the Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
, the Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
, the Visegrad countries, or even further. In 2018 a renewed political declaration was adopted between Benelux and North Rhine-Westphalia to give cooperation a further impetus.
The Benelux is particularly active in the field of intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, cop ...
. The three countries established a Benelux Trademarks Office and a Benelux Designs Office, both situated in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
. In 2005, they concluded a treaty establishing the Benelux Office for Intellectual Property
(BBIE)french: Office Benelux de la Propriété intellectuelle
, image = Boip.logo.115x100.gif
, image_border =
, size = 115
, alt =
, caption =
, map =
, msize =
, malt =
, mcaption =
, abbr ...
, which replaced both offices upon its entry into force on 1 September 2006. This organisation is the official body for the registration of trademarks and designs in the Benelux. In addition, it offers the possibility to formally record the existence of ideas, concepts, designs, prototypes and the like.
Some examples of recent Benelux initiatives include: automatic level recognition of diplomas and degrees within the Benelux for bachelor's and master's programs in 2015, and for all other degrees in 2018; common road inspections in 2014; and a Benelux pilot with digital consignment notes ( e-CMR) in 2017; a new Benelux Treaty on Police Cooperation in 2018, providing for direct access to each other's police databases and population registers within the limits of national legislation, and allowing some police forces to cross borders in some situations. The Benelux is also committed to working together on adaptation to climate change
Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to current or expected effects of climate change.IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary öller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.) InClimat ...
. A joint political declaration in July 2020 called on the European Commission to prioritise cycling in European climate policy and Sustainable Transport strategies, to co-finance the construction of cycling infrastructure
Cycling infrastructure is all infrastructure cyclists are allowed to use. Bikeways include bike paths, bike lanes, cycle tracks, rail trails and, where permitted, sidewalks. Roads used by motorists are also cycling infrastructure, except whe ...
, and to provide funds to stimulate cycling policy.
On 5 June 2018 the Benelux Treaty celebrated its 60 years of existence. In 2018, a Benelux Youth Parliament was created.
In addition to cooperation based on a Treaty, there is also political cooperation in the Benelux context, including summits of the Benelux government leaders. In 2019 a Benelux summit was held in Luxembourg. In 2020, a Benelux summit was held – online, due to the COVID-19 pandemic – under Dutch Presidency on 7 October between the prime ministers.
Cooperation with other geopolitical regions
 The Benelux countries also work together in the so-called Pentalateral Energy Forum, a regional cooperation group formed of five members—the Benelux states,
The Benelux countries also work together in the so-called Pentalateral Energy Forum, a regional cooperation group formed of five members—the Benelux states, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
. Formed on 6 June 2007, the ministers for energy from the various countries represent a total of 200 million residents and 40% of the European electricity network.
In 2017 the members of the Benelux, the Baltic Assembly
The Baltic Assembly (BA) is a regional organisation that promotes intergovernmental cooperation between Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. It attempts to find a common position in relation to many international issues, including economic, politic ...
, three members of the Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
(Sweden, Denmark and Finland), and all the other countries EU member states
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, sought to increase cooperation in the Digital Single Market
On 6 May 2015, the European Commission, led at the time by Jean-Claude Juncker, communicated the Digital Single Market strategy which intends to remove virtual borders, boost digital connectivity, and make it easier for consumers to access cross ...
, as well as discussing social matters, the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union
The economic and monetary union (EMU) of the European Union is a group of policies aimed at converging the economies of member states of the European Union at three stages.
There are three stages of the EMU, each of which consists of progr ...
, immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
and defence cooperation. Foreign relations in the wake of Russia's annexation of Crimea
In February and March 2014, Russia invaded and subsequently annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine. This event took place in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity and is part of the wider Russo-Ukrainian War.
The events in Kyiv ...
and the 2017 Turkish constitutional referendum
A constitutional referendum was held in Turkey on 16 April 2017 on whether to approve 18 proposed amendments to the Turkish constitution that were brought forward by the governing Justice and Development Party (AKP) and the Nationalist Movement ...
were also on the agenda.
Since 2008 the Benelux Union works together with the German Land (state) North Rhine-Westphalia.
In 2018 Benelux Union signed a declaration with France to strengthen cross-border cooperation.
Politics

Benelux institutions
Under the 2008 treaty there are five Benelux institutions: the Benelux Committee of Ministers, the Benelux Council, the Benelux Parliament, the Benelux Court of Justice, the Benelux Secretariat General. Beside these five institutions, the Benelux Organisation for Intellectual Property is also an independent organisation. Benelux Committee of Ministers: The Committee of Ministers is the supreme decision-making body of the Benelux. It includes at least one representative at ministerial level from the three countries. Its composition varies according to its agenda. The ministers determine the orientations and priorities of Benelux cooperation. The presidency of the Committee rotates between the three countries on an annual basis. Benelux Council: The council is composed of senior officials from the relevant ministries. Its composition varies according to its agenda. The council's main task is to prepare the dossiers for the ministers. Benelux InterParliamentary Consultative Council: TheBenelux Parliament
The Benelux Parliament (officially known as the Benelux Interparliamentary Assembly) is one of the institutions of the Benelux economic union. The Parliament was established by an agreement signed by Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg on 5 Nov ...
(officially referred to as an "Interparliamentary Consultative Council") was created in 1955. This parliamentary assembly is composed of 49 members from the respective national parliaments (21 members of the Dutch parliament, 21 members of the Belgian national and regional parliaments, and 7 members of the Luxembourg parliament). Its members inform and advise their respective governments on all Benelux matters. On 20 January 2015, the governments of the three countries, including, as far as Belgium is concerned, the community and regional governments, signed in Brussels the Treaty of the Benelux Interparliamentary Assembly. This treaty entered into force on 1 August 2019. This superseded the 1955 Convention on the Consultative Interparliamentary Council for the Benelux. The official name has been largely obsolete in daily practice for a number of years: both internally in the Benelux and in external references, the name Benelux Parliament has been used ''de facto'' for a number of years now.
Benelux Court of Justice:
The Benelux Court of Justice is an international court. Its mission is to promote uniformity in the application of Benelux legislation. When faced with difficulty interpreting a common Benelux legal rule, national courts must seek an interpretive ruling from the Benelux Court, which subsequently renders a binding decision. The members of the Court are appointed from among the judges of the 'Cour de cassation' of Belgium, the 'Hoge Raad of the Netherlands' and the 'Cour de cassation' of Luxembourg.
Benelux General Secretariat:
The General Secretariat, which is based in Brussels, forms the cooperation platform of the Benelux Union. It acts as the secretariat of the Committee of Ministers, the council and various commissions and working groups. The General Secretariat has years of expertise in the area of Benelux cooperation and is familiar with the policy agreements and differences between the three countries. Building on what already been achieved, the General Secretariat puts its knowledge, network and experience at the service of partners and stakeholders who endorse its mission. It initiates, supports and monitors cooperation results in the areas of economy, sustainability and security.
Benelux works together on the basis of an annual plan embedded in a four-year joint work programme.
Benelux legal instruments
The Benelux Union involves intergovernmental cooperation. The Treaty establishing the Benelux Union explicitly provides that the Benelux Committee of Ministers can resort to four legal instruments (art. 6, paragraph 2, under a), f), g) and h)): 1. Decisions Decisions are legally binding regulations for implementing the Treaty establishing the Benelux Union or other Benelux treaties. Their legally binding force concerns the Benelux states (and their sub-state entities), which have to implement them. However, they have no direct effect towards individual citizens or companies (notwithstanding any indirect protection of their rights based on such decisions as a source of international law). Only national provisions implementing a decision can directly create rights and obligations for citizens or companies. 2. Agreements The Committee of Ministers can draw up agreements, which are then submitted to the Benelux states (and/or their sub-state entities) for signature and subsequent parliamentary ratification. These agreements can deal with any subject matter, also in policy areas that are not yet covered by cooperation in the framework of the Benelux Union. These are in fact traditional treaties, with the same direct legally binding force towards both authorities and citizens or companies. The negotiations do however take place in the established context of the Benelux working groups and institutions, rather than on an ad hoc basis. 3. Recommendations Recommendations are non-binding orientations, adopted at ministerial level, which underpin the functioning of the Benelux Union. These (policy) orientations may not be legally binding, but given their adoption at the highest political level and their legal basis vested directly in the Treaty, they do entail a strong moral obligation for any authority concerned in the Benelux countries. 4. Directives Directives of the Committee of Ministers are mere inter-institutional instructions towards the Benelux Council and/or the Secretariat-General, for which they are binding. This instrument has so far only been used occasionally, basically in order to organise certain activities within a Benelux working group or to give them impetus. All four instruments require the unanimous approval of the members of the Committee of Ministers (and, in the case of agreements, subsequent signature and ratification at national level).Characteristics
Countries
Associated territories
See also
*Admiral Benelux
The Admiral Benelux (ABNL) is the Commanding Officer of the combined military staff of the Royal Netherlands Navy and the Naval Component of the Belgian Armed Forces.
The position of ABNL was created together with the combination of the Staffs o ...
* EU Med Group
EU Med or EuroMed 9 or MED9 (formerly MED7; from EUrope Mediterranean) which is also referred to as "Club Med" and "Med Group", is an alliance of nine Mediterranean and Southern European Union member states: Croatia, Cyprus, France, Greece, Ita ...
* Baltic Assembly
The Baltic Assembly (BA) is a regional organisation that promotes intergovernmental cooperation between Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. It attempts to find a common position in relation to many international issues, including economic, politic ...
* Inner Six
The Inner Six, also known as the Six, the Six founders, or the founding members of the European Union, refers to Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands, the six founding member states of the European Communities, now ...
* Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
* Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
* United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
* Visegrád Group
The Visegrád Group (also known as the Visegrád Four, the V4, or the European Quartet) is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-o ...
* Polish–Czechoslovak confederation
* Proposed United Kingdom Confederation
A British confederation or a confederal UK has been proposed as a concept of constitutional reform of the United Kingdom, in which the countries of the United Kingdom; England, Scotland, Wales, as well as Northern Ireland become separate sovere ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * Willy van Ryckeghem : ''Benelux'' in: The European Economy - Growth and Crisis, Andrea Boltho, Editor, Oxford University Press, 1982, .External links
; Official sites * (in Dutch and French)Benelux Court of Justice
Benelux Office for Intellectual Property
{{Authority control Regions of Europe History of the Low Countries Economic history of Belgium Economic history of Luxembourg Economic history of the Netherlands 1944 establishments in the Netherlands 1944 establishments in Belgium 1944 establishments in Luxembourg International economic organizations Supranational unions Organizations established in 1944 Northwestern Europe Bottom-up regional groups within the European Union