Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of
Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
. It is bordered by
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
to the north, the
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
to the east, and
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
to the west and south. It also shares a water boundary with
Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
to the southeast. It has an area of and a population of 441,471 (2022).
[ Its mainland is about long and wide. It is the least populated and least densely populated country in Central America. Its population growth rate of 1.87% per year (2018 estimate) is the second-highest in the region and one of the highest in the Western Hemisphere. Its ]capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
is Belmopan
Belmopan () is the capital city of Belize. Its population in 2010 was 16,451. In addition to being the smallest capital city in the continental Americas by population, Belmopan is the third-largest settlement in Belize, behind Belize City and S ...
, and its largest city is the namesake city of Belize City
Belize City is the largest city in Belize and was once the capital of the former British Honduras. According to the 2010 census, Belize City has a population of 57,169 people in 16,162 households. It is at the mouth of the Haulover Creek, wh ...
. Belize is often thought of as a Caribbean country in Central America because it has a history similar to that of English-speaking Caribbean nations. Indeed, Belize’s institutions and official language reflect its history as a British colony.
The Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, archit ...
spread into the area of Belize between 1500 BC and AD 300 and flourished until about 1200.[ European contact began in 1492 when ]Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
sailed along the Gulf of Honduras. European exploration was begun by English settlers in 1638. Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Britain both laid claim to the land until Britain defeated the Spanish in the Battle of St. George's Caye
The Battle of St. George's Caye was a military engagement that lasted from 3 to 10 September 1798, off the coast of British Honduras (present-day Belize). However, the name is typically reserved for the final battle that occurred on 10 Septemb ...
(1798). In 1840 it became a British colony known as British Honduras, and a Crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
in 1862. Belize achieved its independence from the United Kingdom on 21 September 1981. It is the only mainland Central American country which is a Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
, with King Charles III as its monarch and head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
, represented by a governor-general
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
.
Belize has a diverse society that is composed of many cultures and languages that reflect its rich history. It is the only Central American country where English is the official language, while Belizean Creole
Belizean Creole (Belizean Creole: ''Belize Kriol'', ''Kriol'') is an English-based creole language spoken by the Belizean Creole people. It is closely related to Miskito Coastal Creole, San Andrés-Providencia Creole, and Jamaican Patois ( Lim ...
is the most widely spoken dialect. Spanish is the second most commonly spoken language, followed by the Mayan languages, German dialects
German dialects are the various traditional local varieties of the German language. Though varied by region, those of the southern half of Germany beneath the Benrath line are dominated by the geographical spread of the High German consonant ...
, and Garifuna
The Garifuna people ( or ; pl. Garínagu in Garifuna) are a people of mixed free African and indigenous American ancestry that originated in the Caribbean island of Saint Vincent and speak Garifuna, an Arawakan language, and Vincentian ...
. Over half the population is multilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all E ...
, due to the diverse linguistic backgrounds of the population. It is known for its September Celebrations, its extensive barrier reef coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s, and punta music.Mesoamerican Biological Corridor
The Mesoamerican Biological Corridor (MBC) is a region that consists of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, and some southern states of Mexico. The area acts as a natural land bridge from South America to North ...
. It is considered a Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
n and Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
nation with strong ties to both the American and Caribbean regions. It is a member of the Caribbean Community
The Caribbean Community (CARICOM or CC) is an intergovernmental organization that is a political and economic union of 15 member states (14 nation-states and one dependency) throughout the Caribbean. They have primary objectives to promote econom ...
(CARICOM), the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC), and the Central American Integration System
The Central American Integration System ( es, Sistema de la Integración Centroamericana, or SICA) has been the economic and political organization of Central American states since 1 February 1993. On 13 December 1991, the ODECA countries (Spa ...
(SICA), the only country to hold full membership in all three regional organizations.
Name
The earliest known record of the name "Belize" appears in the journal of the Dominican priest Fray José Delgado, dating to 1677.Sittee River
Sittee River is a river in Belize. It is also the name of a village along the river.
River
Located in central Belize, the mangroves located at the mouth of this river are the tallest ever reported for the Caribbean region and among the tallest an ...
, Sibun River, and Belize River
The Belize River runs through the center of Belize. It drains more than one-quarter of the country as it winds along the northern edge of the Maya Mountains to the sea just north of Belize City (). The Belize river valley is largely tropical rain ...
, were provided to Delgado by his translator.Itza Itza may refer to:
* Itza people, an ethnic group of Guatemala
* Itzaʼ language, a Mayan language
* Itza Kingdom (disambiguation)
* Itza, Navarre, a town in Spain
See also
* Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza , es, Chichén Itzá , often with ...
".buccaneer
Buccaneers were a kind of privateers or free sailors particular to the Caribbean Sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. First established on northern Hispaniola as early as 1625, their heyday was from Stuart Restoration, the Restoration in 16 ...
, Peter Wallace
Peter James Wallace (born 16 October 1985) is a former Scotland international rugby league footballer who played for the Penrith Panthers and the Brisbane Broncos in the NRL.
A New South Wales State of Origin representative, Wallace began his ...
, who established a settlement at the mouth of the Belize River in 1638.[ Writers and historians have suggested several other possible etymologies, including postulated French and African origins.]
History
Early history
 The
The Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, archit ...
emerged at least three millennia ago in the lowland area of the Yucatán Peninsula and the highlands to the south, in the area of present-day southeastern Mexico, Belize, Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
, and western Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
. Many aspects of this culture persist in the area, despite nearly 500 years of European domination. Prior to about 2500 BC, some hunting and foraging bands settled in small farming villages; they domesticated crops such as corn, beans, squash, and chili peppers.
A profusion of languages and subcultures developed within the Maya core culture. Between about 2500 BC and 250 AD, the basic institutions of Maya civilization emerged.[
]


Maya civilization
The Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, archit ...
spread across the territory of present-day Belize around 1500BC, and flourished until about 900 AD. The recorded history of the middle and southern regions focuses on Caracol, an urban political centre that may have supported over 140,000 people. North of the Maya Mountains
The Maya Mountains are a mountain range located in Belize and eastern Guatemala, in Central America. Etymology
The Maya Mountains were known as the ''Cockscomb'' or ''Coxcomb Mountains'' to Baymen and later Belizeans at least until the mid-2 ...
, the most important political centre was Lamanai
Lamanai (from ''Lama'anayin'', "submerged crocodile" in Yucatec Maya) is a Mesoamerican archaeological site, and was once a major city of the Maya civilization, located in the north of Belize, in Orange Walk District. The site's name is pre-Columbi ...
. In the late Classic Era of Maya civilization (600–1000AD), an estimated 400,000 to 1,000,000 people inhabited the area of present-day Belize.[
When Spanish explorers arrived in the 16th century, the area of present-day Belize included three distinct Maya territories:
* Chetumal province, which encompassed the area around ]Corozal Bay
Corozal Bay is an inlet of Chetumal Bay, indenting northern Belize. Several resort areas are located on the coast of the bay, most notably Corozal Town. The New River (Belize) flows north into the bay. The town of Consejo is located north-northea ...
Dzuluinicob province
which encompassed the area between the New River and the Sibun River, west to Tipu
* a southern territory controlled by the Manche Ch'ol
Manche (, ) is a coastal French département in Normandy, on the English Channel, which is known as ''La Manche'', literally "the sleeve", in French. It had a population of 495,045 in 2019.[Monkey River
Monkey River is a coastal watercourse in southern Belize that rises in the Maya Mountains and discharges to the Caribbean Sea near Monkey River Town. One of Belize's major rivers, Monkey River has northern headwaters which originate in the Cocks ...]
and the Sarstoon River.
Early colonial period (1506–1862)
Spanish conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, O ...
s explored the land and declared it part of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
, but they failed to settle the territory because of its lack of resources and the hostile tribes of the Yucatán.
English pirates sporadically visited the coast of what is now Belize, seeking a sheltered region from which they could attack Spanish ships ''(see English settlement in Belize
The Anglo-Saxon, English, or Baymen's settlement of Belize is traditionally thought to have been effected upon Peter Wallace's 1638 landing at the mouth of Haulover Creek. As this account lacks clear primary sources, however, scholarly discours ...
)'' and cut logwood
''Haematoxylum campechianum'' (blackwood, bloodwood tree, bluewood, campeachy tree, campeachy wood, campeche logwood, campeche wood, Jamaica wood, logwood or logwood tree) is a species of flowering tree in the legume family, Fabaceae, that is na ...
(''Haematoxylum campechianum'') trees. The first British permanent settlement was founded around 1716, nearly 200 years after the Spanish had initially arrived, in what became the Belize District,enslaved Africans
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
to cut logwood trees. This yielded a valuable fixing agent for clothing dyes, and was one of the first ways to achieve a fast black before the advent of artificial dyes. The Spanish granted the British settlers the right to occupy the area and cut logwood in exchange for their help suppressing piracy. The British first appointed a superintendent over the Belize area in 1786. Before then the British government had not recognized the settlement as a colony for fear of provoking a Spanish attack. The delay in government oversight allowed the settlers to establish their own laws and forms of government. During this period, a few successful settlers gained control of the local legislature, known as the Public Meeting, as well as of most of the settlement's land and timber.
Throughout the 18th century, the Spanish attacked Belize every time war broke out with Britain. The
The British first appointed a superintendent over the Belize area in 1786. Before then the British government had not recognized the settlement as a colony for fear of provoking a Spanish attack. The delay in government oversight allowed the settlers to establish their own laws and forms of government. During this period, a few successful settlers gained control of the local legislature, known as the Public Meeting, as well as of most of the settlement's land and timber.
Throughout the 18th century, the Spanish attacked Belize every time war broke out with Britain. The Battle of St. George's Caye
The Battle of St. George's Caye was a military engagement that lasted from 3 to 10 September 1798, off the coast of British Honduras (present-day Belize). However, the name is typically reserved for the final battle that occurred on 10 Septemb ...
was the last of such military engagements, in 1798, between a Spanish fleet and a small force of Baymen
The Baymen were the earliest European settlers along the Bay of Honduras in what eventually became the colony of British Honduras (modern-day Belize).
Settlement
The first Baymen settled in the Belize City area in the 1630s. They were buccane ...
and their slaves. From 3 to 5 September, the Spaniards tried to force their way through Montego Caye shoal, but were blocked by defenders. Spain's last attempt occurred on 10 September, when the Baymen repelled the Spanish fleet in a short engagement with no known casualties on either side. The anniversary of the battle has been declared a national holiday in Belize and is celebrated to commemorate the "first Belizeans" and the defence of their territory taken from the Spanish empire.
As part of the British Empire (1862–1981)

 In the early 19th century, the British sought to reform the settlers, threatening to suspend the Public Meeting unless it observed the government's instructions to eliminate slavery outright. After a generation of wrangling, slavery was abolished in the
In the early 19th century, the British sought to reform the settlers, threatening to suspend the Public Meeting unless it observed the government's instructions to eliminate slavery outright. After a generation of wrangling, slavery was abolished in the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
in 1833. As a result of their enslaved Africans' abilities in the work of mahogany
Mahogany is a straight-grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus ''Swietenia'', indigenous to the AmericasBridgewater, Samuel (2012). ''A Natural History of Belize: Inside the Maya Forest''. Austin: Unive ...
extraction, owners in British Honduras were compensated at £53.69 per enslaved African on average, the highest amount paid in any British territory. This was a form of reparation that was not given to the enslaved Africans at the time, nor since.peonage
Peon (English language, English , from the Spanish language, Spanish ''wikt:peón#Spanish, peón'' ) usually refers to a person subject to peonage: any form of wage labor, financial exploitation, coercive economic practice, or policy in which th ...
. Belize Estate's influence accounts in part for the colony's reliance on the mahogany trade throughout the rest of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century.
The Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
of the 1930s caused a near-collapse of the colony's economy as British demand for timber plummeted. The effects of widespread unemployment were worsened by a devastating hurricane that struck the colony in 1931. Perceptions of the government's relief effort as inadequate were aggravated by its refusal to legalize labour unions or introduce a minimum wage. Economic conditions improved during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, as many Belizean men entered the armed forces or otherwise contributed to the war effort.
 Following the war, the colony's economy stagnated. Britain's decision to
Following the war, the colony's economy stagnated. Britain's decision to devalue
In macroeconomics and modern monetary policy, a devaluation is an official lowering of the value of a country's currency within a fixed exchange-rate system, in which a monetary authority formally sets a lower exchange rate of the national curr ...
the British Honduras dollar in 1949 worsened economic conditions and led to the creation of the People's Committee, which demanded independence. The People's Committee's successor, the People's United Party (PUP), sought constitutional reforms that expanded voting rights to all adults. The first election under universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political stanc ...
was held in 1954 and was decisively won by the PUP, beginning a three-decade period in which the PUP dominated the country's politics. Pro-independence activist George Cadle Price
George Cadle Price, (15 January 191919 September 2011), was a Belizean statesman who served twice as the head of government of Belize from 1961–1984 and 1989–1993. He served as First Minister and Premier under British rule until inde ...
became PUP's leader in 1956 and the effective head of government in 1961, a post he would hold under various titles until 1984.
Under a new constitution, Britain granted British Honduras self-government in 1964. On 1 June 1973, British Honduras was officially renamed Belize.
Independent Belize (since 1981)
Belize was granted independence on 21 September 1981. Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
refused to recognize the new nation because of its longstanding territorial dispute with the British colony, claiming that Belize belonged to Guatemala. About 1,500 British troops remained in Belize to deter any possible incursions.
With Price at the helm, the PUP won all national elections until 1984. In that election, the first national election after independence, the PUP was defeated by the United Democratic Party (UDP). UDP leader Manuel Esquivel
Sir Manuel Amadeo Esquivel (2 May 1940 – 10 February 2022) was a Belizean politician. As leader of the United Democratic Party, he served as Prime Minister from 1984 to 1989, and then again from 1993 to 1998. His party's victory in 1984 was ...
replaced Price as prime minister, with Price himself unexpectedly losing his own House
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
seat to a UDP challenger. The PUP under Price returned to power after elections in 1989. The following year the United Kingdom announced that it would end its military involvement in Belize, and the RAF Harrier detachment was withdrawn the same year, having remained stationed in the country continuously since its deployment had become permanent there in 1980. British soldiers were withdrawn in 1994, but the United Kingdom left behind a military training unit to assist with the newly created Belize Defence Force.
The UDP regained power in the 1993 national election, and Esquivel became prime minister for a second time. Soon afterwards, Esquivel announced the suspension of a pact reached with Guatemala during Price's tenure, claiming Price had made too many concessions to gain Guatemalan recognition. The pact may have curtailed the 130-year-old border dispute between the two countries. Border tensions continued into the early 2000s, although the two countries cooperated in other areas.
In 1996, the Belize Barrier Reef
The Belize Barrier Reef is a series of coral reefs straddling the coast of Belize, roughly offshore in the north and in the south within the country limits. The Belize Barrier Reef is a long section of the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System, ...
, one of the Western Hemisphere's most pristine ecosystems, was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
The PUP won a landslide victory in the 1998 national elections, and PUP leader Said Musa was sworn in as prime minister. In the 2003 elections the PUP maintained its majority, and Musa continued as prime minister. He pledged to improve conditions in the underdeveloped and largely inaccessible southern part of Belize.
In 2005, Belize was the site of unrest
Unrest, also called disaffection, is a sociological phenomenon, including:
* Civil unrest
* Civil disorder
* Domestic terrorism
* Industrial unrest
* Labor unrest
* Rebellion
* Riot
* Strike action
* State of emergency
Notable historical instance ...
caused by discontent with the PUP government, including tax increases in the national budget. On 8 February 2008, Dean Barrow
Dean Oliver Barrow, SC PC (born March 2, 1951) is a politician from Belize who served as prime minister of Belize from 2008 until 2020 and as leader of Belize's United Democratic Party.
An attorney by profession, Barrow served as Belize's ...
was sworn in as prime minister after his UDP won a landslide victory in general elections. Barrow and the UDP were re-elected in 2012 with a considerably smaller majority. Barrow led the UDP to a third consecutive general election victory in November 2015, increasing the party's number of seats from 17 to 19. He said the election would be his last as party leader and preparations are under way for the party to elect his successor.
On 11 November 2020, the People's United Party (PUP), led by Johnny Briceño
John Antonio Briceño (born 17 July 1960) is a Belizean politician who is the 5th and current Prime Minister of Belize since 12 November 2020, and the leader of the People's United Party (PUP) since 2016. He was Leader of the Opposition from 20 ...
, defeated the United Democratic Party (UDP) for the first time since 2003, having won 26 seats out of 31 to form the new government of Belize. Briceño took office as Prime Minister on 12 November.
Government and politics
 Belize is a
Belize is a parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democracy, democratic government, governance of a sovereign state, state (or subordinate entity) where the Executive (government), executive derives its democratic legitimacy ...
constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
. The structure of government is based on the British parliamentary system, and the legal system is modelled on the common law of England
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures.
Principal elements of English law
Although the common law has, historically, been ...
. The head of state is King Charles III, who holds the title King of Belize
The monarchy of Belize is a system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Belize. The current Belizean monarch and head of state since 8 September 2022, is King Charles III. As sovereign, he is the perso ...
. The King lives in the United Kingdom, and is represented in Belize by the governor-general
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
. Executive authority is exercised by the cabinet, which advises the governor-general and is led by the Prime Minister of Belize, who is head of government. Cabinet ministers are members of the majority political party in parliament and usually hold elected seats within it concurrent with their cabinet positions.
The bicameral National Assembly of Belize
The National Assembly is the bicameral legislature of the nation of Belize. It is divided into the House of Representatives, with 31 members, elected by universal suffrage, and the Senate, with 13 members, appointed by the Governor-General in ...
comprises a House of Representatives and a Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
. The 31 members of the House are popularly elected to a maximum five-year term and introduce legislation affecting the development of Belize. The governor-general appoints the 12 members of the Senate, with a Senate president selected by the members. The Senate is responsible for debating and approving bills passed by the House.
Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Parliament of Belize
The National Assembly is the bicameral legislature of the nation of Belize. It is divided into the House of Representatives, with 31 members, elected by universal suffrage, and the Senate, with 13 members, appointed by the Governor-General in co ...
. Constitutional safeguards include freedom of speech, press, worship, movement, and association. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.
Members of the independent judiciary are appointed. The judicial system includes local magistrates grouped under the Magistrates' Court, which hears less serious cases. The Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
(chief justice) hears murder and similarly serious cases, and the Court of Appeal hears appeals from convicted individuals seeking to have their sentences overturned. Defendants may, under certain circumstances, appeal their cases to the Caribbean Court of Justice.
Political culture
In 1935, elections were reinstated, but only 1.8 percent of the population was eligible to vote. In 1954, women were granted the right to vote.
Foreign relations
Belize is a full participating member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
; the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
; the Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS; es, Organización de los Estados Americanos, pt, Organização dos Estados Americanos, french: Organisation des États américains; ''OEA'') is an international organization that was founded on 30 April ...
(OAS); the Central American Integration System
The Central American Integration System ( es, Sistema de la Integración Centroamericana, or SICA) has been the economic and political organization of Central American states since 1 February 1993. On 13 December 1991, the ODECA countries (Spa ...
(SICA); the Caribbean Community
The Caribbean Community (CARICOM or CC) is an intergovernmental organization that is a political and economic union of 15 member states (14 nation-states and one dependency) throughout the Caribbean. They have primary objectives to promote econom ...
(CARICOM); the CARICOM Single Market and Economy (CSME); the Association of Caribbean States (ACS); and the Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ), which currently serves as a final court of appeal for only Barbados, Belize, and Guyana. In 2001 the Caribbean Community heads of government voted on a measure declaring that the region should work towards replacing the UK's Judicial Committee of the Privy Council
The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) is the highest court of appeal for the Crown Dependencies, the British Overseas Territories, some Commonwealth countries and a few institutions in the United Kingdom. Established on 14 Augus ...
as final court of appeal with the Caribbean Court of Justice. It is still in the process of acceding to CARICOM treaties including the trade and single market treaties.
 Belize is an original member (1995) of the
Belize is an original member (1995) of the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
(WTO), and participates actively in its work. The pact involves the Caribbean Forum (CARIFORUM
The Caribbean Forum (CARIFORUM) is a subgroup of the Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States and serves as a base for economic dialogue with the European Union. It was established in 1992. Its membership comprises the 15 Caribbean ...
) subgroup of the Group of African, Caribbean, and Pacific states (ACP). CARIFORUM presently the only part of the wider ACP-bloc that has concluded the full regional trade-pact with the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
.
The British Army Garrison in Belize is used primarily for jungle warfare training, with access to over of jungle terrain.
Belize is a party to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court
The Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court is the treaty that established the International Criminal Court (ICC). It was adopted at a diplomatic conference in Rome, Italy on 17 July 1998Michael P. Scharf (August 1998)''Results of the R ...
.
Armed forces
 The Belize Defence Force (BDF) serves as the country's military and is responsible for protecting the sovereignty of Belize. The BDF, with the Belize National Coast Guard and the Immigration Department, is a department of the Ministry of Defence and Immigration. In 1997 the regular army numbered over 900, the reserve army 381, the air wing 45 and the maritime wing 36, amounting to an overall strength of approximately 1,400.
The Belize Defence Force (BDF) serves as the country's military and is responsible for protecting the sovereignty of Belize. The BDF, with the Belize National Coast Guard and the Immigration Department, is a department of the Ministry of Defence and Immigration. In 1997 the regular army numbered over 900, the reserve army 381, the air wing 45 and the maritime wing 36, amounting to an overall strength of approximately 1,400.["Channel 5 Belize" (28 November 2005),] In 2012, the Belizean government spent about $17 million on the military, constituting 1.08% of the country's gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
(GDP).Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
(see Guatemalan claim to Belizean territory). During the 1980s this included a battalion and No. 1417 Flight RAF
No. 1417 Flight RAF (1417 Flt) was an independent flight of the Royal Air Force which existed between 1941 and 1993 at various times in a variety of roles. This Flight had probably the most interesting incarnations of all the independent aircraft ...
of Harriers. The main British force left in 1994, three years after Guatemala recognized Belizean independence, but the United Kingdom maintained a training presence via the British Army Training and Support Unit Belize (BATSUB) and 25 Flight AAC
25 Flight Army Air Corps is a flight within the British Army's Army Air Corps, currently part of the British Army Training Unit Kenya.
History
The flight was formed in 1987 in Belize where it operated Sioux AH1 helicopters. The flight returne ...
until 2011 when the last British Forces left Ladyville Barracks, with the exception of seconded advisers.
Administrative divisions
 Belize is divided into six districts.
These districts are further divided into 31 constituencies.
Belize is divided into six districts.
These districts are further divided into 31 constituencies. Local government in Belize
Local government in Belize consists of four types of local authorities: city councils, town councils, village councils and community councils. Some rural communities also have an alcalde, a local magistrate who performs both administrative and ju ...
comprises four types of local authorities: city council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counc ...
s, town council
A town council, city council or municipal council is a form of local government for small municipalities.
Usage of the term varies under different jurisdictions.
Republic of Ireland
Town Councils in the Republic of Ireland were the second ti ...
s, village councils
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to ...
and community council
A community council is a public representative body in Great Britain.
In England they may be statutory parish councils by another name, under the Local Government and Public Involvement in Health Act 2007, or they may be non-statutory bodies. In ...
s. The two city councils (Belize City
Belize City is the largest city in Belize and was once the capital of the former British Honduras. According to the 2010 census, Belize City has a population of 57,169 people in 16,162 households. It is at the mouth of the Haulover Creek, wh ...
and Belmopan
Belmopan () is the capital city of Belize. Its population in 2010 was 16,451. In addition to being the smallest capital city in the continental Americas by population, Belmopan is the third-largest settlement in Belize, behind Belize City and S ...
) and seven town councils cover the urban population of the country, while village and community councils cover the rural population.[. Government of Belize. belize.gov.bz]
Guatemalan territorial dispute
Throughout Belize's history, Guatemala has claimed sovereignty over all or part of Belizean territory. This claim is occasionally reflected in maps drawn by Guatemala's government, showing Belize as Guatemala's twenty-third department.Anglo-Guatemalan Treaty of 1859
The history of Guatemala begins with the Maya civilization (300 BC – 250 AD), which was among those that flourished in their country. The country's modern history began with the Spanish conquest of Guatemala in 1524. Most of the great ...
, which obligated the British to build a road between Belize City and Guatemala. At various times, the issue has required mediation by the United Kingdom, Caribbean Community
The Caribbean Community (CARICOM or CC) is an intergovernmental organization that is a political and economic union of 15 member states (14 nation-states and one dependency) throughout the Caribbean. They have primary objectives to promote econom ...
heads of government, the Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS; es, Organización de los Estados Americanos, pt, Organização dos Estados Americanos, french: Organisation des États américains; ''OEA'') is an international organization that was founded on 30 April ...
(OAS), Mexico, and the United States. On 15 April 2018, Guatemala's government held a referendum to determine if the country should take its territorial claim on Belize to the International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; french: Cour internationale de justice, links=no; ), sometimes known as the World Court, is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN). It settles disputes between states in accordanc ...
(ICJ) to settle the long-standing issue. Guatemalans voted 95% yes on the matter. A similar referendum was to be held in Belize on 10 April 2019, but a court ruling led to its postponement. The referendum was held on 8 May 2019, and 55.4% of voters opted to send the matter to the ICJ.
Both countries submitted requests to the ICJ (in 2018 and 2019, respectively) and the ICJ ordered Guatemala's initial brief be submitted by December 2020 and Belize's response by 2022.
Indigenous land claims
Belize backed the United Nations (UN) Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples in 2007, which established legal land rights to indigenous groups. Other court cases have affirmed these rights like the Supreme Court of Belize's 2013 decision to uphold its ruling in 2010 that acknowledges customary land titles as communal land for indigenous peoples. Another such case is the Caribbean Court of Justice's (CCJ) 2015 order on the Belizean government, which stipulated that the country develop a land registry to classify and exercise traditional governance over Mayan lands. Despite these rulings, Belize has made little progress to support the land rights of indigenous communities; for instance, in the two years since the CCJ's decision, Belize's government has failed to launch the Mayan land registry, prompting the group to take action into its own hands.
The exact ramifications of these cases need to be examined. , Belize still struggles to recognize indigenous populations and their respective rights. According to the 50-page voluntary national report Belize created on its progress toward the UN's 2030 Sustainable Development Goals, indigenous groups are not factored into the country's indicators whatsoever. In fact, the groups 'Creole' and 'Garinagu' are not included in the document, and 'Maya' and 'Mestizo' only occur once throughout the entirety of the report. it is yet to be seen if the Belizean government will highlight the consequences of the territorial claim on indigenous land rights prior to the referendum vote in 2019.
Geography
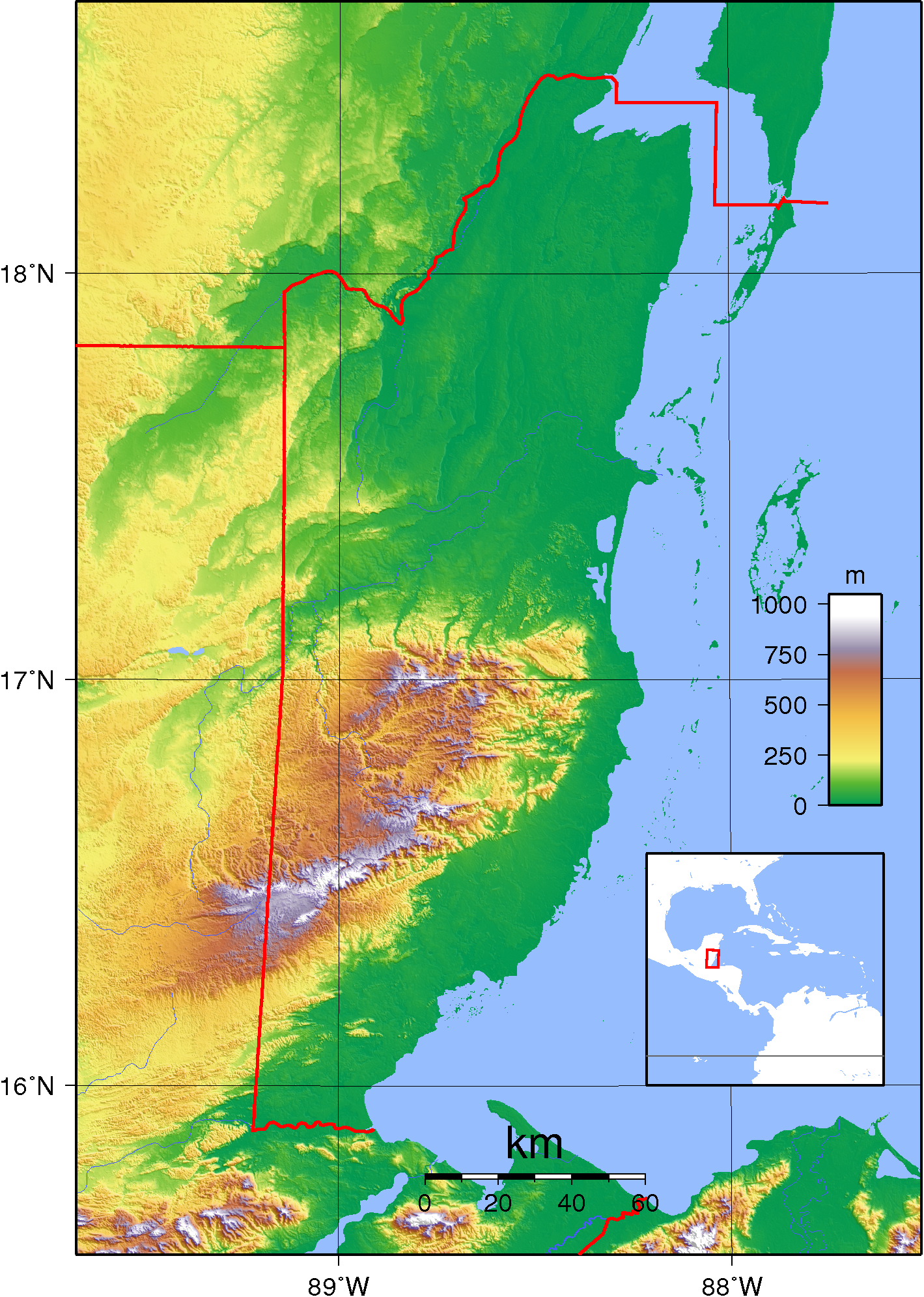
 Belize is on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America. It shares a border on the north with the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, on the west with the Guatemalan department of Petén, and on the south with the Guatemalan department of Izabal. To the east in the Caribbean Sea, the second-longest barrier reef in the world flanks much of the of predominantly
Belize is on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America. It shares a border on the north with the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, on the west with the Guatemalan department of Petén, and on the south with the Guatemalan department of Izabal. To the east in the Caribbean Sea, the second-longest barrier reef in the world flanks much of the of predominantly marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at ...
y coastline. The area of the country totals , an area slightly larger than El Salvador, Israel, New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
, or Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
. The many lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') a ...
s along the coasts and in the northern interior reduces the actual land area to . It is the only Central American country with no Pacific coastline.
Belize is shaped roughly like a rhombus that extends about north-south and about east-west, with a total land boundary length of . The undulating courses of two rivers, the Hondo
Hondo may refer to:
Places
* Rio Hondo (disambiguation), the name of several locations, derived from the Spanish word for "deep"
Canada
* Hondo, Alberta, an unincorporated community
United States
* Hondo, New Mexico, an unincorporated com ...
and the Sarstoon River, define much of the course of the country's northern and southern boundaries. The western border follows no natural features and runs north–south through lowland forest and highland plateau.
The north of Belize consists mostly of flat, swampy coastal plains, in places heavily forested. The flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
is highly diverse considering the small geographical area. The south contains the low mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
of the Maya Mountains
The Maya Mountains are a mountain range located in Belize and eastern Guatemala, in Central America. Etymology
The Maya Mountains were known as the ''Cockscomb'' or ''Coxcomb Mountains'' to Baymen and later Belizeans at least until the mid-2 ...
. The highest point in Belize is Doyle's Delight
Doyle's Delight is the highest peak in Belize at . It lies on the Maya Divide, the main ridge line of the Maya Mountains in southwestern Belize.
The name Doyle's Delight was first coined by Sharon Matola in a 1989 report. The name is based on S ...
at .
Belize's rugged geography has also made the country's coastline and jungle attractive to drug smugglers, who use the country as a gateway into Mexico. In 2011, the United States added Belize to the list of nations considered major drug producers or transit countries for narcotics.
Environment preservation and biodiversity
 Belize has a rich variety of wildlife because of its position between
Belize has a rich variety of wildlife because of its position between North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and South America and a wide range of climates and habitats for plant and animal life. Belize's low human population and approximately of undistributed land make for an ideal home for the more than 5,000 species of plants and hundreds of species of animals, including armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along wi ...
s, snakes, and monkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incomple ...
s.
The Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary
The Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary is a nature reserve in the Stann Creek District of south-central Belize. It was established to protect the forests, fauna and watersheds of an approximately area of the eastern slopes of the Maya Mountains. ...
is a nature reserve in south-central Belize established to protect the forests, fauna, and watersheds of an approximately area of the eastern slopes of the Maya Mountains. The reserve was founded in 1990 as the first wilderness sanctuary for the jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus '' Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
and is regarded by one author as the premier site for jaguar preservation in the world.
Vegetation and flora
While over 60% of Belize's land surface is covered by lush forest,Savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
, scrubland and wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
constitute the remainder of Belize's land cover. Important mangrove ecosystems are also represented across Belize's landscape. Four terrestrial ecoregions lie within the country's borders – the Petén–Veracruz moist forests, Belizian pine forests
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wate ...
, Belizean Coast mangroves
The Belizean Coast mangroves ecoregion covers the brackish and salt-water habitats along the Caribbean Sea coast of Belize, and of Amatique Bay in Guatemala; small parts in the border with Mexico are also present on this ecoregion. The mangroves ...
, and Belizean Reef mangroves.Mesoamerican Biological Corridor
The Mesoamerican Biological Corridor (MBC) is a region that consists of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, and some southern states of Mexico. The area acts as a natural land bridge from South America to North ...
that stretches from southern Mexico to Panama, Belize's biodiversity – both marine
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean.
Marine or marines may refer to:
Ocean
* Maritime (disambiguation)
* Marine art
* Marine biology
* Marine debris
* Marine habitats
* Marine life
* Marine pollution
Military
* ...
and terrestrial – is rich, with abundant flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoo ...
.
 Belize is also a leader in protecting biodiversity and natural resources. According to the World Database on Protected Areas, 37% of Belize's land territory falls under some form of official protection, giving Belize one of the most extensive systems of terrestrial protected areas in the Americas.
Belize is also a leader in protecting biodiversity and natural resources. According to the World Database on Protected Areas, 37% of Belize's land territory falls under some form of official protection, giving Belize one of the most extensive systems of terrestrial protected areas in the Americas.territorial waters
The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potenti ...
, which contain the Belize Barrier Reef
The Belize Barrier Reef is a series of coral reefs straddling the coast of Belize, roughly offshore in the north and in the south within the country limits. The Belize Barrier Reef is a long section of the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System, ...
, are also protected. The Belize Barrier Reef is a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
-recognized World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
and is the second-largest barrier reef in the world, behind Australia's Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, ...
.
A remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth ...
study conducted by the Water Center for the Humid Tropics of Latin America and the Caribbean (CATHALAC) and NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
, in collaboration with the Forest Department and the Land Information Centre (LIC) of the government of Belize's Ministry of Natural Resources and the Environment (MNRE), and published in August 2010 revealed that Belize's forest cover in early 2010 was approximately 62.7%, down from 75.9% in late 1980.USAID
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $27 bi ...
-supporte
SERVIR
study by CATHALAC, NASA, and the MNRE also showed that Belize's protected areas have been extremely effective in protecting the country's forests. While only some 6.4% of forests inside of legally declared protected areas were cleared between 1980 and 2010, over a quarter of forests outside of protected areas were lost between 1980 and 2010.
As a country with a relatively high forest cover and a low deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
rate, Belize has significant potential for participation in initiatives such as REDD. Significantly, the SERVIR study on Belize's deforestationGroup on Earth Observations
The Group on Earth Observations (GEO) coordinates international efforts to build a Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS). It links existing and planned Earth observation systems and supports the development of new ones in cases of pe ...
(GEO), of which Belize is a member nation.
Natural resources and energy
Belize is known to have a number of economically important minerals, but none in quantities large enough to warrant mining. These minerals include dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
, barite
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate ( Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
(source of barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
), bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
(source of aluminium), cassiterite
Cassiterite is a tin oxide mineral, SnO2. It is generally opaque, but it is translucent in thin crystals. Its luster and multiple crystal faces produce a desirable gem. Cassiterite was the chief tin ore throughout ancient history and remains t ...
(source of tin), and gold. In 1990 limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, used in road construction, was the only mineral resource exploited for domestic or export use.
In 2006, the cultivation of newly discovered crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
in the town of Spanish Lookout
Spanish Lookout is a settlement in the Cayo District of Belize in Central America. According to the 2010 census, Spanish Lookout had a population of 2,253 people in 482 households. Spanish Lookout is a community of Mennonites.
The Mennonite commu ...
has presented new prospects and problems for this developing nation.biocapacity
The biocapacity or biological capacity of an ecosystem is an estimate of its production of certain biological materials such as natural resources, and its absorption and filtering of other materials such as carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chem ...
in Belize is much higher than world average. In 2016, Belize had 3.8 global hectaresecological footprint
The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounti ...
of consumption. This means they use more biocapacity than Belize contains. As a result, Belize is running a biocapacity deficit.[
]
Belize Barrier Reef

 The Belize Barrier Reef is a series of
The Belize Barrier Reef is a series of coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s straddling the coast of Belize, roughly offshore in the north and in the south within the country limits. The Belize Barrier Reef is a section of the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System, which is continuous from Cancún on the northeast tip of the Yucatán Peninsula through the Riviera Maya
The Riviera Maya () is a tourism and resort district south of Cancun, Mexico. It straddles the coastal Federal Highway 307, along the Caribbean coastline of the state of Quintana Roo, located in the eastern portion of the Yucatán Peninsula. H ...
up to Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
making it one of the largest coral reef systems in the world.
It is the top tourist destination in Belize, popular for scuba diving and snorkelling, and attracting almost half of its 260,000 visitors. It is also vital to its fishing industry.World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
in 1996 due to its vulnerability and the fact that it contains important natural habitats for in-situ conservation of biodiversity.
Species
The Belize Barrier Reef is home to a large diversity of plants and animals, and is one of the most diverse ecosystems of the world:
* 70 hard coral species
* 36 Alcyonacea, soft coral species
* 500 species of fish
* hundreds of invertebrate species
With ~90% of the reef still yet to be researched, some estimate that only 10% of all species have been discovered.
Conservation
Belize became the first country in the world to completely ban bottom trawling in December 2010. In December 2015, Belize banned offshore oil drilling within of the Barrier Reef and all of its seven World Heritage Sites.
Despite these protective measures, the reef remains under threat from Marine pollution, oceanic pollution as well as uncontrolled tourism, shipping, and fishing. Other threats include hurricanes, along with global warming and the resulting increase in ocean temperatures, which causes coral bleaching. It is claimed by scientists that over 40% of Belize's coral reef has been damaged since 1998.
Climate
 Belize has a tropical climate with pronounced wet season, wet and dry seasons, although there are significant variations in weather patterns by region. Temperatures vary according to elevation, proximity to the coast, and the moderating effects of the northeast trade winds off the Caribbean. Average temperatures in the coastal regions range from in January to in July. Temperatures are slightly higher inland, except for the southern highland plateaus, such as the Mountain Pine Ridge, where it is noticeably cooler year round. Overall, the seasons are marked more by differences in humidity and rainfall than in temperature.
Average rainfall varies considerably, from in the north and west to over in the extreme south. Seasonal differences in rainfall are greatest in the northern and central regions of the country where, between January and April or May, less than of rainfall per month. The dry season is shorter in the south, normally only lasting from February to April. A shorter, less rainy period, known locally as the "little dry", usually occurs in late July or August, after the onset of the rainy season.
Tropical cyclone, Hurricanes have played key—and devastating—roles in History of Belize, Belizean history. In 1931, an unnamed hurricane destroyed over two-thirds of the buildings in Belize City and killed more than 1,000 people. In 1955, Hurricane Janet levelled the northern town of Corozal Town, Corozal. Only six years later, Hurricane Hattie struck the central coastal area of the country, with winds in excess of and storm tides. The devastation of Belize City for the second time in thirty years prompted the relocation of the capital some inland to the planned city of
Belize has a tropical climate with pronounced wet season, wet and dry seasons, although there are significant variations in weather patterns by region. Temperatures vary according to elevation, proximity to the coast, and the moderating effects of the northeast trade winds off the Caribbean. Average temperatures in the coastal regions range from in January to in July. Temperatures are slightly higher inland, except for the southern highland plateaus, such as the Mountain Pine Ridge, where it is noticeably cooler year round. Overall, the seasons are marked more by differences in humidity and rainfall than in temperature.
Average rainfall varies considerably, from in the north and west to over in the extreme south. Seasonal differences in rainfall are greatest in the northern and central regions of the country where, between January and April or May, less than of rainfall per month. The dry season is shorter in the south, normally only lasting from February to April. A shorter, less rainy period, known locally as the "little dry", usually occurs in late July or August, after the onset of the rainy season.
Tropical cyclone, Hurricanes have played key—and devastating—roles in History of Belize, Belizean history. In 1931, an unnamed hurricane destroyed over two-thirds of the buildings in Belize City and killed more than 1,000 people. In 1955, Hurricane Janet levelled the northern town of Corozal Town, Corozal. Only six years later, Hurricane Hattie struck the central coastal area of the country, with winds in excess of and storm tides. The devastation of Belize City for the second time in thirty years prompted the relocation of the capital some inland to the planned city of Belmopan
Belmopan () is the capital city of Belize. Its population in 2010 was 16,451. In addition to being the smallest capital city in the continental Americas by population, Belmopan is the third-largest settlement in Belize, behind Belize City and S ...
.
In 1978, Hurricane Greta-Olivia, Hurricane Greta caused more than US$25 million in damage along the southern coast. In 2000, Hurricane Keith, the wettest tropical cyclone in the nation's record, stalled, and hit the nation as a Category 4 storm on 1 October, causing 19 deaths and at least $280 million in damage. Soon after, on 9 October 2001, Hurricane Iris made landfall at Monkey River Town as a Category 4 storm. The storm demolished most of the homes in the village, and destroyed the banana crop. In 2007, Hurricane Dean made landfall as a Category 5 storm only north of the Belize–Mexico border. Dean caused extensive damage in northern Belize.
In 2010, Belize was directly affected by the Category 2 Hurricane Richard, which made landfall approximately south-southeast of Belize City at around 00:45 UTC on 25 October 2010. The storm moved inland towards Belmopan
Belmopan () is the capital city of Belize. Its population in 2010 was 16,451. In addition to being the smallest capital city in the continental Americas by population, Belmopan is the third-largest settlement in Belize, behind Belize City and S ...
, causing estimated damage of Belize dollar, BZ$33.8 million ($17.4 million 2010 USD), primarily from damage to crops and housing.
The most recent hurricane to affect the nation was Hurricane Nana (2020), Hurricane Nana in 2020.
Economy

 Belize has a small, mostly private enterprise economy that is based primarily on agriculture, agro-based industry, and merchandising, with tourism and construction recently assuming greater importance.
Belize has a small, mostly private enterprise economy that is based primarily on agriculture, agro-based industry, and merchandising, with tourism and construction recently assuming greater importance.crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
, and petroleum. , oil production was .European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, and Caribbean Community, CARICOM.
Industrial infrastructure
 The largest integrated electric utility and the principal distributor in Belize is Belize Electricity Limited. BEL was approximately 70% owned by Fortis Inc., a Canadian investor-owned distribution utility. Fortis took over the management of BEL in 1999, at the invitation of the government of Belize in an attempt to mitigate prior financial problems with the locally managed utility. In addition to its regulated investment in BEL, Fortis owns Belize Electric Company Limited (BECOL), a non-regulated hydroelectric generation business that operates three hydroelectric generating facilities on the Macal River.
On 14 June 2011, the government of Belize nationalized the ownership interest of Fortis Inc. in Belize Electricity Ltd. The utility encountered serious financial problems after the country's Public Utilities Commission (PUC) in 2008 "disallowed the recovery of previously incurred fuel and purchased power costs in customer rates and set customer rates at a level that does not allow BEL to earn a fair and reasonable return", Fortis said in a June 2011 statement. BEL appealed this judgement to the Court of Appeal, with a hearing expected in 2012. In May 2011, the Supreme Court of Belize granted BEL's application to prevent the PUC from taking any enforcement actions pending the appeal. The Belize Chamber of Commerce and Industry issued a statement saying the government had acted in haste and expressed concern over the message it sent to investors.
In August 2009, the government of Belize nationalized Belize Telemedia Limited (BTL), which now competes directly with Speednet. As a result of the nationalization process, the interconnection agreements are again subject to negotiations. Both BTL and Speednet sell basic telephone services, national and international calls, prepaid services, cellular services via GSM 1900 megahertz (MHz) and 4G LTE respectively, international cellular roaming, fixed wireless, fibre-to-the-home internet service, and national and international data networks.
The largest integrated electric utility and the principal distributor in Belize is Belize Electricity Limited. BEL was approximately 70% owned by Fortis Inc., a Canadian investor-owned distribution utility. Fortis took over the management of BEL in 1999, at the invitation of the government of Belize in an attempt to mitigate prior financial problems with the locally managed utility. In addition to its regulated investment in BEL, Fortis owns Belize Electric Company Limited (BECOL), a non-regulated hydroelectric generation business that operates three hydroelectric generating facilities on the Macal River.
On 14 June 2011, the government of Belize nationalized the ownership interest of Fortis Inc. in Belize Electricity Ltd. The utility encountered serious financial problems after the country's Public Utilities Commission (PUC) in 2008 "disallowed the recovery of previously incurred fuel and purchased power costs in customer rates and set customer rates at a level that does not allow BEL to earn a fair and reasonable return", Fortis said in a June 2011 statement. BEL appealed this judgement to the Court of Appeal, with a hearing expected in 2012. In May 2011, the Supreme Court of Belize granted BEL's application to prevent the PUC from taking any enforcement actions pending the appeal. The Belize Chamber of Commerce and Industry issued a statement saying the government had acted in haste and expressed concern over the message it sent to investors.
In August 2009, the government of Belize nationalized Belize Telemedia Limited (BTL), which now competes directly with Speednet. As a result of the nationalization process, the interconnection agreements are again subject to negotiations. Both BTL and Speednet sell basic telephone services, national and international calls, prepaid services, cellular services via GSM 1900 megahertz (MHz) and 4G LTE respectively, international cellular roaming, fixed wireless, fibre-to-the-home internet service, and national and international data networks.
Tourism
A combination of natural factors – climate, the Belize Barrier Reef
The Belize Barrier Reef is a series of coral reefs straddling the coast of Belize, roughly offshore in the north and in the south within the country limits. The Belize Barrier Reef is a long section of the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System, ...
, over 450 offshore Cays (islands), excellent fishing, safe waters for boating, scuba diving, snorkelling and freediving, numerous rivers for rafting, and kayaking, various Jungle (terrain), jungle and wildlife reserves of fauna and flora, for hiking, bird watching, and helicopter touring, as well as many Maya sites – support the thriving tourism and ecotourism industry.
Development costs are high, but the government of Belize has made tourism its second development priority after agriculture. In 2012, tourist arrivals totalled 917,869 (with about 584,683 from the United States) and tourist receipts amounted to over $1.3 billion.
After COVID-19 struck tourism, Belize became the first country in the Caribbean to allow vaccinated travelers to visit without a COVID-19 test.
Transport
Demographics
Belize's population is estimated to be 441,471 in 2022.
Ethnic groups
The Maya
The Maya are thought to have been in Belize and the Yucatán region since the second millennium BCE. Many died in conflicts between constantly warring tribes or by catching disease from invading Europeans. Three Maya groups now inhabit the country: The Yucatec (who came from Yucatán, Mexico, to escape the savage Caste War of Yucatán, Caste War of the 1840s), the Mopan people, Mopan (indigenous to Belize but were forced out to Guatemala by the British for raiding settlements; they returned to Belize to evade enslavement by the Guatemalans in the 19th century), and Q'eqchi' people, Q'eqchi' (also fled from slavery in Guatemala in the 19th century). The latter groups are chiefly found in the Toledo District. The Maya speak their native languages and Spanish, and are also often fluent in English and Belize Kriol.
Creoles
Belizean Creoles are primarily mixed-raced descendants of African slave trade, West and Central Africans who were brought to the British Honduras (present-day Belize along the Bay of Honduras) as well as the English people, English and Scottish people, Scottish log cutters, known as the Baymen
The Baymen were the earliest European settlers along the Bay of Honduras in what eventually became the colony of British Honduras (modern-day Belize).
Settlement
The first Baymen settled in the Belize City area in the 1630s. They were buccane ...
who human trafficking, trafficked them.[(Johnson,Melissa A.) ''The Making of Race and Place in Nineteenth-Century British Honduras''. Environmental History, Vol. 8, No. 4 (Oct., 2003), pp. 598-617](_blank)
Over the years they have also intermarried with Miskito people, Miskito from Nicaragua, Jamaicans and other Caribbean people, Hispanic Belizean, Mestizos, White Caribbeans, Europeans, Garifunas, Maya people, Mayas, and Ethnic Chinese in Belize, Chinese and Asian Indians in Belize, Indians. The latter were brought to Belize as indentured laborers. Majority of Kriols trace their ancestry to several of the aforementioned groups.
For all intents and purposes, Creole is an ethnic and linguistic denomination. Some natives, even with blonde hair and blue eyes, may call themselves Creoles.
Garinagu
 The Garinagu (singular ''Garifuna''), at around 4.5% of the population, are a mix of West/Central African, Arawaks, Arawak, and Island Carib ancestry. Though they were captives removed from their homelands, these people were never documented as slaves. The two prevailing theories are that, in 1635, they were either the survivors of two recorded shipwrecks or somehow took over the ship they came on.
The Garinagu (singular ''Garifuna''), at around 4.5% of the population, are a mix of West/Central African, Arawaks, Arawak, and Island Carib ancestry. Though they were captives removed from their homelands, these people were never documented as slaves. The two prevailing theories are that, in 1635, they were either the survivors of two recorded shipwrecks or somehow took over the ship they came on.
Mestizos
The Mestizo culture are people of mixed Spanish and Maya descent. They originally came to Belize in 1847, to escape the Caste War of Yucatán, Caste War, which occurred when thousands of Mayas rose against the state in Yucatán and massacred over one-third of the population. The surviving others fled across the borders into British territory. The Mestizos are found everywhere in Belize but most make their homes in the northern districts of Corozal and Orange Walk. Some other mestizos came from El Salvador, Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
, Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
, and Nicaragua. The Mestizos are the largest ethnic group in Belize and make up approximately half of the population. The Mestizo towns centre on a main square, and social life focuses on the Catholic Church built on one side of it. Spanish is the main language of most Mestizos and Spanish descendants, but many speak English and Belize Kriol fluently.
German-speaking Mennonites
 The majority of the Mennonites, Mennonite population comprises so-called Russian Mennonites of German descent who settled in the Russian Empire during the 18th and 19th centuries. Most Russian Mennonites live in Mennonite settlements like
The majority of the Mennonites, Mennonite population comprises so-called Russian Mennonites of German descent who settled in the Russian Empire during the 18th and 19th centuries. Most Russian Mennonites live in Mennonite settlements like Spanish Lookout
Spanish Lookout is a settlement in the Cayo District of Belize in Central America. According to the 2010 census, Spanish Lookout had a population of 2,253 people in 482 households. Spanish Lookout is a community of Mennonites.
The Mennonite commu ...
, Shipyard, Belize, Shipyard, Little Belize, and Blue Creek. These Mennonites speak Plautdietsch (a Low German, Low German dialect) in everyday life, but use mostly Standard German for reading (the Bible) and writing. The Plautdietsch-speaking Mennonites in Mexico, Mennonites came mostly from Mexico in the years after 1958 and they are trilingual with proficiency in Spanish. There are also some mainly Pennsylvania Dutch-speaking Old Order Mennonites who came from the United States and Canada in the late 1960s. They live primarily in Upper Barton Creek and associated settlements. These Mennonites attracted people from different Anabaptist backgrounds who formed a new community. They look quite similar to Amish, Old Order Amish, but are different from them.
Other groups
The remaining 5% or so of the population consist of a mix of Indians in Belize, Indians, Ethnic Chinese in Belize, Chinese, White people, Whites from the United Kingdom, United States and Canada, and many other foreign groups brought to assist the country's development. During the 1860s, a large influx of East Indians who spent brief periods in Jamaica and American Civil War veterans from Louisiana and other Southern states established Confederate settlements in British Honduras and introduced commercial sugar cane production to the colony, establishing 11 settlements in the interior. The 20th century saw the arrival of more Asian settlers from Mainland China, India, Syria and Lebanon. Said Musa, the son of an immigrant from Palestine (region), Palestine, was the Prime Minister of Belize from 1998 to 2008. Central American immigrants from El Salvador, Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
, Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
and Nicaragua and expatriate Americans and Africans also began to settle in the country.
Emigration, immigration, and demographic shifts
Creoles and other ethnic groups are emigrating mostly to the United States, but also to the United Kingdom and other developed nations for better opportunities. Based on the latest US Census, the number of Belizeans in the United States is approximately 160,000 (including 70,000 legal residents and naturalized citizens), consisting mainly of Creoles and Garinagu.
Because of conflicts in neighbouring Central American nations, Mestizo refugees from El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras have fled to Belize in significant numbers during the 1980s, and have been significantly adding to this group. These two events have been changing the demographics of the nation for the last 30 years.
Languages
English is the official language of Belize. This stems from the country being a former British colony. Belize is the only country in Central America with English as the official language. Also, English is the primary language of public education, government and most media outlets. About half of Belizeans regardless of ethnicity speak a mostly English-based creole called Belizean Creole, Belize Creole (or ''Kriol'' in Belize Creole). Although English is widely used, Kriol is spoken in all situations whether informal, formal, social or interethnic dialogue, even in meetings of the House of Representatives.
When a Creole language exists alongside its lexifier language, as is the case in Belize, a continuum forms between the Creole and the lexifier language. It is therefore difficult to substantiate or differentiate the number of Belize Creole speakers compared to English speakers. Kriol might best be described as the lingua franca of the nation.
Approximately 50% of Belizeans self-identify as ''Mestizo'', ''Latino sine flexione, Latino'', or ''Hispanic'' and 50–70% speak Caribbean Spanish as a native language. When Belize was a British colony, Spanish was banned in schools but today it is widely spoken. Spanglish, "Kitchen Spanish" is an intermediate form of Spanish mixed with Belize Creole, spoken in the northern towns such as Corozal and San Pedro.multilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all E ...
. Being a small, multiethnic state, surrounded by Spanish-speaking nations, the economic and social benefits from multilingualism are high.
Largest cities
Religion
According to the 2010 census, According to PROLADES, Belize was 64.6% Roman Catholic, 27.8% Protestant, 7.6% Other in 1971. Until the late 1990s, Belize was History of Roman Catholicism in Belize, a Roman Catholic majority country. Catholics formed 57% of the population in 1991, and dropped to 49% in 2000. The percentage of Roman Catholics in the population has been decreasing in the past few decades due to the growth of Protestant churches, other religions and non-religious people.
In addition to Catholics, there has always been Protestantism in Belize, a large accompanying Protestant minority. It was brought by British people, British, German people, German, and other settlers to the British colony of British Honduras. From the beginning, it was largely Anglican and Mennonite in nature. The Protestant community in Belize experienced a large Pentecostal and Seventh-Day Adventist influx tied to the recent spread of various Evangelical Protestant denominations throughout Latin America. Geographically speaking, Mennonites in Belize, German Mennonites live mostly in the rural districts of Cayo and Orange Walk.
The Greek Orthodox Church has a presence in Santa Elena, Belize, Santa Elena.
The Association of Religion Data Archives estimates there were 7,776 Baháʼís in Belize in 2005, or 2.5% of the national population. Their estimates suggest this is the highest proportion of Baháʼís in any country. Their data also states that the Baháʼí Faith is the second most common non-Christian religion in Belize, followed by Judaism. Hinduism is followed by most Indian immigrants. Sikhs were the first Indians in Belize, Indian immigrants to Belize (not counting indentured workers), and the former Chief Justice of Belize George Singh was the son of a Sikh diaspora, Sikh immigrant,
According to PROLADES, Belize was 64.6% Roman Catholic, 27.8% Protestant, 7.6% Other in 1971. Until the late 1990s, Belize was History of Roman Catholicism in Belize, a Roman Catholic majority country. Catholics formed 57% of the population in 1991, and dropped to 49% in 2000. The percentage of Roman Catholics in the population has been decreasing in the past few decades due to the growth of Protestant churches, other religions and non-religious people.
In addition to Catholics, there has always been Protestantism in Belize, a large accompanying Protestant minority. It was brought by British people, British, German people, German, and other settlers to the British colony of British Honduras. From the beginning, it was largely Anglican and Mennonite in nature. The Protestant community in Belize experienced a large Pentecostal and Seventh-Day Adventist influx tied to the recent spread of various Evangelical Protestant denominations throughout Latin America. Geographically speaking, Mennonites in Belize, German Mennonites live mostly in the rural districts of Cayo and Orange Walk.
The Greek Orthodox Church has a presence in Santa Elena, Belize, Santa Elena.
The Association of Religion Data Archives estimates there were 7,776 Baháʼís in Belize in 2005, or 2.5% of the national population. Their estimates suggest this is the highest proportion of Baháʼís in any country. Their data also states that the Baháʼí Faith is the second most common non-Christian religion in Belize, followed by Judaism. Hinduism is followed by most Indian immigrants. Sikhs were the first Indians in Belize, Indian immigrants to Belize (not counting indentured workers), and the former Chief Justice of Belize George Singh was the son of a Sikh diaspora, Sikh immigrant,
Health
Belize has a high prevalence of communicable diseases such as respiratory diseases and intestinal illnesses.[Health Agenda 2007 – 2011]
Ministry of Health, Belize
Education
A number of kindergartens, secondary, and tertiary schools in Belize provide quality education for students—mostly funded by the government. Belize has about a dozen List of universities in Belize, tertiary level institutions, the most prominent of which is the University of Belize, which evolved out of the University College of Belize founded in 1986. Before that St. John's College, Belize, St. John's College, founded in 1877, dominated the tertiary education field. The Open Campus of the University of the West Indies has a site in Belize. It also has campuses in Barbados, Trinidad, and Jamaica. The government of Belize contributes financially to the UWI.
Education in Belize is compulsory between the ages of 6 and 14 years. , the literacy rate in Belize was estimated at 79.7%,
Crime
Belize has moderate rates of violent crime.Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
, but higher than Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
and El Salvador.
Social structure
Belize's social structure is marked by enduring differences in the distribution of wealth, power, and prestige. Because of the small size of Belize's population and the intimate scale of social relations, the social distance between the rich and the poor, while significant, is nowhere as vast as in other Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
and Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
n societies, such as Jamaica and El Salvador. Belize lacks the violent class and racial conflict that has figured so prominently in the social life of its Central American neighbours.[Rutheiser, Charles C., "Structure of Belizean Society". In Merrill.]
Political and economic power remain vested in the hands of the local elite. The sizeable middle group is composed of peoples of different ethnic backgrounds. This middle group does not constitute a unified social class, but rather a number of middle-class and working-class groups, loosely oriented around shared dispositions toward education, cultural respectability, and possibilities for upward social mobility. These beliefs, and the social practices they engender, help distinguish the middle group from the grass roots majority of the Belizean people.[
]
Women
In 2021, the World Economic Forum ranked Belize 90th out of 156 countries in its Global Gender Gap Report. Of all the countries in Latin America and the Caribbean, Belize ranked fourth from last. It ranked higher in the categories of "economic participation and opportunity" and "health and survival", but very low in "political empowerment".
Culture
In Belizean folklore, there are the legends of Lang Bobi Suzi, La Llorona, La Sucia, Tata Duende, Anansi, Xtabay, Sisimite and the cadejo.
Most of the public holidays in Belize are traditional Commonwealth and liturgical year, Christian holidays, although some are specific to Belizean culture such as Garifuna Settlement Day and Heroes and Benefactors' Day, formerly Baron Bliss Day. In addition, the month of September is considered a September Celebrations of Belize, special time of national celebration called September Celebrations with a whole month of activities on a special events calendar. Besides Independence Day and St. George's Caye Day, Belizeans also celebrate Carnival during September, which typically includes several events spread across multiple days, with the main event being the Carnival Road March, usually held the Saturday before 10 September. In some areas of Belize, it is celebrated at the traditional time before Lent (in February).
Cuisine
 Belizean cuisine is an amalgamation of all ethnicities in the nation, and their respectively wide variety of foods. It might best be described as both similar to Mexican/Central American cuisine and Jamaican/Anglo-Caribbean cuisine but very different from these areas as well, with Belizean touches and innovation which have been handed down by generations. All immigrant communities add to the diversity of Belizean food, including the Indian and Chinese communities.
The Belizean diet can be both very modern and traditional. There are no rules. Breakfast typically consists of bread, flour tortillas, or fry jacks (deep fried dough pieces) that are often homemade. Fry jacks are eaten with various cheeses, "fry" beans, various forms of eggs or cereal, along with powdered milk, coffee, or tea. Tacos made from corn or flour tortillas and meat pies can also be consumed for a hearty breakfast from a street vendor. Midday meals are the main meals for Belizeans, usually called "dinner". They vary, from foods such as rice and beans with or without coconut milk, tamales, empanadas, "panades" (fried maize shells with beans or fish), meat pies, escabeche (onion soup), chimole (soup), caldo de pollo, caldo, stewed chicken, and garnaches (fried tortillas with beans, cheese, and sauce) to various constituted dinners featuring some type of rice and beans, meat and salad, or coleslaw. Fried "fry" chicken is another common course.
In rural areas, meals are typically simpler than in cities. The Maya use maize, beans, or Cucurbita, squash for most meals, and the Garifuna are fond of seafood, cassava (particularly made into cassava bread or ereba), and vegetables. The nation abounds with restaurants and fast food establishments that are fairly affordable. Local fruits are quite common, but raw vegetables from the markets less so. Mealtime is a communion for families and schools and some businesses close at midday for lunch, reopening later in the afternoon.
Belizean cuisine is an amalgamation of all ethnicities in the nation, and their respectively wide variety of foods. It might best be described as both similar to Mexican/Central American cuisine and Jamaican/Anglo-Caribbean cuisine but very different from these areas as well, with Belizean touches and innovation which have been handed down by generations. All immigrant communities add to the diversity of Belizean food, including the Indian and Chinese communities.
The Belizean diet can be both very modern and traditional. There are no rules. Breakfast typically consists of bread, flour tortillas, or fry jacks (deep fried dough pieces) that are often homemade. Fry jacks are eaten with various cheeses, "fry" beans, various forms of eggs or cereal, along with powdered milk, coffee, or tea. Tacos made from corn or flour tortillas and meat pies can also be consumed for a hearty breakfast from a street vendor. Midday meals are the main meals for Belizeans, usually called "dinner". They vary, from foods such as rice and beans with or without coconut milk, tamales, empanadas, "panades" (fried maize shells with beans or fish), meat pies, escabeche (onion soup), chimole (soup), caldo de pollo, caldo, stewed chicken, and garnaches (fried tortillas with beans, cheese, and sauce) to various constituted dinners featuring some type of rice and beans, meat and salad, or coleslaw. Fried "fry" chicken is another common course.
In rural areas, meals are typically simpler than in cities. The Maya use maize, beans, or Cucurbita, squash for most meals, and the Garifuna are fond of seafood, cassava (particularly made into cassava bread or ereba), and vegetables. The nation abounds with restaurants and fast food establishments that are fairly affordable. Local fruits are quite common, but raw vegetables from the markets less so. Mealtime is a communion for families and schools and some businesses close at midday for lunch, reopening later in the afternoon.
Music
Bachata is the most popular genre of music along with Punta and has become one of the most popular kinds of music in Belize. It is distinctly Caribbean, and is sometimes said to be ready for international popularization like similarly descended styles (reggae, calypso music, calypso, merengue (music), merengue).
Brukdown is a modern style of Belizean music related to Calypso music, calypso. It evolved out of the music and dance of loggers, especially a form called buru. Reggae, dance hall, and Soca music, soca imported from Jamaica and the rest of the West Indies, rapping, rap, hip-hop, heavy metal and rock music from the United States, are also popular among the youth of Belize.
Sports
 The major sports in Belize are association football, football, basketball, volleyball and Cycle sport, cycling, with smaller followings of boat racing, Sport of athletics, athletics, softball, cricket, Rugby football, rugby and netball. Fishing is also popular in coastal areas of Belize.
The Cross Country Cycling Classic, also known as the "cross country" race or the Holy Saturday Cross Country Cycling Classic, is considered one of the most important Belize sports events. This one-day sports event is meant for amateur cyclists but has also gained worldwide popularity. The history of Cross Country Cycling Classic in Belize dates back to the period when Monrad Metzgen picked up the idea from a small village on the Northern Highway (Belize), Northern Highway (now Phillip Goldson Highway). The people from this village used to cover long distances on their bicycles to attend the weekly game of cricket. He improvised on this observation by creating a sporting event on the difficult terrain of the George Price Highway, Western Highway, which was then poorly built.
Another major annual sporting event in Belize is the La Ruta Maya Belize River Challenge, a 4-day canoe marathon held each year in March. The race runs from San Ignacio, Belize, San Ignacio to
The major sports in Belize are association football, football, basketball, volleyball and Cycle sport, cycling, with smaller followings of boat racing, Sport of athletics, athletics, softball, cricket, Rugby football, rugby and netball. Fishing is also popular in coastal areas of Belize.
The Cross Country Cycling Classic, also known as the "cross country" race or the Holy Saturday Cross Country Cycling Classic, is considered one of the most important Belize sports events. This one-day sports event is meant for amateur cyclists but has also gained worldwide popularity. The history of Cross Country Cycling Classic in Belize dates back to the period when Monrad Metzgen picked up the idea from a small village on the Northern Highway (Belize), Northern Highway (now Phillip Goldson Highway). The people from this village used to cover long distances on their bicycles to attend the weekly game of cricket. He improvised on this observation by creating a sporting event on the difficult terrain of the George Price Highway, Western Highway, which was then poorly built.
Another major annual sporting event in Belize is the La Ruta Maya Belize River Challenge, a 4-day canoe marathon held each year in March. The race runs from San Ignacio, Belize, San Ignacio to Belize City
Belize City is the largest city in Belize and was once the capital of the former British Honduras. According to the 2010 census, Belize City has a population of 57,169 people in 16,162 households. It is at the mouth of the Haulover Creek, wh ...
, a distance of .
National symbols
 The national flower of Belize is the black orchid (''Prosthechea cochleata'', also known as ''Encyclia cochleata''). The national tree is the
The national flower of Belize is the black orchid (''Prosthechea cochleata'', also known as ''Encyclia cochleata''). The national tree is the mahogany
Mahogany is a straight-grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus ''Swietenia'', indigenous to the AmericasBridgewater, Samuel (2012). ''A Natural History of Belize: Inside the Maya Forest''. Austin: Unive ...
tree (''Swietenia macrophylla''), which inspired the national motto ''Sub Umbra Floreo'', which means "Under the shade I flourish". The national ground-dwelling animal is the Baird's tapir and the national bird is the keel-billed toucan (''Ramphastos sulphuratus'').
See also
* Index of Belize-related articles
* Outline of Belize
Explanatory notes
References
External links
Government of Belize
– Official governmental site
Official webpage of Queen Elizabeth II as former Queen of Belize
*
Belize National Emergency Management Organization
– Official governmental site
Belize Wildlife Conservation Network
– Belize Wildlife Conservation Network
CATHALAC
– Water Center for the Humid Tropics of Latin America and the Caribbean
LANIC Belize page
Belize
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Belize
at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
*
Belize
from the BBC News
Key Development Forecasts for Belize
from International Futures
Hydromet.gov.bz
– Official website of the Belize National Meteorological Service
Bileez Kriol Wiki - A wiki in Belizean Creole about Belize
{{coord, 17, 4, N, 88, 42, W, type:country_region:BZ, display=title
Belize,
Countries in Central America
English-speaking countries and territories
Former Spanish colonies
Member states of the Caribbean Community
Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
Member states of the United Nations
Small Island Developing States
Spanish-speaking countries and territories
States and territories established in 1981
Yucatán Peninsula
1981 establishments in Belize
Countries in North America
Countries in the Caribbean
 The
The 

 The British first appointed a superintendent over the Belize area in 1786. Before then the British government had not recognized the settlement as a colony for fear of provoking a Spanish attack. The delay in government oversight allowed the settlers to establish their own laws and forms of government. During this period, a few successful settlers gained control of the local legislature, known as the Public Meeting, as well as of most of the settlement's land and timber.
Throughout the 18th century, the Spanish attacked Belize every time war broke out with Britain. The
The British first appointed a superintendent over the Belize area in 1786. Before then the British government had not recognized the settlement as a colony for fear of provoking a Spanish attack. The delay in government oversight allowed the settlers to establish their own laws and forms of government. During this period, a few successful settlers gained control of the local legislature, known as the Public Meeting, as well as of most of the settlement's land and timber.
Throughout the 18th century, the Spanish attacked Belize every time war broke out with Britain. The  Following the war, the colony's economy stagnated. Britain's decision to
Following the war, the colony's economy stagnated. Britain's decision to  Belize is a
Belize is a  Belize is an original member (1995) of the
Belize is an original member (1995) of the  The Belize Defence Force (BDF) serves as the country's military and is responsible for protecting the sovereignty of Belize. The BDF, with the Belize National Coast Guard and the Immigration Department, is a department of the Ministry of Defence and Immigration. In 1997 the regular army numbered over 900, the reserve army 381, the air wing 45 and the maritime wing 36, amounting to an overall strength of approximately 1,400. In 2005, the maritime wing became part of the Belizean Coast Guard."Channel 5 Belize" (28 November 2005), In 2012, the Belizean government spent about $17 million on the military, constituting 1.08% of the country's
The Belize Defence Force (BDF) serves as the country's military and is responsible for protecting the sovereignty of Belize. The BDF, with the Belize National Coast Guard and the Immigration Department, is a department of the Ministry of Defence and Immigration. In 1997 the regular army numbered over 900, the reserve army 381, the air wing 45 and the maritime wing 36, amounting to an overall strength of approximately 1,400. In 2005, the maritime wing became part of the Belizean Coast Guard."Channel 5 Belize" (28 November 2005), In 2012, the Belizean government spent about $17 million on the military, constituting 1.08% of the country's 
 Belize is on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America. It shares a border on the north with the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, on the west with the Guatemalan department of Petén, and on the south with the Guatemalan department of Izabal. To the east in the Caribbean Sea, the second-longest barrier reef in the world flanks much of the of predominantly
Belize is on the Caribbean coast of northern Central America. It shares a border on the north with the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, on the west with the Guatemalan department of Petén, and on the south with the Guatemalan department of Izabal. To the east in the Caribbean Sea, the second-longest barrier reef in the world flanks much of the of predominantly  Belize has a rich variety of wildlife because of its position between
Belize has a rich variety of wildlife because of its position between 
 The Belize Barrier Reef is a series of
The Belize Barrier Reef is a series of 
 Belize has a small, mostly private enterprise economy that is based primarily on agriculture, agro-based industry, and merchandising, with tourism and construction recently assuming greater importance. The country is also a producer of industrial minerals,
Belize has a small, mostly private enterprise economy that is based primarily on agriculture, agro-based industry, and merchandising, with tourism and construction recently assuming greater importance. The country is also a producer of industrial minerals,  The Garinagu (singular ''Garifuna''), at around 4.5% of the population, are a mix of West/Central African, Arawaks, Arawak, and Island Carib ancestry. Though they were captives removed from their homelands, these people were never documented as slaves. The two prevailing theories are that, in 1635, they were either the survivors of two recorded shipwrecks or somehow took over the ship they came on.
Throughout history they have been incorrectly labelled as Black Caribs. When the British took over Saint Vincent and the Grenadines after the Treaty of Paris (1763), Treaty of Paris in 1763, they were opposed by French settlers and their Garinagu allies. The Garinagu eventually surrendered to the British in 1796. The British separated the more African-looking Garifunas from the more indigenous-looking ones. 5,000 Garinagu were exiled from the Grenadine island of Baliceaux. About 2,500 of them survived the voyage to Roatán, an island off the coast of Honduras. The Garifuna language belongs to the Arawakan languages, Arawakan language family, but has a large number of loanwords from Carib languages and from English.
Because Roatán was too small and infertile to support their population, the Garinagu petitioned the Spanish authorities of Honduras to be allowed to settle on the mainland coast. The Spanish employed them as soldiers, and they spread along the Caribbean coast of Central America. The Garinagu settled in Seine Bight, Punta Gorda, Belize, Punta Gorda and Punta Negra, Belize, by way of Honduras as early as 1802. In Belize, 19 November 1832 is the date officially recognized as "Garifuna Settlement Day" in Dangriga.
According to one genetic study, their ancestry is on average 76% Sub Saharan African, 20% Arawak/Island Carib and 4% European ethnic groups, European.
The Garinagu (singular ''Garifuna''), at around 4.5% of the population, are a mix of West/Central African, Arawaks, Arawak, and Island Carib ancestry. Though they were captives removed from their homelands, these people were never documented as slaves. The two prevailing theories are that, in 1635, they were either the survivors of two recorded shipwrecks or somehow took over the ship they came on.
Throughout history they have been incorrectly labelled as Black Caribs. When the British took over Saint Vincent and the Grenadines after the Treaty of Paris (1763), Treaty of Paris in 1763, they were opposed by French settlers and their Garinagu allies. The Garinagu eventually surrendered to the British in 1796. The British separated the more African-looking Garifunas from the more indigenous-looking ones. 5,000 Garinagu were exiled from the Grenadine island of Baliceaux. About 2,500 of them survived the voyage to Roatán, an island off the coast of Honduras. The Garifuna language belongs to the Arawakan languages, Arawakan language family, but has a large number of loanwords from Carib languages and from English.
Because Roatán was too small and infertile to support their population, the Garinagu petitioned the Spanish authorities of Honduras to be allowed to settle on the mainland coast. The Spanish employed them as soldiers, and they spread along the Caribbean coast of Central America. The Garinagu settled in Seine Bight, Punta Gorda, Belize, Punta Gorda and Punta Negra, Belize, by way of Honduras as early as 1802. In Belize, 19 November 1832 is the date officially recognized as "Garifuna Settlement Day" in Dangriga.
According to one genetic study, their ancestry is on average 76% Sub Saharan African, 20% Arawak/Island Carib and 4% European ethnic groups, European.
 According to PROLADES, Belize was 64.6% Roman Catholic, 27.8% Protestant, 7.6% Other in 1971. Until the late 1990s, Belize was History of Roman Catholicism in Belize, a Roman Catholic majority country. Catholics formed 57% of the population in 1991, and dropped to 49% in 2000. The percentage of Roman Catholics in the population has been decreasing in the past few decades due to the growth of Protestant churches, other religions and non-religious people.
In addition to Catholics, there has always been Protestantism in Belize, a large accompanying Protestant minority. It was brought by British people, British, German people, German, and other settlers to the British colony of British Honduras. From the beginning, it was largely Anglican and Mennonite in nature. The Protestant community in Belize experienced a large Pentecostal and Seventh-Day Adventist influx tied to the recent spread of various Evangelical Protestant denominations throughout Latin America. Geographically speaking, Mennonites in Belize, German Mennonites live mostly in the rural districts of Cayo and Orange Walk.
The Greek Orthodox Church has a presence in Santa Elena, Belize, Santa Elena.
The Association of Religion Data Archives estimates there were 7,776 Baháʼís in Belize in 2005, or 2.5% of the national population. Their estimates suggest this is the highest proportion of Baháʼís in any country. Their data also states that the Baháʼí Faith is the second most common non-Christian religion in Belize, followed by Judaism. Hinduism is followed by most Indian immigrants. Sikhs were the first Indians in Belize, Indian immigrants to Belize (not counting indentured workers), and the former Chief Justice of Belize George Singh was the son of a Sikh diaspora, Sikh immigrant, there was also a Sikh cabinet minister. Muslims claim that there have been Muslims in Belize since the 16th century having been brought over from Africa as slaves, but there are no sources for that claim. The Muslim population of today started in the 1980s. Muslims numbered 243 in 2000 and 577 in 2010 according to the official statistics. and comprise 0.16 percent of the population. A mosque is at the Islamic Mission of Belize (IMB), also known as the Muslim Community of Belize. Another mosque, Masjid Al-Falah, officially opened in 2008 in Belize City.
According to PROLADES, Belize was 64.6% Roman Catholic, 27.8% Protestant, 7.6% Other in 1971. Until the late 1990s, Belize was History of Roman Catholicism in Belize, a Roman Catholic majority country. Catholics formed 57% of the population in 1991, and dropped to 49% in 2000. The percentage of Roman Catholics in the population has been decreasing in the past few decades due to the growth of Protestant churches, other religions and non-religious people.
In addition to Catholics, there has always been Protestantism in Belize, a large accompanying Protestant minority. It was brought by British people, British, German people, German, and other settlers to the British colony of British Honduras. From the beginning, it was largely Anglican and Mennonite in nature. The Protestant community in Belize experienced a large Pentecostal and Seventh-Day Adventist influx tied to the recent spread of various Evangelical Protestant denominations throughout Latin America. Geographically speaking, Mennonites in Belize, German Mennonites live mostly in the rural districts of Cayo and Orange Walk.
The Greek Orthodox Church has a presence in Santa Elena, Belize, Santa Elena.
The Association of Religion Data Archives estimates there were 7,776 Baháʼís in Belize in 2005, or 2.5% of the national population. Their estimates suggest this is the highest proportion of Baháʼís in any country. Their data also states that the Baháʼí Faith is the second most common non-Christian religion in Belize, followed by Judaism. Hinduism is followed by most Indian immigrants. Sikhs were the first Indians in Belize, Indian immigrants to Belize (not counting indentured workers), and the former Chief Justice of Belize George Singh was the son of a Sikh diaspora, Sikh immigrant, there was also a Sikh cabinet minister. Muslims claim that there have been Muslims in Belize since the 16th century having been brought over from Africa as slaves, but there are no sources for that claim. The Muslim population of today started in the 1980s. Muslims numbered 243 in 2000 and 577 in 2010 according to the official statistics. and comprise 0.16 percent of the population. A mosque is at the Islamic Mission of Belize (IMB), also known as the Muslim Community of Belize. Another mosque, Masjid Al-Falah, officially opened in 2008 in Belize City.
 Belizean cuisine is an amalgamation of all ethnicities in the nation, and their respectively wide variety of foods. It might best be described as both similar to Mexican/Central American cuisine and Jamaican/Anglo-Caribbean cuisine but very different from these areas as well, with Belizean touches and innovation which have been handed down by generations. All immigrant communities add to the diversity of Belizean food, including the Indian and Chinese communities.
The Belizean diet can be both very modern and traditional. There are no rules. Breakfast typically consists of bread, flour tortillas, or fry jacks (deep fried dough pieces) that are often homemade. Fry jacks are eaten with various cheeses, "fry" beans, various forms of eggs or cereal, along with powdered milk, coffee, or tea. Tacos made from corn or flour tortillas and meat pies can also be consumed for a hearty breakfast from a street vendor. Midday meals are the main meals for Belizeans, usually called "dinner". They vary, from foods such as rice and beans with or without coconut milk, tamales, empanadas, "panades" (fried maize shells with beans or fish), meat pies, escabeche (onion soup), chimole (soup), caldo de pollo, caldo, stewed chicken, and garnaches (fried tortillas with beans, cheese, and sauce) to various constituted dinners featuring some type of rice and beans, meat and salad, or coleslaw. Fried "fry" chicken is another common course.
In rural areas, meals are typically simpler than in cities. The Maya use maize, beans, or Cucurbita, squash for most meals, and the Garifuna are fond of seafood, cassava (particularly made into cassava bread or ereba), and vegetables. The nation abounds with restaurants and fast food establishments that are fairly affordable. Local fruits are quite common, but raw vegetables from the markets less so. Mealtime is a communion for families and schools and some businesses close at midday for lunch, reopening later in the afternoon.
Belizean cuisine is an amalgamation of all ethnicities in the nation, and their respectively wide variety of foods. It might best be described as both similar to Mexican/Central American cuisine and Jamaican/Anglo-Caribbean cuisine but very different from these areas as well, with Belizean touches and innovation which have been handed down by generations. All immigrant communities add to the diversity of Belizean food, including the Indian and Chinese communities.
The Belizean diet can be both very modern and traditional. There are no rules. Breakfast typically consists of bread, flour tortillas, or fry jacks (deep fried dough pieces) that are often homemade. Fry jacks are eaten with various cheeses, "fry" beans, various forms of eggs or cereal, along with powdered milk, coffee, or tea. Tacos made from corn or flour tortillas and meat pies can also be consumed for a hearty breakfast from a street vendor. Midday meals are the main meals for Belizeans, usually called "dinner". They vary, from foods such as rice and beans with or without coconut milk, tamales, empanadas, "panades" (fried maize shells with beans or fish), meat pies, escabeche (onion soup), chimole (soup), caldo de pollo, caldo, stewed chicken, and garnaches (fried tortillas with beans, cheese, and sauce) to various constituted dinners featuring some type of rice and beans, meat and salad, or coleslaw. Fried "fry" chicken is another common course.
In rural areas, meals are typically simpler than in cities. The Maya use maize, beans, or Cucurbita, squash for most meals, and the Garifuna are fond of seafood, cassava (particularly made into cassava bread or ereba), and vegetables. The nation abounds with restaurants and fast food establishments that are fairly affordable. Local fruits are quite common, but raw vegetables from the markets less so. Mealtime is a communion for families and schools and some businesses close at midday for lunch, reopening later in the afternoon.
 The major sports in Belize are association football, football, basketball, volleyball and Cycle sport, cycling, with smaller followings of boat racing, Sport of athletics, athletics, softball, cricket, Rugby football, rugby and netball. Fishing is also popular in coastal areas of Belize.
The Cross Country Cycling Classic, also known as the "cross country" race or the Holy Saturday Cross Country Cycling Classic, is considered one of the most important Belize sports events. This one-day sports event is meant for amateur cyclists but has also gained worldwide popularity. The history of Cross Country Cycling Classic in Belize dates back to the period when Monrad Metzgen picked up the idea from a small village on the Northern Highway (Belize), Northern Highway (now Phillip Goldson Highway). The people from this village used to cover long distances on their bicycles to attend the weekly game of cricket. He improvised on this observation by creating a sporting event on the difficult terrain of the George Price Highway, Western Highway, which was then poorly built.
Another major annual sporting event in Belize is the La Ruta Maya Belize River Challenge, a 4-day canoe marathon held each year in March. The race runs from San Ignacio, Belize, San Ignacio to
The major sports in Belize are association football, football, basketball, volleyball and Cycle sport, cycling, with smaller followings of boat racing, Sport of athletics, athletics, softball, cricket, Rugby football, rugby and netball. Fishing is also popular in coastal areas of Belize.
The Cross Country Cycling Classic, also known as the "cross country" race or the Holy Saturday Cross Country Cycling Classic, is considered one of the most important Belize sports events. This one-day sports event is meant for amateur cyclists but has also gained worldwide popularity. The history of Cross Country Cycling Classic in Belize dates back to the period when Monrad Metzgen picked up the idea from a small village on the Northern Highway (Belize), Northern Highway (now Phillip Goldson Highway). The people from this village used to cover long distances on their bicycles to attend the weekly game of cricket. He improvised on this observation by creating a sporting event on the difficult terrain of the George Price Highway, Western Highway, which was then poorly built.
Another major annual sporting event in Belize is the La Ruta Maya Belize River Challenge, a 4-day canoe marathon held each year in March. The race runs from San Ignacio, Belize, San Ignacio to  The national flower of Belize is the black orchid (''Prosthechea cochleata'', also known as ''Encyclia cochleata''). The national tree is the
The national flower of Belize is the black orchid (''Prosthechea cochleata'', also known as ''Encyclia cochleata''). The national tree is the