Belgrade Nonet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the
 The first farming people to settle in the region are associated with the
The first farming people to settle in the region are associated with the
 In 442, the area was ravaged by
In 442, the area was ravaged by
 Seven decades after the initial siege, on 28 August 1521, the fort was finally captured by Suleiman the Magnificent, 250,000 Turkish soldiers, and over 100 ships. Subsequently, most of the city was razed to the ground and its entire Orthodox Christian population was deported to Istanbul to an area that has since become known as the Belgrade forest. Belgrade was made the seat of the Pashalik of Belgrade (also known as the Sanjak of Smederevo), and quickly became the second largest Ottoman town in Europe at over 100,000 people, surpassed only by Constantinople. Ottoman rule introduced Ottoman architecture, including numerous mosques, and the city was resurrected—now by Oriental influences. In 1594, a major Banat Uprising, Serb rebellion was crushed by the Ottomans. In retribution, Grand vizier, Grand Vizier Sinan Pasha ordered the relics of Saint Sava to be publicly torched on the Vračar plateau; in the 20th century, the church of Saint Sava was built to commemorate this event.
Occupied by the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburgs three times (Siege of Belgrade (1688), 1688–1690, Kingdom of Serbia (1718–39), 1717–1739, Siege of Belgrade (1789), 1789–1791), headed by the Holy Roman Empire, Holy Roman Princes Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian of Bavaria and Prince Eugene of Savoy, Eugene of Savoy, and field marshal Baron Ernst Gideon von Laudon, respectively, Belgrade was quickly recaptured by the Ottomans and substantially razed each time. During this period, the city was affected by the two Great Serbian Migrations, in which hundreds of thousands of Serbs, led by two Serbian Patriarchs, retreated together with the Austrian soldiers into the Habsburg Empire, settling in today's Vojvodina and Slavonia.
Seven decades after the initial siege, on 28 August 1521, the fort was finally captured by Suleiman the Magnificent, 250,000 Turkish soldiers, and over 100 ships. Subsequently, most of the city was razed to the ground and its entire Orthodox Christian population was deported to Istanbul to an area that has since become known as the Belgrade forest. Belgrade was made the seat of the Pashalik of Belgrade (also known as the Sanjak of Smederevo), and quickly became the second largest Ottoman town in Europe at over 100,000 people, surpassed only by Constantinople. Ottoman rule introduced Ottoman architecture, including numerous mosques, and the city was resurrected—now by Oriental influences. In 1594, a major Banat Uprising, Serb rebellion was crushed by the Ottomans. In retribution, Grand vizier, Grand Vizier Sinan Pasha ordered the relics of Saint Sava to be publicly torched on the Vračar plateau; in the 20th century, the church of Saint Sava was built to commemorate this event.
Occupied by the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburgs three times (Siege of Belgrade (1688), 1688–1690, Kingdom of Serbia (1718–39), 1717–1739, Siege of Belgrade (1789), 1789–1791), headed by the Holy Roman Empire, Holy Roman Princes Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian of Bavaria and Prince Eugene of Savoy, Eugene of Savoy, and field marshal Baron Ernst Gideon von Laudon, respectively, Belgrade was quickly recaptured by the Ottomans and substantially razed each time. During this period, the city was affected by the two Great Serbian Migrations, in which hundreds of thousands of Serbs, led by two Serbian Patriarchs, retreated together with the Austrian soldiers into the Habsburg Empire, settling in today's Vojvodina and Slavonia.
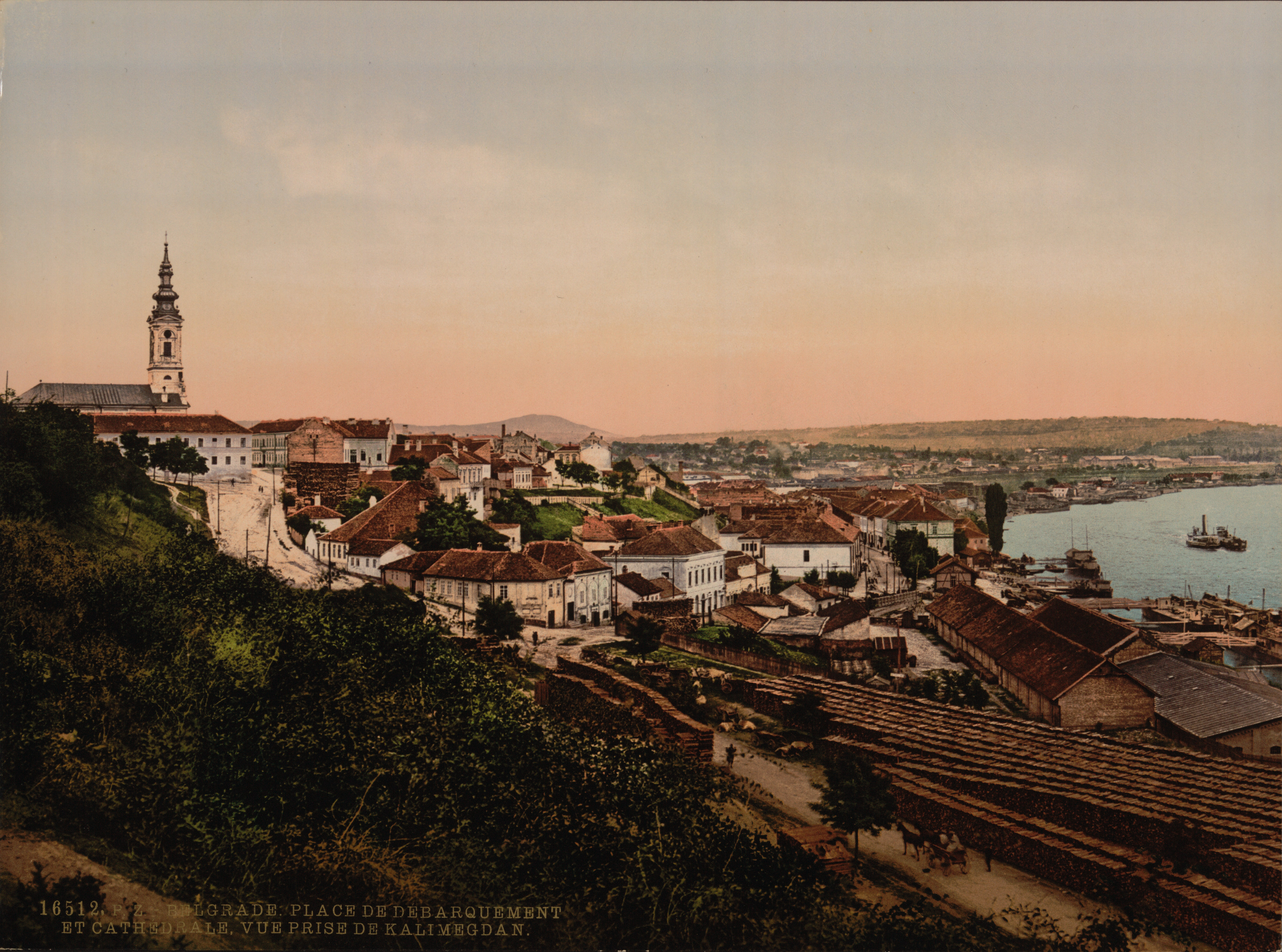 At the beginning of the 19th century, Belgrade was predominantly inhabited by a Muslim population. Traces of Ottoman rule and architecture—such as mosques and bazaars, were to remain a prominent part of Belgrade's townscape into the 19th century; several decades, even, after Serbia was granted autonomy from the Ottoman Empire.
During the First Serbian Uprising, Serbian revolutionaries held the city from 8 January 1807 until 1813, when it was retaken by the Ottomans. After the Second Serbian Uprising in 1815, Serbia achieved some sort of sovereignty, which was formally recognised by the Ottoman Porte, Porte in 1830.
The development of Belgrade architecture after 1815 can be divided into four periods. In the first phase, which lasted from 1815 to 1835, the dominant architectural style was still of a Balkan character, with substantial Ottoman influence. At the same time, an interest in joining the European mainstream allowed Central and Western European architecture to flourish. Between 1835 and 1850, the amount of Neoclassicism, neoclassicist and baroque buildings south of the Austrian border rose considerably, exemplified by St. Michael's Cathedral, Belgrade, St Michael's Cathedral (Serbian: ''Saborna crkva)'', completed in 1840. Between 1850 and 1875, new architecture was characterised by a turn towards the newly popular Romanticism, along with older European architectural styles. Typical of Central European cities in the last quarter of the 19th century, the fourth phase was characterised by an Eclecticism, eclecticist style based on the Renaissance and Baroque periods.
At the beginning of the 19th century, Belgrade was predominantly inhabited by a Muslim population. Traces of Ottoman rule and architecture—such as mosques and bazaars, were to remain a prominent part of Belgrade's townscape into the 19th century; several decades, even, after Serbia was granted autonomy from the Ottoman Empire.
During the First Serbian Uprising, Serbian revolutionaries held the city from 8 January 1807 until 1813, when it was retaken by the Ottomans. After the Second Serbian Uprising in 1815, Serbia achieved some sort of sovereignty, which was formally recognised by the Ottoman Porte, Porte in 1830.
The development of Belgrade architecture after 1815 can be divided into four periods. In the first phase, which lasted from 1815 to 1835, the dominant architectural style was still of a Balkan character, with substantial Ottoman influence. At the same time, an interest in joining the European mainstream allowed Central and Western European architecture to flourish. Between 1835 and 1850, the amount of Neoclassicism, neoclassicist and baroque buildings south of the Austrian border rose considerably, exemplified by St. Michael's Cathedral, Belgrade, St Michael's Cathedral (Serbian: ''Saborna crkva)'', completed in 1840. Between 1850 and 1875, new architecture was characterised by a turn towards the newly popular Romanticism, along with older European architectural styles. Typical of Central European cities in the last quarter of the 19th century, the fourth phase was characterised by an Eclecticism, eclecticist style based on the Renaissance and Baroque periods.
 In 1841, Prince Mihailo Obrenović moved the capital of the Principality of Serbia from Kragujevac to Belgrade. During his first reign (1815–1839), Prince Miloš Obrenović pursued expansion of the city's population through the addition of new settlements, aiming and succeeding to make Belgrade the centre of the Principality's administrative, military and cultural institutions. His project of creating a new market space (the Abadžijska čaršija), however, was less successful; trade continued to be conducted in the centuries-old Donja čaršija and Gornja čaršija. Still, new construction projects were typical for the Christian quarters as the older Muslim quarters declined; from Serbia's autonomy until 1863, the number of Belgrade quarters even decreased, mainly as a consequence of the gradual disappearance of the city's Muslim population. An Ottoman city map from 1863 counts only 9 Muslim quarters (''mahalas''). The names of only five such neighbourhoods are known today: Ali-pašina, Reis-efendijina, Jahja-pašina, Bajram-begova, and Laz Hadži-Mahmudova. Following the Čukur Fountain incident, Belgrade was bombed by the Ottomans.
On 18 April 1867, the Ottoman government ordered the Ottoman garrison, which had been since 1826 the last representation of Ottoman suzerainty in Serbia, withdrawn from Kalemegdan. The forlorn Porte's only stipulation was that the Ottoman flag continue to fly over the fortress alongside the Serbian one. Serbia's ''de facto'' independence dates from this event. In the following years, urban planner Emilijan Josimović had a significant influence on Belgrade. He conceptualised a regulation plan for the city in 1867, in which he proposed the replacement of the town's crooked streets with a grid plan. Of great importance also was the construction of independent Serbian political and cultural institutions, as well as the city's now-plentiful parks. Pointing to Josimović's work, Serbian scholars have noted an important break with Ottoman traditions. However, Istanbul—the capital city of the state to which Belgrade and Serbia ''de jure'' still belonged—underwent similar changes.
In 1841, Prince Mihailo Obrenović moved the capital of the Principality of Serbia from Kragujevac to Belgrade. During his first reign (1815–1839), Prince Miloš Obrenović pursued expansion of the city's population through the addition of new settlements, aiming and succeeding to make Belgrade the centre of the Principality's administrative, military and cultural institutions. His project of creating a new market space (the Abadžijska čaršija), however, was less successful; trade continued to be conducted in the centuries-old Donja čaršija and Gornja čaršija. Still, new construction projects were typical for the Christian quarters as the older Muslim quarters declined; from Serbia's autonomy until 1863, the number of Belgrade quarters even decreased, mainly as a consequence of the gradual disappearance of the city's Muslim population. An Ottoman city map from 1863 counts only 9 Muslim quarters (''mahalas''). The names of only five such neighbourhoods are known today: Ali-pašina, Reis-efendijina, Jahja-pašina, Bajram-begova, and Laz Hadži-Mahmudova. Following the Čukur Fountain incident, Belgrade was bombed by the Ottomans.
On 18 April 1867, the Ottoman government ordered the Ottoman garrison, which had been since 1826 the last representation of Ottoman suzerainty in Serbia, withdrawn from Kalemegdan. The forlorn Porte's only stipulation was that the Ottoman flag continue to fly over the fortress alongside the Serbian one. Serbia's ''de facto'' independence dates from this event. In the following years, urban planner Emilijan Josimović had a significant influence on Belgrade. He conceptualised a regulation plan for the city in 1867, in which he proposed the replacement of the town's crooked streets with a grid plan. Of great importance also was the construction of independent Serbian political and cultural institutions, as well as the city's now-plentiful parks. Pointing to Josimović's work, Serbian scholars have noted an important break with Ottoman traditions. However, Istanbul—the capital city of the state to which Belgrade and Serbia ''de jure'' still belonged—underwent similar changes.
 In May 1868, ''knez'' Mihailo was assassinated with his cousin Anka Konstantinović while riding in a carriage in his country residence.
With the Principality of Serbia, Principality's full independence in 1878 and its transformation into the Kingdom of Serbia in 1882, Belgrade once again became a key city in the Balkans, and developed rapidly. Nevertheless, conditions in Serbia remained those of an overwhelmingly agrarian country, even with the opening of a railway to Niš, Serbia's second city. In 1900, the capital had only 70,000 inhabitants (at the time Serbia numbered 2.5 million). Still, by 1905, the population had grown to more than 80,000 and, by the outbreak of World War I in 1914, it had surpassed the 100,000 citizens, disregarding
In May 1868, ''knez'' Mihailo was assassinated with his cousin Anka Konstantinović while riding in a carriage in his country residence.
With the Principality of Serbia, Principality's full independence in 1878 and its transformation into the Kingdom of Serbia in 1882, Belgrade once again became a key city in the Balkans, and developed rapidly. Nevertheless, conditions in Serbia remained those of an overwhelmingly agrarian country, even with the opening of a railway to Niš, Serbia's second city. In 1900, the capital had only 70,000 inhabitants (at the time Serbia numbered 2.5 million). Still, by 1905, the population had grown to more than 80,000 and, by the outbreak of World War I in 1914, it had surpassed the 100,000 citizens, disregarding
 The First World War began on 28 July 1914 when Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. Most of the subsequent Balkan offensives occurred near Belgrade. Austro-Hungarian Navy, Austro-Hungarian Monitor (warship), monitors shelled Belgrade on 29 July 1914, and it was taken by the Austro-Hungarian Army under General Oskar Potiorek on 30 November. On 15 December, it was re-taken by Serbian Campaign (World War I), Serbian troops under Marshal Radomir Putnik. After a prolonged battle which destroyed much of the city, starting on 6 October 1915, Belgrade fell to German Army (German Empire), German and Austro-Hungarian troops commanded by Field Marshal August von Mackensen on 9 October of the same year. The city was liberated by Serbian and French Army, French troops on 1 November 1918, under the command of Marshal Louis Franchet d'Espèrey of France and Alexander I of Yugoslavia, Crown Prince Alexander of Serbia. Belgrade, decimated as a front-line city, lost the title of largest city in the Kingdom of Serbia, Kingdom to Subotica for some time.
The First World War began on 28 July 1914 when Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. Most of the subsequent Balkan offensives occurred near Belgrade. Austro-Hungarian Navy, Austro-Hungarian Monitor (warship), monitors shelled Belgrade on 29 July 1914, and it was taken by the Austro-Hungarian Army under General Oskar Potiorek on 30 November. On 15 December, it was re-taken by Serbian Campaign (World War I), Serbian troops under Marshal Radomir Putnik. After a prolonged battle which destroyed much of the city, starting on 6 October 1915, Belgrade fell to German Army (German Empire), German and Austro-Hungarian troops commanded by Field Marshal August von Mackensen on 9 October of the same year. The city was liberated by Serbian and French Army, French troops on 1 November 1918, under the command of Marshal Louis Franchet d'Espèrey of France and Alexander I of Yugoslavia, Crown Prince Alexander of Serbia. Belgrade, decimated as a front-line city, lost the title of largest city in the Kingdom of Serbia, Kingdom to Subotica for some time.
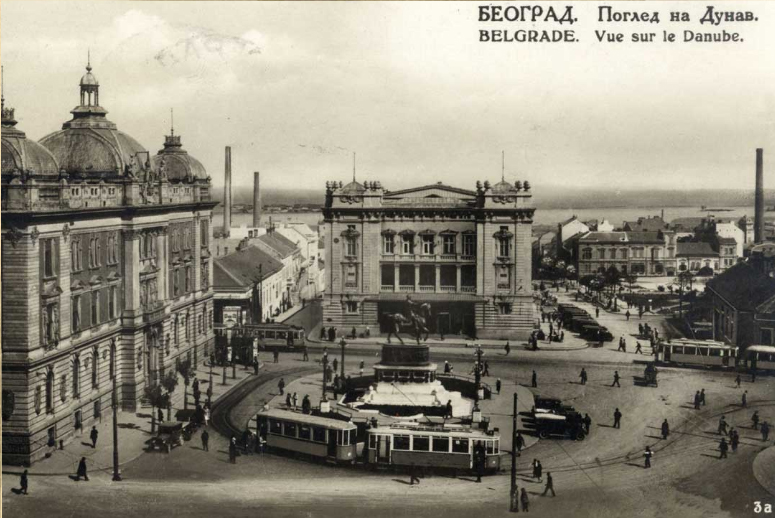 After the war, Belgrade became the capital of the new Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929. The Kingdom was split into Subdivisions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, banovinas and Belgrade, together with
After the war, Belgrade became the capital of the new Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929. The Kingdom was split into Subdivisions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, banovinas and Belgrade, together with
 During the summer and fall of 1941, in reprisal for guerrilla attacks, the Germans carried out several massacres of Belgrade citizens; in particular, members of the History of the Jews in Serbia, Jewish community were subject to mass shootings at the order of General Franz Böhme, the German Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia, Military Governor of Serbia. Böhme rigorously enforced the rule that for every German killed, 100 Serbs or Jews would be shot. Belgrade became the first city in Europe to be declared by the Nazi occupation forces to be Judenfrei. The resistance movement in Belgrade was led by Major Žarko Todorović from 1941 until his arrest in 1943.
Just like Rotterdam, which was devastated twice by both German and Allied bombing, Allied bombing of Yugoslavia in World War II#1944 Easter bombing, Belgrade was bombed once more during World War II, this time by the Allies of World War II, Allies on 16 April 1944, killing at least 1,100 people. This bombing fell on the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christian Orthodox Easter, Easter. Most of the city remained under German occupation until 20 October 1944, when it was liberated by the Red Army and the Communist Partisans (Yugoslavia), Yugoslav Partisans.
On 29 November 1945, Marshal Josip Broz Tito proclaimed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia in Belgrade (later renamed to Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia on 7 April 1963). Higher estimates from the former secret police place the victim count of political persecutions in Belgrade at 10,000.
During the summer and fall of 1941, in reprisal for guerrilla attacks, the Germans carried out several massacres of Belgrade citizens; in particular, members of the History of the Jews in Serbia, Jewish community were subject to mass shootings at the order of General Franz Böhme, the German Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia, Military Governor of Serbia. Böhme rigorously enforced the rule that for every German killed, 100 Serbs or Jews would be shot. Belgrade became the first city in Europe to be declared by the Nazi occupation forces to be Judenfrei. The resistance movement in Belgrade was led by Major Žarko Todorović from 1941 until his arrest in 1943.
Just like Rotterdam, which was devastated twice by both German and Allied bombing, Allied bombing of Yugoslavia in World War II#1944 Easter bombing, Belgrade was bombed once more during World War II, this time by the Allies of World War II, Allies on 16 April 1944, killing at least 1,100 people. This bombing fell on the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christian Orthodox Easter, Easter. Most of the city remained under German occupation until 20 October 1944, when it was liberated by the Red Army and the Communist Partisans (Yugoslavia), Yugoslav Partisans.
On 29 November 1945, Marshal Josip Broz Tito proclaimed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia in Belgrade (later renamed to Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia on 7 April 1963). Higher estimates from the former secret police place the victim count of political persecutions in Belgrade at 10,000.
 In 2014, Belgrade Waterfront, an urban renewal project, was initiated by the Government of Serbia and its Emirati partner, Eagle Hills Properties. Around €3.5 billion was to be jointly invested by the Serbian government and their Emirati partners. The project includes office and luxury apartment buildings, five-star hotels, a shopping mall and the envisioned 'Belgrade Tower'. The project is, however, quite controversial—there are a number of uncertainties regarding its funding, necessity, and its architecture's arguable lack of harmony with the rest of the city.
In addition to Belgrade Waterfront, the city is under rapid development and reconstruction, especially in the area of New Belgrade, Novi Beograd, where (as of 2020) apartment and office buildings were under construction to support the burgeoning Belgrade IT sector, now one of Serbia's largest economic players. In September 2020, there were around 2000 active construction sites in Belgrade.
In 2014, Belgrade Waterfront, an urban renewal project, was initiated by the Government of Serbia and its Emirati partner, Eagle Hills Properties. Around €3.5 billion was to be jointly invested by the Serbian government and their Emirati partners. The project includes office and luxury apartment buildings, five-star hotels, a shopping mall and the envisioned 'Belgrade Tower'. The project is, however, quite controversial—there are a number of uncertainties regarding its funding, necessity, and its architecture's arguable lack of harmony with the rest of the city.
In addition to Belgrade Waterfront, the city is under rapid development and reconstruction, especially in the area of New Belgrade, Novi Beograd, where (as of 2020) apartment and office buildings were under construction to support the burgeoning Belgrade IT sector, now one of Serbia's largest economic players. In September 2020, there were around 2000 active construction sites in Belgrade.
 One of the characteristics of the city terrain is mass wasting. On the territory covered by the General Urban Plan there are 1,155 recorded mass wasting points, out of which 602 are active and 248 are labeled as the 'high risk'. They cover almost 30% of the city territory and include several types of mass wasting. Downhill creeps are located on the slopes above the rivers, mostly on the clay or loam soils, inclined between 7 and 20%. Most critical ones are in Karaburma, Zvezdara, Višnjica, Serbia, Višnjica, Vinča and Ritopek, in the Danube valley, and Umka, and especially its neighbourhood of Duboko, in the Sava valley. They have moving and dormant phases, and some of them have been recorded for centuries. Less active downhill creep areas include the entire Terazijska Terasa, Terazije slope above the Sava (Kalemegdan, Savamala), which can be seen by the inclination of the Pobednik monument and the tower of the St. Michael's Cathedral, Belgrade, Cathedral Church, and the Voždovac section, between Banjica and Autokomanda.
Landslides encompass smaller areas, develop on the steep cliffs, sometimes being inclined up to 90%. They are mostly located in the artificial loess hills of Zemun: Gardoš, Ćukovac and Kalvarija (Zemun), Kalvarija.
However, the majority of the land movement in Belgrade, some 90%, is triggered by the construction works and faulty water supply system (burst pipes, etc.). The neighbourhood of Mirijevo is considered to be the most successful project of fixing the problem. During the construction of the neighbourhood from the 1970s, the terrain was systematically improved and the movement of the land is today completely halted.
One of the characteristics of the city terrain is mass wasting. On the territory covered by the General Urban Plan there are 1,155 recorded mass wasting points, out of which 602 are active and 248 are labeled as the 'high risk'. They cover almost 30% of the city territory and include several types of mass wasting. Downhill creeps are located on the slopes above the rivers, mostly on the clay or loam soils, inclined between 7 and 20%. Most critical ones are in Karaburma, Zvezdara, Višnjica, Serbia, Višnjica, Vinča and Ritopek, in the Danube valley, and Umka, and especially its neighbourhood of Duboko, in the Sava valley. They have moving and dormant phases, and some of them have been recorded for centuries. Less active downhill creep areas include the entire Terazijska Terasa, Terazije slope above the Sava (Kalemegdan, Savamala), which can be seen by the inclination of the Pobednik monument and the tower of the St. Michael's Cathedral, Belgrade, Cathedral Church, and the Voždovac section, between Banjica and Autokomanda.
Landslides encompass smaller areas, develop on the steep cliffs, sometimes being inclined up to 90%. They are mostly located in the artificial loess hills of Zemun: Gardoš, Ćukovac and Kalvarija (Zemun), Kalvarija.
However, the majority of the land movement in Belgrade, some 90%, is triggered by the construction works and faulty water supply system (burst pipes, etc.). The neighbourhood of Mirijevo is considered to be the most successful project of fixing the problem. During the construction of the neighbourhood from the 1970s, the terrain was systematically improved and the movement of the land is today completely halted.
 Belgrade has a humid subtropical climate (''Cfa''), according to Köppen climate classification, with four seasons and uniformly spread precipitation. Monthly averages range from in January to in July, with an annual mean of . There are, on average, 31 days a year when the temperature is above , and 95 days when the temperature is above . Belgrade receives about of precipitation a year, with late spring being wettest. The average annual number of sunny hours is 2,112.
The highest officially recorded temperature in Belgrade was on 24 July 2007, while on the other end, the lowest temperature was on 10 January 1893.
Belgrade has a humid subtropical climate (''Cfa''), according to Köppen climate classification, with four seasons and uniformly spread precipitation. Monthly averages range from in January to in July, with an annual mean of . There are, on average, 31 days a year when the temperature is above , and 95 days when the temperature is above . Belgrade receives about of precipitation a year, with late spring being wettest. The average annual number of sunny hours is 2,112.
The highest officially recorded temperature in Belgrade was on 24 July 2007, while on the other end, the lowest temperature was on 10 January 1893.
 Belgrade is a separate territorial unit in Serbia, with its own autonomous city authority. The Assembly of the City of Belgrade has 110 members, elected on four-year terms. A 13-member City Council, elected by the Assembly and presided over by the mayor and his deputy, has the control and supervision of the city administration, which manages day-to-day administrative affairs. It is divided into 14 Secretariats, each having a specific portfolio such as traffic or health care, and several professional services, agencies and institutes.
The 2022 Belgrade City Assembly election was won by the Serbian Progressive Party, which formed a ruling coalition with the Socialist Party of Serbia. Between 2004 and 2013, the Democratic Party (Serbia), Democratic Party was in power. Due to the importance of Belgrade in political and economic life of Serbia, the office of city's mayor is often described as the third most important office in the state, after the Prime Minister of Serbia, President of the Government and the President of Serbia, President of the Republic.
As the capital city, Belgrade is seat of all Serbian state authorities – executive (government), executive, legislative, judiciary, and the headquarters of almost all national political parties as well as 75 diplomatic missions. This includes the National Assembly (Serbia), National Assembly, the Presidency, the Government of Serbia and all the ministries, Supreme Court of Cassation (Serbia), Supreme Court of Cassation and the Constitutional Court of Serbia, Constitutional Court.
Belgrade is a separate territorial unit in Serbia, with its own autonomous city authority. The Assembly of the City of Belgrade has 110 members, elected on four-year terms. A 13-member City Council, elected by the Assembly and presided over by the mayor and his deputy, has the control and supervision of the city administration, which manages day-to-day administrative affairs. It is divided into 14 Secretariats, each having a specific portfolio such as traffic or health care, and several professional services, agencies and institutes.
The 2022 Belgrade City Assembly election was won by the Serbian Progressive Party, which formed a ruling coalition with the Socialist Party of Serbia. Between 2004 and 2013, the Democratic Party (Serbia), Democratic Party was in power. Due to the importance of Belgrade in political and economic life of Serbia, the office of city's mayor is often described as the third most important office in the state, after the Prime Minister of Serbia, President of the Government and the President of Serbia, President of the Republic.
As the capital city, Belgrade is seat of all Serbian state authorities – executive (government), executive, legislative, judiciary, and the headquarters of almost all national political parties as well as 75 diplomatic missions. This includes the National Assembly (Serbia), National Assembly, the Presidency, the Government of Serbia and all the ministries, Supreme Court of Cassation (Serbia), Supreme Court of Cassation and the Constitutional Court of Serbia, Constitutional Court.
 The city is divided into 17 municipalities. Previously, they were classified into 10 urban (lying completely or partially within borders of the city proper) and 7 suburban municipalities, whose centres are smaller towns. With the new 2010 City statute, they were all given equal status, with the proviso that suburban ones (except Surčin) have certain autonomous powers, chiefly related with construction, infrastructure and public utilities.
Most of the municipalities are situated on the southern side of the Danube and
The city is divided into 17 municipalities. Previously, they were classified into 10 urban (lying completely or partially within borders of the city proper) and 7 suburban municipalities, whose centres are smaller towns. With the new 2010 City statute, they were all given equal status, with the proviso that suburban ones (except Surčin) have certain autonomous powers, chiefly related with construction, infrastructure and public utilities.
Most of the municipalities are situated on the southern side of the Danube and 
 Belgrade is the financial centre of Serbia and Southeast Europe, with a total of of office space. It is also home to the country's National Bank of Serbia, Central Bank. 750,550 people are employed (July 2020) in 120,286 companies, 76,307 enterprises and 50,000 shops. The City of Belgrade itself owns of rentable office space.
As of 2019, Belgrade contained 31.4% of Serbia's employed population and generated over 40.4% of its GDP. The city's nominal Gross Domestic Product, GDP in 2014 was estimated at 16.97 billion USD, amounting to 859,329 RSD ($10,086) per capita. City GDP in 2019 at purchasing power parity was estimated at $52.1bn USD, which was $32,572 per capita in terms of purchasing power parity.
New Belgrade is the country's Central business district and one of Southeastern Europe's financial centres. It offers a range of facilities, such as hotels, congress halls (e.g. Sava Centar), Class A and B office buildings, and business parks (e.g. Airport City Belgrade). Over of land is under construction in New Belgrade, with the value of planned construction over the next three years estimated at over 1.5 billion euros. The Belgrade Stock Exchange is also located in New Belgrade, and has a market capitalization, market capitalisation of €6.5 billion (US$7.1 billion).
With 6,924 companies in the IT sector (), Belgrade is one of the foremost information technology hubs in Southeast Europe. Microsoft's Microsoft Development Center Serbia, Development Center Serbia, located in Belgrade, was, at the time of its establishment, the fifth such programme on the globe. Many global IT companies choose Belgrade as their European or regional centre of operations, such as Asus, Intel, Dell, Huawei, Nutanix, NCR Corporation, NCR etc. The most famous Belgrade IT startups, among others, are Nordeus, ComTrade Group, Mikroelektronika, MicroE, FishingBooker, and Endava d.o.o., Endava. IT facilities in the city include the Mihajlo Pupin Institute and the Ivo Lola Ribar Institute, ILR, as well as the brand-new IT Park Zvezdara. Many prominent IT innovators began their careers in Belgrade, including Voja Antonić and Veselin Jevrosimović.
In December 2021, the average Belgrade monthly net salary stood at 94,463 RSD ($946) in net terms, with the gross equivalent at 128,509 RSD ($1288), while in New Belgrade CBD is Euros 1,059. 88% of the city's households owned a computer, 89% had a broadband internet connection and 93% had pay television services.
According to Cushman & Wakefield, Knez Mihajlova street is 36th most expensive retail street in the world in terms of renting commercial space.
Belgrade is the financial centre of Serbia and Southeast Europe, with a total of of office space. It is also home to the country's National Bank of Serbia, Central Bank. 750,550 people are employed (July 2020) in 120,286 companies, 76,307 enterprises and 50,000 shops. The City of Belgrade itself owns of rentable office space.
As of 2019, Belgrade contained 31.4% of Serbia's employed population and generated over 40.4% of its GDP. The city's nominal Gross Domestic Product, GDP in 2014 was estimated at 16.97 billion USD, amounting to 859,329 RSD ($10,086) per capita. City GDP in 2019 at purchasing power parity was estimated at $52.1bn USD, which was $32,572 per capita in terms of purchasing power parity.
New Belgrade is the country's Central business district and one of Southeastern Europe's financial centres. It offers a range of facilities, such as hotels, congress halls (e.g. Sava Centar), Class A and B office buildings, and business parks (e.g. Airport City Belgrade). Over of land is under construction in New Belgrade, with the value of planned construction over the next three years estimated at over 1.5 billion euros. The Belgrade Stock Exchange is also located in New Belgrade, and has a market capitalization, market capitalisation of €6.5 billion (US$7.1 billion).
With 6,924 companies in the IT sector (), Belgrade is one of the foremost information technology hubs in Southeast Europe. Microsoft's Microsoft Development Center Serbia, Development Center Serbia, located in Belgrade, was, at the time of its establishment, the fifth such programme on the globe. Many global IT companies choose Belgrade as their European or regional centre of operations, such as Asus, Intel, Dell, Huawei, Nutanix, NCR Corporation, NCR etc. The most famous Belgrade IT startups, among others, are Nordeus, ComTrade Group, Mikroelektronika, MicroE, FishingBooker, and Endava d.o.o., Endava. IT facilities in the city include the Mihajlo Pupin Institute and the Ivo Lola Ribar Institute, ILR, as well as the brand-new IT Park Zvezdara. Many prominent IT innovators began their careers in Belgrade, including Voja Antonić and Veselin Jevrosimović.
In December 2021, the average Belgrade monthly net salary stood at 94,463 RSD ($946) in net terms, with the gross equivalent at 128,509 RSD ($1288), while in New Belgrade CBD is Euros 1,059. 88% of the city's households owned a computer, 89% had a broadband internet connection and 93% had pay television services.
According to Cushman & Wakefield, Knez Mihajlova street is 36th most expensive retail street in the world in terms of renting commercial space.
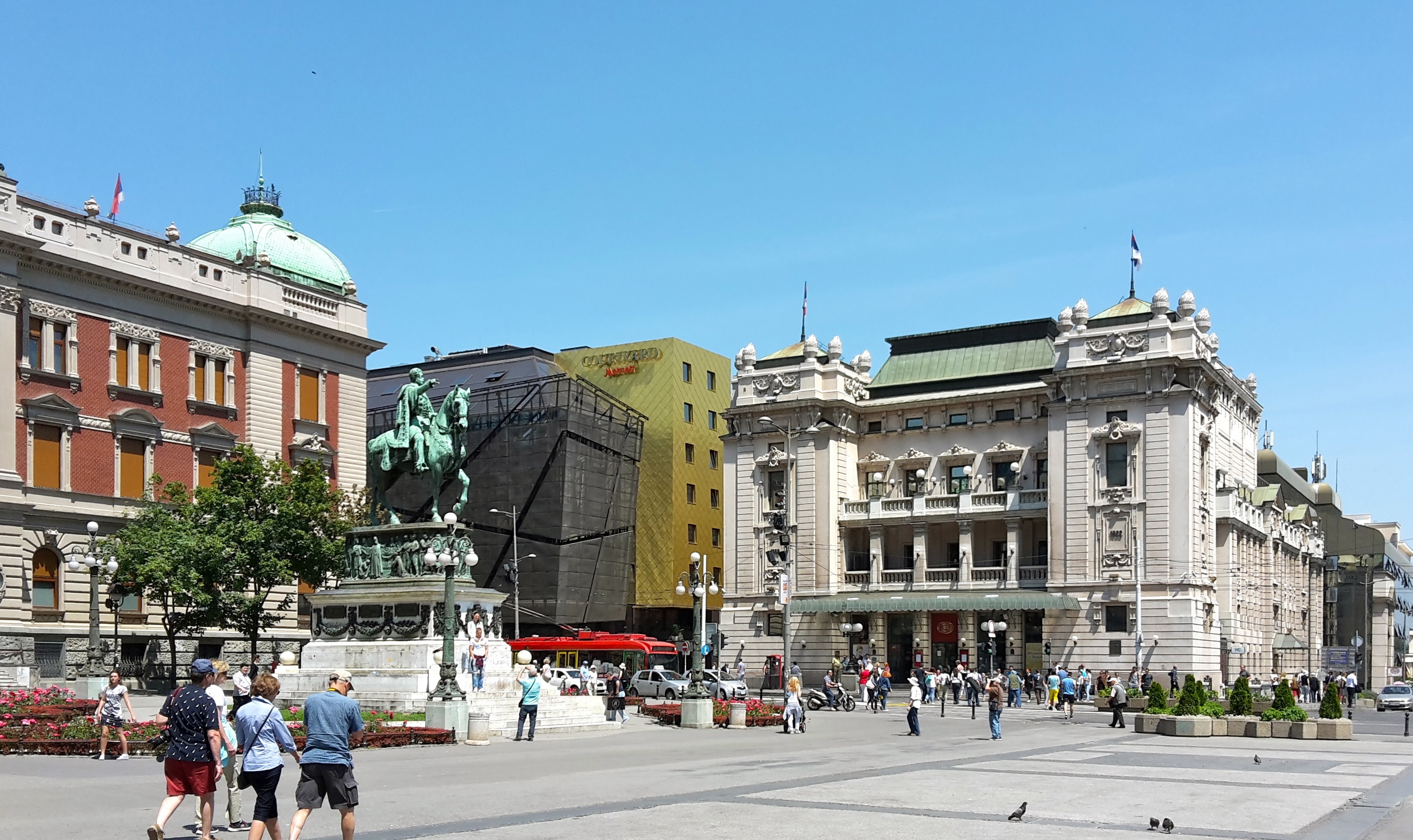 According to BBC, Belgrade is one of five most creative cities in the world.
Belgrade hosts many annual international cultural events, including the FEST (Belgrade), Film Festival, Belgrade International Theatre Festival, Theatre Festival, Belgrade Summer Festival, Summer Festival, Belgrade Music Festival, BEMUS, Belgrade Early Music Festival, Belgrade Book Fair, Book Fair, Belgrade Choir Festival, Eurovision Song Contest 2008, and the Belgrade Beer Fest, Beer Fest. In 2022 Belgrade was also home to the EuroPride, Europride event, even though the president Aleksandar Vučić tried to cancel it. The Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Prize winning author Ivo Andrić wrote his most famous work, ''The Bridge on the Drina'', in Belgrade. Other prominent Belgrade authors include Branislav Nušić, Miloš Crnjanski, Borislav Pekić, Milorad Pavić (writer), Milorad Pavić and Meša Selimović. The most internationally prominent artists from Belgrade are Charles Simic, Marina Abramović and Milovan Destil Marković.
Most of Cinema of Serbia, Serbia's film industry is based in Belgrade. FEST (Belgrade), FEST is an annual film festival that held since 1971, and, through 2013, had been attended by four million people and had presented almost 4,000 films.
The city was one of the main centres of the New wave music in Yugoslavia, Yugoslav new wave in the 1980s: VIS Idoli, Ekatarina Velika, Šarlo Akrobata and Električni Orgazam were all from Belgrade. Other notable Belgrade rock acts include Riblja Čorba, Bajaga i Instruktori and Partibrejkers. Today, it is the centre of the Serbian hip hop scene, with acts such as Beogradski Sindikat, Bad Copy, Škabo, Marčelo, and most of the Bassivity Music stable hailing from or living in the city. There are numerous theatres, the most prominent of which are National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Theatre on Terazije, Yugoslav Drama Theatre, Zvezdara Theatre, and Atelje 212, Atelier 212. The Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts is also based in Belgrade, as well as the National Library of Serbia. Other major libraries include the Belgrade City Library and the Belgrade University Library. Belgrade's two opera houses are: National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre and Madlenianum Opera and Theatre, Madlenianum Opera House. Following the victory of Serbia's representative Marija Šerifović at the Eurovision Song Contest 2007, Belgrade hosted the Contest in
According to BBC, Belgrade is one of five most creative cities in the world.
Belgrade hosts many annual international cultural events, including the FEST (Belgrade), Film Festival, Belgrade International Theatre Festival, Theatre Festival, Belgrade Summer Festival, Summer Festival, Belgrade Music Festival, BEMUS, Belgrade Early Music Festival, Belgrade Book Fair, Book Fair, Belgrade Choir Festival, Eurovision Song Contest 2008, and the Belgrade Beer Fest, Beer Fest. In 2022 Belgrade was also home to the EuroPride, Europride event, even though the president Aleksandar Vučić tried to cancel it. The Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Prize winning author Ivo Andrić wrote his most famous work, ''The Bridge on the Drina'', in Belgrade. Other prominent Belgrade authors include Branislav Nušić, Miloš Crnjanski, Borislav Pekić, Milorad Pavić (writer), Milorad Pavić and Meša Selimović. The most internationally prominent artists from Belgrade are Charles Simic, Marina Abramović and Milovan Destil Marković.
Most of Cinema of Serbia, Serbia's film industry is based in Belgrade. FEST (Belgrade), FEST is an annual film festival that held since 1971, and, through 2013, had been attended by four million people and had presented almost 4,000 films.
The city was one of the main centres of the New wave music in Yugoslavia, Yugoslav new wave in the 1980s: VIS Idoli, Ekatarina Velika, Šarlo Akrobata and Električni Orgazam were all from Belgrade. Other notable Belgrade rock acts include Riblja Čorba, Bajaga i Instruktori and Partibrejkers. Today, it is the centre of the Serbian hip hop scene, with acts such as Beogradski Sindikat, Bad Copy, Škabo, Marčelo, and most of the Bassivity Music stable hailing from or living in the city. There are numerous theatres, the most prominent of which are National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Theatre on Terazije, Yugoslav Drama Theatre, Zvezdara Theatre, and Atelje 212, Atelier 212. The Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts is also based in Belgrade, as well as the National Library of Serbia. Other major libraries include the Belgrade City Library and the Belgrade University Library. Belgrade's two opera houses are: National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre and Madlenianum Opera and Theatre, Madlenianum Opera House. Following the victory of Serbia's representative Marija Šerifović at the Eurovision Song Contest 2007, Belgrade hosted the Contest in
 The most prominent museum in Belgrade is the National Museum of Serbia, National Museum, founded in 1844 and reconstructed from 2003 until June 2018. The museum houses a collection of more than 400,000 exhibits (over 5600 paintings and 8400 drawings and prints, including many foreign masters like Hieronymus Bosch, Bosch, Juan de Flandes, Titian, Tintoretto, Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, Anthony van Dyck, Van Dyck, Cézanne, Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, G.B. Tiepolo, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Renoir, Claude Monet, Monet, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Lautrec, Henri Matisse, Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Picasso, Paul Gauguin, Gauguin, Marc Chagall, Chagall, Vincent van Gogh, Van Gogh, Piet Mondrian, Mondrian etc.) and also the famous Miroslav's Gospel. The Ethnographic Museum (Belgrade), Ethnographic Museum, established in 1901, contains more than 150,000 items showcasing the rural and urban culture of the Balkans, particularly the countries of former Yugoslavia.
The Museum of Contemporary Art (Belgrade), Museum of Contemporary Art was the first contemporary art museum in Yugoslavia and one of the first museums of this type in the world. Following its foundation in 1965, has amassed a collection of more than 8,000 works from art produced across the former Yugoslavia. The museum was closed in 2007, but has since been reopened in 2017 to focus on the modern as well as on the Yugoslav art scenes.
Artist Marina Abramović, who was born in Belgrade, held an exhibition in the Museum of Contemporary Art, which the ''The New York Times, New York Times'' described as one of the most important cultural happenings in the world in 2019. The exhibition was seen by almost 100,000 visitors. Marina Abramović made a stage speech and performance in front of 20,000 people. In the heart of Belgrade you can also find the Museum of Applied Arts, Belgrade, Museum of Applied Arts, a museum that has been awarded for the Institution of the Year 2016 by International Council of Museums, ICOM.
The Military Museum (Belgrade), Military Museum, established in 1878 in Kalemegdan, houses a wide range of more than 25,000 military objects dating from the prehistoric to the medieval to the modern eras. Notable items include Turkish and oriental arms, national banners, and Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav Partisan regalia.
The Museum of Aviation in Belgrade located near Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport has more than 200 aircraft, of which about 50 are on display, and a few of which are the only surviving examples of their type, such as the Fiat G.50. This museum also displays parts of shot down US and NATO aircraft, such as the F-117 Nighthawk, F-117 and F-16 Fighting Falcon, F-16.
The Nikola Tesla Museum, founded in 1952, preserves the personal items of Nikola Tesla, the inventor after whom the Tesla (unit), Tesla unit was named. It holds around 160,000 original documents and around 5,700 personal other items including his urn. The last of the major Belgrade museums is the Museum of Vuk and Dositej, which showcases the lives, work and legacy of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and Dositej Obradović, the 19th century reformer of the Serbian literary language and the first Serbian Minister of Education, respectively. Belgrade also houses the Museum of African Art, Serbia, Museum of African Art, founded in 1977, which has a large collection of art from West Africa.
With around 95,000 copies of national and international films, the Yugoslav Film Archive is the largest in the region and among the 10 largest archives in the world. The institution also operates the Museum of Yugoslav Film Archive, with movie theatre and exhibition hall. The archive's long-standing storage problems were finally solved in 2007, when a new modern depository was opened. The Yugoslav Film Archive also exhibits original Charlie Chaplin's stick and one of the first movies by Auguste and Louis Lumière.
The Belgrade City Museum moved into a new building in downtown in 2006. The museum hosts a range of collections covering the history of urban life since prehistory.
The Museum of Yugoslav History has collections from the Yugoslav era. Beside paintings, the most valuable are Moon rocks donated by Apollo 11 crew Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins (astronaut), Michael Collins while visiting Belgrade in 1969 and from mission Apollo 17 donated by Richard Nixon in 1971. Museum also houses Joseph Stalin's sabre with 260 brilliants and diamonds, donated by Stalin himself.
Museum of Science and Technology (Belgrade), Museum of Science and Technology moved to the building of the first city's power plant in Dorćol in 2005.
The most prominent museum in Belgrade is the National Museum of Serbia, National Museum, founded in 1844 and reconstructed from 2003 until June 2018. The museum houses a collection of more than 400,000 exhibits (over 5600 paintings and 8400 drawings and prints, including many foreign masters like Hieronymus Bosch, Bosch, Juan de Flandes, Titian, Tintoretto, Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, Anthony van Dyck, Van Dyck, Cézanne, Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, G.B. Tiepolo, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Renoir, Claude Monet, Monet, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Lautrec, Henri Matisse, Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Picasso, Paul Gauguin, Gauguin, Marc Chagall, Chagall, Vincent van Gogh, Van Gogh, Piet Mondrian, Mondrian etc.) and also the famous Miroslav's Gospel. The Ethnographic Museum (Belgrade), Ethnographic Museum, established in 1901, contains more than 150,000 items showcasing the rural and urban culture of the Balkans, particularly the countries of former Yugoslavia.
The Museum of Contemporary Art (Belgrade), Museum of Contemporary Art was the first contemporary art museum in Yugoslavia and one of the first museums of this type in the world. Following its foundation in 1965, has amassed a collection of more than 8,000 works from art produced across the former Yugoslavia. The museum was closed in 2007, but has since been reopened in 2017 to focus on the modern as well as on the Yugoslav art scenes.
Artist Marina Abramović, who was born in Belgrade, held an exhibition in the Museum of Contemporary Art, which the ''The New York Times, New York Times'' described as one of the most important cultural happenings in the world in 2019. The exhibition was seen by almost 100,000 visitors. Marina Abramović made a stage speech and performance in front of 20,000 people. In the heart of Belgrade you can also find the Museum of Applied Arts, Belgrade, Museum of Applied Arts, a museum that has been awarded for the Institution of the Year 2016 by International Council of Museums, ICOM.
The Military Museum (Belgrade), Military Museum, established in 1878 in Kalemegdan, houses a wide range of more than 25,000 military objects dating from the prehistoric to the medieval to the modern eras. Notable items include Turkish and oriental arms, national banners, and Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav Partisan regalia.
The Museum of Aviation in Belgrade located near Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport has more than 200 aircraft, of which about 50 are on display, and a few of which are the only surviving examples of their type, such as the Fiat G.50. This museum also displays parts of shot down US and NATO aircraft, such as the F-117 Nighthawk, F-117 and F-16 Fighting Falcon, F-16.
The Nikola Tesla Museum, founded in 1952, preserves the personal items of Nikola Tesla, the inventor after whom the Tesla (unit), Tesla unit was named. It holds around 160,000 original documents and around 5,700 personal other items including his urn. The last of the major Belgrade museums is the Museum of Vuk and Dositej, which showcases the lives, work and legacy of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and Dositej Obradović, the 19th century reformer of the Serbian literary language and the first Serbian Minister of Education, respectively. Belgrade also houses the Museum of African Art, Serbia, Museum of African Art, founded in 1977, which has a large collection of art from West Africa.
With around 95,000 copies of national and international films, the Yugoslav Film Archive is the largest in the region and among the 10 largest archives in the world. The institution also operates the Museum of Yugoslav Film Archive, with movie theatre and exhibition hall. The archive's long-standing storage problems were finally solved in 2007, when a new modern depository was opened. The Yugoslav Film Archive also exhibits original Charlie Chaplin's stick and one of the first movies by Auguste and Louis Lumière.
The Belgrade City Museum moved into a new building in downtown in 2006. The museum hosts a range of collections covering the history of urban life since prehistory.
The Museum of Yugoslav History has collections from the Yugoslav era. Beside paintings, the most valuable are Moon rocks donated by Apollo 11 crew Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins (astronaut), Michael Collins while visiting Belgrade in 1969 and from mission Apollo 17 donated by Richard Nixon in 1971. Museum also houses Joseph Stalin's sabre with 260 brilliants and diamonds, donated by Stalin himself.
Museum of Science and Technology (Belgrade), Museum of Science and Technology moved to the building of the first city's power plant in Dorćol in 2005.
 Belgrade has wildly varying architecture, from the centre of
Belgrade has wildly varying architecture, from the centre of 
 The oldest public structure in Belgrade is a nondescript Turkish türbe, while the oldest house is a modest clay house on Dorćol, from late 18th century. Western influence began in the 19th century, when the city completely transformed from an oriental town to the contemporary architecture of the time, with influences from neoclassicism, romanticism, and academic art. Serbian architects took over the development from the foreign builders in the late 19th century, producing the National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Old Palace (Belgrade), Old Palace, St. Michael's Cathedral (Belgrade), Cathedral Church and later, in the early 20th century, the National Assembly of Serbia, National Assembly and National Museum of Serbia, National Museum, influenced by art nouveau. Elements of Serbo-Byzantine Revival are present in buildings such as House of Vuk's Foundation, old Post Office in Kosovska street, and sacral architecture, such as St. Mark's Church, Belgrade, St. Mark's Church (based on the Gračanica monastery), and the Temple of Saint Sava.
In the socialist period, housing was built quickly and cheaply for the huge influx of people fleeing the countryside following World War II, sometimes resulting in the brutalist architecture of the Blocks (New Belgrade), ''blokovi'' ('blocks') of New Belgrade; a socrealism trend briefly ruled, resulting in buildings like the Dom Sindikata, Trade Union Hall. However, in the mid-1950s, modernism, modernist trends took over, and still dominate the Belgrade architecture.
Belgrade has the second oldest sewer system in Europe. The
The oldest public structure in Belgrade is a nondescript Turkish türbe, while the oldest house is a modest clay house on Dorćol, from late 18th century. Western influence began in the 19th century, when the city completely transformed from an oriental town to the contemporary architecture of the time, with influences from neoclassicism, romanticism, and academic art. Serbian architects took over the development from the foreign builders in the late 19th century, producing the National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Old Palace (Belgrade), Old Palace, St. Michael's Cathedral (Belgrade), Cathedral Church and later, in the early 20th century, the National Assembly of Serbia, National Assembly and National Museum of Serbia, National Museum, influenced by art nouveau. Elements of Serbo-Byzantine Revival are present in buildings such as House of Vuk's Foundation, old Post Office in Kosovska street, and sacral architecture, such as St. Mark's Church, Belgrade, St. Mark's Church (based on the Gračanica monastery), and the Temple of Saint Sava.
In the socialist period, housing was built quickly and cheaply for the huge influx of people fleeing the countryside following World War II, sometimes resulting in the brutalist architecture of the Blocks (New Belgrade), ''blokovi'' ('blocks') of New Belgrade; a socrealism trend briefly ruled, resulting in buildings like the Dom Sindikata, Trade Union Hall. However, in the mid-1950s, modernism, modernist trends took over, and still dominate the Belgrade architecture.
Belgrade has the second oldest sewer system in Europe. The
 As Belgrade became connected via steamboats and railway (after 1884), the number of visitors grew and new hotels were open with the ever luxurious commodities. In Savamala, the hotels ''Bosna'' and ''Bristol'' were opened. Other hotels included ''Solun'' and ''Orient'', which was built near the Financial Park. Tourists which arrived by the Orient Express mostly stayed at the Petrograd Hotel in Savamala#Sava Square, Wilson Square. Hotel ''Srpski Kralj'', at the corner of Uzun Mirkova and Pariska Street was considered the best hotel in Belgrade during the Interbellum. It was destroyed during World War II.
The historic areas and buildings of Belgrade are among the city's premier attractions. They include Skadarlija, the National Museum of Serbia, National Museum and adjacent National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre,
As Belgrade became connected via steamboats and railway (after 1884), the number of visitors grew and new hotels were open with the ever luxurious commodities. In Savamala, the hotels ''Bosna'' and ''Bristol'' were opened. Other hotels included ''Solun'' and ''Orient'', which was built near the Financial Park. Tourists which arrived by the Orient Express mostly stayed at the Petrograd Hotel in Savamala#Sava Square, Wilson Square. Hotel ''Srpski Kralj'', at the corner of Uzun Mirkova and Pariska Street was considered the best hotel in Belgrade during the Interbellum. It was destroyed during World War II.
The historic areas and buildings of Belgrade are among the city's premier attractions. They include Skadarlija, the National Museum of Serbia, National Museum and adjacent National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre,  Elite neighbourhood of Dedinje is situated near the Topčider and Košutnjak parks. The ''Beli dvor'' (''White Palace''), house of royal family Karađorđević dynasty, Karađorđević, is open for visitors. The palace has many valuable artworks. Nearby, Josip Broz Tito's mausoleum, called ''House of Flowers (mausoleum), The House of Flowers'', documents the life of the former Yugoslav president.
Ada Ciganlija is a former island on the Sava, Sava River, and Belgrade's biggest sports and recreational complex. Today it is connected with the right bank of the Sava via two causeways, creating an artificial lake. It is the most popular destination for Belgraders during the city's hot summers. There are of long beaches and sports facilities for various sports including golf, association football, football, basketball, volleyball, rugby union, baseball, and tennis. During summer there are between 200,000 and 300,000 bathers daily.
Elite neighbourhood of Dedinje is situated near the Topčider and Košutnjak parks. The ''Beli dvor'' (''White Palace''), house of royal family Karađorđević dynasty, Karađorđević, is open for visitors. The palace has many valuable artworks. Nearby, Josip Broz Tito's mausoleum, called ''House of Flowers (mausoleum), The House of Flowers'', documents the life of the former Yugoslav president.
Ada Ciganlija is a former island on the Sava, Sava River, and Belgrade's biggest sports and recreational complex. Today it is connected with the right bank of the Sava via two causeways, creating an artificial lake. It is the most popular destination for Belgraders during the city's hot summers. There are of long beaches and sports facilities for various sports including golf, association football, football, basketball, volleyball, rugby union, baseball, and tennis. During summer there are between 200,000 and 300,000 bathers daily.
 Extreme sports are available, such as bungee jumping, water skiing, and paintballing. There are numerous tracks on the island, where it is possible to ride a bike, go for a walk, or go jogging. Apart from Ada, Belgrade has total of 16 islands on the rivers, many still unused. Among them, the Great War Island, at the confluence of Sava, stands out as an oasis of unshattered wildlife (especially birds). These areas, along with nearby Small War Island, are protected by the city's government as a nature preserve. There are List of natural monuments in Belgrade, 37 protected natural resources in the Belgrade urban area, among which eight are geo-heritage sites, i.e. Straževica profile, Mašin Majdan-Topčider, Profile at the Kalemegdan Fortress, Abandoned quarry in Barajevo, Karagača valley, Artesian well in Ovča, Kapela loess profile, and Lake in Sremčica. Other 29 places are biodiversity sites.
Tourist income in 2016 amounted to nearly one billion euros; with a visit of almost a million registered tourists. Of those, in 2019 more than 100,000 tourists arrived by 742 river cruisers. Average annual growth is between 13% and 14%.
As of 2018, there are three officially designated camp grounds in Belgrade. The oldest one is located in Batajnica, along the Batajnica Road. Named "Dunav", it is one of the most visited campsites in the country. Second one is situated within the complex of the ethno-household "Zornić's House" in the village of Baćevac, while the third is located in Ripanj, on the slopes of the Avala mountain. In 2017 some 15,000 overnights were recorded in camps.
Belgrade is a common stop on the EV6 The Rivers Route, Rivers Route, European Long-distance cycling route, cycling route known as "Danube Bike Trail" in Serbia as well as on the Sultans Trail, a long-distance hiking footpath between Vienna and Istanbul.
Extreme sports are available, such as bungee jumping, water skiing, and paintballing. There are numerous tracks on the island, where it is possible to ride a bike, go for a walk, or go jogging. Apart from Ada, Belgrade has total of 16 islands on the rivers, many still unused. Among them, the Great War Island, at the confluence of Sava, stands out as an oasis of unshattered wildlife (especially birds). These areas, along with nearby Small War Island, are protected by the city's government as a nature preserve. There are List of natural monuments in Belgrade, 37 protected natural resources in the Belgrade urban area, among which eight are geo-heritage sites, i.e. Straževica profile, Mašin Majdan-Topčider, Profile at the Kalemegdan Fortress, Abandoned quarry in Barajevo, Karagača valley, Artesian well in Ovča, Kapela loess profile, and Lake in Sremčica. Other 29 places are biodiversity sites.
Tourist income in 2016 amounted to nearly one billion euros; with a visit of almost a million registered tourists. Of those, in 2019 more than 100,000 tourists arrived by 742 river cruisers. Average annual growth is between 13% and 14%.
As of 2018, there are three officially designated camp grounds in Belgrade. The oldest one is located in Batajnica, along the Batajnica Road. Named "Dunav", it is one of the most visited campsites in the country. Second one is situated within the complex of the ethno-household "Zornić's House" in the village of Baćevac, while the third is located in Ripanj, on the slopes of the Avala mountain. In 2017 some 15,000 overnights were recorded in camps.
Belgrade is a common stop on the EV6 The Rivers Route, Rivers Route, European Long-distance cycling route, cycling route known as "Danube Bike Trail" in Serbia as well as on the Sultans Trail, a long-distance hiking footpath between Vienna and Istanbul.
 Many weekend visitors—particularly from Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia and Slovenia—prefer Belgrade nightlife to that of their own capitals due to its perceived friendly atmosphere, plentiful clubs and bars, cheap drinks, lack of significant language barriers, and a lack of night life regulation.
One of the most famous sites for alternative cultural happenings in the city is the SKC (Student Cultural Centre), located right across from Belgrade's highrise landmark, the Beograđanka, Belgrade Palace tower. Concerts featuring famous local and foreign bands are often held at the centre. SKC is also the site of various art exhibitions, as well as public debates and discussions.
A more traditional Serbian nightlife experience, accompanied by traditional music known as ''Starogradska muzika, Starogradska'' (roughly translated as ''Old Town Music''), typical of northern Serbia's urban environments, is most prominent in Skadarlija, the city's old Bohemianism, bohemian neighbourhood where the poets and artists of Belgrade gathered in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Skadar Street (the centre of Skadarlija) and the surrounding neighbourhood are lined with some of Belgrade's best and oldest traditional restaurants (called kafanas in Serbian), which date back to that period.
At one end of the neighbourhood stands Belgrade's oldest beer brewery, founded in the first half of the 19th century. One of the city's oldest kafanas is the Znak pitanja ('?').
''The Times'' reported that Europe's best nightlife can be found in Belgrade. In the Lonely Planet ''1000 Ultimate Experiences'' guide of 2009, Belgrade was placed at the 1st spot among the top 10 party cities in the world.
Many weekend visitors—particularly from Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia and Slovenia—prefer Belgrade nightlife to that of their own capitals due to its perceived friendly atmosphere, plentiful clubs and bars, cheap drinks, lack of significant language barriers, and a lack of night life regulation.
One of the most famous sites for alternative cultural happenings in the city is the SKC (Student Cultural Centre), located right across from Belgrade's highrise landmark, the Beograđanka, Belgrade Palace tower. Concerts featuring famous local and foreign bands are often held at the centre. SKC is also the site of various art exhibitions, as well as public debates and discussions.
A more traditional Serbian nightlife experience, accompanied by traditional music known as ''Starogradska muzika, Starogradska'' (roughly translated as ''Old Town Music''), typical of northern Serbia's urban environments, is most prominent in Skadarlija, the city's old Bohemianism, bohemian neighbourhood where the poets and artists of Belgrade gathered in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Skadar Street (the centre of Skadarlija) and the surrounding neighbourhood are lined with some of Belgrade's best and oldest traditional restaurants (called kafanas in Serbian), which date back to that period.
At one end of the neighbourhood stands Belgrade's oldest beer brewery, founded in the first half of the 19th century. One of the city's oldest kafanas is the Znak pitanja ('?').
''The Times'' reported that Europe's best nightlife can be found in Belgrade. In the Lonely Planet ''1000 Ultimate Experiences'' guide of 2009, Belgrade was placed at the 1st spot among the top 10 party cities in the world.
 Since 1996, semiannual (autumn/winter and spring/summer seasons) fashion weeks are held citywide. Numerous Serbian and foreign designers and fashion brands have their shows during Belgrade Fashion Week. The festival, which collaborates with London Fashion Week, has helped launch the international careers of local talents such as George Styler and Ana Ljubinković. British fashion designer Roksanda Ilincic, who was born in the city, also frequently presents her runway shows in Belgrade.
In addition to fashion, there are two major design shows held in Belgrade every year which attract international architects and industrial designers such as Karim Rashid, Daniel Libeskind, Patricia Urquiola, and Konstantin Grcic. Both the Mikser Festival and Belgrade Design Week feature lectures, exhibits and competitions. Furthermore, international designers like Sacha Lakic, Ana Kraš, Bojana Sentaler, and Marek Djordjevic are originally from Belgrade.
Since 1996, semiannual (autumn/winter and spring/summer seasons) fashion weeks are held citywide. Numerous Serbian and foreign designers and fashion brands have their shows during Belgrade Fashion Week. The festival, which collaborates with London Fashion Week, has helped launch the international careers of local talents such as George Styler and Ana Ljubinković. British fashion designer Roksanda Ilincic, who was born in the city, also frequently presents her runway shows in Belgrade.
In addition to fashion, there are two major design shows held in Belgrade every year which attract international architects and industrial designers such as Karim Rashid, Daniel Libeskind, Patricia Urquiola, and Konstantin Grcic. Both the Mikser Festival and Belgrade Design Week feature lectures, exhibits and competitions. Furthermore, international designers like Sacha Lakic, Ana Kraš, Bojana Sentaler, and Marek Djordjevic are originally from Belgrade.
 Belgrade has two state universities and several private institutions of higher education. The University of Belgrade, founded in 1808 as a Grandes écoles, ''grande école'', is the oldest institution of higher learning in Serbia. Having developed with much of the rest of the city in the 19th century, several university buildings are recognised as forming a constituent part of Belgrade's architecture and cultural heritage. With enrolment numbers of nearly 90,000 students, the university is one of Europe's largest.
The city is also home to 195 primary (elementary) schools and 85 secondary schools. The primary school system has 162 regular schools, 14 Special education, special schools, 15 art schools, and 4 adult schools, while the secondary school system has 51 vocational schools, 21 Gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, 8 art schools and 5 special schools. The 230,000 pupils are managed by 22,000 employees in over 500 buildings, covering around .
Belgrade has two state universities and several private institutions of higher education. The University of Belgrade, founded in 1808 as a Grandes écoles, ''grande école'', is the oldest institution of higher learning in Serbia. Having developed with much of the rest of the city in the 19th century, several university buildings are recognised as forming a constituent part of Belgrade's architecture and cultural heritage. With enrolment numbers of nearly 90,000 students, the university is one of Europe's largest.
The city is also home to 195 primary (elementary) schools and 85 secondary schools. The primary school system has 162 regular schools, 14 Special education, special schools, 15 art schools, and 4 adult schools, while the secondary school system has 51 vocational schools, 21 Gymnasium (school), gymnasiums, 8 art schools and 5 special schools. The 230,000 pupils are managed by 22,000 employees in over 500 buildings, covering around .

 Belgrade has an extensive public transport system consisting of buses (118 urban lines and more than 300 suburban lines), trams (12 lines), trolleybuses (8 lines) and S-Train BG Voz (6 lines). Buses, trolleybuses and trams are run by GSP Beograd and Lasta Beograd, SP Lasta in cooperation with private companies on some bus routes. The S-train network, BG Voz, run by city government in cooperation with Serbian Railways, is a part of the integrated transport system, and has three lines (Batajnica-Ovča and Ovča-Resnik and Belgrade centre-Mladenovac), with more announced. The BusPlus ticketing system based on contactless smart cards began operating in February 2012. Daily connections link the capital to other towns in Serbia and many other European destinations through the city's Belgrade Bus Station, central bus station.
Beovoz was the regional rail, suburban/commuter railway network that provided mass-transit services in the city, similar to Paris's Réseau Express Régional, RER and Toronto's GO Transit. The main usage of system was to connect the suburbs with the city centre. Beovoz was operated by Serbian Railways. However, this system was abolished back in 2013, mostly due to introduction of more efficient BG Voz. Belgrade is one of the last big European capitals and cities with over a million people to have no metro or subway or other rapid transit system. As of November 2021, Belgrade Metro is currently under construction, which will have 2 lines. The first line is expected to be operational by August 2028.
Belgrade has an extensive public transport system consisting of buses (118 urban lines and more than 300 suburban lines), trams (12 lines), trolleybuses (8 lines) and S-Train BG Voz (6 lines). Buses, trolleybuses and trams are run by GSP Beograd and Lasta Beograd, SP Lasta in cooperation with private companies on some bus routes. The S-train network, BG Voz, run by city government in cooperation with Serbian Railways, is a part of the integrated transport system, and has three lines (Batajnica-Ovča and Ovča-Resnik and Belgrade centre-Mladenovac), with more announced. The BusPlus ticketing system based on contactless smart cards began operating in February 2012. Daily connections link the capital to other towns in Serbia and many other European destinations through the city's Belgrade Bus Station, central bus station.
Beovoz was the regional rail, suburban/commuter railway network that provided mass-transit services in the city, similar to Paris's Réseau Express Régional, RER and Toronto's GO Transit. The main usage of system was to connect the suburbs with the city centre. Beovoz was operated by Serbian Railways. However, this system was abolished back in 2013, mostly due to introduction of more efficient BG Voz. Belgrade is one of the last big European capitals and cities with over a million people to have no metro or subway or other rapid transit system. As of November 2021, Belgrade Metro is currently under construction, which will have 2 lines. The first line is expected to be operational by August 2028.
 The new Belgrade Centre railway station is the hub for almost all the national and international trains.
The high-speed rail that connects Belgrade with Novi Sad started its service at 19 March 2022. The extension towards Subotica and Budapest is under construction, and there are plans for southwards extension towards Niš and North Macedonia.
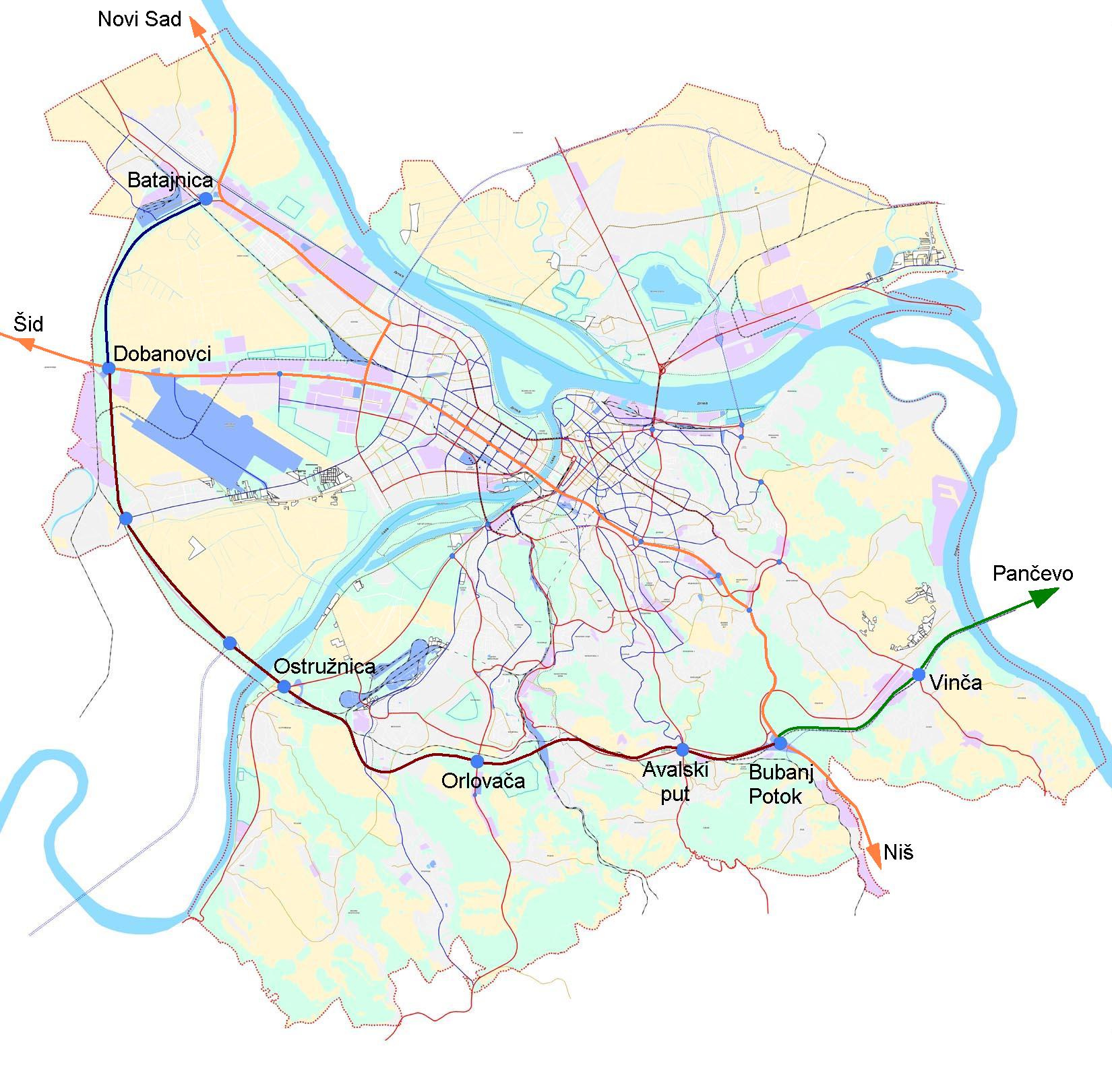
The city is placed along the Pan-European corridors Pan-European Corridor X, X and VII. The motorway system provides for easy access to Novi Sad and Budapest to the north, Niš to the south, and Zagreb to the west. Expressway is also toward Pančevo and new Expressway construction toward Obrenovac (Montenegro) is scheduled for March 2017. Belgrade bypass is connecting the E70 in Serbia, E70 and E75 in Serbia, E75 motorways and is under construction.
Situated at the confluence of two major rivers, the Danube and the Sava, Belgrade has 11 bridges, the most important of which are Branko's bridge, the Ada Bridge, Pupin Bridge and the Gazela Bridge, the last two of which connect the core of the city to New Belgrade. In addition, an 'inner magistral semi-ring' is almost done and include a new Ada Bridge across the Sava river and a new Pupin Bridge across Danube river, which eased commuting within the city and unload the Gazela and Branko's bridge traffic.
The Port of Belgrade is on the Danube, and allows the city to receive goods by river. The city is also served by Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport, west of the city centre, near Surčin. At its peak in 1986, almost 3 million passengers travelled through the airport, though that number dwindled to a trickle in the 1990s. Following renewed growth in 2000, the number of passengers reached approximately 2 million in 2004 and 2005, over 2.6 million passengers in 2008, reaching over 3 million passengers. A record with over 4 million passengers was broken in 2014, when Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport became the second fastest growing major airport in Europe. The numbers continued to grow steadily and the all-time peak of over 6 million passengers was reached in 2019.
The new Belgrade Centre railway station is the hub for almost all the national and international trains.
The high-speed rail that connects Belgrade with Novi Sad started its service at 19 March 2022. The extension towards Subotica and Budapest is under construction, and there are plans for southwards extension towards Niš and North Macedonia.
The city is placed along the Pan-European corridors Pan-European Corridor X, X and VII. The motorway system provides for easy access to Novi Sad and Budapest to the north, Niš to the south, and Zagreb to the west. Expressway is also toward Pančevo and new Expressway construction toward Obrenovac (Montenegro) is scheduled for March 2017. Belgrade bypass is connecting the E70 in Serbia, E70 and E75 in Serbia, E75 motorways and is under construction.
Situated at the confluence of two major rivers, the Danube and the Sava, Belgrade has 11 bridges, the most important of which are Branko's bridge, the Ada Bridge, Pupin Bridge and the Gazela Bridge, the last two of which connect the core of the city to New Belgrade. In addition, an 'inner magistral semi-ring' is almost done and include a new Ada Bridge across the Sava river and a new Pupin Bridge across Danube river, which eased commuting within the city and unload the Gazela and Branko's bridge traffic.
The Port of Belgrade is on the Danube, and allows the city to receive goods by river. The city is also served by Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport, west of the city centre, near Surčin. At its peak in 1986, almost 3 million passengers travelled through the airport, though that number dwindled to a trickle in the 1990s. Following renewed growth in 2000, the number of passengers reached approximately 2 million in 2004 and 2005, over 2.6 million passengers in 2008, reaching over 3 million passengers. A record with over 4 million passengers was broken in 2014, when Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport became the second fastest growing major airport in Europe. The numbers continued to grow steadily and the all-time peak of over 6 million passengers was reached in 2019.
 List of Belgrade's sister and twin cities:
* Coventry, UK, since 1957
* Chicago, USA, since 2005
* Ljubljana, Slovenia, since 2010
* Skopje, North Macedonia, since 2012
* Shanghai, China, since 2018
* Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 2020
Other friendships and cooperations, protocols, memorandums:
* Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 2018, Memorandum of Understanding on Cooperation
* Rabat, Morocco, since 2017, Partnership and Cooperation Agreement
* Seoul, South Korea, since 2017, Memorandum of Understanding on Friendly Exchanges and Cooperation
* Astana, Kazakhstan, since 2016, Agreement on Cooperation
* Tehran, Iran, since 2016, Agreement on Cooperation
* Corfu (city), Corfu, Greece, since 2010, Protocol on Cooperation
* Shenzhen, China, since 2009, Agreement on Cooperation
* Zagreb, Croatia, since 2003, Letter of Intent
* Kyiv, Ukraine, since 2002, Agreement on Cooperation
* Algiers, Algeria, since 1991 declaration of mutual interests
* Tel Aviv, Israel, since 1990, Agreement on Cooperation
* Bucharest, Romania, since 1999, Agreement on Cooperation
* Beijing, China, since 1980, Agreement on Cooperation
* Rome, Italy, since 1971, Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation
* Athens, Greece, since 1966, Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation
Some of the city's municipalities are also twinned to small cities or districts of other big cities; for details see their respective articles.
Belgrade has received various domestic and international honours, including the French Légion d'honneur (proclaimed 21 December 1920; Belgrade is one of four cities outside France, alongside Liège, Luxembourg (city), Luxembourg and Volgograd, to receive this honour), the Czechoslovak War Cross 1918, Czechoslovak War Cross (awarded 8 October 1925), the Yugoslavian Order of the Karađorđe's Star (awarded 18 May 1939) and the Yugoslavian Order of the People's Hero (proclaimed on 20 October 1974, the 30th anniversary of the overthrow of Nazi Germany, Nazi German occupation during World War II). All of these decorations were received for the war efforts during World War I and World War II. In 2006, ''Financial Times magazine ''FDi magazine, Foreign Direct Investment'' awarded Belgrade the title of ''City of the Future of Southern Europe''.
List of Belgrade's sister and twin cities:
* Coventry, UK, since 1957
* Chicago, USA, since 2005
* Ljubljana, Slovenia, since 2010
* Skopje, North Macedonia, since 2012
* Shanghai, China, since 2018
* Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 2020
Other friendships and cooperations, protocols, memorandums:
* Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 2018, Memorandum of Understanding on Cooperation
* Rabat, Morocco, since 2017, Partnership and Cooperation Agreement
* Seoul, South Korea, since 2017, Memorandum of Understanding on Friendly Exchanges and Cooperation
* Astana, Kazakhstan, since 2016, Agreement on Cooperation
* Tehran, Iran, since 2016, Agreement on Cooperation
* Corfu (city), Corfu, Greece, since 2010, Protocol on Cooperation
* Shenzhen, China, since 2009, Agreement on Cooperation
* Zagreb, Croatia, since 2003, Letter of Intent
* Kyiv, Ukraine, since 2002, Agreement on Cooperation
* Algiers, Algeria, since 1991 declaration of mutual interests
* Tel Aviv, Israel, since 1990, Agreement on Cooperation
* Bucharest, Romania, since 1999, Agreement on Cooperation
* Beijing, China, since 1980, Agreement on Cooperation
* Rome, Italy, since 1971, Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation
* Athens, Greece, since 1966, Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation
Some of the city's municipalities are also twinned to small cities or districts of other big cities; for details see their respective articles.
Belgrade has received various domestic and international honours, including the French Légion d'honneur (proclaimed 21 December 1920; Belgrade is one of four cities outside France, alongside Liège, Luxembourg (city), Luxembourg and Volgograd, to receive this honour), the Czechoslovak War Cross 1918, Czechoslovak War Cross (awarded 8 October 1925), the Yugoslavian Order of the Karađorđe's Star (awarded 18 May 1939) and the Yugoslavian Order of the People's Hero (proclaimed on 20 October 1974, the 30th anniversary of the overthrow of Nazi Germany, Nazi German occupation during World War II). All of these decorations were received for the war efforts during World War I and World War II. In 2006, ''Financial Times magazine ''FDi magazine, Foreign Direct Investment'' awarded Belgrade the title of ''City of the Future of Southern Europe''.
City of BelgradeTourist Organisation of Belgrade
{{Authority control Belgrade, Capitals in Europe Districts of Serbia Metropolitan areas of Serbia Statistical regions of Serbia Port cities in Serbia Ancient cities in Serbia Populated places established in the 3rd century BC Populated places on the Danube Šumadija Recipients of the Czechoslovak War Cross Recipients of the Legion of Honour Populated places on the Sava Starčevo–Körös–Criș culture
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
in Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
. It is located at the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
of the Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally th ...
and Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewhat different sense, with only the ...
and the Balkan Peninsula
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. Nearly 1,166,763 million people live within the administrative limits of the City of Belgrade. It is the third largest of all cities on the Danube river.
Belgrade is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Europe and the world. One of the most important prehistoric cultures of Europe, the Vinča culture
The Vinča culture (), also known as Turdaș culture or Turdaș–Vinča culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast Europe, dated to the period 5700–4500 BC or 5300–4700/4500 BC.. Named for its type site, Vinča-Belo Brdo ...
, evolved within the Belgrade area in the 6th millennium BC. In antiquity, Thraco
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
-Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
inhabited the region and, after 279 BC, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
settled the city, naming it '' Singidūn''. It was conquered by the Romans under the reign of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
and awarded Roman city rights
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the tradition ...
in the mid-2nd century. It was settled by the Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
in the 520s, and changed hands several times between the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
, the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
, and the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
before it became the seat of the Serbian king Stefan Dragutin
Stefan Dragutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Драгутин, hu, Dragutin István; 1244 – 12 March 1316) was King of Serbia from 1276 to 1282. From 1282, he ruled a separate kingdom which included northern Serbia, and (from 1284) the neigh ...
in 1284. Belgrade served as capital of the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate ( sr, / ) was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is generally considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire and ...
during the reign of Stefan Lazarević
Stefan Lazarević ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Лазаревић, 1377 – 19 July 1427), also known as Stefan the Tall ( sr, Стефан Високи / ''Stefan Visoki''), was the ruler of Serbia as prince (1389–1402) and despot (1402–1427), ...
, and then his successor Đurađ Branković
Đurađ Branković (; sr-cyr, Ђурађ Бранковић; hu, Brankovics György; 1377 – 24 December 1456) was the Serbian Despot from 1427 to 1456. He was one of the last Serbian medieval rulers. He was a participant in the battle of Anka ...
returned it to the Hungarian king in 1427. Noon bells in support of the Hungarian army against the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
during the siege in 1456 have remained a widespread church tradition to this day. In 1521, Belgrade was conquered by the Ottomans and became the seat of the Sanjak of Smederevo
The Sanjak of Smederevo ( tr, Semendire Sancağı; sr, / ), also known in historiography as the Pashalik of Belgrade ( tr, Belgrad Paşalığı; sr, / ), was an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman administrative unit (sanjak), that existed between the 1 ...
. It frequently passed from Ottoman to Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
rule, which saw the destruction of most of the city during the Ottoman–Habsburg wars
The Ottoman–Habsburg wars were fought from the 16th through the 18th centuries between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy, which was at times supported by the Kingdom of Hungary, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and Habsburg Spai ...
.
In the period after the Serbian Revolution
The Serbian Revolution ( sr, Српска револуција / ''Srpska revolucija'') was a national uprising and constitutional change in Serbia that took place between 1804 and 1835, during which this territory evolved from an Ottoman prov ...
, Belgrade again was named the capital of Serbia in 1841. Northern Belgrade remained the southernmost Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
post until 1918, when it was attached to the city, due to former Austro-Hungarian territories becoming part of the new Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Belgrade was the capital of Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
from its creation
Creation may refer to:
Religion
*''Creatio ex nihilo'', the concept that matter was created by God out of nothing
* Creation myth, a religious story of the origin of the world and how people first came to inhabit it
* Creationism, the belief tha ...
in 1918 to its dissolution
Dissolution may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
* ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers
* ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music
* Dissolution, in mu ...
in 2006. In a fatally strategic position, the city has been battled over in 115 wars and razed 44 times, being bombed five times and besieged many times.
Being Serbia's primate city
A primate city is a city that is the largest in its country, province, Federated state, state, or region, and disproportionately larger than any others in the urban hierarchy. A ''primate city distribution'' is a rank-size distribution that has on ...
, Belgrade has special administrative status within Serbia. It is the seat of the central government, administrative bodies, and government ministries, as well as home of almost all of the largest Serbian companies, media, and scientific institutions. Belgrade is classified as a Beta- Global City. The city is home to the Clinical Centre of Serbia
The University Clinical Centre of Serbia ( sr, Универзитетски клинички центар Србије; abbr. УKЦС / UKCS) is an academic medical centre located in Belgrade, Serbia. It serves as the main medical centre for both ...
, one of the hospital complexes with the largest capacity in the world, the Church of Saint Sava, one of the largest Orthodox church buildings, and the Štark Arena
The Štark Arena ( sr-cyrl, Штарк арена), also known as Belgrade Arena ( sr-cyrl, Београдска арена), is a multi-purpose indoor arena located in Belgrade, Serbia. It is designed as a universal hall for sports, cultural ev ...
, one of the indoor arenas with the largest capacity in Europe. Belgrade hosted major international events such as the Danube River Conference of 1948
The Danube River Conference of 1948 was held in Belgrade, Yugoslavia, to develop a new international regime for the development and control of the Danube in the wake of World War II. It was the first postwar conference pitting the victorious All ...
, the first Non-Aligned Movement Summit
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
(1961), the first major gathering of the OSCE
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, prom ...
(1977–1978), Eurovision Song Contest
The Eurovision Song Contest (), sometimes abbreviated to ESC and often known simply as Eurovision, is an international songwriting competition organised annually by the European Broadcasting Union (EBU), featuring participants representing pr ...
(2008
File:2008 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Lehman Brothers went bankrupt following the Subprime mortgage crisis; Cyclone Nargis killed more than 138,000 in Myanmar; A scene from the opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing; ...
), as well as sports events such as the first FINA World Aquatics Championships
The FINA World Championships or World Aquatics Championships are the World Championships for aquatics sports: Swimming (sport), swimming, Diving (sport), diving, high diving, open water swimming, artistic swimming, and water polo. They are run b ...
(1973
Events January
* January 1 - The United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland and Denmark enter the European Economic Community, which later becomes the European Union.
* January 15 – Vietnam War: Citing progress in peace negotiations, U.S. ...
), UEFA Euro
The UEFA European Football Championship, less formally the European Championship and informally the Euro, is the primary association football tournament organised by the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA). The competition is contes ...
(1976
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phila ...
), Summer Universiade
The Universiade is an international multi-sport event, organized for university athletes by the International University Sports Federation (FISU). The name is a portmanteau of the words "University" and "Olympiad".
The Universiade is referred t ...
(2009
File:2009 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: The vertical stabilizer of Air France Flight 447 is pulled out from the Atlantic Ocean; Barack Obama becomes the first African American to become President of the United States; 2009 Iran ...
) and EuroBasket
EuroBasket, also commonly referred to as the European Basketball Championship, is the main international basketball competition that is contested quadrennially, by the senior men's national teams that are governed by FIBA Europe, which is the E ...
three times (1961
Events January
* January 3
** United States President Dwight D. Eisenhower announces that the United States has severed diplomatic and consular relations with Cuba ( Cuba–United States relations are restored in 2015).
** Aero Flight 311 ...
, 1975
It was also declared the ''International Women's Year'' by the United Nations and the European Architectural Heritage Year by the Council of Europe.
Events
January
* January 1 - Watergate scandal (United States): John N. Mitchell, H. R. ...
, 2005
File:2005 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: Hurricane Katrina in the Gulf of Mexico; the Funeral of Pope John Paul II is held in Vatican City; "Me at the zoo", the first video ever to be uploaded to YouTube; Eris was discovered in ...
).
History
Prehistory
Chipped stone tools found inZemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
show that the area around Belgrade was inhabited by nomadic foragers in the Palaeolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
and Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
eras. Some of these tools are of Mousterian industry
The Mousterian (or Mode III) is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the lat ...
—belonging to Neanderthals
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an Extinction, extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ag ...
rather than modern humans. Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic
associated with European early modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the Levant, where t ...
and Gravettian
The Gravettian was an archaeological industry of the European Upper Paleolithic that succeeded the Aurignacian circa 33,000 years BP. It is archaeologically the last European culture many consider unified, and had mostly disappeared by 2 ...
tools have also been discovered near the area, indicating some settlement between 50,000 and 20,000 years ago.
 The first farming people to settle in the region are associated with the
The first farming people to settle in the region are associated with the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
Starčevo culture
The Starčevo culture is an archaeological culture of Southeastern Europe, dating to the Neolithic period between ''c.'' 6200 and 4500 BCE. It originates in the spread of the Neolithic package of peoples and technological innovations including far ...
, which flourished between 6200 and 5200 BC. There are several Starčevo sites in and around Belgrade, including the eponymous site of Starčevo. The Starčevo culture was succeeded by the Vinča culture
The Vinča culture (), also known as Turdaș culture or Turdaș–Vinča culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast Europe, dated to the period 5700–4500 BC or 5300–4700/4500 BC.. Named for its type site, Vinča-Belo Brdo ...
(5500–4500 BC), a more sophisticated farming culture that grew out of the earlier Starčevo settlements and also named for a site in the Belgrade region (Vinča-Belo Brdo
Vinča-Belo Brdo ( sr, Винча-Бело брдо) is an archaeological site in Vinča, a suburb of Belgrade, Serbia. The tell of Belo Brdo ('White Hill') is almost entirely made up of the remains of human settlement, and was occupied severa ...
). The Vinča culture is known for its very large settlements, one of the earliest settlements by continuous habitation and some of the largest in prehistoric Europe. Also associated with the Vinča culture are anthropomorphic figurines such as the Lady of Vinča
The word ''lady'' is a term for a girl or woman, with various connotations. Once used to describe only women of a high social class or status, the equivalent of lord, now it may refer to any adult woman, as gentleman can be used for men. Inform ...
, the earliest known copper metallurgy in Europe, and a proto-writing
Proto-writing consists of visible marks communicating limited information. Such systems emerged from earlier traditions of symbol systems in the early Neolithic, as early as the 7th millennium BC in Eastern Europe and China. They used ideograph ...
form developed prior to the Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ians and Minoans known as the Old European script
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
*Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Mai ...
, which dates back to around 5300 BC. Within the city proper, on Cetinjska Street, a skull of a Paleolithic human dated to before 5000 BC was discovered in 1890.
Antiquity
Evidence of early knowledge about Belgrade's geographical location comes from a variety of ancient myths and legends. The ridge overlooking the confluence of theSava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally th ...
and Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
rivers, for example, has been identified as one of the places in the story of Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He w ...
and the Argonauts
The Argonauts (; Ancient Greek: ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, '' Argo'', ...
. In the time of antiquity, too, the area was populated by Paleo-Balkan tribes, including the Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
and the Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
, who ruled much of Belgrade's surroundings. Specifically, Belgrade was at one point inhabited by the Thraco-Dacian tribe Singi; following Celtic invasion in 279 BC, the Scordisci
The Scordisci ( el, Σκορδίσκοι) were a Celtic Iron Age cultural group centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morava) and Danube rivers. They were historically n ...
wrested the city from their hands, naming it ''Singidūn'' (''d, ūn'', fortress). In 34–33 BC, the Roman army reached Belgrade. It became the romanised
Romanization or romanisation, in linguistics, is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and ...
''Singidunum
Singidunum ( sr, Сингидунум/''Singidunum'') was an ancient city which later evolved into modern Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. The name is of Celts, Celtic origin, going back to the time when Celtic tribe Scordisci settled the area in ...
'' in the 1st century AD and, by the mid-2nd century, the city was proclaimed a ''municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (pl. ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ("duty holders"), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the privi ...
'' by the Roman authorities, evolving into a full-fledged '' colonia'' (the highest city class) by the end of the century. While the first Christian Emperor of Rome —Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
, also known as Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
—was born in the territory of Naissus to the city's south, Roman Christianity's champion, Flavius Iovianus (Jovian), was born in Singidunum. Jovian reestablished Christianity as the official religion of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, ending the brief revival of traditional Roman religions under his predecessor Julian the Apostate
Julian ( la, Flavius Claudius Julianus; grc-gre, Ἰουλιανός ; 331 – 26 June 363) was Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplato ...
. In 395 AD, the site passed to the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. Across the Sava from Singidunum was the Celtic city of Taurunum (Zemun); the two were connected with a bridge throughout Roman and Byzantine times.
Middle Ages
 In 442, the area was ravaged by
In 442, the area was ravaged by Attila the Hun
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and Ea ...
. In 471, it was taken by Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy b ...
, king of the Ostrogoths, who continued into Italy. As the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the larg ...
left, another Germanic tribe, the Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion a ...
, invaded the city. In 539 it was retaken by the Byzantines. In 577, some 100,000 Slavs poured into Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
and Illyricum, pillaging cities and more permanently settling the region. The Avars, under Bayan I
Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602.
As the Göktürk Empire expanded westwards on the Eurasian Steppe during the 6th century, peoples such as the Avars (also known as the ''Pseudo-Avars'', ''Obri'' ...
, conquered the whole region and its new Slavic population by 582. Following Byzantine reconquest, the Byzantine chronicle ''De Administrando Imperio
''De Administrando Imperio'' ("On the Governance of the Empire") is the Latin title of a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Eastern Roman Emperor Constantine VII. The Greek title of the work is ("To yown son Romanos"). It is a domes ...
'' mentions the White Serbs
The Sorbs, also known as White Serbs in Serbian historiography, were an Early Slavic tribe settled between Saale-Elbe valley up to Lusatian Neisse (in present-day Saxony and Thuringia), and part of the Wends. In the 7th century, the tribe joined ...
, who had stopped in Belgrade on their way back home, asking the ''strategos
''Strategos'', plural ''strategoi'', Linguistic Latinisation, Latinized ''strategus'', ( el, στρατηγός, pl. στρατηγοί; Doric Greek: στραταγός, ''stratagos''; meaning "army leader") is used in Greek language, Greek to ...
'' for lands; they received provinces in the west, towards the Adriatic, which they would rule as subjects to Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was List of Byzantine emperors, Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exa ...
(610–641). In 829, Khan Omurtag
Omurtag (or Omortag) ( bg, Омуртаг; original gr, Μορτάγων and Ομουρτάγ', Inscription No.64. Retrieved 10 April 2012.) was a Great Khan (''Kanasubigi'') of Bulgaria from 814 to 831. He is known as "the Builder".
In the very ...
was able to add Singidunum and its environs to the First Bulgarian Empire.
The first record of the name ''Belograd'' appeared on April, 16th, 878, in a Papal missive to Bulgarian ruler Boris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
. This name would appear in several variants: ''Alba Bulgarica'' in Latin, ''Griechisch Weissenburg'' in High German, ''Nándorfehérvár'' in Hungarian, and ''Castelbianco'' in Venetian, among other names, all variations of 'white fortress'. For about four centuries, the city would become a battleground between the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, the medieval Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, and the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between the ...
. Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar S ...
(976–1025) installed a garrison in Belgrade. The city hosted the armies of the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and the Second Crusade
The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusa ...
, but, while passing through during the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity (Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
, Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on ...
and his 190,000 crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
saw Belgrade in ruins.
King Stefan Dragutin
Stefan Dragutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Драгутин, hu, Dragutin István; 1244 – 12 March 1316) was King of Serbia from 1276 to 1282. From 1282, he ruled a separate kingdom which included northern Serbia, and (from 1284) the neigh ...
(r. 1276–1282) received Belgrade from his father-in-law, Stephen V of Hungary
Stephen V ( hu, V. István, hr, Stjepan V., sk, Štefan V; before 18 October 1239 – 6 August 1272, Csepel Island) was King of Hungary and Croatia between 1270 and 1272, and Duke of Styria from 1258 to 1260. He was the oldest son of Kin ...
, in 1284, and it served as the capital of the Kingdom of Syrmia
The Realm of Stefan Dragutin ( sr, Област Стефана Драгутина / ''Oblast Stefana Dragutina'') was a medieval Serb kingdom. Initially, it was a vassal kingdom of the Kingdom of Hungary, but subsequently became an independent k ...
, a vassal state to the Kingdom of Hungary. Dragutin (Hungarian: ''Dragutin István'') is regarded as the first Serbian king to rule over Belgrade.
Following the battles of Maritsa (1371) and Kosovo field (1389), Moravian Serbia, to Belgrade's south, began to fall to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
The northern regions of what is now Serbia persisted as the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate ( sr, / ) was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is generally considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire and ...
, with Belgrade as its capital. The city flourished under Stefan Lazarević
Stefan Lazarević ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Лазаревић, 1377 – 19 July 1427), also known as Stefan the Tall ( sr, Стефан Високи / ''Stefan Visoki''), was the ruler of Serbia as prince (1389–1402) and despot (1402–1427), ...
, the son of Serbian prince Lazar Hrebeljanović
Lazar Hrebeljanović ( sr-cyr, Лазар Хребељановић; ca. 1329 – 15 June 1389) was a medieval Serbian ruler who created the largest and most powerful state on the territory of the disintegrated Serbian Empire. Lazar's state, ...
. Lazarević built a castle with a citadel and towers, of which only the Despot's tower and the west wall remain. He also refortified the city's ancient walls, allowing the Despotate to resist Ottoman conquest for almost 70 years. During this time, Belgrade was a haven for many Balkan peoples fleeing Ottoman rule, and is thought to have had a population ranging between 40,000 and 50,000 people.
In 1427, Stefan's successor Đurađ Branković
Đurađ Branković (; sr-cyr, Ђурађ Бранковић; hu, Brankovics György; 1377 – 24 December 1456) was the Serbian Despot from 1427 to 1456. He was one of the last Serbian medieval rulers. He was a participant in the battle of Anka ...
, returning Belgrade to the Hungarian king
This is a list of Hungarian monarchs, that includes the grand princes (895–1000) and the kings and ruling queens of Hungary (1000–1918).
The Principality of Hungary established 895 or 896, following the 9th-century Hungarian conquest of the ...
, made Smederevo fortress, Smederevo his new capital. Even though the Ottomans had captured most of the Serbian Despotate
The Serbian Despotate ( sr, / ) was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is generally considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire and ...
, Belgrade, known as Nándorfehérvár in Hungarian, was Siege of Belgrade (1440), unsuccessfully besieged in 1440 and 1456. As the city presented an obstacle to the Ottoman advance into Hungary and further, over 100,000 Ottoman soldiers Siege of Belgrade (1456), besieged it in 1456, in which the Christian army led by the Hungarian General John Hunyadi successfully defended it. The ''noon bell'' ordered by Pope Callixtus III commemorates the victory throughout the Christian world to this day.
Ottoman rule and Austrian invasions
 Seven decades after the initial siege, on 28 August 1521, the fort was finally captured by Suleiman the Magnificent, 250,000 Turkish soldiers, and over 100 ships. Subsequently, most of the city was razed to the ground and its entire Orthodox Christian population was deported to Istanbul to an area that has since become known as the Belgrade forest. Belgrade was made the seat of the Pashalik of Belgrade (also known as the Sanjak of Smederevo), and quickly became the second largest Ottoman town in Europe at over 100,000 people, surpassed only by Constantinople. Ottoman rule introduced Ottoman architecture, including numerous mosques, and the city was resurrected—now by Oriental influences. In 1594, a major Banat Uprising, Serb rebellion was crushed by the Ottomans. In retribution, Grand vizier, Grand Vizier Sinan Pasha ordered the relics of Saint Sava to be publicly torched on the Vračar plateau; in the 20th century, the church of Saint Sava was built to commemorate this event.
Occupied by the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburgs three times (Siege of Belgrade (1688), 1688–1690, Kingdom of Serbia (1718–39), 1717–1739, Siege of Belgrade (1789), 1789–1791), headed by the Holy Roman Empire, Holy Roman Princes Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian of Bavaria and Prince Eugene of Savoy, Eugene of Savoy, and field marshal Baron Ernst Gideon von Laudon, respectively, Belgrade was quickly recaptured by the Ottomans and substantially razed each time. During this period, the city was affected by the two Great Serbian Migrations, in which hundreds of thousands of Serbs, led by two Serbian Patriarchs, retreated together with the Austrian soldiers into the Habsburg Empire, settling in today's Vojvodina and Slavonia.
Seven decades after the initial siege, on 28 August 1521, the fort was finally captured by Suleiman the Magnificent, 250,000 Turkish soldiers, and over 100 ships. Subsequently, most of the city was razed to the ground and its entire Orthodox Christian population was deported to Istanbul to an area that has since become known as the Belgrade forest. Belgrade was made the seat of the Pashalik of Belgrade (also known as the Sanjak of Smederevo), and quickly became the second largest Ottoman town in Europe at over 100,000 people, surpassed only by Constantinople. Ottoman rule introduced Ottoman architecture, including numerous mosques, and the city was resurrected—now by Oriental influences. In 1594, a major Banat Uprising, Serb rebellion was crushed by the Ottomans. In retribution, Grand vizier, Grand Vizier Sinan Pasha ordered the relics of Saint Sava to be publicly torched on the Vračar plateau; in the 20th century, the church of Saint Sava was built to commemorate this event.
Occupied by the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburgs three times (Siege of Belgrade (1688), 1688–1690, Kingdom of Serbia (1718–39), 1717–1739, Siege of Belgrade (1789), 1789–1791), headed by the Holy Roman Empire, Holy Roman Princes Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian of Bavaria and Prince Eugene of Savoy, Eugene of Savoy, and field marshal Baron Ernst Gideon von Laudon, respectively, Belgrade was quickly recaptured by the Ottomans and substantially razed each time. During this period, the city was affected by the two Great Serbian Migrations, in which hundreds of thousands of Serbs, led by two Serbian Patriarchs, retreated together with the Austrian soldiers into the Habsburg Empire, settling in today's Vojvodina and Slavonia.
Principality and Kingdom of Serbia
 At the beginning of the 19th century, Belgrade was predominantly inhabited by a Muslim population. Traces of Ottoman rule and architecture—such as mosques and bazaars, were to remain a prominent part of Belgrade's townscape into the 19th century; several decades, even, after Serbia was granted autonomy from the Ottoman Empire.
During the First Serbian Uprising, Serbian revolutionaries held the city from 8 January 1807 until 1813, when it was retaken by the Ottomans. After the Second Serbian Uprising in 1815, Serbia achieved some sort of sovereignty, which was formally recognised by the Ottoman Porte, Porte in 1830.
The development of Belgrade architecture after 1815 can be divided into four periods. In the first phase, which lasted from 1815 to 1835, the dominant architectural style was still of a Balkan character, with substantial Ottoman influence. At the same time, an interest in joining the European mainstream allowed Central and Western European architecture to flourish. Between 1835 and 1850, the amount of Neoclassicism, neoclassicist and baroque buildings south of the Austrian border rose considerably, exemplified by St. Michael's Cathedral, Belgrade, St Michael's Cathedral (Serbian: ''Saborna crkva)'', completed in 1840. Between 1850 and 1875, new architecture was characterised by a turn towards the newly popular Romanticism, along with older European architectural styles. Typical of Central European cities in the last quarter of the 19th century, the fourth phase was characterised by an Eclecticism, eclecticist style based on the Renaissance and Baroque periods.
At the beginning of the 19th century, Belgrade was predominantly inhabited by a Muslim population. Traces of Ottoman rule and architecture—such as mosques and bazaars, were to remain a prominent part of Belgrade's townscape into the 19th century; several decades, even, after Serbia was granted autonomy from the Ottoman Empire.
During the First Serbian Uprising, Serbian revolutionaries held the city from 8 January 1807 until 1813, when it was retaken by the Ottomans. After the Second Serbian Uprising in 1815, Serbia achieved some sort of sovereignty, which was formally recognised by the Ottoman Porte, Porte in 1830.
The development of Belgrade architecture after 1815 can be divided into four periods. In the first phase, which lasted from 1815 to 1835, the dominant architectural style was still of a Balkan character, with substantial Ottoman influence. At the same time, an interest in joining the European mainstream allowed Central and Western European architecture to flourish. Between 1835 and 1850, the amount of Neoclassicism, neoclassicist and baroque buildings south of the Austrian border rose considerably, exemplified by St. Michael's Cathedral, Belgrade, St Michael's Cathedral (Serbian: ''Saborna crkva)'', completed in 1840. Between 1850 and 1875, new architecture was characterised by a turn towards the newly popular Romanticism, along with older European architectural styles. Typical of Central European cities in the last quarter of the 19th century, the fourth phase was characterised by an Eclecticism, eclecticist style based on the Renaissance and Baroque periods.
 In 1841, Prince Mihailo Obrenović moved the capital of the Principality of Serbia from Kragujevac to Belgrade. During his first reign (1815–1839), Prince Miloš Obrenović pursued expansion of the city's population through the addition of new settlements, aiming and succeeding to make Belgrade the centre of the Principality's administrative, military and cultural institutions. His project of creating a new market space (the Abadžijska čaršija), however, was less successful; trade continued to be conducted in the centuries-old Donja čaršija and Gornja čaršija. Still, new construction projects were typical for the Christian quarters as the older Muslim quarters declined; from Serbia's autonomy until 1863, the number of Belgrade quarters even decreased, mainly as a consequence of the gradual disappearance of the city's Muslim population. An Ottoman city map from 1863 counts only 9 Muslim quarters (''mahalas''). The names of only five such neighbourhoods are known today: Ali-pašina, Reis-efendijina, Jahja-pašina, Bajram-begova, and Laz Hadži-Mahmudova. Following the Čukur Fountain incident, Belgrade was bombed by the Ottomans.
On 18 April 1867, the Ottoman government ordered the Ottoman garrison, which had been since 1826 the last representation of Ottoman suzerainty in Serbia, withdrawn from Kalemegdan. The forlorn Porte's only stipulation was that the Ottoman flag continue to fly over the fortress alongside the Serbian one. Serbia's ''de facto'' independence dates from this event. In the following years, urban planner Emilijan Josimović had a significant influence on Belgrade. He conceptualised a regulation plan for the city in 1867, in which he proposed the replacement of the town's crooked streets with a grid plan. Of great importance also was the construction of independent Serbian political and cultural institutions, as well as the city's now-plentiful parks. Pointing to Josimović's work, Serbian scholars have noted an important break with Ottoman traditions. However, Istanbul—the capital city of the state to which Belgrade and Serbia ''de jure'' still belonged—underwent similar changes.
In 1841, Prince Mihailo Obrenović moved the capital of the Principality of Serbia from Kragujevac to Belgrade. During his first reign (1815–1839), Prince Miloš Obrenović pursued expansion of the city's population through the addition of new settlements, aiming and succeeding to make Belgrade the centre of the Principality's administrative, military and cultural institutions. His project of creating a new market space (the Abadžijska čaršija), however, was less successful; trade continued to be conducted in the centuries-old Donja čaršija and Gornja čaršija. Still, new construction projects were typical for the Christian quarters as the older Muslim quarters declined; from Serbia's autonomy until 1863, the number of Belgrade quarters even decreased, mainly as a consequence of the gradual disappearance of the city's Muslim population. An Ottoman city map from 1863 counts only 9 Muslim quarters (''mahalas''). The names of only five such neighbourhoods are known today: Ali-pašina, Reis-efendijina, Jahja-pašina, Bajram-begova, and Laz Hadži-Mahmudova. Following the Čukur Fountain incident, Belgrade was bombed by the Ottomans.
On 18 April 1867, the Ottoman government ordered the Ottoman garrison, which had been since 1826 the last representation of Ottoman suzerainty in Serbia, withdrawn from Kalemegdan. The forlorn Porte's only stipulation was that the Ottoman flag continue to fly over the fortress alongside the Serbian one. Serbia's ''de facto'' independence dates from this event. In the following years, urban planner Emilijan Josimović had a significant influence on Belgrade. He conceptualised a regulation plan for the city in 1867, in which he proposed the replacement of the town's crooked streets with a grid plan. Of great importance also was the construction of independent Serbian political and cultural institutions, as well as the city's now-plentiful parks. Pointing to Josimović's work, Serbian scholars have noted an important break with Ottoman traditions. However, Istanbul—the capital city of the state to which Belgrade and Serbia ''de jure'' still belonged—underwent similar changes.
 In May 1868, ''knez'' Mihailo was assassinated with his cousin Anka Konstantinović while riding in a carriage in his country residence.
With the Principality of Serbia, Principality's full independence in 1878 and its transformation into the Kingdom of Serbia in 1882, Belgrade once again became a key city in the Balkans, and developed rapidly. Nevertheless, conditions in Serbia remained those of an overwhelmingly agrarian country, even with the opening of a railway to Niš, Serbia's second city. In 1900, the capital had only 70,000 inhabitants (at the time Serbia numbered 2.5 million). Still, by 1905, the population had grown to more than 80,000 and, by the outbreak of World War I in 1914, it had surpassed the 100,000 citizens, disregarding
In May 1868, ''knez'' Mihailo was assassinated with his cousin Anka Konstantinović while riding in a carriage in his country residence.
With the Principality of Serbia, Principality's full independence in 1878 and its transformation into the Kingdom of Serbia in 1882, Belgrade once again became a key city in the Balkans, and developed rapidly. Nevertheless, conditions in Serbia remained those of an overwhelmingly agrarian country, even with the opening of a railway to Niš, Serbia's second city. In 1900, the capital had only 70,000 inhabitants (at the time Serbia numbered 2.5 million). Still, by 1905, the population had grown to more than 80,000 and, by the outbreak of World War I in 1914, it had surpassed the 100,000 citizens, disregarding Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
, which still belonged to Austria-Hungary.
The first-ever projection of motion pictures in the Balkans and Central Europe was held in Belgrade in June 1896 by André Carr, a representative of the Auguste and Louis Lumière, Lumière brothers. He shot the first motion pictures of Belgrade in the next year; however, they have not been preserved. The first permanent cinema was opened in 1909 in Belgrade.
World War I: German-Austrian invasion
 The First World War began on 28 July 1914 when Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. Most of the subsequent Balkan offensives occurred near Belgrade. Austro-Hungarian Navy, Austro-Hungarian Monitor (warship), monitors shelled Belgrade on 29 July 1914, and it was taken by the Austro-Hungarian Army under General Oskar Potiorek on 30 November. On 15 December, it was re-taken by Serbian Campaign (World War I), Serbian troops under Marshal Radomir Putnik. After a prolonged battle which destroyed much of the city, starting on 6 October 1915, Belgrade fell to German Army (German Empire), German and Austro-Hungarian troops commanded by Field Marshal August von Mackensen on 9 October of the same year. The city was liberated by Serbian and French Army, French troops on 1 November 1918, under the command of Marshal Louis Franchet d'Espèrey of France and Alexander I of Yugoslavia, Crown Prince Alexander of Serbia. Belgrade, decimated as a front-line city, lost the title of largest city in the Kingdom of Serbia, Kingdom to Subotica for some time.
The First World War began on 28 July 1914 when Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. Most of the subsequent Balkan offensives occurred near Belgrade. Austro-Hungarian Navy, Austro-Hungarian Monitor (warship), monitors shelled Belgrade on 29 July 1914, and it was taken by the Austro-Hungarian Army under General Oskar Potiorek on 30 November. On 15 December, it was re-taken by Serbian Campaign (World War I), Serbian troops under Marshal Radomir Putnik. After a prolonged battle which destroyed much of the city, starting on 6 October 1915, Belgrade fell to German Army (German Empire), German and Austro-Hungarian troops commanded by Field Marshal August von Mackensen on 9 October of the same year. The city was liberated by Serbian and French Army, French troops on 1 November 1918, under the command of Marshal Louis Franchet d'Espèrey of France and Alexander I of Yugoslavia, Crown Prince Alexander of Serbia. Belgrade, decimated as a front-line city, lost the title of largest city in the Kingdom of Serbia, Kingdom to Subotica for some time.
Kingdom of Yugoslavia
 After the war, Belgrade became the capital of the new Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929. The Kingdom was split into Subdivisions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, banovinas and Belgrade, together with
After the war, Belgrade became the capital of the new Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929. The Kingdom was split into Subdivisions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, banovinas and Belgrade, together with Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
and Pančevo, formed a separate administrative unit.
During this period, the city experienced fast growth and significant modernisation. Belgrade's population grew to 239,000 by 1931 (with the inclusion of Zemun), and to 320,000 by 1940. The population growth rate between 1921 and 1948 averaged 4.08% a year.
In 1927, Belgrade's first airport opened, and in 1929, its first radio station began broadcasting. The Pančevo Bridge, which crosses the Danube, was opened in 1935, while King Alexander Bridge over the Sava was opened in 1934. On 3 September 1939 the first Belgrade Grand Prix, the last Grand Prix motor racing race before the outbreak of World War II, was held around the Belgrade Fortress and was followed by 80,000 spectators. The winner was Tazio Nuvolari.
World War II: German invasion
On 25 March 1941, the government of regent Prince Paul of Yugoslavia, Crown Prince Paul signed the Tripartite Pact, joining the Axis powers of World War II, Axis powers in an effort to stay out of the Second World War and keep Yugoslavia neutral during the conflict. This was immediately followed by mass protests in Belgrade and a military coup d'état led by Air Force commander General Dušan Simović, who proclaimed Peter II of Yugoslavia, King Peter II to be of age to rule the realm. As a result, the city was Operation Retribution (1941), heavily bombed by the Luftwaffe on 6 April 1941, killing up to 2,274 people. Yugoslavia was then Invasion of Yugoslavia, invaded by Nazi Germany, German, Kingdom of Italy, Italian, Hungary between the two world wars, Hungarian, and Military history of Bulgaria during World War II, Bulgarian forces. Belgrade was captured by subterfuge, with six German soldiers led by their officer Fritz Klingenberg feigning threatening size, forcing the city to capitulate. Belgrade was more directly occupied by the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army in the same month and became the seat of the puppet Nedić regime, headed by its namesake general. Some of today's parts of Belgrade were incorporated in the Independent State of Croatia in occupied Yugoslavia, another puppet state, where Ustashe regime carried out the Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, Genocide of Serbs. During the summer and fall of 1941, in reprisal for guerrilla attacks, the Germans carried out several massacres of Belgrade citizens; in particular, members of the History of the Jews in Serbia, Jewish community were subject to mass shootings at the order of General Franz Böhme, the German Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia, Military Governor of Serbia. Böhme rigorously enforced the rule that for every German killed, 100 Serbs or Jews would be shot. Belgrade became the first city in Europe to be declared by the Nazi occupation forces to be Judenfrei. The resistance movement in Belgrade was led by Major Žarko Todorović from 1941 until his arrest in 1943.
Just like Rotterdam, which was devastated twice by both German and Allied bombing, Allied bombing of Yugoslavia in World War II#1944 Easter bombing, Belgrade was bombed once more during World War II, this time by the Allies of World War II, Allies on 16 April 1944, killing at least 1,100 people. This bombing fell on the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christian Orthodox Easter, Easter. Most of the city remained under German occupation until 20 October 1944, when it was liberated by the Red Army and the Communist Partisans (Yugoslavia), Yugoslav Partisans.
On 29 November 1945, Marshal Josip Broz Tito proclaimed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia in Belgrade (later renamed to Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia on 7 April 1963). Higher estimates from the former secret police place the victim count of political persecutions in Belgrade at 10,000.
During the summer and fall of 1941, in reprisal for guerrilla attacks, the Germans carried out several massacres of Belgrade citizens; in particular, members of the History of the Jews in Serbia, Jewish community were subject to mass shootings at the order of General Franz Böhme, the German Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia, Military Governor of Serbia. Böhme rigorously enforced the rule that for every German killed, 100 Serbs or Jews would be shot. Belgrade became the first city in Europe to be declared by the Nazi occupation forces to be Judenfrei. The resistance movement in Belgrade was led by Major Žarko Todorović from 1941 until his arrest in 1943.
Just like Rotterdam, which was devastated twice by both German and Allied bombing, Allied bombing of Yugoslavia in World War II#1944 Easter bombing, Belgrade was bombed once more during World War II, this time by the Allies of World War II, Allies on 16 April 1944, killing at least 1,100 people. This bombing fell on the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christian Orthodox Easter, Easter. Most of the city remained under German occupation until 20 October 1944, when it was liberated by the Red Army and the Communist Partisans (Yugoslavia), Yugoslav Partisans.
On 29 November 1945, Marshal Josip Broz Tito proclaimed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia in Belgrade (later renamed to Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia on 7 April 1963). Higher estimates from the former secret police place the victim count of political persecutions in Belgrade at 10,000.
Socialist Yugoslavia
When the war ended, the city was left with 11,500 demolished housing units. During the post-war period, Belgrade grew rapidly as the capital of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, renewed Yugoslavia, developing as a major industrial centre. In 1948, construction of New Belgrade started. In 1958, Belgrade's first television station began broadcasting. In 1961, the conference of Non-Aligned Movement, Non-Aligned Countries was held in Belgrade under Tito's chairmanship. In 1962, Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport was built. In 1968, 1968 student demonstrations in Belgrade, major student protests led to several street clashes between students and the police. In 1972, Belgrade faced 1972 Yugoslav smallpox outbreak, smallpox outbreak, the last major outbreak of smallpox in Europe since World War II. Between October 1977 and March 1978, the city hosted the first major gathering of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe with the aim of implementing the Helsinki Accords from, while in 1980 Belgrade hosted the UNESCO General Conference. Josip Broz Tito died in May 1980 and his Death and state funeral of Josip Broz Tito, funeral in Belgrade was attended by high officials and state delegations from 128 of the 154 Member states of the United Nations, members of the United Nations from both sides of the Iron Curtain, based on which it became one of the largest funerals in history.Breakup of Yugoslavia
On 9 March 1991, March 9, 1991 protest, massive demonstrations led by Vuk Drašković were held in the city against Slobodan Milošević. According to various media outlets, there were between 100,000 and 150,000 people on the streets. Two people were killed, 203 injured and 108 arrested during the protests, and later that day tanks were deployed onto the streets to restore order. Many 1991–1992 anti-war protests in Belgrade, anti-war protests were held in Belgrade, while the most massive protests was dedicated to solidarity with the victims from the Siege of Sarajevo, besieged Sarajevo. 1996–1997 protests in Serbia, Further anti-government protests were held in Belgrade from November 1996 to February 1997 against the same government after alleged electoral fraud in local elections. These protests brought Zoran Đinđić to power, the first mayor of Belgrade since World War II who did not belong to the League of Communists of Yugoslavia or its later offshoot, the Socialist Party of Serbia. In 1999, during the Kosovo War, NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, NATO bombings caused damage to the city. Among the sites bombed were various ministry buildings, the Radio Television of Serbia, RTS building, hospitals, Hotel Jugoslavija, the Ušće Tower, Central Committee building, Avala Tower, and the NATO Bombing of the Chinese embassy in Belgrade, Chinese embassy. After the Yugoslav Wars, Serbia became home to highest number of refugees and internally displaced persons in Europe, while more than third settled in Belgrade. After the 2000 Yugoslavian general election, 2000 presidential elections, Belgrade was the site of major public protests, with over half a million people on the streets. These demonstrations resulted in the Overthrow of Slobodan Milošević, ousting of president Milošević as a part of the Otpor! movement.Development
 In 2014, Belgrade Waterfront, an urban renewal project, was initiated by the Government of Serbia and its Emirati partner, Eagle Hills Properties. Around €3.5 billion was to be jointly invested by the Serbian government and their Emirati partners. The project includes office and luxury apartment buildings, five-star hotels, a shopping mall and the envisioned 'Belgrade Tower'. The project is, however, quite controversial—there are a number of uncertainties regarding its funding, necessity, and its architecture's arguable lack of harmony with the rest of the city.
In addition to Belgrade Waterfront, the city is under rapid development and reconstruction, especially in the area of New Belgrade, Novi Beograd, where (as of 2020) apartment and office buildings were under construction to support the burgeoning Belgrade IT sector, now one of Serbia's largest economic players. In September 2020, there were around 2000 active construction sites in Belgrade.
In 2014, Belgrade Waterfront, an urban renewal project, was initiated by the Government of Serbia and its Emirati partner, Eagle Hills Properties. Around €3.5 billion was to be jointly invested by the Serbian government and their Emirati partners. The project includes office and luxury apartment buildings, five-star hotels, a shopping mall and the envisioned 'Belgrade Tower'. The project is, however, quite controversial—there are a number of uncertainties regarding its funding, necessity, and its architecture's arguable lack of harmony with the rest of the city.
In addition to Belgrade Waterfront, the city is under rapid development and reconstruction, especially in the area of New Belgrade, Novi Beograd, where (as of 2020) apartment and office buildings were under construction to support the burgeoning Belgrade IT sector, now one of Serbia's largest economic players. In September 2020, there were around 2000 active construction sites in Belgrade.
Geography
Topography
Belgrade lies Above mean sea level, above sea level and is located at theconfluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
and Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally th ...
rivers. The historical core of Belgrade, Belgrade Fortress, Kalemegdan, lies on the right banks of both rivers. Since the 19th century, the city has been expanding to the south and east; after World War II, New Belgrade was built on the left bank of the Sava river, connecting Belgrade with Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
. Smaller, chiefly residential communities across the Danube, like Krnjača, Kotež and Borča, also merged with the city, while Pančevo, a heavily industrialised satellite city, remains a separate town. The city has an urban area of , while together with its metropolitan area it covers .
On the right bank of the Sava, central Belgrade has a hilly terrain, while the highest point of Belgrade proper is Torlak (Belgrade), Torlak hill at . The mountains of Avala () and Kosmaj () lie south of the city. Across the Sava and Danube, the land is mostly flat, consisting of alluvial plains and loam, loessial plateaus.
 One of the characteristics of the city terrain is mass wasting. On the territory covered by the General Urban Plan there are 1,155 recorded mass wasting points, out of which 602 are active and 248 are labeled as the 'high risk'. They cover almost 30% of the city territory and include several types of mass wasting. Downhill creeps are located on the slopes above the rivers, mostly on the clay or loam soils, inclined between 7 and 20%. Most critical ones are in Karaburma, Zvezdara, Višnjica, Serbia, Višnjica, Vinča and Ritopek, in the Danube valley, and Umka, and especially its neighbourhood of Duboko, in the Sava valley. They have moving and dormant phases, and some of them have been recorded for centuries. Less active downhill creep areas include the entire Terazijska Terasa, Terazije slope above the Sava (Kalemegdan, Savamala), which can be seen by the inclination of the Pobednik monument and the tower of the St. Michael's Cathedral, Belgrade, Cathedral Church, and the Voždovac section, between Banjica and Autokomanda.
Landslides encompass smaller areas, develop on the steep cliffs, sometimes being inclined up to 90%. They are mostly located in the artificial loess hills of Zemun: Gardoš, Ćukovac and Kalvarija (Zemun), Kalvarija.
However, the majority of the land movement in Belgrade, some 90%, is triggered by the construction works and faulty water supply system (burst pipes, etc.). The neighbourhood of Mirijevo is considered to be the most successful project of fixing the problem. During the construction of the neighbourhood from the 1970s, the terrain was systematically improved and the movement of the land is today completely halted.
One of the characteristics of the city terrain is mass wasting. On the territory covered by the General Urban Plan there are 1,155 recorded mass wasting points, out of which 602 are active and 248 are labeled as the 'high risk'. They cover almost 30% of the city territory and include several types of mass wasting. Downhill creeps are located on the slopes above the rivers, mostly on the clay or loam soils, inclined between 7 and 20%. Most critical ones are in Karaburma, Zvezdara, Višnjica, Serbia, Višnjica, Vinča and Ritopek, in the Danube valley, and Umka, and especially its neighbourhood of Duboko, in the Sava valley. They have moving and dormant phases, and some of them have been recorded for centuries. Less active downhill creep areas include the entire Terazijska Terasa, Terazije slope above the Sava (Kalemegdan, Savamala), which can be seen by the inclination of the Pobednik monument and the tower of the St. Michael's Cathedral, Belgrade, Cathedral Church, and the Voždovac section, between Banjica and Autokomanda.
Landslides encompass smaller areas, develop on the steep cliffs, sometimes being inclined up to 90%. They are mostly located in the artificial loess hills of Zemun: Gardoš, Ćukovac and Kalvarija (Zemun), Kalvarija.
However, the majority of the land movement in Belgrade, some 90%, is triggered by the construction works and faulty water supply system (burst pipes, etc.). The neighbourhood of Mirijevo is considered to be the most successful project of fixing the problem. During the construction of the neighbourhood from the 1970s, the terrain was systematically improved and the movement of the land is today completely halted.
Climate
 Belgrade has a humid subtropical climate (''Cfa''), according to Köppen climate classification, with four seasons and uniformly spread precipitation. Monthly averages range from in January to in July, with an annual mean of . There are, on average, 31 days a year when the temperature is above , and 95 days when the temperature is above . Belgrade receives about of precipitation a year, with late spring being wettest. The average annual number of sunny hours is 2,112.
The highest officially recorded temperature in Belgrade was on 24 July 2007, while on the other end, the lowest temperature was on 10 January 1893.
Belgrade has a humid subtropical climate (''Cfa''), according to Köppen climate classification, with four seasons and uniformly spread precipitation. Monthly averages range from in January to in July, with an annual mean of . There are, on average, 31 days a year when the temperature is above , and 95 days when the temperature is above . Belgrade receives about of precipitation a year, with late spring being wettest. The average annual number of sunny hours is 2,112.
The highest officially recorded temperature in Belgrade was on 24 July 2007, while on the other end, the lowest temperature was on 10 January 1893.
Administration
 Belgrade is a separate territorial unit in Serbia, with its own autonomous city authority. The Assembly of the City of Belgrade has 110 members, elected on four-year terms. A 13-member City Council, elected by the Assembly and presided over by the mayor and his deputy, has the control and supervision of the city administration, which manages day-to-day administrative affairs. It is divided into 14 Secretariats, each having a specific portfolio such as traffic or health care, and several professional services, agencies and institutes.
The 2022 Belgrade City Assembly election was won by the Serbian Progressive Party, which formed a ruling coalition with the Socialist Party of Serbia. Between 2004 and 2013, the Democratic Party (Serbia), Democratic Party was in power. Due to the importance of Belgrade in political and economic life of Serbia, the office of city's mayor is often described as the third most important office in the state, after the Prime Minister of Serbia, President of the Government and the President of Serbia, President of the Republic.
As the capital city, Belgrade is seat of all Serbian state authorities – executive (government), executive, legislative, judiciary, and the headquarters of almost all national political parties as well as 75 diplomatic missions. This includes the National Assembly (Serbia), National Assembly, the Presidency, the Government of Serbia and all the ministries, Supreme Court of Cassation (Serbia), Supreme Court of Cassation and the Constitutional Court of Serbia, Constitutional Court.
Belgrade is a separate territorial unit in Serbia, with its own autonomous city authority. The Assembly of the City of Belgrade has 110 members, elected on four-year terms. A 13-member City Council, elected by the Assembly and presided over by the mayor and his deputy, has the control and supervision of the city administration, which manages day-to-day administrative affairs. It is divided into 14 Secretariats, each having a specific portfolio such as traffic or health care, and several professional services, agencies and institutes.
The 2022 Belgrade City Assembly election was won by the Serbian Progressive Party, which formed a ruling coalition with the Socialist Party of Serbia. Between 2004 and 2013, the Democratic Party (Serbia), Democratic Party was in power. Due to the importance of Belgrade in political and economic life of Serbia, the office of city's mayor is often described as the third most important office in the state, after the Prime Minister of Serbia, President of the Government and the President of Serbia, President of the Republic.
As the capital city, Belgrade is seat of all Serbian state authorities – executive (government), executive, legislative, judiciary, and the headquarters of almost all national political parties as well as 75 diplomatic missions. This includes the National Assembly (Serbia), National Assembly, the Presidency, the Government of Serbia and all the ministries, Supreme Court of Cassation (Serbia), Supreme Court of Cassation and the Constitutional Court of Serbia, Constitutional Court.
Municipalities
 The city is divided into 17 municipalities. Previously, they were classified into 10 urban (lying completely or partially within borders of the city proper) and 7 suburban municipalities, whose centres are smaller towns. With the new 2010 City statute, they were all given equal status, with the proviso that suburban ones (except Surčin) have certain autonomous powers, chiefly related with construction, infrastructure and public utilities.
Most of the municipalities are situated on the southern side of the Danube and
The city is divided into 17 municipalities. Previously, they were classified into 10 urban (lying completely or partially within borders of the city proper) and 7 suburban municipalities, whose centres are smaller towns. With the new 2010 City statute, they were all given equal status, with the proviso that suburban ones (except Surčin) have certain autonomous powers, chiefly related with construction, infrastructure and public utilities.
Most of the municipalities are situated on the southern side of the Danube and Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally th ...
rivers, in the Šumadija region. Three municipalities (Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
, New Belgrade, Novi Beograd, and Surčin), are on the northern bank of the Sava in the Syrmia region and the municipality of Palilula (Belgrade), Palilula, spanning the Danube, is in both the Šumadija and Banat regions.

Demographics
According to the 2011 census, the city has a population of 1,166,763, while the urban area of Belgrade (with adjacent urban settlements of Borča, Ovča, and Surčin included) has 1,233,796 inhabitants, and the population of the metropolitan area (the administrative area of the City of Belgrade) stands at 1,659,440 people. Belgrade is home to many ethnicities from across the former Yugoslavia and the wider Balkans region. The main ethnic groups are: Serbs (1,505,448), Romani people, Roma (27,325), Montenegrins (ethnic group), Montenegrins (9,902), Yugoslavs (8,061), Croats of Serbia, Croats (7,752), Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians (6,970), and Muslims (South-Slavic ethnic group), ethnic Muslims (3,996). Many people came to the city as economic migrants from smaller towns and the countryside, while tens of thousands arrived as refugees from Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnia-Herzegovina and Kosovo, as a result of the Yugoslav wars of the 1990s. Between 10,000 and 20,000 Han Chinese, Chinese people are estimated to live in Belgrade and, since their arrival in the mid-1990s, Blocks (New Belgrade), Block 70 in New Belgrade has been known colloquially as the Chinese quarter. Many Middle Easterners, mainly from Syria, Iran, Jordan and Iraq, arrived in order to pursue their studies during the 1970s and 1980s, and have remained in the city. Throughout the 19th and early 20th century, small communities of Aromanians, Czechs, Greeks, Germans, Hungarians, Jews, Turkish people, Turks, Armenians and Russians, Russian White émigrés also existed in Belgrade. There are two suburban settlements with significant minority population today: Ovča and the village of Boljevci, both with about one quarter of their population being Romanians and Slovaks, respectively. Although there are several historic religious communities in Belgrade, the religious makeup of the city is relatively homogeneous. The Serbian Orthodox Church, Serbian Orthodox community is by far the largest, with 1,475,168 adherents. There are also 31,914 Muslims, 13,720 Roman Catholics, and 3,128 Protestantism, Protestants. There once was a significant History of the Jews in Serbia, Jewish community in Belgrade but, following the World War II History of Serbia#Serbia in World War I, Nazi occupation of the city and subsequent Jewish emigration, their numbers have fallen from over 10,000 to just 295. Belgrade also used to have one of the largest Buddhist colonies in Europe outside Russia when some 400 mostly Buddhist Kalmyks settled on the outskirts of Belgrade following the Russian Civil War. The first Buddhist temple in Europe was built in Belgrade in 1929. Most of them moved away after the World War II and their temple, Belgrade pagoda, was abandoned, claimed by the new Communist regime and eventually demolished.Economy
Culture
 According to BBC, Belgrade is one of five most creative cities in the world.
Belgrade hosts many annual international cultural events, including the FEST (Belgrade), Film Festival, Belgrade International Theatre Festival, Theatre Festival, Belgrade Summer Festival, Summer Festival, Belgrade Music Festival, BEMUS, Belgrade Early Music Festival, Belgrade Book Fair, Book Fair, Belgrade Choir Festival, Eurovision Song Contest 2008, and the Belgrade Beer Fest, Beer Fest. In 2022 Belgrade was also home to the EuroPride, Europride event, even though the president Aleksandar Vučić tried to cancel it. The Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Prize winning author Ivo Andrić wrote his most famous work, ''The Bridge on the Drina'', in Belgrade. Other prominent Belgrade authors include Branislav Nušić, Miloš Crnjanski, Borislav Pekić, Milorad Pavić (writer), Milorad Pavić and Meša Selimović. The most internationally prominent artists from Belgrade are Charles Simic, Marina Abramović and Milovan Destil Marković.
Most of Cinema of Serbia, Serbia's film industry is based in Belgrade. FEST (Belgrade), FEST is an annual film festival that held since 1971, and, through 2013, had been attended by four million people and had presented almost 4,000 films.
The city was one of the main centres of the New wave music in Yugoslavia, Yugoslav new wave in the 1980s: VIS Idoli, Ekatarina Velika, Šarlo Akrobata and Električni Orgazam were all from Belgrade. Other notable Belgrade rock acts include Riblja Čorba, Bajaga i Instruktori and Partibrejkers. Today, it is the centre of the Serbian hip hop scene, with acts such as Beogradski Sindikat, Bad Copy, Škabo, Marčelo, and most of the Bassivity Music stable hailing from or living in the city. There are numerous theatres, the most prominent of which are National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Theatre on Terazije, Yugoslav Drama Theatre, Zvezdara Theatre, and Atelje 212, Atelier 212. The Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts is also based in Belgrade, as well as the National Library of Serbia. Other major libraries include the Belgrade City Library and the Belgrade University Library. Belgrade's two opera houses are: National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre and Madlenianum Opera and Theatre, Madlenianum Opera House. Following the victory of Serbia's representative Marija Šerifović at the Eurovision Song Contest 2007, Belgrade hosted the Contest in
According to BBC, Belgrade is one of five most creative cities in the world.
Belgrade hosts many annual international cultural events, including the FEST (Belgrade), Film Festival, Belgrade International Theatre Festival, Theatre Festival, Belgrade Summer Festival, Summer Festival, Belgrade Music Festival, BEMUS, Belgrade Early Music Festival, Belgrade Book Fair, Book Fair, Belgrade Choir Festival, Eurovision Song Contest 2008, and the Belgrade Beer Fest, Beer Fest. In 2022 Belgrade was also home to the EuroPride, Europride event, even though the president Aleksandar Vučić tried to cancel it. The Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Prize winning author Ivo Andrić wrote his most famous work, ''The Bridge on the Drina'', in Belgrade. Other prominent Belgrade authors include Branislav Nušić, Miloš Crnjanski, Borislav Pekić, Milorad Pavić (writer), Milorad Pavić and Meša Selimović. The most internationally prominent artists from Belgrade are Charles Simic, Marina Abramović and Milovan Destil Marković.
Most of Cinema of Serbia, Serbia's film industry is based in Belgrade. FEST (Belgrade), FEST is an annual film festival that held since 1971, and, through 2013, had been attended by four million people and had presented almost 4,000 films.
The city was one of the main centres of the New wave music in Yugoslavia, Yugoslav new wave in the 1980s: VIS Idoli, Ekatarina Velika, Šarlo Akrobata and Električni Orgazam were all from Belgrade. Other notable Belgrade rock acts include Riblja Čorba, Bajaga i Instruktori and Partibrejkers. Today, it is the centre of the Serbian hip hop scene, with acts such as Beogradski Sindikat, Bad Copy, Škabo, Marčelo, and most of the Bassivity Music stable hailing from or living in the city. There are numerous theatres, the most prominent of which are National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Theatre on Terazije, Yugoslav Drama Theatre, Zvezdara Theatre, and Atelje 212, Atelier 212. The Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts is also based in Belgrade, as well as the National Library of Serbia. Other major libraries include the Belgrade City Library and the Belgrade University Library. Belgrade's two opera houses are: National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre and Madlenianum Opera and Theatre, Madlenianum Opera House. Following the victory of Serbia's representative Marija Šerifović at the Eurovision Song Contest 2007, Belgrade hosted the Contest in 2008
File:2008 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Lehman Brothers went bankrupt following the Subprime mortgage crisis; Cyclone Nargis killed more than 138,000 in Myanmar; A scene from the opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing; ...
.
There is more than 1650 public sculptures on the territory of Belgrade.
Museums
 The most prominent museum in Belgrade is the National Museum of Serbia, National Museum, founded in 1844 and reconstructed from 2003 until June 2018. The museum houses a collection of more than 400,000 exhibits (over 5600 paintings and 8400 drawings and prints, including many foreign masters like Hieronymus Bosch, Bosch, Juan de Flandes, Titian, Tintoretto, Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, Anthony van Dyck, Van Dyck, Cézanne, Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, G.B. Tiepolo, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Renoir, Claude Monet, Monet, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Lautrec, Henri Matisse, Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Picasso, Paul Gauguin, Gauguin, Marc Chagall, Chagall, Vincent van Gogh, Van Gogh, Piet Mondrian, Mondrian etc.) and also the famous Miroslav's Gospel. The Ethnographic Museum (Belgrade), Ethnographic Museum, established in 1901, contains more than 150,000 items showcasing the rural and urban culture of the Balkans, particularly the countries of former Yugoslavia.
The Museum of Contemporary Art (Belgrade), Museum of Contemporary Art was the first contemporary art museum in Yugoslavia and one of the first museums of this type in the world. Following its foundation in 1965, has amassed a collection of more than 8,000 works from art produced across the former Yugoslavia. The museum was closed in 2007, but has since been reopened in 2017 to focus on the modern as well as on the Yugoslav art scenes.
Artist Marina Abramović, who was born in Belgrade, held an exhibition in the Museum of Contemporary Art, which the ''The New York Times, New York Times'' described as one of the most important cultural happenings in the world in 2019. The exhibition was seen by almost 100,000 visitors. Marina Abramović made a stage speech and performance in front of 20,000 people. In the heart of Belgrade you can also find the Museum of Applied Arts, Belgrade, Museum of Applied Arts, a museum that has been awarded for the Institution of the Year 2016 by International Council of Museums, ICOM.
The Military Museum (Belgrade), Military Museum, established in 1878 in Kalemegdan, houses a wide range of more than 25,000 military objects dating from the prehistoric to the medieval to the modern eras. Notable items include Turkish and oriental arms, national banners, and Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav Partisan regalia.
The Museum of Aviation in Belgrade located near Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport has more than 200 aircraft, of which about 50 are on display, and a few of which are the only surviving examples of their type, such as the Fiat G.50. This museum also displays parts of shot down US and NATO aircraft, such as the F-117 Nighthawk, F-117 and F-16 Fighting Falcon, F-16.
The Nikola Tesla Museum, founded in 1952, preserves the personal items of Nikola Tesla, the inventor after whom the Tesla (unit), Tesla unit was named. It holds around 160,000 original documents and around 5,700 personal other items including his urn. The last of the major Belgrade museums is the Museum of Vuk and Dositej, which showcases the lives, work and legacy of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and Dositej Obradović, the 19th century reformer of the Serbian literary language and the first Serbian Minister of Education, respectively. Belgrade also houses the Museum of African Art, Serbia, Museum of African Art, founded in 1977, which has a large collection of art from West Africa.
With around 95,000 copies of national and international films, the Yugoslav Film Archive is the largest in the region and among the 10 largest archives in the world. The institution also operates the Museum of Yugoslav Film Archive, with movie theatre and exhibition hall. The archive's long-standing storage problems were finally solved in 2007, when a new modern depository was opened. The Yugoslav Film Archive also exhibits original Charlie Chaplin's stick and one of the first movies by Auguste and Louis Lumière.
The Belgrade City Museum moved into a new building in downtown in 2006. The museum hosts a range of collections covering the history of urban life since prehistory.
The Museum of Yugoslav History has collections from the Yugoslav era. Beside paintings, the most valuable are Moon rocks donated by Apollo 11 crew Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins (astronaut), Michael Collins while visiting Belgrade in 1969 and from mission Apollo 17 donated by Richard Nixon in 1971. Museum also houses Joseph Stalin's sabre with 260 brilliants and diamonds, donated by Stalin himself.
Museum of Science and Technology (Belgrade), Museum of Science and Technology moved to the building of the first city's power plant in Dorćol in 2005.
The most prominent museum in Belgrade is the National Museum of Serbia, National Museum, founded in 1844 and reconstructed from 2003 until June 2018. The museum houses a collection of more than 400,000 exhibits (over 5600 paintings and 8400 drawings and prints, including many foreign masters like Hieronymus Bosch, Bosch, Juan de Flandes, Titian, Tintoretto, Peter Paul Rubens, Rubens, Anthony van Dyck, Van Dyck, Cézanne, Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, G.B. Tiepolo, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Renoir, Claude Monet, Monet, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Lautrec, Henri Matisse, Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Picasso, Paul Gauguin, Gauguin, Marc Chagall, Chagall, Vincent van Gogh, Van Gogh, Piet Mondrian, Mondrian etc.) and also the famous Miroslav's Gospel. The Ethnographic Museum (Belgrade), Ethnographic Museum, established in 1901, contains more than 150,000 items showcasing the rural and urban culture of the Balkans, particularly the countries of former Yugoslavia.
The Museum of Contemporary Art (Belgrade), Museum of Contemporary Art was the first contemporary art museum in Yugoslavia and one of the first museums of this type in the world. Following its foundation in 1965, has amassed a collection of more than 8,000 works from art produced across the former Yugoslavia. The museum was closed in 2007, but has since been reopened in 2017 to focus on the modern as well as on the Yugoslav art scenes.
Artist Marina Abramović, who was born in Belgrade, held an exhibition in the Museum of Contemporary Art, which the ''The New York Times, New York Times'' described as one of the most important cultural happenings in the world in 2019. The exhibition was seen by almost 100,000 visitors. Marina Abramović made a stage speech and performance in front of 20,000 people. In the heart of Belgrade you can also find the Museum of Applied Arts, Belgrade, Museum of Applied Arts, a museum that has been awarded for the Institution of the Year 2016 by International Council of Museums, ICOM.
The Military Museum (Belgrade), Military Museum, established in 1878 in Kalemegdan, houses a wide range of more than 25,000 military objects dating from the prehistoric to the medieval to the modern eras. Notable items include Turkish and oriental arms, national banners, and Yugoslav Partisans, Yugoslav Partisan regalia.
The Museum of Aviation in Belgrade located near Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport has more than 200 aircraft, of which about 50 are on display, and a few of which are the only surviving examples of their type, such as the Fiat G.50. This museum also displays parts of shot down US and NATO aircraft, such as the F-117 Nighthawk, F-117 and F-16 Fighting Falcon, F-16.
The Nikola Tesla Museum, founded in 1952, preserves the personal items of Nikola Tesla, the inventor after whom the Tesla (unit), Tesla unit was named. It holds around 160,000 original documents and around 5,700 personal other items including his urn. The last of the major Belgrade museums is the Museum of Vuk and Dositej, which showcases the lives, work and legacy of Vuk Stefanović Karadžić and Dositej Obradović, the 19th century reformer of the Serbian literary language and the first Serbian Minister of Education, respectively. Belgrade also houses the Museum of African Art, Serbia, Museum of African Art, founded in 1977, which has a large collection of art from West Africa.
With around 95,000 copies of national and international films, the Yugoslav Film Archive is the largest in the region and among the 10 largest archives in the world. The institution also operates the Museum of Yugoslav Film Archive, with movie theatre and exhibition hall. The archive's long-standing storage problems were finally solved in 2007, when a new modern depository was opened. The Yugoslav Film Archive also exhibits original Charlie Chaplin's stick and one of the first movies by Auguste and Louis Lumière.
The Belgrade City Museum moved into a new building in downtown in 2006. The museum hosts a range of collections covering the history of urban life since prehistory.
The Museum of Yugoslav History has collections from the Yugoslav era. Beside paintings, the most valuable are Moon rocks donated by Apollo 11 crew Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins (astronaut), Michael Collins while visiting Belgrade in 1969 and from mission Apollo 17 donated by Richard Nixon in 1971. Museum also houses Joseph Stalin's sabre with 260 brilliants and diamonds, donated by Stalin himself.
Museum of Science and Technology (Belgrade), Museum of Science and Technology moved to the building of the first city's power plant in Dorćol in 2005.
Architecture
 Belgrade has wildly varying architecture, from the centre of
Belgrade has wildly varying architecture, from the centre of Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
, typical of a Central European town, to the more modern architecture and spacious layout of Novi Beograd, New Belgrade. The oldest architecture is found in Kalemegdan Park. Outside of Kalemegdan, the oldest buildings date only from the 18th century, due to its geographic position and frequent wars and destructions.

 The oldest public structure in Belgrade is a nondescript Turkish türbe, while the oldest house is a modest clay house on Dorćol, from late 18th century. Western influence began in the 19th century, when the city completely transformed from an oriental town to the contemporary architecture of the time, with influences from neoclassicism, romanticism, and academic art. Serbian architects took over the development from the foreign builders in the late 19th century, producing the National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Old Palace (Belgrade), Old Palace, St. Michael's Cathedral (Belgrade), Cathedral Church and later, in the early 20th century, the National Assembly of Serbia, National Assembly and National Museum of Serbia, National Museum, influenced by art nouveau. Elements of Serbo-Byzantine Revival are present in buildings such as House of Vuk's Foundation, old Post Office in Kosovska street, and sacral architecture, such as St. Mark's Church, Belgrade, St. Mark's Church (based on the Gračanica monastery), and the Temple of Saint Sava.
In the socialist period, housing was built quickly and cheaply for the huge influx of people fleeing the countryside following World War II, sometimes resulting in the brutalist architecture of the Blocks (New Belgrade), ''blokovi'' ('blocks') of New Belgrade; a socrealism trend briefly ruled, resulting in buildings like the Dom Sindikata, Trade Union Hall. However, in the mid-1950s, modernism, modernist trends took over, and still dominate the Belgrade architecture.
Belgrade has the second oldest sewer system in Europe. The
The oldest public structure in Belgrade is a nondescript Turkish türbe, while the oldest house is a modest clay house on Dorćol, from late 18th century. Western influence began in the 19th century, when the city completely transformed from an oriental town to the contemporary architecture of the time, with influences from neoclassicism, romanticism, and academic art. Serbian architects took over the development from the foreign builders in the late 19th century, producing the National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Old Palace (Belgrade), Old Palace, St. Michael's Cathedral (Belgrade), Cathedral Church and later, in the early 20th century, the National Assembly of Serbia, National Assembly and National Museum of Serbia, National Museum, influenced by art nouveau. Elements of Serbo-Byzantine Revival are present in buildings such as House of Vuk's Foundation, old Post Office in Kosovska street, and sacral architecture, such as St. Mark's Church, Belgrade, St. Mark's Church (based on the Gračanica monastery), and the Temple of Saint Sava.
In the socialist period, housing was built quickly and cheaply for the huge influx of people fleeing the countryside following World War II, sometimes resulting in the brutalist architecture of the Blocks (New Belgrade), ''blokovi'' ('blocks') of New Belgrade; a socrealism trend briefly ruled, resulting in buildings like the Dom Sindikata, Trade Union Hall. However, in the mid-1950s, modernism, modernist trends took over, and still dominate the Belgrade architecture.
Belgrade has the second oldest sewer system in Europe. The Clinical Centre of Serbia
The University Clinical Centre of Serbia ( sr, Универзитетски клинички центар Србије; abbr. УKЦС / UKCS) is an academic medical centre located in Belgrade, Serbia. It serves as the main medical centre for both ...
spreads over 34 hectares and consists of about 50 buildings, while also has 3,150 beds considered to be the highest number in Europe, and among List of hospitals by capacity, highest in the world.
Tourism
Lying on the main artery connecting Europe and Asia, as well as, eventually, the Orient Express, Belgrade has been a popular place for travellers through the centuries. In 1843, on Dubrovačka Street (today Kralj Petar Street ), Serbia's ''knez (title), knez'' Mihailo Obrenović built a large edifice which became the first hotel in Belgrade: ''Kod jelena'' ('at the deer's'), in the neighbourhood of Kosančićev Venac. Many criticised the move at the time due to the cost and the size of the building, and it soon became the gathering point of the Principality's wealthiest citizens. Colloquially, the building was also referred to as the ''staro zdanje'', or the 'old edifice'. It remained a hotel until 1903 before being demolished in 1938. After the ''staro zdanje'', numerous hotels were built in the second half of the 19th century: ''Nacional'' and ''Grand'', also in Kosančićev Venac, ''Srpski Kralj'', ''Srpska Kruna'', ''Grčka Kraljica'' near Kalemegdan, ''Balkan'' and ''Pariz'' in Terazije, ''London, Belgrade, London'', etc. As Belgrade became connected via steamboats and railway (after 1884), the number of visitors grew and new hotels were open with the ever luxurious commodities. In Savamala, the hotels ''Bosna'' and ''Bristol'' were opened. Other hotels included ''Solun'' and ''Orient'', which was built near the Financial Park. Tourists which arrived by the Orient Express mostly stayed at the Petrograd Hotel in Savamala#Sava Square, Wilson Square. Hotel ''Srpski Kralj'', at the corner of Uzun Mirkova and Pariska Street was considered the best hotel in Belgrade during the Interbellum. It was destroyed during World War II.
The historic areas and buildings of Belgrade are among the city's premier attractions. They include Skadarlija, the National Museum of Serbia, National Museum and adjacent National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre,
As Belgrade became connected via steamboats and railway (after 1884), the number of visitors grew and new hotels were open with the ever luxurious commodities. In Savamala, the hotels ''Bosna'' and ''Bristol'' were opened. Other hotels included ''Solun'' and ''Orient'', which was built near the Financial Park. Tourists which arrived by the Orient Express mostly stayed at the Petrograd Hotel in Savamala#Sava Square, Wilson Square. Hotel ''Srpski Kralj'', at the corner of Uzun Mirkova and Pariska Street was considered the best hotel in Belgrade during the Interbellum. It was destroyed during World War II.
The historic areas and buildings of Belgrade are among the city's premier attractions. They include Skadarlija, the National Museum of Serbia, National Museum and adjacent National Theatre in Belgrade, National Theatre, Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
, Nikola Pašić Square, Terazije, Studentski Trg, Students' Square, the Belgrade Fortress, Kalemegdan Fortress, Knez Mihailova, Knez Mihailova Street, the Parliament of Serbia, Parliament, the Temple of Saint Sava, Church of Saint Sava, and the The Old Palace, Old Palace. On top of this, there are many parks, monuments, museums, cafés, restaurants and shops on both sides of the river. The hilltop Monument to the Unknown Hero, Avala Monument and Avala Tower offer views over the city. According to ''The Guardian'', Dorcol is the one of top ten coolest suburbs and in Europe.
 Elite neighbourhood of Dedinje is situated near the Topčider and Košutnjak parks. The ''Beli dvor'' (''White Palace''), house of royal family Karađorđević dynasty, Karađorđević, is open for visitors. The palace has many valuable artworks. Nearby, Josip Broz Tito's mausoleum, called ''House of Flowers (mausoleum), The House of Flowers'', documents the life of the former Yugoslav president.
Ada Ciganlija is a former island on the Sava, Sava River, and Belgrade's biggest sports and recreational complex. Today it is connected with the right bank of the Sava via two causeways, creating an artificial lake. It is the most popular destination for Belgraders during the city's hot summers. There are of long beaches and sports facilities for various sports including golf, association football, football, basketball, volleyball, rugby union, baseball, and tennis. During summer there are between 200,000 and 300,000 bathers daily.
Elite neighbourhood of Dedinje is situated near the Topčider and Košutnjak parks. The ''Beli dvor'' (''White Palace''), house of royal family Karađorđević dynasty, Karađorđević, is open for visitors. The palace has many valuable artworks. Nearby, Josip Broz Tito's mausoleum, called ''House of Flowers (mausoleum), The House of Flowers'', documents the life of the former Yugoslav president.
Ada Ciganlija is a former island on the Sava, Sava River, and Belgrade's biggest sports and recreational complex. Today it is connected with the right bank of the Sava via two causeways, creating an artificial lake. It is the most popular destination for Belgraders during the city's hot summers. There are of long beaches and sports facilities for various sports including golf, association football, football, basketball, volleyball, rugby union, baseball, and tennis. During summer there are between 200,000 and 300,000 bathers daily.
 Extreme sports are available, such as bungee jumping, water skiing, and paintballing. There are numerous tracks on the island, where it is possible to ride a bike, go for a walk, or go jogging. Apart from Ada, Belgrade has total of 16 islands on the rivers, many still unused. Among them, the Great War Island, at the confluence of Sava, stands out as an oasis of unshattered wildlife (especially birds). These areas, along with nearby Small War Island, are protected by the city's government as a nature preserve. There are List of natural monuments in Belgrade, 37 protected natural resources in the Belgrade urban area, among which eight are geo-heritage sites, i.e. Straževica profile, Mašin Majdan-Topčider, Profile at the Kalemegdan Fortress, Abandoned quarry in Barajevo, Karagača valley, Artesian well in Ovča, Kapela loess profile, and Lake in Sremčica. Other 29 places are biodiversity sites.
Tourist income in 2016 amounted to nearly one billion euros; with a visit of almost a million registered tourists. Of those, in 2019 more than 100,000 tourists arrived by 742 river cruisers. Average annual growth is between 13% and 14%.
As of 2018, there are three officially designated camp grounds in Belgrade. The oldest one is located in Batajnica, along the Batajnica Road. Named "Dunav", it is one of the most visited campsites in the country. Second one is situated within the complex of the ethno-household "Zornić's House" in the village of Baćevac, while the third is located in Ripanj, on the slopes of the Avala mountain. In 2017 some 15,000 overnights were recorded in camps.
Belgrade is a common stop on the EV6 The Rivers Route, Rivers Route, European Long-distance cycling route, cycling route known as "Danube Bike Trail" in Serbia as well as on the Sultans Trail, a long-distance hiking footpath between Vienna and Istanbul.
Extreme sports are available, such as bungee jumping, water skiing, and paintballing. There are numerous tracks on the island, where it is possible to ride a bike, go for a walk, or go jogging. Apart from Ada, Belgrade has total of 16 islands on the rivers, many still unused. Among them, the Great War Island, at the confluence of Sava, stands out as an oasis of unshattered wildlife (especially birds). These areas, along with nearby Small War Island, are protected by the city's government as a nature preserve. There are List of natural monuments in Belgrade, 37 protected natural resources in the Belgrade urban area, among which eight are geo-heritage sites, i.e. Straževica profile, Mašin Majdan-Topčider, Profile at the Kalemegdan Fortress, Abandoned quarry in Barajevo, Karagača valley, Artesian well in Ovča, Kapela loess profile, and Lake in Sremčica. Other 29 places are biodiversity sites.
Tourist income in 2016 amounted to nearly one billion euros; with a visit of almost a million registered tourists. Of those, in 2019 more than 100,000 tourists arrived by 742 river cruisers. Average annual growth is between 13% and 14%.
As of 2018, there are three officially designated camp grounds in Belgrade. The oldest one is located in Batajnica, along the Batajnica Road. Named "Dunav", it is one of the most visited campsites in the country. Second one is situated within the complex of the ethno-household "Zornić's House" in the village of Baćevac, while the third is located in Ripanj, on the slopes of the Avala mountain. In 2017 some 15,000 overnights were recorded in camps.
Belgrade is a common stop on the EV6 The Rivers Route, Rivers Route, European Long-distance cycling route, cycling route known as "Danube Bike Trail" in Serbia as well as on the Sultans Trail, a long-distance hiking footpath between Vienna and Istanbul.
Nightlife
Belgrade has a reputation for vibrant nightlife; many Nightclub, clubs that are open until dawn can be found throughout the city. The most recognisable nightlife features of Belgrade are the barges (''splav'') spread along the banks of the Sava and Danube Rivers. Many weekend visitors—particularly from Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia and Slovenia—prefer Belgrade nightlife to that of their own capitals due to its perceived friendly atmosphere, plentiful clubs and bars, cheap drinks, lack of significant language barriers, and a lack of night life regulation.
One of the most famous sites for alternative cultural happenings in the city is the SKC (Student Cultural Centre), located right across from Belgrade's highrise landmark, the Beograđanka, Belgrade Palace tower. Concerts featuring famous local and foreign bands are often held at the centre. SKC is also the site of various art exhibitions, as well as public debates and discussions.
A more traditional Serbian nightlife experience, accompanied by traditional music known as ''Starogradska muzika, Starogradska'' (roughly translated as ''Old Town Music''), typical of northern Serbia's urban environments, is most prominent in Skadarlija, the city's old Bohemianism, bohemian neighbourhood where the poets and artists of Belgrade gathered in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Skadar Street (the centre of Skadarlija) and the surrounding neighbourhood are lined with some of Belgrade's best and oldest traditional restaurants (called kafanas in Serbian), which date back to that period.
At one end of the neighbourhood stands Belgrade's oldest beer brewery, founded in the first half of the 19th century. One of the city's oldest kafanas is the Znak pitanja ('?').
''The Times'' reported that Europe's best nightlife can be found in Belgrade. In the Lonely Planet ''1000 Ultimate Experiences'' guide of 2009, Belgrade was placed at the 1st spot among the top 10 party cities in the world.
Many weekend visitors—particularly from Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia and Slovenia—prefer Belgrade nightlife to that of their own capitals due to its perceived friendly atmosphere, plentiful clubs and bars, cheap drinks, lack of significant language barriers, and a lack of night life regulation.
One of the most famous sites for alternative cultural happenings in the city is the SKC (Student Cultural Centre), located right across from Belgrade's highrise landmark, the Beograđanka, Belgrade Palace tower. Concerts featuring famous local and foreign bands are often held at the centre. SKC is also the site of various art exhibitions, as well as public debates and discussions.
A more traditional Serbian nightlife experience, accompanied by traditional music known as ''Starogradska muzika, Starogradska'' (roughly translated as ''Old Town Music''), typical of northern Serbia's urban environments, is most prominent in Skadarlija, the city's old Bohemianism, bohemian neighbourhood where the poets and artists of Belgrade gathered in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Skadar Street (the centre of Skadarlija) and the surrounding neighbourhood are lined with some of Belgrade's best and oldest traditional restaurants (called kafanas in Serbian), which date back to that period.
At one end of the neighbourhood stands Belgrade's oldest beer brewery, founded in the first half of the 19th century. One of the city's oldest kafanas is the Znak pitanja ('?').
''The Times'' reported that Europe's best nightlife can be found in Belgrade. In the Lonely Planet ''1000 Ultimate Experiences'' guide of 2009, Belgrade was placed at the 1st spot among the top 10 party cities in the world.
Sport and recreation
There are approximately one-thousand sports facilities in Belgrade, many of which are capable of serving all levels of sporting events. Ada Ciganlija island, lake and beaches are one of the most important recreational areas in the city. With total of 8 km beaches, with lot of bars, caffe's, restaurants and sport facilities, Ada Ciganlija attracts many visitors especially in summertime. Košutnjak park forest with numerous running and bike trails, sport facilities for all sports with indoor and outdoor pools is also very popular. Located only 2 km from Ada Ciganlija. During the 60s and 70s Belgrade held a number of major international events such as the first ever World Aquatics Championships in1973
Events January
* January 1 - The United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland and Denmark enter the European Economic Community, which later becomes the European Union.
* January 15 – Vietnam War: Citing progress in peace negotiations, U.S. ...
, UEFA Euro 1976, 1976 European Football Championship and 1972–73 European Cup, 1973 European Cup Final, European Athletics Championships in 1962 European Athletics Championships, 1962 and European Athletics Indoor Championships, European Indoor Games in 1969, European Basketball Championships in 1961
Events January
* January 3
** United States President Dwight D. Eisenhower announces that the United States has severed diplomatic and consular relations with Cuba ( Cuba–United States relations are restored in 2015).
** Aero Flight 311 ...
and 1975
It was also declared the ''International Women's Year'' by the United Nations and the European Architectural Heritage Year by the Council of Europe.
Events
January
* January 1 - Watergate scandal (United States): John N. Mitchell, H. R. ...
, European Volleyball Championship for 1975 Men's European Volleyball Championship, men and 1975 Women's European Volleyball Championship, women in 1975 and World Amateur Boxing Championships in 1978 World Amateur Boxing Championships, 1978.
Since the early 2000s Belgrade again hosts major sporting events nearly every year. Some of these include EuroBasket 2005, European Handball Championship (2012 European Men's Handball Championship, men's and 2012 European Women's Handball Championship, women's) in 2012, 2013 World Women's Handball Championship, World Handball Championship for women in 2013, European Volleyball Championships for men in 2005 European Volleyball Championship, 2005 for men and 2011 Women's European Volleyball Championship, 2011 for women, the 2006 and 2016 European Water Polo Championship, the European Youth Olympic Festival 2007 and the Universiade, 2009 Summer Universiade. More recently, Belgrade hosted European Athletics Indoor Championships in 2017 and the basketball EuroLeague Final Four tournaments in 2018 and 2022. Global and continental championships in other sports such as tennis, futsal, judo, karate, wrestling, rowing (sport), rowing, kickboxing, table tennis, and chess have also been held in recent years.
The city is home to Serbia's two biggest and most successful association football, football clubs, Red Star Belgrade and FK Partizan, Partizan Belgrade. Red Star won the UEFA Champions League (''European Cup'') in 1990–91 European Cup, 1991, and Partizan was runner-up in 1965–66 European Cup, 1966. The two major stadiums in Belgrade are the ''Marakana'' (Red Star Stadium) and the Partizan Stadium. The Eternal derby (Serbia), Eternal derby is between Red Star and Partizan.
Štark Arena
The Štark Arena ( sr-cyrl, Штарк арена), also known as Belgrade Arena ( sr-cyrl, Београдска арена), is a multi-purpose indoor arena located in Belgrade, Serbia. It is designed as a universal hall for sports, cultural ev ...
with capacity of 19,384 spectators is one of the largest indoor arenas in Europe. It is used for major sporting events and large concerts. In May 2008 it was the venue for the Eurovision Song Contest 2008, 53rd Eurovision Song Contest. The Aleksandar Nikolić Hall is the main venue of basketball clubs KK Partizan, European champion of 1992, and KK Crvena zvezda.
In recent years, Belgrade has also given rise to several world-class tennis players such as Ana Ivanovic, Jelena Janković and Novak Djokovic. Ivanovic and Djokovic are the first female and male Belgraders, respectively, to win Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam singles titles and been List of ATP number 1 ranked singles tennis players, ATP number 1 with Jelena Janković. The Serbian national team won the 2010 Davis Cup World Group, 2010 Davis Cup, beating the French team in the finals played in the Belgrade Arena.
Belgrade Marathon is held annually since 1988. Belgrade was a candidate to host 1992 and 1996 Summer Olympic Games.
Fashion and design
 Since 1996, semiannual (autumn/winter and spring/summer seasons) fashion weeks are held citywide. Numerous Serbian and foreign designers and fashion brands have their shows during Belgrade Fashion Week. The festival, which collaborates with London Fashion Week, has helped launch the international careers of local talents such as George Styler and Ana Ljubinković. British fashion designer Roksanda Ilincic, who was born in the city, also frequently presents her runway shows in Belgrade.
In addition to fashion, there are two major design shows held in Belgrade every year which attract international architects and industrial designers such as Karim Rashid, Daniel Libeskind, Patricia Urquiola, and Konstantin Grcic. Both the Mikser Festival and Belgrade Design Week feature lectures, exhibits and competitions. Furthermore, international designers like Sacha Lakic, Ana Kraš, Bojana Sentaler, and Marek Djordjevic are originally from Belgrade.
Since 1996, semiannual (autumn/winter and spring/summer seasons) fashion weeks are held citywide. Numerous Serbian and foreign designers and fashion brands have their shows during Belgrade Fashion Week. The festival, which collaborates with London Fashion Week, has helped launch the international careers of local talents such as George Styler and Ana Ljubinković. British fashion designer Roksanda Ilincic, who was born in the city, also frequently presents her runway shows in Belgrade.
In addition to fashion, there are two major design shows held in Belgrade every year which attract international architects and industrial designers such as Karim Rashid, Daniel Libeskind, Patricia Urquiola, and Konstantin Grcic. Both the Mikser Festival and Belgrade Design Week feature lectures, exhibits and competitions. Furthermore, international designers like Sacha Lakic, Ana Kraš, Bojana Sentaler, and Marek Djordjevic are originally from Belgrade.
Media
Belgrade is the most important media hub in Serbia. The city is home to the main headquarters of the national broadcaster Radio Television of Serbia, Radio Television Serbia (RTS), which is a public service broadcaster. The most popular commercial broadcaster is RTV Pink, a Serbian media multinational, known for its popular entertainment programmes. One of the most popular commercial broadcasters is B92, another media company, which has its own TV station, radio station, and music and book publishing arms, as well as the most popular website on the Serbian internet. Other TV stations broadcasting from Belgrade include Prva Srpska Televizija, 1Prva (formerly ''Fox televizija''), Nova.rs, Nova, N1 (television), N1 and others which only cover the greater Belgrade municipal area, such as RTV Studio B, Studio B. High-circulation daily newspapers published in Belgrade include ''Politika'', ''Blic'', ''Alo!'', ''Kurir'' and ''Danas (newspaper), Danas''. There are two sporting dailies, ''Sportski žurnal'' and ''DSL Sport, Sport'', and one economic daily, ''Privredni pregled''. A new free distribution daily, ''24 sata (Serbia), 24 sata'', was founded in the autumn of 2006. Also, Serbian editions of licensed magazines such as ''Harper's Bazaar'', ''Elle (magazine), Elle'', ''Cosmopolitan Serbia, Cosmopolitan'', ''National Geographic (magazine), National Geographic'', ''Men's Health'', ''Grazia'' and others have their headquarters in the city.Education
Transportation

 Belgrade has an extensive public transport system consisting of buses (118 urban lines and more than 300 suburban lines), trams (12 lines), trolleybuses (8 lines) and S-Train BG Voz (6 lines). Buses, trolleybuses and trams are run by GSP Beograd and Lasta Beograd, SP Lasta in cooperation with private companies on some bus routes. The S-train network, BG Voz, run by city government in cooperation with Serbian Railways, is a part of the integrated transport system, and has three lines (Batajnica-Ovča and Ovča-Resnik and Belgrade centre-Mladenovac), with more announced. The BusPlus ticketing system based on contactless smart cards began operating in February 2012. Daily connections link the capital to other towns in Serbia and many other European destinations through the city's Belgrade Bus Station, central bus station.
Beovoz was the regional rail, suburban/commuter railway network that provided mass-transit services in the city, similar to Paris's Réseau Express Régional, RER and Toronto's GO Transit. The main usage of system was to connect the suburbs with the city centre. Beovoz was operated by Serbian Railways. However, this system was abolished back in 2013, mostly due to introduction of more efficient BG Voz. Belgrade is one of the last big European capitals and cities with over a million people to have no metro or subway or other rapid transit system. As of November 2021, Belgrade Metro is currently under construction, which will have 2 lines. The first line is expected to be operational by August 2028.
Belgrade has an extensive public transport system consisting of buses (118 urban lines and more than 300 suburban lines), trams (12 lines), trolleybuses (8 lines) and S-Train BG Voz (6 lines). Buses, trolleybuses and trams are run by GSP Beograd and Lasta Beograd, SP Lasta in cooperation with private companies on some bus routes. The S-train network, BG Voz, run by city government in cooperation with Serbian Railways, is a part of the integrated transport system, and has three lines (Batajnica-Ovča and Ovča-Resnik and Belgrade centre-Mladenovac), with more announced. The BusPlus ticketing system based on contactless smart cards began operating in February 2012. Daily connections link the capital to other towns in Serbia and many other European destinations through the city's Belgrade Bus Station, central bus station.
Beovoz was the regional rail, suburban/commuter railway network that provided mass-transit services in the city, similar to Paris's Réseau Express Régional, RER and Toronto's GO Transit. The main usage of system was to connect the suburbs with the city centre. Beovoz was operated by Serbian Railways. However, this system was abolished back in 2013, mostly due to introduction of more efficient BG Voz. Belgrade is one of the last big European capitals and cities with over a million people to have no metro or subway or other rapid transit system. As of November 2021, Belgrade Metro is currently under construction, which will have 2 lines. The first line is expected to be operational by August 2028.
 The new Belgrade Centre railway station is the hub for almost all the national and international trains.
The high-speed rail that connects Belgrade with Novi Sad started its service at 19 March 2022. The extension towards Subotica and Budapest is under construction, and there are plans for southwards extension towards Niš and North Macedonia.
The city is placed along the Pan-European corridors Pan-European Corridor X, X and VII. The motorway system provides for easy access to Novi Sad and Budapest to the north, Niš to the south, and Zagreb to the west. Expressway is also toward Pančevo and new Expressway construction toward Obrenovac (Montenegro) is scheduled for March 2017. Belgrade bypass is connecting the E70 in Serbia, E70 and E75 in Serbia, E75 motorways and is under construction.
Situated at the confluence of two major rivers, the Danube and the Sava, Belgrade has 11 bridges, the most important of which are Branko's bridge, the Ada Bridge, Pupin Bridge and the Gazela Bridge, the last two of which connect the core of the city to New Belgrade. In addition, an 'inner magistral semi-ring' is almost done and include a new Ada Bridge across the Sava river and a new Pupin Bridge across Danube river, which eased commuting within the city and unload the Gazela and Branko's bridge traffic.
The Port of Belgrade is on the Danube, and allows the city to receive goods by river. The city is also served by Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport, west of the city centre, near Surčin. At its peak in 1986, almost 3 million passengers travelled through the airport, though that number dwindled to a trickle in the 1990s. Following renewed growth in 2000, the number of passengers reached approximately 2 million in 2004 and 2005, over 2.6 million passengers in 2008, reaching over 3 million passengers. A record with over 4 million passengers was broken in 2014, when Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport became the second fastest growing major airport in Europe. The numbers continued to grow steadily and the all-time peak of over 6 million passengers was reached in 2019.
The new Belgrade Centre railway station is the hub for almost all the national and international trains.
The high-speed rail that connects Belgrade with Novi Sad started its service at 19 March 2022. The extension towards Subotica and Budapest is under construction, and there are plans for southwards extension towards Niš and North Macedonia.
The city is placed along the Pan-European corridors Pan-European Corridor X, X and VII. The motorway system provides for easy access to Novi Sad and Budapest to the north, Niš to the south, and Zagreb to the west. Expressway is also toward Pančevo and new Expressway construction toward Obrenovac (Montenegro) is scheduled for March 2017. Belgrade bypass is connecting the E70 in Serbia, E70 and E75 in Serbia, E75 motorways and is under construction.
Situated at the confluence of two major rivers, the Danube and the Sava, Belgrade has 11 bridges, the most important of which are Branko's bridge, the Ada Bridge, Pupin Bridge and the Gazela Bridge, the last two of which connect the core of the city to New Belgrade. In addition, an 'inner magistral semi-ring' is almost done and include a new Ada Bridge across the Sava river and a new Pupin Bridge across Danube river, which eased commuting within the city and unload the Gazela and Branko's bridge traffic.
The Port of Belgrade is on the Danube, and allows the city to receive goods by river. The city is also served by Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport, west of the city centre, near Surčin. At its peak in 1986, almost 3 million passengers travelled through the airport, though that number dwindled to a trickle in the 1990s. Following renewed growth in 2000, the number of passengers reached approximately 2 million in 2004 and 2005, over 2.6 million passengers in 2008, reaching over 3 million passengers. A record with over 4 million passengers was broken in 2014, when Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport became the second fastest growing major airport in Europe. The numbers continued to grow steadily and the all-time peak of over 6 million passengers was reached in 2019.
International cooperation and honors
 List of Belgrade's sister and twin cities:
* Coventry, UK, since 1957
* Chicago, USA, since 2005
* Ljubljana, Slovenia, since 2010
* Skopje, North Macedonia, since 2012
* Shanghai, China, since 2018
* Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 2020
Other friendships and cooperations, protocols, memorandums:
* Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 2018, Memorandum of Understanding on Cooperation
* Rabat, Morocco, since 2017, Partnership and Cooperation Agreement
* Seoul, South Korea, since 2017, Memorandum of Understanding on Friendly Exchanges and Cooperation
* Astana, Kazakhstan, since 2016, Agreement on Cooperation
* Tehran, Iran, since 2016, Agreement on Cooperation
* Corfu (city), Corfu, Greece, since 2010, Protocol on Cooperation
* Shenzhen, China, since 2009, Agreement on Cooperation
* Zagreb, Croatia, since 2003, Letter of Intent
* Kyiv, Ukraine, since 2002, Agreement on Cooperation
* Algiers, Algeria, since 1991 declaration of mutual interests
* Tel Aviv, Israel, since 1990, Agreement on Cooperation
* Bucharest, Romania, since 1999, Agreement on Cooperation
* Beijing, China, since 1980, Agreement on Cooperation
* Rome, Italy, since 1971, Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation
* Athens, Greece, since 1966, Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation
Some of the city's municipalities are also twinned to small cities or districts of other big cities; for details see their respective articles.
Belgrade has received various domestic and international honours, including the French Légion d'honneur (proclaimed 21 December 1920; Belgrade is one of four cities outside France, alongside Liège, Luxembourg (city), Luxembourg and Volgograd, to receive this honour), the Czechoslovak War Cross 1918, Czechoslovak War Cross (awarded 8 October 1925), the Yugoslavian Order of the Karađorđe's Star (awarded 18 May 1939) and the Yugoslavian Order of the People's Hero (proclaimed on 20 October 1974, the 30th anniversary of the overthrow of Nazi Germany, Nazi German occupation during World War II). All of these decorations were received for the war efforts during World War I and World War II. In 2006, ''Financial Times magazine ''FDi magazine, Foreign Direct Investment'' awarded Belgrade the title of ''City of the Future of Southern Europe''.
List of Belgrade's sister and twin cities:
* Coventry, UK, since 1957
* Chicago, USA, since 2005
* Ljubljana, Slovenia, since 2010
* Skopje, North Macedonia, since 2012
* Shanghai, China, since 2018
* Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 2020
Other friendships and cooperations, protocols, memorandums:
* Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 2018, Memorandum of Understanding on Cooperation
* Rabat, Morocco, since 2017, Partnership and Cooperation Agreement
* Seoul, South Korea, since 2017, Memorandum of Understanding on Friendly Exchanges and Cooperation
* Astana, Kazakhstan, since 2016, Agreement on Cooperation
* Tehran, Iran, since 2016, Agreement on Cooperation
* Corfu (city), Corfu, Greece, since 2010, Protocol on Cooperation
* Shenzhen, China, since 2009, Agreement on Cooperation
* Zagreb, Croatia, since 2003, Letter of Intent
* Kyiv, Ukraine, since 2002, Agreement on Cooperation
* Algiers, Algeria, since 1991 declaration of mutual interests
* Tel Aviv, Israel, since 1990, Agreement on Cooperation
* Bucharest, Romania, since 1999, Agreement on Cooperation
* Beijing, China, since 1980, Agreement on Cooperation
* Rome, Italy, since 1971, Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation
* Athens, Greece, since 1966, Agreement on Friendship and Cooperation
Some of the city's municipalities are also twinned to small cities or districts of other big cities; for details see their respective articles.
Belgrade has received various domestic and international honours, including the French Légion d'honneur (proclaimed 21 December 1920; Belgrade is one of four cities outside France, alongside Liège, Luxembourg (city), Luxembourg and Volgograd, to receive this honour), the Czechoslovak War Cross 1918, Czechoslovak War Cross (awarded 8 October 1925), the Yugoslavian Order of the Karađorđe's Star (awarded 18 May 1939) and the Yugoslavian Order of the People's Hero (proclaimed on 20 October 1974, the 30th anniversary of the overthrow of Nazi Germany, Nazi German occupation during World War II). All of these decorations were received for the war efforts during World War I and World War II. In 2006, ''Financial Times magazine ''FDi magazine, Foreign Direct Investment'' awarded Belgrade the title of ''City of the Future of Southern Europe''.
See also
*List of people from Belgrade *List of cities and towns on Danube riverReferences
Informational notes
Sources
* * * * *External links
City of Belgrade
{{Authority control Belgrade, Capitals in Europe Districts of Serbia Metropolitan areas of Serbia Statistical regions of Serbia Port cities in Serbia Ancient cities in Serbia Populated places established in the 3rd century BC Populated places on the Danube Šumadija Recipients of the Czechoslovak War Cross Recipients of the Legion of Honour Populated places on the Sava Starčevo–Körös–Criș culture