|
Second Crusade
The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade (1096–1099) by King Baldwin I of Jerusalem in 1098. While it was the first Crusader state to be founded, it was also the first to fall. The Second Crusade was announced by Pope Eugene III, and was the first of the crusades to be led by European kings, namely Louis VII of France and Conrad III of Germany, with help from a number of other European nobles. The armies of the two kings marched separately across Europe. After crossing Byzantine territory into Anatolia, both armies were separately defeated by the Seljuk Turks. The main Western Christian source, Odo of Deuil, and Syriac Christian sources claim that the Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos secretly hindered the crusaders' progress, particularly in Anatolia, where he is allege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were intended to recover Holy Land, Jerusalem and its surrounding area from Muslim conquests, Islamic rule. Beginning with the First Crusade, which resulted in the recovery of Jerusalem in 1099, dozens of Crusades were fought, providing a focal point of European history for centuries. In 1095, Pope Pope Urban II, Urban II proclaimed the First Crusade at the Council of Clermont. He encouraged military support for List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos, AlexiosI against the Seljuk Empire, Seljuk Turks and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. The first Crusaders had a variety of motivations, including religious salvation, satisfying feud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Edessa
The County of Edessa (Latin: ''Comitatus Edessanus'') was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century. Ferdinandi, Sergio (2017). La Contea Franca di Edessa. Fondazione e Profilo Storico del Primo Principato Crociato nel Levante (1098-1150). Pontificia Università Antonianum - Rome. . Its seat was the city of Edessa (present-day Şanlıurfa, Turkey). In the late Byzantine period, Edessa became the centre of intellectual life within the Syriac Orthodox Church. As such it also became the centre for the translation of Ancient Greek philosophy into Syriac, which provided a stepping stone for the subsequent translations into Arabic. When the Crusades arrived, it was still important enough to tempt a side-expedition after the siege of Antioch. Baldwin of Boulogne, the first Count of Edessa, became King of Jerusalem, and subsequent counts were his cousins. Unlike the other Crusader states, the County was landlocked. It was remote from the other states and was not on particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France In The Middle Ages
The Kingdom of France in the Middle Ages (roughly, from the 10th century to the middle of the 15th century) was marked by the fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and West Francia (843–987); the expansion of royal control by the House of Capet (987–1328), including their struggles with the virtually independent principalities (duchies and counties, such as the Normandy#Norman expansion, Norman and County of Anjou, Angevin regions) that had developed following the Viking invasions and through the piecemeal dismantling of the Carolingian Empire and the creation and extension of administrative/state control (notably under Philip II of France, Philip II Augustus and Louis IX of France, Louis IX) in the 13th century; and the rise of the House of Valois (1328–1589), including the protracted dynastic crisis against the House of Plantagenet and their Angevin Empire, dominated by the Kingdom of England, cumulating in the Hundred Years' War (1337–1453), compounded by the catastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Saint Lazarus
The Order of Saint Lazarus of Jerusalem, also known as the Leper Brothers of Jerusalem or simply as Lazarists, was a Catholic military order (monastic society), military order founded by crusaders around 1119 at a leprosy, leper hospital in Jerusalem, Kingdom of Jerusalem, whose care became its original purpose, named after its patron saint, rich man and Lazarus, Lazarus. It was recognised by King Fulk of Jerusalem in 1142 and canonically recognised as a hospitaller and military order of chivalry under the rule of Saint Augustine in the Papal bull ''Cum a Nobis Petitur'' of Pope Alexander IV in 1255. Although they were centred on their charism of caring for those afflicted with leprosy, the knights of the Order of Saint Lazarus notably fought in the Battle of La Forbie in 1244 and in the Siege of Acre (1291), Defense of Acre in 1291.Wise (2012) The Cathedra, titular seat was successively situated at Jerusalem, Acre, Israel, Saint-Jean-d'Acre and - after the fall of the Kingdom of J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canons Regular Of The Holy Sepulchre
The Canons Regular of the Holy Sepulchre were a Catholic religious order of canons regular of the Rule of Saint Augustine, said to have been founded in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, then the capital of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, and recognised in 1113 by a Papal bull of Pope Paschal II. Other accounts have it that they were founded earlier, during the rule of Godfrey of Bouillon (1099–1100). After the fall of Jerusalem to Saladin, the Canons fled the Holy Land along with other Latin Christians. They first settled briefly on Cyprus, where they established Bellapais Abbey, before proceeding to settle in various countries of Europe. The Canons Regular of the Holy Sepulchre was suppressed in 1489 by Pope Innocent VIII (1484–1492). On March 28, 1489, the pope, at the instigation of the Order of Malta, issued a bull by which the Order of Canons Regular of the Holy Sepulchre was to be dissolved and transferred to the Order of Malta. However, the independence of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
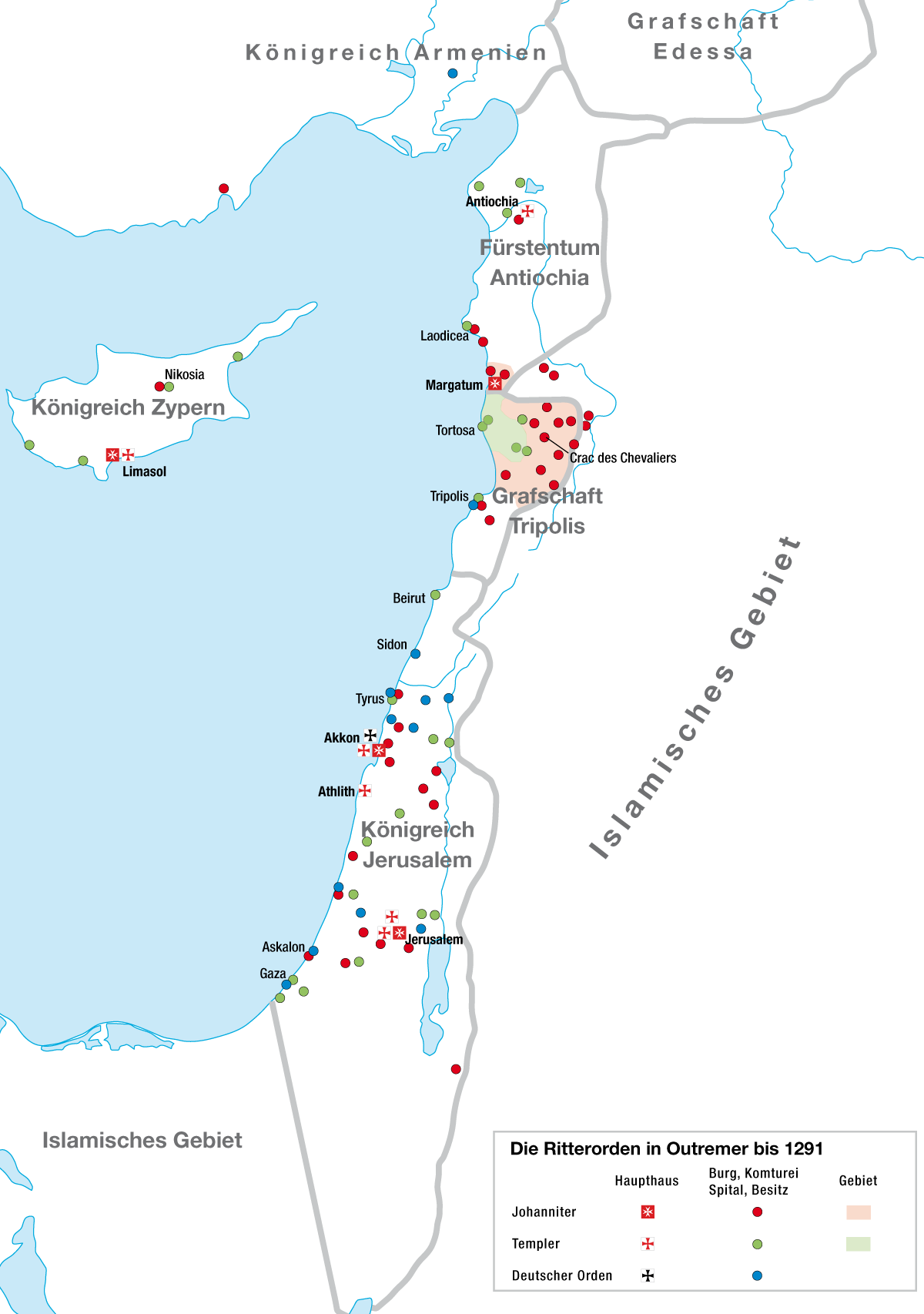
Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic Church, Catholic Military order (religious society), military order. It was headquartered in the Kingdom of Jerusalem until 1291, on the island of Hospitaller Rhodes, Rhodes from 1310 until 1522, in Hospitaller Malta, Malta from 1530 until 1798 and at Saint Petersburg from 1799 until 1801. Today several organizations continue the Hospitaller tradition, specifically the mutually recognized orders of St. John, which are the Sovereign Military Order of Malta, the Order of Saint John (chartered 1888), Most Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John, the Order of Saint John (Bailiwick of Brandenburg), Bailiwick of Brandenburg of the Chivalric Order of Saint John, the Order of Saint John in the Netherlands, and the Order of Saint John in Sweden. The Hospitallers arose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross , colors_label = Attire , march = , mascot = Two knights riding a single horse , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = The Crusades, including: , anniversaries = , decorations = , battle_honours = , commander1 = Hugues de Payens , commander1_label = First Grand Master , commander2 = Jacques de Molay , commander2_label = Last Grand Master , commander3 = , commander3_label = , notable_commanders = The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon ( la, Pauperes commilitones Christi Templique Salomonici), also known as the Order of Solomon's Temple, the Knights Templar, or simply the Templars, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Order (society)
A military order ( la, militaris ordo) is a Christian religious society of knights. The original military orders were the Knights Templar, the Knights Hospitaller, the Order of Saint James, the Order of Calatrava, and the Teutonic Knights. They arose in the Middle Ages in association with the Crusades, both in the Holy Land, the Baltics, and the Iberian peninsula; their members being dedicated to the protection of pilgrims and the defence of the Crusader states. They are the predecessors of chivalric orders. Most members of military orders were laymen who took religious vows, such as of poverty, chastity, and obedience, according to monastic ideals. The orders owned houses called commanderies all across Europe and had a hierarchical structure of leadership with the grand master at the top. The Knights Templar, the largest and most influential of the military orders, was suppressed in the early fourteenth century; only a handful of orders were established and recognized aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Antioch
The Principality of Antioch was one of the crusader states created during the First Crusade which included parts of modern-day Turkey and Syria. The principality was much smaller than the County of Edessa or the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It extended around the northeastern edge of the Mediterranean, bordering the County of Tripoli to the south, Edessa to the east, and the Byzantine Empire or the Kingdom of Armenia to the northwest, depending on the date. It had roughly 20,000 inhabitants in the 12th century, most of whom were Armenians and Greek Orthodox Christians, with a few Muslims outside the city itself. Most of the crusaders who settled there were of Norman origin, notably from the Norman Kingdom of southern Italy, as were the first rulers of the principality, who surrounded themselves with loyal subjects. Few of the inhabitants apart from the Crusaders were Roman Catholic even though the city was under the jurisdiction of the Latin Patriarchate of Antioch, established in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Tripoli
The County of Tripoli (1102–1289) was the last of the Crusader states. It was founded in the Levant in the modern-day region of Tripoli, northern Lebanon and parts of western Syria which supported an indigenous population of Christians, Druze and Muslims. When the Frankish Crusaders – mostly southern French forces – captured the region in 1109, Bertrand of Toulouse became the first count of Tripoli as a vassal of King Baldwin I of Jerusalem. From that time, the rule of the county was decided not strictly by inheritance but by factors such as military force (external and civil war), favour and negotiation. In 1289 the County of Tripoli fell to Sultan Qalawun of the Muslim Mamluks of Cairo. The county was absorbed into Mamluk Egypt. Capture by Christian forces Raymond IV of Toulouse was one of the wealthiest and most powerful of the crusaders.Tyerman C"God's war – a new history of the crusades"Harvard University Press. February, 2009. Even so, after the First Crusade, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1099 until the siege of Acre in 1291. Its history is divided into two periods with a brief interruption in its existence, beginning with its collapse after the siege of Jerusalem in 1187 and its restoration after the Third Crusade in 1192. The original Kingdom of Jerusalem lasted from 1099 to 1187 before being almost entirely overrun by the Ayyubid Sultanate under Saladin. Following the Third Crusade, it was re-established in Acre in 1192. The re-established state is commonly known as the "Second Kingdom of Jerusalem" or alternatively as the "Kingdom of Acre" after its new capital city. Acre remained t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusader States
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political intrigue. The four states were the County of Edessa (10981150), the Principality of Antioch (10981287), the County of Tripoli (11021289), and the Kingdom of Jerusalem (10991291). The Kingdom of Jerusalem covered what is now Israel and Palestine, the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and adjacent areas. The other northern states covered what are now Syria, south-eastern Turkey, and Lebanon. The description "Crusader states" can be misleading, as from 1130 very few of the Frankish population were crusaders. The term Outremer, used by medieval and modern writers as a synonym, is derived from the French for ''overseas''. In 1098, the armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem passed through Syria. The crusader Baldwin of Boulogne replaced the Greek Orthodox ruler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
.jpg)