Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* '' Our ...
in the south-east of
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
. With an area of , Bavaria is the
largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is
second in population only to
North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhab ...
, but due to its large size its population density is
below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
(its capital and largest city and also the third
largest city in Germany),
Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
, and
Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the '' ...
.
The
history of Bavaria
The history of Bavaria stretches from its earliest settlement and its formation as a stem duchy in the 6th century through its inclusion in the Holy Roman Empire to its status as an independent kingdom and finally as a large '' Bundesland'' (st ...
includes its earliest settlement by
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of
Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west w ...
and
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the nort ...
. It became the
Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria ( German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under ...
(a
stem duchy
A stem duchy (german: Stammesherzogtum, from ''Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Bavarians and Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the German Empire at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dynasty (death ...
) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
. It was later incorporated into the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, became an independent kingdom after 1806, joined the Prussian-led
German Empire in 1871 while retaining its title of kingdom, and finally became a
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* '' Our ...
of the
Federal Republic of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south ...
in 1949.
Bavaria has a unique culture, largely because of the state's
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
heritage and conservative traditions.
Bavarians
Bavarians ( Bavarian: ''Boarn'', Standard German: ''Baiern'') are an ethnographic group of Germans of the Bavaria region, a state within Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as the Bavarian language, native to Altbayern ("Old Bavar ...
have traditionally been proud of their culture, which includes a
language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
,
cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
, architecture, festivals and elements of
Alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National P ...
symbolism. The state also has the second largest economy among the
German states by GDP figures, giving it a status as a wealthy German region.
Contemporary Bavaria also includes parts of the historical regions of
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper F ...
and
Swabia.
History
Antiquity

The Bavarians emerged in a region north of the
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, ...
, previously inhabited by
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
, which had been part of the Roman provinces of
Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west w ...
and
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the nort ...
.
The Bavarians spoke a Germanic dialect which developed into
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
during the early Middle Ages, however, unlike other
Germanic groups, they probably did not migrate from elsewhere when Western Roman influence collapsed.
Rather, they seem to have coalesced out of other groups left behind by the Roman withdrawal late in the 5th century. These peoples may have included the Celtic
Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom the ...
, some remaining
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
,
Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
Origi ...
,
Allemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
,
Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic
*
*
*
people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only surviving contemporary reports about the Germanic tribe are those of the Romans, whose empire had its bord ...
,
Thuringians
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into conf ...
,
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
,
Scirians
The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones".
The Sciri were mentioned already in the late 3rd century BC as participants in a raid on the ...
,
Rugians
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his ''Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Som ...
,
Heruli
The Heruli (or Herules) were an early Germanic people. Possibly originating in Scandinavia, the Heruli are first mentioned by Roman authors as one of several " Scythian" groups raiding Roman provinces in the Balkans and the Aegean Sea, attacking ...
. The name "Bavarian" ("
Baiuvarii
The Baiuvarii or Bavarians (german: Bajuwaren) were a Germanic people. The Baiuvarii had settled modern-day Bavaria (which is named after them), Austria, and South Tyrol by the 6th century AD, and are considered the ancestors of modern-day Ba ...
") means "Men of Baia" which may indicate Bohemia, the homeland of the Celtic
Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom the ...
and later of the Marcomanni. They first appear in written sources circa 520.
A 17th century Jewish chronicler
David Solomon Ganz, citing
Cyriacus Spangenberg
Cyriacus Spangenberg (7 June 1528 – 10 February 1604) was a German theologian, Protestant reformer and historian, son of the reformer (1484–1550).
Cyriacus was born in Nordhausen. As a student, he was a fellow tenant of Martin Luther
...
, claimed that the diocese was named after an ancient Bohemian king, Boiia, in the 14th century BC.
[Dovid Solomon Ganz, Tzemach Dovid (3rd edition), part 2, Warsaw 1878, pp. 71, 85]
online
)
Middle Ages
From about 554 to 788, the house of
Agilolfing
The Agilolfings were a noble family that ruled the Duchy of Bavaria on behalf of their Merovingian suzerains from about 550 until 788. A cadet branch of the Agilolfings also ruled the Kingdom of the Lombards intermittently from 616 to 712.
They ...
ruled the
Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria ( German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under ...
, ending with
Tassilo III
Tassilo III ( 741 – c. 796) was the duke of Bavaria from 748 to 788, the last of the house of the Agilolfings. The Son of Duke Odilo of Bavaria and Hitrud, the Daughter of Charles Martell.
Tassilo, then still a child, began his rule as a Frank ...
who was deposed by
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Em ...
.
Three early dukes are named in
Frankish sources:
Garibald I
Garibald I (also Garivald; la, Garibaldus; born 540) was Duke (or King) of Bavaria from 555 until 591. He was the head of the Agilolfings, and the ancestor of the Bavarian dynasty that ruled the Kingdom of the Lombards.
Biography
After the d ...
may have been appointed to the office by the
Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
kings and married the
Lombard princess Walderada when the church forbade her to King
Chlothar I
Chlothar I, sometime called "the Old" (French: le Vieux), (died December 561) also anglicised as Clotaire, was a king of the Franks of the Merovingian dynasty and one of the four sons of Clovis I.
Chlothar's father, Clovis I, divided the kingd ...
in 555. Their daughter,
Theodelinde, became
Queen of the Lombards in northern Italy and Garibald was forced to flee to her when he fell out with his Frankish overlords.
Garibald's successor,
Tassilo I, tried unsuccessfully to hold the eastern frontier against the expansion of
Slavs and
Avars around 600. Tassilo's son
Garibald II seems to have achieved a balance of power between 610 and 616.
After Garibald II, little is known of the Bavarians until
Duke Theodo I, whose reign may have begun as early as 680. From 696 onward, he invited churchmen from the west to organize churches and strengthen Christianity in his duchy. (It is unclear what Bavarian religious life consisted of before this time.)
His son,
Theudebert Theudebert (also Theodobert, Theudibert, Theodebert, Theodbert, Dietbert, Tibert, etc.E. W. Förstemann, ''Altdeutsches Namenbuch'', 18561168f./ref>) is a Germanic dithematic name, composed from the elements '' theo-'' "people" and ''bert'' "brig ...
, led a decisive Bavarian campaign to intervene in a succession dispute in the
Lombard Kingdom
The Kingdom of the Lombards ( la, Regnum Langobardorum; it, Regno dei Longobardi; lmo, Regn di Lombard) also known as the Lombard Kingdom; later the Kingdom of (all) Italy ( la, Regnum totius Italiae), was an early medieval state established ...
in 714, and married his sister Guntrud to the Lombard
King Liutprand. At Theodo's death the duchy was divided among his sons, but reunited under his grandson
Hugbert.

At Hugbert's death (735) the duchy passed to a distant relative named
Odilo, from neighboring
Alemannia (modern southwest Germany and northern Switzerland). Odilo issued a
law code for Bavaria, completed the process of church organization in partnership with
St. Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of ...
(739), and tried to intervene in Frankish succession disputes by fighting for the claims of the
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
Grifo. He was defeated near
Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the '' ...
in 743 but continued to rule until his death in 748.
Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations o ...
completed the people's conversion to Christianity in the early 8th century.
Tassilo III
Tassilo III ( 741 – c. 796) was the duke of Bavaria from 748 to 788, the last of the house of the Agilolfings. The Son of Duke Odilo of Bavaria and Hitrud, the Daughter of Charles Martell.
Tassilo, then still a child, began his rule as a Frank ...
(b. 741 – d. after 796) succeeded his father at the age of eight after an unsuccessful attempt by Grifo to rule Bavaria. He initially ruled under Frankish oversight but began to function independently from 763 onward. He was particularly noted for founding new monasteries and for expanding eastwards, fighting
Slavs in the
eastern Alps
Eastern Alps is the name given to the eastern half of the Alps, usually defined as the area east of a line from Lake Constance and the Alpine Rhine valley up to the Splügen Pass at the Alpine divide and down the Liro River to Lake Como in t ...
and along the
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
and colonizing these lands.
After 781, however, his cousin Charlemagne began to pressure Tassilo to submit and finally deposed him in 788. The deposition was not entirely legitimate.
Dissenters attempted a coup against Charlemagne at Tassilo's old capital of
Regensburg in 792, led by his own son
Pépin the Hunchback. The king had to drag Tassilo out of imprisonment to formally renounce his rights and titles at the Assembly of Frankfurt in 794. This is the last appearance of Tassilo in the sources, and he probably died a monk. As all of his family were also forced into monasteries, this was the end of the Agilolfing dynasty.

For the next 400 years numerous families held the duchy, rarely for more than three generations. With the revolt of duke
Henry the Quarrelsome in 976, Bavaria lost large territories in the south and south east.
The territory of ''
Ostarrichi'' was elevated to a duchy in its own right and given to the
Babenberger family. This event marks the founding of
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. Later the counts of
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
next to other princes began to act more independently from the dukes of Bavaria, and the new
Duchy of Merania
The Duchy of Merania, it, Ducato di Merania, sl, Vojvodina Meranija, hr, Vojvodina Meranije was a fiefdom of the Holy Roman Empire from 1152 until 1248. The dukes of Merania were recognised as princes of the Empire enjoying imperial immediacy a ...
was created from lordships once under the jurisdiction of the Duchy of Bavaria.
The last, and one of the most important, of the dukes of Bavaria was
Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German pr ...
of the
house of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconia, Franconian family from ...
, founder of Munich, and ''de facto'' the second most powerful man in the empire as the ruler of two duchies. When in 1180, Henry the Lion was deposed as Duke of
Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
and Bavaria by his cousin,
Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt ...
(a.k.a. "Barbarossa" for his red beard), Bavaria was awarded as
fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of f ...
to the
Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate ...
family, counts palatinate of Schyren ("Scheyern" in modern German). They ruled for 738 years, from 1180 to 1918. In 1180 however also
Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered to ...
was separated from Bavaria. The
Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine of ...
by Rhine (''Kurpfalz'' in German) was also acquired by the
House of Wittelsbach in 1214, which they would subsequently hold for six centuries.
The first of several divisions of the duchy of Bavaria occurred in 1255. With the extinction of the
Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
in 1268,
Swabian territories were acquired by the Wittelsbach dukes.
Emperor Louis the Bavarian acquired
Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 square ...
,
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
,
Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
and
Hainaut for his House but released the
Upper Palatinate
The Upper Palatinate (german: Oberpfalz, , ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany, and is located in the east of Bavaria.
Geography
The Upper Palatinate is a landscape with low mountains and numerous ponds and lakes ...
for the Palatinate branch of the Wittelsbach in 1329. That time also
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
finally became independent from the
Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria ( German: ''Herzogtum Bayern'') was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (''duces'') under ...
.
In the 14th and 15th centuries, upper and lower Bavaria were repeatedly subdivided. Four Duchies existed after the division of 1392:
Bavaria-Straubing
Bavaria-Straubing denotes the widely scattered territorial inheritance in the Wittelsbach house of Bavaria that were governed by independent dukes of Bavaria-Straubing between 1353 and 1432; a map (''illustration'') of these marches and outliers ...
,
Bavaria-Landshut
Bavaria-Landshut (german: Bayern-Landshut) was a duchy in the Holy Roman Empire from 1353 to 1503.
History
The creation of the duchy was the result of the death of Emperor Louis IV the Bavarian. In the Treaty of Landsberg 1349, which divided ...
,
Bavaria-Ingolstadt
Bavaria-Ingolstadt ( or ') was a duchy which was part of the Holy Roman Empire from 1392 to 1447.
History
After the death of Stephen II in 1375, his sons Stephen III, Frederick, and John II jointly ruled Bavaria-Landshut. After seventeen yea ...
and
Bavaria-Munich
Bavaria-Munich (german: Bayern-München) was a duchy that was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1392 to 1505.
History
After the death of Stephen II in 1375, his sons Stephen III, Frederick, and John II jointly ruled Bavaria- ...
. In 1506 with the
Landshut War of Succession
The War of the Succession of Landshut resulted from a dispute between the duchies of Bavaria-Munich (''Bayern-München'' in German) and Bavaria-Landshut (''Bayern-Landshut''). An earlier agreement between the different Wittelsbach lines, the T ...
, the other parts of Bavaria were reunited, and Munich became the sole capital. The country became a center of the Jesuit-inspired
Counter-Reformation.

Electorate of Bavaria
In 1623 the Bavarian duke replaced his relative of the Palatinate branch, the
Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine of ...
in the early days of the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battl ...
and acquired the powerful
prince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the Holy Roman Emperor, emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century ...
al dignity in the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, determining its Emperor thence forward, as well as special legal status under the empire's laws.
During the early and mid-18th century the ambitions of the Bavarian prince electors led to several wars with Austria as well as occupations by Austria (
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
,
War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George' ...
with the election of a Wittelsbach emperor instead of a Habsburg).
From 1777 onward, and after the younger Bavarian branch of the family had died out with elector
Max III Joseph, Bavaria and the
Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate (german: Kurpfalz) or the Palatinate (), officially the Electorate of the Palatinate (), was a state that was part of the Holy Roman Empire. The electorate had its origins under the rulership of the Counts Palatine of ...
were governed once again in
personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more State (polity), states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some e ...
, now by the Palatinian lines.
The new state also comprised the
Duchies of Jülich and
Berg as these on their part were in personal union with the Palatinate.
Kingdom of Bavaria
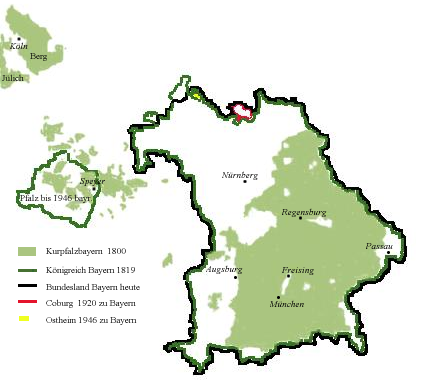
When
Napoleon abolished the Holy Roman Empire, Bavaria became – by grace of Napoleon – a
kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
in 1806 due, in part, to the
Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria a ...
.
Its area doubled after the Duchy of Jülich was ceded to France, as the Electoral Palatinate was divided between France and the
Grand Duchy of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden (german: Großherzogtum Baden) was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918.
It came into existence in the 12th century as the Margraviate of Baden and sub ...
. The Duchy of Berg was given to
Jerome Bonaparte.
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
and
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
were temporarily reunited with Bavaria but finally ceded to Austria by the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
.
In return Bavaria was allowed to annex the modern-day region of
Palatinate
Palatinate or county palatine may refer to:
*the territory or jurisdiction of a count palatine
United Kingdom and Ireland
*County palatine in England and Ireland
* Palatinate (award), student sporting award of Durham University
*Palatinate (col ...
to the west of the
Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
and
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper F ...
in 1815. Between 1799 and 1817, the leading minister, Count
Montgelas
Maximilian Karl Joseph Franz de Paula Hieronymus de Garnerin de la Thuile, Count von Montgelas (german: Maximilian Karl Joseph Franz de Paula Hieronymus de Garnerin de la Thuille Graf von Montgelas; 12 September 1759 Munich – 14 June 1838 ...
, followed a strict policy of modernisation copying Napoleonic France; he laid the foundations of centralized administrative structures that survived the monarchy and, in part, have retained core validity through the 20st century.
In May 1808, a first constitution was passed by
Maximilian I, being modernized in 1818. This second version established a bicameral Parliament with a House of Lords (''Kammer der Reichsräte'') and a House of Commons (''Kammer der Abgeordneten''). That constitution was followed until the collapse of the monarchy at the end of
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.
After the rise of
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
to power in the early 18th century, Bavaria preserved its independence by playing off the rivalry of Prussia and
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. Allied to Austria, it was defeated along with Austria in the 1866
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
and was not incorporated into the
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated st ...
of 1867, but the question of
German unity was still alive. When
France declared war on Prussia in 1870, all the south German states (Baden, Württemberg, Hessen-Darmstadt and Bavaria) aside from Austria, joined the Prussian forces and ultimately joined the Federation, which was renamed
''Deutsches Reich'' (German Empire) in 1871.
Bavaria continued formally as a monarchy, and it had some special rights within the federation (such as an army, railways, postal service and a diplomatic body of its own) but the diplomatic body were later undone by Wilhelm II who declared them illegal and got rid of the diplomatic service.
Part of the German Empire

When Bavaria became part of the newly formed German Empire, this action was considered controversial by
Bavarian nationalists who had wanted to retain independence from the rest of Germany, as had Austria.
As Bavaria had a heavily Catholic majority population, many people resented being ruled by the mostly
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
northerners of
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
. As a direct result of the Bavarian-Prussian feud, political parties formed to encourage Bavaria to break away and regain its independence.
In the early 20th century,
Wassily Kandinsky
Wassily Wassilyevich Kandinsky (; rus, Василий Васильевич Кандинский, Vasiliy Vasilyevich Kandinskiy, vɐˈsʲilʲɪj vɐˈsʲilʲjɪvʲɪtɕ kɐnʲˈdʲinskʲɪj; – 13 December 1944) was a Russian painter a ...
,
Paul Klee
Paul Klee (; 18 December 1879 – 29 June 1940) was a Swiss-born German artist. His highly individual style was influenced by movements in art that included expressionism, cubism, and surrealism. Klee was a natural draftsman who experimented wi ...
,
Henrik Ibsen
Henrik Johan Ibsen (; ; 20 March 1828 – 23 May 1906) was a Norwegian playwright and theatre director. As one of the founders of modernism in theatre, Ibsen is often referred to as "the father of realism" and one of the most influential pla ...
, and other artists were drawn to Bavaria, especially to the
Schwabing
Schwabing is a borough in the northern part of Munich, the capital of the German state of Bavaria. It is part of the city borough 4 (Schwabing-West) and the city borough 12 (Schwabing-Freimann). The population of Schwabing is estimated about 100 ...
district of Munich, a center of international artistic activity.
Free State of Bavaria

''Free State'' has been an adopted designation after the abolition of monarchy in the aftermath of World War I in several German states.
On 12 November 1918,
Ludwig III
Ludwig III (Ludwig Luitpold Josef Maria Aloys Alfried; 7 January 1845 – 18 October 1921) was the last King of Bavaria, reigning from 1913 to 1918. Initially he served in the Bavarian military as a lieutenant and went on to hold the rank of Oberl ...
signed a document, the
Anif declaration, releasing both civil and military officers from their oaths; the
newly formed republican government, or "People's State" of Socialist premier
Kurt Eisner
Kurt Eisner (; 14 May 1867 21 February 1919)"Kurt Eisner – Encyclopædia Britannica" (biography), ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2006, Britannica.com webpageBritannica-KurtEisner. was a German politician, revolutionary, journalist, and theatre c ...
, interpreted this as an abdication. To date, however, no member of the House of Wittelsbach has ever formally declared renunciation of the throne.
On the other hand, none has ever since officially called upon their Bavarian or Stuart claims. Family members are active in cultural and social life, including the head of the house,
Franz, Duke of Bavaria
Franz Bonaventura Adalbert Maria Herzog von Bayern (born 14 July 1933), commonly known by the courtesy title Duke of Bavaria, is the head of the House of Wittelsbach, the former ruling family of the Kingdom of Bavaria. His great-grandfather Ki ...
. They step back from any announcements on public affairs, showing approval or disapproval solely by Franz's presence or absence.
Eisner was assassinated in February 1919, ultimately leading to a Communist revolt and the short-lived
Bavarian Soviet Republic
The Bavarian Soviet Republic, or Munich Soviet Republic (german: Räterepublik Baiern, Münchner Räterepublik),Hollander, Neil (2013) ''Elusive Dove: The Search for Peace During World War I''. McFarland. p.283, note 269. was a short-lived unre ...
being proclaimed 6 April 1919. After violent suppression by elements of the German Army and notably the
Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European military volunteer units, or paramilitary, that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenary or private armies, reg ...
, the Bavarian Soviet Republic fell in May 1919. The
Bamberg Constitution
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle ...
(') was enacted on 12 or 14 August 1919 and came into force on 15 September 1919 creating the Free State of Bavaria within the
Weimar Republic
The German Reich, commonly referred to as the Weimar Republic,, was a historical period of Germany from 9 November 1918 to 23 March 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is also r ...
.
Extremist activity further increased, notably the 1923
Beer Hall Putsch
The Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch,Dan Moorhouse, ed schoolshistory.org.uk, accessed 2008-05-31.Known in German as the or was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party ( or NSDAP) leader Adolf Hitler, Erich Ludendorff and oth ...
led by the
National Socialists
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Naz ...
, and Munich and Nuremberg became seen as
Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hit ...
strongholds during the
Weimar Republic
The German Reich, commonly referred to as the Weimar Republic,, was a historical period of Germany from 9 November 1918 to 23 March 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is also r ...
and
Nazi dictatorship. However, in the crucial
German federal election, March 1933
Federal elections were held in Germany on 5 March 1933, after the Nazis lawfully acquired power pursuant to the terms of Weimar Constitution on 30 January 1933 and just six days after the Reichstag fire. Nazi stormtroopers had unleashed a wides ...
, the Nazis received less than 50% of the votes cast in Bavaria.
As a manufacturing centre, Munich was heavily bombed during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and was occupied by U.S. troops, becoming a major part of the American Zone of
Allied-occupied Germany
Germany was already de facto occupied by the Allies from the real fall of Nazi Germany in World War II on 8 May 1945 to the establishment of the East Germany on 7 October 1949. The Allies (United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and ...
(1945–47) and then of
"Bizonia".
The Rhenish Palatinate was detached from Bavaria in 1946 and made part of the new state
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the ...
. During the
Cold War, Bavaria was part of
West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
. In 1949, the Free State of Bavaria chose not to sign the Founding Treaty (''Gründungsvertrag'') for the formation of the Federal Republic of Germany, opposing the division of Germany into two countries after
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
The
Bavarian Parliament
The Landtag of Bavaria, officially known in English as the Bavarian State Parliament, is the unicameral legislature of the German state of Bavaria. The parliament meets in the Maximilianeum in Munich.
Elections to the Landtag are held every ...
did not sign the
Basic Law of Germany
The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany (german: Grundgesetz für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland) is the constitution of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany.
The West German Constitution was approved in Bonn on 8 May 1949 an ...
, mainly because it was seen as not granting sufficient powers to the individual ''Länder'' (states), but at the same time decided that it would still come into force in Bavaria if two-thirds of the other ''Länder'' ratified it.
All of the other ''Länder'' ratified it, however, so it became law.
Bavarian identity

Bavarians have often emphasized a separate national identity and considered themselves as "Bavarians" first, "Germans" second.
In the 19th-century sense, an independent Bavarian State only existed from 1806–71. This feeling started to come about more strongly among Bavarians when the
Kingdom of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria (german: Königreich Bayern; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German E ...
was forced by
Bismarck to join the Protestant Prussian-dominated
German Empire in 1871, while the
Bavarian nationalists wanted to keep Bavaria as Catholic and an independent state. Aside from the minority
Bavaria Party
The Bavaria Party (german: Bayernpartei, BP) is an autonomist, regionalist and conservative political party in the state of Bavaria, Germany. The party was founded in 1946, describes itself as patriotic Bavarian and advocates Bavarian independence ...
, most Bavarians now accept Bavaria is part of Germany.
Another consideration is that Bavarians foster different cultural identities:
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper F ...
in the north, speaking
East Franconian German
East Franconian (german: Ostfränkisch) or Mainfränkisch, usually referred to as Franconian (') in German, is a dialect which is spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, ...
; Bavarian Swabia in the south west, speaking
Swabian German; and
Altbayern
Altbayern ( Bavarian: ''Oidbayern'', also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the ...
(so-called "Old Bavaria", the regions forming the "historic", pentagon-shaped Bavaria before the acquisitions through the Vienna Congress, at present the districts of the Upper Palatinate, Lower and Upper Bavaria) speaking
Austro-Bavarian
Bavarian (german: Bairisch , Bavarian: ''Boarisch'') or alternately Austro-Bavarian, is a West Germanic language, part of the Upper German family, together with Alemannic and East Franconian.
Bavarian is spoken by approximately 12 million pe ...
.
In Munich, the Old Bavarian dialect was widely spread, but nowadays
High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
is predominantly spoken there.
Flags and coat of arms
Flags
Uniquely among German states, Bavaria has two official flags of equal status, one with a white and blue stripe, the other with white and blue
lozenges. Either may be used by civilians and government offices, who are free to choose between them.
Unofficial versions of the flag, especially a lozenge style with coat of arms, are sometimes used by civilians.
Coat of arms
The modern coat of arms of Bavaria was designed by Eduard Ege in 1946, following heraldic traditions.
*The Golden Lion: At the dexter chief, sable, a
lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
rampant Or, armed and langued gules. This represents the administrative region of Upper Palatinate.
*The "
Franconian Rake": At the sinister chief, per
fess
In heraldry, a fess or fesse (from Middle English ''fesse'', from Old French ''faisse'', from Latin ''fascia'', "band") is a charge on a coat of arms (or flag) that takes the form of a band running horizontally across the centre of the shield. ...
dancetty, gules, and argent. This represents the administrative regions of Upper, Middle and Lower Franconia.
*The Blue "Pantier" (mythical creature from
French heraldry
French heraldry is the use of heraldic symbols in France. Although it had a considerable history, existing from the 11th century, such formality has largely died out in France, as far as regulated personal heraldry is concerned. Civic heraldry on ...
, sporting a flame instead of a tongue): At the dexter base, argent, a Pantier rampant azure, armed Or and langued gules. This represents the regions of Lower and Upper Bavaria.
*The Three Lions: At the sinister base, Or, three lions passant guardant sable, armed and langued gules. This represents Swabia.
*The White-And-Blue inescutcheon: The
inescutcheon
In heraldry, an escutcheon () is a shield that forms the main or focal element in an achievement of arms. The word can be used in two related senses. In the first sense, an escutcheon is the shield upon which a coat of arms is displayed. In the ...
of white and blue fusils askance was originally the coat of arms of the Counts of Bogen, adopted in 1247 by the House of Wittelsbach. The white-and-blue fusils are indisputably the emblem of Bavaria and these arms today symbolize Bavaria as a whole. Along with the People's Crown, it is officially used as the Minor Coat of Arms.
*The People's Crown (''Volkskrone''): The coat of arms is surmounted by a
crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
with a golden band inset with precious stones and decorated with five ornamental leaves. This crown first appeared in the coat of arms to symbolize sovereignty of
the people
The ''Sunday People'' is a British tabloid Sunday newspaper. It was founded as ''The People'' on 16 October 1881.
At one point owned by Odhams Press, The ''People'' was acquired along with Odhams by the Mirror Group in 1961, along with the ' ...
after the royal crown was eschewed in 1923.
Geography

Bavaria shares international borders with
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
(
Salzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Austro-Bavarian) is the fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Salzburg was founded ...
,
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
,
Upper Austria
Upper Austria (german: Oberösterreich ; bar, Obaöstareich) is one of the nine states or of Austria. Its capital is Linz. Upper Austria borders Germany and the Czech Republic, as well as the other Austrian states of Lower Austria, Styria, an ...
and
Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( , ; gsw, label= Vorarlbergisch, Vorarlbearg, , or ) is the westernmost state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the ...
) and the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
(
Karlovy Vary
Karlovy Vary (; german: Karlsbad, formerly also spelled ''Carlsbad'' in English) is a spa city in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 46,000 inhabitants. It lies on the confluence of the rivers Ohře and Teplá. It is ...
,
Plzeň and
South Bohemian Region
The South Bohemian Region ( cs, Jihočeský kraj; , ) is an administrative unit (''kraj'') of the Czech Republic, located mostly in the southern part of its historical land of Bohemia, with a small part in southwestern Moravia. The western part ...
s), as well as with
Switzerland (across
Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Lak ...
to the
Canton of St. Gallen
The canton of St. Gallen, also canton of St Gall (german: link=no, Kanton St. Gallen ; rm, Chantun Son Gagl; french: Canton de Saint-Gall; it, Canton San Gallo), is a canton of Switzerland. The capital is St. Gallen.
Located in northeaster ...
).
All of these countries are part of the
Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and ...
, so the borders are completely open (except during COVID-19).
Neighboring states within Germany are
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
,
Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Da ...
,
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
, and
Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
. Two major rivers flow through the state: the
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
(''Donau'') and the
Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
*Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
* ...
. The
Bavarian Alps
The Bavarian Alps (german: Bayerische Alpen) is a collective name for several mountain ranges of the Northern Limestone Alps within the German state of Bavaria.
Geography
The term in its wider sense refers to that part of the Eastern Alps tha ...
define the border with Austria (including the Austrian federal-states of Vorarlberg, Tyrol and Salzburg), and within the range is the highest peak in Germany: the
Zugspitze
The Zugspitze (), at above sea level, is the highest peak of the Wetterstein Mountains as well as the highest mountain in Germany. It lies south of the town of Garmisch-Partenkirchen, and the Austria–Germany border runs over its western su ...
.
The
Bavarian Forest
The village of Zell in the Bavarian Forest
The Bavarian Forest ( German: ' or ''Bayerwald''; bar, Boarischa Woid) is a wooded, low-mountain region in Bavaria, Germany that is about 100 kilometres long. It runs along the Czech border and is ...
and the
Bohemian Forest
The Bohemian Forest, known in Czech as Šumava () and in German as Böhmerwald, is a low mountain range in Central Europe. Geographically, the mountains extend from Plzeň Region and South Bohemia in the Czech Republic to Austria and Bavaria ...
form the vast majority of the frontier with the Czech Republic and Bohemia.
The major cities in Bavaria are
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
(''München''),
Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
(''Nürnberg''),
Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the '' ...
,
Regensburg,
Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is a city in the region of Franconia in the north of the German state of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the '' Regierungsbezirk'' Lower Franconia. It spans the banks of the Main River.
Würzbur ...
,
Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an Independent city#Germany, independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area ...
,
Fürth
Fürth (; East Franconian: ; yi, פיורדא, Fiurda) is a city in northern Bavaria, Germany, in the administrative division ('' Regierungsbezirk'') of Middle Franconia. It is now contiguous with the larger city of Nuremberg, the centres of ...
, and
Erlangen
Erlangen (; East Franconian: ''Erlang'', Bavarian: ''Erlanga'') is a Middle Franconian city in Bavaria, Germany. It is the seat of the administrative district Erlangen-Höchstadt (former administrative district Erlangen), and with 116,062 inhabi ...
.
The
geographic center of the European Union is located in the northwestern corner of Bavaria.
Climate
At lower elevations the climate is classified according to
Köppen’s guide as “
Cfb” or “
Dfb” at lower altitudes, then at higher altitudes the climate becomes “
Dfc” and “
ET”.
The summer months have been getting hotter in recent years.
For example, June 2019 was the warmest June in Bavaria since weather observations have been recorded
and the winter 2019/2020 was 3 degrees Celsius warmer than the average temperature for many years all over Bavaria. On 20 December 2019 a record temperature of was recorded in
Piding
Piding is an approved climatic spa in Bavaria near to the border of Austria close to Bad Reichenhall and Freilassing.
Geography
Geographical position
Piding is located in the middle of the ''Landkreis'' Berchtesgadener Land.
The municipal area ...
. In general winter months are seeing more precipitation which is taking the form of rain more often than that of snow compared to the past.
Extreme weather
Extreme weather or extreme climate events includes unexpected, unusual, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Often, extreme events are based on a locati ...
like the
2013 European floods
Extreme flooding in Central Europe began after several days of heavy rain in late May and early June 2013. Flooding and damages primarily affected south and east German states (Thuringia, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Lower Saxony, Bavaria and Baden-W� ...
or the
2019 European heavy snowfalls
Nineteen or 19 may refer to:
* 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20
* one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019
Films
* ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film
* ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film
Music ...
is occurring more and more often. One effect of the continuing warming is the melting of almost all Bavarian
Alpine glaciers: Of the five glaciers of Bavaria only the
Höllentalferner
The Höllentalferner is a glacier in the western Wetterstein Mountains. It is a cirque glacier that covers the upper part of the Höllental valley and its location in a rocky bowl between the Riffelwandspitzen and Germany's highest mountain, the ...
is predicted to exist over a longer time perspective. The
Südliche Schneeferner has almost vanished since the 1980s.
Administrative divisions
Administrative regions

Bavaria is divided into seven administrative regions called ' (singular '). Each of these regions has a state agency called the ' (district government).
*
Altbayern
Altbayern ( Bavarian: ''Oidbayern'', also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the ...
:
#
Upper Palatinate
The Upper Palatinate (german: Oberpfalz, , ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany, and is located in the east of Bavaria.
Geography
The Upper Palatinate is a landscape with low mountains and numerous ponds and lakes ...
(''german: Oberpfalz'')
#
Upper Bavaria
Upper Bavaria (german: Oberbayern, ; ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany.
Geography
Upper Bavaria is located in the southern portion of Bavaria, and is centered on the city of Munich, both state capital and s ...
(')
#
Lower Bavaria
Lower Bavaria (german: Niederbayern, Bavarian: ''Niedabayern'') is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany, located in the east of the state.
Geography
Lower Bavaria is subdivided into two regions () – Landshut and Donau-W ...
(')
*
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper F ...
:
#
Upper Franconia
Upper Franconia (german: Oberfranken) is a '' Regierungsbezirk'' (administrative 'Regierungs''region 'bezirk'' of the state of Bavaria, southern Germany. It forms part of the historically significant region of Franconia, the others being Middle ...
(')
#
Middle Franconia
Middle Franconia (german: Mittelfranken, ) is one of the three administrative regions of Franconia in Bavaria, Germany. It is located in the west of Bavaria and borders the state of Baden-Württemberg. The administrative seat is Ansbach; however, ...
(')
#
Lower Franconia
Lower Franconia (german: Unterfranken) is one of seven districts of Bavaria, Germany. The districts of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia make up the region of Franconia.
History
After the founding of the Kingdom of Bavaria the state was total ...
(')
*
Swabia:
#
Swabia (')
Bezirke
' (districts) are the third communal layer in Bavaria; the others are the ' and the ' or '. The ' in Bavaria are territorially identical with the ', but they are self-governing regional corporation, having their own parliaments. In the other larger states of Germany, there are only ' as administrative divisions and no self-governing entities at the level of the ' as the ' in Bavaria.
Population and area
Districts
The second communal layer is made up of 71 rural districts (called ', singular ') that are comparable to counties, as well as the 25 independent cities (', singular '), both of which share the same administrative responsibilities.

Rural districts:
Independent cities:
Municipalities
The 71 rural districts are on the lowest level divided into 2,031 regular municipalities (called ', singular '). Together with the 25 independent cities (', which are in effect municipalities independent of ' administrations), there are a total of 2,056 municipalities in Bavaria.




In 44 of the 71 rural districts, there are a total of 215
unincorporated area
An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. Widespread unincorporated communities and areas are a distinguishing feature of the United States and Canada. Most other countries of the world either have ...
s (as of 1 January 2005, called ', singular '), not belonging to any municipality, all uninhabited, mostly forested areas, but also four lakes (-without islands, -without island , , which are the three largest lakes of Bavaria, and ).
Major cities and towns
Source: Bayerisches Landesamt für Statistik und Datenverarbeitung
Politics
Bavaria has a multiparty system dominated by the conservative
Christian Social Union (CSU), which has won every election since 1945 with the exception of the 1950 ballot. Other important parties are
The Greens, which became the second biggest political party in the 2018 local parliament elections and the center-left
Social Democrats
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote s ...
(SPD), who have dominated the city of
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
until 2020. Hitherto,
Wilhelm Hoegner has been the only SPD candidate to ever become Minister-President; notable successors in office include multi-term Federal Minister
Franz Josef Strauss
Franz Josef Strauss ( ; 6 September 1915 – 3 October 1988) was a German politician. He was the long-time chairman of the Christian Social Union in Bavaria (CSU) from 1961 until 1988, member of the federal cabinet in different positions between ...
, a key figure among
West German
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
conservatives during the
Cold War years, and
Edmund Stoiber
Edmund Rüdiger Stoiber (born 28 September 1941) is a German politician who served as the 16th Minister President of the state of Bavaria between 1993 and 2007 and chairman of the Christian Social Union (CSU) between 1999 and 2007. In 2002, he r ...
, who both failed with their bids for
Chancellorship.
The German
Greens and the center-right
Free Voters
Free Voters (german: Freie Wähler, FW or FWG) in Germany may belong to an association of people which participates in an election without having the status of a registered political party. Usually it involves a locally organized group of voters ...
have been represented in the state parliament since 1986 and 2008 respectively.
In the
2003 elections the CSU won a
⅔ supermajority – something no party had ever achieved in postwar Germany. However, in the subsequent
2008 elections
The following elections occurred in the year 2008.
* Electoral calendar 2008
* 2008 United Nations Security Council election
Africa
* 2008 Angolan legislative election
* 2008 Anjouan presidential election
* 2008 Republic of the Congo Senate elec ...
the CSU lost the absolute majority for the first time in 46 years.
The losses were partly attributed by some to the CSU's stance for an anti-smoking bill. (A first anti-smoking law had been proposed by the CSU and passed but was watered down after the election, after which a referendum enforced a strict antismoking bill with a large majority).
Current Landtag

The
last state elections were held on 14 October 2018 in which the CSU lost its absolute majority in the state parliament in part due to the party's stances as part of the federal government, winning 37.2% of the vote; the party's second worst local election outcome in its history after 1950. The Greens who had surged in the polls leading up to the election have replaced the social-democratic SPD as the second biggest force in the
Landtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non- ...
with 17.6% of the vote. The SPD lost over half of its previous share compared to 2013 with a mere 9.7% in 2018. The liberals of the FDP were again able to reach the five-percent-threshold in order to receive mandates in parliament after they were not part of the ''Landtag'' after the 2013 elections. Also entering the new parliament were the right-wing populist Alternative for Germany (AfD), with 10.2% of the vote.
The center-right Free Voters party gained 11.6% of the vote and formed a government coalition with the CSU which led to the subsequent reelection of Markus Söder as
Minister-President of Bavaria.
Government
*
Bavarian Cabinet since 12 November 2018
The
Constitution of Bavaria
The Constitution of the Free State of Bavaria was enacted on 8 December 1946. It is the fourth constitutional document in Bavarian history after the Constitution of 1808, the Constitution of the Kingdom of Bavaria in 1818 and the Bamberg Cons ...
of the Free State of Bavaria was enacted on 8 December 1946. The new Bavarian Constitution became the basis for the Bavarian State after the Second World War.
Bavaria has a
unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multi ...
' (English: State Parliament), elected by universal suffrage. Until December 1999, there was also a ', or
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the e ...
, whose members were chosen by social and economic groups in Bavaria, but following a referendum in 1998, this institution was abolished.
The Bavarian State Government consists of the
Minister-President of Bavaria, eleven Ministers and six Secretaries of State. The Minister-President is elected for a period of five years by the State Parliament and is head of state. With the approval of the State Parliament he appoints the members of the State Government. The State Government is composed of the:
*
State Chancellery (')
*Ministry of the
Interior
Interior may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Interior'' (Degas) (also known as ''The Rape''), painting by Edgar Degas
* ''Interior'' (play), 1895 play by Belgian playwright Maurice Maeterlinck
* ''The Interior'' (novel), by Lisa See
* Interior de ...
, for Sport and Integration (')
*Ministry for Housing, Construction and Transport (')
*Ministry of Justice (')
*Ministry for Education and Culture (')
*Ministry for Science and Art (')
*Ministry of Finance and for Home Affairs (')
*Ministry for Economic Affairs, Regional Development and Energy (')
*Ministry for Environment and Consumer Protection (')
*Ministry for Food, Agriculture and Forestry (')
*Ministry for Family, Labour and Social Affairs (')
*Ministry for Health and Care (')
*Ministry for Digital Affairs (')
Political processes also take place in the seven regions (' or ') in Bavaria, in the 71 rural districts (') and the 25 towns and cities forming their own districts ('), and in the 2,031 local authorities (').
In 1995 Bavaria introduced
direct democracy on the local level in a
referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
. This was initiated bottom-up by an association called ''Mehr Demokratie'' (English: More Democracy). This is a grass-roots organization which campaigns for the right to citizen-initiated referendums. In 1997 the Bavarian Supreme Court tightened the regulations considerably (including by introducing a turn-out quorum). Nevertheless, Bavaria has the most advanced regulations on local direct democracy in Germany. This has led to a spirited citizens' participation in communal and municipal affairs—835 referendums took place from 1995 through 2005.
Minister-presidents of Bavaria since 1945

Designation as a "free state"
Unlike most German states (''Länder''), which simply designate themselves as "State of" (''Land
..'), Bavaria uses the style of "Free State of Bavaria" (''Freistaat Bayern''). The difference from other states is purely terminological, as German constitutional law does not draw a distinction between "States" and "Free States". The situation is thus analogous to the United States, where
some states use the style "Commonwealth" rather than "State". The term "Free State", a creation of the 19th century and intended to be a German alternative to (or translation of) the Latin-derived ''republic'' was common among the states of the
Weimar Republic
The German Reich, commonly referred to as the Weimar Republic,, was a historical period of Germany from 9 November 1918 to 23 March 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is also r ...
, after German monarchies had been abolished. Unlike most other states – many of which were new creations – Bavaria has resumed this terminology after
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. Two other states,
Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
and
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
, also call themselves "Free State".
Arbitrary arrest and human rights
In July 2017, Bavaria's parliament enacted a new revision of the "Gefährdergesetz", allowing the authorities to imprison a person for a three months term, renewable indefinitely, when they haven't committed a crime but it is assumed that they might commit a crime "in the near future". Critics like the prominent journalist
Heribert Prantl
Heribert Prantl (born 30 July 1953 in Nittenau, Bavaria, Germany) is a German author, journalist and jurist (former judge, prosecutor and lawyer).
At the ''Süddeutsche Zeitung'' he was head of the department of domestic policy from 1995 to 2017, ...
have called the law "shameful" and compared it to
Guantanamo Bay detention camp
The Guantanamo Bay detention camp ( es, Centro de detención de la bahía de Guantánamo) is a United States military prison located within Guantanamo Bay Naval Base, also referred to as Guantánamo, GTMO, and Gitmo (), on the coast of Guant ...
, assessed it to be in violation of the
European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by t ...
, and also compared it to the legal situation in Russia, where a similar law allows for imprisonment for a maximum term of two years (i.e., not indefinitely).
Economy
Bavaria has long had one of the largest economies of any region in Germany, and in Europe. Its
gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
(GDP) in 2007 exceeded €434 billion (about U.S. $600 billion). This makes Bavaria itself one of the largest economies in Europe, and only 20 countries in the world have a higher GDP. The GDP of the region increased to €617.1 billion in 2018, accounting for 18.5% of German economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was €43,500 or 145% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 114% of the EU average. This makes Bavaria one of the wealthiest regions in Europe. Bavaria has strong economic ties with
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
,
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
,
Switzerland, and
Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative Regions ...
.
In 2019 GDP was €832.4 ($905.7) billion, €48,323 ($52,577.3) per capita.
Agriculture
The most distinctive high points of Bavarian agriculture are:
*
Hop growing in region
Hallertau
The Hallertau or Holledau is an area in Bavaria, Germany. With an area of 178 km², it is listed as the largest continuous hop-planting area in the world.Bentley, James; Catling, Christopher; & Locke, Tim (1994). ''Munich and Bavaria''. Chicago: ...
, which is up to 80% of German production and exported worldwide.
*Inland
aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lotus ...
of
carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
s and
trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-sa ...
.
*The well-hydrated alpine meadows are used to produce large quantities of quality milk, which is used to make a variety of cheese (including
blue-veined cheese), yogurt and butter (
Meggle).
*The cultivation of
asparagus
Asparagus, or garden asparagus, folk name sparrow grass, scientific name ''Asparagus officinalis'', is a perennial flowering plant species in the genus '' Asparagus''. Its young shoots are used as a spring vegetable.
It was once classified ...
is widespread, which is a very popular new season vegetable. In season ("Spargelzeit") restaurants offer special separated aspargaus menu . There is an asparagus museum in
Schrobenhausen
Schrobenhausen (; Central Bavarian: ''Schrobenhausn'') is a town in the district of Neuburg-Schrobenhausen in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated on the River Paar approx. south-west of Ingolstadt and north-east of Augsburg.
The town hosts notabl ...
.
*There are farms producing venison from
deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the ...
and
roe
Roe ( ) or hard roe is the fully ripe internal egg masses in the ovaries, or the released external egg masses, of fish and certain marine animals such as shrimp, scallop, sea urchins and squid. As a seafood, roe is used both as a cooked ing ...
.
*
Viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for ''vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ran ...
is widespread in
Lower Franconia
Lower Franconia (german: Unterfranken) is one of seven districts of Bavaria, Germany. The districts of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia make up the region of Franconia.
History
After the founding of the Kingdom of Bavaria the state was total ...
.
*Good ecology and strict control allow produce a large amount of organic products ("bio") and baby food.
Hopfenernte_in_der_Holledau_%28Hallertau%29.JPG, Hop garten
Allgaeu.jpg, Allgäuer meadows
Spargel_sauce_hollandaise.jpg, Asparagus with sauce hollandaise
Spaziergang_durch_Klingenberg_am_Main._04.jpg, Vineyards in Klingenberg-am-Main
Industries
Bavaria has the best developed industry in Germany and the lowest unemployment rate with 2.9% as of October 2021.
Branches:
*Oil refining. Although there is oil production in Bavaria, it does not meet domestic needs. Most of the oil is imported via pipelines from the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
(Russian oil) and from the Italian port of
Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
(Near East oil). Three refineries are situated near
Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an Independent city#Germany, independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area ...
and another one in
Burghausen. Last one is a part of Bavarian chemical triangle and delivery row materials to other chemical plants.
Raffinerie_Esso_Ingolstadt.jpg, Refinery Ingolstadt
TAL-Br%C3%BCcke01.jpg , transalpine pipeline
*Automotive is the most important and best developed Bavarian industry, which included manufacture of luxury cars (4
BMW and 2
Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The o ...
plants, R&D centers, test tracks), trucks (
Traton MAN), special vehicles (
Tadano Faun), buses (
Evobus/Setra) and automotive parts (engines, electronics, cables, seats, interiors, cabrio roofs, heating and brake systems, software). Bavaria has the second-most employees (207,829) in the automotive industry of all German states after Baden-Württemberg as of 2018.
2019 BMW 740Li Automatic facelift 3.0.jpg , BMW 7 Series
Audi_A5_Cabriolet_F5_at_IAA_2019_IMG_0173.jpg, Audi A5
MAN_TGX_18.640_XXL_Modell_2020_Fahrerhaus.jpg, MAN TGX
Faun HK 100-05.jpg , Faun HK 100
Setra_S515HDH_Schneider_Langendorf.jpg, Setra S515HDH
*Aerospace and defense, which manufacture multi-role attack jet
Eurofighter Typhoon
The Eurofighter Typhoon is a European multinational twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter. The Typhoon was designed originally as an air-superiority fighter and is manufactured by a consortium of Airbus, BAE Systems and Leonar ...
, missiles from
MBDA
MBDA is a European multinational developer and manufacturer of missiles.[MBDA Inc. US Division Co ...](_blank)
and
Diehl Defence
Diehl Defence GmbH & Co. KG is a German arms manufacturer and a division of the Diehl Stiftung with headquarters in Überlingen. Diehl Defence mainly produces missiles and ammunition. Diehl BGT Defence was founded in 2004 as result of the merger ...
, parts of rocket
Ariane, regional jet
Dornier 728, ultra-light planes from
Grob Aerospace
Grob Aircraft, formerly Grob Aerospace, is a German aircraft manufacturer, specialising in gliders and general aviation.
Since its foundation in 1971, Grob Aircraft produced a range of aircraft. Initially focusing on gliders, it soon grew ...
, turbo jet engines for civil and military applications from
MTU Aero Engines
MTU Aero Engines AG is a German aircraft engine manufacturer. MTU develops, manufactures and provides service support for military and civil aircraft engines. MTU Aero Engines was formerly known as MTU München.
History
While the Munich-based en ...
, helicopters
Airbus
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft throughout the world. The company has three divisions: '' ...
, main battle tank
Leopard 2
The Leopard 2 is a 3rd generation main battle tank originally developed by Krauss-Maffei in the 1970s for the West German army. The tank first entered service in 1979 and succeeded the earlier Leopard 1 as the main battle tank of the West G ...
, drones, composite parts, avionics, radars, propellants, initiators, powder, munitions. In Munich suburban
Oberpfaffenhofen
Oberpfaffenhofen is a village that is part of the municipality of Weßling in the district of Starnberg, Bavaria, Germany. It is located about from the city center of Munich.
Village
The village is home to the Oberpfaffenhofen Airport and a ...
situated control center of European satellite navigation system
Galileo,
German Space Operations Center
The German Space Operations Center (GSOC; german: Deutsches Raumfahrt-Kontrollzentrum) is the mission control center of German Aerospace Center (DLR) in Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich, Germany.
Tasks
The GSOC performs the following tasks in ...
, Microwaves and Radar Institute, Institute of Communications and Navigation, Remote Sensing Technology Institute, Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics, Institute for Software Technology, Institute of System Dynamics and Control.
Typhoon_f2_zj910_arp.jpg, Eurofighter Typhoon
Grob_120_TP-A_%E2%80%98D-ETPX%E2%80%99.jpg , Grob G 120TP
Eurocopter_EC-665_Tiger_UHT%2C_Germany_-_Army_AN1547187.jpg , Airbus EC-665 Tiger
PARS3LR.jpg , PARS 3 LR
Leopard_2_A5_der_Bundeswehr.jpg, Leopard 2
*Other transport manufacturing also represents in Bavaria. Even exists ship yards, for example
Bavaria Yachtbau
Bavaria Yachtbau was founded in 1978 by Winfried Herrman, a window manufacturer, and Josef Meltl, a yacht charter broker. By 2006, the company had grown to produce approximately 3,500 sailing and motor yachts and employing 600 people. Bavaria Ya ...
, despite location many hundreds kilometers from sea away; manufacturing of 4-stroke marine diesel engine, which using in cruise liners, ferries and warships. Rail technique produce in Munich-Allach (locomotive
Siemens Vectron
The Vectron is a locomotive series made by Siemens Mobility, introduced at the 2010 InnoTrans trade fair in four prototype versions: diesel, multi-system, and both AC and DC electric power. The diesel version has been replaced in 2018 by a du ...
) and rail maintenance vehicle in
Freilassing
Freilassing (), until 1923 Salzburghofen is a town of some 16,000 inhabitants in the southeastern corner of Bavaria, Germany. It belongs to the "Regierungsbezirk" Oberbayern and the "Landkreis" (County) of Berchtesgadener Land.
Located very close ...
.
Bavaria-yachts-r40-motorboat.jpg, Bavaria R40
Schiffsmotor_MAN.JPG, MAN marine diesel
Hungary%2C_Budapest%2C_Ferencv%C3%A1ros_pu.%2C_D-Rpool_Siemens_Vectron_004.JPG, Siemens Vectron
DB_711_211_Oberleitungswartung_Altenburg_2014.jpg, Robel BR 711.2
*Electronics. Chip design centers situated in Munich area (
Infineon
Infineon Technologies AG is a German semiconductor manufacturer founded in 1999, when the semiconductor operations of the former parent company Siemens AG were spun off. Infineon has about 50,280 employees and is one of the ten largest semicond ...
,
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the devel ...
,
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
). There are 3
FAB
Fab or FAB may refer to:
Commerce
* Fab (brand), a frozen confectionery
* Fab (website), an e-commerce design web site
* The FAB Awards, a food and beverage award
* FAB Link, a European electricity link
* Flavoured alcoholic beverage or alcop ...
s: Infineon in
Regensburg, Texas Instruments in
Freising
Freising () is a university town in Bavaria, Germany, and the capital of the Freising ''Landkreis'' (district), with a population of about 50,000.
Location
Freising is the oldest town between Regensburg and Bolzano, and is located on the ...
and Osram Optosemiconductors also in
Regensburg. Power semiconductors are manufactured by
Semikron.
CNC
Numerical control (also computer numerical control, and commonly called CNC) is the automated control of machining tools (such as drills, lathes, mills, grinders, routers and 3D printers) by means of a computer. A CNC machine processes a pie ...
controls are produced by
Heidenhain
Dr. Johannes Heidenhain GmbH is a privately owned enterprise located in Traunreut, Germany that manufactures numerical controls for machine tools, as well as mechatronic measuring devices for length and angle.
Their linear and angle encoders a ...
,
Traunreut
Traunreut (; Central Bavarian: ''Traunreit'') is a town in southeastern Bavaria, Germany in the Traunstein district. It is located at . Traunreut lies in the heart of the Chiemgau region between Munich and Salzburg, approximately 10 km ...
and
Siemens,
Amberg
Amberg () is a town in Bavaria, Germany. It is located in the Upper Palatinate, roughly halfway between Regensburg and Bayreuth. In 2020, over 42,000 people lived in the town.
History
The town was first mentioned in 1034, at that time under t ...
. Silicon wafer for electronic manufacturing are delivered from
Siltronic
Siltronic AG is a manufacturer of wafers made of hyperpure silicon, the basis for modern micro- and nanotechnology. The Munich-based company is one of the world's leading manufacturers of wafers for the semiconductor industry.
History
The compa ...
plant in
Burghausen.
Campeon_Neubiberg.jpg, Campeon - Infineon and Intel R&D centers
TNC530_72dpi.jpg, CNC controls Heidehain iTNC 530
S71500.JPG, Programmable logic controller Siemens Simatic S7-1500
Wafer_2_Zoll_bis_8_Zoll.jpg, Silicon wafers
*Medical equipment. In
Erlangen
Erlangen (; East Franconian: ''Erlang'', Bavarian: ''Erlanga'') is a Middle Franconian city in Bavaria, Germany. It is the seat of the administrative district Erlangen-Höchstadt (former administrative district Erlangen), and with 116,062 inhabi ...
is a headquarters of
Siemens Healthineers which produce devices for
computer tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
, interventional X-ray systems, radiation therapy, molecular and magnetic resonance imaging, software.
Brainlab
Brainlab is a privately held German medical technology company headquartered in Munich, Bavaria. Brainlab develops software and hardware for radiotherapy and radiosurgery, and the surgical fields of neurosurgery, ENT and craniomaxillofacial, spi ...
creates software and hardware for
image-guided surgery Image-guided surgery (IGS) is any surgical procedure where the surgeon uses tracked surgical instruments in conjunction with preoperative or intraoperative images in order to directly or indirectly guide the procedure. Image guided surgery systems ...
.
Roche Diagnostics
F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, commonly known as Roche, is a Swiss multinational healthcare company that operates worldwide under two divisions: Pharmaceuticals and Diagnostics. Its holding company, Roche Holding AG, has shares listed on the SIX S ...
in
Penzberg
Penzberg (; Central Bavarian: ''Benschberg'') is a city (although some see it as a town) in the Weilheim-Schongau district, in Bavaria, Germany. It is located about 50 km south of Munich, and had a population of around 17,000 in 2020. A histo ...
manufactures therapeutic proteins, diagnostic tests, reagents, analyze system and biopharma products.
SiemensEcamDuet.JPG, Siemens E.Cam Duet
*Brewery. Bavaria has long tradition of brewery, near a half of all German breweries are located here (645 of 1300). All possible types of breweries exist: home brewery of hotel or restaurant, belong to big international concern, state-owned, castle or monastery breweries. The perfect quality of beer is guaranteed by 500-years law ("
Reinheitsgebot
The ''Reinheitsgebot'' (, literally "purity order") is a series of regulations limiting the ingredients in beer in Germany and the states of the former Holy Roman Empire. The best known version of the law was adopted in Bavaria in 1516 (by Wil ...
"), which allow as beer ingredients only water, hops, yeast and malt of barley, wheat or rye. But difference of roasting, fermentation or mixing allow to produce many different types of beers (not brand).
Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime m ...
at 2009 tasted beer from Brauerei
Aying
Aying is a municipality in the district of Munich in Bavaria, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies ...
,
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
at 2015 also tasted Bavarian beer of Karg Brauerei in
Murnau. In
Freising
Freising () is a university town in Bavaria, Germany, and the capital of the Freising ''Landkreis'' (district), with a population of about 50,000.
Location
Freising is the oldest town between Regensburg and Bolzano, and is located on the ...
situated research center Weihenstephan for brewing and food quality.
Brauerei_Aying_GO-2.jpg , Brauerei Aying
Murnau_am_Staffelsee%2C_straatzicht2_foto1_2012-08-16_11.49.jpg, Murnau am Staffelsee
Kalttanks.Weissbier.Brauerei.Aying.jpg, Cold reservoirs
MUC_MaxVorstadt_L%C3%B6wenbr%C3%A4u_Sudkessel.jpg, Tanks
Companies
Many large companies are headquartered in Bavaria, including
Adidas,
Allianz
Allianz ( , ) is a German multinational financial services company headquartered in Munich, Germany. Its core businesses are insurance and asset management.
The company is one of the world's largest insurers and financial services groups. T ...
,
Airbus
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft throughout the world. The company has three divisions: '' ...
,
Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The o ...
,
BMW,
Brose
Brose is a Scots word for an uncooked form of porridge: oatmeal (and/or other meals) is mixed with boiling water (or stock) and allowed to stand for a short time. It is eaten with salt and butter, milk or buttermilk. A version of brose made wi ...
,
BSH Hausgeräte
BSH Hausgeräte GmbH (, stylized as B/S/H/) is the largest manufacturer of home appliances in Europe and one of the leading companies in the sector worldwide. The group stemmed from a joint venture set up in May 1967 between Robert Bosch GmbH ( ...
,
HypoVereinsbank
UniCredit Bank AG, better known under its brand name HypoVereinsbank (HVB), is the fifth-largest of the German financial institutions, ranked according to its total assets, and the fourth-largest bank in Germany according to the number of its e ...
,
Infineon
Infineon Technologies AG is a German semiconductor manufacturer founded in 1999, when the semiconductor operations of the former parent company Siemens AG were spun off. Infineon has about 50,280 employees and is one of the ten largest semicond ...
,
KUKA
KUKA is a German manufacturer of industrial robots and systems for factory automation. It has been predominantly owned by the Chinese company Midea Group since 2016.
The KUKA Robotics Corporation has 25 subsidiaries, mostly sales and servi ...
,
Traton
Traton SE, known as the Traton Group (formerly Volkswagen Truck & Bus AG), is a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group and one of the world's largest commercial vehicle manufacturers, with its MAN, Scania, Navistar, and Volkswagen Caminhões e Ônib ...
,
MTU Aero Engines
MTU Aero Engines AG is a German aircraft engine manufacturer. MTU develops, manufactures and provides service support for military and civil aircraft engines. MTU Aero Engines was formerly known as MTU München.
History
While the Munich-based en ...
,
Munich Re
Munich Re Group or Munich Reinsurance Company (german: Münchener Rück; Münchener Rückversicherungs-Gesellschaft) is a German multinational insurance company based in Munich, Germany. It is one of the world's leading reinsurers. ERGO, a Munic ...
,
Osram
Osram Licht AG is a German company that makes electric lights, headquartered in Munich and Premstätten (Austria). Osram positions itself as a high-tech photonics company that is increasingly focusing on sensor technology, visualization and t ...
,
Puma,
Rohde & Schwarz
Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co KG (, ) is an international electronics group specializing in the fields of electronic test equipment, broadcast & media, cybersecurity, radiomonitoring and radiolocation, and radiocommunication. The company provides p ...
,
Schaeffler
Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. KG, also known as Schaeffler Group (''Schaeffler-Gruppe'' in German), is a German manufacturer of rolling element bearings for automotive, aerospace and industrial uses. It was founded in 1946 by brothers Dr ...
,
Siemens,
Wacker Chemie
Wacker Chemie AG is a German multinational chemical company which was founded in 1914 by Alexander Wacker. The company is controlled by the Wacker family holding more than 50 percent of the shares. The corporation is operating more than 25 prod ...
,
Linde
Linde may refer to:
Places
*Lindes and Ramsberg Mountain District, a former district in Sweden, see Lindesberg Municipality
*Lipka, Złotów County, a village in Poland, called Linde before World War II
Rivers
*Linde (Tollense), a river of Meckle ...
,
Vitesco Technologies
Vitesco Technologies Group AG (known until autumn 2019 as ''Continental Powertrain''), headquartered in Regensburg, is a German automotive supplier for drivetrain and powertrain technologies. Vitesco Technologies was a business area of Continental ...
,
Webasto
Webasto SE is a company based in Stockdorf, Germany which makes sunroofs, electric-car chargers and air-conditioning systems. Holger Engelmann is the CEO of the company.
History
Coronavirus outbreak
Webasto owns 11 locations in China, inc ...
,
Grob,
Heidenhain
Dr. Johannes Heidenhain GmbH is a privately owned enterprise located in Traunreut, Germany that manufactures numerical controls for machine tools, as well as mechatronic measuring devices for length and angle.
Their linear and angle encoders a ...
,
Koenig & Bauer,
Kaeser Compressors,
Krones,
Knorr-Bremse
Knorr-Bremse AG is a German manufacturer of braking systems for rail and commercial vehicles that has operated in the field for over 110 years. Other products in Group's portfolio include intelligent door systems, control components, air ...
,
Wacker Neuson
Wacker Neuson SE (formerly: Wacker Construction Equipment AG) with headquarters in Munich is a manufacturer of construction equipment and compact machines for concrete and construction site technology listed on the stock market. The group inclu ...
,
Krauss-Maffei Wegmann
Krauss-Maffei Wegmann GmbH & Co. KG (KMW) is an arms industry company based in Munich, Germany. The company produces various types of equipment as well as rail locomotives, tanks, self-propelled artillery, and other armoured vehicles.
KMW was ...
,
Siltronic
Siltronic AG is a manufacturer of wafers made of hyperpure silicon, the basis for modern micro- and nanotechnology. The Munich-based company is one of the world's leading manufacturers of wafers for the semiconductor industry.
History
The compa ...
,
Leoni,
Fielmann
Fielmann AG is a German eye-wear company.
The Fielmann stock is listed in the German SDAX index and at the northern German regional HASPAX index. With 5% of all optical stores, Fielmann achieved a 22% sales market share and a 53% market share ...
,
MediaMarkt,
Conrad Electronic,
BayWa
BayWa AG (until 1972: ''Bayerische Warenvermittlung landwirtschaftlicher Genossenschaften AG'') is an internationally active group headquartered in Munich. Originally founded to support domestic agriculture, the company expanded its activitie ...
,
ProSiebenSat.1 Media
ProSiebenSat.1 Media SE (officially abbreviated as P7S1, formerly ProSiebenSat.1 Media AG) is a German mass media & digital company. It operates in three segments: Entertainment, Dating and Commerce & Ventures. The company is listed on the Fran ...
,
Telefónica Germany
Telefónica Germany GmbH & Co. OHG (; also called Telefónica Deutschland ) is a provider of broadband, landline and mobile telecommunications in Germany. The company trades as O2 (typeset as O2).
The company was renamed from Telefónica O ...
,
Knauf
Knauf Gips KG is a multinational, family-owned company based in Iphofen, Germany, well known for drywall gypsum boards, founded in 1932. The company is a producer of building materials and construction systems comprising construction materials fo ...
,
Rehau
Rehau is a town in the district of Hof, in Bavaria, Germany. The first documented name of Rehau was "Resawe" in the year 1234. Rehau is situated in the Fichtelgebirge, 12 km southeast of Hof, and 12 km west of Aš. Formerly a fairl ...
,
Giesecke+Devrient.
Also American companies open a lot of research and development centers in Munich region:
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
(chip design),
Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
(data security),
IBM (Watson technology),
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the devel ...
(drones and telecommunication chips),
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
(3D-printers and additive manufacturing),
Gleason (gears manufacturing),
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globa ...
(chip design and manufacturing),
Coherent (lasers).
Tourism
With 40 million tourists in 2019, Bavaria is the most visited German state and one of Europe's leading tourist destinations.
Attractions:
*Amusement parks: Legoland in
Günzburg
Günzburg (; Swabian: ''Genzburg'') is a town in Bavaria, Germany. It is a ''Große Kreisstadt'' and the capital of the Swabian district Günzburg. This district was constituted in 1972 by combining the city of Günzburg – which had not ...
, Bayern-Park in
Reisbach (Vils)
Reisbach is a market town in Bavaria. It lies on the Vils River, and belongs to the administrative region of Niederbayern.
Neighbouring communities
The neighbouring communities, listed clockwise, are Mamming, Landau an der Isar, Simbach ...
, Playmobil in
Zirndorf
Zirndorf () is a town, which is part of the district of Fürth. It is located in northern Bavaria, Germany in the Regierungsbezirk of Middle Franconia.
Neighbouring municipalities
The following towns and municipalities share borders with Zirn ...
, Skyline Park in
Bad Wörishofen
Bad Wörishofen () is a spa town in the district of Unterallgäu in Bavaria, Germany, known for the water-cure ( hydrotherapy) developed by Sebastian Kneipp (1821–1897), a Catholic priest who lived there for 42 years. Many of the resort hotels ...
and Bavaria Filmstadt in
Grünwald
*Christmas markets in
Rothenburg ob der Tauber
Rothenburg ob der Tauber () is a town in the district of Ansbach of Mittelfranken (Middle Franconia), the Franconia region of Bavaria, Germany. It is well known for its well-preserved medieval old town, a destination for tourists from around the ...
,
Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
and
Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
*Factory-Outlet-Centers:
Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an Independent city#Germany, independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area ...
Village and
Wertheim Village
*Festivals:
Oktoberfest
The Oktoberfest (; bar, Wiesn, Oktobafest) is the world's largest Volksfest, featuring a beer festival and a travelling carnival. It is held annually in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. It is a 16- to 18-day folk festival running from mid- or la ...
Neuschwanstein Castle from Marienbrücke, 2011 May.jpg, Schloss Neuschwanstein
Neuschwanstein Castle (german: Schloss Neuschwanstein, , Southern Bavarian: ''Schloss Neischwanstoa'') is a 19th-century historicist palace on a rugged hill above the village of Hohenschwangau near Füssen in southwest Bavaria, Germany. The pa ...
Würzburger Residenz, Gartenfront.jpg, Würzburger Residenz
Aschaffenburger Schloss.jpg, Schloss Johannisburg
Schloss Johannisburg is a schloss in the town of Aschaffenburg, in Franconia in the state of Bavaria, Germany. It was erected between 1605 and 1614 by the architect for Johann Schweikhard von Kronberg, Prince Bishop of Mainz. Until 1803, it ...
in Aschaffenburg
Aschaffenburg (; South Franconian: ''Aschebersch'') is a town in northwest Bavaria, Germany. The town of Aschaffenburg is not part of the district of Aschaffenburg, but is its administrative seat.
Aschaffenburg belonged to the Archbishopric ...
Bamberger Dom BW 6h.JPG, Bamberger Dom
Coburg-Ehrenburg1.jpg, Schloss Ehrenburg
Ehrenburg Palace (German: ''Schloss Ehrenburg'') is a palace in Coburg, Franconia, Germany. It served as the main Coburg residence for the ruling princes from the 1540s until 1918. The palace's exterior today mostly reflects Gothic Revival style. ...
in Coburg
Haus Theresienstein 20221012 HOF05904.png, Hofer Theresienstein
Nürnberger Burg im Herbst 2013.jpg, Nürnberger Kaiserburg
Regensburg-steinerne-Bruecke.jpg, Steinerne Brücke
The Stone Bridge (''Steinerne Brücke'') in Regensburg, Germany, is a 12th-century bridge across the Danube linking the Old Town with Stadtamhof. For more than 800 years, until the 1930s, it was the city's only bridge across the river. It is a mas ...
und Dom in Regensburg
Walhalla, Donaustauf.JPG, Walhalla, Donaustauf bei Regensburg
Befreiungshalle1, Kelheim, Deutschland.JPG, Befreiungshalle
The Befreiungshalle (''"Hall of Liberation"'', ) is a neoclassical monument on the Michelsberg hill above the town of Kelheim in Bavaria, Germany. It stands upstream of Regensburg on the river Danube at the confluence of the Danube and the A ...
, Kelheim
A rathausplatz.jpg, Augsburger Rathaus und Perlachturm
The 70-metre-tall Perlachturm is a belltower in front of the church of St. Peter am Perlach in the central district of Augsburg, Germany. It originated as a watchtower in the 10th century. The existing Renaissance structure was built in the 1610 ...
Bartholomae-2005.jpg, St. Bartholomä Church am Königssee
Hintersee.jpg, Hintersee in Ramsau bei Berchtesgaden
Suro mh.jpg, Preserved blast furnance 3 of Maxhütte in Sulzbach-Rosenberg
Sulzbach-Rosenberg ( bar, label= Northern Bavarian, Suizboch-Rosnberg) is a municipality in the Amberg-Sulzbach district, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated approximately 14 km northwest of Amberg, and 50 km east of Nuremberg. The town ...
Amberg Stadtbrille.JPG, Stadtbrille Amberg
Amberg () is a town in Bavaria, Germany. It is located in the Upper Palatinate, roughly halfway between Regensburg and Bayreuth. In 2020, over 42,000 people lived in the town.
History
The town was first mentioned in 1034, at that time under t ...
St. Martin in Landshut.jpg, St. Martin Church ( Landshut)
Passauer Dom.jpg, Dom St. Stephan in Passau
Kongresshalle Dutzendteich Nürnberg MW01.jpg, Die Kongresshalle mit Doku-Zentrum auf dem Reichsparteitagsgelände in Nürnberg
Rothenburg BW 4.JPG, Rothenburg ob der Tauber
Rothenburg ob der Tauber () is a town in the district of Ansbach of Mittelfranken (Middle Franconia), the Franconia region of Bavaria, Germany. It is well known for its well-preserved medieval old town, a destination for tourists from around the ...
Rathaus and Marienplatz from Peterskirche - August 2006.jpg, Marienplatz
Marienplatz ( English: Mary's Square, i.e. St. Mary, Our Lady's Square) is a central square in the city centre of Munich, Germany. It has been the city's main square since 1158.
History
During the Middle Ages, markets and tournaments were hel ...
Unemployment
The unemployment rate stood at 2.6% in October 2018, the lowest in Germany and one of the lowest in the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
.
Demographics

Bavaria has a population of approximately 13.1 million inhabitants (2020). 8 of the
80 largest cities in Germany are located within Bavaria with Munich being the largest (1,484,226 inhabitants, approximately 6.1 million when including the broader metropolitan area), followed by
Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
(518,370 inhabitants, approximately 3.6 million when including the broader metropolitan area),
Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the '' ...
(296,582 inhabitants) and
Regensburg (153,094 inhabitants). All other cities in Bavaria had less than 150,000 inhabitants each in 2020. Population density in Bavaria was , below the national average of . Foreign nationals resident in Bavaria (both
immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, ...
and
refugees
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution. /
asylum seekers
An asylum seeker is a person who leaves their country of residence, enters another country and applies for asylum (i.e., international protection) in that other country. An asylum seeker is an immigrant who has been forcibly displaced and m ...
) were principally from other EU countries and Turkey.
Vital statistics
Culture
Some features of the Bavarian culture and mentality are remarkably distinct from the rest of Germany. Noteworthy differences (especially in rural areas, less significant in the major cities) can be found with respect to religion, traditions, and language.
Religion

Bavarian culture (''
Altbayern
Altbayern ( Bavarian: ''Oidbayern'', also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the ...
'') has a long and predominant tradition of
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
faith. Pope emeritus
Benedict XVI (Joseph Alois Ratzinger) was born in
Marktl am Inn
Marktl, or often unofficially called ''Marktl am Inn'' ("Little market on the river Inn"), is a village and historic market municipality in the state of Bavaria, Germany, near the Austrian border, in the Altötting district of Upper Bavaria. The ...
in
Upper Bavaria
Upper Bavaria (german: Oberbayern, ; ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany.
Geography
Upper Bavaria is located in the southern portion of Bavaria, and is centered on the city of Munich, both state capital and s ...
and was
Cardinal-Archbishop of Munich and Freising. Otherwise, the culturally
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper F ...
n and
Swabian regions of the modern State of Bavaria are historically more diverse in religiosity, with both Catholic and
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
traditions. In 1925, 70.0% of the Bavarian population was
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
, 28.8% was
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
, 0.7% was
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, and 0.5% was placed in other religious categories.
46.9% of Bavarians adhered to Catholicism (a decline from 70.4% in 1970).
17.2 percent of the population adheres to the
Evangelical Lutheran Church in Bavaria The Evangelical Lutheran Church in Bavaria (german: Evangelisch-Lutherische Kirche in Bayern) is a Lutheran member church of the Evangelical Church in Germany in the German state of Bavaria.
The seat of the church is in Munich. The '' Landesbischof ...
, which has also declined since 1970.
Three percent was
Orthodox,
Muslims make up 4.0% of the population of Bavaria. 31.9 percent of Bavarians are irreligious or adhere to other religions.
Traditions
Bavarians commonly emphasize pride in their traditions. Traditional costumes collectively known as
Tracht
''Tracht'' () refers to traditional garments in German-speaking countries and regions. Although the word is most often associated with Bavarian, Austrian, South Tyrolian and Trentino garments, including lederhosen and dirndls, many other German-s ...
are worn on special occasions and include in
Altbayern
Altbayern ( Bavarian: ''Oidbayern'', also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the ...
Lederhosen
Lederhosen (; , ; singular in German usage: ''Lederhose'') are short or knee-length leather breeches that are worn as traditional garments in some regions of German-speaking countries. The longer ones are generally called ''Bundhosen'' or ''Kni ...
for males and Dirndl for females. Centuries-old folk music is performed. The Maypole tradition in Bavaria, Maibaum, or Maypole (which in the Middle Ages served as the community's business directory, as figures on the pole represented the trades of the village), and the bagpipes of the Upper Palatinate region bear witness to the Paganism in the Eastern Alps, ancient Celtic and Germanic remnants of cultural heritage of the region. There are many traditional Bavarian sports disciplines, e.g. the Aperschnalzen, competitive whipcracking.
Whether in Bavaria, overseas or with citizens from other nations Bavarians continue to cultivate their traditions. They hold festivals and dances to keep their heritage alive.
Food and drink
Bavarians tend to place a great value on Bavarian cuisine, food and drink. In addition to their renowned dishes, Bavarians also consume many items of food and drink which are unusual elsewhere in Germany; for example ("white sausage") or in some instances a variety of entrails. At folk festivals and in many beer gardens, beer is traditionally served by the litre (in a ). Bavarians are particularly proud of the traditional , or beer purity law, initially established by the Duke of Bavaria for the City of Munich (i.e. the court) in 1487 and the duchy in 1516. According to this law, only three ingredients were allowed in beer: water, barley, and hops. In 1906 the made its way to all-German law, and remained a law in Germany until the EU partly struck it down in 1987 as incompatible with the European common market. German breweries, however, cling to the principle, and Bavarian breweries still comply with it in order to distinguish their beer brands. Bavarians are also known as some of the world's most prolific beer drinkers, with an average annual consumption of 170 liters per person.
Bavaria is also home to the Franconia (wine region), Franconia wine region, which is situated along the river
Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
*Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
* ...
in Franconia. The region has produced wine (''Frankenwein'') for over 1,000 years and is famous for its use of the Bocksbeutel wine bottle. The production of wine forms an integral part of the regional culture, and many of its villages and cities hold their own wine festivals (Weinfeste) throughout the year.
Krustenbraten_mit_Dunkelbierso%C3%9Fe.jpg, Schweinsbraten
N%C3%BCrnberger_Rostbratw%C3%BCrste.JPG, Nürnberger Rostbratwürste
Language and dialects
Three German dialects are most commonly spoken in Bavaria: Austro-Bavarian in Old Bavaria (Upper Bavaria, Lower Bavaria and the Upper Palatinate),
Swabian German (an Alemannic German dialect) in the Bavarian part of Swabia (south west) and
East Franconian German
East Franconian (german: Ostfränkisch) or Mainfränkisch, usually referred to as Franconian (') in German, is a dialect which is spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, ...
in Franconia (North). In the small town Ludwigsstadt in the north, district Kronach in Upper Franconia, Thuringian dialect is spoken. During the 20th century an increasing part of the population began to speak Standard German (Hochdeutsch), mainly in the cities.
Ethnography
Bavarians consider themselves to be Egalitarianism, egalitarian and informal. Their sociability can be experienced at the annual
Oktoberfest
The Oktoberfest (; bar, Wiesn, Oktobafest) is the world's largest Volksfest, featuring a beer festival and a travelling carnival. It is held annually in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. It is a 16- to 18-day folk festival running from mid- or la ...
, the world's largest beer festival, which welcomes around six million visitors every year, or in the famous beer gardens. In traditional Bavarian beer gardens, patrons may bring their own food but buy beer only from the brewery that runs the beer garden.
Sports
Football

Bavaria is home to several football clubs including FC Bayern Munich, 1. FC Nürnberg, FC Augsburg, TSV 1860 Munich, FC Ingolstadt 04 and SpVgg Greuther Fürth. Bayern Munich is the most successful football team in Germany having won a record 30 List of German football champions, German titles and 6 UEFA Champions League titles. They are followed by 1. FC Nürnberg who have won 9 titles. SpVgg Greuther Fürth have won 3 championships while TSV 1860 Munich have been champions once.
Basketball
Bavaria is also home to several professional basketball teams, including FC Bayern Munich (Basketball), FC Bayern Munich, Brose Baskets Bamberg, s.Oliver Würzburg, Nürnberg Falcons BC and TSV Oberhaching Tropics.
Ice hockey
There are five Bavarian ice hockey teams playing in the German top-tier league Deutsche Eishockey Liga, DEL: EHC Red Bull München, Nürnberg Ice Tigers, Augsburger Panther, ERC Ingolstadt, and Straubing Tigers.
Notable people
Many famous people have been born or lived in present-day Bavaria:
*Kings: Arnulf of Carinthia, Carloman of Bavaria, Charles the Fat, Lothair I, Louis the Child, Louis the German, Louis the Younger, Ludwig I of Bavaria, Ludwig II of Bavaria, Ludwig III of Bavaria, Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria, Maximilian II of Bavaria, Otto, King of Bavaria
*Religious leaders: Pope Benedict XVI (Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger); Pope Damasus II, Pope Victor II.
*Painters: Albrecht Dürer, Albrecht Altdorfer, Carl Spitzweg, Erwin Eisch, Franz von Lenbach, Franz Stuck, Franz von Stuck, Franz Marc, Gabriele Münter, Hans Holbein the Elder, Johann Christian Reinhart, Lucas Cranach the Elder, Lucas Cranach,
Paul Klee
Paul Klee (; 18 December 1879 – 29 June 1940) was a Swiss-born German artist. His highly individual style was influenced by movements in art that included expressionism, cubism, and surrealism. Klee was a natural draftsman who experimented wi ...
.
*Classical musicians Orlande de Lassus, Orlando di Lasso, Christoph Willibald Gluck, Leopold Mozart, Max Reger, Richard Wagner, Richard Strauss, Carl Orff, Johann Pachelbel, Theobald Boehm, Klaus Nomi.
*Other musicians Hans-Jürgen Buchner, Barbara Dennerlein, Klaus Doldinger, Franzl Lang, Bands: Spider Murphy Gang, Sportfreunde Stiller, Obscura (band), Obscura, Michael Bredl
*Opera singers Jonas Kaufmann, Diana Damrau.
*Writers, poets and playwrights Hans Sachs, Jean Paul, Friedrich Rückert, August von Platen-Hallermünde, Frank Wedekind, Christian Morgenstern, Oskar Maria Graf, Bertolt Brecht, Lion Feuchtwanger, Thomas Mann, Klaus Mann, Golo Mann, Ludwig Thoma, Michael Ende, Ludwig Aurbacher.
*Scientists Max Planck, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, Werner Heisenberg, Adam Ries, Joseph von Fraunhofer, Georg Ohm, Johannes Stark, Carl von Linde, Ludwig Prandtl, Rudolf Mössbauer, Lothar Rohde, Hermann Schwarz, Robert Huber, Martin Behaim, Levi Strauss, Rudolf Diesel, Feodor Lynen, Georges J. F. Köhler, Erwin Neher, Ernst Otto Fischer, Johann Deisenhofer.
*Physicians Alois Alzheimer, Max Joseph von Pettenkofer, Sebastian Kneipp.
*Politicians Ludwig Erhard, Horst Seehofer, Christian Ude,
Kurt Eisner
Kurt Eisner (; 14 May 1867 21 February 1919)"Kurt Eisner – Encyclopædia Britannica" (biography), ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2006, Britannica.com webpageBritannica-KurtEisner. was a German politician, revolutionary, journalist, and theatre c ...
, Franz-Josef Strauß, Roman Herzog, Leonard John Rose, Henry Kissinger.
*Football players Max Morlock, Karl Mai, Franz Beckenbauer, Sepp Maier, Gerd Müller, Paul Breitner, Bernd Schuster, Klaus Augenthaler, Lothar Matthäus, Philipp Lahm, Bastian Schweinsteiger, Holger Badstuber, Thomas Müller, Mario Götze, Dietmar Hamann, Stefan Reuter
*Other sportspeople Bernhard Langer, Dirk Nowitzki
*Actors Michael Herbig, Werner Stocker (actor), Werner Stocker, Helmut Fischer, Walter Sedlmayr, Gustl Bayrhammer, Ottfried Fischer, Ruth Drexel, Elmar Wepper, Fritz Wepper, Uschi Glas, Yank Azman.
*Entertainers Siegfried Fischbacher
*Film directors Helmut Dietl, Rainer Werner Fassbinder, Bernd Eichinger, Joseph Vilsmaier, Hans Steinhoff, Heinz Badewitz and Werner Herzog.
*Designers Peter Schreyer, Damir Doma
*Entrepreneurs Charles Diebold, Adi Dassler, Rudolf Dassler, Levi Strauss
*Military Claus von Stauffenberg
*Nazis: Sepp Dietrich, Karl Fiehler, Karl Gebhardt, Hermann Göring, Heinrich Himmler, Alfred Jodl, Josef Kollmer, Josef Mengele, Ernst Röhm, Franz Ritter von Epp, Julius Streicher
*Others: Kaspar Hauser, The Smith of Kochel, Mathias Kneißl, Matthias Klostermayr, Anneliese Michel, Herluka von Bernried
See also
* Outline of Germany
* Former countries in Europe after 1815
* List of Bavaria-related topics
* List of Premiers of Bavaria
* List of rulers of Bavaria
References
Citations
General and cited sources
*
External links
Official government websiteOfficial website of Bayern Tourismus Marketing GmbHBavarian Studies in History and CultureAußenwirtschaftsportal BayernStatistics*
{{Authority control
Bavaria,
Boii
States of Germany
States of the Weimar Republic
 The Bavarians emerged in a region north of the
The Bavarians emerged in a region north of the  At Hugbert's death (735) the duchy passed to a distant relative named Odilo, from neighboring Alemannia (modern southwest Germany and northern Switzerland). Odilo issued a law code for Bavaria, completed the process of church organization in partnership with
At Hugbert's death (735) the duchy passed to a distant relative named Odilo, from neighboring Alemannia (modern southwest Germany and northern Switzerland). Odilo issued a law code for Bavaria, completed the process of church organization in partnership with  For the next 400 years numerous families held the duchy, rarely for more than three generations. With the revolt of duke Henry the Quarrelsome in 976, Bavaria lost large territories in the south and south east.
The territory of '' Ostarrichi'' was elevated to a duchy in its own right and given to the Babenberger family. This event marks the founding of
For the next 400 years numerous families held the duchy, rarely for more than three generations. With the revolt of duke Henry the Quarrelsome in 976, Bavaria lost large territories in the south and south east.
The territory of '' Ostarrichi'' was elevated to a duchy in its own right and given to the Babenberger family. This event marks the founding of 
 When Napoleon abolished the Holy Roman Empire, Bavaria became – by grace of Napoleon – a
When Napoleon abolished the Holy Roman Empire, Bavaria became – by grace of Napoleon – a  ''Free State'' has been an adopted designation after the abolition of monarchy in the aftermath of World War I in several German states.
On 12 November 1918,
''Free State'' has been an adopted designation after the abolition of monarchy in the aftermath of World War I in several German states.
On 12 November 1918,  Bavarians have often emphasized a separate national identity and considered themselves as "Bavarians" first, "Germans" second.
In the 19th-century sense, an independent Bavarian State only existed from 1806–71. This feeling started to come about more strongly among Bavarians when the
Bavarians have often emphasized a separate national identity and considered themselves as "Bavarians" first, "Germans" second.
In the 19th-century sense, an independent Bavarian State only existed from 1806–71. This feeling started to come about more strongly among Bavarians when the  Bavaria shares international borders with
Bavaria shares international borders with 

 In 44 of the 71 rural districts, there are a total of 215
In 44 of the 71 rural districts, there are a total of 215 
 Bavarian culture (''
Bavarian culture ('' Bavaria is home to several football clubs including FC Bayern Munich, 1. FC Nürnberg, FC Augsburg, TSV 1860 Munich, FC Ingolstadt 04 and SpVgg Greuther Fürth. Bayern Munich is the most successful football team in Germany having won a record 30 List of German football champions, German titles and 6 UEFA Champions League titles. They are followed by 1. FC Nürnberg who have won 9 titles. SpVgg Greuther Fürth have won 3 championships while TSV 1860 Munich have been champions once.
Bavaria is home to several football clubs including FC Bayern Munich, 1. FC Nürnberg, FC Augsburg, TSV 1860 Munich, FC Ingolstadt 04 and SpVgg Greuther Fürth. Bayern Munich is the most successful football team in Germany having won a record 30 List of German football champions, German titles and 6 UEFA Champions League titles. They are followed by 1. FC Nürnberg who have won 9 titles. SpVgg Greuther Fürth have won 3 championships while TSV 1860 Munich have been champions once.