Battle Of Horseshoe Bend (Kentucky) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Horseshoe Bend (also known as ''Tohopeka'', ''Cholocco Litabixbee'', or ''The Horseshoe''), was fought during the
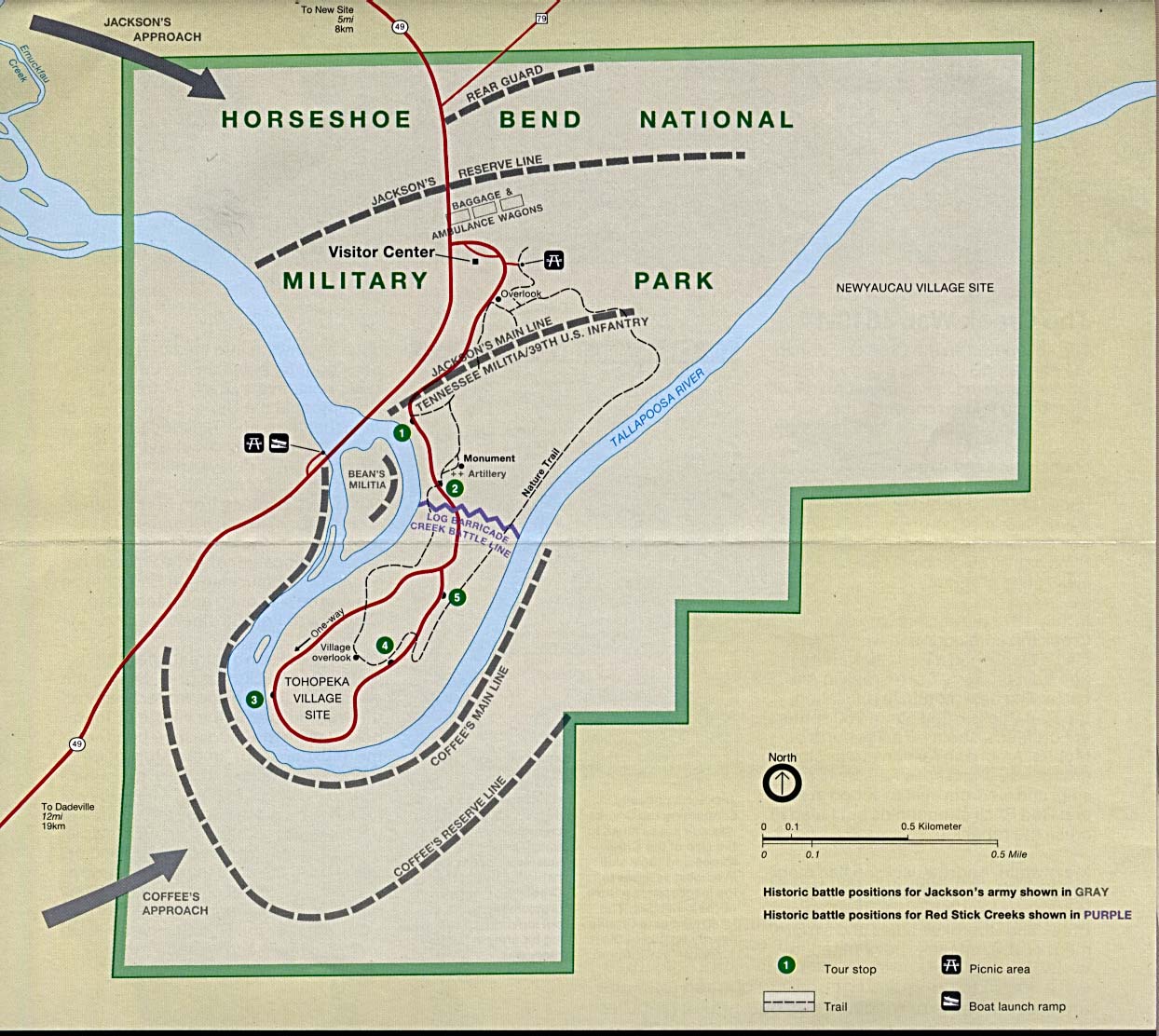


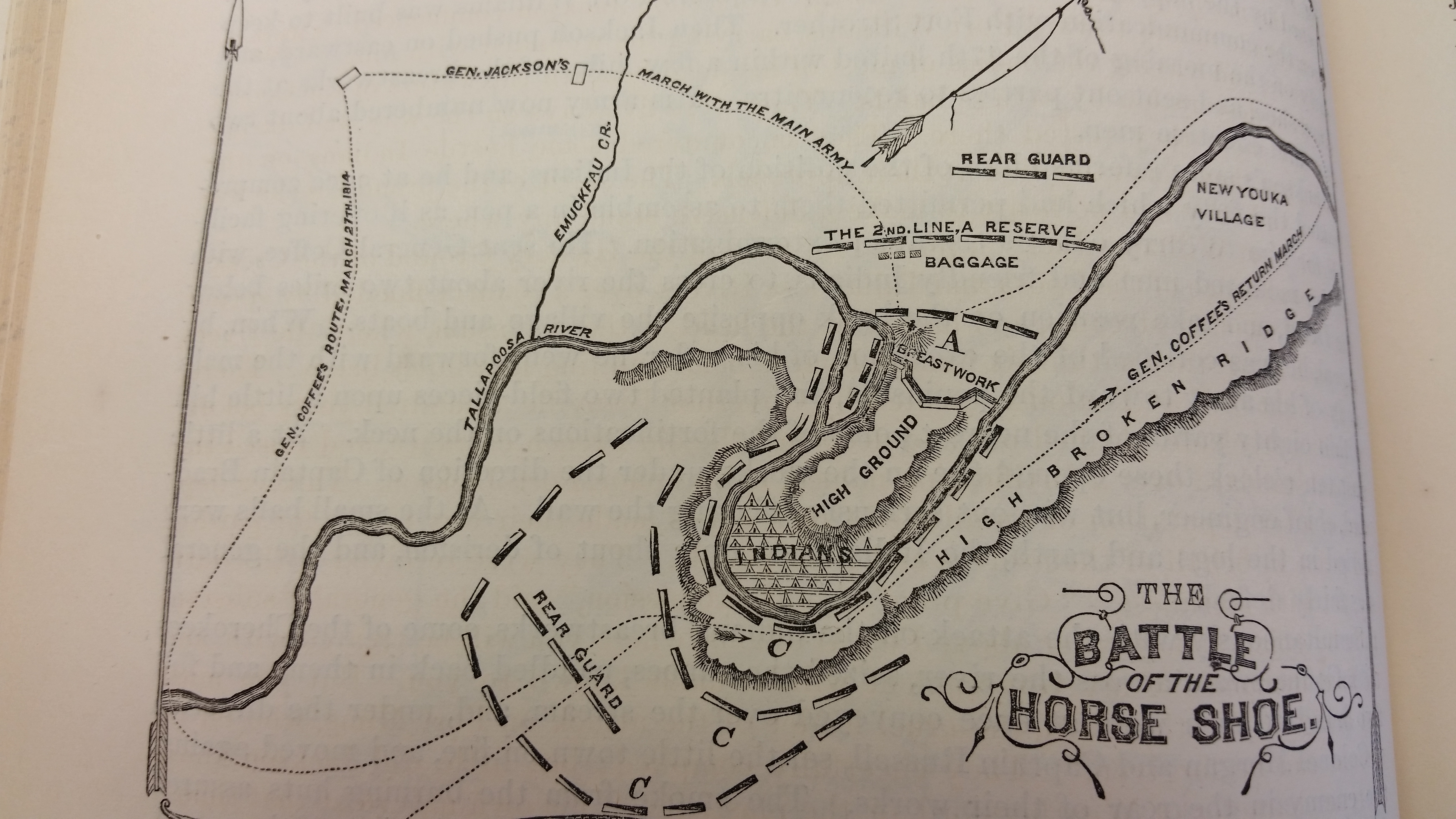 On March 27, 1814, General Andrew Jackson led troops consisting of 2,700 American soldiers, 500 Cherokee, and 100 Lower Creek allies up a steep hill near Tehopeka. From this vantage point, Jackson would begin his attack on the Red Stick fortification. At 6:30am, he split his troops and sent roughly 1,300 men to cross the
On March 27, 1814, General Andrew Jackson led troops consisting of 2,700 American soldiers, 500 Cherokee, and 100 Lower Creek allies up a steep hill near Tehopeka. From this vantage point, Jackson would begin his attack on the Red Stick fortification. At 6:30am, he split his troops and sent roughly 1,300 men to cross the
Andrew Jackson and Early Tennessee History
' (Nashville: Ambrose Printing Company, 1918), pp. 356-359. charged the breastworks and engaged the Red Sticks in hand-to-hand combat.
"The Battle of Horseshoe Bend: Collision of Cultures"
National Park Service's Teaching with Historic Places.
A map of Creek War Battle Sites
PCL Map Collection at the University of Texas at Austin.
"Battle of Horseshoe Bend"
, ''Encyclopedia of Alabama''
Mrs. Dunham Rowland, "The Mississippi Territory in the War of 1812"
''Publications of the Mississippi Historical Society,'' Volume 4, 1921, pp. 7–156
"If you visited Horseshoe Bend Battlefield today"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Battle Of Horseshoe Bend (1814) Battles involving the Cherokee Horseshoe Bend (1814) 1814 in the United States
War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
in the Mississippi Territory
The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 7, 1798, until December 10, 1817, when the western half of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi. T ...
, now central Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
. On March 27, 1814, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
forces and Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
allies under Major General Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
defeated the Red Sticks
Red Sticks (also Redsticks, Batons Rouges, or Red Clubs), the name deriving from the red-painted war clubs of some Native American Creeks—refers to an early 19th-century traditionalist faction of these people in the American Southeast. Made u ...
, a part of the Creek
A creek in North America and elsewhere, such as Australia, is a stream that is usually smaller than a river. In the British Isles it is a small tidal inlet.
Creek may also refer to:
People
* Creek people, also known as Muscogee, Native Americans
...
Indian tribe who opposed American expansion, effectively ending the Creek War
The Creek War (1813–1814), also known as the Red Stick War and the Creek Civil War, was a regional war between opposing Indigenous American Creek factions, European empires and the United States, taking place largely in modern-day Alabama ...
.
Background
TheCreek Indians
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsGeorgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
and the eastern part of the Mississippi Territory
The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 7, 1798, until December 10, 1817, when the western half of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi. T ...
had become divided into two factions: the Upper Creek (or Red Sticks
Red Sticks (also Redsticks, Batons Rouges, or Red Clubs), the name deriving from the red-painted war clubs of some Native American Creeks—refers to an early 19th-century traditionalist faction of these people in the American Southeast. Made u ...
), a majority who opposed American expansion and sided with the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and the colonial authorities of Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida ( es, La Florida) was the first major European land claim and attempted settlement in North America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, ...
during the War of 1812; and the Lower Creek, who were more assimilated into the Anglo
Anglo is a prefix indicating a relation to, or descent from, the Angles, England, English culture, the English people or the English language, such as in the term '' Anglosphere''. It is often used alone, somewhat loosely, to refer to people ...
culture, had a stronger relationship with the U.S. Indian Agent
In United States history, an Indian agent was an individual authorized to interact with American Indian tribes on behalf of the government.
Background
The federal regulation of Indian affairs in the United States first included development of t ...
Benjamin Hawkins
Benjamin Hawkins (August 15, 1754June 6, 1816) was an American planter, statesman and a U.S. Indian agent He was a delegate to the Continental Congress and a United States Senator from North Carolina, having grown up among the planter elite. ...
, and sought to remain on good terms with the Americans.
The Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
war leader Tecumseh
Tecumseh ( ; October 5, 1813) was a Shawnee chief and warrior who promoted resistance to the expansion of the United States onto Native American lands. A persuasive orator, Tecumseh traveled widely, forming a Native American confederacy and ...
visited Creek and other Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
Indian towns in 1811–1812 to recruit warriors to join his war against American territorial encroachment. The Red Sticks, young men who wanted to revive traditional religious and cultural practices, were already forming, resisting assimilation. They began to raid American frontier settlements. When the Lower Creek helped U.S. forces to capture and punish leading raiders, the Lower Creek were punished in turn by the Red Sticks.
In 1813, militia troops intercepted a Red Stick party returning from obtaining arms in (Spanish colonial) Pensacola
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal ci ...
. While they were looting the material, the Red Sticks returned and defeated them, at what became known as the Battle of Burnt Corn
The Battle of Burnt Corn, also known as the Battle of Burnt Corn Creek, was an encounter between United States armed forces and Creek Indians that took place July 27, 1813 in present-day southern Alabama. The battle was part of the Creek War.
B ...
. Red Sticks' raiding of enemy settlements continued; and in August 1813 they attacked an American outpost at Fort Mims Mims or MIMS may refer to:
Acronyms
* Mandarin Immersion Magnet School, Houston, Texas
* MediCiti Institute of Medical Sciences, a medical college near Hyderabad, India
* Membrane-introduction mass spectrometry
* Monthly Index of Medical Special ...
.
After the Fort Mims massacre, frontier settlers appealed to the government for help. Since Federal military forces were committed to waging the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
against Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, the governments of Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, and the Mississippi Territory
The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 7, 1798, until December 10, 1817, when the western half of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi. T ...
organized militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
forces, which together with Lower Creek and Cherokee allies, fought against the Red Sticks.
After leaving Fort Williams in the spring of 1814, Jackson's army cut its way through the forest to within six miles (10 km) of Chief Menawa's Red Stick camp ''Tehopeka'', near a bend in the Tallapoosa River
The Tallapoosa River runs U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 27, 2011 from the southern end of the Appalachian Mountains in Georgia, United States, southward and wes ...
called "Horseshoe Bend"—located in what is now central Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
, east of present-day Alexander City
Alexander City, known to locals as "Alex City", is the largest city in Tallapoosa County, Alabama, United States, with a population of 14,843 as of the 2020 census. It has been the largest community in Tallapoosa County since 1910. It is know ...
. Jackson sent General John Coffee
John R. Coffee (June 2, 1772 – July 7, 1833) was an American planter of Irish descent, and state militia brigadier general in Tennessee. He commanded troops under General Andrew Jackson during the Creek Wars (1813–14) and during the Battle o ...
with the mounted infantry
Mounted infantry were infantry who rode horses instead of marching. The original dragoons were essentially mounted infantry. According to the 1911 ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', "Mounted rifles are half cavalry, mounted infantry merely specially m ...
and the Indian allies south across the river to surround the Red Sticks' camp, while Jackson stayed with the rest of the 2,000 infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine i ...
north of the camp.Robert Remini, ''Andrew Jackson and the Course of American Empire, 1767-1821,'' (1977) ch. 13 Added to the militia units were the 39th United States Infantry
The 39th United States Infantry was a regiment of the Regular Army (United States), regular Army. It was authorized on January 29, 1813, and recruited in the East by Col. Williams of Tennessee. It was commanded by Colonel John Williams (Tennessee ...
and about 600 Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
, Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
, and Lower Creek, fighting against the Red Stick Creek warriors.
American Forces
West Tennessee Militia: Major General Andrew JacksonBattle



 On March 27, 1814, General Andrew Jackson led troops consisting of 2,700 American soldiers, 500 Cherokee, and 100 Lower Creek allies up a steep hill near Tehopeka. From this vantage point, Jackson would begin his attack on the Red Stick fortification. At 6:30am, he split his troops and sent roughly 1,300 men to cross the
On March 27, 1814, General Andrew Jackson led troops consisting of 2,700 American soldiers, 500 Cherokee, and 100 Lower Creek allies up a steep hill near Tehopeka. From this vantage point, Jackson would begin his attack on the Red Stick fortification. At 6:30am, he split his troops and sent roughly 1,300 men to cross the Tallapoosa River
The Tallapoosa River runs U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 27, 2011 from the southern end of the Appalachian Mountains in Georgia, United States, southward and wes ...
and surround the Creek village. Then, at 10:30 a.m., Jackson's remaining troops began an artillery barrage which consisted of two cannons firing for about two hours. Little damage was caused to the Red Sticks or their 400-yard-long, log-and-dirt fortifications. In fact, Jackson was quite impressed with the measures the Red Sticks took to protect their position. As he later wrote:
Soon, Jackson ordered a bayonet
A bayonet (from French ) is a knife, dagger, sword, or spike-shaped weapon designed to fit on the end of the muzzle of a rifle, musket or similar firearm, allowing it to be used as a spear-like weapon.Brayley, Martin, ''Bayonets: An Illustr ...
charge. The 39th U.S. Infantry, led by Colonel John Williams
John Towner Williams (born February 8, 1932)Nylund, Rob (15 November 2022)Classic Connection review ''WBOI'' ("For the second time this year, the Fort Wayne Philharmonic honored American composer, conductor, and arranger John Williams, who wa ...
,Samuel G. Heiskell, Andrew Jackson and Early Tennessee History
' (Nashville: Ambrose Printing Company, 1918), pp. 356-359. charged the breastworks and engaged the Red Sticks in hand-to-hand combat.
Sam Houston
Samuel Houston (, ; March 2, 1793 – July 26, 1863) was an American general and statesman who played an important role in the Texas Revolution. He served as the first and third president of the Republic of Texas and was one of the first two i ...
(the future statesman and leader of Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
) served as a third lieutenant in Jackson's army. Houston was one of the first to make it over the log barricade alive and received a wound from a Creek arrow that troubled him for the rest of his life.
Meanwhile, the troops under the command of General John Coffee
John R. Coffee (June 2, 1772 – July 7, 1833) was an American planter of Irish descent, and state militia brigadier general in Tennessee. He commanded troops under General Andrew Jackson during the Creek Wars (1813–14) and during the Battle o ...
had successfully crossed the river and surrounded the encampment. They joined the fight and gave Jackson a great advantage. The Creek warriors refused to surrender, though, and the battle lasted for more than five hours. At the end, roughly 800 of the 1,000 Red Stick warriors present at the battle were killed. In contrast, Jackson lost fewer than 50 men during the fight and reported 154 wounded.
After the battle, Jackson's troops made bridle reins from skin taken from Indian corpses, conducted a body count by cutting off the tips of their noses, and sent their clothing as souvenirs to the "ladies of Tennessee."
Chief Menawa
Menawa, first called ''Hothlepoya'' (c. 1765 – c. 1836-40), was a Muscogee (Creek) chief and military leader. He was of mixed race, with a Creek mother and a fur trader father of mostly Scots ancestry. As the Creek had a matrilineal syst ...
was severely wounded but survived; he led about 200 of the original 1,000 warriors across the river and toward safety, to join the Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, an ...
tribe in Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida ( es, La Florida) was the first major European land claim and attempted settlement in North America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, ...
.
Results
On August 9, 1814, Andrew Jackson forced the Creek to sign theTreaty of Fort Jackson
The Treaty of Fort Jackson (also known as the Treaty with the Creeks, 1814) was signed on August 9, 1814 at Fort Jackson near Wetumpka, Alabama following the defeat of the Red Stick (Upper Creek) resistance by United States allied forces at t ...
. The Creek Nation
The Muscogee Nation, or Muscogee (Creek) Nation, is a federally recognized Native American tribe based in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The nation descends from the historic Muscogee Confederacy, a large group of indigenous peoples of the South ...
was forced to cede —half of central Alabama and part of southern Georgia—to the United States government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fede ...
; this included territory of the Lower Creek, who had been allies of the United States. Jackson had determined the areas from his sense of security needs. Of the Jackson forced the Creek to cede , which was claimed by the Cherokee Nation
The Cherokee Nation (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᎯ ᎠᏰᎵ ''Tsalagihi Ayeli'' or ᏣᎳᎩᏰᎵ ''Tsalagiyehli''), also known as the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, is the largest of three Cherokee federally recognized tribes in the United States. It ...
, which had also allied with the United States. Jackson was promoted to Major General after getting agreement to the treaty.
Capture of Pensacola, Battle of New Orleans
After the battle, Jackson sent his friend and trusted scout, John Gordon, Captain of the Spies, to secretly go to the Spanish fort atPensacola
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal ci ...
to find out if the British were using it as a base to arm the Red Stick Creeks. Gordon travelled through hundreds of miles of hostile Creek territory to find the British flag flying at Pensacola and British officers arming and training Creeks. Jackson, with this knowledge, took Pensacola, a controversial move which led ultimately to further battle against the British in New Orleans.
This victory, along with that at the Battle of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the French ...
, greatly contributed to Jackson's favorable national reputation and his popularity. He was well known when he ran successfully for President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
in 1828.
Legacy
The battlefield is preserved in theHorseshoe Bend National Military Park
Horseshoe Bend National Military Park is a 2,040-acre, U.S. national military park managed by the National Park Service that is the site of the last battle of the Creek War on March 27, 1814. General Andrew Jackson's Tennessee militia, aided by ...
.
Two currently active battalions of the Regular Army (2nd and 3rd Battalions of the 7th Infantry Regiment) perpetuate the lineage of the old 39th Infantry Regiment, which fought at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend.
In fiction
Eric Flint
Eric Flint (February 6, 1947 – July 17, 2022) was an American author, editor, and e-publisher. The majority of his main works are alternate history science fiction, but he also wrote humorous fantasy adventures. His works have been listed ...
has written a series of alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, altern ...
novels, '' Trail of Glory,'' that begin with the Battle of Horseshoe Bend. In Flint's version, Houston is only lightly wounded in the battle, allowing him freedom to develop his career, in turn facilitating the author's objectives.
The main character of Paulette Jiles
Paulette Jiles (aka Paulette K. Jiles, Paulette Jiles-Johnson) (born 4 April 1943) is an American poet, memoirist, and novelist.
Personal life
Paulette Kay Jiles was born in 1943 in Salem, Missouri. She attended college at the University of ...
' novel News of the World
The ''News of the World'' was a weekly national Tabloid journalism#Red tops, red top Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloid newspaper published every Sunday in the United Kingdom from 1843 to 2011. It was at one time the world's highest-selling En ...
, 'Captain' Jefferson Kyle Kidd, has a backstory that includes fighting as a youth of 16 in this battle under Jackson
Jackson may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Jackson (name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the surname or given name
Places
Australia
* Jackson, Queensland, a town in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson North, Q ...
.
Notes
References
*Andrew Burstein, * *Steve Rajtar, ''Indian War Sites,'' (McFarland and Company, Inc., 1999) *Robert Remini, ''Andrew Jackson and the Course of American Empire, 1767-1821'' (1977) ch. 13Further reading
* Holland, James W. "Andrew Jackson and the Creek War: Victory at the Horseshoe Bend," ''Alabama Review,'' Oct 1968, Vol. 21 Issue 4, pp 243–275 * Kanon, Thomas. "A Slow, Laborious Slaughter": The Battle of Horseshoe Bend," ''Tennessee Historical Quarterly,'' March 1999, Vol. 58 Issue 1, pp 2–15 * Remini, Robert V. ''Andrew Jackson and His Indian Wars'' (2001), ch 4External links
"The Battle of Horseshoe Bend: Collision of Cultures"
National Park Service's Teaching with Historic Places.
A map of Creek War Battle Sites
PCL Map Collection at the University of Texas at Austin.
"Battle of Horseshoe Bend"
, ''Encyclopedia of Alabama''
Mrs. Dunham Rowland, "The Mississippi Territory in the War of 1812"
''Publications of the Mississippi Historical Society,'' Volume 4, 1921, pp. 7–156
"If you visited Horseshoe Bend Battlefield today"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Battle Of Horseshoe Bend (1814) Battles involving the Cherokee Horseshoe Bend (1814) 1814 in the United States
Horseshoe Bend Horseshoe Bend may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Horseshoe Bend, New South Wales, an inner city suburb in the City of Maitland in the Hunter Region
* Horseshoe Bend Station, a pastoral lease that operates as a cattle station in the Alice Sprin ...
Native American history of Alabama
Andrew Jackson
1814 in Mississippi Territory
March 1814 events