Barnstaple railway station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
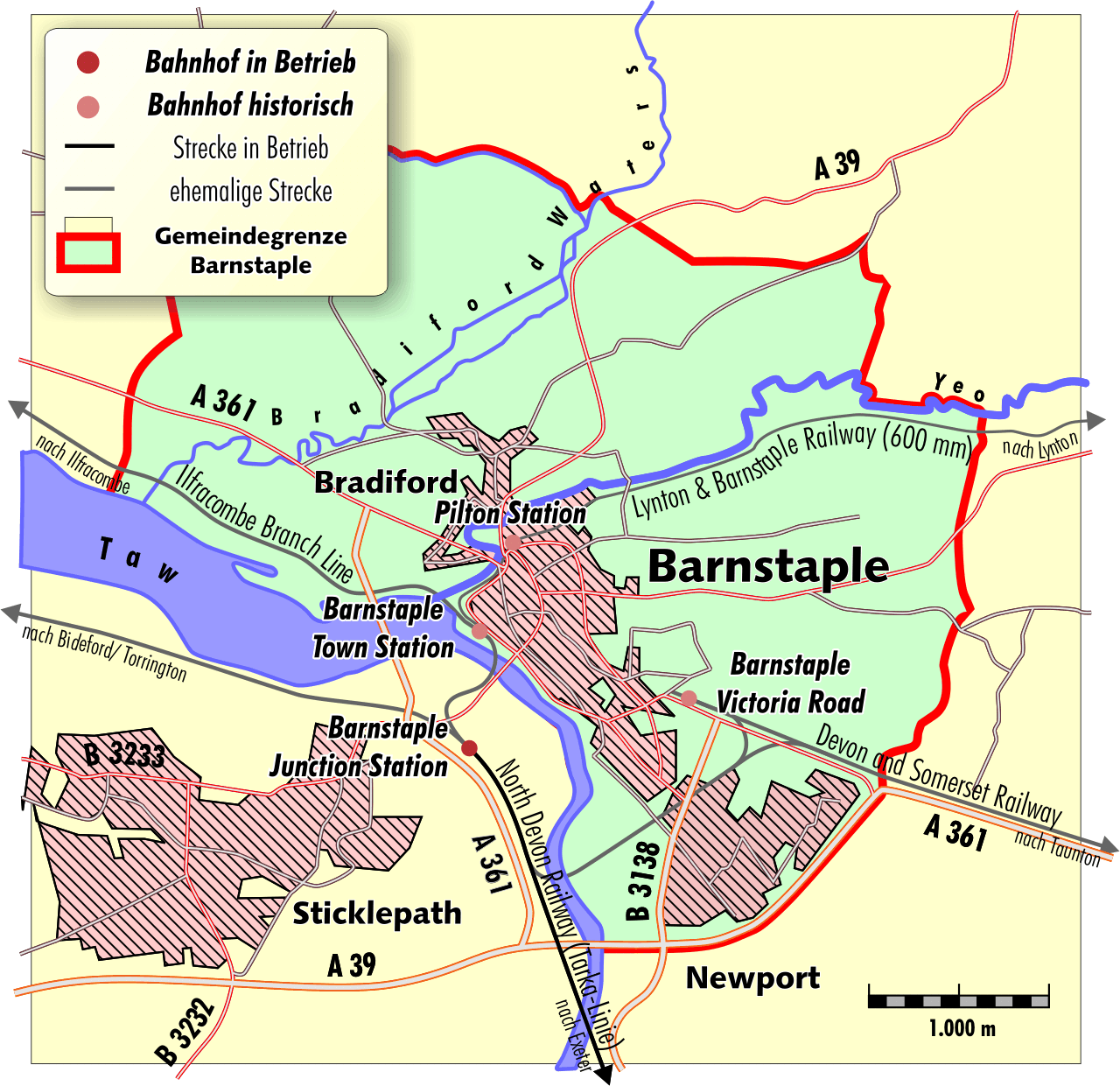
Barnstaple railway station is the northern terminus of the
 The Taw Vale Railway & Dock opened a railway to carry goods traffic between a quay at Fremington Pill and Barnstaple in August 1848. William Thorne, who worked the horse-drawn trains, built a warehouse at the terminus in Barnstaple which was by the Sticklepath
The Taw Vale Railway & Dock opened a railway to carry goods traffic between a quay at Fremington Pill and Barnstaple in August 1848. William Thorne, who worked the horse-drawn trains, built a warehouse at the terminus in Barnstaple which was by the Sticklepath  With the creation of British Railways in 1948 there was opportunity to rationalise the facilities in Barnstaple. Most of the goods traffic was handled at the Victoria Road station although full wagons loads were still handled at Barnstaple Junction. Victoria Road closed to passengers on 12 June 1960 so all trains from Taunton ran to Barnstaple Junction. During the next ten years most of the lines around Barnstaple closed. Passenger services on the Bideford route ceased from 2 October 1965, the Taunton service was withdrawn from 3 October 1966, and the Ilfracombe branch closed on 5 October 1970. This just left the service to Exeter and Barnstaple Junction became plain Barnstaple once more. On 21 May 1971 the track was simplified and the line to was reduced to just one track. The goods trains to Victoria Road were withdrawn on 30 May 1970 and those on the Bideford line stopped on 31 August 1982.
A new booking office was opened on 10 November 1981 but the second platform was closed in August 1990. In 2008 a café was opened in the former station master's house.
With the creation of British Railways in 1948 there was opportunity to rationalise the facilities in Barnstaple. Most of the goods traffic was handled at the Victoria Road station although full wagons loads were still handled at Barnstaple Junction. Victoria Road closed to passengers on 12 June 1960 so all trains from Taunton ran to Barnstaple Junction. During the next ten years most of the lines around Barnstaple closed. Passenger services on the Bideford route ceased from 2 October 1965, the Taunton service was withdrawn from 3 October 1966, and the Ilfracombe branch closed on 5 October 1970. This just left the service to Exeter and Barnstaple Junction became plain Barnstaple once more. On 21 May 1971 the track was simplified and the line to was reduced to just one track. The goods trains to Victoria Road were withdrawn on 30 May 1970 and those on the Bideford line stopped on 31 August 1982.
A new booking office was opened on 10 November 1981 but the second platform was closed in August 1990. In 2008 a café was opened in the former station master's house.
 The railway station is on the west side of the
The railway station is on the west side of the
 All services at Barnstaple are operated by Great Western Railway. There is generally one train per hour to but a very small number of services continue to or from other routes in East Devon on weekdays. The route mainly uses the diesel units.
All services at Barnstaple are operated by Great Western Railway. There is generally one train per hour to but a very small number of services continue to or from other routes in East Devon on weekdays. The route mainly uses the diesel units.
James May's Great Train Race: Tarka Trail 2
Tarka Line
The Tarka Line, also known as the North Devon Line, is a local railway line in Devon, England, linking the city of Exeter with the town of Barnstaple via a number of local villages, operated by Great Western Railway (GWR). The line opened in ...
and serves the town of Barnstaple, Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
. It is from at milepost 211.25 from . It is managed by Great Western Railway, which also operates the train service.
It opened in 1854 but from 1874 until 1970 it was known as Barnstaple Junction railway station as it was the junction between lines to , , and Exeter.
History
 The Taw Vale Railway & Dock opened a railway to carry goods traffic between a quay at Fremington Pill and Barnstaple in August 1848. William Thorne, who worked the horse-drawn trains, built a warehouse at the terminus in Barnstaple which was by the Sticklepath
The Taw Vale Railway & Dock opened a railway to carry goods traffic between a quay at Fremington Pill and Barnstaple in August 1848. William Thorne, who worked the horse-drawn trains, built a warehouse at the terminus in Barnstaple which was by the Sticklepath turnpike
Turnpike often refers to:
* A type of gate, another word for a turnstile
* In the United States, a toll road
Turnpike may also refer to:
Roads United Kingdom
* A turnpike road, a principal road maintained by a turnpike trust, a body with powers ...
gate and the bridge across the River Taw
The River Taw () rises at Taw Head, a spring on the central northern flanks of Dartmoor, crosses North Devon and at the town of Barnstaple, formerly a significant port, empties into Bideford Bay in the Bristol Channel, having formed a large ...
.
On 1 August 1854 the North Devon Railway
The North Devon Railway was a railway company which operated a line from Cowley Bridge Junction, near Exeter, to Bideford in Devon, England, later becoming part of the London and South Western Railway's system. Originally planned as a broad ga ...
(as the Taw Vale was now known) opened a gauge line from where it linked with the Exeter and Crediton Railway
The Exeter and Crediton Railway was a broad gauge railway that linked Exeter and Crediton, Devon, England. It was 5¼ miles (8½ km) long.
Although built in 1847, it was not opened until 12 May 1851 due to disagreement about the gau ...
. The traffic on the original line between Barnstaple and Fremington had ceased in 1851 and this line was now rebuilt to the North Devon's broad gauge, reopening as part of the route to on 2 November 1855. The North Devon Railway was amalgamated into the London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter ...
(LSWR) on 1 January 1865 by which time the LSWR had already laid a third rail from Exeter to Bideford so that its gauge trains could use the line.
A single platform on the river side of the line served passengers. A goods yard was laid out between the passenger station and the river which included a goods shed behind the platform and William Thorne's old warehouse. A second platform was added on 20 July 1874 when the Ilfracombe Branch Line opened. This included a new station at on the other side of the river so the original 'Barnstaple' station was renamed Barnstaple Junction. Three years later, on 30 April 1877, the LSWR ceased operating broad gauge trains to Barnstaple.
The Devon and Somerset Railway
The Devon and Somerset Railway (D&SR) was a cross-country line that connected Barnstaple in Devon, England, to the network of the Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) near Taunton. It was opened in stages between 1871 and 1873 and closed in 1966. ...
had opened its own station in Barnstaple at Victoria Road in 1873 but from 1876 this was operated by the Great Western Railway (GWR). A connection was opened between the GWR station and the LSWR at Barnstaple Junction on 1 June 1887. This crossed the river on its own bridge and joined the LSWR line south of the Junction station. Some GWR trains continued beyond Barnstaple to In 1891 a second track was brought into use on the Exeter line as far as .The station was further enlarged and resignalled between 1922 and 1924. This included cutting back the hill above the station so that a new track could be added behind the platform that had been built in 1874 to provide an additional platform face.
 With the creation of British Railways in 1948 there was opportunity to rationalise the facilities in Barnstaple. Most of the goods traffic was handled at the Victoria Road station although full wagons loads were still handled at Barnstaple Junction. Victoria Road closed to passengers on 12 June 1960 so all trains from Taunton ran to Barnstaple Junction. During the next ten years most of the lines around Barnstaple closed. Passenger services on the Bideford route ceased from 2 October 1965, the Taunton service was withdrawn from 3 October 1966, and the Ilfracombe branch closed on 5 October 1970. This just left the service to Exeter and Barnstaple Junction became plain Barnstaple once more. On 21 May 1971 the track was simplified and the line to was reduced to just one track. The goods trains to Victoria Road were withdrawn on 30 May 1970 and those on the Bideford line stopped on 31 August 1982.
A new booking office was opened on 10 November 1981 but the second platform was closed in August 1990. In 2008 a café was opened in the former station master's house.
With the creation of British Railways in 1948 there was opportunity to rationalise the facilities in Barnstaple. Most of the goods traffic was handled at the Victoria Road station although full wagons loads were still handled at Barnstaple Junction. Victoria Road closed to passengers on 12 June 1960 so all trains from Taunton ran to Barnstaple Junction. During the next ten years most of the lines around Barnstaple closed. Passenger services on the Bideford route ceased from 2 October 1965, the Taunton service was withdrawn from 3 October 1966, and the Ilfracombe branch closed on 5 October 1970. This just left the service to Exeter and Barnstaple Junction became plain Barnstaple once more. On 21 May 1971 the track was simplified and the line to was reduced to just one track. The goods trains to Victoria Road were withdrawn on 30 May 1970 and those on the Bideford line stopped on 31 August 1982.
A new booking office was opened on 10 November 1981 but the second platform was closed in August 1990. In 2008 a café was opened in the former station master's house.
Engine shed
The North Devon Railway had anengine shed
The motive power depot (MPD) or locomotive depot, or traction maintenance depot (TMD), is the place where locomotives are usually housed, repaired and maintained when not being used. They were originally known as "running sheds", "engine shed ...
and workshops at Barnstaple along with a turntable
A phonograph, in its later forms also called a gramophone (as a trademark since 1887, as a generic name in the UK since 1910) or since the 1940s called a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogu ...
. These continued to be used by the LSWR although the workshops were closed in 1894. In later days the two-track timber engine shed was situated near the entrance to the goods yard and the turntable was replaced by a larger version. The former GWR shed at Victoria Road closed at the beginning of 1951 after when their locomotives were serviced at the Barnstaple Junction shed. This shed was closed after steam trains were replaced by diesels in 1964. At one time there were 44 engine driver
A train driver, engine driver, engineman or locomotive driver, commonly known as an engineer or railroad engineer in the United States and Canada, and also as a locomotive handler, locomotive operator, train operator, or motorman, is a pers ...
s and 44 firemen
A firefighter is a first responder and rescuer extensively trained in firefighting, primarily to extinguish hazardous fires that threaten life, property, and the environment as well as to rescue people and in some cases or jurisdictions also ...
at Barnstaple but by 1968 there were just 10 and 4 respectively, and none from 1971.
Description
River Taw
The River Taw () rises at Taw Head, a spring on the central northern flanks of Dartmoor, crosses North Devon and at the town of Barnstaple, formerly a significant port, empties into Bideford Bay in the Bristol Channel, having formed a large ...
near the Long Bridge
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mens ...
and the junction of the A3125 and A361 roads; the town centre is on the east side. A footpath under the road gives access to the cycle and footpath along the disused railway towards Bideford which forms part of the South West Coast Path. The access road to the station goes through a retail park which is built on the site of the railway goods yard. The old stone building by the A3125 road is William Thorne's warehouse of 1848 which is now Grade II listed.
The station building contains the ticket office, toilets, café and a cycle hire office. The platform is long enough for an 11-coach train. There is just a single track in use (the second platform is derelict) but there is a siding with a loop line just south of the platform. The ticket office is usually open every day and a ticket machine is also provided. There is both a car park and bicycle rack.
Services
Community railway
The railway between Barnstaple and Exeter is designated as acommunity railway
Community rail in Britain is the support of railway lines and stations by local organisations, usually through community rail partnerships (CRPs) comprising railway operators, local councils, and other community organisations, and rail user group ...
and is supported by marketing provided by the Devon and Cornwall Rail Partnership
The Devon and Cornwall Rail Partnership is the largest Community Rail Partnership in the United Kingdom. It was formed in 1991 to promote the use of, and improvements to, rural railways in Devon and Cornwall, and also to promote the places serv ...
. The line is promoted as the Tarka Line
The Tarka Line, also known as the North Devon Line, is a local railway line in Devon, England, linking the city of Exeter with the town of Barnstaple via a number of local villages, operated by Great Western Railway (GWR). The line opened in ...
.
Proposed developments
The Barnstaple to Bideford route was mentioned in the Association of Train Operating Companies 2009 '' Connecting Communities: Expanding Access to the Rail Network'' report which recommended some closed lines that could be rebuilt to restore railway services to large communities. Following from the reopening of theDartmoor line
The Dartmoor line is a railway line in Devon, England. From , the line runs alongside the Tarka Line to the site of the former Coleford Junction where it diverges west to . Previously a heritage line, it is owned by Network Rail.
The route ...
to in 2021, a local 'Atlantic Coast to Exeter' campaign resumed interest in reopening the line from Barnstaple to Bideford.
Cultural references
''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
'' included the Barnstaple station café in its 2009 list of 'the ten best station cafés'.
This line to Bideford was recreated in miniature for one day in 2009 using OO gauge
OO gauge or OO scale (also, 00 gauge and 00 scale) is the most popular standard-gauge model railway standard in the United Kingdom, outside of which it is virtually unknown. OO gauge is one of several 4 mm-scale standards (4 mm to 1 foot, ...
track for episode 6 of James May's Toy Stories
''James May's Toy Stories'' is a UK documentary television series created and presented by James May, and produced by Plum Pictures for the BBC. The programme focused on bringing some of the most notable toys conceived in the past into the mode ...
, an attempt to build the longest ever model railway orchestrated by James May
James Daniel May (born 16 January 1963) is an English television presenter and journalist. He is best known as a co-presenter of the motoring programme '' Top Gear'' alongside Jeremy Clarkson and Richard Hammond from 2003 until 2015. He also ...
. Although the track was restored between the two towns the model railway trains were only able to reach the site of Instow
Instow is a village in north Devon, England. It is on the estuary where the rivers Taw and Torridge meet, between the villages of Westleigh and Yelland and on the opposite bank to Appledore. There is an electoral ward with the same name. Th ...
signalbox
On a rail transport system, signalling control is the process by which control is exercised over train movements by way of railway signals and block systems to ensure that trains operate safely, over the correct route and to the proper timetabl ...
due to the weather and vandalism. May stated that he chose the location for the attempt due to his desire to see the line restored. He repeated the experiment more successfully in 2011.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Barnstaple Railway StationRailway station
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
Railway stations in Devon
Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1854
Former London and South Western Railway stations
Railway stations served by Great Western Railway
Industrial archaeological sites in Devon
1854 establishments in England
DfT Category E stations