Bard College Clemente Program on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bard College is a
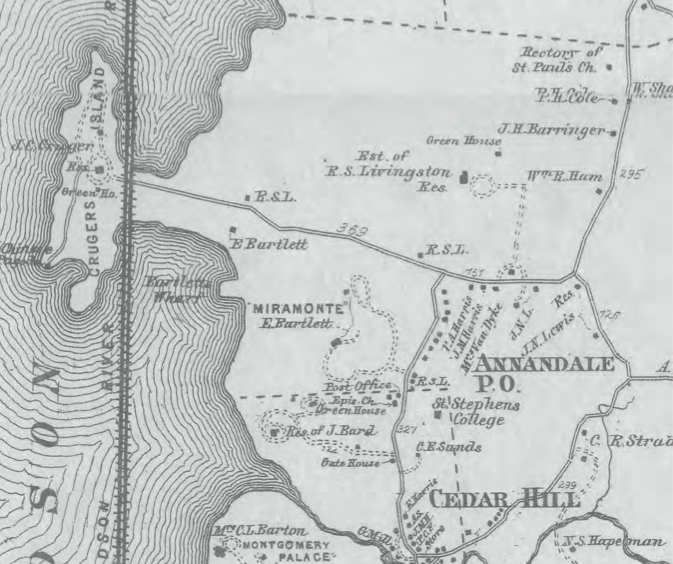 During much of the nineteenth century, the land now owned by Bard was mainly composed of several
During much of the nineteenth century, the land now owned by Bard was mainly composed of several
 In the 20th century, social and cultural changes amongst New York's high society would bring about the demise of the great estates. In 1914, Louis Hamersley purchased the fire-damaged Ward Manor/Almont estate and erected a Tudor style mansion and gatehouse, or what is today known as Ward Manor. Hamersley expanded his estate in 1926 by acquiring the abandoned Cruger's Island estate. That same year, after Hamersley's combined estate was purchased by William Ward, it was donated to charity and served as a retirement home for almost four decades.
By the mid-1900s, Bard's campus significantly expanded. The Blithewood estate was donated to the college in 1951, and in 1963, Bard purchased of the Ward Manor estate, including the main manor house. The rest of the Ward Manor estate is now the Tivoli Bays
In the 20th century, social and cultural changes amongst New York's high society would bring about the demise of the great estates. In 1914, Louis Hamersley purchased the fire-damaged Ward Manor/Almont estate and erected a Tudor style mansion and gatehouse, or what is today known as Ward Manor. Hamersley expanded his estate in 1926 by acquiring the abandoned Cruger's Island estate. That same year, after Hamersley's combined estate was purchased by William Ward, it was donated to charity and served as a retirement home for almost four decades.
By the mid-1900s, Bard's campus significantly expanded. The Blithewood estate was donated to the college in 1951, and in 1963, Bard purchased of the Ward Manor estate, including the main manor house. The rest of the Ward Manor estate is now the Tivoli Bays
 The campus of Bard College is in
The campus of Bard College is in
 In 1990, Bard College acquired, on permanent loan, art collector Marieluise Hessel's substantial collection of important contemporary artwork. In 2006, Hessel contributed another $8 million (USD) for the construction of a 17,000-square-foot addition to Bard's Center for Curatorial Studies building, in which the collection is exhibited.
The Bard Prison Initiative (BPI) provides a liberal arts degree to incarcerated individuals ( prison education) in five prisons in New York State, and enrolls nearly 200 students. Since federal funding for prison education programs was eliminated in 1994, BPI is one of only a small number of programs of its kind in the country.
Bard awards the Bard Fiction Prize annually to "a promising emerging writer who is an American citizen aged 39 years or younger at the time of application". The prize is $30,000 and an appointment as writer-in-residence at the college.
The
In 1990, Bard College acquired, on permanent loan, art collector Marieluise Hessel's substantial collection of important contemporary artwork. In 2006, Hessel contributed another $8 million (USD) for the construction of a 17,000-square-foot addition to Bard's Center for Curatorial Studies building, in which the collection is exhibited.
The Bard Prison Initiative (BPI) provides a liberal arts degree to incarcerated individuals ( prison education) in five prisons in New York State, and enrolls nearly 200 students. Since federal funding for prison education programs was eliminated in 1994, BPI is one of only a small number of programs of its kind in the country.
Bard awards the Bard Fiction Prize annually to "a promising emerging writer who is an American citizen aged 39 years or younger at the time of application". The prize is $30,000 and an appointment as writer-in-residence at the college.
The  In June 2011, Bard officially acquired the
In June 2011, Bard officially acquired the
File:Blythe Danner - 1980.jpg,
File:Toni Morrison.jpg, Toni Morrison, Nobel Prize, Nobel and Pulitzer Prize-winning author
File:Roy Lichtenstein.jpg, Roy Lichtenstein, pop artist
File:Hannah Arendt 1924.jpg, Notable alumni of Bard include fraternal songwriters Richard M. Sherman and Robert B. Sherman, comedian and actor
File:Bard College - IMG 7998.JPG, Franklin W. Olin Humanities Building
File:Bard College - IMG 7991.JPG, Chapel of the Holy Innocents
File:Bard College - IMG 8009.JPG, Robbins House
File:Bard College - IMG 8006.JPG, Milton and Sally Avery Arts Center
File:Bard College - IMG 8003.JPG, Kline Commons
File:Bard College - IMG 7997.JPG, Stevenson Library
File:Bard College - IMG 7993.JPG, Stone Row
File:Bard College - IMG 7992.JPG, Aspinwall Hall
File:Bard College - IMG 7987.JPG, Ward Gate
File:Fisher at Bard College.jpg, Richard B. Fisher Center for the Performing Arts
File:Bard College - IMG 8005.JPG, Center for Curatorial Studies and Art in Contemporary Culture, CCS Hessel Museum
File:Montgomery Place 2008.jpg, Montgomery Place
Official athletics website
{{Authority control Bard College, Columbia University 1860 establishments in New York (state) Educational institutions established in 1860 Liberal arts colleges in New York (state) Red Hook, New York Annandale-on-Hudson, New York Universities and colleges affiliated with the Episcopal Church (United States) Universities and colleges in Dutchess County, New York Private universities and colleges in New York (state) Tourist attractions in Dutchess County, New York Undesirable organizations in Russia
private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
liberal arts college
A liberal arts college or liberal arts institution of higher education is a college with an emphasis on undergraduate study in liberal arts and sciences. Such colleges aim to impart a broad general knowledge and develop general intellectual capac ...
in Annandale-on-Hudson, New York
Annandale-on-Hudson is a hamlet in Dutchess County, New York, United States, located in the Hudson Valley town of Red Hook, across the Hudson River from Kingston. The hamlet consists mainly of the Bard College campus.
Municipal services
Emerge ...
. The campus overlooks the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between N ...
and Catskill Mountains
The Catskill Mountains, also known as the Catskills, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains, located in southeastern New York. As a cultural and geographic region, the Catskills are generally defined as those areas c ...
, and is within the Hudson River Historic District—a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
.
Founded in 1860, the institution consists of a liberal arts college and a conservatory, as well as eight graduate programs offering over 20 graduate degrees in the arts and sciences. The college has a network of over 35 affiliated programs, institutes, and centers, spanning twelve cities, five states, seven countries
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state (polity), state, nation, or other polity, political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, so ...
, and four continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
s.
History
Origins and early years
 During much of the nineteenth century, the land now owned by Bard was mainly composed of several
During much of the nineteenth century, the land now owned by Bard was mainly composed of several country estates
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while th ...
. These estates were called Blithewood, Bartlett, Sands, Cruger's Island, and Ward Manor/Almont.
In 1853, John Bard and Margaret Bard purchased a part of the Blithewood estate and renamed it Annandale. John Bard was the grandson of Samuel Bard, a prominent doctor, a founder of Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
's medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, M ...
, and physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
to George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
. John Bard was also the nephew of the Rev. John McVickar, a professor at Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
. The family had strong connections with the Episcopal Church and Columbia.
The following year, in 1854, John and Margaret established a parish school
A parochial school is a private primary or secondary school affiliated with a religious organization, and whose curriculum includes general religious education in addition to secular subjects, such as science, mathematics and language arts. The ...
on their estate in order to educate the area's children. A wood-frame cottage
A cottage, during Feudalism in England, England's feudal period, was the holding by a cottager (known as a Cotter (farmer), cotter or ''bordar'') of a small house with enough garden to feed a family and in return for the cottage, the cottager ...
, known today as Bard Hall, served as a school on weekdays and a chapel
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common ty ...
on weekends. In 1857, the Bards expanded the parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or m ...
by building the Chapel of the Holy Innocents next to Bard Hall. During this time, John Bard remained in close contact with the New York leaders of the Episcopal Church. The Church suggested that he found a theological college
A seminary, school of theology, theological seminary, or divinity school is an educational institution for educating students (sometimes called ''seminarians'') in scripture, theology, generally to prepare them for ordination to serve as clergy, ...
.
With the promise of outside financial support, John Bard donated the unfinished Chapel, and the surrounding , to the diocese in November 1858. In March 1860, St. Stephen's College was founded. In 1861, construction began on the first St. Stephen's College building, a stone collegiate gothic
Collegiate Gothic is an architectural style subgenre of Gothic Revival architecture, popular in the late-19th and early-20th centuries for college and high school buildings in the United States and Canada, and to a certain extent Europ ...
dormitory
A dormitory (originated from the Latin word ''dormitorium'', often abbreviated to dorm) is a building primarily providing sleeping and residential quarters for large numbers of people such as boarding school, high school, college or university s ...
called Aspinwall. During its initial years, the college relied on wealthy benefactors, like trustee
Trustee (or the holding of a trusteeship) is a legal term which, in its broadest sense, is a synonym for anyone in a position of trust and so can refer to any individual who holds property, authority, or a position of trust or responsibility to t ...
Cornelius Vanderbilt
Cornelius Vanderbilt (May 27, 1794 – January 4, 1877), nicknamed "the Commodore", was an American business magnate who built his wealth in railroads and shipping. After working with his father's business, Vanderbilt worked his way into lead ...
, for funding.
The college began taking shape within four decades. In 1866, Ludlow Hall, an administrative building, was erected. Preston Hall was built in 1873 and used as a refectory. A set of four dormitories, collectively known as Stone Row, were completed in 1891. And in 1895, the Greek revival
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement which began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe and the United States and Canada, but ...
Hoffman Memorial Library was built. The school officially changed its name to Bard College in 1934 in honor of its founder.
Growth and secularization
 In the 20th century, social and cultural changes amongst New York's high society would bring about the demise of the great estates. In 1914, Louis Hamersley purchased the fire-damaged Ward Manor/Almont estate and erected a Tudor style mansion and gatehouse, or what is today known as Ward Manor. Hamersley expanded his estate in 1926 by acquiring the abandoned Cruger's Island estate. That same year, after Hamersley's combined estate was purchased by William Ward, it was donated to charity and served as a retirement home for almost four decades.
By the mid-1900s, Bard's campus significantly expanded. The Blithewood estate was donated to the college in 1951, and in 1963, Bard purchased of the Ward Manor estate, including the main manor house. The rest of the Ward Manor estate is now the Tivoli Bays
In the 20th century, social and cultural changes amongst New York's high society would bring about the demise of the great estates. In 1914, Louis Hamersley purchased the fire-damaged Ward Manor/Almont estate and erected a Tudor style mansion and gatehouse, or what is today known as Ward Manor. Hamersley expanded his estate in 1926 by acquiring the abandoned Cruger's Island estate. That same year, after Hamersley's combined estate was purchased by William Ward, it was donated to charity and served as a retirement home for almost four decades.
By the mid-1900s, Bard's campus significantly expanded. The Blithewood estate was donated to the college in 1951, and in 1963, Bard purchased of the Ward Manor estate, including the main manor house. The rest of the Ward Manor estate is now the Tivoli Bays nature preserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or o ...
.
In 1919, Fr. Bernard Iddings Bell Bernard Iddings Bell (October 13, 1886 – September 5, 1958) was an American Christian author, Episcopal priest, and conservative cultural commentator. His religious writings, social critiques, and homilies on post-war society were acclaimed in t ...
became Bard's youngest president at the age of 34. His adherence to classical education, decorum, and dress eventually clashed with the school's push towards Deweyism
"My Pedagogic Creed" is an article written by John Dewey and published in ''School Journal'' in 1897.Dewey, John (1897). My Pedagogic Creed. ''School Journal'', 54(3), 77–80. The article is broken into 5 sections, with each paragraph beginning " ...
and secularization, and he resigned in 1933.
In 1928, Bard merged with Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
, serving as an undergraduate school similar to Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
. Under the agreement, Bard remained affiliated with the Episcopal Church and retained control of its finances. The merger raised Bard's prestige; however, it failed to provide financial support to the college during the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. So dire was Bard's financial situation that in 1932, then-Governor of New York and College trustee Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
sent a telegram to the likes of John D. Rockefeller, Jr.
John Davison Rockefeller Jr. (January 29, 1874 – May 11, 1960) was an American financier and philanthropist, and the only son of Standard Oil co-founder John D. Rockefeller.
He was involved in the development of the vast office complex in ...
, George Eastman and Frederick William Vanderbilt requesting donations for the college.
On May 26, 1933, Dr. Donald Tewksbury, a Columbia professor, was appointed dean of the college. Although dean for only four years, Tewksbury had a lasting impact on the school. Tewksbury, an educational philosopher, had extensive ideas regarding higher education. While he was dean, Tewksbury steered the college into a more secular direction and changed its name from St. Stephen's to Bard. He also placed a heavy academic emphasis on the arts, something atypical of colleges at the time, and set the foundations for Bard's Moderation and Senior Project requirement. While Tewksbury never characterized Bard's curriculum as "progressive
Progressive may refer to:
Politics
* Progressivism, a political philosophy in support of social reform
** Progressivism in the United States, the political philosophy in the American context
* Progressive realism, an American foreign policy par ...
," the school would later be considered an early adopter of progressive education. In his 1943 study of early progressive colleges, titled ''General Education in the Progressive College'', Louis T. Benezet
Louis Tomlinson Benezet (June 29, 1915 in La Crosse, Wisconsin – January 23, 2002 in Mill Valley, California) was an American educator, education administrator and multiple U.S. university president. He was the son of Louis P. Bénézet, a pr ...
used Bard as one of his three case studies
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context. For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular fi ...
.
During the 1940s, Bard provided a haven for intellectual refugees fleeing Europe. These included Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
, the political theorist, Stefan Hirsch
Stefan Hirsch (January 2, 1899 – September 28, 1964) was an American artist. Many of his paintings have the hard edges, smooth surfaces, and simplified forms of the precisionists and their typical subjects—cityscapes and industrial scenes� ...
, the precisionist
Precisionism was a modernist art movement that emerged in the United States after World War I. Influenced by Cubism, Purism, and Futurism, Precisionist artists reduced subjects to their essential geometric shapes, eliminated detail, and often us ...
painter; Felix Hirsch
Felix Eduard Hirsch (Berlin, 7 February 1902 – 12 December 1982 Newtown, Pennsylvania) was a journalist for the ''Berliner Tageblatt'' and latterly; historian, librarian and professor at Bard College in New York. As a journalist in Berlin, Hirs ...
, the political editor of the '' Berliner Tageblatt''; the violinist Emil Hauser; the linguist Hans Marchand
Hans Marchand (1 October 1907 – 13 December 1978) was a German linguist. He studied Romance languages, English and Latin, and after fleeing Germany during the Third Reich was a lecturer of linguistics at Istanbul, Yale University, and Bard Colle ...
; the noted psychologist Werner Wolff; and the philosopher Heinrich Blücher
Heinrich Friedrich Ernst Blücher (29 January 1899 – 31 October 1970) was a German poet and philosopher. He was the second husband of Hannah Arendt whom he had first met in Paris in 1936. During his life in America, Blücher traveled in popu ...
.
Arendt is buried at Bard, alongside her husband Heinrich Blücher, as is eminent novelist Philip Roth
Philip Milton Roth (March 19, 1933 – May 22, 2018) was an American novelist and short story writer.
Roth's fiction—often set in his birthplace of Newark, New Jersey—is known for its intensely autobiographical character, for philosophicall ...
.
In 1944, as a result of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, enrollment significantly dropped putting financial stress on the college. In order to increase enrollment, the college became co-educational, thereby severing all ties with Columbia. The college became an independent, secular, institution in 1944. Thus enrollment more than doubled, from 137 students in 1944, to 293 in 1947. In the 1950s, with the addition of the Blithewood estate and Tewksbury Hall, the college would increase its enrollment by 150 students.
Late twentieth and early twenty-first century
Donald Fagen
Donald Jay Fagen (born January 10, 1948) is an American musician best known as the co-founder, lead singer, co-songwriter, and keyboardist of the band Steely Dan, formed in the early 1970s with musical partner Walter Becker. In addition to his w ...
and Walter Becker's experiences at Bard prompted them to write the 1973 song " My Old School" for their rock group, Steely Dan
Steely Dan is an American rock band founded in 1971 in New York by Walter Becker (guitars, bass, backing vocals) and Donald Fagen (keyboards, lead vocals). Initially the band had a stable lineup, but in 1974, Becker and Fagen retired from live ...
. Fagen wrote another Steely Dan song, "Rikki Don't Lose That Number
"Rikki Don't Lose That Number" is a single released in 1974 by rock/jazz rock group Steely Dan and the opening track of their third album ''Pretzel Logic''. It was the most successful single of the group's career, peaking at number 4 on the ''Bi ...
", about novelist, artist and former Bard faculty spouse Rikki Ducornet
Rikki Ducornet (; born Erica DeGre; April 19, 1943) is an American writer, poet, and artist. Her work has been described as “linguistically explosive and socially relevant,” and praised for “deploy ngtactics familiar to the historical avan ...
.
In 2020, Bard College, along with Central European University, became the founding members of the Open Society University Network, a collaborative global education initiative endowed with US$1 billion. As part of this new initiative, the college received a US$100 million gift from the Open Society Foundations
Open Society Foundations (OSF), formerly the Open Society Institute, is a Grant (money), grantmaking network founded and chaired by business magnate George Soros. Open Society Foundations financially supports civil society groups around the wo ...
which ranks among the largest financial contributions to a U.S. institution in recent history.
In June 2021, Bard College was declared an 'undesirable institution' in Russia, becoming the first international higher education organization to be branded with this designation. Bard president Botstein hypothesize that this tag was due their association with and funding from the Open Society Foundations
Open Society Foundations (OSF), formerly the Open Society Institute, is a Grant (money), grantmaking network founded and chaired by business magnate George Soros. Open Society Foundations financially supports civil society groups around the wo ...
(also classified 'undesirable' in Russia) and related
''Related'' is an American comedy-drama television series that aired on The WB from October 5, 2005, to March 20, 2006. It revolves around the lives of four close-knit sisters of Italian descent, raised in Brooklyn and living in Manhattan.
The ...
conspiracy theories about George Soros.
Campus
Annandale-on-Hudson
Annandale-on-Hudson is a hamlet in Dutchess County, New York, United States, located in the Hudson Valley town of Red Hook, across the Hudson River from Kingston. The hamlet consists mainly of the Bard College campus.
Municipal services
Emerge ...
, a hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
in Dutchess County, New York
Dutchess County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 295,911. The county seat is the city of Poughkeepsie. The county was created in 1683, one of New York's first twelve counties, and later orga ...
, United States, in the town of Red Hook. It contains more than 70 buildings with a total gross building space of and was listed as a census-designated place in 2020. Campus buildings represent varied architectural style
An architectural style is a set of characteristics and features that make a building or other structure notable or historically identifiable. It is a sub-class of style in the visual arts generally, and most styles in architecture relate closely ...
s, but the campus remains heavily influenced by the Collegiate Gothic
Collegiate Gothic is an architectural style subgenre of Gothic Revival architecture, popular in the late-19th and early-20th centuries for college and high school buildings in the United States and Canada, and to a certain extent Europ ...
and Postmodern
Postmodernism is an intellectual stance or mode of discourseNuyen, A.T., 1992. The Role of Rhetorical Devices in Postmodernist Discourse. Philosophy & Rhetoric, pp.183–194. characterized by skepticism toward the " grand narratives" of moderni ...
styles.
Bard's historic buildings are associated with the early development of the college and the history of the Hudson River estates ( see Bard College History). During a late twentieth-century building boom, the college embraced a trend of building signature buildings designed by prominent architects like Venturi, Gehry
Frank Owen Gehry, , FAIA (; ; born ) is a Canadian-born American architect and designer. A number of his buildings, including his private residence in Santa Monica, California, have become world-renowned attractions.
His works are considered ...
, and Viñoly.
In January 2016, Bard purchased Montgomery Place
Montgomery Place, now Bard College: The Montgomery Place Campus, near Barrytown, New York, United States, is an early 19th-century estate that has been designated a National Historic Landmark. It is also a contributing property to the Hudson R ...
, a estate adjacent to the Bard campus, with significant historic and cultural assets. The estate consists of a historic mansion, a farm, and some 20 smaller buildings. The college purchased the property from Historic Hudson Valley, the historical preservation organization that had owned Montgomery Place since the late 1980s. The addition of this property brings Bard's total campus size to nearly along the Hudson River in Annandale-on-Hudson
Annandale-on-Hudson is a hamlet in Dutchess County, New York, United States, located in the Hudson Valley town of Red Hook, across the Hudson River from Kingston. The hamlet consists mainly of the Bard College campus.
Municipal services
Emerge ...
, New York.
Academics
Bard is a college of the liberal arts and sciences. In the undergraduate college, Bard offersBachelor of Arts
Bachelor of arts (BA or AB; from the Latin ', ', or ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate program in the arts, or, in some cases, other disciplines. A Bachelor of Arts degree course is generally completed in three or four years ...
and Bachelor of Science
A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for programs that generally last three to five years.
The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Science was the University of ...
degrees. There are 23 academic departments that offer over 40 major programs, as well as 12 interdisciplinary concentrations. The college was the first in the nation to offer a human rights
Human rights are Morality, moral principles or Social norm, normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for ce ...
major. In the 2011–2012 academic year, the college held 1,345 classes.
In the three weeks preceding their first semester, first-year students attend the Language and Thinking (L&T) program, an intensive, writing-centered introduction to the liberal arts. The interdisciplinary program, established in 1981, aims to "cultivate habits of thoughtful reading and discussion, clear articulation, accurate self-critique, and productive collaboration." The program covers philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
, science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
, fiction
Fiction is any creative work, chiefly any narrative work, portraying individuals, events, or places that are imaginary, or in ways that are imaginary. Fictional portrayals are thus inconsistent with history, fact, or plausibility. In a traditi ...
, and religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
. In 2011, the core readings included works by Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
, Franz Kafka
Franz Kafka (3 July 1883 – 3 June 1924) was a German-speaking Bohemian novelist and short-story writer, widely regarded as one of the major figures of 20th-century literature. His work fuses elements of realism and the fantastic. It ...
, Frans de Waal, Stephen Jay Gould
Stephen Jay Gould (; September 10, 1941 – May 20, 2002) was an American paleontologist, evolutionary biologist, and historian of science. He was one of the most influential and widely read authors of popular science of his generation. Gould sp ...
, Clifford Geertz
Clifford James Geertz (; August 23, 1926 – October 30, 2006) was an American anthropologist who is remembered mostly for his strong support for and influence on the practice of symbolic anthropology and who was considered "for three decades. ...
, M. NourbeSe Philip
Marlene Nourbese Philip (born 3 February 1947), usually credited as M. NourbeSe Philip, is a Canadian poet, novelist, playwright, essayist and short story writer.
Life and works
Born in the Caribbean in Woodlands, Moriah, Trinidad and Tobago, W ...
, and Sophocles
Sophocles (; grc, Σοφοκλῆς, , Sophoklễs; 497/6 – winter 406/5 BC)Sommerstein (2002), p. 41. is one of three ancient Greek tragedians, at least one of whose plays has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or co ...
.
The capstone of the Bard undergraduate experience is the Senior Project, commonly referred to as SPROJ amongst its students. As with moderation, this project takes different forms in different departments. Many students write a paper of around eighty pages, which is then, as with work for moderation, critiqued by a board of three professors. Arts students must organize a series of concerts, recitals, or shows, or produce substantial creative work; math and science students, as well as some social science students, undertake research projects.
Rankings and admissions
In its 2021 edition of college rankings, '' U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Bard tied for 54th overall, 4th in "Most Innovative Schools", tied at 30th for "Best Undergraduate Teaching", and 40th for "Best Value" among liberal arts colleges in the United States. In September 2011,Travel+Leisure
''Travel + Leisure'' is a travel magazine based in New York City, New York. Published 12 times a year, it has 4.8 million readers, according to its corporate media kit. It is published by Dotdash Meredith, a subsidiary of IAC, with trademark rig ...
named the college as one of the most beautiful campuses in the United States.
Bard has been named a top producer of U.S. Fulbright
The Fulbright Program, including the Fulbright–Hays Program, is one of several United States Cultural Exchange Programs with the goal of improving intercultural relations, cultural diplomacy, and intercultural competence between the people of ...
Scholars. Many Bard alumni have also been named Watson Fellows, Critical Language Scholarship recipients, Davis Projects for Peace Prize winners, Rhodes Scholars
The Rhodes Scholarship is an international postgraduate award for students to study at the University of Oxford, in the United Kingdom.
Established in 1902, it is the oldest graduate scholarship in the world. It is considered among the world' ...
, Marshall Scholars, and Peace Corps
The Peace Corps is an independent agency and program of the United States government that trains and deploys volunteers to provide international development assistance. It was established in March 1961 by an executive order of President John F. ...
fellows, among other postgraduate awards.
Endowment
Bard has access to multiple, distinct endowments. Bard, along with Central European University, is a founding member of theOpen Society University Network
Open or OPEN may refer to:
Music
* Open (band), Australian pop/rock band
* The Open (band), English indie rock band
* ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969
* ''Open'' (Gotthard album), 1999
* ''Open'' (Cowboy Junkies album), 2001
* ''Open'' (YF ...
, endowed with $1 billion. Bard also maintains a separate endowment of approximately $267 million, a large portion of which is exclusively dedicated to its graduate programs in the arts. In July 2020, Bard received a gift of $100 million from the Open Society Foundations
Open Society Foundations (OSF), formerly the Open Society Institute, is a Grant (money), grantmaking network founded and chaired by business magnate George Soros. Open Society Foundations financially supports civil society groups around the wo ...
, which will dispense $10 million yearly over a period of ten years. In April 2021, Bard received a $500 million endowment challenge grant from philanthropist George Soros. Once matched, on a five-year timeline, Bard will have an endowment of more than $1 billion.
Programs, centers, and associated institutes
Bard has developed several innovative graduate programs and research institutes, including the Milton Avery Graduate School of the Arts, the Levy Economics Institute which began offering a Masters of Science in Economic Theory and Policy in 2014, theCenter for Curatorial Studies and Art in Contemporary Culture
Founded in 1990, the Center for Curatorial Studies, Bard College (CCS Bard) is an exhibition and research center dedicated to the study of art and exhibition practices from the 1960s to the present. The Center initiated its graduate program in 1994 ...
, the Bard Center for Environmental Policy, the Bard College Conservatory of Music
The Bard College Conservatory of Music is part of Bard College in Annandale-on-Hudson, New York. Founded in 2005, the program is unique among music conservatories in the United States in that all undergraduate students are required to participa ...
, the ICP-Bard Program in Advanced Photographic Studies in Manhattan, the Master of Arts in Teaching Program (MAT), the Bard College Clemente Program, and the Bard Graduate Center in Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
.
 In 1990, Bard College acquired, on permanent loan, art collector Marieluise Hessel's substantial collection of important contemporary artwork. In 2006, Hessel contributed another $8 million (USD) for the construction of a 17,000-square-foot addition to Bard's Center for Curatorial Studies building, in which the collection is exhibited.
The Bard Prison Initiative (BPI) provides a liberal arts degree to incarcerated individuals ( prison education) in five prisons in New York State, and enrolls nearly 200 students. Since federal funding for prison education programs was eliminated in 1994, BPI is one of only a small number of programs of its kind in the country.
Bard awards the Bard Fiction Prize annually to "a promising emerging writer who is an American citizen aged 39 years or younger at the time of application". The prize is $30,000 and an appointment as writer-in-residence at the college.
The
In 1990, Bard College acquired, on permanent loan, art collector Marieluise Hessel's substantial collection of important contemporary artwork. In 2006, Hessel contributed another $8 million (USD) for the construction of a 17,000-square-foot addition to Bard's Center for Curatorial Studies building, in which the collection is exhibited.
The Bard Prison Initiative (BPI) provides a liberal arts degree to incarcerated individuals ( prison education) in five prisons in New York State, and enrolls nearly 200 students. Since federal funding for prison education programs was eliminated in 1994, BPI is one of only a small number of programs of its kind in the country.
Bard awards the Bard Fiction Prize annually to "a promising emerging writer who is an American citizen aged 39 years or younger at the time of application". The prize is $30,000 and an appointment as writer-in-residence at the college.
The Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
Center for Politics and Humanities is located at Bard College. The center hosts an annual public conference, offers courses, runs various related academic programs, and houses research fellows, and is directed by Dr. Roger Berkowitz, a legal scholar and an associate professor of politics, philosophy, and human rights.
In February 2009, Bard announced the first dual degree program between a Palestinian university and an American institution of higher education. The college entered into a collaboration with Al-Quds University
Al-Quds University ( ar, جامعة القدس) is a Palestinian university with campuses in Jerusalem, Abu Dis, al-Bireh, and Hebron.
Overview
The idea of establishing an institution of higher learning in the outskirts of Jerusalem was con ...
involving an honors college, a master's program in teaching and a model high school.
In accordance with AlQuds-Bard requirements, students are not allowed to decide their major during the first year of their studies; instead, as a liberal arts college, students are advised to diverge in different classes that would allow them to decide what program they would like to take interest in as in the following year. Students are encouraged to look upon different classes to help them decide the subject they would mostly enjoy studying. Bard gives students the opportunity to dissect different programs before committing to a specific major. As a policy, throughout a student's undergraduate years, they must distribute their credits among different courses so that they can liberally experience the different courses Bard has to offer.
 In June 2011, Bard officially acquired the
In June 2011, Bard officially acquired the Longy School of Music
Longy School of Music of Bard College is a private music school in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1915 as the Longy School of Music, it was one of the four independent degree-granting music schools in the Boston region along with the New E ...
in Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston, ...
, and in November 2011, Bard took ownership of the European College of Liberal Arts in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
, Germany, to become Bard College Berlin
Bard College Berlin (formerly known as ECLA or European College of Liberal Arts) is a private, non-profit institution of higher education in Berlin, Germany. It was founded as a non-profit association in 1999. Courses are taught in the English lan ...
.
In 2013, Bard entered into a comprehensive agreement with Soochow University in Suzhou
Suzhou (; ; Suzhounese: ''sou¹ tseu¹'' , Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Soochow, is a major city in southern Jiangsu province, East China. Suzhou is the largest city in Jiangsu, and a major economic center and focal point of trade ...
, China, that will include a joint program between the Soochow University School of Music and the Bard College Conservatory of Music, exploration leading to the establishment of The Bard College Liberal Arts Academy at Soochow University, and student exchange.
In 2020, Bard announced that through the new Franklin and Eleanor Roosevelt Advanced Achievement Scholars program the college will offer admission to high school juniors within 120 miles from the college based on an essay process based on the popular Bard Entrance Exam, first launched in 2013.
Student life
Over 120 student clubs are financed through Bard's Convocation Fund, which is distributed once a semester by an elected student body and ratified during a public forum. Bard College has one print newspaper, the '' Bard Free Press,'' which was awarded a Best in Show title by theAssociated Collegiate Press
The Associated Collegiate Press (ACP) is the largest and oldest national membership organization for college student media in the United States. The ACP is a division of the National Scholastic Press Association. It awards the newspaper, mag ...
in 2013. In 2003, the ''Bard Free Press'' won Best Campus Publication in ''SPIN Magazine
''Spin'' (stylized in all caps) is an American music magazine founded in 1985 by publisher Bob Guccione, Jr. Now owned by Next Management Partners, the magazine is an online publication since it stopped issuing a print edition in 2012.
Histor ...
s ''first annual Campus Awards. Student-run literary magazines include the semiannual ''Lux, The Moderator,'' and ''Sui Generis'', a journal of translations and of original poetry in languages other than English. ''The Draft'', a human rights journal, the ''Bard Journal of the Social Sciences,'' ''Bard Science Journal'', and ''Qualia'', a philosophy journal, are also student-published. ''Bard Papers'' is a privately funded literary magazine operated jointly between faculty and students.
Other prominent student groups include: the International Students Organization (ISO), Afropulse, Latin American Student Organization (LASO), Caribbean Student Association (CSA), Asian Student Organization (ASO), Bard Musical Theatre Company (BMTC), Black Student Organization (BSO), Anti-Capitalism Feminist Coalition, Body Image Discussion Group, Self-Injury Support and Discussion, Bard Film Committee, Queer Student Association, Trans Life Collective, The Scale Project, Student Labor Dialogue, Bard Debate Union, Bard Model UN, Surrealist Training Circus, Bard Bike Co-Op, Bard Bars, Bard POC Theater Ensemble, and college radio
Campus radio (also known as college radio, university radio or student radio) is a type of radio station that is run by the students of a college, university or other educational institution. Programming may be exclusively created or produced ...
station WXBC. WXBC was founded in 1947. In 2006, WXBC was nominated for "Station of the Year" and "Biggest Improvement" in the CMJ
CMJ Holdings Corp. is a music events and online media company, originally founded in 1978, which ran a website, hosted an annual festival in New York City, and published two magazines, ''CMJ New Music Monthly'' and ''CMJ New Music Report''. Th ...
College Radio Awards.
Bard has a strong independent music scene considering its isolation and size. The college's Old Gym was once a popular location for concerts and parties in the 1980s, 1990s, and early 2000s. In 2004, the Old Gym was shut down and in spring 2006 transformed into a student-run theater by students Brel Froebe, Julie Rossman, and Kell Condon. Many activities that once took place there now occur in the smaller SMOG building. SMOG is now primarily used as a music venue featuring student-run bands. Student-run theater is also popular: dozens of student directed and written productions are put on each semester and a 24 Hour Theater Festival is held at least once a year.
Athletics
Bard College teams participate as a member of theNational Collegiate Athletic Association
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges an ...
's Division III
In sport, the Third Division, also called Division 3, Division Three, or Division III, is often the third-highest division of a league, and will often have promotion and relegation with divisions above and below.
Association football
*Belgian Thir ...
. The Raptors are a member of the Liberty League
The Liberty League is an intercollegiate athletic conference affiliated with the National Collegiate Athletic Association's Division III. Member schools are top institutions that are all located in the state of New York.
History
It was founded ...
. Prior conference affiliations include the Skyline Conference
The Skyline Conference is a college athletic conference based in the New York City area that competes in the NCAA's Division III.
The league was originally chartered on May 16, 1989, as a men's basketball conference and now sponsors 17 sports (ni ...
and the former Hudson Valley Athletic Conference. Women's sports include basketball, cross country, lacrosse, soccer, swimming & diving, tennis, track & field, volleyball and squash. Men's sports include baseball, basketball, cross country, soccer, squash, swimming & diving, tennis, track & field and volleyball.
One of the more popular club sports on campus is rugby. Bard College Rugby Football Club fields men's and women's teams that compete in the Tristate Conference, affiliated with National Collegiate Rugby. Additional club sports include: ultimate frisbee, fencing, and equestrian.
Alumni and faculty
Blythe Danner
Blythe Katherine Danner (born February 3, 1943) is an American actress. Accolades she has received include two Primetime Emmy Awards for Best Supporting Actress in a Drama Series for her role as Izzy Huffstodt on '' Huff'' (2004–2006), and a ...
, Emmy
The Emmy Awards, or Emmys, are an extensive range of awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international television industry. A number of annual Emmy Award ceremonies are held throughout the calendar year, each with the ...
and Tony
Tony may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Tony (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Gregory Tony (born 1978), American law enforcement officer
* Motu Tony (born 1981), New Zealand international rugby leagu ...
-winning actress
File:ChevyChaseMar10.jpg, Chevy Chase
Cornelius Crane "Chevy" Chase (; born October 8, 1943) is an American comedian, actor and writer. He became a key cast member in the first season of ''Saturday Night Live'', where his recurring ''Weekend Update'' segment became a staple of the ...
, comedian known for his work with ''Saturday Night Live
''Saturday Night Live'' (often abbreviated to ''SNL'') is an American late-night live television sketch comedy and variety show created by Lorne Michaels and developed by Dick Ebersol that airs on NBC and Peacock. Michaels currently serves a ...
''
File:Todd Haynes at the 2009 Tribeca Film Festival.jpg, Todd Haynes, filmmaker
File:Adam Yauch crop.jpg, Adam Yauch, rapper from The Beastie Boys
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
File:Peter Sarsgaard (31957641966) (cropped).jpg, Peter Sarsgaard, actor
File:Gaby Hoffman (cropped).jpg, Gaby Hoffmann, actress
File:Adam Conover photograph.jpg, Adam Conover, host of ''Adam Ruins Everything''
File:Raphael Bob-Waksberg.png, Raphael Bob-Waksberg, creator of ''BoJack Horseman''
File:Gia Coppola 2016.png, Gia Coppola, filmmaker known for ''Palo Alto (2013 film), Palo Alto'', member of the Coppola family tree, Coppola family
File:Pulitzer2018-ronan-farrow-20180530-wp.jpg, Ronan Farrow, Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist
File:Lana Wachowski, Fantastic Fest, Cloud Atlas.jpg, Lana Wachowski, film and television director, writer and producer ''The Matrix (franchise), The Matrix'' (franchise)
File:Donald Fagen singing.jpg, Donald Fagen
Donald Jay Fagen (born January 10, 1948) is an American musician best known as the co-founder, lead singer, co-songwriter, and keyboardist of the band Steely Dan, formed in the early 1970s with musical partner Walter Becker. In addition to his w ...
, musician and co-founder of Steely Dan
Steely Dan is an American rock band founded in 1971 in New York by Walter Becker (guitars, bass, backing vocals) and Donald Fagen (keyboards, lead vocals). Initially the band had a stable lineup, but in 1974, Becker and Fagen retired from live ...
File:Walter-Becker.jpg, Walter Becker, musician and co-founder of Steely Dan
Steely Dan is an American rock band founded in 1971 in New York by Walter Becker (guitars, bass, backing vocals) and Donald Fagen (keyboards, lead vocals). Initially the band had a stable lineup, but in 1974, Becker and Fagen retired from live ...
File:Ali Wentworth 2012 Shankbone.JPG, Alexandra Wentworth, actor/comedian
File:Nick Zinner.jpg, Nick Zinner, musician (Yeah Yeah Yeahs, Head Wound City)
File:Chris Claremont 01 (9514659384).jpg, Chris Claremont, comic book writer ''X-Men''
File:James Cox Chambers Farm.jpg, James Cox Chambers, American billionaire heir
File:Asher Edelman, 1993, by Erling Mandelmann.png, Asher Edelman, investment banker
File:Matt Taibbi Occupy Wall Street 01.jpg, Matt Taibbi, journalist
File:Tom Ford cropped 2009.jpg, Tom Ford, fashion designer
File:Coen brothers Cannes 2015 2 (CROPPED).jpg, Joel and Ethan Coen, Academy Award-winning filmmakers
File:Tim Griffin (Deutsches Filminstitut & Filmmuseum).jpg, Tim Griffin (curator), Tim Griffin, curator
File:TracyNelson1981.jpg, Tracy Nelson (actress), Tracy Nelson, actress
File:Frances Bean Cobain Jan 2015.jpg, Francis Bean Cobain, musician and daughter of the late Kurt Cobain from Nirvana (band)
Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
, political theorist
File:Kyle-cassidy-neil-gaiman-April-2013.jpg, Neil Gaiman, bestselling author
File:Chinua Achebe, 1966.jpg, Chinua Achebe, Nigerian novelist
File:Walter Russell Mead - Chatham House 2012.jpg, Walter Russell Mead, academic
File:DMendelsohn.jpg, Daniel Mendelsohn, writer
File:Kelly Reichardt-4432.jpg, Kelly Reichardt, film director and screenwriter
File:Stephen Shore at CO Berlin, 2016.jpg, Stephen Shore, photographer
File:Simpson, Mona MBFI.jpg, Mona Simpson, novelist
File:Ashbery-2010-09-12.jpg, John Ashbery, poet
File:Saul Bellow (Herzog portrait).jpg, Saul Bellow, writer
File:Ralph Ellison photo portrait seated.jpg, Ralph Ellison, novelist
File:Robert Kelly, photo by Charlotte Mandell.jpg, Robert Kelly (poet), Robert Kelly, poet
File:DanielFish2019.png, Daniel Fish, theater director
Chevy Chase
Cornelius Crane "Chevy" Chase (; born October 8, 1943) is an American comedian, actor and writer. He became a key cast member in the first season of ''Saturday Night Live'', where his recurring ''Weekend Update'' segment became a staple of the ...
(1967); Walter Becker and Donald Fagen
Donald Jay Fagen (born January 10, 1948) is an American musician best known as the co-founder, lead singer, co-songwriter, and keyboardist of the band Steely Dan, formed in the early 1970s with musical partner Walter Becker. In addition to his w ...
of Steely Dan
Steely Dan is an American rock band founded in 1971 in New York by Walter Becker (guitars, bass, backing vocals) and Donald Fagen (keyboards, lead vocals). Initially the band had a stable lineup, but in 1974, Becker and Fagen retired from live ...
(1969); actors Blythe Danner
Blythe Katherine Danner (born February 3, 1943) is an American actress. Accolades she has received include two Primetime Emmy Awards for Best Supporting Actress in a Drama Series for her role as Izzy Huffstodt on '' Huff'' (2004–2006), and a ...
(1965), Adrian Grenier, Gaby Hoffmann, Larry Hagman; filmmakers Gia Coppola, Todd Haynes (MFA), Sadie Bennings (MFA), The Wachowskis, Lana Wachowski (dropped out); Herb Ritts, photographer; Christopher Guest, actor/director (''This is Spinal Tap'', ''Waiting for Guffman'', ''Best in Show''); songwriters Billy Steinberg (Madonna (entertainer), Madonna's "Like A Virgin," Cyndi Lauper, Cyndi Lauper's "True Colors," The Bangles "Eternal Flame"); Anne Bogart, theater director; Howard E. Koch, screenwriter (''Casablanca'', ''Letter from an Unknown Woman''); David Cote (writer), David Cote, writer; Adam Conover, comedian and creator of ''Adam Ruins Everything''; Raphael Bob-Waksberg, comedian and creator of ''Bojack Horseman''; classical composer Bruce Wolosoff; Ronan Farrow, journalist who exposed the Harvey Weinstein scandal; writer and social theorist Albert Jay Nock, journalist and author Matt Taibbi, and Adam Yauch of the Beastie Boys. Other notable alumni include artist Freya Powell and Tschabalala Self.
Among the college's most well-known former faculty are Hannah Arendt
Hannah Arendt (, , ; 14 October 1906 – 4 December 1975) was a political philosopher, author, and Holocaust survivor. She is widely considered to be one of the most influential political theorists of the 20th century.
Arendt was born ...
, Toni Morrison, Heinrich Blücher
Heinrich Friedrich Ernst Blücher (29 January 1899 – 31 October 1970) was a German poet and philosopher. He was the second husband of Hannah Arendt whom he had first met in Paris in 1936. During his life in America, Blücher traveled in popu ...
, Roy Lichtenstein, Mary McCarthy (author), Mary McCarthy, Arthur Penn, John Ashbery, Richard Teitelbaum, Mary Lee Settle and Chinua Achebe. Current faculty who are well-known include Stephen Shore, An-My Lê, Neil Gaiman, Bill T. Jones, Daniel Mendelsohn, Joan Tower, Masha Gessen, Kelly Reichardt, Francine Prose, Ann Lauterbach, Charles Burnett (director), Charles Burnett, Valeria Luiselli, Tan Dun, Tschabalala Self, and Sky Hopinka.
Gallery
References
External links
*Official athletics website
{{Authority control Bard College, Columbia University 1860 establishments in New York (state) Educational institutions established in 1860 Liberal arts colleges in New York (state) Red Hook, New York Annandale-on-Hudson, New York Universities and colleges affiliated with the Episcopal Church (United States) Universities and colleges in Dutchess County, New York Private universities and colleges in New York (state) Tourist attractions in Dutchess County, New York Undesirable organizations in Russia