Bacterial Phyla And Superphyla on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one
 The word ''bacteria'' is the plural of the
The word ''bacteria'' is the plural of the
 The ancestors of bacteria were unicellular microorganisms that were the first forms of life to appear on Earth, about 4 billion years ago. For about 3 billion years, most organisms were microscopic, and bacteria and archaea were the dominant forms of life. Although bacterial
The ancestors of bacteria were unicellular microorganisms that were the first forms of life to appear on Earth, about 4 billion years ago. For about 3 billion years, most organisms were microscopic, and bacteria and archaea were the dominant forms of life. Although bacterial
 Size. Bacteria display a wide diversity of shapes and sizes. Bacterial cells are about one-tenth the size of eukaryotic cells and are typically 0.5–5.0
Size. Bacteria display a wide diversity of shapes and sizes. Bacterial cells are about one-tenth the size of eukaryotic cells and are typically 0.5–5.0  Multicellularity. Most bacterial species exist as single cells; others associate in characteristic patterns: ''
Multicellularity. Most bacterial species exist as single cells; others associate in characteristic patterns: ''

 Bacteria do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, and their
Bacteria do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, and their

 Some
Some

 Unlike in multicellular organisms, increases in cell size ( cell growth) and reproduction by
Unlike in multicellular organisms, increases in cell size ( cell growth) and reproduction by
 Most bacteria have a single circular
Most bacteria have a single circular
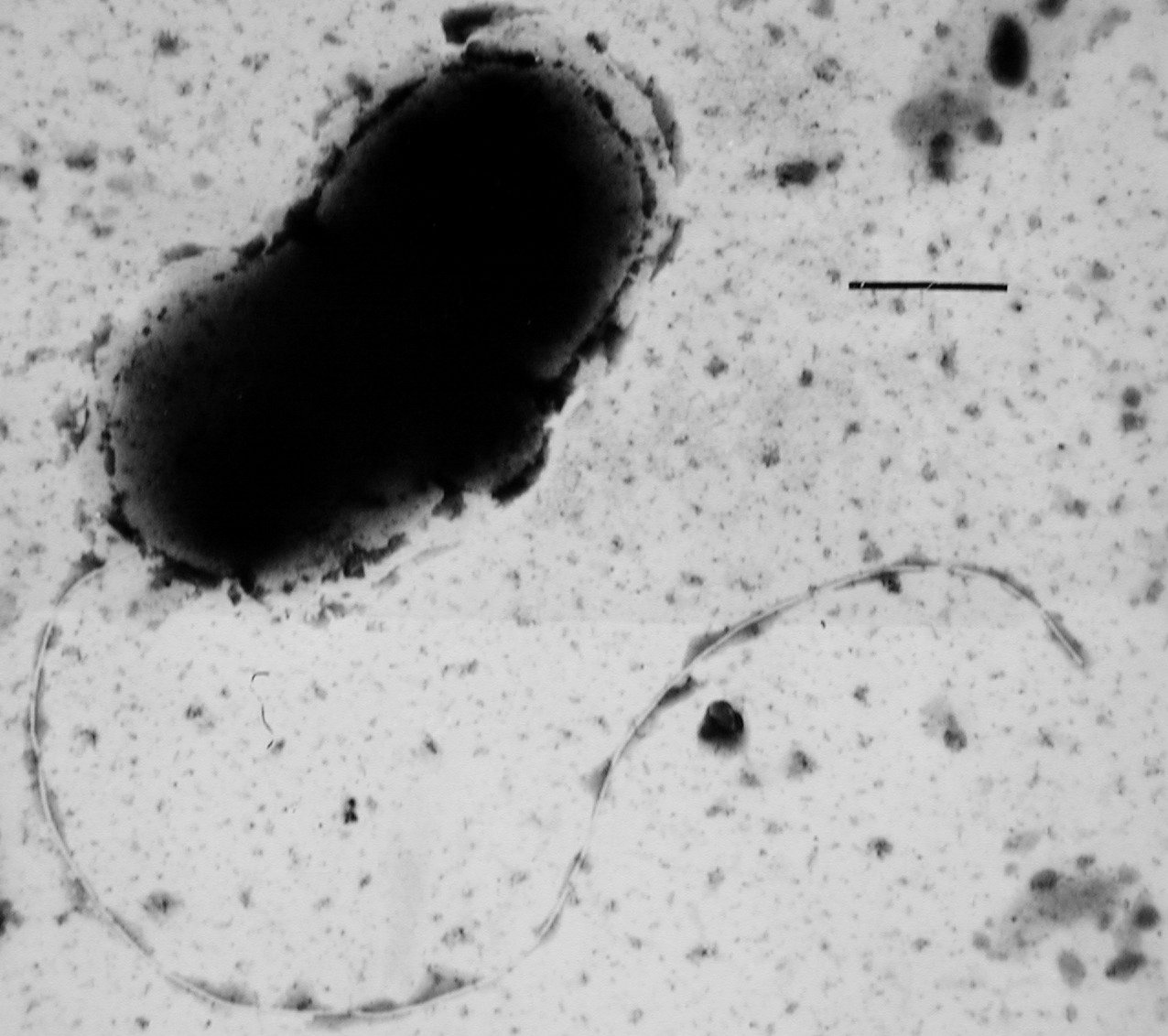 Many bacteria are
Many bacteria are  Bacteria can use flagella in different ways to generate different kinds of movement. Many bacteria (such as '' E. coli'') have two distinct modes of movement: forward movement (swimming) and tumbling. The tumbling allows them to reorient and makes their movement a three-dimensional
Bacteria can use flagella in different ways to generate different kinds of movement. Many bacteria (such as '' E. coli'') have two distinct modes of movement: forward movement (swimming) and tumbling. The tumbling allows them to reorient and makes their movement a three-dimensional
 Despite their apparent simplicity, bacteria can form complex associations with other organisms. These symbiosis, symbiotic associations can be divided into parasitism, Mutualism (biology), mutualism and commensalism.
Despite their apparent simplicity, bacteria can form complex associations with other organisms. These symbiosis, symbiotic associations can be divided into parasitism, Mutualism (biology), mutualism and commensalism.
 The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decomposition, decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immune system, immunity or innate immunity, innate resistance against many microorganisms. Unlike some
The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decomposition, decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immune system, immunity or innate immunity, innate resistance against many microorganisms. Unlike some  Each species of pathogen has a characteristic spectrum of interactions with its human host (biology), hosts. Some organisms, such as ''Staphylococcus'' or ''Streptococcus'', can cause skin infections,
Each species of pathogen has a characteristic spectrum of interactions with its human host (biology), hosts. Some organisms, such as ''Staphylococcus'' or ''Streptococcus'', can cause skin infections,
On-line text book on bacteriology (2015)
{{Authority control Bacteria, Bacteriology Domains (biology)
biological cell
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and ...
. They constitute a large domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
** Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
*Do ...
of prokaryotic
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s. Typically a few micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of ...
s in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
, and are present in most of its habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
s. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weap ...
, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyc ...
by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. ...
. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is ...
of dead bodies
''Dead Bodies'' is a 2003 Irish drama film by Robert Quinn starring Andrew Scott, Katy Davis, Eamonn Owens, Darren Healy and Kelly Reilly. The screenplay was written by Derek Landy.
Plot
Tommy McGann (Scott) gets back together with his ex-girlf ...
; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction
Putrefaction is the fifth stage of death, following pallor mortis, algor mortis, rigor mortis, and livor mortis. This process references the breaking down of a body of an animal, such as a human, post-mortem. In broad terms, it can be vie ...
stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seep
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature of the see ...
s, extremophile
An extremophile (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "love") is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e. environments that make survival challenging such as due to extreme tempe ...
bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The und ...
and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
relationships with plants and animals. Most bacteria have not been characterised and there are many species that cannot be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology Bacteriology is the branch and specialty of biology that studies the morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry of bacteria as well as many other aspects related to them. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classific ...
, a branch of microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, ...
.
Humans and most other animals carry millions of bacteria. Most are in the gut
Gut or guts may refer to:
Anatomy
* Abdomen or belly, the region of a vertebrate between the chest and pelvis
* Abdominal obesity or "a gut", a large deposit of belly fat
* Gastrointestinal tract or gut, the system of digestive organs
* Ins ...
, and there are many on the skin. Most of the bacteria in and on the body are harmless or rendered so by the protective effects of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
, and many are beneficial Beneficial may refer to:
Organizations
* Beneficial Corporation, a consumer finance company founded in 1914 that was ultimately bought by HSBC Corporation
** Beneficial Loan Society, the former name of Beneficial Corporation
** Beneficial Finance, ...
, particularly the ones in the gut. However, several species of bacteria are pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
and cause infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
s, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The s ...
, leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria '' Mycobacterium leprae'' or '' Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve da ...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
, tetanus
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by '' Clostridium tetani'', and is characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usuall ...
and bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium ('' Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as ...
. The most common fatal bacterial diseases are respiratory infection
Respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are infectious diseases involving the respiratory tract. An infection of this type usually is further classified as an upper respiratory tract infection (URI or URTI) or a lower respiratory tract infection (L ...
s. Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s are used to treat bacterial infections and are also used in farming, making antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistanc ...
a growing problem. Bacteria are important in sewage treatment
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding e ...
and the breakdown of oil spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into ...
s, the production of cheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During product ...
and yogurt
Yogurt (; , from tr, yoğurt, also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial fermentation of milk. The bacteria used to make yogurt are known as ''yogurt cultures''. Fermentation of sugars in the milk by these bact ...
through fermentation, the recovery of gold, palladium, copper and other metals in the mining sector, as well as in biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
, and the manufacture of antibiotics and other chemicals.
Once regarded as plant
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
s constituting the class ''Schizomycetes'' ("fission fungi"), bacteria are now classified as prokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Conn ...
. Unlike cells of animals and other eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
s, bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
and rarely harbour membrane-bound
A biological membrane, biomembrane or cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that separates the interior of a cell from the external environment or creates intracellular compartments by serving as a boundary between one part of the ce ...
organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' t ...
s. Although the term ''bacteria'' traditionally included all prokaryotes, the scientific classification
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
changed after the discovery in the 1990s that prokaryotes consist of two very different groups of organisms that evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation te ...
from an ancient common ancestor. These evolutionary domains are called Bacteria and Archaea.
Etymology
 The word ''bacteria'' is the plural of the
The word ''bacteria'' is the plural of the New Latin
New Latin (also called Neo-Latin or Modern Latin) is the revival of Literary Latin used in original, scholarly, and scientific works since about 1500. Modern scholarly and technical nomenclature, such as in zoological and botanical taxonomy ...
', which is the latinisation of the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
('), the diminutive
A diminutive is a root word that has been modified to convey a slighter degree of its root meaning, either to convey the smallness of the object or quality named, or to convey a sense of intimacy or endearment. A ( abbreviated ) is a word-form ...
of ('), meaning "staff, cane", because the first ones to be discovered were rod-shaped
A bacillus (), also called a bacilliform bacterium or often just a rod (when the context makes the sense clear), is a rod-shaped bacterium or archaeon. Bacilli are found in many different taxonomic groups of bacteria. However, the name '' Bacil ...
.
Origin and early evolution
fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s exist, such as stromatolite
Stromatolites () or stromatoliths () are layered sedimentary formations ( microbialite) that are created mainly by photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria, and Pseudomonadota (formerly proteobacteria). ...
s, their lack of distinctive morphology prevents them from being used to examine the history of bacterial evolution, or to date the time of origin of a particular bacterial species. However, gene sequences can be used to reconstruct the bacterial phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spe ...
, and these studies indicate that bacteria diverged first from the archaeal/eukaryotic lineage. The most recent common ancestor
In biology and genetic genealogy, the most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as the last common ancestor (LCA) or concestor, of a set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all the organisms of the set are descended. The ...
of bacteria and archaea was probably a hyperthermophile
A hyperthermophile is an organism that thrives in extremely hot environments—from 60 °C (140 °F) upwards. An optimal temperature for the existence of hyperthermophiles is often above 80 °C (176 °F). Hyperthermophiles are often within the doma ...
that lived about 2.5 billion–3.2 billion years ago. The earliest life on land may have been bacteria some 3.22 billion years ago.
Bacteria were also involved in the second great evolutionary divergence, that of the archaea and eukaryotes. Here, eukaryotes resulted from the entering of ancient bacteria into endosymbiotic
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
associations with the ancestors of eukaryotic cells, which were themselves possibly related to the Archaea. This involved the engulfment by proto-eukaryotic cells of alphaproteobacteria
Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria). The Magnetococcales and Mariprofundales are considered basal or sister to the Alphaproteobacteria. The Alphaproteobacteria are highly diverse and ...
l symbionts
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
to form either mitochondria or hydrogenosome
A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in some anaerobic ciliates, flagellates, and fungi. Hydrogenosomes are highly variable organelles that have presumably evolved from protomitochondria to produce molecular hydrogen and ATP in ...
s, which are still found in all known Eukarya (sometimes in highly reduced form In statistics, and particularly in econometrics, the reduced form of a system of equations is the result of solving the system for the endogenous variables. This gives the latter as functions of the exogenous variables, if any. In econometrics, t ...
, e.g. in ancient "amitochondrial" protozoa). Later, some eukaryotes that already contained mitochondria also engulfed cyanobacteria-like organisms, leading to the formation of chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it ...
s in algae and plants. This is known as primary endosymbiosis.
Habitat
Bacteria are ubiquitous, living in every possible habitat on the planet including soil, underwater, deep in Earth's crust and even such extreme environments as acidic hot springs and radioactive waste. There are approximately 2×1030 bacteria on Earth, forming abiomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms biom ...
that is only exceeded by plants. They are abundant in lakes and oceans, in arctic ice, and geothermal springs where they provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. They live on and in plants and animals. Most do not cause diseases, are beneficial to their environments, and are essential for life. The soil is a rich source of bacteria and a few grams contain around a thousand million of them. They are all essential to soil ecology, breaking down toxic waste and recycling nutrients. They are even found in the atmosphere and one cubic metre of air holds around one hundred million bacterial cells. The oceans and seas harbour around 3 x 1026 bacteria which provide up to 50% of the oxygen humans breathe. Only around 2% of bacterial species have been fully studied.
Morphology
micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of ...
s in length. However, a few species are visible to the unaided eye—for example, '' Thiomargarita namibiensis'' is up to half a millimetre long, ''Epulopiscium fishelsoni
"''Candidatus'' Epulonipiscium" is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria that have a symbiotic relationship with surgeonfish. These bacteria are known for their unusually large size, many ranging from 200–700 μm in length. Until the discovery of ...
'' reaches 0.7 mm, and '' Thiomargarita magnifica'' can reach even 2 cm in length, which is 50 times larger than other known bacteria. Among the smallest bacteria are members of the genus ''Mycoplasma
''Mycoplasma'' is a genus of bacteria that, like the other members of the class '' Mollicutes'', lack a cell wall around their cell membranes. Peptidoglycan ( murein) is absent. This characteristic makes them naturally resistant to antibiotic ...
'', which measure only 0.3 micrometres, as small as the largest virus
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and ...
es. Some bacteria may be even smaller, but these ultramicrobacteria are not well-studied.
Shape. Most bacterial species are either spherical, called '' cocci'' (''singular coccus'', from Greek ''kókkos'', grain, seed), or rod shaped, called ''bacilli
Bacilli is a taxonomic class of bacteria that includes two orders, Bacillales and Lactobacillales, which contain several well-known pathogens such as ''Bacillus anthracis'' (the cause of anthrax). ''Bacilli'' are almost exclusively gram-posit ...
'' (''sing''. bacillus, from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
''baculus'', stick). Some bacteria, called ''vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive ...
'', are shaped like slightly curved rods or comma shaped; others can be spiral shaped, called '' spirilla'', or tightly coiled, called '' spirochaetes''. A small number of other unusual shapes have been described, such as star-shaped bacteria. This wide variety of shapes is determined by the bacterial cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mec ...
and cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is comp ...
, and is important because it can influence the ability of bacteria to acquire nutrients, attach to surfaces, swim through liquids and escape predators.
Neisseria
''Neisseria'' is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, ''N. meningitidis'' and '' N. gonorrhoeae''.
''Neisseria'' species are Gram-negativ ...
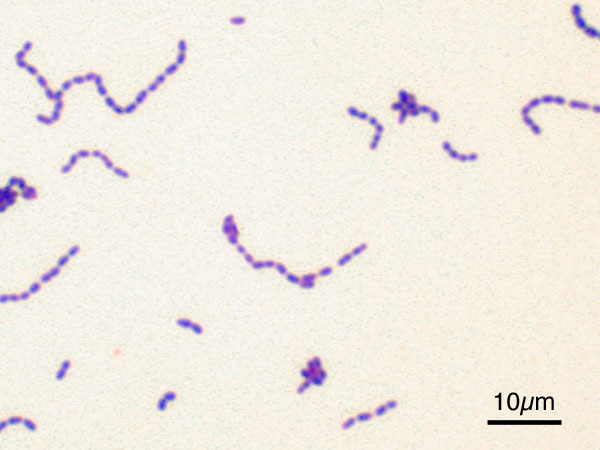
'' forms diploids (pairs), streptococci
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci ...
form chains, and staphylococci
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultativ ...
group together in "bunch of grapes" clusters. Bacteria can also group to form larger multicellular structures, such as the elongated filaments of ''Actinomycetota
The ''Actinomycetota'' (or ''Actinobacteria'') are a phylum of all gram-positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great economic importance to humans because agriculture and forests depend on their contributions to soi ...
'' species, the aggregates of ''Myxobacteria
The myxobacteria ("slime bacteria") are a group of bacteria that predominantly live in the soil and feed on insoluble organic substances. The myxobacteria have very large genomes relative to other bacteria, e.g. 9–10 million nucleotides except ...
'' species, and the complex hyphae of ''Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, ...
'' species. These multicellular structures are often only seen in certain conditions. For example, when starved of amino acids, myxobacteria detect surrounding cells in a process known as quorum sensing
In biology, quorum sensing or quorum signalling (QS) is the ability to detect and respond to cell population density by gene regulation. As one example, QS enables bacteria to restrict the expression of specific genes to the high cell densities a ...
, migrate towards each other, and aggregate to form fruiting bodies up to 500 micrometres long and containing approximately 100,000 bacterial cells. In these fruiting bodies, the bacteria perform separate tasks; for example, about one in ten cells migrate to the top of a fruiting body and differentiate into a specialised dormant state called a myxospore, which is more resistant to drying and other adverse environmental conditions.
Biofilms. Bacteria often attach to surfaces and form dense aggregations called biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular ...
s, and larger formations known as microbial mat
A microbial mat is a multi-layered sheet of microorganisms, mainly bacteria and archaea, or bacteria alone. Microbial mats grow at interfaces between different types of material, mostly on submerged or moist surfaces, but a few survive in desert ...
s. These biofilms and mats can range from a few micrometres in thickness to up to half a metre in depth, and may contain multiple species of bacteria, protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the e ...
s and archaea. Bacteria living in biofilms display a complex arrangement of cells and extracellular components, forming secondary structures, such as microcolonies, through which there are networks of channels to enable better diffusion of nutrients. In natural environments, such as soil or the surfaces of plants, the majority of bacteria are bound to surfaces in biofilms. Biofilms are also important in medicine, as these structures are often present during chronic bacterial infections or in infections of implanted medical device
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assur ...
s, and bacteria protected within biofilms are much harder to kill than individual isolated bacteria.
Cellular structure
Intracellular structures
The bacterial cell is surrounded by acell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the ...
, which is made primarily of phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids ty ...
s. This membrane encloses the contents of the cell and acts as a barrier to hold nutrients, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s and other essential components of the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
within the cell. Unlike eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
, bacteria usually lack large membrane-bound structures in their cytoplasm such as a nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
, mitochondria, chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it ...
s and the other organelles present in eukaryotic cells. However, some bacteria have protein-bound organelles in the cytoplasm which compartmentalize aspects of bacterial metabolism, such as the carboxysome
Carboxysomes are bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) consisting of polyhedral protein shells filled with the enzymes ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO)—the predominant enzyme in carbon fixation and the rate limiting e ...
. Additionally, bacteria have a multi-component cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is comp ...
to control the localisation of proteins and nucleic acids within the cell, and to manage the process of cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
.
Many important biochemical
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology ...
reactions, such as energy generation, occur due to concentration gradients
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', ''number concentration'', a ...
across membranes, creating a potential
Potential generally refers to a currently unrealized ability. The term is used in a wide variety of fields, from physics to the social sciences to indicate things that are in a state where they are able to change in ways ranging from the simple r ...
difference analogous to a battery. The general lack of internal membranes in bacteria means these reactions, such as electron transport, occur across the cell membrane between the cytoplasm and the outside of the cell or periplasm
The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the ''periplasmic space'' in gram-negative bacteria. Using cryo-electron microscopy it has been found tha ...
. However, in many photosynthetic bacteria the plasma membrane is highly folded and fills most of the cell with layers of light-gathering membrane. These light-gathering complexes may even form lipid-enclosed structures called chlorosomes in green sulfur bacteria.
 Bacteria do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, and their
Bacteria do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, and their gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
tic material is typically a single circular bacterial chromosome of DNA located in the cytoplasm in an irregularly shaped body called the nucleoid
The nucleoid (meaning '' nucleus-like'') is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell ...
. The nucleoid contains the chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
with its associated proteins and RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
. Like all other organism
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
s, bacteria contain ribosomes for the production of proteins, but the structure of the bacterial ribosome is different from that of eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
s and archaea.
Some bacteria produce intracellular nutrient storage granules, such as glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
, polyphosphate
Polyphosphates are salts or esters of polymeric oxyanions formed from tetrahedral PO4 (phosphate) structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. Polyphosphates can adopt linear or a cyclic ring structures. In biology, the polyphosphate e ...
, sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
or polyhydroxyalkanoates
Polyhydroxyalkanoates or PHAs are polyesters produced in nature by numerous microorganisms, including through bacterial fermentation of sugars or lipids. When produced by bacteria they serve as both a source of energy and as a carbon store. M ...
. Bacteria such as the photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
cyanobacteria, produce internal gas vacuoles, which they use to regulate their buoyancy, allowing them to move up or down into water layers with different light intensities and nutrient levels.
Extracellular structures
Around the outside of the cell membrane is thecell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mec ...
. Bacterial cell walls are made of peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid Cell wall#Bacterial_cell_walls, cell wall (murein sac ...
(also called murein), which is made from polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with ...
chains cross-linked by peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. ...
s containing D-amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s. Bacterial cell walls are different from the cell walls of plant
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
s and fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
, which are made of cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
and chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
, respectively. The cell wall of bacteria is also distinct from that of achaea, which do not contain peptidoglycan. The cell wall is essential to the survival of many bacteria, and the antibiotic penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
(produced by a fungus called ''Penicillium
''Penicillium'' () is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
Some members of the genus produce ...
'') is able to kill bacteria by inhibiting a step in the synthesis of peptidoglycan.
There are broadly speaking two different types of cell wall in bacteria, that classify bacteria into Gram-positive bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bact ...
and Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wa ...
. The names originate from the reaction of cells to the Gram stain
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish ba ...
, a long-standing test for the classification of bacterial species.
Gram-positive bacteria possess a thick cell wall containing many layers of peptidoglycan and teichoic acids. In contrast, Gram-negative bacteria have a relatively thin cell wall consisting of a few layers of peptidoglycan surrounded by a second lipid membrane containing lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer ...
s and lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, sur ...
s. Most bacteria have the Gram-negative cell wall, and only members of the ''Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the ea ...
'' group and actinomycetota
The ''Actinomycetota'' (or ''Actinobacteria'') are a phylum of all gram-positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great economic importance to humans because agriculture and forests depend on their contributions to soi ...
(previously known as the low G+C and high G+C Gram-positive bacteria, respectively) have the alternative Gram-positive arrangement. These differences in structure can produce differences in antibiotic susceptibility; for instance, vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infection ...
can kill only Gram-positive bacteria and is ineffective against Gram-negative pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
s, such as ''Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacte ...
'' or ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aer ...
''. Some bacteria have cell wall structures that are neither classically Gram-positive or Gram-negative. This includes clinically important bacteria such as mycobacteria
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (''M. tuberculosis'') and ...
which have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall like a Gram-positive bacterium, but also a second outer layer of lipids.
In many bacteria, an S-layer An S-layer (surface layer) is a part of the cell envelope found in almost all archaea, as well as in many types of bacteria.
The S-layers of both archaea and bacteria consists of a monomolecular layer composed of only one (or, in a few cases, two) ...
of rigidly arrayed protein molecules covers the outside of the cell. This layer provides chemical and physical protection for the cell surface and can act as a macromolecular
A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biophysical processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. The ...
diffusion barrier A diffusion barrier is a thin layer (usually micrometres thick) of metal usually placed between two other metals. It is done to act as a barrier to protect either one of the metals from corrupting the other..
Adhesion of a plated metal layer to it ...
. S-layers have diverse functions and are known to act as virulence factors in ''Campylobacter
''Campylobacter'' (meaning "curved bacteria") is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. ''Campylobacter'' typically appear comma- or s-shaped, and are motile. Some ''Campylobacter'' species can infect humans, sometimes causing campylobacteriosis, a d ...
'' species and contain surface enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s in ''Bacillus stearothermophilus
''Geobacillus stearothermophilus'' (previously ''Bacillus stearothermophilus'') is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive bacterium and a member of the phylum Bacillota. The bacterium is a thermophile and is widely distributed in soil, hot springs, ocean s ...
''.

Flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
are rigid protein structures, about 20 nanometres in diameter and up to 20 micrometres in length, that are used for motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
. Flagella are driven by the energy released by the transfer of ions down an electrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and t ...
across the cell membrane.
Fimbriae (sometimes called " attachment pili") are fine filaments of protein, usually 2–10 nanometres in diameter and up to several micrometres in length. They are distributed over the surface of the cell, and resemble fine hairs when seen under the electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a ...
. Fimbriae are believed to be involved in attachment to solid surfaces or to other cells, and are essential for the virulence of some bacterial pathogens. Pili Pili may refer to:
Common names of plants
* ''Canarium ovatum'', a Philippine tree that is a source of the pili nut
* ''Heteropogon contortus'', a Hawaiian grass used to thatch structures
Places
* Pili, Camarines Sur, is a municipality in the ...
(''sing''. pilus) are cellular appendages, slightly larger than fimbriae, that can transfer genetic material
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main clas ...
between bacterial cells in a process called conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
* Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change ...
where they are called conjugation pili or sex pili (see bacterial genetics, below). They can also generate movement where they are called type IV pili.
Glycocalyx
The glycocalyx, also known as the pericellular matrix, is a glycoprotein and glycolipid covering that surrounds the cell membranes of bacteria, epithelial cells, and other cells. In 1970, Martinez-Palomo discovered the cell coating in animal cel ...
is produced by many bacteria to surround their cells, and varies in structural complexity: ranging from a disorganised slime layer of extracellular polymeric substance
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) are natural polymers of high molecular weight secreted by microorganisms into their environment. EPSs establish the functional and structural integrity of biofilms, and are considered the fundamental comp ...
s to a highly structured capsule. These structures can protect cells from engulfment by eukaryotic cells such as macrophages (part of the human immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
). They can also act as antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
s and be involved in cell recognition, as well as aiding attachment to surfaces and the formation of biofilms.
The assembly of these extracellular structures is dependent on bacterial secretion system
Bacterial secretion systems are protein complexes present on the cell membranes of bacteria for secretion of substances. Specifically, they are the cellular devices used by pathogenic bacteria to secrete their virulence factors (mainly of protein ...
s. These transfer proteins from the cytoplasm into the periplasm or into the environment around the cell. Many types of secretion systems are known and these structures are often essential for the virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host.
In most, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its ability to ...
of pathogens, so are intensively studied.
Endospores
 Some
Some genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial ...
of Gram-positive bacteria, such as ''Bacillus
''Bacillus'' (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum '' Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacil ...
'', ''Clostridium
''Clostridium'' is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-positive bacteria. Species of ''Clostridium'' inhabit soils and the intestinal tract of animals, including humans. This genus includes several significant human pathogens, including the causative ...
'', '' Sporohalobacter'', ''Anaerobacter
''Anaerobacter'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria related to '' Clostridium''. They are anaerobic chemotrophs and are unusual spore-formers as they produce more than one spore per bacterial cell (up to five). They fix nitrogen
Nitrogen ...
'', and '' Heliobacterium'', can form highly resistant, dormant structures called ''endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not ...
s''. Endospores develop within the cytoplasm of the cell; generally a single endospore develops in each cell. Each endospore contains a core of DNA and ribosomes surrounded by a cortex layer and protected by a multilayer rigid coat composed of peptidoglycan and a variety of proteins.
Endospores show no detectable metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
and can survive extreme physical and chemical stresses, such as high levels of UV light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
, gamma radiation
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically s ...
, detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are m ...
s, disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than s ...
s, heat, freezing, pressure, and desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. ...
. In this dormant state, these organisms may remain viable for millions of years, and endospores even allow bacteria to survive exposure to the vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
and radiation in space, possibly bacteria could be distributed throughout the Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. A ...
by space dust, meteoroid
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mic ...
s, asteroids
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. ...
, comets
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
, planetoids or via directed panspermia
Directed panspermia is the deliberate transport of microorganisms into space to be used as introduced species on lifeless but habitable astronomical objects.
Historically, Shklovskii and Sagan (1966) and Crick and Orgel (1973) hypothesized that li ...
. Endospore-forming bacteria can also cause disease: for example, anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The s ...
can be contracted by the inhalation of ''Bacillus anthracis
''Bacillus anthracis'' is a gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium that causes anthrax, a deadly disease to livestock and, occasionally, to humans. It is the only permanent (obligate) pathogen within the genus '' Bacillus''. Its infection is ...
'' endospores, and contamination of deep puncture wounds with ''Clostridium tetani
''Clostridium tetani'' is a common soil bacterium and the causative agent of tetanus. Vegetative cells of ''Clostridium tetani'' are usually rod-shaped and up to 2.5 μm long, but they become enlarged and tennis racket- or drumstick-shaped when ...
'' endospores causes tetanus
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by '' Clostridium tetani'', and is characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usuall ...
, which like botulism
Botulism is a rare and potentially fatal illness caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium '' Clostridium botulinum''. The disease begins with weakness, blurred vision, feeling tired, and trouble speaking. This may then be followed by weakn ...
is caused by a toxin released by the bacteria that grow from the spores. Clostridioides difficile infection
''Clostridioides difficile'' infection
(CDI or C-diff), also known as ''Clostridium difficile'' infection, is a symptomatic infection due to the spore-forming bacterium ''Clostridioides difficile''. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, fever, na ...
, which is a problem in healthcare settings is also caused by spore-forming bacteria.
Metabolism
Bacteria exhibit an extremely wide variety ofmetabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cel ...
types. The distribution of metabolic traits within a group of bacteria has traditionally been used to define their taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
, but these traits often do not correspond with modern genetic classifications. Bacterial metabolism is classified into nutritional groups on the basis of three major criteria: the source of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
, the electron donor
In chemistry, an electron donor is a chemical entity that donates electrons to another compound. It is a reducing agent that, by virtue of its donating electrons, is itself oxidized in the process.
Typical reducing agents undergo permanent che ...
s used, and the source of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes ...
used for growth.
Bacteria either derive energy from light using photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
(called phototrophy), or by breaking down chemical compounds using oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
(called chemotroph
A Chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic molecule, organic (chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic compound, inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph de ...
y). Chemotrophs use chemical compounds as a source of energy by transferring electrons from a given electron donor to a terminal electron acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mista ...
in a redox reaction
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a de ...
. This reaction releases energy that can be used to drive metabolism. Chemotrophs are further divided by the types of compounds they use to transfer electrons. Bacteria that use inorganic compounds such as hydrogen, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
, or ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogeno ...
as sources of electrons are called lithotroph
Lithotrophs are a diverse group of organisms using an inorganic substrate (usually of mineral origin) to obtain reducing equivalents for use in biosynthesis (e.g., carbon dioxide fixation) or energy conservation (i.e., ATP production) via aerob ...
s, while those that use organic compounds are called organotrophs. The compounds used to receive electrons are also used to classify bacteria: aerobic organism
Aerobic means "requiring air," in which "air" usually means oxygen.
Aerobic may also refer to
* Aerobic exercise, prolonged exercise of moderate intensity
* Aerobics, a form of aerobic exercise
* Aerobic respiration, the aerobic process of ...
s use oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
as the terminal electron acceptor, while anaerobic organisms use other compounds such as nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble ...
, sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic ion, polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salt (chemistry), ...
, or carbon dioxide.
Many bacteria get their carbon from other organic carbon
Total organic carbon (TOC) is the amount of carbon found in an organic compound and is often used as a non-specific indicator of water quality or cleanliness of pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment. TOC may also refer to the amount of organic c ...
, called heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
y. Others such as cyanobacteria and some purple bacteria
Purple bacteria or purple photosynthetic bacteria are Gram-negative proteobacteria that are phototrophic, capable of producing their own food via photosynthesis. They are pigmented with bacteriochlorophyll ''a'' or ''b'', together with various ...
are autotroph
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Works", ...
ic, meaning that they obtain cellular carbon by fixing
Fixing may refer to:
* The present participle of the verb "to fix", an action meaning maintenance, repair, and operations
* "fixing someone up" in the context of arranging or finding a social date for someone
* "Fixing", craving an addictive drug, ...
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
. In unusual circumstances, the gas methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
can be used by methanotroph
Methanotrophs (sometimes called methanophiles) are prokaryotes that metabolize methane as their source of carbon and chemical energy. They are bacteria or archaea, can grow aerobically or anaerobically, and require single-carbon compounds to ...
ic bacteria as both a source of electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary partic ...
s and a substrate for carbon anabolism
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct molecules from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catabolism is the breaking-do ...
.
In many ways, bacterial metabolism provides traits that are useful for ecological stability and for human society. One example is that some bacteria called diazotroph Diazotrophs are bacteria and archaea that fix gaseous nitrogen in the atmosphere into a more usable form such as ammonia.
A diazotroph is a microorganism that is able to grow without external sources of fixed nitrogen. Examples of organisms that ...
s have the ability to fix nitrogen gas using the enzyme nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only fam ...
. This environmentally important trait can be found in bacteria of most metabolic types listed above. This leads to the ecologically important processes of denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitr ...
, sulfate reduction, and acetogenesis Acetogenesis is a process through which acetate is produced either by the reduction of CO2 or by the reduction of organic acids, rather than by the oxidative breakdown of carbohydrates or ethanol, as with acetic acid bacteria.
The different bact ...
, respectively. Bacterial metabolic processes are also important in biological responses to pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
; for example, sulfate-reducing bacteria
Sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) or sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) are a group composed of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfate-reducing archaea (SRA), both of which can perform anaerobic respiration utilizing sulfate () as termin ...
are largely responsible for the production of the highly toxic forms of mercury ( methyl- and dimethylmercury
Dimethylmercury (( C H3)2 Hg) is an extremely toxic organomercury compound. A highly volatile, reactive, flammable, and colorless liquid, dimethylmercury is one of the strongest known neurotoxins, with a quantity of less than 0.1 mL capable of i ...
) in the environment. Non-respiratory anaerobes use fermentation to generate energy and reducing power, secreting metabolic by-products (such as ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a h ...
in brewing) as waste. Facultative anaerobe
A facultative anaerobic organism is an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to fermentation if oxygen is absent.
Some examples of facultatively anaerobic bacteria are ''Staphylococcus' ...
s can switch between fermentation and different terminal electron acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mista ...
s depending on the environmental conditions in which they find themselves.
Growth and reproduction
 Unlike in multicellular organisms, increases in cell size ( cell growth) and reproduction by
Unlike in multicellular organisms, increases in cell size ( cell growth) and reproduction by cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
are tightly linked in unicellular organisms. Bacteria grow to a fixed size and then reproduce through binary fission
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that ta ...
, a form of asexual reproduction. Under optimal conditions, bacteria can grow and divide extremely rapidly, and some bacterial populations can double as quickly as every 17 minutes. In cell division, two identical clone
Clone or Clones or Cloning or Cloned or The Clone may refer to:
Places
* Clones, County Fermanagh
* Clones, County Monaghan, a town in Ireland
Biology
* Clone (B-cell), a lymphocyte clone, the massive presence of which may indicate a pathologi ...
daughter cells are produced. Some bacteria, while still reproducing asexually, form more complex reproductive structures that help disperse the newly formed daughter cells. Examples include fruiting body formation by myxobacteria
The myxobacteria ("slime bacteria") are a group of bacteria that predominantly live in the soil and feed on insoluble organic substances. The myxobacteria have very large genomes relative to other bacteria, e.g. 9–10 million nucleotides except ...
and aerial hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one o ...
e formation by ''Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, ...
'' species, or budding. Budding involves a cell forming a protrusion that breaks away and produces a daughter cell.
In the laboratory, bacteria are usually grown using solid or liquid media. Solid growth media
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss '' Physcomitrella patens''. Diff ...
, such as agar plate
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.
Individual microorganisms placed on the plate w ...
s, are used to isolate pure cultures of a bacterial strain. However, liquid growth media are used when the measurement of growth or large volumes of cells are required. Growth in stirred liquid media occurs as an even cell suspension, making the cultures easy to divide and transfer, although isolating single bacteria from liquid media is difficult. The use of selective media (media with specific nutrients added or deficient, or with antibiotics added) can help identify specific organisms.
Most laboratory techniques for growing bacteria use high levels of nutrients to produce large amounts of cells cheaply and quickly. However, in natural environments, nutrients are limited, meaning that bacteria cannot continue to reproduce indefinitely. This nutrient limitation has led the evolution of different growth strategies (see r/K selection theory
In ecology, ''r''/''K'' selection theory relates to the selection of combinations of traits in an organism that trade off between quantity and quality of offspring. The focus on either an increased quantity of offspring at the expense of individ ...
). Some organisms can grow extremely rapidly when nutrients become available, such as the formation of algal and cyanobacterial
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
blooms that often occur in lakes during the summer. Other organisms have adaptations to harsh environments, such as the production of multiple antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s by streptomyces that inhibit the growth of competing microorganisms. In nature, many organisms live in communities (e.g., biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular ...
s) that may allow for increased supply of nutrients and protection from environmental stresses. These relationships can be essential for growth of a particular organism or group of organisms (syntrophy In biology, syntrophy, synthrophy, or cross-feeding (from Greek ''syn'' meaning together, ''trophe'' meaning nourishment) is the phenomenon of one species feeding on the metabolic products of another species to cope up with the energy limitations by ...
).
Bacterial growth
250px, Growth is shown as ''L'' = log(numbers) where numbers is the number of colony forming units per ml, versus ''T'' (time.)
Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providin ...
follows four phases. When a population of bacteria first enter a high-nutrient environment that allows growth, the cells need to adapt to their new environment. The first phase of growth is the lag phase, a period of slow growth when the cells are adapting to the high-nutrient environment and preparing for fast growth. The lag phase has high biosynthesis rates, as proteins necessary for rapid growth are produced. The second phase of growth is the logarithmic phase, also known as the exponential phase. The log phase is marked by rapid exponential growth
Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a ...
. The rate at which cells grow during this phase is known as the ''growth rate'' (''k''), and the time it takes the cells to double is known as the ''generation time'' (''g''). During log phase, nutrients are metabolised at maximum speed until one of the nutrients is depleted and starts limiting growth. The third phase of growth is the '' stationary phase'' and is caused by depleted nutrients. The cells reduce their metabolic activity and consume non-essential cellular proteins. The stationary phase is a transition from rapid growth to a stress response state and there is increased expression of genes involved in DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
, antioxidant metabolism and nutrient transport. The final phase is the death phase where the bacteria run out of nutrients and die.
Genetics
 Most bacteria have a single circular
Most bacteria have a single circular chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
that can range in size from only 160,000 base pairs in the endosymbiotic
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
bacteria '' Carsonella ruddii'', to 12,200,000 base pairs (12.2 Mbp) in the soil-dwelling bacteria ''Sorangium cellulosum
''Sorangium cellulosum'' is a soil-dwelling Gram-negative bacterium of the group myxobacteria. It is motile and shows gliding motility. Under stressful conditions this motility, as in other myxobacteria, the cells congregate to form fruiting bod ...
''. There are many exceptions to this, for example some ''Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, ...
'' and ''Borrelia
''Borrelia'' is a genus of bacteria of the spirochete phylum. Several species cause Lyme disease, also called Lyme borreliosis, a zoonotic, vector-borne disease transmitted by ticks. Other species of ''Borrelia'' cause relapsing fever, and are t ...
'' species contain a single linear chromosome, while some ''Vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive ...
'' species contain more than one chromosome. Bacteria can also contain plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; howev ...
s, small extra-chromosomal molecules of DNA that may contain genes for various useful functions such as antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistanc ...
, metabolic capabilities, or various virulence factors.
Bacteria genomes usually encode a few hundred to a few thousand genes. The genes in bacterial genomes are usually a single continuous stretch of DNA and although several different types of intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene ...
s do exist in bacteria, these are much rarer than in eukaryotes.
Bacteria, as asexual organisms, inherit an identical copy of the parent's genomes and are clonal. However, all bacteria can evolve by selection on changes to their genetic material DNA caused by genetic recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukary ...
or mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s. Mutations come from errors made during the replication of DNA or from exposure to mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer i ...
s. Mutation rates vary widely among different species of bacteria and even among different clones of a single species of bacteria. Genetic changes in bacterial genomes come from either random mutation during replication or "stress-directed mutation", where genes involved in a particular growth-limiting process have an increased mutation rate.
Some bacteria also transfer genetic material between cells. This can occur in three main ways. First, bacteria can take up exogenous DNA from their environment, in a process called transformation
Transformation may refer to:
Science and mathematics
In biology and medicine
* Metamorphosis, the biological process of changing physical form after birth or hatching
* Malignant transformation, the process of cells becoming cancerous
* Tran ...
. Many bacteria can naturally take up DNA from the environment, while others must be chemically altered in order to induce them to take up DNA. The development of competence in nature is usually associated with stressful environmental conditions, and seems to be an adaptation for facilitating repair of DNA damage in recipient cells. The second way bacteria transfer genetic material is by transduction, when the integration of a bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bact ...
introduces foreign DNA into the chromosome. Many types of bacteriophage exist, some infect and lyse their host bacteria, while others insert into the bacterial chromosome. Bacteria resist phage infection through restriction modification system The restriction modification system (RM system) is found in bacteria and other prokaryotic organisms, and provides a defense against foreign DNA, such as that borne by bacteriophages.
Bacteria have restriction enzymes, also called restriction ...
s that degrade foreign DNA, and a system that uses CRISPR
CRISPR () (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bac ...
sequences to retain fragments of the genomes of phage that the bacteria have come into contact with in the past, which allows them to block virus replication through a form of RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by o ...
. The third method of gene transfer is conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
* Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change ...
, whereby DNA is transferred through direct cell contact. In ordinary circumstances, transduction, conjugation, and transformation involve transfer of DNA between individual bacteria of the same species, but occasionally transfer may occur between individuals of different bacterial species and this may have significant consequences, such as the transfer of antibiotic resistance. In such cases, gene acquisition from other bacteria or the environment is called horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring ( reproduction). ...
and may be common under natural conditions.
Behaviour
Movement
motile
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
(able to move themselves) and do so using a variety of mechanisms. The best studied of these are flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
, long filaments that are turned by a motor at the base to generate propeller-like movement. The bacterial flagellum is made of about 20 proteins, with approximately another 30 proteins required for its regulation and assembly. The flagellum is a rotating structure driven by a reversible motor at the base that uses the electrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and t ...
across the membrane for power.
 Bacteria can use flagella in different ways to generate different kinds of movement. Many bacteria (such as '' E. coli'') have two distinct modes of movement: forward movement (swimming) and tumbling. The tumbling allows them to reorient and makes their movement a three-dimensional
Bacteria can use flagella in different ways to generate different kinds of movement. Many bacteria (such as '' E. coli'') have two distinct modes of movement: forward movement (swimming) and tumbling. The tumbling allows them to reorient and makes their movement a three-dimensional random walk
In mathematics, a random walk is a random process that describes a path that consists of a succession of random steps on some mathematical space.
An elementary example of a random walk is the random walk on the integer number line \mathbb ...
. Bacterial species differ in the number and arrangement of flagella on their surface; some have a single flagellum (''monotrichous
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide Motility#Cellular level, motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A m ...
''), a flagellum at each end ('' amphitrichous''), clusters of flagella at the poles of the cell ('' lophotrichous''), while others have flagella distributed over the entire surface of the cell ('' peritrichous''). The flagella of a unique group of bacteria, the spirochaete
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (), (synonym Spirochaetes) which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or ...
s, are found between two membranes in the periplasmic space. They have a distinctive helical
Helical may refer to:
* Helix
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is ...
body that twists about as it moves.
Two other types of bacterial motion are called twitching motility that relies on a structure called the type IV pilus, and gliding motility Gliding motility is a type of translocation used by microorganisms that is independent of propulsive structures such as flagella, pili, and fimbriae. Gliding allows microorganisms to travel along the surface of low aqueous films. The mechanisms of ...
, that uses other mechanisms. In twitching motility, the rod-like pilus extends out from the cell, binds some substrate, and then retracts, pulling the cell forward.
Motile bacteria are attracted or repelled by certain stimuli in behaviours called ''taxes
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, o ...
'': these include chemotaxis, phototaxis
Phototaxis is a kind of taxis, or locomotory movement, that occurs when a whole organism moves towards or away from a stimulus of light. This is advantageous for phototrophic organisms as they can orient themselves most efficiently to receive l ...
, energy taxis, and magnetotaxis. In one peculiar group, the myxobacteria, individual bacteria move together to form waves of cells that then differentiate to form fruiting bodies containing spores. The myxobacteria move only when on solid surfaces, unlike ''E. coli'', which is motile in liquid or solid media.
Several '' Listeria'' and ''Shigella
''Shigella'' is a genus of bacteria that is Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, non-spore-forming, nonmotile, rod-shaped, and genetically closely related to '' E. coli''. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who first discovered it in 189 ...
'' species move inside host cells by usurping the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is comp ...
, which is normally used to move organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' t ...
s inside the cell. By promoting actin
Actin is a protein family, family of Globular protein, globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in myofibril, muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all Eukaryote, eukaryotic cel ...
polymerisation
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many for ...
at one pole of their cells, they can form a kind of tail that pushes them through the host cell's cytoplasm.
Communication
A few bacteria have chemical systems that generate light. Thisbioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some ...
often occurs in bacteria that live in association with fish, and the light probably serves to attract fish or other large animals.
Bacteria often function as multicellular aggregates known as biofilms
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular po ...
, exchanging a variety of molecular signals for inter-cell communication, and engaging in coordinated multicellular behaviour.
The communal benefits of multicellular cooperation include a cellular division of labour, accessing resources that cannot effectively be used by single cells, collectively defending against antagonists, and optimising population survival by differentiating into distinct cell types. For example, bacteria in biofilms can have more than 500 times increased resistance to antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
agents than individual "planktonic" bacteria of the same species.
One type of inter-cellular communication by a molecular signal is called quorum sensing
In biology, quorum sensing or quorum signalling (QS) is the ability to detect and respond to cell population density by gene regulation. As one example, QS enables bacteria to restrict the expression of specific genes to the high cell densities a ...
, which serves the purpose of determining whether there is a local population density that is sufficiently high that it is productive to invest in processes that are only successful if large numbers of similar organisms behave similarly, as in excreting digestive enzymes or emitting light.
Quorum sensing allows bacteria to coordinate gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. ...
, and enables them to produce, release and detect autoinducer
Autoinducers are signaling molecules that are produced in response to changes in cell-population density. As the density of quorum sensing bacterial cells increases so does the concentration of the autoinducer. Detection of signal molecules by ba ...
s or pheromones
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavi ...
which accumulate with the growth in cell population.
Classification and identification


Classification Classification is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood.
Classification is the grouping of related facts into classes.
It may also refer to:
Business, organizat ...
seeks to describe the diversity of bacterial species by naming and grouping organisms based on similarities. Bacteria can be classified on the basis of cell structure, cellular metabolism or on differences in cell components, such as DNA, fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s, pigments, antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
s and quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds benzene.html" ;"title="uch as benzene">uch as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with ...
s. While these schemes allowed the identification and classification of bacterial strains, it was unclear whether these differences represented variation between distinct species or between strains of the same species. This uncertainty was due to the lack of distinctive structures in most bacteria, as well as lateral gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). H ...
between unrelated species. Due to lateral gene transfer, some closely related bacteria can have very different morphologies and metabolisms. To overcome this uncertainty, modern bacterial classification emphasises molecular systematics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
, using genetic techniques such as guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleobases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached ...
ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
determination, genome-genome hybridisation, as well as sequencing
In genetics and biochemistry, sequencing means to determine the primary structure (sometimes incorrectly called the primary sequence) of an unbranched biopolymer. Sequencing results in a symbolic linear depiction known as a sequence which succi ...
genes that have not undergone extensive lateral gene transfer, such as the rRNA gene. Classification of bacteria is determined by publication in the International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, and Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. The International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology (ICSB) maintains international rules for the naming of bacteria and taxonomic categories and for the ranking of them in the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC) governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea.P. H. A. Sneath, 2003. A short hist ...
.
Historically, bacteria were considered a part of the Plantae
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
, the Plant kingdom, and were called "Schizomycetes" (fission-fungi). For this reason, collective bacteria and other microorganisms in a host are often called "flora".
The term "bacteria" was traditionally applied to all microscopic, single-cell prokaryotes. However, molecular systematics showed prokaryotic life to consist of two separate domains, originally called Eubacteria and Archaebacteria, but now called Bacteria and Archaea that evolved independently from an ancient common ancestor. The archaea and eukaryotes are more closely related to each other than either is to the bacteria. These two domains, along with Eukarya, are the basis of the three-domain system
The three-domain system is a biological classification introduced by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler, and Mark Wheelis in 1990 that divides cellular life forms into three domains, namely Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryota or Eukarya. The key differenc ...
, which is currently the most widely used classification system in microbiology. However, due to the relatively recent introduction of molecular systematics and a rapid increase in the number of genome sequences that are available, bacterial classification remains a changing and expanding field. For example, Cavalier-Smith argued that the Archaea and Eukaryotes evolved from Gram-positive bacteria.
The identification of bacteria in the laboratory is particularly relevant in medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion ...
, where the correct treatment is determined by the bacterial species causing an infection. Consequently, the need to identify human pathogens was a major impetus for the development of techniques to identify bacteria.
The ''Gram stain
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish ba ...
'', developed in 1884 by Hans Christian Gram, characterises bacteria based on the structural characteristics of their cell walls. The thick layers of peptidoglycan in the "Gram-positive" cell wall stain purple, while the thin "Gram-negative" cell wall appears pink. By combining morphology and Gram-staining, most bacteria can be classified as belonging to one of four groups (Gram-positive cocci, Gram-positive bacilli, Gram-negative cocci and Gram-negative bacilli). Some organisms are best identified by stains other than the Gram stain, particularly mycobacteria or ''Nocardia'', which show acid fast
Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacterial and eukaryotic cells, as well as some sub-cellular structures, specifically their resistance to decolorization by acids during laboratory staining procedures. Once stained as part of a ...
ness on Ziehl–Neelsen or similar stains. Other organisms may need to be identified by their growth in special media, or by other techniques, such as serology
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given ...
.
Culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these grou ...
techniques are designed to promote the growth and identify particular bacteria, while restricting the growth of the other bacteria in the sample. Often these techniques are designed for specific specimens; for example, a sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways (the trachea and bronchi). In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections and cytological investigation ...
sample will be treated to identify organisms that cause pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
, while stool specimens are cultured on selective media to identify organisms that cause diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin ...
, while preventing growth of non-pathogenic bacteria. Specimens that are normally sterile, such as blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in th ...
, urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellular ...
or spinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the bra ...
, are cultured under conditions designed to grow all possible organisms. Once a pathogenic organism has been isolated, it can be further characterised by its morphology, growth patterns (such as aerobic or anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to:
*Adhesive#Anaerobic, Anaerobic ad ...
growth), patterns of hemolysis, and staining.
As with bacterial classification, identification of bacteria is increasingly using molecular methods, and mass spectroscopy. Most bacteria have not been characterised and there are may species that cannot be grown in the laboratory. Diagnostics using DNA-based tools, such as polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
, are increasingly popular due to their specificity and speed, compared to culture-based methods. These methods also allow the detection and identification of " viable but nonculturable" cells that are metabolically active but non-dividing. However, even using these improved methods, the total number of bacterial species is not known and cannot even be estimated with any certainty. Following present classification, there are a little less than 9,300 known species of prokaryotes, which includes bacteria and archaea; but attempts to estimate the true number of bacterial diversity have ranged from 107 to 109 total species—and even these diverse estimates may be off by many orders of magnitude.
Phyla
Valid phyla
The following phyla have been validly published according to theBacteriological Code
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC) governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea.P. H. A. Sneath, 2003. A short histor ...
:
* Acidobacteriota
Acidobacteriota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. Its members are physiologically diverse and ubiquitous, especially in soils, but are under-represented in culture.
Description
Members of this phylum are physiologically diverse, and can b ...
* Actinomycetota
The ''Actinomycetota'' (or ''Actinobacteria'') are a phylum of all gram-positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great economic importance to humans because agriculture and forests depend on their contributions to soi ...
* Aquificota
* Armatimonadota
''Armatimonadota'' is a phylum of gram-negative bacteria.
History
''Armatimonadota'' was originally described solely on the basis of environmental 16S rRNA gene clone sequences, and was temporarily titled candidate phylum OP10. However, in 2 ...
* Atribacterota
''Atribacterota'' is a phylum of bacteria, which are common in anoxic sediments rich in methane. They are distributed worldwide and in some cases abundant in anaerobic marine sediments, geothermal springs, and oil deposits. Genetic analyze ...
* Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the ea ...
* Bacteroidota
The phylum Bacteroidota (synonym Bacteroidetes) is composed of three large classes of Gram-negative, nonsporeforming, anaerobic or aerobic, and rod-shaped bacteria that are widely distributed in the environment, including in soil, sediments, and ...
* Balneolota
* Bdellovibrionota
* Caldisericota
* Calditrichota
* Campylobacterota
Campylobacterota are a phylum of bacteria. All species of this phylum are Gram-negative.
The Campylobacterota consist of few known genera, mainly the curved to spirilloid '' Wolinella'' spp., '' Helicobacter'' spp., and ''Campylobacter'' spp. Mo ...
* Chlamydiota
The Chlamydiota (synonym Chlamydiae) are a bacterial phylum and class whose members are remarkably diverse, including pathogens of humans and animals, symbionts of ubiquitous protozoa, and marine sediment forms not yet well understood. All of ...
* Chlorobiota
The green sulfur bacteria are a phylum of obligately anaerobic photoautotrophic bacteria that metabolize sulfur.
Green sulfur bacteria are nonmotile (except ''Chloroherpeton thalassium'', which may glide) and capable of anoxygenic photosynthesi ...
* Chloroflexota
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for phot ...
* Chrysiogenota
* Coprothermobacterota
* Deferribacterota
The Deferribacteraceae are a family of gram-negative bacteria which make energy by anaerobic respiration.Huber, H., and Stetter, K.O. "Family I. ''Deferribacteraceae'' fam. nov." In: Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed., vol. 1 (T ...
* Deinococcota
''Deinococcota'' (synonym, ''Deinococcus-Thermus'') is a phylum of bacteria with a single class, ''Deinococci'', that are highly resistant to environmental hazards, also known as extremophiles.
These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them ...
* Dictyoglomota
* Elusimicrobiota
* Fibrobacterota
* Fusobacteriota
* Gemmatimonadota
* Ignavibacteriota
* Lentisphaerota
* Mycoplasmatota
* Myxococcota
* Nitrospinota
* Nitrospirota
Nitrospirota is a phylum of bacteria. It includes multiple genera, such as '' Nitrospira'', the largest. The first member of this phylum, '' Nitrospira marina'', was discovered in 1985. The second member, '' Nitrospira moscoviensis'', was discove ...
* Planctomycetota
The Planctomycetota are a phylum of widely distributed bacteria, occurring in both aquatic and terrestrial habitats. They play a considerable role in global carbon and nitrogen cycles, with many species of this phylum capable of anaerobic ammoniu ...
* Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The ...
* Rhodothermota
* Spirochaetota
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (), (synonym Spirochaetes) which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or ...
* Synergistota
* Thermodesulfobacteriota
The Thermodesulfobacteriota are a phylum of thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria.
A pathogenic intracellular thermodesulfobacteriote has recently been identified.
Phylogeny
The phylogeny is based on phylogenomic analysis:
See also
* ...
* Thermomicrobiota
* Thermotogota
* Verrucomicrobiota
Verrucomicrobiota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated specie ...
Provisional phyla
The following phyla have been proposed, but have not been validly published according to the Bacteriological Code (including those that have ''candidatus
In prokaryote nomenclature, ''Candidatus'' (Latin for candidate of Roman office) is used to name prokaryotic phyla that are well characterized but yet-uncultured. Contemporary sequencing approaches, such as 16S sequencing or metagenomics, provid ...
'' status):
* "''Candidatus'' Abawacabacteria"
* "Abditibacteriota
Abditibacteriota is a bacterial phylum previously known as FBP candidatus, which is widespread in extreme environments on Earth, from polar and desert ecosystems to wastewater and contaminated mining sites. The first cultured representative came ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Absconditabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Acetothermia"
* "''Candidatus'' Adlerbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Aerophobetes"
* "''Candidatus'' Amesbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Aminicenantes"
* "''Candidatus'' Andersenbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Azambacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Beckwithbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Berkelbacteria
Berkelbacteria (formerly ACD58) is a bacterial phylum with candidate status, meaning there are no cultured representatives for this group. It is part of the Candidate Phyla Radiation.
Berkelbacteria was first reported in 2012, at which time it ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Binatota"
* "''Candidatus'' Bipolaricaulota"
* "''Candidatus'' Blackallbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Blackburnbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Brennerbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Brownbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Buchananbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Caldatribacteriota"
* "''Candidatus'' Calescamantes"
* "''Candidatus'' Campbellbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Chisholmbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Cloacimonetes"
* "''Candidatus'' Coatesbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Collierbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Colwellbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Cryosericota"
* "''Candidatus'' Curtissbacteria"
* " Cyanobacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Dadabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Daviesbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Delongbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Delphibacteria
Delphibacteria is a candidate bacterial phylum in the FCB group. The phylum was first proposed after analysis of two genomes from the mouths of two bottlenose dolphins. "Dephibacteria" was proposed in recognition of the first genomic representat ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Dependentiae"
* "''Candidatus'' Desantisbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Dojkabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Dormibacteraeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Doudnabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Edwardsbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Eisenbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Elulimicrobiota"
* "''Candidatus'' Eremiobacterota"
* "''Candidatus'' Falkowbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Fermentibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Fertabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Fervidibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Firestonebacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Fischerbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Fraserbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Genascibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Giovannonibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Glassbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Goldbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Gottesmanbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Gracilibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Gribaldobacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Handelsmanbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Harrisonbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Howlettbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Hugbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Hydrogenedentes"
* "''Candidatus'' Hydrothermae"
* "''Candidatus'' Hydrothermota"
* "''Candidatus'' Jacksonbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Jorgensenbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Kaiserbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Kapabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Katanobacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Kerfeldbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Komeilibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Krumholzibacteriota"
* "''Candidatus'' Kryptonia"
* "''Candidatus'' Kuenenbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Lambdaproteobacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Latescibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Levybacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Lindowbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Liptonbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Lloydbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Magasanikbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Margulisbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Marinimicrobia"
* "''Candidatus'' Mcinerneyibacteriota"
* "''Candidatus'' Melainabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Microgenomates"
* "''Candidatus'' Modulibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Moisslbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Montesolbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Moranbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Muirbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Muproteobacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Nealsonbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Niyogibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Nomurabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Omnitrophica"
* "''Candidatus'' Pacebacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Parcubacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Parcunitrobacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Peregrinibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Poribacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Portnoybacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Pyropristinus"
* "''Candidatus'' Ratteibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Raymondbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Riflebacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Roizmanbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Rokubacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Ryanbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Saccharibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Saganbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Schekmanbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Shapirobacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Spechtbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Stahlbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Staskawiczbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Sumerlaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Sungbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Tagabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Taylorbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Tectomicrobia"
* "''Candidatus'' Terrybacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Teskebacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Tianyabacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Torokbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Uhrbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Veblenbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Vogelbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Wallbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Wildermuthbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Wirthbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Woesebacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Wolfebacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Woykebacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Yanofskybacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Yonathbacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Zambryskibacteria"
* "''Candidatus'' Zixibacteria"
Genera ''incertae sedis''
The following bacteria genera have not been assigned to a phylum, class, or order: * "Fermentobadaceae" Haiying 1995 ** "Guhaiyingella" Haiying 1995 * Not assigned to a family: ** "''Candidatus'' Aegiribacteria" Hamilton et al. 2016 ** Archaeoscillatoriopsis Schopf 1993 ** "Eoleptonema" Awramik et al. 1983 ** "''Candidatus'' Epulonipiscium" corrig. Montgomery and Pollak 1988 ** "''Candidatus'' Ovibacter" corrig. Fenchel and Thar 2004 ** "''Primaevifilum''" Schopf 1983 ** "''Rappaport (bacterium), Rappaport''" Waldman Ben-Asher et al. 2017Interactions with other organisms
 Despite their apparent simplicity, bacteria can form complex associations with other organisms. These symbiosis, symbiotic associations can be divided into parasitism, Mutualism (biology), mutualism and commensalism.
Despite their apparent simplicity, bacteria can form complex associations with other organisms. These symbiosis, symbiotic associations can be divided into parasitism, Mutualism (biology), mutualism and commensalism.
Commensals
The word "commensalism" is derived from the word "commensal", meaning "eating at the same table" and all plants and animals are colonised by commensal bacteria. In humans and other animals millions of them live on the skin, the airways, the gut and other orifices. Referred to as "normal flora", or "commensals", these bacteria usually cause no harm but may occasionally invade other sites of the body and cause infection. ''Escherichia coli'' is a commensal in the human gut but can cause urinary tract infections. Similarly, streptoccoci, which are part of the normal flora of the human mouth, can cause subacute bacterial endocarditis, heart disease.Predators
Some species of bacteria kill and then consume other microorganisms, these species are called ''predatory bacteria''. These include organisms such as ''Myxococcus xanthus'', which forms swarms of cells that kill and digest any bacteria they encounter. Other bacterial predators either attach to their prey in order to digest them and absorb nutrients or invade another cell and multiply inside the cytosol. These predatory bacteria are thought to have evolved from Detritivore, saprophages that consumed dead microorganisms, through adaptations that allowed them to entrap and kill other organisms.Mutualists
Certain bacteria form close spatial associations that are essential for their survival. One such mutualistic association, called interspecies hydrogen transfer, occurs between clusters of anaerobic bacteria that consume organic acids, such as butyric acid or propionic acid, and produce hydrogen, and methanogenic archaea that consume hydrogen. The bacteria in this association are unable to consume the organic acids as this reaction produces hydrogen that accumulates in their surroundings. Only the intimate association with the hydrogen-consuming archaea keeps the hydrogen concentration low enough to allow the bacteria to grow. In soil, microorganisms that reside in the Rhizosphere (ecology), rhizosphere (a zone that includes the root surface and the soil that adheres to the root after gentle shaking) carry out nitrogen fixation, converting nitrogen gas to nitrogenous compounds. This serves to provide an easily absorbable form of nitrogen for many plants, which cannot fix nitrogen themselves. Many other bacteria are found as symbionts Bacteria in the human body, in humans and other organisms. For example, the presence of over 1,000 bacterial species in the normal human gut flora of the intestines can contribute to gut immunity, synthesise vitamins, such as folic acid, vitamin K and biotin, convert Milk protein, sugars to lactic acid (see ''Lactobacillus''), as well as fermenting complex undigestible carbohydrates. The presence of this gut flora also inhibits the growth of potentially pathogenic bacteria (usually through competitive exclusion) and these beneficial bacteria are consequently sold as probiotic dietary supplements. Nearly all Life, animal life is dependent on bacteria for survival as only bacteria and some archaea possess the genes and enzymes necessary to synthesize Vitamin B12, vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, and provide it through the food chain. Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that is involved in themetabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
of every cell of the human body. It is a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA replication, DNA synthesis, and in both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It is particularly important in the normal functioning of the nervous system via its role in the myelinogenesis, synthesis of myelin.
Pathogens
 The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decomposition, decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immune system, immunity or innate immunity, innate resistance against many microorganisms. Unlike some
The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decomposition, decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immune system, immunity or innate immunity, innate resistance against many microorganisms. Unlike some virus
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and ...
es, bacteria evolve relatively slowly so many bacterial diseases also occur in other animals.
If bacteria form a parasitic association with other organisms, they are classed as pathogens. Pathogenic bacteria are a major cause of human death and disease and cause infections such as tetanus
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by '' Clostridium tetani'', and is characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usuall ...
(caused by ''Clostridium tetani
''Clostridium tetani'' is a common soil bacterium and the causative agent of tetanus. Vegetative cells of ''Clostridium tetani'' are usually rod-shaped and up to 2.5 μm long, but they become enlarged and tennis racket- or drumstick-shaped when ...
''), typhoid fever, diphtheria, syphilis, cholera, foodborne illness, leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria '' Mycobacterium leprae'' or '' Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve da ...
(caused by ''Mycobacterium leprae'') and tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
(caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''). A pathogenic cause for a known medical disease may only be discovered many years later, as was the case with ''Helicobacter pylori'' and Timeline of peptic ulcer disease and Helicobacter pylori, peptic ulcer disease. Bacterial diseases are also important in agriculture, with bacteria causing leaf spot, fire blight and Wilting, wilts in plants, as well as Johne's disease, Mastitis in dairy cattle, mastitis, salmonellosis, salmonella and anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The s ...
in farm animals.
 Each species of pathogen has a characteristic spectrum of interactions with its human host (biology), hosts. Some organisms, such as ''Staphylococcus'' or ''Streptococcus'', can cause skin infections,
Each species of pathogen has a characteristic spectrum of interactions with its human host (biology), hosts. Some organisms, such as ''Staphylococcus'' or ''Streptococcus'', can cause skin infections, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
, meningitis and sepsis, a systemic Inflammation, inflammatory response producing shock (circulatory), shock, massive vasodilator, vasodilation and death. Yet these organisms are also part of the normal human flora and usually exist on the skin or in the nose without causing any disease at all. Other organisms invariably cause disease in humans, such as ''Rickettsia'', which are obligate intracellular parasites able to grow and reproduce only within the cells of other organisms. One species of ''Rickettsia'' causes typhus, while another causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever. ''Chlamydia (bacterium), Chlamydia'', another phylum of obligate intracellular parasites, contains species that can cause pneumonia or urinary tract infection and may be involved in coronary heart disease. Some species, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aer ...
'', ''Burkholderia cenocepacia'', and ''Mycobacterium avium complex, Mycobacterium avium'', are opportunistic infection, opportunistic pathogens and cause disease mainly in people who are immunosuppression, immunosuppressed or have cystic fibrosis. Some bacteria produce Microbial toxin, toxins, which cause diseases. These are endotoxins, which come from broken bacterial cells, and exotoxins, which are produced by bacteria and released into the environment. The bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' for example, produces a powerful exotoxin that cause respiratory paralysis, and ''Salmonellae'' produce an endotoxin that causes gastroenteritis. Some exotoxins can be converted to toxoids, which are used as vaccines to prevent the disease.
Bacterial infections may be treated with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s, which are classified as Bactericide, bacteriocidal if they kill bacteria or bacteriostatic if they just prevent bacterial growth. There are many types of antibiotics, and each class enzyme inhibitor, inhibits a process that is different in the pathogen from that found in the host. An example of how antibiotics produce selective toxicity are chloramphenicol and puromycin, which inhibit the bacterial ribosome, but not the structurally different eukaryotic ribosome. Antibiotics are used both in treating human disease and in intensive farming to promote animal growth, where they may be contributing to the rapid development of antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistanc ...
in bacterial populations. Infections can be prevented by antiseptic measures such as sterilising the skin prior to piercing it with the needle of a syringe, and by proper care of indwelling catheters. Surgical and dental instruments are also sterilization (microbiology), sterilised to prevent contamination by bacteria. Disinfectants such as bleach are used to kill bacteria or other pathogens on surfaces to prevent contamination and further reduce the risk of infection.
Significance in technology and industry
Bacteria, often lactic acid bacteria, such as ''Lactobacillus'' species and ''Lactococcus'' species, in combination with yeasts and Mold (fungus), moulds, have been used for thousands of years in the preparation of fermentation (food), fermented foods, such ascheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During product ...
, Pickling, pickles, soy sauce, sauerkraut, vinegar, wine and yogurt
Yogurt (; , from tr, yoğurt, also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial fermentation of milk. The bacteria used to make yogurt are known as ''yogurt cultures''. Fermentation of sugars in the milk by these bact ...
.
The ability of bacteria to degrade a variety of organic compounds is remarkable and has been used in waste processing and bioremediation. Bacteria capable of digesting the hydrocarbons in petroleum are often used to clean up oil spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into ...
s. Fertiliser was added to some of the beaches in Prince William Sound in an attempt to promote the growth of these naturally occurring bacteria after the 1989 Exxon Valdez oil spill, ''Exxon Valdez'' oil spill. These efforts were effective on beaches that were not too thickly covered in oil. Bacteria are also used for the bioremediation of industrial toxic wastes. In the chemical industry, bacteria are most important in the production of enantiomerically pure chemicals for use as pharmaceutical company, pharmaceuticals or agrichemicals.
Bacteria can also be used in the place of pesticides in the biological pest control. This commonly involves ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (also called BT), a Gram-positive, soil dwelling bacterium. Subspecies of this bacteria are used as a Lepidopteran-specific insecticides under trade names such as Dipel and Thuricide. Because of their specificity, these pesticides are regarded as environmentally friendly, with little or no effect on humans, wildlife, pollinators and most other beneficial insects.
Because of their ability to quickly grow and the relative ease with which they can be manipulated, bacteria are the workhorses for the fields of molecular biology, genetics and biochemistry. By making mutations in bacterial DNA and examining the resulting phenotypes, scientists can determine the function of genes, enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
s and metabolic pathways in bacteria, then apply this knowledge to more complex organisms. This aim of understanding the biochemistry of a cell reaches its most complex expression in the synthesis of huge amounts of enzyme kinetics, enzyme kinetic and gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. ...
data into mathematical models of entire organisms. This is achievable in some well-studied bacteria, with models of ''Escherichia coli'' metabolism now being produced and tested. This understanding of bacterial metabolism and genetics allows the use of biotechnology to bioengineering, bioengineer bacteria for the production of therapeutic proteins, such as insulin, growth factors, or antibody, antibodies.
Because of their importance for research in general, samples of bacterial strains are isolated and preserved in Biological Resource Centers. This ensures the availability of the strain to scientists worldwide.
History of bacteriology
Bacteria were first observed by the Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1676, using a single-lens microscope of his own design. He then published his observations in a series of letters to the Royal Society of London. Bacteria were Leeuwenhoek's most remarkable microscopic discovery. They were just at the limit of what his simple lenses could make out and, in one of the most striking hiatuses in the history of science, no one else would see them again for over a century. His observations had also included protozoans which he called animalcules, and his findings were looked at again in the light of the more recent findings of cell theory. Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg introduced the word "bacterium" in 1828. In fact, his ''Bacterium (genus), Bacterium'' was a genus that contained non-spore-forming rod-shaped bacteria, as opposed to ''Bacillus'', a genus of spore-forming rod-shaped bacteria defined by Ehrenberg in 1835. Louis Pasteur demonstrated in 1859 that the growth of microorganisms causes the fermentation (food), fermentation process, and that this growth is not due to spontaneous generation (yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, commonly associated with fermentation, are not bacteria, but ratherfungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
). Along with his contemporary Robert Koch, Pasteur was an early advocate of the germ theory of disease. Before them, Ignaz Semmelweis and Joseph Lister had realised the importance of sanitized hands in medical work. Semmelweis ideas was rejected and his book on the topic condemned by the medical community, but after Lister doctors started sanitizing their hands in the 1870s. While Semmelweis who started with rules about handwashing in his hospital in the 1840s predated the spread of the ideas about germs themselves and attributed diseases to "decomposing animal organic matter", Lister was active later.
Robert Koch, a pioneer in medical microbiology, worked on cholera, anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The s ...
and tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
. In his research into tuberculosis Koch finally proved the germ theory, for which he received a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel Prize in 1905. In Koch's postulates, he set out criteria to test if an organism is the cause of a disease, and these postulates are still used today.
Ferdinand Cohn is said to be a founder of bacteriology, studying bacteria from 1870. Cohn was the first to classify bacteria based on their morphology.
Though it was known in the nineteenth century that bacteria are the cause of many diseases, no effective antiseptic, antibacterial treatments were available. In 1910, Paul Ehrlich developed the first antibiotic, by changing dyes that selectively stained ''Treponema pallidum''—the spirochaete
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (), (synonym Spirochaetes) which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or ...
that causes syphilis—into compounds that selectively killed the pathogen. Ehrlich had been awarded a 1908 Nobel Prize for his work on immunology, and pioneered the use of stains to detect and identify bacteria, with his work being the basis of the Gram stain
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish ba ...
and the Ziehl–Neelsen stain.
A major step forward in the study of bacteria came in 1977 when Carl Woese recognised that archaea have a separate line of evolutionary descent from bacteria. This new phylogenetic taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
depended on the sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA, and divided prokaryotes into two evolutionary domains, as part of the three-domain system
The three-domain system is a biological classification introduced by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler, and Mark Wheelis in 1990 that divides cellular life forms into three domains, namely Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryota or Eukarya. The key differenc ...
.
See also
* Genetically modified bacteria * Marine prokaryotesReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * *External links
On-line text book on bacteriology (2015)
{{Authority control Bacteria, Bacteriology Domains (biology)