Bacillus Thuringiensis Ssp. Aizawai on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
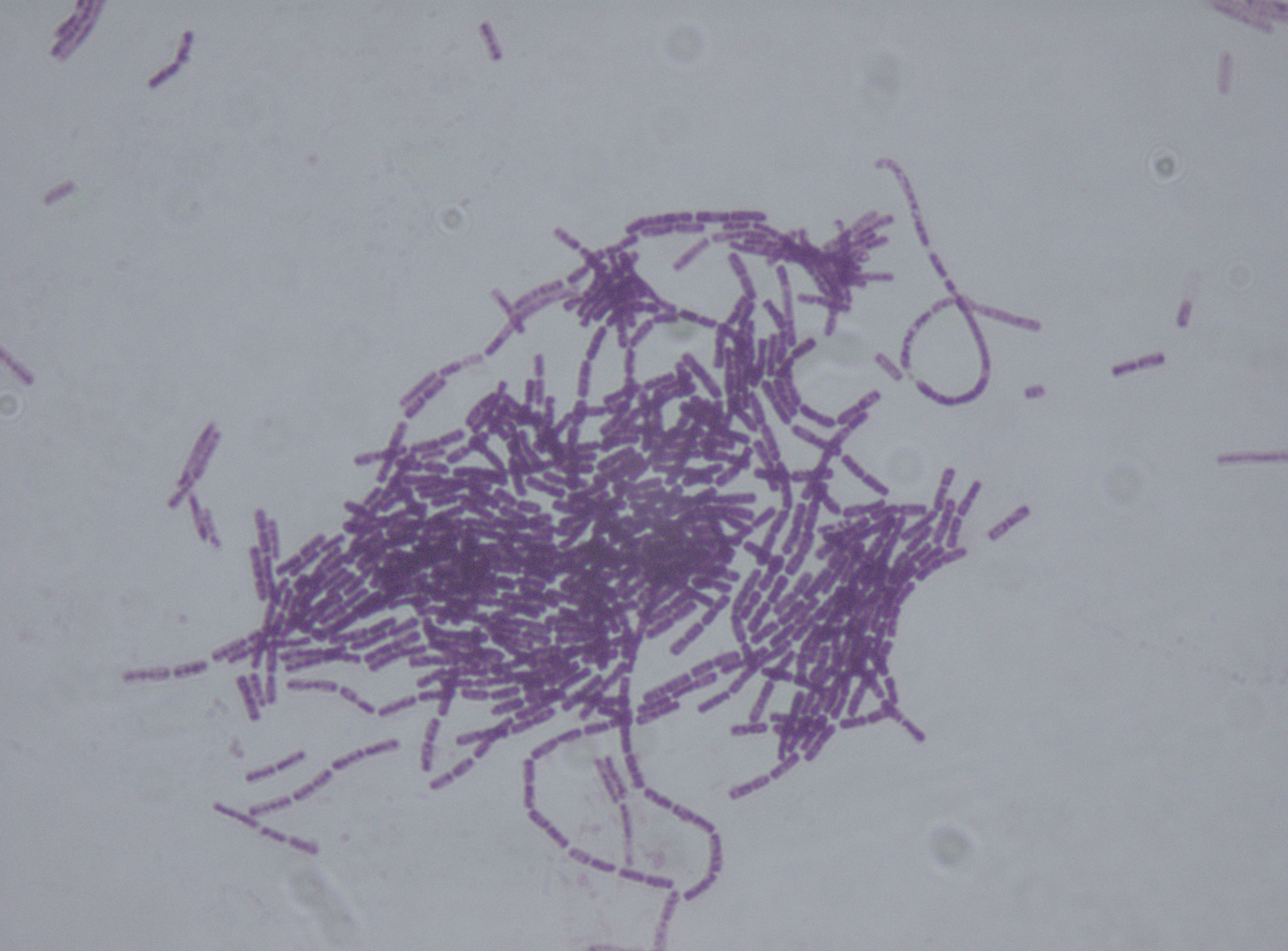 ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of
Bacillus thuringiensis Fact Sheet
/ref> The insect stops eating and starves to death; live Bt bacteria may also colonize the insect, which can contribute to death. Death occurs within a few hours or weeks. The midgut bacteria of susceptible larvae may be required for ''B. thuringiensis'' insecticidal activity. A ''B. thuringiensis'' small RNA called BtsR1 can silence the Cry5Ba toxin expression when outside the host by binding to the RBS site of the Cry5Ba toxin transcript to avoid nematode behavioral defenses. The silencing results in an increase of the bacteria ingestion by '' C. elegans''. The expression of BtsR1 is then reduced after ingestion, resulting in Cry5Ba toxin production and host death. In 1996 another class of insecticidal proteins in Bt was discovered: the vegetative insecticidal proteins (Vip; ). Vip proteins do not share sequence homology with Cry proteins, in general do not compete for the same receptors, and some kill different insects than do Cry proteins. In 2000, a novel subgroup of Cry protein, designated parasporin, was discovered from non-insecticidal ''B. thuringiensis'' isolates. The proteins of parasporin group are defined as ''B. thuringiensis'' and related bacterial parasporal proteins that are not hemolytic, but capable of preferentially killing cancer cells. As of January 2013, parasporins comprise six subfamilies: PS1 to PS6.
GM crops: Battlefield
Nature 461, 27-32 (2009) Similarly, ''B. thuringiensis'' has been widely used for controlling '' Spodoptera littoralis'' larvae growth due to their detrimental pest activities in Africa and Southern Europe. However, '' S. littoralis'' showed resistance to many strains of ''B. thuriginesis'' and were only effectively controlled by a few strains.
 * Biological insecticides
* Genetically modified food
*
* Biological insecticides
* Genetically modified food
*
Bacillus thuringiensis General Fact Sheet
(National Pesticide Information Center)
Bacillus thuringiensis Technical Fact Sheet
(National Pesticide Information Center)
Research project and results
The Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Specificity Database
at Natural Resources Canada
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' Taxonomy (NIH)
Bacillus thuringiensis
genomes and related information a
PATRIC
a Bioinformatics Resource Center funded b
NIAID
bEcon - Economics literature about the impacts of genetically engineered (GE) crops in developing economies
Type strain of ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase
{{Taxonbar, from=Q310467 thuringiensis Biopesticides Genetically modified organisms in agriculture Bacteria described in 1915
 ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sym ...
s of various types of moths and butterflies
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the Order (biology), order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The ...
, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as '' Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite.
During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal protein
Protein crystallization is the process of formation of a regular array of individual protein molecules stabilized by crystal contacts. If the crystal is sufficiently ordered, it will diffract. Some proteins naturally form crystalline arrays, lik ...
s (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of ''Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of ...
using Bt genes, such as Bt corn
Genetically modified maize (corn) is a genetically modified crop. Specific maize strains have been genetically engineered to express agriculturally-desirable traits, including resistance to pests and to herbicides. Maize strains with both trait ...
. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control of mosquitoes and of fungus gnat
Fungus gnats are small, dark, short-lived gnats, of the families Sciaridae, Diadocidiidae, Ditomyiidae, Keroplatidae, Bolitophilidae, and Mycetophilidae (order Diptera); they comprise six of the seven families placed in the superfamily Sciaroide ...
s.
As a toxic mechanism, ''cry'' proteins bind to specific receptors on the membranes of mid-gut ( epithelial) cells of the targeted pests, resulting in their rupture. Other organisms (including humans, other animals and non-targeted insects) that lack the appropriate receptors in their gut cannot be affected by the ''cry'' protein, and therefore are not affected by Bt.
Taxonomy and discovery
In 1902, ''B. thuringiensis'' was first discovered insilkworm
The domestic silk moth (''Bombyx mori''), is an insect from the moth family Bombycidae. It is the closest relative of ''Bombyx mandarina'', the wild silk moth. The silkworm is the larva or caterpillar of a silk moth. It is an economically imp ...
s by Japanese sericultural engineer . He named it ''B. sotto'', using the Japanese word , here referring to bacillary paralysis. In 1911, German microbiologist Ernst Berliner
Ernst Berliner (15 September 1880–October 1957) was a German scientist with contributions to microbiology, entomology, and biochemistry.
Life and career
Ernst Berliner was born in Berlin to Albrecht Berliner and Hedwig (née Koppen). He attend ...
rediscovered it when he isolated it as the cause of a disease called ' in flour moth caterpillars in Thuringia (hence the specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
''thuringiensis'', "Thuringian"). ''B. sotto'' would later be reassigned as ''B. thuringiensis'' var. ''sotto''.
In 1976, Robert A. Zakharyan reported the presence of a plasmid in a strain of ''B. thuringiensis'' and suggested the plasmid's involvement in endospore and crystal formation. ''B. thuringiensis'' is closely related to ''B. cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are ha ...
'', a soil bacterium, and ''B. anthracis
''Bacillus anthracis'' is a gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium that causes anthrax, a deadly disease to livestock and, occasionally, to humans. It is the only permanent (obligate) pathogen within the genus '' Bacillus''. Its infection is a ...
'', the cause of anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium ''Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The sk ...
; the three organisms differ mainly in their plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; how ...
s. Like other members of the genus, all three are anaerobe
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenate ...
s capable of producing endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., no ...
s.
Species group placement
''B. thuringiensis'' is placed in the ''Bacillus cereus'' group which is variously defined as: seven closely related species: ''B. cereus'' ''sensu stricto'' ('' B. cereus''), '' B. anthracis'', ''B. thuringiensis'', '' B. mycoides'', '' B. pseudomycoides'', and '' B. cytotoxicus''; or as six species in a ''Bacillus cereus'' sensu lato: '' B. weihenstephanensis'', ''B. mycoides'', ''B. pseudomycoides'', ''B. cereus'', ''B. thuringiensis'', and ''B. anthracis''. Within this grouping ''B.t.'' is more closely related to ''B.ce.'' It is more distantly related to ''B.w.'', ''B.m.'', ''B.p.'', and ''B.cy.''Subspecies
There are several dozen recognized subspecies of ''B. thuringiensis''. Subspecies commonly used as insecticides include ''B. thuringiensis'' subspecies ''kurstaki'' (Btk), subspecies '' israelensis'' (Bti) and (Bta). Some Bti lineages are clonal.Genetics
Some strains are known to carry the same genes that produce enterotoxins in ''B. cereus'', and so it is possible that the entire ''B. cereus'' sensu lato group may have the potential to beenteropathogen
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydr ...
s.
The proteins that ''B. thuringiensis'' is most known for are encoded by ''cry'' genes. In most strains of ''B. thuringiensis'', these genes are located on a plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; how ...
(in other words ''cry'' is not a chromosomal gene in most strains). If these plasmids are lost it becomes indistinguishable from ''B. cereus'' as ''B. thuringiensis'' has no other species characteristics. Plasmid exchange has been observed both naturally and experimentally both within ''B.t.'' and between ''B.t.'' and two congeners, ''B. cereus'' and ''B. mycoides''.
plcR
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are har ...
is an indispensable transcription regulator
In molecular biology and genetics, transcriptional regulation is the means by which a cell regulates the conversion of DNA to RNA (transcription), thereby orchestrating gene activity. A single gene can be regulated in a range of ways, from al ...
of most virulence factors, its absence greatly reducing virulence and toxicity. Some strains do naturally complete their life cycle with an inactivated plcR. It is half of a two-gene operon along with the heptapeptide . papR is part of quorum sensing in ''B. thuringiensis''.
Various strains including ''Btk'' ATCC 33679 carry plasmids belonging to the wider pXO1-like family. (The pXO1 family being a ''B. cereus''-common family with members of ≈330kb length. They differ from pXO1 by replacement of the pXO1 pathogenicity island.) The insect parasite ''Btk'' HD73 carries a pXO2-like plasmid PXO may refer to:
*Prospective Executive Officer, in Prospective Commanding Officer
*Professor X the Overseer, a hip-hop musician
*IATA airport code for Porto Santo Airport
*Parallax Online, a provider of free services over the internet in FreeSpac ...
( pBT9727) lacking the 35kb pathogenicity island of pXO2 itself, and in fact having no identifiable virulence factors. (The pXO2 family does not have replacement of the pathogenicity island, instead simply lacking that part of pXO2.)
The genomes of the ''B. cereus'' group may contain two types of intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene. ...
s, dubbed group I and group II. ''B.t'' strains have variously 0-5 group Is and 0-13 group IIs.
There is still insufficient information to determine whether chromosome-plasmid coevolution
In biology, coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection. The term sometimes is used for two traits in the same species affecting each other's evolution, as well ...
to enable adaptation to particular environmental niches has occurred or is even possible.
Common with ''B. cereus'' but so far not found elsewhere - including in other members of the species group - are the efflux pump BC3663, the ''N''-acyl--amino-acid amidohydrolase BC3664, and the methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein BC5034
Highway 5 is a north–south route in southern British Columbia, Canada. Highway 5 connects the southern Trans-Canada route (Highway 1) with the northern Trans-Canada/Yellowhead route (Highway 16), providing the shortest land connection between ...
.
Proteome
Has similar proteome diversity to close relative ''B. cereus''.Mechanism of insecticidal action
Upon sporulation, ''B. thuringiensis'' forms crystals of two types of proteinaceous insecticidal delta endotoxins (δ-endotoxins) called crystal proteins or Cry proteins, which are encoded by ''cry'' genes, andCyt protein
Delta endotoxins (δ-endotoxins) are pore-forming toxins produced by ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' species of bacteria. They are useful for their insecticidal action and are the primary toxin produced by Bt maize/corn. During spore formation ...
s.
Cry toxins have specific activities against insect species of the orders Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) is an order (biology), order of insects that includes butterfly, butterflies and moths (both are called lepidopterans). About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 Family (biology), families and 46 Taxonomic r ...
(moths and butterflies), Diptera
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...
(flies and mosquitoes), Coleoptera
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...
(beetles) and Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order (biology), order of insects, comprising the sawfly, sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are Par ...
( wasps, bee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyly, monophyletic lineage within the ...
s, ants and sawflies), as well as against nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...
s. Thus, ''B. thuringiensis'' serves as an important reservoir of Cry toxins for production of biological insecticides and insect-resistant genetically modified crops
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of ''Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of ...
. When insects ingest toxin crystals, their alkaline digestive tracts denature the insoluble crystals, making them soluble and thus amenable to being cut with proteases found in the insect gut, which liberate the toxin from the crystal. The Cry toxin is then inserted into the insect gut cell membrane, paralyzing the digestive tract and forming a pore.W.S. Cranshaw, Colorado State University Extension Office. Last updated March 26, 2013Bacillus thuringiensis Fact Sheet
/ref> The insect stops eating and starves to death; live Bt bacteria may also colonize the insect, which can contribute to death. Death occurs within a few hours or weeks. The midgut bacteria of susceptible larvae may be required for ''B. thuringiensis'' insecticidal activity. A ''B. thuringiensis'' small RNA called BtsR1 can silence the Cry5Ba toxin expression when outside the host by binding to the RBS site of the Cry5Ba toxin transcript to avoid nematode behavioral defenses. The silencing results in an increase of the bacteria ingestion by '' C. elegans''. The expression of BtsR1 is then reduced after ingestion, resulting in Cry5Ba toxin production and host death. In 1996 another class of insecticidal proteins in Bt was discovered: the vegetative insecticidal proteins (Vip; ). Vip proteins do not share sequence homology with Cry proteins, in general do not compete for the same receptors, and some kill different insects than do Cry proteins. In 2000, a novel subgroup of Cry protein, designated parasporin, was discovered from non-insecticidal ''B. thuringiensis'' isolates. The proteins of parasporin group are defined as ''B. thuringiensis'' and related bacterial parasporal proteins that are not hemolytic, but capable of preferentially killing cancer cells. As of January 2013, parasporins comprise six subfamilies: PS1 to PS6.
Use of spores and proteins in pest control
Spores and crystalline insecticidal proteins produced by ''B. thuringiensis'' have been used to control insect pests since the 1920s and are often applied as liquid sprays. They are now used as specificinsecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
s under trade names such as DiPel and Thuricide. Because of their specificity, these pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampri ...
s are regarded as environmentally friendly, with little or no effect on humans, wildlife, pollinator
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.
Insects are the maj ...
s, and most other beneficial insects, and are used in organic farming; however, the manuals for these products do contain many environmental and human health warnings, and a 2012 European regulatory peer review of five approved strains found, while data exist to support some claims of low toxicity to humans and the environment, the data are insufficient to justify many of these claims.
New strains of Bt are developed and introduced over time as insects develop resistance to Bt, or the desire occurs to force mutations to modify organism characteristics, or to use homologous recombinant genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including t ...
to improve crystal size and increase pesticidal activity, or broaden the host range of Bt and obtain more effective formulations. Each new strain is given a unique number and registered with the U.S. EPA and allowances may be given for genetic modification depending on "its parental strains, the proposed pesticide use pattern, and the manner and extent to which the organism has been genetically modified". Formulations of Bt that are approved for organic farming in the US are listed at the website of the Organic Materials Review Institute
Organic may refer to:
* Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity
* Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ
Chemistry
* Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product o ...
(OMRI) and several university extension websites offer advice on how to use Bt spore or protein preparations in organic farming.
Use of Bt genes in genetic engineering of plants for pest control
The Belgian companyPlant Genetic Systems
Plant Genetic Systems (PGS), since 2002 part of Bayer CropScience, is a biotech company located in Ghent, Belgium. The focus of its activities is the genetic engineering of plants. The company is best known for its work in the development of inse ...
(now part of Bayer CropScience) was the first company (in 1985) to develop genetically modified crops
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of ''Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of ...
( tobacco) with insect tolerance by expressing ''cry'' genes from ''B. thuringiensis''; the resulting crops contain delta endotoxin. The Bt tobacco was never commercialized; tobacco plants are used to test genetic modifications since they are easy to manipulate genetically and are not part of the food supply.
Usage
In 1985, were approved safe by theEnvironmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
, making it the first human-modified pesticide-producing crop to be approved in the US, though many plants produce pesticides naturally, including tobacco, coffee plants, cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
, and black walnut
''Juglans nigra'', the eastern American black walnut, is a species of deciduous tree in the walnut family, Juglandaceae, native to North America. It grows mostly in riparian zones, from southern Ontario, west to southeast South Dakota, south t ...
. This was the 'New Leaf' potato, and it was removed from the market in 2001 due to lack of interest.
In 1996, was approved, which killed the European corn borer and related species; subsequent Bt genes were introduced that killed corn rootworm larvae.
The Bt genes engineered into crops and approved for release include, singly and stacked: Cry1A.105, CryIAb, CryIF, Cry2Ab, Cry3Bb1, Cry34Ab1, Cry35Ab1, mCry3A, and VIP, and the engineered crops include corn and cotton.
Corn genetically modified to produce VIP was first approved in the US in 2010.
In India, by 2014, more than seven million cotton farmers, occupying twenty-six million acres, had adopted .
Monsanto developed a and the glyphosate-resistance gene for the Brazilian market, which completed the Brazilian regulatory process in 2010.
- specifically ''Populus
''Populus'' is a genus of 25–30 species of deciduous flowering plants in the family Salicaceae, native to most of the Northern Hemisphere. English names variously applied to different species include poplar (), aspen, and cottonwood.
The we ...
'' hybrids - have been developed. They do suffer lesser leaf damage from insect herbivory. The results have not been entirely positive however: The intended result - better timber yield - was not achieved, with no growth advantage despite that reduction in herbivore damage; one of their major pests still preys upon the transgenic trees; and besides that, their leaf litter decomposes differently due to the transgenic toxins, resulting in alterations to the aquatic insect
Aquatic insects or water insects live some portion of their life cycle in the water. They feed in the same ways as other insects. Some ''diving'' insects, such as predatory diving beetles, can hunt for food underwater where land-living insects c ...
populations nearby.
Safety studies
The use of Bt toxins as plant-incorporated protectants prompted the need for extensive evaluation of their safety for use in foods and potential unintended impacts on the environment.Dietary risk assessment
Concerns over the safety of consumption of genetically modified plant materials that contain Cry proteins have been addressed in extensive dietary risk assessment studies. As a toxic mechanism, ''cry'' proteins bind to specific receptors on the membranes of mid-gut ( epithelial) cells of the targeted pests, resulting in their rupture. While the target pests are exposed to the toxins primarily through leaf and stalk material, Cry proteins are also expressed in other parts of the plant, including trace amounts in maize kernels which are ultimately consumed by both humans and animals. However, other organisms (including humans, other animals and non-targeted insects) that lack the appropriate receptors in their gut cannot be affected by the ''cry'' protein, and therefore are not affected by Bt.=Toxicology studies
= Animal models have been used to assess human health risk from consumption of products containing Cry proteins. The United States Environmental Protection Agency recognizes mouse acute oral feeding studies where doses as high as 5,000 mg/kg body weight resulted in no observed adverse effects. Research on other known toxic proteins suggests that , further suggesting that Bt toxins are not toxic to mammals. The results of toxicology studies are further strengthened by the lack of observed toxicity from decades of use of ''B. thuringiensis'' and its crystalline proteins as an insecticidal spray.=Allergenicity studies
= Introduction of a new protein raised concerns regarding the potential for allergic responses in sensitive individuals. Bioinformatic analysis of known allergens has indicated there is no concern of allergic reactions as a result of consumption of Bt toxins. Additionally,skin prick testing
Skin allergy testing comprises a range of methods for medical diagnosis of allergies that attempts to provoke a small, controlled, allergic response.
Methods
A microscopic amount of an allergen is introduced to a patient's skin by various mean ...
using purified Bt protein resulted in no detectable production of toxin-specific IgE antibodies, even in atopic patients.
=Digestibility studies
= Studies have been conducted to evaluate the fate of Bt toxins that are ingested in foods. Bt toxin proteins have been shown to digest within minutes of exposure to simulated gastric fluids. The instability of the proteins in digestive fluids is an additional indication that Cry proteins are unlikely to be allergenic, since most known food allergens resist degradation and are ultimately absorbed in the small intestine.Ecological risk assessment
Ecological risk assessment aims to ensure there is no unintended impact on non-target organisms and no contamination of natural resources as a result of the use of a new substance, such as the use of Bt in genetically modified crops. The impact of Bt toxins on the environments where transgenic plants are grown has been evaluated to ensure no adverse effects outside of targeted crop pests.=Persistence in environment
= Concerns over possible environmental impact from accumulation of Bt toxins from plant tissues, pollen dispersal, and direct secretion from roots have been investigated. Bt toxins may persist in soil for over 200 days, with half-lives between 1.6 and 22 days. Much of the toxin is initially degraded rapidly by microorganisms in the environment, while some is adsorbed by organic matter and persists longer. Some studies, in contrast, claim that the toxins do not persist in the soil. Bt toxins are less likely to accumulate in bodies of water, but pollen shed orsoil runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water occurring on the ground surface when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when the s ...
may deposit them in an aquatic ecosystem. Fish species are not susceptible to Bt toxins if exposed.
=Impact on non-target organisms
= The toxic nature of Bt proteins has an adverse impact on many major crop pests, but ecological risk assessments have been conducted to ensure safety of beneficial non-target organisms that may come into contact with the toxins. Widespread concerns over toxicity in non-target lepidopterans, such as the monarch butterfly, have been disproved through proper exposure characterization, where it was determined that non-target organisms are not exposed to high enough amounts of the Bt toxins to have an adverse effect on the population. Soil-dwelling organisms, potentially exposed to Bt toxins through root exudates, are not impacted by the growth of Bt crops.Insect resistance
Multiple insects have developed a resistance to ''B. thuringiensis''. In November 2009, Monsanto scientists found thepink bollworm
The pink bollworm (''Pectinophora gossypiella''; es, lagarta rosada) is an insect known for being a pest in cotton farming. The adult is a small, thin, gray moth with fringed wings. The larva is a dull white caterpillar with eight pairs of legs w ...
had become resistant to the first-generation Bt cotton in parts of Gujarat, India - that generation expresses one Bt gene, ''Cry1Ac''. This was the first instance of Bt resistance confirmed by Monsanto anywhere in the world. Monsanto responded by introducing a second-generation cotton with multiple Bt proteins, which was rapidly adopted. Bollworm resistance to first-generation Bt cotton was also identified in Australia, China, Spain, and the United States. Additionally, resistance to Bt was documented in field population of diamondback moth in Hawaii, the continental US, and Asia. Studies in the cabbage looper have suggested that a mutation in the membrane transporter ABCC2 can confer resistance to Bt ''Cry1Ac''.
Secondary pests
Several studies have documented surges in "sucking pests" (which are not affected by Bt toxins) within a few years of adoption of Bt cotton. In China, the main problem has been withmirids
The Miridae are a large and diverse insect family at one time known by the taxonomic synonym Capsidae. Species in the family may be referred to as capsid bugs or "mirid bugs". Common names include plant bugs, leaf bugs, and grass bugs. It is the ...
, which have in some cases "completely eroded all benefits from Bt cotton cultivation". The increase in sucking pests depended on local temperature and rainfall conditions and increased in half the villages studied. The increase in insecticide use for the control of these secondary insects was far smaller than the reduction in total insecticide use due to Bt cotton adoption. Another study in five provinces in China found the reduction in pesticide use in Bt cotton cultivars is significantly lower than that reported in research elsewhere, consistent with the hypothesis suggested by recent studies that more pesticide sprayings are needed over time to control emerging secondary pests, such as aphids, spider mites, and lygus bugs.
Similar problems have been reported in India, with both mealy bugs
Mealybugs are insects in the family (biology), family Pseudococcidae, unarmored scale insects found in moist, warm habitats. Many species are considered pest (animal), pests as they feed on plant juices of greenhouse plants, house plants and sub ...
and aphids although a survey of small Indian farms between 2002 and 2008 concluded Bt cotton adoption has led to higher yields and lower pesticide use, decreasing over time.
Controversies
The controversies surrounding Bt use are among the many genetically modified food controversies more widely.Lepidopteran toxicity
The most publicised problem associated with Bt crops is the claim that pollen from Bt maize could kill themonarch butterfly
The monarch butterfly or simply monarch (''Danaus plexippus'') is a milkweed butterfly (subfamily Danainae) in the family Nymphalidae. Other common names, depending on region, include milkweed, common tiger, wanderer, and black-veined brown. It ...
. The paper produced a public uproar and demonstrations against Bt maize; however by 2001 several follow-up studies coordinated by the USDA had asserted that "the most common types of Bt maize pollen are not toxic to monarch larvae in concentrations the insects would encounter in the fields."Emily Waltz for Nature News. September 2, 200GM crops: Battlefield
Nature 461, 27-32 (2009) Similarly, ''B. thuringiensis'' has been widely used for controlling '' Spodoptera littoralis'' larvae growth due to their detrimental pest activities in Africa and Southern Europe. However, '' S. littoralis'' showed resistance to many strains of ''B. thuriginesis'' and were only effectively controlled by a few strains.
Wild maize genetic mixing
A study published in ''Nature'' in 2001 reported Bt-containing maize genes were found in maize in its center of origin, Oaxaca, Mexico. Another ''Nature'' paper published in 2002 claimed that the previous paper's conclusion was the result of anartifact Artifact, or artefact, may refer to:
Science and technology
* Artifact (error), misleading or confusing alteration in data or observation, commonly in experimental science, resulting from flaws in technique or equipment
** Compression artifact, a ...
caused by an inverse polymerase chain reaction and that "the evidence available is not sufficient to justify the publication of the original paper." A significant controversy happened over the paper and ''Nature''s unprecedented notice.
A subsequent large-scale study in 2005 failed to find any evidence of genetic mixing in Oaxaca. A 2007 study found the "transgenic proteins expressed in maize were found in two (0.96%) of 208 samples from farmers' fields, located in two (8%) of 25 sampled communities." Mexico imports a substantial amount of maize from the U.S., and due to formal and informal seed networks among rural farmers, many potential routes are available for transgenic maize to enter into food and feed webs. One study found small-scale (about 1%) introduction of transgenic sequences in sampled fields in Mexico; it did not find evidence for or against this introduced genetic material being inherited by the next generation of plants. That study was immediately criticized, with the reviewer writing, "Genetically, any given plant should be either non-transgenic or transgenic, therefore for leaf tissue of a single transgenic plant, a GMO level close to 100% is expected. In their study, the authors chose to classify leaf samples as transgenic despite GMO levels of about 0.1%. We contend that results such as these are incorrectly interpreted as positive and are more likely to be indicative of contamination in the laboratory."
Colony collapse disorder
As of 2007, a new phenomenon called colony collapse disorder (CCD) began affectingbee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyly, monophyletic lineage within the ...
hives all over North America. Initial speculation on possible causes included new parasites, pesticide use, and the use of Bt transgenic crops. The Mid-Atlantic Apiculture Research and Extension Consortium
The Mid-Atlantic Apiculture Research and Extension Consortium (MAAREC), established in 1997, is a regional group focused on addressing the pest management crisis facing the beekeeping industry in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. A ...
found no evidence that pollen from Bt crops is adversely affecting bees. According to the USDA, "Genetically modified (GM) crops, most commonly Bt corn, have been offered up as the cause of CCD. But there is no correlation between where GM crops are planted and the pattern of CCD incidents. Also, GM crops have been widely planted since the late 1990s, but CCD did not appear until 2006. In addition, CCD has been reported in countries that do not allow GM crops to be planted, such as Switzerland. German researchers have noted in one study a possible correlation between exposure to Bt pollen and compromised immunity to '' Nosema''." The actual cause of CCD was unknown in 2007, and scientists believe it may have multiple exacerbating causes.
Beta-exotoxins
Some isolates of ''B. thuringiensis'' produce a class of insecticidal small molecules called beta-exotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, simi ...
, the common name for which is thuringiensin. A consensus document produced by the OECD says: "Beta-exotoxins are known to be toxic to humans and almost all other forms of life and its presence is prohibited in ''B. thuringiensis'' microbial products". Thuringiensins are nucleoside analogues. They inhibit RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
activity, a process common to all forms of life, in rats and bacteria alike.
Other hosts
Opportunistic pathogen of animals other than insects, causingnecrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
, pulmonary infection, and/or food poisoning
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease) ...
. How common this is, is unknown, because these are always taken to be ''B. cereus'' infections and are rarely tested for the ''Cry'' and ''Cyt'' proteins that are the only factor distinguishing ''B. thuringiensis'' from ''B. cereus''.
See also
 * Biological insecticides
* Genetically modified food
*
* Biological insecticides
* Genetically modified food
* Western corn rootworm
The Western corn rootworm, ''Diabrotica virgifera virgifera'', is one of the most devastating corn rootworm species in North America, especially in the midwestern corn-growing areas such as Iowa. A related species, the Northern corn rootworm, ...
* Cry1Ac
* Diamondback moth
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
Bacillus thuringiensis General Fact Sheet
(National Pesticide Information Center)
Bacillus thuringiensis Technical Fact Sheet
(National Pesticide Information Center)
Research project and results
The Bacillus thuringiensis Toxin Specificity Database
at Natural Resources Canada
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' Taxonomy (NIH)
Bacillus thuringiensis
genomes and related information a
PATRIC
a Bioinformatics Resource Center funded b
NIAID
bEcon - Economics literature about the impacts of genetically engineered (GE) crops in developing economies
Type strain of ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase
{{Taxonbar, from=Q310467 thuringiensis Biopesticides Genetically modified organisms in agriculture Bacteria described in 1915