Babylon High School on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babili''
*
Kassite
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon ...
: ''Karanduniash'', ''Karduniash''
, image = Street in Babylon.jpg
, image_size=250px
, alt = A partial view of the ruins of Babylon
, caption = A partial view of the ruins of Babylon
, map_type = Near East#West Asia#Iraq
, relief = yes
, map_alt = Babylon lies in the center of Iraq
, coordinates =
, location = Hillah
Hillah ( ar, ٱلْحِلَّة ''al-Ḥillah''), also spelled Hilla, is a city in central Iraq on the Hilla branch of the Euphrates River, south of Baghdad. The population is estimated at 364,700 in 1998. It is the capital of Babylon Province a ...
, Babil Governorate
Babil Governorate or Babylon Province ( ar, محافظة بابل ''Muḥāfaẓa Bābil'') is a governorate in central Iraq. It has an area of , with an estimated population of 2,065,042 people in 2018. The provincial capital is the city of Hill ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, region = Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
, type = Settlement
, part_of = Babylonia
, length =
, width =
, area =
, height =
, builder =
, material =
, built =
, abandoned =
, epochs =
, cultures = Sumerian, Akkadian, Amorite, Kassite, Assyrian, Chaldean, Achaemenid, Hellenistic, Parthian, Sasanian, Muslim
, dependency_of =
, occupants =
, event =
, excavations =
, archaeologists = Hormuzd Rassam
Hormuzd Rassam ( ar, هرمز رسام; syr, ܗܪܡܙܕ ܪܣܐܡ; 182616 September 1910), was an Assyriologist and author.
He is known for making a number of important archaeological discoveries from 1877 to 1882, including the clay tablets tha ...
, Robert Koldewey
Robert Johann Koldewey (10 September 1855 – 4 February 1925) was a German archaeologist, famous for his in-depth excavation of the ancient city of Babylon in modern-day Iraq. He was born in Blankenburg am Harz in Germany, the duchy of Brunswick, ...
, Taha Baqir
Taha Baqir ( ar, طه باقر ') (born 1912 in Babylon, Ottoman Iraq – 28 February 1984) was an Iraqi Assyriologist, author, cuneiformist, linguist, historian, and former curator of the National Museum of Iraq.
Baqir is considered one of Iraq' ...
, recent Iraqi Assyriologist
Assyriology (from Greek , ''Assyriā''; and , ''-logia'') is the archaeological, anthropological, and linguistic study of Assyria and the rest of ancient Mesopotamia (a region that encompassed what is now modern Iraq, northeastern Syria, southea ...
, condition = Ruined
, ownership = Public
, management =
, website =
, notes =
, embedded=
Babylon was the capital city of the ancient Babylonian Empire
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state ...
, which itself is a term referring to either of two separate empires in the Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
n area in antiquity. These two empires achieved regional dominance between the 19th and 15th centuries BC, and again between the 7th and 6th centuries BC. The city, built along both banks of the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
river, had steep embankments to contain the river's seasonal floods. The site of the ancient city lies just south of present-day Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
.
The earliest known mention of Babylon as a small town appears on a clay tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets ( Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age.
Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a sty ...
from the reign of Sargon of Akkad (2334–2279 BC) of the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad () and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one ...
. Babylon was merely a religious and cultural centre at this point and neither an independent state nor a large city; like the rest of Mesopotamia, it was subject to the Akkadian Empire which united all the Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule. After the collapse of the Akkadian Empire, the south Mesopotamian region was dominated by the Gutian people
The Guti () or Quti, also known by the derived exonyms Gutians or Guteans, were a nomadic people of West Asia, around the Zagros Mountains (Modern Iran) during ancient times. Their homeland was known as Gutium ( Sumerian: ,''Gu-tu-umki'' or ,' ...
for a few decades before the rise of the Third Dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC ( middle chronology) Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider t ...
, which, apart from northern Assyria, encompassed the whole of Mesopotamia, including the town of Babylon.
The town became part of a small independent city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
with the rise of the first Babylonian Empire, now known as the Old Babylonian Empire, in the 19th century BC. The Amorite
The Amorites (; sux, 𒈥𒌅, MAR.TU; Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒊒𒌝 or 𒋾𒀉𒉡𒌝/𒊎 ; he, אֱמוֹרִי, 'Ĕmōrī; grc, Ἀμορραῖοι) were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the Levant who also occupied la ...
king Hammurabi
Hammurabi (Akkadian: ; ) was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from to BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered Elam and the city-states ...
founded the short-lived Old Babylonian Empire
The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to BC – BC, and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty ...
in the 18th century BC. He built Babylon into a major city and declared himself its king. Southern Mesopotamia became known as Babylonia, and Babylon eclipsed Nippur as the region's holy city. The empire waned under Hammurabi's son Samsu-iluna
Samsu-iluna (Amorite: ''Shamshu''; c. 1750–1712 BC) was the seventh king of the founding Amorite dynasty of Babylon, ruling from 1750 BC to 1712 BC ( middle chronology), or from 1686 to 1648 BC (short chronology). He was the son and successor of ...
, and Babylon spent long periods under Assyrian, Kassite
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon ...
and Elamite domination. After the Assyrians had destroyed and then rebuilt it, Babylon became the capital of the short-lived Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bei ...
, a neo-Assyrian
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
successor state, from 609 to 539 BC. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon ranked as one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity. The first known list of seven wonders dates back to the 2 ...
. After the fall of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, the city came under the rule of the Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
, Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, Parthian, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
, and Muslim empires. The last known record of habitation of the town dates from the 10th century AD, when it was referred to as the "small village of Babel".
It has been estimated that Babylon was the largest city in the world , and again . It was perhaps the first city to reach a population above 200,000.Tertius Chandler. ''Four Thousand Years of Urban Growth: An Historical Census'' (1987), St. David's University Press (). . See Historical urban community sizes. Estimates for the maximum extent of its area range from 890 to .
The remains of the city are in present-day Hillah
Hillah ( ar, ٱلْحِلَّة ''al-Ḥillah''), also spelled Hilla, is a city in central Iraq on the Hilla branch of the Euphrates River, south of Baghdad. The population is estimated at 364,700 in 1998. It is the capital of Babylon Province a ...
, Babil Governorate
Babil Governorate or Babylon Province ( ar, محافظة بابل ''Muḥāfaẓa Bābil'') is a governorate in central Iraq. It has an area of , with an estimated population of 2,065,042 people in 2018. The provincial capital is the city of Hill ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, about south of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
, and its boundaries have been based on the perimeter of the ancient outer city walls, an area of about . They comprise a large tell of broken mud-brick buildings and debris. The main sources of information about Babylon—excavation of the site itself, references in cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sh ...
texts found elsewhere in Mesopotamia, references in the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
, descriptions in other classical writing (especially by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
), and second-hand descriptions (citing the work of Ctesias
Ctesias (; grc-gre, Κτησίας; fl. fifth century BC), also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Historical events
Ctesias, who lived in the fi ...
and Berossus
Berossus () or Berosus (; grc, Βηρωσσος, Bērōssos; possibly derived from akk, , romanized: , "Bel is his shepherd") was a Hellenistic-era Babylonian writer, a priest of Bel Marduk and astronomer who wrote in the Koine Greek language ...
)—present an incomplete and sometimes contradictory picture of the ancient city, even at its peak in the sixth century BC. UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
inscribed Babylon as a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 2019. The site receives thousands of visitors each year, almost all of whom are Iraqis. Construction is rapidly increasing, which has caused encroachments on the ruins.
Name
The spelling ''Babylon'' is the Latin representation ofGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''Babylṓn'' (), derived from the native ( Babylonian) ', meaning "gate of the god(s)".
The cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sh ...
spelling was (KA₂.DIG̃IR.RA). This would correspond to the Sumerian phrase ''kan dig̃irak''.
The sign 𒆍 (KA₂) is the logogram for "gate", 𒀭 ( DIG̃IR) means "god", and 𒊏 (RA) represents the coda of the word ''dig̃ir'' (-r) followed by the genitive suffix ''-ak''. The final 𒆠 ( ) is a determinative indicating that the previous signs are to be understood as a place name.
Archibald Sayce
The Rev. Archibald Henry Sayce (25 September 18454 February 1933) was a pioneer British Assyriologist and linguist, who held a chair as Professor of Assyriology at the University of Oxford from 1891 to 1919. He was able to write in at least twe ...
, writing in the 1870s, postulated that the Semitic name was a loan-translation of the original Sumerian name.
However, the "gate of god" interpretation is increasingly viewed as a Semitic folk etymology to explain an unknown original non-Semitic placename. I. J. Gelb
Ignace Jay Gelb (October 14, 1907, Tarnau, Austria-Hungary (now Tarnów, Poland) - December 22, 1985, Chicago, Illinois) was a Polish-American ancient historian and Assyriologist who pioneered the scientific study of writing systems.
Early lif ...
in 1955 argued that the original name was ''Babilla'', of unknown meaning and origin, as there were other similarly named places in Sumer, and there are no other examples of Sumerian place-names being replaced with Akkadian translations. He deduced that it later transformed into Akkadian ', and that the Sumerian name ''Kan-dig̃irak'' was a loan translation of the Semitic folk etymology, and not the original name. The re-translation of the Semitic name into Sumerian would have taken place at the time of the "Neo-Sumerian" Third Dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC ( middle chronology) Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider t ...
. (''Bab- Il'').
In the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' בָּבֶל ''Bavel'', Tib. ''Bāḇel''; syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāwēl'', arc, בבל Bāḇel; in ar, بَابِل ''Bābil''), interpreted in the


 The ancient city, built along both banks of the
The ancient city, built along both banks of the
 The main sources of information about Babylon—excavation of the site itself, references in
The main sources of information about Babylon—excavation of the site itself, references in
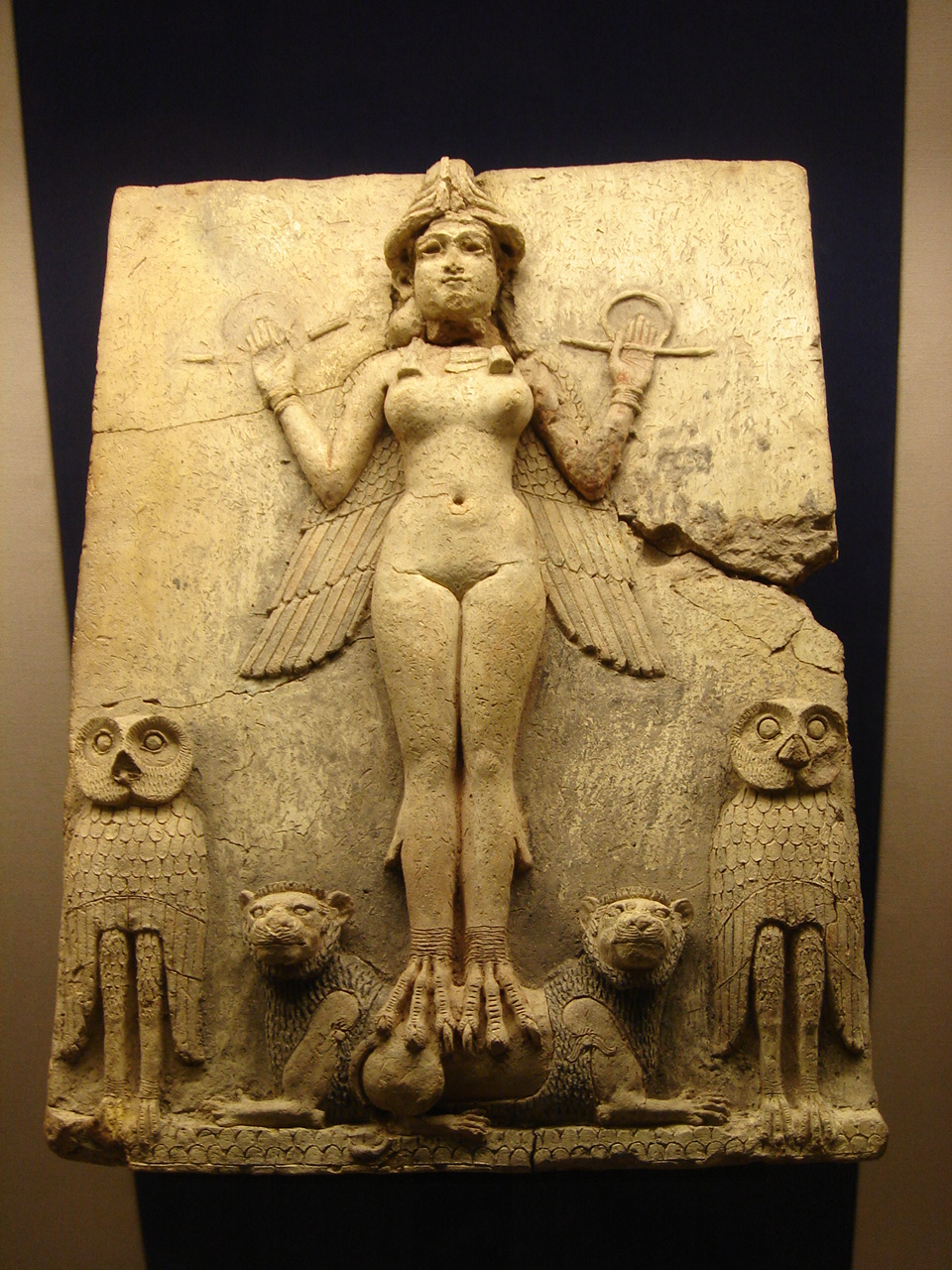 The first attested mention of Babylon was in the late 3rd millennium BC during the Akkadian Empire reign of ruler
The first attested mention of Babylon was in the late 3rd millennium BC during the Akkadian Empire reign of ruler
 According to a Babylonian king list,
According to a Babylonian king list,
 During the rule of the
During the rule of the
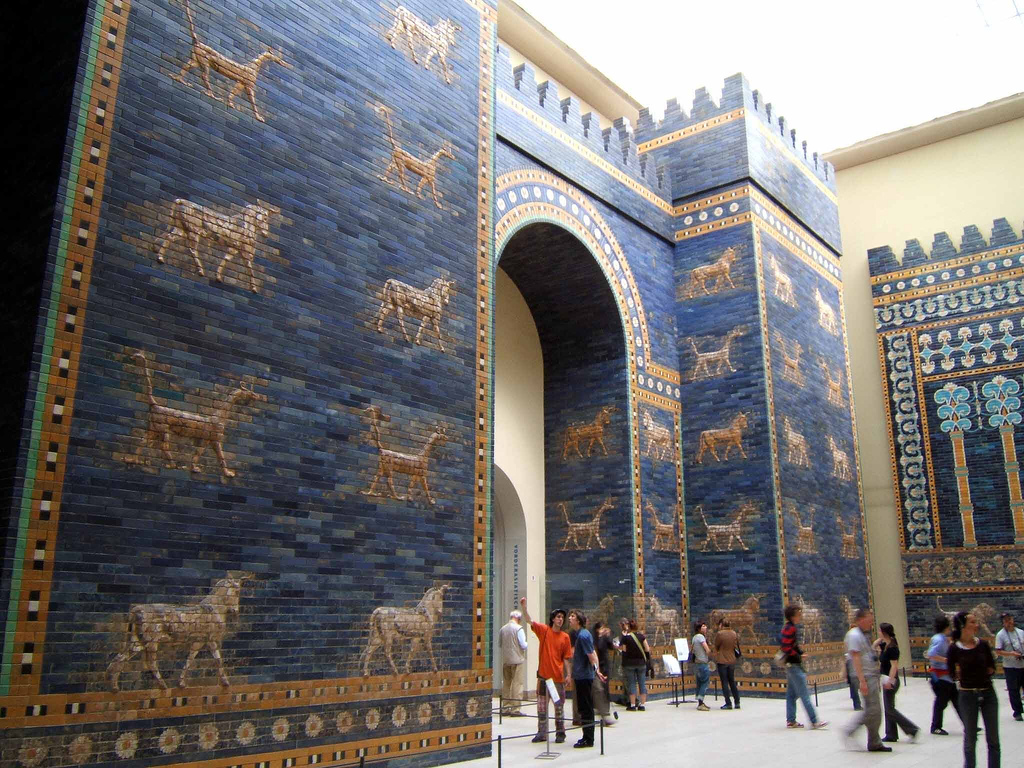

 Under Nabopolassar, Babylon escaped Assyrian rule, and the allied Medo-Babylonian armies finally destroyed the Assyrian Empire between 626 BC and 609 BC. Babylon thus became the capital of the Neo-Babylonian (sometimes called the Chaldean) Empire.
With the recovery of Babylonian independence, a new era of architectural activity ensued, particularly during the reign of his son Nebuchadnezzar II (604–561 BC). Nebuchadnezzar ordered the complete reconstruction of the imperial grounds, including the Etemenanki ziggurat, and the construction of the Ishtar Gate—the most prominent of eight gates around Babylon. A reconstruction of the Ishtar Gate is located in the Pergamon Museum in Berlin.
Nebuchadnezzar is also credited with the construction of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the
Under Nabopolassar, Babylon escaped Assyrian rule, and the allied Medo-Babylonian armies finally destroyed the Assyrian Empire between 626 BC and 609 BC. Babylon thus became the capital of the Neo-Babylonian (sometimes called the Chaldean) Empire.
With the recovery of Babylonian independence, a new era of architectural activity ensued, particularly during the reign of his son Nebuchadnezzar II (604–561 BC). Nebuchadnezzar ordered the complete reconstruction of the imperial grounds, including the Etemenanki ziggurat, and the construction of the Ishtar Gate—the most prominent of eight gates around Babylon. A reconstruction of the Ishtar Gate is located in the Pergamon Museum in Berlin.
Nebuchadnezzar is also credited with the construction of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the
 According to Books of Chronicles, 2 Chronicles 36 of the
According to Books of Chronicles, 2 Chronicles 36 of the
Excavated and Unexcavated Libraries in Babylon
", in Cancik-Kirschbaum et al. (2011), pp. 47–67. said to have been used in cities from Baghdad to Basra.Julian E. Reade, "Disappearance and rediscovery"; in Finkel & Seymour, eds., ''Babylon'' (2009); pp. 13–30. European travellers, in many cases, could not discover the city's location, or mistook Fallujah for it. Benjamin of Tudela, a 12th-century traveller, mentions Babylon, but it is not clear if he went there. Others referred to
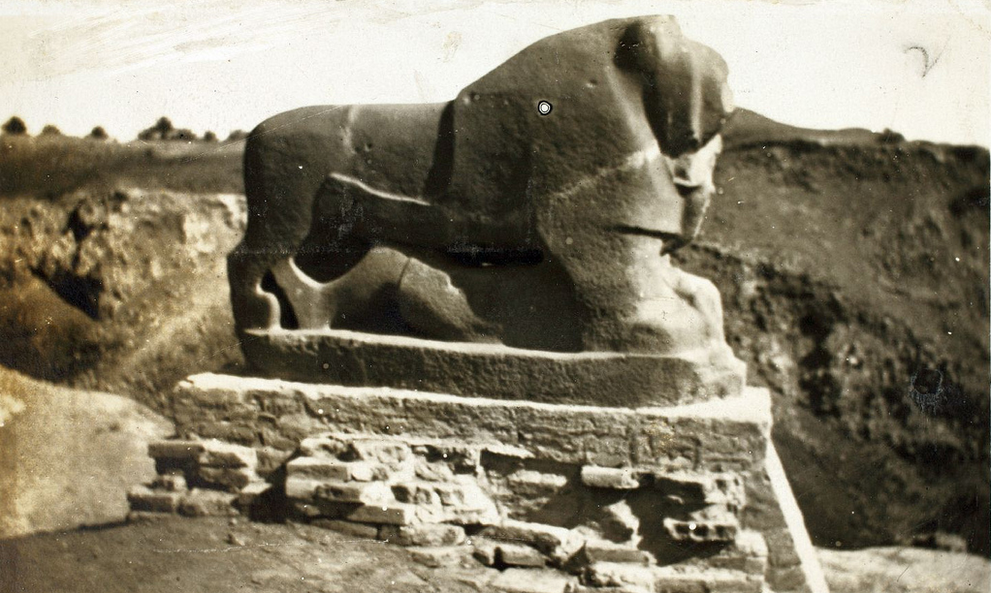
 The eighteenth century saw an increasing flow of travellers to Babylon, including Carsten Niebuhr and Pierre-Joseph de Beauchamp, as well as measurements of its latitude. Beauchamp's memoir, published in English translation in 1792, provoked the British East India Company to direct its agents in Baghdad and Basra to acquire Mesopotamian relics for shipment to London.
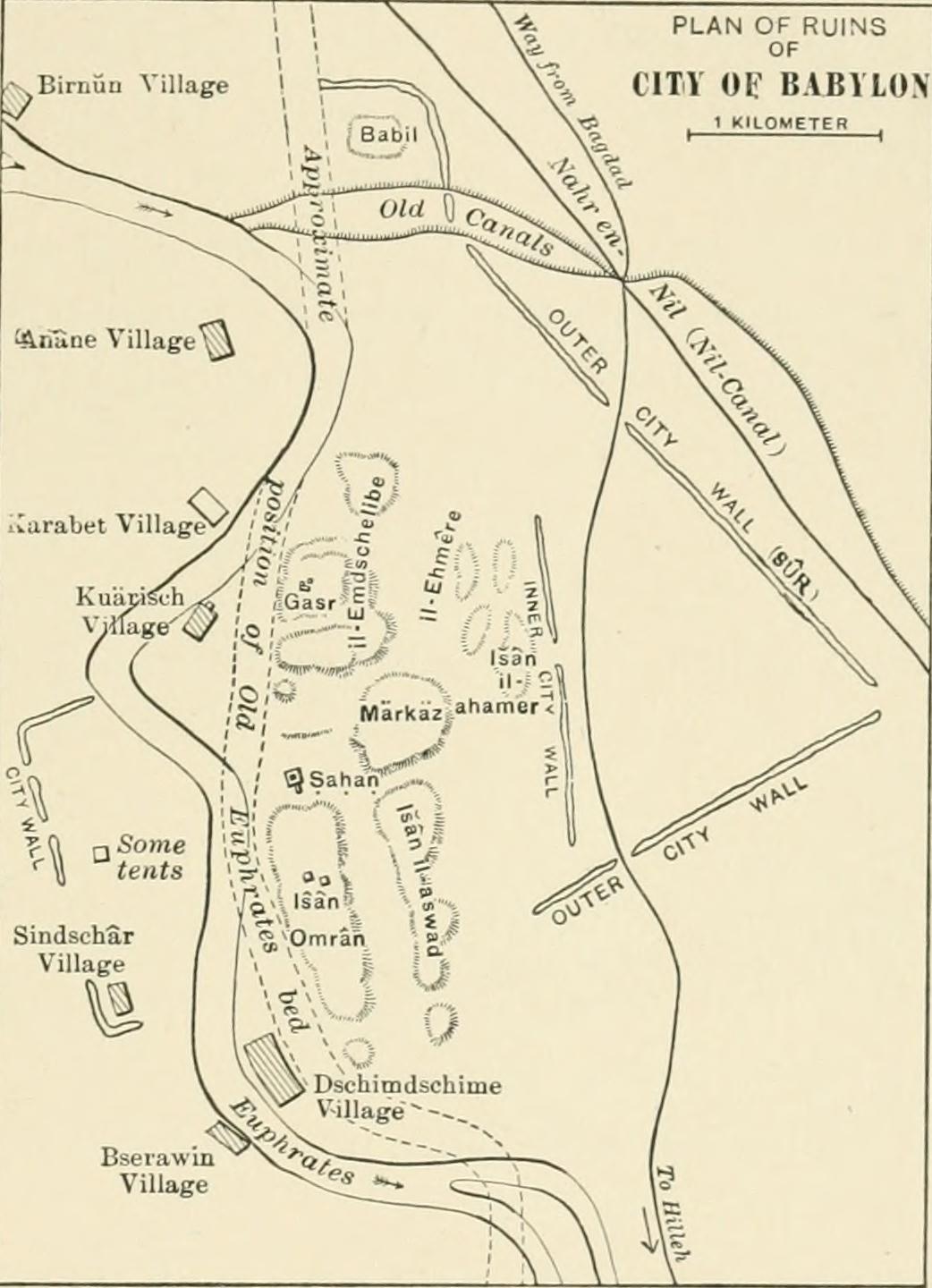
By 1905, there were several villages in Babylon, one of which was Qwaresh with about 200 households located within the boundaries of the ancient inner city walls. The village grew due to the need for laborers during the German Oriental Society excavations (1899-1917).
The eighteenth century saw an increasing flow of travellers to Babylon, including Carsten Niebuhr and Pierre-Joseph de Beauchamp, as well as measurements of its latitude. Beauchamp's memoir, published in English translation in 1792, provoked the British East India Company to direct its agents in Baghdad and Basra to acquire Mesopotamian relics for shipment to London.
By 1905, there were several villages in Babylon, one of which was Qwaresh with about 200 households located within the boundaries of the ancient inner city walls. The village grew due to the need for laborers during the German Oriental Society excavations (1899-1917).
 Sir Henry Rawlinson, 1st Baronet, Henry Rawlinson and George Smith (Assyriologist), George Smith worked there briefly in 1854. The next excavation was conducted by
Sir Henry Rawlinson, 1st Baronet, Henry Rawlinson and George Smith (Assyriologist), George Smith worked there briefly in 1854. The next excavation was conducted by  A team from the Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft, German Oriental Society led by
A team from the Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft, German Oriental Society led by

 Before modern archaeological excavations in Mesopotamia, the appearance of Babylon was largely a mystery, and typically envisioned by Western artists as a hybrid between ancient Egyptian, classical Greek, and contemporary Ottoman culture.
Due to Babylon's historical significance as well as references to it in the
Before modern archaeological excavations in Mesopotamia, the appearance of Babylon was largely a mystery, and typically envisioned by Western artists as a hybrid between ancient Egyptian, classical Greek, and contemporary Ottoman culture.
Due to Babylon's historical significance as well as references to it in the
File:René-Antoine Houasse - Nabuchodonosor et Semiramis fait élever les jardins de Babylone (Versailles).jpg, ''Nebuchadnezzar II ordering the construction of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon to please his consort Amytis of Babylon, Amytis'', René-Antoine Houasse, René-Antoine Houasse, 1676
File:History of babylon.jpg, Contemporary artwork depicting Babylon at the height of its stature
File:The fall of Babylon; Cyrus the Great defeating the Chaldean Wellcome V0034440.jpg, ''The Fall of Babylon'', mezzotint by John Martin, 1831
File:John Martin - The Daughters of Jerusalem Weeping by the Waters of Babylon - B1975.4.639 - Yale Center for British Art.jpg, ''The Daughters of Jerusalem Weeping by the Waters of Babylon'', by John Martin (painter), John Martin, 1834
File:Johann Georg Platzer - Alexander der Große empfängt die Schlüssel von Babylon.jpg, ''Alexander the Great receiving the keys of Babylon'', by Johann Georg Platzer, c. 1740
File:Apocalypse figurée des ducs de Savoie - Escorial E Vit.5 - Fall of Babylon.png, ''Figured Apocalypse of the Dukes of Savoy'' – Escorial E Vit.5 – Fall of Babylon, 15h century
File:The Walls of Babylon LACMA 65.37.292.jpg, ''The Walls of Babylon'' by Antonio Tempesta, 1610
Memoir on the Ruins of Babylon
'. Third Edition, 1818. ** 1818
Second Memoir on Babylon
** 1839. ''Narrative of a journey to the site of Babylon in 1811.'' Posthumous compilation. * * *
Modern Wars and Ancient Governance: Archaeology and Textual Finds from First Millennium BCE Babylon – Odette Boivin – ANE Today – Nov 2022
– The Babylonian Akītu Festival and the Ritual Humiliation of the King – Sam Mirelman – ANE Today – Sep 2022
*
Site Photographs of Babylon – Oriental Institute
1901–1906 Jewish Encyclopedia, Babylon
''Beyond Babylon: art, trade, and diplomacy in the second millennium B.C.''
Issued in connection with an exhibition held Nov. 18, 2008-Mar. 15, 2009, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York * Osama S. M. Amin,
Visiting the ancient city of Babylon
, ''Ancient History Et Cetera'', 17 November 2014. * Video of reconstructed palace:
*
UNESCO Final Report on Damage Assessment in Babylon
{{authority control Babylon, Amorite cities Archaeological sites in Iraq Articles containing video clips Babil Governorate Former populated places in Iraq Hebrew Bible cities Historic Jewish communities Levant Nimrod Populated places established in the 3rd millennium BC Populated places disestablished in the 10th century 1811 archaeological discoveries Populated places on the Euphrates River World Heritage Sites in Iraq
'' בָּבֶל ''Bavel'', Tib. ''Bāḇel''; syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāwēl'', arc, בבל Bāḇel; in ar, بَابِل ''Bābil''), interpreted in the
Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
to mean "confusion
In medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
", from the verb ''bilbél'' (, "to confuse"). The modern English verb, ' ("to speak foolish, excited, or confusing talk"), is popularly thought to derive from this name but there is no direct connection.
In Pali
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pāli Canon'' or '' Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of '' Theravāda'' Buddh ...
and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
literature, the name appears as ''Bāveru''.
Ancient records in some situations use "Babylon" as a name for other cities, including cities like Borsippa within Babylon's sphere of influence, and Nineveh for a short period after the Assyrian sack of Babylon.
Geography


 The ancient city, built along both banks of the
The ancient city, built along both banks of the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
river, had steep embankments to contain the river's seasonal floods. The remains of the city are in present-day Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq, about south of Baghdad, comprising a large tell of broken mud-brick buildings and debris. The site at Babylon consists of a number of mounds covering an area of about , oriented north to south, along the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
to the west. Originally, the river roughly bisected the city, but the course of the river has since shifted so that most of the remains of the former western part of the city are now inundated. Some portions of the city wall to the west of the river also remain.
Only a small portion of the ancient city (3% of the area within the inner walls; 1.5% of the area within the outer walls; 0.1% at the depth of Middle and Old Babylon) has been excavated. Known remains include:
* Kasr – also called Palace or Castle, it is the location of the Neo-Babylonian
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bein ...
ziggurat Etemenanki and lies in the center of the site.
* Amran Ibn Ali – the highest of the mounds at to the south. It is the site of Esagila
The Ésagila or Esangil ( sux, , ''"temple whose top is lofty"'') was a temple dedicated to Marduk, the protector god of Babylon. It lay south of the ziggurat Etemenanki.
Description
In this temple was the statue of Marduk, surrounded by cu ...
, a temple of Marduk that also contained shrines to Ea and Nabu
Nabu ( akk, cuneiform: 𒀭𒀝 Nabû syr, ܢܵܒܼܘܼ\ܢܒܼܘܿ\ܢܵܒܼܘܿ Nāvū or Nvō or Nāvō) is the ancient Mesopotamian patron god of literacy, the rational arts, scribes, and wisdom.
Etymology and meaning
The Akkadian "nab ...
.
* Homera – a reddish-colored mound on the west side. Most of the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
remains are here.
* Babil – a mound about high at the northern end of the site. Its bricks have been subject to looting since ancient times. It held a palace built by Nebuchadnezzar.
Archaeologists have recovered few artifacts predating the Neo-Babylonian period. The water table in the region has risen greatly over the centuries, and artifacts from the time before the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bei ...
are unavailable to current standard archaeological methods. Additionally, the Neo-Babylonians conducted significant rebuilding projects in the city, which destroyed or obscured much of the earlier record. Babylon was pillaged numerous times after revolting against foreign rule, most notably by the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-centra ...
and Elamites in the 2nd millennium, then by the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
and the Achaemenid Empire in the 1st millennium BC. Much of the western half of the city is now beneath the river, and other parts of the site have been mined for commercial building materials.
Only the Koldewey expedition recovered artifacts from the Old Babylonian period. These included 967 clay tablets, stored in private houses, with Sumerian literature and lexical documents.
Nearby ancient settlements are Kish
Kish may refer to:
Geography
* Gishi, Nagorno-Karabakh, Azerbaijan, a village also called Kish
* Kiş, Shaki, Azerbaijan, a village and municipality also spelled Kish
* Kish Island, an Iranian island and a city in the Persian Gulf
* Kish, Iran, ...
, Borsippa, Dilbat
Dilbat (modern Tell ed-Duleim or Tell al-Deylam, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian minor '' tell'' (hill city) located southeast from Babylon on the eastern bank of the Western Euphrates in modern-day Al-Qādisiyyah, Iraq. The ziggurat E-ibe-Anu, de ...
, and Kutha
Kutha, Cuthah, Cuth or Cutha ( ar, كُوثَا, Sumerian: Gudua), modern Tell Ibrahim ( ar, تَلّ إِبْرَاهِيم), formerly known as Kutha Rabba ( ar, كُوثَىٰ رَبَّا), is an archaeological site in Babil Governorate, Iraq. ...
. Marad and Sippar
Sippar ( Sumerian: , Zimbir) was an ancient Near Eastern Sumerian and later Babylonian city on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Its '' tell'' is located at the site of modern Tell Abu Habbah near Yusufiyah in Iraq's Baghdad Governorate, som ...
were in either direction along the Euphrates.
Sources
 The main sources of information about Babylon—excavation of the site itself, references in
The main sources of information about Babylon—excavation of the site itself, references in cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sh ...
texts found elsewhere in Mesopotamia, references in the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
, descriptions in other classical writing (especially by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
), and second-hand descriptions (citing the work of Ctesias
Ctesias (; grc-gre, Κτησίας; fl. fifth century BC), also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Historical events
Ctesias, who lived in the fi ...
and Berossus
Berossus () or Berosus (; grc, Βηρωσσος, Bērōssos; possibly derived from akk, , romanized: , "Bel is his shepherd") was a Hellenistic-era Babylonian writer, a priest of Bel Marduk and astronomer who wrote in the Koine Greek language ...
)—present an incomplete and sometimes contradictory picture of the ancient city, even at its peak in the sixth century BC. Babylon was described, perhaps even visited, by a number of classical historians including Ctesias
Ctesias (; grc-gre, Κτησίας; fl. fifth century BC), also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Historical events
Ctesias, who lived in the fi ...
, Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
, Quintus Curtius Rufus, Strabo, and Cleitarchus
Cleitarchus or Clitarchus ( el, Κλείταρχος) was one of the historians of Alexander the Great. Son of the historian Dinon of Colophon, he spent a considerable time at the court of Ptolemy Lagus. He was active in the mid to late 4th cent ...
. These reports are of variable accuracy and some of the content was politically motivated, but these still provide useful information.
Historical knowledge of early Babylon must be pieced together from epigraphic remains found elsewhere, such as at Uruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.Harm ...
, Nippur, Sippar
Sippar ( Sumerian: , Zimbir) was an ancient Near Eastern Sumerian and later Babylonian city on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Its '' tell'' is located at the site of modern Tell Abu Habbah near Yusufiyah in Iraq's Baghdad Governorate, som ...
, Mari, and Haradum
Haradum (modern Khirbit ed-Diniye (also Khirbet ed-Diniyé), Iraq) was an ancient Near East city on the middle Euphrates about 90 kilometers southeast of Mari. It was part of the ancient region of Suhum. The name of the town meant "the place w ...
.
Early references
The earliest known mention of Babylon as a small town appears on a clay tablet from the reign of Sargon of Akkad (2334–2279 BC) of the Akkadian Empire. References to the city of Babylon can be found in Akkadian and Sumerian literature from the late third millennium BC. One of the earliest is a tablet describing the Akkadian king Šar-kali-šarri laying the foundations in Babylon of new temples for Annūnı̄tum andIlaba
Ilaba was a Mesopotamian god. He is best attested as the tutelary deity of the kings of the Akkadian Empire, and functioned both as their personal god and as the city god of Akkad. Textual sources indicate he was a warlike deity, frequently desc ...
. Babylon also appears in the administrative records of the Third Dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC ( middle chronology) Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider t ...
, which collected in-kind tax payments and appointed an '' ensi'' as local governor.Wilfred G. Lambert, "Babylon: Origins"; in Cancik-Kirschbaum et al. (2011), pp. 71–76.
The so-called Weidner Chronicle (also known as ''ABC 19'') states that Sargon of Akkad ( in the short chronology) had built Babylon "in front of Akkad" (ABC 19:51). A later chronicle states that Sargon "dug up the dirt of the pit of Babylon, and made a counterpart of Babylon next to Akkad". (ABC 20:18–19). Van de Mieroop has suggested that those sources may refer to the much later Assyrian king Sargon II of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
rather than Sargon of Akkad.
Classical dating
Ctesias
Ctesias (; grc-gre, Κτησίας; fl. fifth century BC), also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Historical events
Ctesias, who lived in the fi ...
, quoted by Diodorus Siculus and in George Syncellus
George Syncellus ( el, Γεώργιος Σύγκελλος, ''Georgios Synkellos''; died after 810) was a Byzantine chronicler and ecclesiastic. He had lived many years in Palestine (probably in the Old Lavra of Saint Chariton or Souka, near Tekoa ...
's ''Chronographia'', claimed to have access to manuscripts from Babylonian archives, which date the founding of Babylon to 2286 BC, under the reign of its first king, Belus. A similar figure is found in the writings of Berossus
Berossus () or Berosus (; grc, Βηρωσσος, Bērōssos; possibly derived from akk, , romanized: , "Bel is his shepherd") was a Hellenistic-era Babylonian writer, a priest of Bel Marduk and astronomer who wrote in the Koine Greek language ...
, who, according to Pliny, stated that astronomical observations commenced at Babylon 490 years before the Greek era of Phoroneus, indicating 2243 BC. Stephanus of Byzantium wrote that Babylon was built 1002 years before the date given by Hellanicus of Lesbos
Hellanicus (or Hellanikos) of Lesbos (Greek: , ''Ἑllánikos ὁ Lésvios''), also called Hellanicus of Mytilene (Greek: , ''Ἑllánikos ὁ Mutilēnaῖos'') was an ancient Greek logographer who flourished during the latter half of the 5th cen ...
for the siege of Troy (1229 BC), which would date Babylon's foundation to 2231 BC. All of these dates place Babylon's foundation in the 23rd century BC
The 23rd century BC was a century that lasted from the year 2300 BC to 2201 BC.
Events
* 2334 BC – 2279 BC: ( short chronology) Sargon of Akkad's conquest of Mesopotamia.
*c. 2300 BC: Indus Valley civilisation (Harappan) flourishing in mode ...
; however, cuneiform records have not been found to correspond with these classical (post-cuneiform) accounts.
History
 The first attested mention of Babylon was in the late 3rd millennium BC during the Akkadian Empire reign of ruler
The first attested mention of Babylon was in the late 3rd millennium BC during the Akkadian Empire reign of ruler Shar-Kali-Sharri
Shar-Kali-Sharri (, '' DShar-ka-li-Sharri''; reigned c. 2217–2193 BC middle chronology, c. 2153–2129 BC short chronology) was a king of the Akkadian Empire.
Rule
Succeeding his father Naram-Sin in c. 2217 BC, he came to the throne in an age ...
one of whose year names mentions building two temples there. Babylon was ruled by ensi (governors) for the empire. Some of the known governors were Abba, Arši-aḫ, Itūr-ilum, Murteli, Unabatal, and Puzur-Tutu. After that nothing is heard of the city until the time of Sumu-la-El. After around 1950 BC Amorite kingdoms appear in Uruk and Larsa in the south.
Old Babylonian period
Amorite
The Amorites (; sux, 𒈥𒌅, MAR.TU; Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒊒𒌝 or 𒋾𒀉𒉡𒌝/𒊎 ; he, אֱמוֹרִי, 'Ĕmōrī; grc, Ἀμορραῖοι) were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking people from the Levant who also occupied la ...
rule in Babylon began () with a chieftain named Sumu-abum, who declared independence from the neighboring city-state of Kazallu Kazalla or Kazallu is the name given in Akkadian sources to a city in the ancient Near East whose locations is unknown. Its god is Numushda.
History
Under its king Kashtubila, Kazalla warred against Sargon of Akkad in the 24th or 23rd century B ...
. Sumu-la-El, whose dates may be concurrent with those of Sumu-abum, is usually given as the progenitor of the First Babylonian dynasty
The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to BC – BC, and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty ...
. Both are credited with building the walls of Babylon. In any case, the records describe Sumu-la-El's military successes establishing a regional sphere of influence for Babylon.
Babylon was initially a minor city-state, and controlled little surrounding territory; its first four Amorite rulers did not assume the title of king. The older and more powerful states of, Elam, Isin, and Larsa
Larsa ( Sumerian logogram: UD.UNUGKI, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossos and connected with the biblical Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the cult ...
overshadowed Babylon until it became the capital of Hammurabi
Hammurabi (Akkadian: ; ) was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from to BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered Elam and the city-states ...
's short-lived empire about a century later. Hammurabi (r. 1792–1750 BC) is famous for codifying the laws of Babylonia into the '' Code of Hammurabi''. He conquered all of the cities and city states of southern Mesopotamia, including Isin, Larsa
Larsa ( Sumerian logogram: UD.UNUGKI, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossos and connected with the biblical Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the cult ...
, Ur, Uruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.Harm ...
, Nippur, Lagash
Lagash (cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian: ''Lagaš''), was an ancient city state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Ash Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash (modern Al-Hiba) w ...
, Eridu
Eridu (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , NUN.KI/eridugki; Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''irîtu''; modern Arabic language, Arabic: Tell Abu Shahrain) is an archaeological site in southern Mesopotamia (modern Dhi Qar Governorate, Iraq). Eridu was l ...
, Kish
Kish may refer to:
Geography
* Gishi, Nagorno-Karabakh, Azerbaijan, a village also called Kish
* Kiş, Shaki, Azerbaijan, a village and municipality also spelled Kish
* Kish Island, an Iranian island and a city in the Persian Gulf
* Kish, Iran, ...
, Adab, Eshnunna
Eshnunna (modern Tell Asmar in Diyala Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian (and later Akkadian) city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Although situated in th ...
, Akshak
Akshak ( Sumerian: , akšak) was a city of ancient Sumer, situated on the northern boundary of Akkad, sometimes identified with Babylonian Upi (Greek Opis).
History
Akshak first appears in records of ca. 2500 BC. In the Sumerian text ''Dumuzid' ...
, Shuruppak, Bad-tibira
Bad-tibira ( Sumerian: , bad3-tibiraki), "Wall of the Copper Worker(s)", or "Fortress of the Smiths", identified as modern Tell al-Madineh (also Tell Madineh), between Ash Shatrah and Tell as-Senkereh (ancient Larsa) in southern Iraq, was an anci ...
, Sippar
Sippar ( Sumerian: , Zimbir) was an ancient Near Eastern Sumerian and later Babylonian city on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Its '' tell'' is located at the site of modern Tell Abu Habbah near Yusufiyah in Iraq's Baghdad Governorate, som ...
, and Girsu
Girsu ( Sumerian ; cuneiform ) was a city of ancient Sumer, situated some northwest of Lagash, at the site of modern Tell Telloh, Dhi Qar Governorate, Iraq.
History
Girsu was possibly inhabited in the Ubaid period (5300-4800 BC), but sig ...
, coalescing them into one kingdom, ruled from Babylon. Hammurabi also invaded and conquered Elam to the east, and the kingdoms of Mari and Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center t ...
to the northwest. After a conflict with the Old Assyrian period
The Old Assyrian period was the second stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of the city of Assur from its rise as an independent city-state under Puzur-Ashur I 2025 BC to the foundation of a larger Assyrian territorial state after th ...
king Ishme-Dagan
Ishme-Dagan ( akk, , Diš-me- Dda-gan, ''Išme-Dagān''; ''fl.'' ''c.'' 1889 BC — ''c.'' 1871 BC by the short chronology of the ancient near east) was the 4th king of the First Dynasty of Isin, according to the "''Sumerian King List''" (''S ...
, he forced his successor to pay tribute late in his reign.
After the reign of Hammurabi, the whole of southern Mesopotamia came to be known as Babylonia. From this time, Babylon supplanted Nippur and Eridu
Eridu (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , NUN.KI/eridugki; Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''irîtu''; modern Arabic language, Arabic: Tell Abu Shahrain) is an archaeological site in southern Mesopotamia (modern Dhi Qar Governorate, Iraq). Eridu was l ...
as the major religious centers of southern Mesopotamia. Hammurabi's empire destabilized after his death. The far south of Mesopotamia broke away, forming the native Sealand Dynasty
The First Sealand dynasty, (URU.KÙKIWhere ŠEŠ-ḪA of King List A and ŠEŠ-KÙ-KI of King List B are read as URU.KÙ.KI) or the 2nd Dynasty of Babylon (although it was independent of Amorite-ruled Babylon), very speculatively c. 1732–1460 B ...
, and the Elamites appropriated territory in eastern Mesopotamia. The Amorite dynasty remained in power in Babylon, which again became a small city state. After the destruction of the city the Kassites rose to control the region.
Texts from Old Babylon often include references to Shamash, the sun-god of Sippar, treated as a supreme deity, and Marduk, considered as his son. Marduk was later elevated to a higher status and Shamash lowered, perhaps reflecting Babylon's rising political power.
Middle Babylon
In 1595 BC the city was overthrown by theHittite Empire
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-centr ...
from Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. Thereafter, Kassites from the Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgr ...
captured the city of Babylon, renaming it Karduniash, ushering in a dynasty that lasted for 435 years, until 1160 BC.
Babylon weakened during the Kassite
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon ...
era, and as a result, Kassite Babylon began paying tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
to the Pharaoh of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Thutmose III
Thutmose III (variously also spelt Tuthmosis or Thothmes), sometimes called Thutmose the Great, was the sixth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Officially, Thutmose III ruled Egypt for almost 54 years and his reign is usually dated from 2 ...
, following his eighth campaign against Mitanni. Kassite Babylon eventually became subject to the Middle Assyrian Empire (1365–1053 BC) to the north, and Elam to the east, with both powers vying for control of the city.
By 1155 BC, after continued attacks and annexing of territory by the Assyrians and Elamites, the Kassites were deposed in Babylon. An Akkadian south Mesopotamian dynasty then ruled for the first time. However, Babylon remained weak and subject to domination by Assyria. Its ineffectual native kings were unable to prevent new waves of foreign West Semitic settlers from the deserts of the Levant, including the Arameans and Suteans in the 11th century BC, and finally the Chaldeans in the 9th century BC, entering and appropriating areas of Babylonia for themselves. The Arameans briefly ruled in Babylon during the late 11th century BC.
Assyrian period
 During the rule of the
During the rule of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
(911–609 BC), Babylonia was under constant Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
n domination or direct control. During the reign of Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
of Assyria, Babylonia was in a constant state of revolt, led by a chieftain named Merodach-Baladan, in alliance with the Elamites, and suppressed only by the complete destruction of the city of Babylon. In 689 BC, its walls, temples and palaces were razed, and the rubble was thrown into the Arakhtu, the sea bordering the earlier Babylon on the south. The destruction of the religious center shocked many, and the subsequent murder of Sennacherib by two of his own sons while praying to the god Nisroch
Nisroch ( ''Nīsrōḵ''; arc, ܢܝܼܫܪܵܟ݂; el, Νεσεραχ; la, Nesroch) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, an Assyrian god in whose temple King Sennacherib was worshiping when he was assassinated by his sons Adrammelech and Sharezer ...
was considered an act of atonement. Consequently, his successor, Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
hastened to rebuild the old city and make it his residence for part of the year. After his death, Babylonia was governed by his elder son, the Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
n prince Shamash-shum-ukin
Shamash-shum-ukin ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning "Shamash has established the name"), was king of Babylon as a vassal of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 668 BC to his death in 648. Born into the Assyrian royal family, Shamash-shum-ukin was ...
, who eventually started a civil war in 652 BC against his own brother, Ashurbanipal, who ruled in Nineveh. Shamash-shum-ukin enlisted the help of other peoples against Assyria, including Elam, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, the Chaldeans, and Suteans of southern Mesopotamia, and the Canaanites and Arabs dwelling in the deserts south of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
.
Once again, Babylon was besieged by the Assyrians, starved into surrender and its allies were defeated. Ashurbanipal celebrated a "service of reconciliation", but did not venture to "take the hands" of Bel (mythology), Bel. An Assyrian governor named Kandalanu was appointed as ruler of the city. Ashurbanipal did collect texts from Babylon for inclusion in his extensive Library of Ashurbanipal, library at Ninevah.
After the death of Ashurbanipal, the Assyrian empire was destabilized due to a series of internal civil wars throughout the reigns of the Assyrian kings Ashur-etil-ilani, Sin-shumu-lishir, and Sinsharishkun. Eventually, Babylon, like many other parts of the Near East, took advantage of the chaos within Assyria to free itself from Assyrian rule. In the subsequent overthrow of the Assyrian Empire by an alliance of peoples, the Babylonians saw another example of divine vengeance.
Neo-Babylonian Empire


 Under Nabopolassar, Babylon escaped Assyrian rule, and the allied Medo-Babylonian armies finally destroyed the Assyrian Empire between 626 BC and 609 BC. Babylon thus became the capital of the Neo-Babylonian (sometimes called the Chaldean) Empire.
With the recovery of Babylonian independence, a new era of architectural activity ensued, particularly during the reign of his son Nebuchadnezzar II (604–561 BC). Nebuchadnezzar ordered the complete reconstruction of the imperial grounds, including the Etemenanki ziggurat, and the construction of the Ishtar Gate—the most prominent of eight gates around Babylon. A reconstruction of the Ishtar Gate is located in the Pergamon Museum in Berlin.
Nebuchadnezzar is also credited with the construction of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the
Under Nabopolassar, Babylon escaped Assyrian rule, and the allied Medo-Babylonian armies finally destroyed the Assyrian Empire between 626 BC and 609 BC. Babylon thus became the capital of the Neo-Babylonian (sometimes called the Chaldean) Empire.
With the recovery of Babylonian independence, a new era of architectural activity ensued, particularly during the reign of his son Nebuchadnezzar II (604–561 BC). Nebuchadnezzar ordered the complete reconstruction of the imperial grounds, including the Etemenanki ziggurat, and the construction of the Ishtar Gate—the most prominent of eight gates around Babylon. A reconstruction of the Ishtar Gate is located in the Pergamon Museum in Berlin.
Nebuchadnezzar is also credited with the construction of the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity. The first known list of seven wonders dates back to the 2 ...
, said to have been built for his homesick wife, Amytis of Babylon, Amytis. Whether the gardens actually existed is a matter of dispute. German archaeologist Robert Koldewey
Robert Johann Koldewey (10 September 1855 – 4 February 1925) was a German archaeologist, famous for his in-depth excavation of the ancient city of Babylon in modern-day Iraq. He was born in Blankenburg am Harz in Germany, the duchy of Brunswick, ...
speculated that he had discovered its foundations, but many historians disagree about the location. Stephanie Dalley has argued that the hanging gardens were actually located in the Assyrian capital, Nineveh.
Nebuchadnezzar is also notoriously associated with the Babylonian exile of the Jews, the result of an imperial technique of pacification, used also by the Assyrians, in which ethnic groups in conquered areas were Resettlement policy of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, deported en masse to the capital. According to the Hebrew Bible, he Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), destroyed Solomon's Temple and Babylonian captivity, exiled the Jews to Babylon. The defeat was also recorded in the Babylonian Chronicles.
Persian conquest
In 539 BC, the Neo-Babylonian Empire fell to Cyrus the Great, king ofPersia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, with a military engagement known as the Battle of Opis. Babylon's walls were considered impenetrable. The only way into the city was through one of its many gates or through the Euphrates River. Metal grates were installed underwater, allowing the river to flow through the city walls while preventing intrusion. The Persians devised a plan to enter the city via the river. During a Babylonian national feast, Cyrus' troops upstream diverted the Euphrates River, allowing Cyrus' soldiers to enter the city through the lowered water. The Persian army conquered the outlying areas of the city while the majority of Babylonians at the city center were unaware of the breach. The account was elaborated upon by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
; or see and is also mentioned in parts of the Hebrew Bible. Herodotus also described a moat, an enormously tall and broad wall cemented with bitumen and with buildings on top, and a hundred gates to the city. He also writes that the Babylonians wear turbans and perfume and bury their dead in honey, that they practice ritual prostitution, and that three tribes among them Piscivore, eat nothing but fish. The hundred gates can be considered a reference to Homer, and following the pronouncement of Archibald Henry Sayce in 1883, Herodotus' account of Babylon has largely been considered to represent Greek folklore rather than an authentic voyage to Babylon. However, recently, Dalley and others have suggested taking Herodotus' account seriously.
 According to Books of Chronicles, 2 Chronicles 36 of the
According to Books of Chronicles, 2 Chronicles 36 of the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Achaemenid The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
Persia, the ancient Babylonian arts of astronomy and mathematics were revitalized, and Babylonian scholars completed maps of constellations. The city became the administrative capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire and remained prominent for over two centuries. Many important archaeological discoveries have been made that can provide a better understanding of that era.
The early Persian kings had attempted to maintain the religious ceremonies of Marduk, who was the most important god, but by the reign of Darius III, over-taxation and the strain of numerous wars led to a deterioration of Babylon's main shrines and canals, and the destabilization of the surrounding region. There were numerous attempts at rebellion and in 522 BC (Nebuchadnezzar III), 521 BC (Nebuchadnezzar IV) and 482 BC (Bel-shimani and Shamash-eriba) native Babylonian kings briefly regained independence. However, these revolts were quickly repressed and Babylon remained under Persian rule for two centuries, until Alexander the Great's entry in 331 BC.
'' Achaemenid The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
Hellenistic period
In October of 331 BC, Darius III, the lastAchaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
king of the Persian Empire, was defeated by the forces of the Ancient Macedonians, Ancient Macedonian ruler Alexander the Great, Alexander at the Battle of Gaugamela.
Under Alexander, Babylon again flourished as a center of learning and commerce. However, following Alexander's death in 323 BC in the palace of Nebuchadnezzar, his empire was divided amongst his generals, the Diadochi, and Wars of the Diadochi, decades of fighting soon began. The constant turmoil virtually emptied the city of Babylon. A tablet dated 275 BC states that the inhabitants of Babylon were transported to Seleucia, where a palace and a temple (Esagila
The Ésagila or Esangil ( sux, , ''"temple whose top is lofty"'') was a temple dedicated to Marduk, the protector god of Babylon. It lay south of the ziggurat Etemenanki.
Description
In this temple was the statue of Marduk, surrounded by cu ...
) were built. With this deportation, Babylon became insignificant as a city, although more than a century later, sacrifices were still performed in its old sanctuary.
Renewed Persian rule
Under the Parthian and Sassanid Empires, Babylon (like Assyria) became a province of these Persian Empires for nine centuries, until after AD 650. Although it was captured briefly by Trajan in AD 116 to be part of the newly conquered province of Mesopotamia (Roman province), Mesopotamia, his successor Hadrian relinquished his conquests east of the Euphrates river, which became again the Roman Empire's eastern boundary. However, Babylon maintained its own culture and people, who spoke varieties of Aramaic, and who continued to refer to their homeland as Babylon. Examples of their culture are found in the Babylonian Talmud, the Gnostic Mandaeism, Mandaean religion, East Syrian Rite, Eastern Rite Christianity and Manichaeism, the religion of the philosopher Mani (prophet), Mani. Christianity was introduced to Mesopotamia in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD, and Babylon was the seat of a Bishop of the Church of the East until well after the Early Muslim conquests, Arab/Islamic conquest. Coins from the Parthian, Sasanian and Arabic periods excavated in Babylon demonstrate the continuity of settlement there.Muslim conquest
In the mid-7th century, Mesopotamia was invaded and settled by the expanding Muslim Empire, and a period of Islamization followed. Babylon was dissolved as a province and Aramaic and Church of the East Christianity eventually became marginalized. Ibn Hawqal (10th century) and the Arab scholar, al-Qazwini (13th century), describe Babylon (Babil) as a small village. The latter described a well referred to as the 'Dungeon of Daniel' that was visited by Christians and Jews during holidays. The grave-shrine of Amran ibn Ali was visited by Muslims. Babylon is mentioned in medieval Arabic writings as a source of bricks,Olof Pedersén,Excavated and Unexcavated Libraries in Babylon
", in Cancik-Kirschbaum et al. (2011), pp. 47–67. said to have been used in cities from Baghdad to Basra.Julian E. Reade, "Disappearance and rediscovery"; in Finkel & Seymour, eds., ''Babylon'' (2009); pp. 13–30. European travellers, in many cases, could not discover the city's location, or mistook Fallujah for it. Benjamin of Tudela, a 12th-century traveller, mentions Babylon, but it is not clear if he went there. Others referred to
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
as Babylon or New Babylon and described various structures encountered in the region as the Tower of Babel. Pietro della Valle travelled to the village of Babil in Babylon in the 17th century and noted the existence of both baked and dried mudbricks cemented with bitumen.
Modern era

 The eighteenth century saw an increasing flow of travellers to Babylon, including Carsten Niebuhr and Pierre-Joseph de Beauchamp, as well as measurements of its latitude. Beauchamp's memoir, published in English translation in 1792, provoked the British East India Company to direct its agents in Baghdad and Basra to acquire Mesopotamian relics for shipment to London.
By 1905, there were several villages in Babylon, one of which was Qwaresh with about 200 households located within the boundaries of the ancient inner city walls. The village grew due to the need for laborers during the German Oriental Society excavations (1899-1917).
The eighteenth century saw an increasing flow of travellers to Babylon, including Carsten Niebuhr and Pierre-Joseph de Beauchamp, as well as measurements of its latitude. Beauchamp's memoir, published in English translation in 1792, provoked the British East India Company to direct its agents in Baghdad and Basra to acquire Mesopotamian relics for shipment to London.
By 1905, there were several villages in Babylon, one of which was Qwaresh with about 200 households located within the boundaries of the ancient inner city walls. The village grew due to the need for laborers during the German Oriental Society excavations (1899-1917).
Excavation and research
Claudius Rich, working for the British East India Company in Baghdad, excavated Babylon in 1811–12 and again in 1817. Captain Robert Mignan explored the site briefly in 1827 and in 1829 he completed a map of Babylon which includes the location of several villages. William Loftus (archaeologist), William Loftus visited there in 1849. Austen Henry Layard made some soundings during a brief visit in 1850 before abandoning the site. Fulgence Fresnel, Julius Oppert and Felix Thomas heavily excavated Babylon from 1852 to 1854. However, much of their work was lost in the Dur-Sharrukin#The Qurnah Disaster, Qurnah Disaster when a transport ship and four rafts sank on the Tigris river in May 1855. They had been carrying over 200 crates of artifacts from various excavation missions when they were attacked by Tigris river pirates near Al-Qurnah. Recovery efforts, assisted by the Ottoman authorities and British Residence in Baghdad, loaded the equivalent of 80 crates on a ship for Le Havre in May 1856. Few antiquities from the Fresnel mission would make it to France. Subsequent efforts to recover the lost antiquities from the Tigris, including a Japanese expedition in 1971–72, have been largely unsuccessful. Sir Henry Rawlinson, 1st Baronet, Henry Rawlinson and George Smith (Assyriologist), George Smith worked there briefly in 1854. The next excavation was conducted by
Sir Henry Rawlinson, 1st Baronet, Henry Rawlinson and George Smith (Assyriologist), George Smith worked there briefly in 1854. The next excavation was conducted by Hormuzd Rassam
Hormuzd Rassam ( ar, هرمز رسام; syr, ܗܪܡܙܕ ܪܣܐܡ; 182616 September 1910), was an Assyriologist and author.
He is known for making a number of important archaeological discoveries from 1877 to 1882, including the clay tablets tha ...
on behalf of the British Museum. Work began in 1879, continuing until 1882, and was prompted by widespread looting of the site. Using industrial scale digging in search of artifacts, Rassam recovered a large quantity of cuneiform tablets and other finds. The zealous excavation methods, common at the time, caused significant damage to the archaeological context. Many tablets had appeared on the market in 1876 before Rassam's excavation began.
 A team from the Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft, German Oriental Society led by
A team from the Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft, German Oriental Society led by Robert Koldewey
Robert Johann Koldewey (10 September 1855 – 4 February 1925) was a German archaeologist, famous for his in-depth excavation of the ancient city of Babylon in modern-day Iraq. He was born in Blankenburg am Harz in Germany, the duchy of Brunswick, ...
conducted the first scientific Excavation (archaeology), archaeological excavations at Babylon. The work was conducted daily from 1899 until 1917. The primary efforts of the dig involved the temple of Marduk and the processional way leading up to it, as well as the city wall. Artifacts, including pieces of the Ishtar Gate and hundreds of recovered tablets, were sent back to Germany, where Koldewey's colleague Walter Andrae reconstructed them into displays at the Vorderasiatisches Museum Berlin. The German archaeologists fled before Middle-Eastern theatre of World War I, oncoming British troops in 1917, and again, many objects went missing in the following years.
Further work by the German Archaeological Institute was conducted by Heinrich J. Lenzen in 1956 and Hansjörg Schmid in 1962. Lenzen's work dealt primarily with the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
theatre, and Schmid focused on the temple ziggurat Etemenanki.
The site was excavated in 1974 on behalf of the Turin Centre for Archaeological Research and Excavations in the Middle East and Asia and the Iraqi-Italian Institute of Archaeological Sciences. The focus was on clearing up issues raised by re-examination of the old German data. Additional work in 1987–1989 concentrated on the area surrounding the Ishara and Ninurta temples in the Shu-Anna city-quarter of Babylon.
During the restoration efforts in Babylon, the Iraqi State Organization for Antiquities and Heritage conducted extensive research, excavation and clearing, but wider publication of these archaeological activities has been limited. Indeed, most of the known tablets from all modern excavations remain unpublished.
Iraqi government
The site of Babylon has been a cultural asset toIraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
since the creation of the modern Iraqi state in 1921. The site was officially protected and excavated by the Mandatory Iraq, Kingdom of Iraq under British Administration, which later became the Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq, and its successors: the Arab Federation, the Iraqi Republic (1958-1968), Iraqi Republic, Ba'athist Iraq (also officially called the Iraqi Republic), and the Republic of Iraq. Babylonian images periodically appear on Iraqi postcards and stamps. In the 1960s, a replica of the Ishtar Gate and a reconstruction of Ninmakh Temple were built on site.
On 14 February 1978, the Ba'athist government of Iraq under Saddam Hussein began the "Archaeological Restoration of Babylon Project": reconstructing features of the ancient city atop its ruins. These features included the Southern Palace of Nebuchadnezzar, with 250 rooms, five courtyards, and a 30-meter entrance arch. The project also reinforced the Processional Way, the Lion of Babylon (statue), Lion of Babylon, and an amphitheater constructed in the city's Hellenistic era. In 1982, the government minted a set of seven coins displaying iconic features of Babylon. A Babylon International Festival was held in September 1987, and annually thereafter until 2002 (excepting 1990 and 1991), to showcase this work. The proposed reconstruction of the Hanging Gardens and the great ziggurat never took place.John Curtis, "The Site of Babylon Today"; in Finkel & Seymour, eds., ''Babylon'' (2009); pp. 213–220.John Curtis, "The Present Condition of Babylon"; in Cancik-Kirschbaum et al. (2011).
Hussein installed a portrait of himself and Nebuchadnezzar at the entrance to the ruins and inscribed his name on many of the bricks, in imitation of Nebuchadnezzar. One frequent inscription reads: "This was built by Saddam Hussein, son of Nebuchadnezzar, to glorify Iraq". These bricks became sought after as collectors' items after Hussein's downfall. Similar projects were conducted at Nineveh, Nimrud, Assur and Hatra, to demonstrate the magnificence of Arab achievement.
In the 1980s, Saddam Hussein completely removed the village of Qwaresh, displacing its residents. He later constructed a modern palace in that area called Saddam Hill over some of the old ruins, in the pyramidal style of a ziggurat. In 2003, he intended to have a Aerial lift, cable car line constructed over Babylon, but plans were halted by the 2003 invasion of Iraq.
Under US and Polish occupation
Following the 2003 invasion of Iraq, the area around Babylon came under the control of United States, US troops, before being handed over to Polish involvement in the 2003 invasion of Iraq, Polish forces in September 2003. US forces under the command of General James T. Conway of the I Marine Expeditionary Force were criticized for building the military base "Camp Alpha", with a helipad and other facilities on ancient Babylonian ruins during the Iraq War. US forces have occupied the site for some time and have caused irreparable damage to the archaeological record. In a report of the British Museum's Near East department, Dr. John Curtis described how parts of the archaeological site were levelled to create a landing area for helicopters, and parking lots for heavy vehicles. Curtis wrote of the occupation forces: A US military spokesman claimed that engineering operations were discussed with the "head of the Babylon museum". The head of the Iraqi State Board for Heritage and Antiquities, Donny George, said that the "mess will take decades to sort out" and criticised Polish Armed Forces, Polish troops for causing "terrible damage" to the site. Poland resolved in 2004 to place the city under Iraq control, and commissioned a report titled ''Report Concerning the Condition of the Preservation of the Babylon Archaeological Site'', which it presented at a meeting on 11–13 December 2004. In 2005, the site was handed over to the Iraqi Ministry of Culture. In April 2006, Colonel John Coleman, former Chief of Staff for the I Marine Expeditionary Force, offered to issue an apology for the damage done by military personnel under his command. However, he also claimed that the US presence had deterred far greater damage by other looters. An article published in April 2006 stated that UN officials and Iraqi leaders have plans to restore Babylon, making it into a cultural center. Two museums and a library, containing replicas of artifacts and local maps and reports, were raided and destroyed.Present-day
In May 2009, the provincial government of Babil Governorate, Babil reopened the site to tourists and over 35,000 people visited in 2017. An oil pipeline runs through an outer wall of the city. On 5 July 2019, the site of Babylon was inscribed as aUNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
Thousands of people reside in Babylon within the perimeter of the ancient outer city walls, and communities in and around them are "rapidly developing from compact, dense settlements to sprawling suburbia despite laws restricting constructions". Modern villages include Zwair West, Sinjar Village, Qwaresh, and Al-Jimjmah among which the first two are better off economically. Most residents primarily depend on daily wage earning or have government jobs in Hillah, Al-Hillah, while few cultivate dates, citrus fruits, figs, fodder for livestock and limited cash crops, although income from the land alone is not enough to sustain a family. Both Shi'a and Sunni Muslims live in Sinjar village with mosques for both groups.
The State Board of Antiquities and Heritage (SBAH) is the main authority responsible for the conservation of the archeological site. They are assisted by Antiquity and Heritage Police and maintain a permanent presence there. The World Monuments Fund is also involved in research and conservation. The SBAH Provincial Inspectorate Headquarters is located within the boundaries of the ancient inner city walls on the east side and several staff members and their families reside in subsidized housing in this area.
Cultural importance

 Before modern archaeological excavations in Mesopotamia, the appearance of Babylon was largely a mystery, and typically envisioned by Western artists as a hybrid between ancient Egyptian, classical Greek, and contemporary Ottoman culture.
Due to Babylon's historical significance as well as references to it in the
Before modern archaeological excavations in Mesopotamia, the appearance of Babylon was largely a mystery, and typically envisioned by Western artists as a hybrid between ancient Egyptian, classical Greek, and contemporary Ottoman culture.
Due to Babylon's historical significance as well as references to it in the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
, the word "Babylon" in various languages has acquired a generic meaning of a large, bustling diverse city. Examples include:
* ''Babylon'' is used in reggae music as a concept in the Rastafari movement#Zion vs. Babylon, Rastafari belief system, denoting the materialistic capitalist world, or any form of imperialist evil. It is believed that Babylon actively seeks to exploit and oppress the people of the world, specifically people of African descent. It is believed by Rastafarians that Babylon attempts to forbid the smoking of ganja because this sacred herb opens minds to the truth.
* Freemasonry, which has its own versions of biblical legends, classically considered Babylon as its birthplace and a haven for science and knowledge.
* ''Babylon 5'' – a science fiction series set on a futuristic space station that acts as a trading and diplomatic nexus between many different cultures. Many stories focus on the theme of different societies and cultures uniting, respecting differences, and learning from each other rather than fighting or looking on each other with prejudice and suspicion.
* ''Babylon A.D.'' takes place in New York City, decades in the future.
* Babilonas (Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name for "Babylon") is a real estate development in Lithuania.
*"Chromatica, Babylon" is a song by Lady Gaga that uses allusions to ancient Biblical themes to discuss gossip.
* ''Eternals (film), Eternals'' (2021), depicts Babylon on its greatest extent and is shown to be protected and aided in its development by the eternals.
Biblical narrative
In theBook of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
, Babel (Babylon) is described as founded by Nimrod along with Uruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.Harm ...
, Akkad (city), Akkad and perhaps Calneh—all of them in Shinar ("Calneh" is now sometimes translated not as a proper name but as the phrase "all of them"). Another story is given in Genesis 11, which describes a united human race, speaking one language, migrating to Shinar to establish a city and tower—the Tower of Babel. God halts construction of the tower by scattering humanity across the earth and confusing their communication so they are unable to understand each other in the same language.
After Hezekiah, the king of Judah, became ill, Baladan, king of Babylon, sent a letter and gifts to him. Hezekiah showed all of his treasures to the delegation, and the prophet Isaiah later said to him: "Behold, the days are coming when everything that is in your house, and what your fathers have stored up to this day, will be carried to Babylon; nothing will be left." Some 200 years later, Nebuchadnezzar, the king of Babylon, invaded Judah, laid siege to Jerusalem and deported the Jews to Babylon.
The prophet Daniel lived in Babylon for most of his life. Nebuchadnezzar made Daniel ruler over the entire province of Babylon for having interpreted his dream. Years later, Belshazzar held a banquet, at which fingers of a hand appeared and wrote on a wall. Daniel was called to provide an interpretation of the writings, upon which he explained that God had put an end to Belshazzar's kingdom. Belshazzar was killed that very night, and Darius the Mede took over the kingdom.
The Book of Isaiah says the following regarding Babylon: "It will be like Sodom and Gomorrah when God overthrew them. It will never be inhabited or lived in for all generations; no Arab will pitch his tent there; no shepherds will make their flocks lie down there." The Book of Jeremiah says that Babylon will "never again be inhabited" and that "no one will live there, nor will anyone of mankind reside in it" and that it will be a land in which "no one of mankind passes". The territories of Babylon, Edom, Bozrah, Moab, Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre, Hazor, and the sons of Ammon are all predicted in the Bible to become like Sodom and Gomorrah, or uninhabited forever.
Several Biblical prophecy scholars, most notably Chuck Missler, maintain that the "Doom of Babylon" as described in detail in Isaiah 13–14, Jeremiah 50–51, and possibly Revelation 17–18 must refer to a literal, future destruction of an actual city. Missler has written that Babylon has yet to be completely destroyed as prophesied by Isaiah and Jeremiah. The Persians were able to take Babylon without a fight in 539 BC.
In Jewish tradition, Babylon symbolizes an oppressor against which righteous believers must struggle. In Christianity, Babylon symbolizes worldliness and evil. Prophecies sometimes symbolically link the kings of Babylon with Lucifer. Nebuchadnezzar II, sometimes conflated with Nabonidus, appears as the foremost ruler in this narrative.
The Book of Revelation in the Christian Bible refers to Babylon many centuries after it ceased to be a major political center. The city is personified by the "Whore of Babylon", riding on a The Beast (Revelation), scarlet beast with seven heads and ten horns, and drunk on the blood of the righteous. Some scholars of apocalyptic literature believe this Babylon (New Testament), New Testament "Babylon" to be a dysphemism for the Roman Empire. Other scholars suggest that Babylon in the book of Revelation has a symbolic significance that extends beyond mere identification with the first century Roman empire.Craig R. Koester, ''Revelation'' (New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press, 2014), 506, 684
Babylon in art
See also
* Akitu * Cities of the ancient Near East * Jehoiachin's Rations Tablets * List of Kings of Babylon * Tomb of DanielNotes
References
Sources
* * Cancik-Kirschbaum, Eva, Margarete van Ess, & Joachim Marzahn, eds. (2011). ''Babylon: Wissenskultur in Orient und Okzident''. Berlin/Boston: De Gruyter. . * Finkel, I. L. and M. J. Seymour, eds. ''Babylon''. Oxford University Press, 2009. . Exhibition organized by British Museum, Musée du Louvre & Réunion des Musées Nationaux, and Staatliche Museen zu Berlin. * Mario Liverani, Liverani, Mario. ''Imagining Babylon: The Modern Story of an Ancient City''. Translated from Italian to English by Ailsa Campbell. Boston: De Gruyter, 2016. . Originally published as ''Immaginare Babele'' in 2013. * * * * * Vedeler, Harold Torger. ''A Social and Economic Survey of the Reign of Samsuiluna of Babylon (1794–1712 BC).'' PhD dissertation accepted at Yale, May 2006.Further reading
* * and (paperback) * – originally published in German * Claudius Rich, Rich, Claudius: ** 1815.Memoir on the Ruins of Babylon
'. Third Edition, 1818. ** 1818
Second Memoir on Babylon
** 1839. ''Narrative of a journey to the site of Babylon in 1811.'' Posthumous compilation. * * *
External links
Modern Wars and Ancient Governance: Archaeology and Textual Finds from First Millennium BCE Babylon – Odette Boivin – ANE Today – Nov 2022
– The Babylonian Akītu Festival and the Ritual Humiliation of the King – Sam Mirelman – ANE Today – Sep 2022
*
Site Photographs of Babylon – Oriental Institute
1901–1906 Jewish Encyclopedia, Babylon
''Beyond Babylon: art, trade, and diplomacy in the second millennium B.C.''
Issued in connection with an exhibition held Nov. 18, 2008-Mar. 15, 2009, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York * Osama S. M. Amin,
Visiting the ancient city of Babylon
, ''Ancient History Et Cetera'', 17 November 2014. * Video of reconstructed palace:
*
UNESCO Final Report on Damage Assessment in Babylon
{{authority control Babylon, Amorite cities Archaeological sites in Iraq Articles containing video clips Babil Governorate Former populated places in Iraq Hebrew Bible cities Historic Jewish communities Levant Nimrod Populated places established in the 3rd millennium BC Populated places disestablished in the 10th century 1811 archaeological discoveries Populated places on the Euphrates River World Heritage Sites in Iraq