
Bisphenol A controversy centers on concerns and debates about the biomedical significance of
bisphenol A (BPA), which is a precursor to polymers that are used in some consumer products, including some food containers. The concerns began with the hypothesis that BPA is an
endocrine disruptor, i.e. it mimics endocrine hormones and thus has the unintended and possibly far-reaching effects on people in physical contact with the chemical.
Since 2008, several governments have investigated its safety, which prompted some retailers to withdraw
polycarbonate products. The U.S.
Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) ended its authorization of the use of BPA in
baby bottle
A baby bottle, nursing bottle, or feeding bottle is a bottle with an attached ''teat'' (also called a ''nipple'' in the US) on the top opening, on which can be suckled, and from thereby drunk directly. It is typically used by infants and young ...
s and infant formula packaging, based on market abandonment, not safety.
The European Union and Canada have banned BPA use in baby bottles.
The U.S. FDA states "BPA is safe at the current levels occurring in foods" based on extensive research, including two more studies issued by the agency in early 2014. The
European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
(EFSA) reviewed new scientific information on BPA in 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011 and 2015: EFSA's experts concluded on each occasion that they could not identify any new evidence which would lead them to revise their opinion that the known level of exposure to BPA is safe; however, the EFSA does recognize some uncertainties, and will continue to investigate them.
In February 2016, France stated that it intends to propose BPA as a
REACH Regulation
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006. REACH addresses the production and use of chemical substances, and their potential impacts on both human he ...
candidate
substance of very high concern
A substance of very high concern (SVHC) is a chemical substance (or part of a group of chemical substances) concerning which it has been proposed that use within the European Union be subject to authorisation under the REACH Regulation. Indeed, l ...
(SVHC).
The
European Chemicals Agency
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA; ) is an agency of the European Union which manages the technical and administrative aspects of the implementation of the European Union regulation called Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restrict ...
agreed to the proposal in June 2017.
Production
The BPA controversy has gained momentum because of the quantity of BPA produced by the chemical industry. World production capacity of BPA was 1 million tons in the 1980s,
and more than 2.2 million tons in 2009. It is a
high production volume chemical. In 2003, U.S. consumption was 856,000 tons, 72% of which used to make polycarbonate plastic and 21% going into epoxy resins.
In the U.S., less than 5% of the BPA produced is used in food contact applications,
but remains in the canned food industry and printing applications such as sales receipts.
On 20 February 2018, ''Packaging Digest'' reported that "At least 90%" of food cans no longer contained BPA.

Occurrence
BPA is rarely encountered in industrial products: it is invariably bound in a polymeric structure. Concerns therefore about exposure focus on the degradation, mainly by hydrolysis, of these polymers and the plastic objects derived therefrom.
Polycarbonate plastic, which is formed from BPA, is used to make a variety of common products including baby and water bottles, sports equipment, medical and dental devices,
dental fillings
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure su ...
sealants, CDs and DVDs, household electronics, eyeglass lenses,
, and the lining of water pipes.
BPA is also used in the synthesis of
polysulfone
Polysulfones are a family of high performance thermoplastics. These polymers are known for their toughness and stability at high temperatures. Technically used polysulfones contain an aryl- SO2-aryl subunit. Due to the high cost of raw material ...
s and
polyether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be ...
ketones, as an
antioxidant in some
plasticizer
A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.
Plasticiz ...
s, and as a
polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many fo ...
inhibitor in
PVC. Epoxy resins derived from bisphenol A are used as coatings on the inside of almost all food and
beverage can
A drink can (or beverage can) is a metal container designed to hold a fixed portion of liquid such as carbonated soft drinks, alcoholic drinks, fruit juices, teas, herbal teas, energy drinks, etc. Drink cans are made of aluminum (75% of ...
s;
however, due to BPA health concerns, in Japan epoxy coating was mostly replaced by
PET film.
Bisphenol A is a preferred color developer in
carbonless copy paper
Carbonless copy paper (CCP), non-carbon copy paper, or NCR paper (No Carbon Required, taken from the initials of its creator, National Cash Register) is a type of coated paper designed to transfer information written on the front onto sheets benea ...
and thermal
point of sale receipt paper. When used in thermal paper, BPA is present as "free" (i.e., discrete, non-polymerized) BPA, which is likely to be more available for exposure than BPA polymerized into a resin or plastic. Upon handling, BPA in thermal paper can be transferred to skin, and there is some concern that residues on hands could be ingested through incidental hand-to-mouth contact. Furthermore, some studies suggest that dermal absorption may contribute some small fraction to the overall human exposure. European data indicate that the use of BPA in paper may also contribute to the presence of BPA in the stream of recycled paper and in landfills. Although there are no estimates for the amount of BPA used in thermal paper in the United States, in Western Europe, the volume of BPA reported to be used in thermal paper in 2005/2006 was 1,890 tonnes per year, while total production was estimated at 1,150,000 tonnes per year. (Figures taken from 2012 EPA draft paper.) Studies document potential spreading and accumulation of BPA in paper recycling, suggesting its presence for decades in paper recycling loop even after a hypothetical ban.
Epoxy resin may or may not contain BPA, and is employed to bind
gutta percha
Gutta-percha is a tree of the genus '' Palaquium'' in the family Sapotaceae. The name also refers to the rigid, naturally biologically inert, resilient, electrically nonconductive, thermoplastic latex derived from the tree, particularly from ...
in some root canal procedures.
Biomedical history
In the early 1930s, the British biochemist Edward
Charles Dodds tested BPA as an artificial estrogen, but found it to be 37,000 times less effective than estradiol.
Dodds eventually developed a structurally similar compound,
diethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with a ...
(DES), which was used as a synthetic estrogen drug in women and animals until it was banned due to its risk of causing cancer; the ban on use of DES in humans came in 1971 and in animals, in 1979.
BPA was never used as a drug.
BPA's ability to mimic the effects of natural estrogen derives from the similarity of phenol groups on both BPA and
estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development o ...
, which enable this synthetic molecule to trigger estrogenic pathways in the body.
Typically phenol-containing molecules similar to BPA are known to exert weak estrogenic activities, thus it is also considered an endocrine disrupter (ED) and estrogenic chemical. Xenoestrogens is another category the chemical BPA fits under because of its capability to interrupt the network that regulates the signals which control the reproductive development in humans and animals.
In 1997, adverse effects of low-dose BPA exposure in laboratory animals were first proposed.
Modern studies began finding possible connections to health issues caused by exposure to BPA during pregnancy and during development. See
Public health regulatory history in the United States and
Chemical manufacturers' reactions to bans. As of 2014, research and debates are ongoing as to whether BPA should be banned or not.

A 2007 study investigated the interaction between bisphenol A's and
estrogen-related receptor γ (ERR-γ). This
orphan receptor
In biochemistry, an orphan receptor is a protein that has a similar structure to other identified receptors but whose endogenous ligand has not yet been identified. If a ligand for an orphan receptor is later discovered, the receptor is referred to ...
(endogenous ligand unknown) behaves as a constitutive activator of transcription. BPA seems to bind strongly to ERR-γ (
dissociation constant = 5.5 nM), but only weakly to the ER.
BPA binding to ERR-γ preserves its basal constitutive activity.
It can also protect it from deactivation from the SERM
4-hydroxytamoxifen
Afimoxifene, also known as 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and by its tentative brand name TamoGel, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group and an active metabolite of tamoxifen. The drug is under development ...
(afimoxifene).
This may be the mechanism by which BPA acts as a
xenoestrogen
Xenoestrogens are a type of xenohormone that imitates estrogen. They can be either synthetic or natural chemical compounds. Synthetic xenoestrogens include some widely used industrial compounds, such as PCBs, BPA, and phthalates, which have estr ...
.
Different expression of ERR-γ in different parts of the body may account for variations in bisphenol A effects. For instance, ERR-γ has been found in high concentration in the
placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
, explaining reports of high bisphenol accumulation in this tissue.
BPA has also been found to act as an
agonist of the
GPER
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPER'' gene. GPER binds to and is activated by the female sex hormone estradiol and is responsible ...
(GPR30).
Safety
Health effects

According to the
European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
"BPA poses no health risk to consumers of any age group (including unborn children, infants and adolescents) at current exposure levels".
But in 2017 the
European Chemicals Agency
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA; ) is an agency of the European Union which manages the technical and administrative aspects of the implementation of the European Union regulation called Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restrict ...
concluded that BPA should be listed as a substance of very high concern due to its properties as an
endocrine disruptor.
In 2012, the United States'
Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) banned the use of BPA in
baby bottle
A baby bottle, nursing bottle, or feeding bottle is a bottle with an attached ''teat'' (also called a ''nipple'' in the US) on the top opening, on which can be suckled, and from thereby drunk directly. It is typically used by infants and young ...
s intended for children under 12 months.
The
Natural Resources Defense Council
The Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) is a United States-based 501(c)(3) non-profit international environmental advocacy group, with its headquarters in New York City and offices in Washington D.C., San Francisco, Los Angeles, Chicago, Bo ...
called the move inadequate, saying the FDA needed to ban BPA from all food packaging.
The FDA maintains that the agency continues to support the safety of BPA for use in products that hold food.
The U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also holds the position that BPA is not a health concern. In 2011, Andrew Wadge, the chief scientist of the United Kingdom's
Food Standards Agency
, type = Non-ministerial government department
, nativename =
, nativename_a =
, nativename_r =
, logo = Food Standards Agency.svg
, logo_width =
, logo_caption =
, seal =
, seal_width =
, seal_caption =
, picture =
, picture_width =
...
, commented on a 2011 U.S. study on dietary exposure of adult humans to BPA,
saying, "This corroborates other independent studies and adds to the evidence that BPA is rapidly absorbed, detoxified, and eliminated from humans – therefore is not a health concern."
The
Endocrine Society said in 2015 that the results of ongoing laboratory research gave grounds for concern about the potential hazards of
endocrine-disrupting chemicals – including BPA – in the environment, and that on the basis of the
precautionary principle
The precautionary principle (or precautionary approach) is a broad epistemological, philosophical and legal approach to innovations with potential for causing harm when extensive scientific knowledge on the matter is lacking. It emphasizes caut ...
these substances should continue to be assessed and tightly regulated.
A 2016 review of the literature said that the potential harms caused by BPA were a topic of scientific debate and that further investigation was a priority because of the association between BPA exposure and adverse human health effects including reproductive and developmental effects and metabolic disease.
United States expert panel conclusions
In 2007, the U.S. federal government invited experts to Chapel Hill, North Carolina to perform a scientific assessment of literature on BPA. Thirty-eight experts in fields involved with bisphenol A gathered in
Chapel Hill, North Carolina to review several hundred studies on BPA, many conducted by members of the group. At the end of the meeting, the group issued the Chapel Hill Consensus Statement,
which stated "BPA at concentrations found in the human body is associated with organizational changes in the prostate, breast, testis, mammary glands, body size, brain structure and chemistry, and behavior of laboratory animals."
[ The Chapel Hill Consensus Statement stated that average BPA levels in people were above those that cause harm to many animals in laboratory experiments. It noted that while BPA is not persistent in the environment or in humans, ]biomonitoring
In analytical chemistry, biomonitoring is the measurement of the body burden of toxic chemical compounds, elements, or their metabolites, in biological substances. Often, these measurements are done in blood and urine. Biomonitoring is performed ...
surveys indicate that exposure is continuous. This is problematic because acute animal exposure studies are used to estimate daily human exposure to BPA, and no studies that had examined BPA pharmacokinetics in animal models had followed continuous low-level exposures. The authors added that measurement of BPA levels in serum and other body fluids suggests the possibilities that BPA intake is much higher than accounted for or that BPA can bioaccumulate in some conditions (such as pregnancy).[ Despite this report, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) BPA Task Force (formed in April 2008), concluded that products containing BPA were safe. In 2009, the FDA Science Board Subcommittee on Bisphenol A, an external committee assigned to review the FDA's report "concluded that the FDA failed to conduct a rigorous or extensive exposure assessment", leading the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to conduct their own assessment.][
The United States Federal Interagency Working Group (FIW) included a goal to reduce BPA exposure in the 2 December 2010 release of their 2020 Healthy People national objectives for improving the health of all Americans.
]
Metabolic disease
Numerous animal studies have demonstrated an association between endocrine disrupting chemicals (including BPA) and obesity.PPAR-gamma
Peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ or PPARG), also known as the glitazone reverse insulin resistance
receptor, or NR1C3 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group C, member 3) is a type II nuclear receptor functioning as a tra ...
receptor, and disruption of neural circuits that regulate feeding behavior.estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
but newer evidence indicates that it is a potent mimicker. When it binds to estrogen receptors it triggers alternative estrogenic effects that begin outside of the nucleus. This different path induced by BPA has been shown to alter glucose and lipid metabolism in animal studies.
There are different effects of BPA exposure during different stages of development. During adulthood, BPA exposure modifies insulin sensitivity and insulin release without affecting weight.
Thyroid function
 A 2007 review concluded that bisphenol-A has been shown to bind to thyroid hormone receptor and perhaps has selective effects on its functions.
A 2007 review concluded that bisphenol-A has been shown to bind to thyroid hormone receptor and perhaps has selective effects on its functions.triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate.
Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxine ...
and concluded that "available evidence suggests that governing agencies need to regulate the use of thyroid-disrupting chemicals, particularly as such uses relate exposures of pregnant women, neonates and small children to the agents".
Neurological effects
Limited epidemiological evidence suggests that exposure to BPA in the uterus and during childhood is associated with poor behavioral outcomes in humans. Exposure may be associated with higher levels of anxiety, depression, hyperactivity, and aggression in children.National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
determined that there was "some concern" about BPA's effects on fetal and infant brain development and behavior.[Staff, FDA. January 2010; Updated March 2013]
Bisphenol A (BPA): Use in Food Contact Application
Accessed 7 May 2013[Staff, FDA, DRAFT version 14 August 200]
Draft Assessment of Bisphenol A for Use in Food Contact Applications
Accessed 7 May 2013
A 2007 literature review concluded that BPA, like other chemicals that mimic estrogen (xenoestrogens), should be considered as a player within the nervous system that can regulate or alter its functions through multiple pathways. A 2008 review of animal research found that low-dose BPA maternal exposure can cause long-term consequences for the neurobehavioral development in mice.
 A 2009 review raised concerns about a BPA effect on the anteroventral periventricular nucleus.
A 2009 review raised concerns about a BPA effect on the anteroventral periventricular nucleus.
Disruption of the dopaminergic system
 A 2008 review of human participants has concluded that BPA mimics estrogenic activity and affects various dopaminergic processes to enhance mesolimbic dopamine activity resulting in hyperactivity, attention deficits, and a heightened sensitivity to drugs of abuse.
A 2008 review of human participants has concluded that BPA mimics estrogenic activity and affects various dopaminergic processes to enhance mesolimbic dopamine activity resulting in hyperactivity, attention deficits, and a heightened sensitivity to drugs of abuse.
Cancer
According to the WHO's INFOSAN, carcinogenicity studies conducted under the U.S. National Toxicology Program have shown increases in leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
and testicular interstitial cell tumors in male rats. However, according to the note, "these studies have not been considered as convincing evidence of a potential cancer risk because of the doubtful statistical significance of the small differences in incidences from controls."
Breast cancer
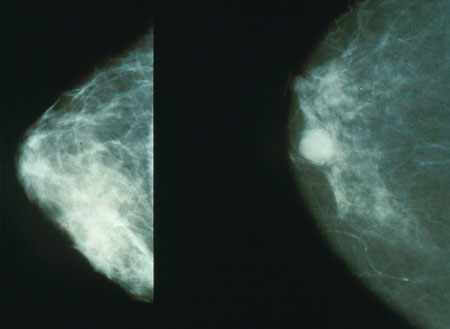 Higher susceptibility to breast cancer has been found in many studies of rodents and primates exposed to BPA.
Higher susceptibility to breast cancer has been found in many studies of rodents and primates exposed to BPA.
=Mechanism of action
=
BPA is an endocrine disruptor, meaning BPA has a similar structure to oestrogen (ligand) and can bind to the oestrogen receptor ERα and ERβ and activate it.
Fertility
As of 2022, current evidence shows a possible positive correlation between BPA levels, lower sperm quality, decreased motility and an increase in sperm immaturity.endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition of excessive proliferation of the cells of the endometrium, or inner lining of the uterus.
Most cases of endometrial hyperplasia result from high levels of estrogens, combined with insufficient levels of t ...
.
Sexual function
Higher BPA exposure has been associated with increased self-reporting of decreased male sexual function but few studies examining this relationship have been conducted.
Asthma
Studies in mice have found a link between BPA exposure and asthma; a 2010 study on mice has concluded that perinatal
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
exposure to 10 µg/ml of BPA in drinking water enhances allergic sensitization and bronchial inflammation and responsiveness in an animal model of asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
.Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it ...
journal saying while the study does not show that BPA causes asthma or wheezing, "it's an important study because we don't know a lot right now about how BPA affects immune response and asthma...They measured BPA at different ages, measured asthma and wheeze at multiple points, and still found consistent associations."
Animal research
The first evidence of the estrogenicity of bisphenol A came from experiments on rats conducted in the 1930s,estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
and has been shown to cause negative health effects in animal studies. Bisphenol A closely mimics the structure and function of the hormone estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development o ...
by binding to and activating the same estrogen receptor as the natural hormone.[Draft Screening Assessment for The Challenge Phenol, 4,4' -(1-methylethylidene)bis- (Bisphenol A)Chemical Abstracts Service Registry Number 80-05-7.](_blank)
Health Canada, 2008.
A study from 2008 concluded that blood levels of bisphenol A in neonatal mice are the same whether it is injected or ingested.placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
, explaining reports of high bisphenol accumulation in this tissue.
Environmental effects
In 2010, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon pro ...
reported that over one million pounds of BPA are released into the environment annually.half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable at ...
of 4.5 days, and an air half-life of less than one day, BPA's ubiquity makes it an important pollutant
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effects, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming (i.e. minerals or extracted compounds like o ...
. BPA has a low rate of evaporation from water and soil, which presents issues, despite its biodegradability
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradati ...
and low concern for bio-accumulation. BPA has low volatility in the atmosphere and a low vapor pressure
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in English-speaking countries other than the US; see spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phas ...
between 5.00 and 5.32 Pascals. BPA has a high water solubility
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be rep ...
of about 120 mg/L and most of its reactions in the environment are aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be re ...
. An interesting fact is that BPA dust is flammable if ignited, but it has a minimal explosive concentration in air. Also, in aqueous solutions, BPA has shown absorption of wavelengths greater than 250 nm.nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular nitrogen (), with a strong triple covalent bond, in the air is converted into ammonia () or related nitrogenous compounds, typically in soil or aquatic systems but also in industry. Atmo ...
at the roots of leguminous
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock for ...
plants associated with the bacterial symbiont ''Sinorhizobium meliloti
''Ensifer meliloti'' (formerly ''Rhizobium meliloti'' and ''Sinorhizobium meliloti'') are an aerobic, Gram-negative, and diazotrophic species of bacteria. ''S. meliloti'' are motile and possess a cluster of peritrichous flagella. ''S. meliloti'' ...
.'' A 2013 study also observed changes in plant health due to BPA exposure. The study exposed soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu a ...
seedlings to various concentrations of BPA and saw changes in root growth, nitrate production, ammonium production, and changes in the activities of nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase. At low doses of BPA, the growth of roots were improved, the amount of nitrate in roots increased, the amount of ammonium in roots decreased, and the nitrate and nitrite reductase activities remained unchanged. However, at considerably higher concentrations of BPA, the opposite effects were seen for all but an increase in nitrate concentration and a decrease in nitrite and nitrate reductase activities. Nitrogen is both a plant nutritional substance, but also the basis of growth and development in plants. Changing concentrations of BPA can be harmful to the ecology of an ecosystem, as well as to humans if the plants are produced to be consumed.
The amount of absorbed BPA on sediment was also seen to decrease with increases in temperature, as demonstrated by a study in 2006 with various plants from the XiangJiang River
The Xiang River is the chief river of the Lake Dongting drainage system of the middle Yangtze, the largest river in Hunan Province, China. It is the 2nd largest tributary (after Min River) in terms of surface runoff, the 5th largest tributar ...
in Central-South China. In general, as temperature increases, the water solubility of a compound increases. Therefore, the amount of sorbate that enters the solid phase will lower at the equilibrium point
In mathematics, specifically in differential equations, an equilibrium point is a constant solution to a differential equation.
Formal definition
The point \tilde\in \mathbb^n is an equilibrium point for the differential equation
:\frac = \ ...
. It was also observed that the adsorption process of BPA on sediment is exothermic, the molar formation enthalpy
Enthalpy , a property of a thermodynamic system, is the sum of the system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant ...
, ΔH°, was negative, the free energy ΔG°, was negative, and the molar entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynam ...
, ΔS°, was positive. This indicates that the adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which ...
of BPA is driven by enthalpy. The adsorption of BPA has also been observed to decrease with increasing pH.
A 2005 study conducted in the United States had found that 91–98% of BPA may be removed from water during treatment at municipal water treatment plants. A more detailed explanation of aqueous reactions of BPA can be observed in the Degradation of BPA section below. Nevertheless, a 2009 meta-analysis of BPA in the surface water system showed BPA present in surface water and sediment in the United States and Europe. According to Environment Canada in 2011, "BPA can currently be found in municipal wastewater. ��nitial assessment shows that at low levels, bisphenol A can harm fish and organisms over time."
BPA affects growth, reproduction, and development in aquatic organisms. Among freshwater organisms, fish appear to be the most sensitive species. Evidence of endocrine-related effects in fish, aquatic invertebrates, amphibians, and reptiles has been reported at environmentally relevant exposure levels lower than those required for acute toxicity. There is a widespread variation in reported values for endocrine-related effects, but many fall in the range of 1μg/L to 1 mg/L.plasticizer
A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.
Plasticiz ...
s on wildlife published by the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
with a focus on aquatic and terrestrial annelids
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecolog ...
, molluscs
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estim ...
, crustaceans
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
, insects, fish and amphibians concluded that BPA affects reproduction in all studied animal groups, impairs development in crustaceans and amphibians and induces genetic aberrations.
Vertebrates
BPA is known as an endocrine disruptor compound (EDC) and has major neurological effects on vertebrates.
Reproductive effects
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an environmental contaminant that disrupts the ecosystem, with the most profound effects observed in vertebrates.zygotic
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual ...
development showing that it is just as dangerous as BPA.
Behavioral effects
BPA has major effects on the behavior of vertebrates, especially in their sensory processing systems. In zebrafish BPA can disrupt the signaling in the endocrine system and affect auditory development and function.
Positions of national and international bodies
World Health Organization
In November 2009, the WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
announced to organize an expert consultation in 2010 to assess low-dose BPA exposure health effects, focusing on the nervous and behavioral system and exposure to young children.
United States
In 2013, the FDA posted on its web site: "Is BPA safe? Yes. Based on FDA's ongoing safety review of scientific evidence, the available information continues to support the safety of BPA for the approved uses in food containers and packaging. People are exposed to low levels of BPA because, like many packaging components, very small amounts of BPA may migrate from the food packaging into foods or beverages."
Australia and New Zealand
In 2009 the Australia and New Zealand Food Safety Authority ( Food Standards Australia New Zealand) did not see any health risk with bisphenol A baby bottle
A baby bottle, nursing bottle, or feeding bottle is a bottle with an attached ''teat'' (also called a ''nipple'' in the US) on the top opening, on which can be suckled, and from thereby drunk directly. It is typically used by infants and young ...
s if the manufacturer's instructions were followed, as levels of exposure were very low and would not pose a significant health risk. It added that "the move by overseas manufacturers to stop using BPA in baby bottles is a voluntary action and not the result of a specific action by regulators." In 2008 it had suggested the use of glass baby bottles if parents had concerns.
In 2012 the Australian Government introduced a voluntary phase out of BPA use in polycarbonate baby bottles.
Canada
In April 2008, Health Canada concluded that, while adverse health effects were not expected, the margin of safety was too small for formula-fed infantsCanadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999
The ''Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999'' (''CEPA, 1999''; french: Loi canadienne sur la protection de l'environnement (1999)) is an act of the 36th Parliament of Canada, whose goal is to contribute to sustainable development through po ...
.
European Union
The 2008 European Union Risk Assessment Report on , published by the European Commission and European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
(EFSA), concluded that -based products, such as polycarbonate plastic and epoxy resins, are safe for consumers and the environment when used as intended. By October 2008, after the Lang Study was published, the EFSA issued a statement concluding that the study provided no grounds to revise the current Tolerable Daily Intake (TDI) level for BPA of bodyweight.
On 22 December 2009, the EU Environment ministers released a statement expressing concerns over recent studies showing adverse effects of exposure to endocrine disruptors.
In September 2010, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) concluded after a "comprehensive evaluation of recent toxicity data ��that no new study could be identified, which would call for a revision of the current TDI".baby bottle
A baby bottle, nursing bottle, or feeding bottle is a bottle with an attached ''teat'' (also called a ''nipple'' in the US) on the top opening, on which can be suckled, and from thereby drunk directly. It is typically used by infants and young ...
s containing the organic compound by , according to John Dalli
John Dalli (born 5 October 1948) is a Maltese former politician who served as Cabinet Minister in various Maltese governments between 1987 and 2010. He was European Commissioner for Health and Consumer Policy between 2010 and 2012.
Maltese po ...
, commissioner in charge of health and consumer policy. This was backed by a majority of EU governments.baby bottle
A baby bottle, nursing bottle, or feeding bottle is a bottle with an attached ''teat'' (also called a ''nipple'' in the US) on the top opening, on which can be suckled, and from thereby drunk directly. It is typically used by infants and young ...
s was forbidden in all EU-countries.
Denmark
In May 2009, the Danish parliament passed a resolution to ban the use of BPA in baby bottles, which had not been enacted by April 2010. In March 2010, a temporary ban was declared by the Health Minister.
Belgium
In March 2010, senator Philippe Mahoux proposed legislation to ban BPA in food contact plastics. In May 2011, senators Dominique Tilmans and Jacques Brotchi proposed legislation to ban BPA from thermal paper.
France
On 5 February 2010, the French Food Safety Agency (AFSSA) questioned the previous assessments of the health risks of BPA, especially in regard to behavioral effects observed in rat pups following exposure in utero and during the first months of life. In April 2010, the AFFSA suggested the adoption of better labels for food products containing BPA.
On 24 March 2010, the French Senate unanimously approved a proposition of law to ban BPA from baby bottles. The National Assembly (Lower House) approved the text on 23 June 2010, which has been applicable law since 2 July 2010. On 12 October 2011, the French National Assembly voted a law forbidding the use of Bisphenol A in products aimed at less than 3-year-old children for 2013, and 2014 for all food containers.
On 9 October 2012, the French Senate adopted unanimously the law proposition to suspend manufacture, import, export and marketing of all food containers that include bisphenol A for 2015. The ban of bisphenol A in 2013 for food products designed for children less than 3-years-old was maintained.
Germany
On 19 September 2008, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung, BfR) stated that there was no reason to change the current risk assessment for bisphenol A on the basis of the Lang Study.
In October 2009, the German environmental organization Bund für Umwelt und Naturschutz Deutschland
Bund für Umwelt und Naturschutz Deutschland (; BUND, ) is a German non-governmental organisation (NGO) dedicated to preserving nature and protecting the environment. The name means "German Federation for the Environment and Nature Conservation". ...
requested a ban on BPA for children's products, especially pacifiers, and products that make contact with food. In response, some manufacturers voluntarily removed the problematic pacifiers from the market.
Netherlands
On 3 March 2016, the (NVWA) issued cautionary recommendations to the Minister of Health, Welfare, and Sport and the Secretary for Economic Affairs
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with th ...
, on the public intake of BPA, especially for vulnerable groups such as women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, and those with developing immune systems such as children below the age of 10. This was done in response to recent published research, and conclusions reached by the European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002, ...
. It also called for the concentration of BPA in drinking water to be lowered below 0.2 µg/L, in line with the maximum tolerable intake they recommend.
Switzerland
In February 2009, the Swiss Federal Office for Public Health, based on reports of other health agencies, stated that the intake of bisphenol A from food represents no risk to the consumer, including newborns and infants. However, in the same statement, it advised for proper use of polycarbonate baby bottles and listed alternatives.
Sweden
By 26 May 1995, the Swedish Chemicals Agency asked for a BPA ban in baby bottles, but the Swedish Food Safety Authority prefers to await the expected European Food Safety Authority's updated review. The Minister of Environment said to wait for the EFSA review but not for too long.
From March 2011 it is prohibited to manufacture babybottles containing bisphenol A and from July 2011 they can not be bought in stores. On 12 April 2012, the Swedish government announced that Sweden will ban BPA in cans containing food for children under the age of three.
Since January 2, 2020, BPA has been banned in thermal recepits, as a consequence of the EU wide ban.
United Kingdom
In December 2009, responding to a letter from a group of seven scientists that urged the UK Government to "adopt a standpoint consistent with the approach taken by other Governments who have ended the use of BPA in food contact products marketed at children", the UK Food Standards Agency reaffirmed, in January 2009, its view that "exposure of UK consumers to BPA from all sources, including food contact materials
Food contact materials are materials that are intended to be in contact with food. These can be things that are quite obvious like a glass or a can for soft drinks as well as machinery in a food factory or a coffee machine.
Food contact materia ...
, was well below levels considered harmful".
Turkey
As of 10 June 2011, Turkey banned the use of BPA in baby bottles and other PC items produced for babies.
Japan
Between 1998 and 2003, the canning industry voluntarily replaced its BPA-containing epoxy resin can liners with BPA-free polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in many of its products. For other products, it switched to a different epoxy lining that yielded much less migration of BPA into food than the previously used resin. In addition, polycarbonate tableware for school lunches was replaced by BPA-free plastics.
Human exposure sources
The major human exposure route to BPA is diet, including ingestion of contaminated food and water.
It is especially likely to leach from plastics when they are cleaned with harsh detergents or when they contain acidic or high-temperature liquids. BPA is used to form epoxy resin coating of water pipes; in older buildings, such resin coatings are used to avoid replacement of deteriorating pipes. In the workplace, while handling and manufacturing products which contain BPA, inhalation and dermal exposures are the most probable routes.CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
had found bisphenol A in the urine of 95% of adults sampled in 1988–1994Reference dose A reference dose is the United States Environmental Protection Agency's maximum acceptable oral dose of a toxic substance.Reference doses are most commonly determined for pesticides. The EPA defines an oral reference dose (abbreviated RfD) as:
es ...
(RfD) for BPA is 50 µg/kg/day which is not enforceable but is the recommended safe level of exposure. The most sensitive animal studies show effects at much lower doses,Harvard School of Public Health
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health is the public health school of Harvard University, located in the Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. The school grew out of the Harvard- MIT School for Health Officers, the nation's firs ...
indicated that BPA used in the lining of food cans is absorbed by the food and then ingested by consumers. Of 75 participants, half ate a lunch of canned vegetable soup for five days, followed by five days of fresh soup, while the other half did the same experiment in reverse order. "The analysis revealed that when participants ate the canned soup, they experienced more than a 1,000 percent increase in their urinary concentrations of BPA, compared to when they dined on fresh soup."
A 2009 study found that drinking from polycarbonate bottles increased urinary bisphenol A levels by two-thirds, from 1.2 μg/g creatinine to 2 μg/g creatinine. Consumer groups recommend that people wishing to lower their exposure to bisphenol A avoid canned food
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container ( jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although ...
and polycarbonate plastic containers (which shares resin identification code
The ASTM International Resin Identification Coding System, often abbreviated RIC, is a set of symbols appearing on plastic products that identify the plastic resin out of which the product is made. It was developed in 1988 by the Society of t ...
7 with many other plastics) unless the packaging indicates the plastic is bisphenol A-free. To avoid the possibility of BPA leaching into food or drink, the National Toxicology Panel recommends avoiding microwaving
A microwave oven (commonly referred to as a microwave) is an electric oven that heats and cooks food by exposing it to electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range. This induces polar molecules in the food to rotate and produce ...
food in plastic containers, putting plastics in the dishwasher
A dishwasher is a machine that is used to clean dishware, cookware, and cutlery automatically. Unlike manual dishwashing, which relies heavily on physical scrubbing to remove soiling, the mechanical dishwasher cleans by spraying hot water, ty ...
, or using harsh detergents.
Besides diet, exposure can also occur through air and through skin absorption.thermal paper
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
and carbonless copy paper
Carbonless copy paper (CCP), non-carbon copy paper, or NCR paper (No Carbon Required, taken from the initials of its creator, National Cash Register) is a type of coated paper designed to transfer information written on the front onto sheets benea ...
, which would be expected to be more available for exposure than BPA bound into resin or plastic.paper currency
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issued ...
in a wallet for 24 hours cause a dramatic increase in the concentration of BPA in paper currency, making paper money a secondary source of exposure.
Fetal and early-childhood exposures
A 2009 study found higher urinary concentrations in young children than in adults under typical exposure scenarios.
Regulation
Public health regulatory history in the United States
Charles Schumer
Charles Ellis Schumer ( ; born November 23, 1950) is an American politician serving as Senate Majority Leader since January 20, 2021. A member of the Democratic Party, Schumer is in his fourth Senate term, having held his seat since 1999, and ...
introduced a 'BPA-Free Kids Act of 2008' to the U.S. Senate seeking to ban BPA in any product designed for use by children and require the Center for Disease Control
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
to conduct a study about the health effects of BPA exposure. It was reintroduced in 2009 in both Senate and House, but died in committee each time.Diana Zuckerman
Diana M. Zuckerman (born 16 June 1950) is an American health policy analyst who focuses on the implications of policies for public health and patients' health. She specializes in national health policy, particularly in women's health and the saf ...
, president of the National Research Center for Women and Families
The National Center for Health Research (formerly known as the National Research Center for Women & Families) is a Washington, D.C.-based non-profit organization founded in 1999, providing health-related services such as providing free information ...
, criticized the FDA in her testimony at the FDA's public meeting on the draft assessment of bisphenol A for use in food contact applications, that "At the very least, the FDA should require a prominent warning on products made with BPA".
In March 2009 Suffolk County, New York became the first county to pass legislation to ban baby beverage containers made with bisphenol A. By March 2009, legislation to ban bisphenol A had been proposed in both House and Senate.
In the same month, Rochelle Tyl, author of two studies used by FDA to assert BPA safety in August 2008, said those studies did not claim that BPA is safe, because they were not designed to cover all aspects of the chemical's effects. In May 2009, Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
and Chicago were the first U.S. jurisdictions to pass regulations limiting or banning BPA. In June 2009, the FDA announced its decision to reconsider the BPA safety levels. Grassroots political action led Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
to become the first U.S. state to ban bisphenol A not only from infant formula and baby food containers, but also from any reusable food or beverage container. In July 2009, the California Environmental Protection Agency's Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Identification Committee in the California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment
The Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment, commonly referred to as OEHHA (pronounced oh-EEE-ha), is a specialized department within the cabinet-level California Environmental Protection Agency ( CalEPA) with responsibility for evaluatin ...
unanimously voted against placing Bisphenol A on the state's list of chemicals that are believed to cause reproductive harm. The panel was concerned over the growing scientific evidence showing BPA's reproductive harm in animals, found that there was insufficient data of the effects in humans. Critics pointed out that the same panel failed to add second-hand smoke
Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called secondhand smoke (SHS), or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by persons other than the intended "active" smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke enters an environment, causing its inhalat ...
to the list until 2006, and only one chemical was added to the list in the last three years. In September, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency announced that it was evaluating BPA for an action plan development. In October, the NIH
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
announced $30,000,000 in stimulus
A stimulus is something that causes a physiological response. It may refer to:
*Stimulation
**Stimulus (physiology), something external that influences an activity
**Stimulus (psychology), a concept in behaviorism and perception
*Stimulus (economi ...
grants to study the health effects of BPA. This money was supposed to result in many peer-reviewed publications.
On 15 January 2010, the FDA expressed "some concern", the middle level in its scale of concerns, about the potential effects of BPA on the brain, behavior, and prostate gland in fetuses, infants, and young children, and announced that it was taking reasonable steps to reduce human exposure to BPA in the food supply. However, the FDA was not recommending that families change the use of infant formula or foods, as it saw the benefit of a stable source of good nutrition as outweighing the potential risk from BPA exposure.Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
released information to help parents to reduce children's BPA exposure. As of 2010 many U.S. states were considering some sort of BPA ban.
In June 2010 the 2008–2009 Annual Report of the President's Cancer Panel was released and recommended: "Because of the long latency period of many cancers, the available evidence argues for a precautionary approach
The precautionary principle (or precautionary approach) is a broad epistemological, philosophical and legal approach to innovations with potential for causing harm when extensive scientific knowledge on the matter is lacking. It emphasizes cauti ...
to these diverse chemicals, which include (…) bisphenol A". In August 2010, the Maine Board of Environmental Protection voted unanimously to ban the sale of baby bottles and other reusable food and beverage containers made with bisphenol A as of January 2012. In February 2011, the newly elected governor of Maine, Paul LePage
Paul Richard LePage (; born October 9, 1948) is an American politician who served as the 74th Governor of Maine from 2011 to 2019. A member of the Republican Party, LePage served two terms as a city councilor in Waterville, Maine, before being ...
, gained national attention when he spoke on a local TV news show saying he hoped to repeal the ban because, "There hasn't been any science that identifies that there is a problem" and added: "The only thing that I've heard is if you take a plastic bottle and put it in the microwave and you heat it up, it gives off a chemical similar to estrogen. So the worst case is some women may have little beards." In April 2011, the Maine legislature passed a bill to ban the use of BPA in baby bottles, sippy cups, and other reusable food and beverage containers, effective 1 January 2012. Governor LePage refused to sign the bill.
In October 2011, California banned BPA from baby bottles and toddlers' drinking cups, effective 1 July 2013. By 2011, 26 states had proposed legislation that would ban certain uses of BPA. Many bills died in committee. In July 2011, the American Medical Association
The American Medical Association (AMA) is a professional association and lobbying group of physicians and medical students. Founded in 1847, it is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Membership was approximately 240,000 in 2016.
The AMA's sta ...
(AMA) declared feeding products for babies and infants that contain BPA should be banned. It recommended better federal oversight of BPA and clear labeling of products containing it. It stressed the importance of the FDA to "actively incorporate current science into the regulation of food and beverage BPA-containing products."
In 2012, the FDA concluded an assessment of scientific research on the effects of BPA and stated in the March 2012 Consumer Update that "the scientific evidence at this time does not suggest that the very low levels of human exposure to BPA through the diet are unsafe" although recognizing "potential uncertainties in the overall interpretation of these studies including route of exposure used in the studies and the relevance of animal models to human health. The FDA is continuing to pursue additional research to resolve these uncertainties." Yet on 17 July 2012, the FDA banned BPA from baby bottles and sippy cups. A FDA spokesman said the agency's action was not based on safety concerns and that "the agency continues to support the safety of BPA for use in products that hold food."American Chemistry Council
American Chemistry Council (ACC), formerly known as the Manufacturing Chemists' Association (at its founding in 1872) and then as the Chemical Manufacturers' Association (from 1978 until 2000), is an industry trade association for American chemic ...
, the chemical industry's main trade association, who believed that a ban would boost consumer confidence. The ban was criticized as "purely cosmetic" by the Environmental Working Group
The Environmental Working Group (EWG) is an American activist group that specializes in research and advocacy in the areas of agricultural subsidies, toxic chemicals, drinking water pollutants, and corporate accountability. EWG is a nonprofit ...
, which stated that "If the agency truly wants to prevent people from being exposed to this toxic chemical associated with a variety of serious and chronic conditions it should ban its use in cans of infant formula, food and beverages." The Natural Resources Defense Council
The Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) is a United States-based 501(c)(3) non-profit international environmental advocacy group, with its headquarters in New York City and offices in Washington D.C., San Francisco, Los Angeles, Chicago, Bo ...
called the move inadequate saying, the FDA needs to ban BPA from all food packaging.
Environmental regulation in the United States
On 30 December 2009 EPA released a so-called action plan
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 fil ...
for four chemicals, including BPA, which would have added it to the list of "chemicals of concern" regulated under the Toxic Substances Control Act
The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) is a United States law, passed by the 94th United States Congress in 1976 and administered by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), that regulates chemicals not regulated by other U. ...
. In February 2010, after lobbyists for the chemical industry had met with administration officials, the EPA delayed BPA regulation by not including the chemical.
On 29 March 2010, EPA published a revised action plan for BPA as "chemical of concern". In October 2010 an advanced Notice of Proposed Rulemaking
A Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) is a public notice that is issued by law when an independent agency of the US government wishes to add, remove, or change a rule or regulation as part of the rulemaking process. The notice is an important ...
for BPA testing was published in the Federal Register July 2011. After more than 3 years at the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs (OIRA), part of the Office of Management and Budget
The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, pol ...
(OMB), which has to review draft proposals within 3 months, OIRA had not done so.
In September 2013 EPA withdrew its 2010 draft BPA rule. saying the rule was "no longer necessary", because EPA was taking a different track at looking at chemicals, a so-called "Work Plan" of more than 80 chemicals for risk assessment and risk reduction. Another proposed rule that EPA withdrew would have limited industry's claims of confidential business information (CBI) for the health and safety studies needed, when new chemicals are submitted under TSCA for review. The EPA said it continued "to try to reduce unwarranted claims of confidentiality and has taken a number of significant steps that have had dramatic results... tightening policies for CBI claims and declassifying unwarranted confidentiality claims, challenging companies to review existing CBI claims to ensure that they are still valid and providing easier and enhanced access to a wider array of information."
The chemical industry group American Chemistry Council
American Chemistry Council (ACC), formerly known as the Manufacturing Chemists' Association (at its founding in 1872) and then as the Chemical Manufacturers' Association (from 1978 until 2000), is an industry trade association for American chemic ...
commended EPA for "choosing a course of action that will ultimately strengthen the performance of the nation's primary chemical management law." Richard Denison, senior scientist with the Environmental Defense Fund
Environmental Defense Fund or EDF (formerly known as Environmental Defense) is a United States-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group. The group is known for its work on issues including global warming, ecosystem restoration, oceans, and hu ...
, commented "both rules were subject to intense opposition and lobbying from the chemical industry" and "Faced presumably with the reality that he Office of Information and Regulatory Affairswas never going to let EPA even propose the rules for public comment, EPA decided to withdraw them."
On 29 January 2014 EPA released a final alternatives assessment Alternatives assessment or alternatives analysis is a problem-solving approach used in environmental design, technology, and policy. It aims to minimize environmental harm by comparing multiple potential solutions in the context of a specific proble ...
for BPA in thermal paper as part of its Design for the Environment Design for the Environment (DfE) is a design approach to reduce the overall human health and environmental impact of a product, process or service, where impacts are considered across its life cycle. Different software tools have been developed to a ...
program.
Chemical manufacturers reactions to bans
In March 2009 the six largest U.S. producers of baby bottles decided to stop using bisphenol A in their products. The same month Sunoco, a producer of gasoline and chemicals, refused to sell BPA to companies for use in food and water containers for children younger than 3, saying it could not be certain of the compound's safety.
In May 2009, Lyndsey Layton from the Washington Post accused manufacturers of food and beverage containers and some of their biggest customers of the public relations and lobbying strategy to block government BPA bans. She noted that, "Despite more than 100 published studies by government scientists and university laboratories that have raised health concerns about the chemical, the Food and Drug Administration has deemed it safe largely because of two studies, both funded by a chemical industry trade group". In August 2009 the '' Milwaukee Journal Sentinel'' investigative series into BPA and its effects showed the Society of the Plastics Industry
Founded in 1937, the Society of the Plastics Industry, Inc. was a professional society representing individuals in the plastics industry. In 2010, the organization began doing business as SPI: The Plastics Industry Trade Association, before changi ...
plans of a major public relations blitz to promote BPA, including plans to attack and discredit those who report or comment negatively on BPA and its effects.
BPA free, unknown substitute
The chemical industry over time responded to criticism of BPA by promoting "BPA-free" products. For example, in 2010, General Mills
General Mills, Inc., is an American multinational manufacturer and marketer of branded processed consumer foods sold through retail stores. Founded on the banks of the Mississippi River at Saint Anthony Falls in Minneapolis, the company orig ...
announced it had found a "BPA-free alternative" can liner that works with tomatoes. It said it would begin using the BPA-free alternative in tomato products sold by its organic foods subsidiary Muir Glen with that year's tomato harvest. As of 2014, General Mills has refused to state which alternative chemical it uses, and whether it uses it on any of its other canned products.
BPA free, epoxyfree
A minority of companies have stated what alternative compound(s) they use. Following an inquiry by Representative Edward Markey
Edward John Markey (born July 11, 1946) is an American lawyer, politician, and former Army reservist who has served as the junior United States senator from Massachusetts since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the U.S. representat ...
(D-Mass) seventeen companies replied saying they were going BPA-free, including Campbell Soup Company and General Mills Inc.Bisphenol S
Bisphenol S (BPS) is an organic compound with the formula (HOC6H4)2SO2. It has two phenol functional groups on either side of a sulfonyl group. It is commonly used in curing fast-drying epoxy resin adhesives. It is classified as a bisphenol, ...
; only four stated the alternative to BPA that they will be using. ConAgra
Conagra Brands, Inc. (formerly ConAgra Foods) is an American consumer packaged goods holding company headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Conagra makes and sells products under various brand names that are available in supermarkets, restaurants, ...
stated in 2013 "alternate liners for tomatoes are vinyl
Vinyl may refer to:
Chemistry
* Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a particular vinyl polymer
* Vinyl cation, a type of carbocation
* Vinyl group, a broad class of organic molecules in chemistry
* Vinyl polymer, a group of polymers derived from vinyl ...
...New aerosol cans are lined with polyester resin Polyester resins are synthetic resins formed by the reaction of dibasic organic acids and polyhydric alcohols. Maleic anhydride is a commonly used raw material with diacid functionality in unsaturated polyester resins. Unsaturated polyester res ...
". Eden Foods
Eden Foods, Inc., (also known as Eden Organic) is an organic food company based in Clinton, Michigan. It is best known for its Edensoy line of organic soy milk, and its line of organic Japanese foods and condiments. The company claims to be the o ...
stated that only their "beans are canned with a liner of an oleoresinous c-enamel that does not contain the endocrine disruptor BPA. Oleoresin Oleoresins are semi-solid extracts composed of resin and essential or fatty oil, obtained by evaporation of the solvents used for their production. The oleoresin of conifers is known as crude turpentine or gum turpentine, which consists of oil of ...
is a mixture of oil and resin extracted from plants such as pine or balsam fir". Hain Celestial Group
The Hain Celestial Group, Inc. is an American food company whose main focus is natural foods and botanically-based personal care products. Its products range from herbal teas, sold by its Celestial Seasonings brand to snacks offered through its Te ...
will use "modified polyester and/ or acrylic
Acrylic may refer to:
Chemicals and materials
* Acrylic acid, the simplest acrylic compound
* Acrylate polymer, a group of polymers (plastics) noted for transparency and elasticity
* Acrylic resin, a group of related thermoplastic or thermosett ...
… by June 2014 for our canned soups, beans, and vegetables". Heinz stated in 2011 it "intend to replace epoxy linings in all our food containers…. We have prioritized baby foods", and in 2012 "no BPA in any plastic containers we use".
BPA substitute BPS
Some "BPA free" plastics are made from epoxy containing a compound called bisphenol S (BPS). BPS shares a similar structure and versatility to BPA and has been used in numerous products from currency to thermal receipt paper. Widespread human exposure to BPS was confirmed in an analysis of urine samples taken in the U.S., Japan, China, and five other Asian countries. Researchers found BPS in all the receipt paper, 87 percent of the paper currency and 52 percent of recycled paper they tested. The study found that people may be absorbing 19 times more BPS through their skin than the amount of BPA they absorbed, when it was more widely used.
Phenol-based substitutes
Among potential substitutes for BPA, phenol-based chemicals closely related to BPA have been identified. The non-extensive list includes bisphenol E (BPE), bisphenols B (BPB), 4-cumylphenol (HPP) and bisphenol F (BPF), with only BPS being currently used as main substitute in thermal paper.
Degradation of BPA
Microbial degradation
The enzyme 4-hydroxyacetophenone monooxygenase, which can be found in '' Pseudomonas fluorescens'', uses (4-hydroxyphenyl)ethan-1-one, NADPH, H+ and O2 to produce 4-hydroxyphenyl acetate, NADP+, and H2O.
The fungus ''Cunninghamella elegans
''Cunninghamella elegans'' is a species of fungus in the genus '' Cunninghamella'' found in soil.
It can be grown in Sabouraud dextrose broth, a liquid medium used for cultivation of yeasts and molds from liquid which are normally sterile.
As ...
'' is also able to degrade synthetic phenolic compounds like bisphenol A.
Plant degradation
''Portulaca oleracea
''Portulaca oleracea'' (common purslane, also known as little hogweed, or pursley) is an annual (actually tropical perennial in USDA growing zones 10–11) succulent in the family Portulacaceae.
Description
The plant may reach in height. It ...
'' efficiently removes bisphenol A from a hydroponic solution. How this happens is unclear.
Photodegradation
Photodegradation Photodegradation is the alteration of materials by light. Commonly, the term is used loosely to refer to the combined action of sunlight and air, which cause oxidation and hydrolysis. Often photodegradation is intentionally avoided, since it destro ...
is BPA's main method of natural weathering in the environment, via the Photo Fries rearrangement. Experimentally, BPA has been shown to photodegrade in reactions catalyzed by zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, and tin dioxide, as methods of water decontamination procedures.phenyl salicylate
Phenyl salicylate, or salol, is the organic compound with the formula C6H5O2C6H4OH. It is a white solid. It is occasionally used in sunscreens and as an antiseptic.
Production and reactions
The title compound was synthesized first in 1883 by th ...
and dihydroxybenzophenone derivatives before the energized ring releases carbon dioxide. In aqueous solution, BPA shows UV absorption of wavelengths between 250 nm and 360 nm, and the Photo Fries degradation occurs at wavelengths less than 300 nm.
Combustion of BPA
 Hydroxyl radicals are powerful
Hydroxyl radicals are powerful oxidants
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxi ...
that transform BPA into different forms of phenolic group compounds. The advanced photocatalytic oxidation of BPA, using compounds like sodium hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite (commonly known in a dilute solution as bleach) is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula NaOCl (or NaClO), comprising a sodium cation () and a hypochlorite anion (or ). It may also be viewed as the sodium s ...
, NaOCl, as the oxidizing agent, can accelerate the degradation efficiency by releasing oxygen into the water. This decomposition occurs when BPA is exposed to UV irradiation.
Oxidation of BPA by ozone
 During water treatment, BPA can be removed through
During water treatment, BPA can be removed through ozonation
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
. A 2008 study has identified the degradation products of this reaction, through the use of liquid chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a ...
and mass spectrometry.
Kinetics of BPA degradation
In 1991, the first explanation of the rate of BPA degradation through ozonation was determined.
References
Further reading
*
*
External links
International Chemical Safety Cards – Bisphenol A
NIOSH, partly updated in October 2005. Retrieved 8 April 2015
FDA, November 2014. Retrieved 8 April 2015
BPA Data Gap Analysis
FDA, undated. Retrieved 8 April 2015
Bisphenol A website
Polycarbonate/BPA Global Group, American Chemistry Council. Retrieved 8 April 2015
Bisphenol A articles
Environmental Health Perspectives
''Environmental Health Perspectives'' (''EHP'') is a peer-reviewed open access journal published monthly with support from the U.S. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIE ...
by NIEHS
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) conducts research into the effects of the environment on human disease, as one of the 27 institutes and centers of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is located in the Rese ...
. Retrieved 8 April 2015 (200 articles)(open access)
Bisphenol A
ChemSub Online. Retrieved 8 April 2015
How to Protect Your Baby from BPA (Bisphenol A)
Brochure, 2 pages, 2009, Massachusetts Department of Public Health. Retrieved 8 April 2015
Plastic Not Fantastic with Bisphenol A
19 February 2008 By David Biello, www.scientificamerican.com. Retrieved 8 April 2015
Hazard in a bottle. The plastics industry's Pyrrhic victory
Attempt to regulate BPA in California defeated, ''The Economist'', 22 August 2008
Lyndsey Layton. Washington Post, 23 February 2010. Retrieved 8 April 2015
*
i
Science Friday
24 October 2014.
U.S. FDA statement, 2008
{{Authority control
Endocrine disruptors
Medical controversies
Nonsteroidal antiandrogens
Plasticizers
Selective estrogen receptor modulators
Xenoestrogens
 A 2007 study investigated the interaction between bisphenol A's and estrogen-related receptor γ (ERR-γ). This
A 2007 study investigated the interaction between bisphenol A's and estrogen-related receptor γ (ERR-γ). This  According to the
According to the  A 2007 review concluded that bisphenol-A has been shown to bind to thyroid hormone receptor and perhaps has selective effects on its functions.
A 2009 review about environmental chemicals and thyroid function raised concerns about BPA effects on
A 2007 review concluded that bisphenol-A has been shown to bind to thyroid hormone receptor and perhaps has selective effects on its functions.
A 2009 review about environmental chemicals and thyroid function raised concerns about BPA effects on  A 2009 review raised concerns about a BPA effect on the anteroventral periventricular nucleus.
A 2009 review raised concerns about a BPA effect on the anteroventral periventricular nucleus.
 Higher susceptibility to breast cancer has been found in many studies of rodents and primates exposed to BPA. However, it is the impact BPA has on breast cancer development in humans is unclear, as it is difficult to quantify an individual's BPA exposure over their lifetime. BPA, which includes a phenolic structure, has shown an association with agonist and antagonistic endocrine receptors that facilitate endocrine disorders such as breast and prostate cancer. Other endocrine disorders include infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome, and precocious puberty.
More oxidative stress in breast cancer cells were found to be directly proportional to BPA exposure as per the findings in several in vitro studies. Additionally, work related exposure to BPA, and women who are postmenopausal have suggested an increase in breast cancer incidence.
Higher susceptibility to breast cancer has been found in many studies of rodents and primates exposed to BPA. However, it is the impact BPA has on breast cancer development in humans is unclear, as it is difficult to quantify an individual's BPA exposure over their lifetime. BPA, which includes a phenolic structure, has shown an association with agonist and antagonistic endocrine receptors that facilitate endocrine disorders such as breast and prostate cancer. Other endocrine disorders include infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome, and precocious puberty.
More oxidative stress in breast cancer cells were found to be directly proportional to BPA exposure as per the findings in several in vitro studies. Additionally, work related exposure to BPA, and women who are postmenopausal have suggested an increase in breast cancer incidence.

 Hydroxyl radicals are powerful
Hydroxyl radicals are powerful  During water treatment, BPA can be removed through
During water treatment, BPA can be removed through