B-Raf Inhibitor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
BRAF is a human
 Conserved Region 3 (CR3), residues 457–717, makes up B-Raf's enzymatic kinase domain. This largely conserved structure is bi-lobal, connected by a short hinge region. The smaller N-lobe (residues 457–530) is primarily responsible for
Conserved Region 3 (CR3), residues 457–717, makes up B-Raf's enzymatic kinase domain. This largely conserved structure is bi-lobal, connected by a short hinge region. The smaller N-lobe (residues 457–530) is primarily responsible for
 To effectively catalyze protein phosphorylation via the bimolecular substitution of serine and threonine residues with
To effectively catalyze protein phosphorylation via the bimolecular substitution of serine and threonine residues with
 BAY43-9006 (
BAY43-9006 (
 PLX4032 (
PLX4032 (
Finding faults in BRAF
— Cancer Research UK blog post about the discovery of cancer-causing BRAF mutations (incl video) * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no Oncogenes EC 2.7.11
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
that encodes a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
called B-Raf. The gene is also referred to as proto-oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
B-Raf and v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, while the protein is more formally known as serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf.
The B-Raf protein is involved in sending signals
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
inside cells which are involved in directing cell growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than ...
. In 2002, it was shown to be mutated
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitos ...
in some human cancers.
Certain other inherited ''BRAF'' mutations cause birth defects.
Drugs that treat cancers driven by ''BRAF'' mutations have been developed. Two of these drugs, vemurafenib
Vemurafenib (INN, marketed as Zelboraf) is an inhibitor of the B-Raf enzyme developed by Plexxikon (now part of Daiichi-Sankyo) and Genentech for the treatment of late-stage melanoma.; The name "vemurafenib" comes from V600E mutated BRAF in ...
and dabrafenib
Dabrafenib, sold under the brand name Tafinlar & Rafinlar ( both by Novartis) among others, is a medication for the treatment of cancers associated with a mutated version of the gene BRAF. Dabrafenib acts as an inhibitor of the associated enzym ...
are approved by FDA for treatment of late-stage melanoma. Vemurafenib was the first approved drug to come out of fragment-based drug discovery.
Function
B-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of growthsignal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
protein kinases. This protein plays a role in regulating the MAP kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine (i.e., a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase). MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses ...
/ ERKs signaling pathway, which affects cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
, differentiation, and secretion.
Structure
B-Raf is a 766-amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
, regulated signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
serine/threonine-specific protein kinase. Broadly speaking, it is composed of three conserved domains characteristic of the Raf kinase family: conserved region 1 (CR1), a Ras
Ras or RAS may refer to:
Arts and media
* RAS Records Real Authentic Sound, a reggae record label
* Rundfunk Anstalt Südtirol, a south Tyrolese public broadcasting service
* Rás 1, an Icelandic radio station
* Rás 2, an Icelandic radio stati ...
- GTP-binding self-regulatory domain, conserved region 2 (CR2), a serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form un ...
-rich hinge region, and conserved region 3 (CR3), a catalytic protein kinase domain that phosphorylates a consensus sequence
In molecular biology and bioinformatics, the consensus sequence (or canonical sequence) is the calculated order of most frequent residues, either nucleotide or amino acid, found at each position in a sequence alignment. It serves as a simplified r ...
on protein substrates. In its active conformation, B-Raf forms dimers via hydrogen-bonding
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
and electrostatic interactions of its kinase domains.
CR1
Conserved region 1 autoinhibits B-Raf's kinase domain (CR3) so that B-Raf signaling is regulated rather than constitutive. Residues 155–227 make up theRas
Ras or RAS may refer to:
Arts and media
* RAS Records Real Authentic Sound, a reggae record label
* Rundfunk Anstalt Südtirol, a south Tyrolese public broadcasting service
* Rás 1, an Icelandic radio station
* Rás 2, an Icelandic radio stati ...
-binding domain (RBD), which binds to Ras-GTP's effector domain to release CR1 and halt kinase inhibition. Residues 234–280 comprise a phorbol
Phorbol is a natural, plant-derived organic compound. It is a member of the tigliane family of diterpenes. Phorbol was first isolated in 1934 as the hydrolysis product of croton oil, which is derived from the seeds of the purging croton, '' Croto ...
ester/ DAG-binding zinc finger motif that participates in B-Raf membrane docking after Ras-binding.
CR2
Conserved Region 2 (CR2) provides a flexible linker that connects CR1 and CR3 and acts as a hinge.CR3
 Conserved Region 3 (CR3), residues 457–717, makes up B-Raf's enzymatic kinase domain. This largely conserved structure is bi-lobal, connected by a short hinge region. The smaller N-lobe (residues 457–530) is primarily responsible for
Conserved Region 3 (CR3), residues 457–717, makes up B-Raf's enzymatic kinase domain. This largely conserved structure is bi-lobal, connected by a short hinge region. The smaller N-lobe (residues 457–530) is primarily responsible for ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
binding while the larger C-lobe (residues 535–717) binds substrate proteins. The active site is the cleft between the two lobes, and the catalytic Asp
Asp may refer to:
Places
* Asp, part of Densbüren, Aargau, Switzerland
* Aspe (''Asp'' in Valencian), Alicante, Spain
* Asp Lake, a lake in Minnesota
Animals
* Asp (fish)
* Asp (snake), in antiquity, one of several venomous snakes
** ''Cera ...
576 residue is located on the C-lobe, facing the inside of this cleft.
Subregions
P-Loop The P-loop of B-Raf (residues 464–471) stabilizes the non-transferablephosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
groups of ATP during enzyme ATP-binding. Specifically, S467, F468, and G469 backbone amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is ...
s hydrogen-bond to the β-phosphate of ATP to anchor the molecule. B-Raf functional motifs have been determined by analyzing the homology of PKA
PKA may refer to:
* Professionally known as:
** Pen name
** Stage persona
* p''K''a, the symbol for the acid dissociation constant at logarithmic scale
* Protein kinase A, a class of cAMP-dependent enzymes
* Pi Kappa Alpha, the North-American so ...
analyzed by Hanks and Hunter to the B-Raf kinase domain.
Nucleotide-Binding Pocket
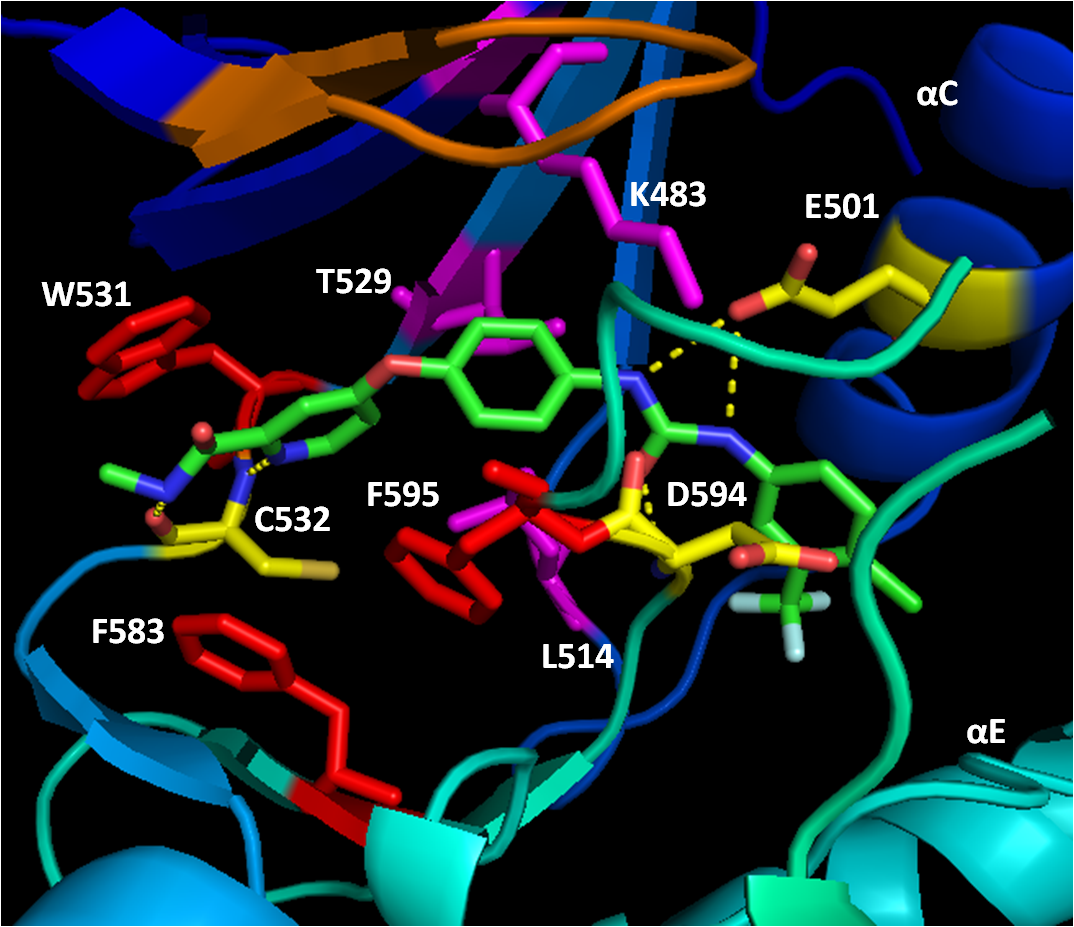
V471, C532, W531, T529, L514, and A481 form a hydrophobic pocket within which the adenine of ATP is anchored through Van der Waals attractions upon ATP binding.
Catalytic Loop
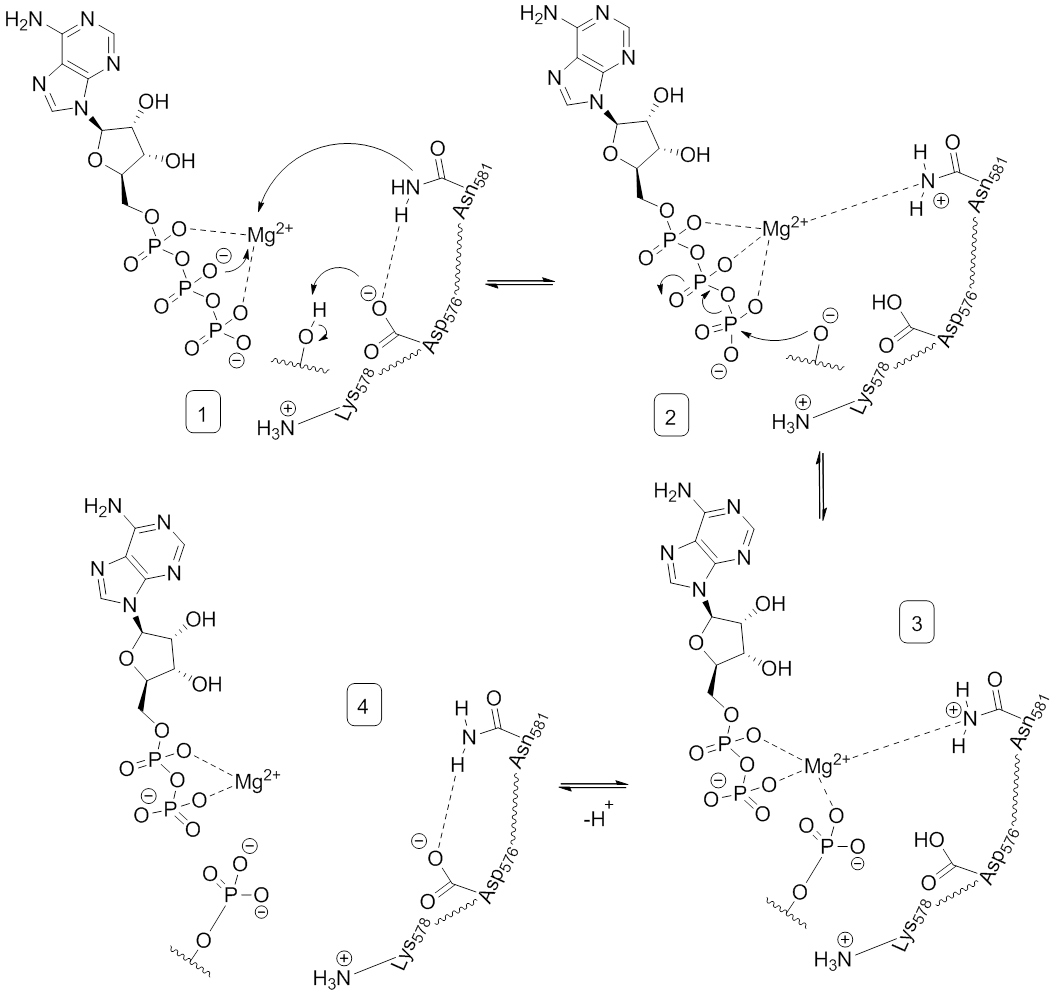
Residues 574–581 compose a section of the kinase domain responsible for supporting the transfer of the γ-phosphate of ATP to B-Raf's protein substrate. In particular, D576 acts as a proton acceptor to activate the nucleophilic hydroxyl oxygen on substrate serine or threonine residues, allowing the phosphate transfer reaction to occur mediated by base-catalysis.
DFG Motif
D594, F595, and G596 compose a motif central to B-Raf's function in both its inactive and active state. In the inactive state, F595 occupies the nucleotide-binding pocket, prohibiting ATP from entering and decreasing the likelihood of enzyme catalysis. In the active state, D594 chelates
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...
the divalent magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
that stabilizes the β- and γ-phosphate groups of ATP, orienting the γ-phosphate for transfer.
Activation Loop
Residues 596–600 form strong hydrophobic interactions with the P-loop in the inactive conformation of the kinase, locking the kinase in its inactive state until the activation loop
In molecular biology, an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure, typically in the absence of its macromolecular interaction partners, such as other proteins or RNA. IDPs rang ...
is phosphorylated, destabilizing these interactions with the presence of negative charge. This triggers the shift to the active state of the kinase. Specifically, L597 and V600 of the activation loop interact with G466, F468, and V471 of the P-loop to keep the kinase domain inactive until it is phosphorylated.
Enzymology
B-Raf is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase. As such, it catalyzes the phosphorylation ofserine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form un ...
and threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO� ...
residues in a consensus sequence
In molecular biology and bioinformatics, the consensus sequence (or canonical sequence) is the calculated order of most frequent residues, either nucleotide or amino acid, found at each position in a sequence alignment. It serves as a simplified r ...
on target proteins by ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
, yielding ADP
Adp or ADP may refer to:
Aviation
* Aéroports de Paris, airport authority for the Parisian region in France
* Aeropuertos del Perú, airport operator for airports in northern Peru
* SLAF Anuradhapura, an airport in Sri Lanka
* Ampara Air ...
and a phosphorylated protein as products. Since it is a highly regulated signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
, B-Raf must first bind Ras
Ras or RAS may refer to:
Arts and media
* RAS Records Real Authentic Sound, a reggae record label
* Rundfunk Anstalt Südtirol, a south Tyrolese public broadcasting service
* Rás 1, an Icelandic radio station
* Rás 2, an Icelandic radio stati ...
- GTP before becoming active as an enzyme. Once B-Raf is activated, a conserved protein kinase catalytic core phosphorylates protein substrates by promoting the nucleophilic attack of the activated substrate serine or threonine hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
oxygen atom on the γ-phosphate group of ATP through bimolecular nucleophilic substitution
The SN2 reaction is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry. In this mechanism, one bond is broken and one bond is formed in a concerted way, i.e., in one step. The name SN2 refers to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the m ...
.
Activation
Relieving CR1 autoinhibition
The kinase (CR3) domain of human Raf kinases is inhibited by two mechanisms: autoinhibition by its ownregulatory
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. For ...
Ras
Ras or RAS may refer to:
Arts and media
* RAS Records Real Authentic Sound, a reggae record label
* Rundfunk Anstalt Südtirol, a south Tyrolese public broadcasting service
* Rás 1, an Icelandic radio station
* Rás 2, an Icelandic radio stati ...
- GTP-binding CR1 domain and a lack of post-translational phosphorylation of key serine and tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Gr ...
residues (S338 and Y341 for c-Raf) in the CR2 hinge region. During B-Raf activation, the protein's autoinhibitory CR1 domain first binds Ras-GTP's effector domain to the CR1 Ras-binding domain (RBD) to release the kinase CR3 domain like other members of the human Raf kinase family. The CR1-Ras interaction is later strengthened through the binding of the cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
-rich subdomain (CRD) of CR1 to Ras and membrane phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s. Unlike A-Raf and C-Raf, which must be phosphorylated on hydroxyl-containing CR2 residues before fully releasing CR1 to become active, B-Raf is constituitively phosphorylated on CR2 S445. This allows the negatively charged phosphoserine to immediately repel CR1 through steric and electrostatic interactions once the regulatory domain is unbound, freeing the CR3 kinase domain to interact with substrate proteins.
CR3 domain activation
After the autoinhibitory CR1 regulatory domain is released, B-Raf's CR3kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
domain must change to its ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
-binding active conformer before it can catalyze protein phosphorylation
Protein phosphorylation is a reversible post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural ...
. In the inactive conformation, F595 of the DFG motif blocks the hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
adenine
Adenine () ( symbol A or Ade) is a nucleobase (a purine derivative). It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine. Its derivati ...
binding pocket while activation loop
In molecular biology, an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure, typically in the absence of its macromolecular interaction partners, such as other proteins or RNA. IDPs rang ...
residues form hydrophobic interactions with the P-loop, stopping ATP
ATP may refer to:
Companies and organizations
* Association of Tennis Professionals, men's professional tennis governing body
* American Technical Publishers, employee-owned publishing company
* ', a Danish pension
* Armenia Tree Project, non ...
from accessing its binding site. When the activation loop is phosphorylated, the negative charge of the phosphate is unstable in the hydrophobic environment of the P-loop. As a result, the activation loop changes conformation, stretching out across the C-lobe of the kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
domain. In this process, it forms stabilizing β-sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a gen ...
interactions with the β6 strand. Meanwhile, the phosphorylated residue approaches K507, forming a stabilizing salt bridge to lock the activation loop into place. The DFG motif changes conformation with the activation loop, causing F595 to move out of the adenine nucleotide binding site and into a hydrophobic pocket bordered by the αC and αE helices. Together, DFG and activation loop movement upon phosphorylation open the ATP binding site. Since all other substrate-binding and catalytic domains are already in place, phosphorylation of the activation loop alone activates B-Raf's kinase domain through a chain reaction that essentially removes a lid from an otherwise-prepared active site.
Mechanism of catalysis
 To effectively catalyze protein phosphorylation via the bimolecular substitution of serine and threonine residues with
To effectively catalyze protein phosphorylation via the bimolecular substitution of serine and threonine residues with ADP
Adp or ADP may refer to:
Aviation
* Aéroports de Paris, airport authority for the Parisian region in France
* Aeropuertos del Perú, airport operator for airports in northern Peru
* SLAF Anuradhapura, an airport in Sri Lanka
* Ampara Air ...
as a leaving group, B-Raf must first bind ATP and then stabilize the transition state
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked wi ...
as the γ-phosphate of ATP is transferred.
ATP binding
B-Raf binds ATP by anchoring the adenine nucleotide in a nonpolar pocket (yellow, Figure 1) and orienting the molecule through hydrogen-bonding and electrostatic interactions with phosphate groups. In addition to the P-loop and DFG motif phosphate binding described above, K483 and E501 play key roles in stabilizing non-transferable phosphate groups. The positive charge on the primaryamine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
of K483 allows it to stabilize the negative charge on ATP α- and β-phosphate groups when ATP binds. When ATP is not present, the negative charge of the E501 carboxyl group balances this charge.
Phosphorylation
Once ATP is bound to the B-Raf kinase domain, D576 of the catalytic loop activates a substrate hydroxyl group, increasing its nucleophilicity to kinetically drive the phosphorylation reaction while other catalytic loop residues stabilize the transition state.(Figure 2). N581 chelates the divalent magnesium cation associated with ATP to help orient the molecule for optimal substitution. K578 neutralizes the negative charge on the γ-phosphate group of ATP so that the activated ser/thr substrate residue won't experience as much electron-electron repulsion when attacking the phosphate. After the phosphate group is transferred, ADP and the new phosphoprotein are released.Inhibitors
Since constitutively active B-Raf mutants commonly cause cancer (see Clinical Significance) by excessively signaling cells to grow, inhibitors of B-Raf have been developed for both the inactive and active conformations of the kinase domain as cancer therapeutic candidates.Sorafenib
 BAY43-9006 (
BAY43-9006 (Sorafenib
Sorafenib, sold under the brand name Nexavar, is a kinase inhibitor drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer (advanced renal cell carcinoma), advanced primary liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma), FLT3-ITD positive AML and r ...
, Nexavar) is a V600E mutant
In biology, and especially in genetics, a mutant is an organism or a new genetic character arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is generally an alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome or chromosome of an organism. It ...
B-Raf and C-Raf inhibitor approved by the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
for the treatment of primary liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
and kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
cancer. Bay43-9006 disables the B-Raf kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
domain by locking the enzyme in its inactive form. The inhibitor accomplishes this by blocking the ATP binding pocket through high-affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Partn ...
for the kinase domain. It then binds key activation loop and DFG motif residues to stop the movement of the activation loop and DFG motif to the active conformation. Finally, a trifluoromethyl phenyl moiety sterically blocks the DFG motif and activation loop active conformation site, making it impossible for the kinase domain to shift conformation to become active.
The distal pyridyl
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a d ...
ring of BAY43-9006 anchors in the hydrophobic nucleotide-binding pocket of the kinase N-lobe, interacting with W531, F583, and F595. The hydrophobic interactions with catalytic loop F583 and DFG motif F595 stabilize the inactive conformation of these structures, decreasing the likelihood of enzyme activation. Further hydrophobic interaction of K483, L514, and T529 with the center phenyl ring increase the affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Partn ...
of the kinase domain for the inhibitor. Hydrophobic interaction of F595 with the center ring as well decreases the energetic favorability of a DFG conformation switch further. Finally, polar interactions of BAY43-9006 with the kinase domain continue this trend of increasing enzyme affinity for the inhibitor and stabilizing DFG residues in the inactive conformation. E501 and C532 hydrogen bond the urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important r ...
and pyridyl groups of the inhibitor respectively while the urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important r ...
carbonyl accepts a hydrogen bond from D594's backbone amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is ...
nitrogen to lock the DFG motif in place.
The trifluoromethyl phenyl moiety cements the thermodynamic favorability of the inactive conformation when the kinase domain is bound to BAY43-9006 by sterically blocking the hydrophobic pocket between the αC and αE helices that the DFG motif and activation loop would inhabit upon shifting to their locations in the active conformation of the protein.
Vemurafenib
 PLX4032 (
PLX4032 (Vemurafenib
Vemurafenib (INN, marketed as Zelboraf) is an inhibitor of the B-Raf enzyme developed by Plexxikon (now part of Daiichi-Sankyo) and Genentech for the treatment of late-stage melanoma.; The name "vemurafenib" comes from V600E mutated BRAF in ...
) is a V600 mutant
In biology, and especially in genetics, a mutant is an organism or a new genetic character arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is generally an alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome or chromosome of an organism. It ...
B-Raf inhibitor approved by the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
for the treatment of late-stage melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye ( ...
. Unlike BAY43-9006, which inhibits the inactive form of the kinase domain, Vemurafenib inhibits the active "DFG-in" form of the kinase, firmly anchoring itself in the ATP-binding site. By inhibiting only the active form of the kinase, Vemurafenib selectively inhibits the proliferation of cells with unregulated B-Raf, normally those that cause cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
.
Since Vemurafenib only differs from its precursor, PLX4720, in a phenyl ring added for pharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ...
reasons, PLX4720's mode of action is equivalent to Vemurafenib's. PLX4720 has good affinity for the ATP binding site partially because its anchor region, a 7-aza indole bicyclic, only differs from the natural adenine that occupies the site in two places where nitrogen atoms have been replaced by carbon. This enables strong intermolecular interactions like N7 hydrogen bonding to C532 and N1 hydrogen bonding to Q530 to be preserved. Excellent fit within the ATP-binding hydrophobic pocket (C532, W531, T529, L514, A481) increases binding affinity as well. Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ...
linker hydrogen bonding to water and difluoro-phenyl fit in a second hydrophobic pocket (A481, V482, K483, V471, I527, T529, L514, and F583) contribute to the exceptionally high binding affinity overall. Selective binding to active Raf is accomplished by the terminal propyl group that binds to a Raf-selective pocket created by a shift of the αC helix. Selectivity for the active conformation of the kinase is further increased by a pH-sensitive deprotonated sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. ...
group that is stabilized by hydrogen bonding with the backbone peptide NH of D594 in the active state. In the inactive state, the inhibitor's sulfonamide group interacts with the backbone carbonyl of that residue instead, creating repulsion. Thus, Vemurafenib binds preferentially to the active state of B-Raf's kinase domain.
Clinical significance
Mutations in the ''BRAF'' gene can cause disease in two ways. First, mutations can be inherited and cause birth defects. Second, mutations can appear later in life and cause cancer, as an oncogene. Inherited mutations in this gene cause cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, a disease characterized by heart defects, mental retardation and a distinctive facial appearance. Mutations in this gene have been found in cancers, includingnon-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. ...
, colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel m ...
, malignant melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye ( ...
, papillary thyroid carcinoma, non-small-cell lung carcinoma, adenocarcinoma of the lung
Adenocarcinoma of the lung is the most common type of lung cancer, and like other forms of lung cancer, it is characterized by distinct cellular and molecular features. It is classified as one of several non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), to di ...
, brain tumors
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondar ...
including glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is one of the most aggressive types of cancer that begin within the brain. Initially, signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality ch ...
and pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) is a brain tumor that occurs most frequently in children and teenagers. At Boston Children's Hospital, the average age at diagnosis is 12 years.
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma usually develops within the suprat ...
as well as inflammatory diseases like Erdheim-Chester disease.
The V600E mutation of the BRAF gene has been associated with hairy cell leukemia in numerous studies and has been suggested for use in screening for Lynch syndrome to reduce the number of patients undergoing unnecessary MLH1
DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 or MutL protein homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MLH1 gene located on chromosome 3. It is a gene commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Orthologs of human MLH1 h ...
sequencing.
Mutants
More than 30 mutations of the ''BRAF'' gene associated with human cancers have been identified. The frequency of BRAF mutations varies widely in human cancers, from more than 80% inmelanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye ( ...
s and nevi
Nevus (plural nevi) is a nonspecific medical term for a visible, circumscribed, chronic lesion of the skin or mucosa. The term originates from ''nævus'', which is Latin for "birthmark"; however, a nevus can be either congenital (present at bir ...
, to as little as 0–18% in other tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s, such as 1–3% in lung cancers and 5% in colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel m ...
. In 90% of the cases, thymine is substituted with adenine at nucleotide 1799. This leads to valine (V) being substituted for by glutamate (E) at codon 600 (now referred to as V600E V600E is a mutation of the BRAF gene in which valine (V) is substituted by glutamic acid (E) at amino acid 600. It is a driver mutation in a proportion of certain diagnoses, including melanoma, hairy cell leukemia, papillary thyroid carcinoma, ...
) in the activation segment that has been found in human cancers. This mutation has been widely observed in papillary thyroid carcinoma, colorectal cancer, melanoma and non-small-cell lung cancer. BRAF-V600E mutation are present in 57% of Langerhans cell histiocytosis patients. The V600E mutation is a likely driver mutation in 100% of cases of hairy cell leukaemia
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon hematological malignancy characterized by an accumulation of abnormal B lymphocytes. It is usually classified as a subtype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Hairy cell leukemia makes up about 2% of all leu ...
. * High frequency of BRAF V600E mutations have been detected in ameloblastoma, a benign but locally infiltrative odontogenic neoplasm. The V600E mutation may also be linked, as a single-driver mutation (a genetic 'smoking gun') to certain cases of papillary craniopharyngioma
A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor derived from pituitary gland embryonic tissue that occurs most commonly in children, but also affects adults. It may present at any age, even in the prenatal and neonatal periods, but peak incidence ...
development.*
Other mutations which have been found are R461I, I462S, G463E, G463V, G465A, G465E, G465V, G468A, G468E, G469R, N580S, E585K, D593V, F594L, G595R, L596V, T598I, V599D, V599E, V599K, V599R, V600K, A727V, etc. and most of these mutations are clustered to two regions: the glycine-rich P loop of the N lobe and the activation segment and flanking regions. These mutations change the activation segment from inactive state to active state, for example in the previous cited paper it has been reported that the aliphatic side chain of Val599 interacts with the phenyl ring of Phe467 in the P loop. Replacing the medium-sized hydrophobic Val side chain with a larger and charged residue as found in human cancer(Glu, Asp, Lys, or Arg) would be expected to destabilize the interactions that maintain the DFG motif in an inactive conformation, so flipping the activation segment into the active position. Depending on the type of mutation the kinase activity towards MEK may also vary. Most of the mutants stimulate enhanced B-Raf kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
activity toward MEK. However, a few mutants act through a different mechanism because although their activity toward MEK is reduced, they adopt a conformation that activates wild-type C-RAF, which then signals to ERK.
BRAF-V600E
* BRAF V600E is a determinant of sensitivity toproteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases.
Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by w ...
inhibitors. Vulnerability to proteasome inhibitors is dependent on persistent BRAF signaling, because BRAF-V600E blockade by PLX4720 reversed sensitivity to carfilzomib
Carfilzomib, sold under the brand name Kyprolis, is an anti-cancer medication acting as a selective proteasome inhibitor. Chemically, it is a tetrapeptide epoxyketone and an analog of epoxomicin. It was developed by Onyx Pharmaceuticals.
The U. ...
in BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer cells. Proteasome inhibition
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases.
Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by whi ...
might represent a valuable targeting strategy in BRAF V600E-mutant colorectal tumors.
BRAF inhibitors
As mentioned above, some pharmaceutical firms are developing specific inhibitors of mutated B-raf protein foranticancer An anticarcinogen (also known as a carcinopreventive agent) is a substance that counteracts the effects of a carcinogen or inhibits the development of cancer. Anticarcinogens are different from anticarcinoma agents (also known as anticancer or ant ...
use because BRAF is a well-understood, high yield target. Vemurafenib
Vemurafenib (INN, marketed as Zelboraf) is an inhibitor of the B-Raf enzyme developed by Plexxikon (now part of Daiichi-Sankyo) and Genentech for the treatment of late-stage melanoma.; The name "vemurafenib" comes from V600E mutated BRAF in ...
(RG7204 or PLX4032) was licensed by the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
as Zelboraf for the treatment of metastatic melanoma in August 2011 based on Phase III clinical data. Improved survival was seen, as well as a response rate to treatment of 53%, compared to from 7-12% with the former best chemotherapeutic treatment, dacarbazine. In clinical trials, B-Raf increased metastatic melanoma patient chance of survival. In spite of the drug's high efficacy, 20% of tumors still develop resistance to the treatment. In mice, 20% of tumors become resistant after 56 days. While the mechanisms of this resistance are still disputed, some hypotheses include the overexpression of B-Raf to compensate for high concentrations of Vemurafenib and upstream upregulation of growth signaling.
More general B-Raf inhibitor
BRAF is a human gene that encodes a protein called B-Raf. The gene is also referred to as proto-oncogene B-Raf and v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, while the protein is more formally known as serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf.
T ...
s include GDC-0879, PLX-4720, Sorafenib
Sorafenib, sold under the brand name Nexavar, is a kinase inhibitor drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer (advanced renal cell carcinoma), advanced primary liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma), FLT3-ITD positive AML and r ...
, dabrafenib
Dabrafenib, sold under the brand name Tafinlar & Rafinlar ( both by Novartis) among others, is a medication for the treatment of cancers associated with a mutated version of the gene BRAF. Dabrafenib acts as an inhibitor of the associated enzym ...
and encorafenib
Encorafenib, sold under the brand name Braftovi, is a medication for the treatment of certain melanoma cancers. It is a small molecule BRAF inhibitor that targets key enzymes in the MAPK signaling pathway. This pathway occurs in many different ...
.
Interactions
BRAF (gene) has been shown tointeract
Advocates for Informed Choice, dba interACT or interACT Advocates for Intersex Youth, is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization using innovative strategies to advocate for the legal and human rights of children with intersex traits. The organizati ...
with:
* AKT1,
* C-Raf,
* HRAS, and
* YWHAB.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
*Finding faults in BRAF
— Cancer Research UK blog post about the discovery of cancer-causing BRAF mutations (incl video) * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no Oncogenes EC 2.7.11