Andranik Ozanian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Andranik Ozanian, commonly known as General Andranik or simply Andranik;. Also spelled Antranik or Antranig 25 February 186531 August 1927), was an Armenian military commander and statesman, the best known '' fedayi'' and a key figure of the Armenian national liberation movement. From the late 19th century to the early 20th century, he was one of the main Armenian leaders of military efforts for the independence of
 Andranik Ozanian was born on 25 February 1865, in the town of Shabin-Karahisar (Şebinkarahisar),
Andranik Ozanian was born on 25 February 1865, in the town of Shabin-Karahisar (Şebinkarahisar),
 Aghbiur Serob, the main leader of the '' fedayi'' in the 1890s, was killed in 1899 by a Kurdish chieftain, Bushare Khalil Bey. Months later, Bey committed further atrocities against the Armenians by killing a priest, two young men and 25 women and children in Talvorik, a village in the
Aghbiur Serob, the main leader of the '' fedayi'' in the 1890s, was killed in 1899 by a Kurdish chieftain, Bushare Khalil Bey. Months later, Bey committed further atrocities against the Armenians by killing a priest, two young men and 25 women and children in Talvorik, a village in the 

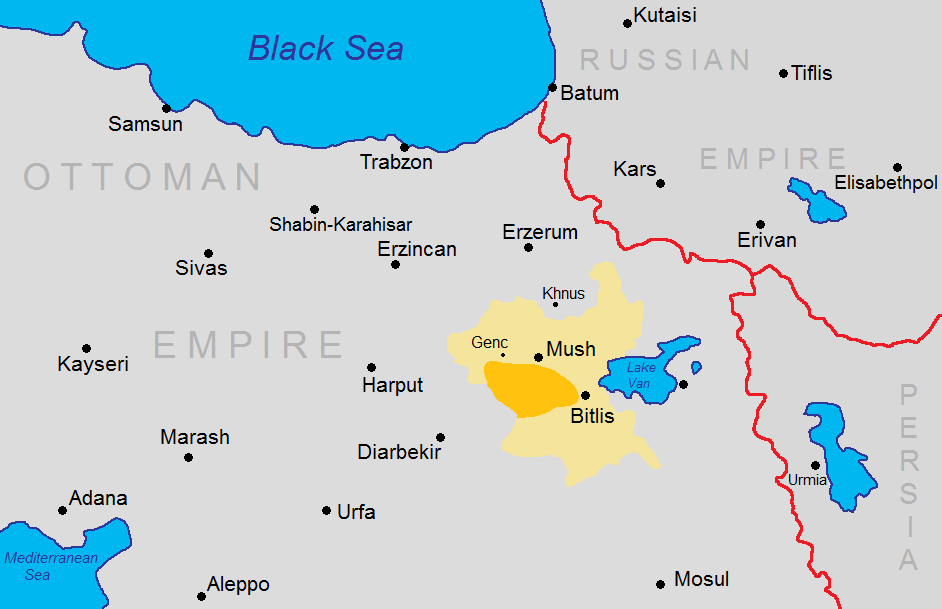 The first clashes took place in January 1904 between the ''fedayi'' and Kurdish irregulars supported by the Ottoman government. The Turkish offensive started in early April with an estimated 10,000 to 20,000 soldiers and 7,000 Kurdish irregulars put against 100 to 200 Armenian ''fedayi'' and 700 to 1,000 local Armenian men. Hrayr was killed during the intense fighting; Andranik survived and resumed the fight. Between 7,000 and 10,000 Armenian civilians were killed during the two months of the uprising, while about 9,000 were left homeless. Around 4,000 Sasun villagers were forced into exile after the uprising.
After weeks of fighting and cannon bombardment of the Armenian villages, the Ottoman forces and Kurdish irregulars suppressed the uprising by May 1904; they outnumbered the Armenian forces several times. Minor clashes occurred thereafter. According to Christopher J. Walker, the ''fedayi'' came "near to organising an uprising and shaking Ottoman power in Armenia," but "even then it was unthinkable that the empire would lose any of her territory, since the idea of intervention was far from Russia." Trotsky wrote that international attention was on the
The first clashes took place in January 1904 between the ''fedayi'' and Kurdish irregulars supported by the Ottoman government. The Turkish offensive started in early April with an estimated 10,000 to 20,000 soldiers and 7,000 Kurdish irregulars put against 100 to 200 Armenian ''fedayi'' and 700 to 1,000 local Armenian men. Hrayr was killed during the intense fighting; Andranik survived and resumed the fight. Between 7,000 and 10,000 Armenian civilians were killed during the two months of the uprising, while about 9,000 were left homeless. Around 4,000 Sasun villagers were forced into exile after the uprising.
After weeks of fighting and cannon bombardment of the Armenian villages, the Ottoman forces and Kurdish irregulars suppressed the uprising by May 1904; they outnumbered the Armenian forces several times. Minor clashes occurred thereafter. According to Christopher J. Walker, the ''fedayi'' came "near to organising an uprising and shaking Ottoman power in Armenia," but "even then it was unthinkable that the empire would lose any of her territory, since the idea of intervention was far from Russia." Trotsky wrote that international attention was on the
 From Persia, Andranik moved to the Caucasus, where he met the Armenian leaders in
From Persia, Andranik moved to the Caucasus, where he met the Armenian leaders in
 In 1907 Andranik settled in
In 1907 Andranik settled in
 With the outbreak of
With the outbreak of
 The
The
 After the Ottoman forces were effectively stopped at Sardarabad, the Armenian National Council declared the independence of the Russian Armenian lands on 28 May 1918. Andranik condemned this move and denounced the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. Angry with the Dashnaks, he favored good relations with Bolshevik Russia instead. Andranik refused to acknowledge the Republic of Armenia, which he regarded as little more than "a pawn in the grip of ttomanTurkey․" He condemned the singing of the
After the Ottoman forces were effectively stopped at Sardarabad, the Armenian National Council declared the independence of the Russian Armenian lands on 28 May 1918. Andranik condemned this move and denounced the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. Angry with the Dashnaks, he favored good relations with Bolshevik Russia instead. Andranik refused to acknowledge the Republic of Armenia, which he regarded as little more than "a pawn in the grip of ttomanTurkey․" He condemned the singing of the
 As the Turkish forces moved towards Nakhichevan, Andranik with his Armenian Special Striking Division moved to the mountainous region of
As the Turkish forces moved towards Nakhichevan, Andranik with his Armenian Special Striking Division moved to the mountainous region of
 The Ottoman Empire was officially defeated in the First World War and the
The Ottoman Empire was officially defeated in the First World War and the
 During the winter of 1918–19, Zangezur was isolated from Karabakh and Yerevan by snow. The refugees intensified the famine and epidemic conditions and gave way to inflation. In December 1918, Andranik withdrew from Karabakh to
During the winter of 1918–19, Zangezur was isolated from Karabakh and Yerevan by snow. The refugees intensified the famine and epidemic conditions and gave way to inflation. In December 1918, Andranik withdrew from Karabakh to  At the end of February 1919, Andranik was ready to leave Zangezur. Gibbon suggested Andranik and his soldiers leave by Baku-Tiflis railway at
At the end of February 1919, Andranik was ready to leave Zangezur. Gibbon suggested Andranik and his soldiers leave by Baku-Tiflis railway at
 From 1919 to 1922, Andranik traveled around Europe and the United States seeking support for the Armenian refugees. He visited Paris and London, where he tried to persuade the Allied powers to occupy Turkish Armenia. In 1919, during his visit to France, Andranik was bestowed the title of
From 1919 to 1922, Andranik traveled around Europe and the United States seeking support for the Armenian refugees. He visited Paris and London, where he tried to persuade the Allied powers to occupy Turkish Armenia. In 1919, during his visit to France, Andranik was bestowed the title of  When he returned to Europe, Andranik married Nevarte Kurkjian in Paris on 15 May 1922;
When he returned to Europe, Andranik married Nevarte Kurkjian in Paris on 15 May 1922;
 Andranik is considered a national hero by Armenians worldwide. He is also seen as a legendary figure in Armenian culture. In a series of polls in 2006–08, Andranik consistently placed second after Vazgen Sargsyan in the list of Armenian national heroes and leaders.
During the Soviet period, his legacy and those of other Armenian national heroes were diminished and "any reference to them would be dangerous since they represented the strive for independence," especially prior to the
Andranik is considered a national hero by Armenians worldwide. He is also seen as a legendary figure in Armenian culture. In a series of polls in 2006–08, Andranik consistently placed second after Vazgen Sargsyan in the list of Armenian national heroes and leaders.
During the Soviet period, his legacy and those of other Armenian national heroes were diminished and "any reference to them would be dangerous since they represented the strive for independence," especially prior to the
 The first statue of Andranik in Armenia was erected in 1967 in the village of Ujan. Another early statue in Armenia was erected in Voskehask, near Gyumri, in 1969. More statues have been erected after Armenia's independence from the Soviet Union in 1991; three of which can be found in the Armenian capital of Yerevan—in
The first statue of Andranik in Armenia was erected in 1967 in the village of Ujan. Another early statue in Armenia was erected in Voskehask, near Gyumri, in 1969. More statues have been erected after Armenia's independence from the Soviet Union in 1991; three of which can be found in the Armenian capital of Yerevan—in

 Andranik has been figured prominently in the Armenian literature, sometimes as a fictional character. The Western Armenian writer Siamanto wrote a poem entitled "Andranik", which was published in Geneva in 1905. The first book about Andranik was published during his lifetime. In 1920, Vahan Totovents, under the pen name Arsen Marmarian, published the book ''Gen. Andranik and His Wars'' (Զոր. Անդրանիկ և իր պատերազմները) in Entente-occupied Constantinople. The famed Armenian-American writer William Saroyan wrote a short story titled ''Antranik of Armenia'', which was included in his collection of short stories ''Inhale and Exhale'' (1936). Another US-based Armenian writer Hamastegh's novel ''The White Horseman'' (Սպիտակ Ձիավորը, 1952) was based on Andranik and other ''fedayi''. Hovhannes Shiraz, one of the most prominent Armenian poets of the 20th century, wrote at least two poems about Andranik; one in 1963 and another in 1967. The latter one, titled ''Statue to Andranik'' (Արձան Անդրանիկին), was published in 1991 after Shiraz's death.
Andranik has been figured prominently in the Armenian literature, sometimes as a fictional character. The Western Armenian writer Siamanto wrote a poem entitled "Andranik", which was published in Geneva in 1905. The first book about Andranik was published during his lifetime. In 1920, Vahan Totovents, under the pen name Arsen Marmarian, published the book ''Gen. Andranik and His Wars'' (Զոր. Անդրանիկ և իր պատերազմները) in Entente-occupied Constantinople. The famed Armenian-American writer William Saroyan wrote a short story titled ''Antranik of Armenia'', which was included in his collection of short stories ''Inhale and Exhale'' (1936). Another US-based Armenian writer Hamastegh's novel ''The White Horseman'' (Սպիտակ Ձիավորը, 1952) was based on Andranik and other ''fedayi''. Hovhannes Shiraz, one of the most prominent Armenian poets of the 20th century, wrote at least two poems about Andranik; one in 1963 and another in 1967. The latter one, titled ''Statue to Andranik'' (Արձան Անդրանիկին), was published in 1991 after Shiraz's death.
 Through his military career, Andranik was awarded with a number of medals and orders by governments of four countries. Andranik's medals and sword were moved to Armenia and given to the
Through his military career, Andranik was awarded with a number of medals and orders by governments of four countries. Andranik's medals and sword were moved to Armenia and given to the
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
.
He became active in an armed struggle against the Ottoman government and Kurdish irregulars in the late 1880s. Andranik joined the Armenian Revolutionary Federation
The Armenian Revolutionary Federation ( hy, Հայ Յեղափոխական Դաշնակցութիւն, ՀՅԴ ( classical spelling), abbr. ARF or ARF-D) also known as Dashnaktsutyun (collectively referred to as Dashnaks for short), is an Armenian ...
(Dashnaktustyun) party and, along with other '' fedayi'' (militias), sought to defend the Armenian peasantry living in their ancestral homeland, an area known as Western (or Turkish) Armeniaat the time part of the Ottoman Empire. His revolutionary activities ceased and he left the Ottoman Empire after the unsuccessful uprising in Sasun in 1904. In 1907, Andranik left Dashnaktustyun because he disapproved of its cooperation with the Young Turks, a party which years later perpetrated the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily through t ...
. Between 1912 and 1913, together with Garegin Nzhdeh, Andranik led a few hundred Armenian volunteers within the Bulgarian army against the Ottomans during the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
.
From the early stages of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, Andranik commanded the first Armenian volunteer battalion within the Russian Imperial army against the Ottoman Empire, capturing and later governing much of the traditional Armenian homeland. After the Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
, the Russian army retreated and left the Armenian irregulars outnumbered against the Turks. Andranik led the defense of Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses the double-headed eagle as ...
in early 1918, but was forced to retreat eastward. By May 1918, Turkish forces stood near Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and i ...
the future Armenian capitaland were halted at the Battle of Sardarabad
The Battle of Sardarabad ( hy, Սարդարապատի ճակատամարտ, translit=Sardarapati chakatamart; tr, Serdarabad Muharebesi) was a battle of the Caucasus campaign of World War I that took place near Sardarabad, Armenia, from 21 to ...
. The Dashnak-dominated Armenian National Council declared the independence of Armenia and signed the Treaty of Batum
The Treaty of Batum was signed in Batum on 4 June 1918, between the Ottoman Empire and the three Transcaucasian states: the First Republic of Armenia, the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and the Democratic Republic of Georgia. It was the first ...
with the Ottoman Empire, by which Armenia gave up its rights to Western Armenia. Andranik never accepted the existence of the First Republic of Armenia
The First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն), was the first modern Armenian state since the loss of Armenian statehood in the Middle ...
because it included only a small part of the area many Armenians hoped to make independent. Andranik, independently from the Republic of Armenia, fought in Zangezur
Zangezur ( hy, Զանգեզուր) is a historical and geographical region in Eastern Armenia on the slopes of the Zangezur Mountains which largely corresponds to the Syunik Province of the Republic of Armenia. It was ceded to Russia by Qajar I ...
against the Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Azerbaijan
* Azerbaijanis
* Azerbaijani language
See also
* Azerbaijan (disambiguation)
* Azeri (disambiguation)
* Azerbaijani cuisine
* Culture of Azerbaijan
The culture of Azerbaijan ...
and Turkish armies, and helped to keep it within Armenia.
Andranik left Armenia in 1919 due to disagreements with the Armenian government and spent his last years of life in Europe and the United States seeking relief for Armenian refugees. He settled in Fresno, California
Fresno () is a major city in the San Joaquin Valley of California, United States. It is the county seat of Fresno County and the largest city in the greater Central Valley region. It covers about and had a population of 542,107 in 2020, maki ...
in 1922 and died five years later in 1927. Andranik is greatly admired as a national hero by Armenians; numerous statues of him have been erected in several countries. Streets and squares were named after Andranik, and songs, poems and novels have been written about him, making him a legendary figure in Armenian culture.
Early life
 Andranik Ozanian was born on 25 February 1865, in the town of Shabin-Karahisar (Şebinkarahisar),
Andranik Ozanian was born on 25 February 1865, in the town of Shabin-Karahisar (Şebinkarahisar), Sivas Vilayet
The Vilayet of Sivas (, ota, ولايت سيوس, Vilâyet-i Sivas) was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire, and was one of the Six Armenian vilayets. The vilayet was bordered by Erzurum Vilayet to the east, ...
, Ottoman Empire, to Mariam and Toros Ozanian. Andranik means "firstborn" in Armenian. His paternal ancestors came from the nearby village of Ozan (now Ozanlı) in the early 18th century and settled in Shabin-Karahisar to avoid persecution from the Turks. His ancestors took the surname Ozanian in honor of their hometown. Andranik's mother died when he was one year old and his elder sister Nazeli took care of him. Andranik went to the local Musheghian School from 1875 to 1882 and thereafter worked in his father's carpentry shop. He married at the age of 17, but his wife died a year later while giving birth to their sonwho also died days after the birth.
The situation of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire
Armenians in the Ottoman Empire (or Ottoman Armenians) mostly belonged to either the Armenian Apostolic Church or the Armenian Catholic Church. They were part of the Armenian millet until the Tanzimat reforms in the nineteenth century equa ...
had worsened under the reign of Abdul Hamid II, who sought to unify all Muslims under his rule. In 1882, Andranik was arrested for assaulting a Turkish ''gendarme
Wrong info! -->
A gendarmerie () is a military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term ''gendarme'' () is derived from the medieval French expression ', which translates to "Man-at-arms, men-at-arms" ...
'' for mistreating Armenians. With the help of his friends, he escaped from prison. He settled in the Ottoman capital Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in 1884 and stayed there until 1886, working as a carpenter. He began his revolutionary activities in 1888 in the province of Sivas. Andranik joined the Hunchak party in 1891. He was arrested in 1892 for taking part in the assassination of Constantinople's police chief, Yusup Mehmet Beyknown for his anti-Armenianismon 9 February. Andranik once again escaped from prison. In 1892, he joined the newly created Armenian Revolutionary Federation
The Armenian Revolutionary Federation ( hy, Հայ Յեղափոխական Դաշնակցութիւն, ՀՅԴ ( classical spelling), abbr. ARF or ARF-D) also known as Dashnaktsutyun (collectively referred to as Dashnaks for short), is an Armenian ...
(ARF or Dashnaktsutyun). During the Hamidian massacres
The Hamidian massacres also called the Armenian massacres, were massacres of Armenians in the Ottoman Empire in the mid-1890s. Estimated casualties ranged from 100,000 to 300,000, Akçam, Taner (2006) '' A Shameful Act: The Armenian Genocide a ...
, Andranik with other ''fedayi'' defended the Armenian villages of Mush and Sasun
Sason ( hy, Սասուն, translit=Sasun, ku, Qabilcewz, ar, قبل جوز; formerly known as Sasun or Sassoun) is a district and town in the Batman Province of Turkey. It was formerly part of the sanjak of Siirt, which was in Diyarbakır ...
from attacks of the Turks and the Kurdish '' Hamidiye'' units. The massacres, which occurred between 1894 and 1896 and are named after Sultan Abdul Hamid II
Abdülhamid or Abdul Hamid II ( ota, عبد الحميد ثانی, Abd ül-Hamid-i Sani; tr, II. Abdülhamid; 21 September 1842 10 February 1918) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 31 August 1876 to 27 April 1909, and the last sultan to ...
, killed between 80,000 and 300,000 people.
In 1897, Andranik went to Tiflis
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million pe ...
the largest city of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
and a major center of Armenian culture at the timewhere the ARF headquarters was located. Andranik returned to Turkish Armenia "entrusted with extensive powers, and with a large supply of arms" for the ''fedayi''. Several dozen Russian Armenians joined him, with whom he went to the Mush-Sasun area where Aghbiur Serob was operating. Serob's forces had already established semi-independent Armenian areas by expelling the Ottoman government representatives.
Leader of the ''fedayi''
 Aghbiur Serob, the main leader of the '' fedayi'' in the 1890s, was killed in 1899 by a Kurdish chieftain, Bushare Khalil Bey. Months later, Bey committed further atrocities against the Armenians by killing a priest, two young men and 25 women and children in Talvorik, a village in the
Aghbiur Serob, the main leader of the '' fedayi'' in the 1890s, was killed in 1899 by a Kurdish chieftain, Bushare Khalil Bey. Months later, Bey committed further atrocities against the Armenians by killing a priest, two young men and 25 women and children in Talvorik, a village in the Sasun
Sason ( hy, Սասուն, translit=Sasun, ku, Qabilcewz, ar, قبل جوز; formerly known as Sasun or Sassoun) is a district and town in the Batman Province of Turkey. It was formerly part of the sanjak of Siirt, which was in Diyarbakır ...
region. Andranik replaced Serob as the head of the Armenian irregular forces "with 38 villages under his command" in the Mush-Sasun region of Western Armenia, where a "warlike semi-independent Armenian peasantry" lived. Andranik sought to kill Bey; he captured and reportedly decapitated the chieftain, and took the medal given to Bey by Sultan Abdul Hamid II
Abdülhamid or Abdul Hamid II ( ota, عبد الحميد ثانی, Abd ül-Hamid-i Sani; tr, II. Abdülhamid; 21 September 1842 10 February 1918) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 31 August 1876 to 27 April 1909, and the last sultan to ...
. Andranik thus earned an undisputed authority among his ''fedayi''.
Although small groups of Armenian ''fedayi'' conducted an armed struggle against the Ottoman state and the Kurdish tribes, the situation in Western Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: Արեւմտեան Հայաստան, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the eastern parts of Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that are part of the historical homeland of the Armenians. Weste ...
deteriorated as the European powers stood indifferent to the Armenian Question. Article 61 of the 1878 Treaty of Berlin intended the Ottoman government to "carry out, without further delay, the improvements and reforms demanded by local requirements in the provinces inhabited by the Armenians, and to guarantee their security against the Circassians and Kurds" remained unimplemented. According to Christopher J. Walker, the attention of the European powers was on Macedonia, while Russia was "in no mood for reactivating the Armenian question."


Battle of Holy Apostles Monastery
In November 1901 the ''fedayi'' clashed with the Ottoman troops in what later became known as theBattle of Holy Apostles Monastery
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
. One of the best-known episodes of Andranik's revolutionary activities, it was an attempt by the Ottoman government to suppress his activities. Since Andranik had gained more influence over the region, more than 5,000 Turkish soldiers were sent after him and his band. The Turks chased and eventually circled him and his men, numbering around 50, at the Arakelots (Holy Apostles) Monastery in early November. A regiment under the command of Ferikh Pasha and Ali Pasha besieged the fort-like monastery. The Turkish generals leading the army of twelve hundred men asked the ''fedayi'' to negotiate their surrender.
After weeks of resistance and negotiationsin which Armenian clergy and the headman of Mush and foreign consuls took partAndranik and his companions left the monastery and fled in small groups. According to Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein. ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky; uk, link= no, Лев Давидович Троцький; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trotskij'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky''. (), was a Russian ...
, Andranikdressed in the uniform of a Turkish officer"went the rounds of the entire guard, talking to them in excellent Turkish," and "at the same time showing the way out to his own men." After breaking through the siege of the monastery, Andranik gained legendary stature among provincial Armenians. He became so popular that the men he led came to refer to him always by his first name. Andranik intended to attract the attention of the foreign consuls at Mush to the plight of the Armenian peasants and to provide hope for the oppressed Armenians of the eastern provinces. According to Trotsky, Andranik's "political thinking took shape in a setting of Carbonari
The Carbonari () was an informal network of secret revolutionary societies active in Italy from about 1800 to 1831. The Italian Carbonari may have further influenced other revolutionary groups in France, Portugal, Spain, Brazil, Uruguay and Ru ...
st activity and diplomatic intrigue."
1904 Sasun uprising and exodus
In 1903, Andranik demanded the Ottoman government stop the harassment of Armenians and implement reforms in the Armenian provinces. Most ''fedayi'' were concentrated in the mountainous region ofSasun
Sason ( hy, Սասուն, translit=Sasun, ku, Qabilcewz, ar, قبل جوز; formerly known as Sasun or Sassoun) is a district and town in the Batman Province of Turkey. It was formerly part of the sanjak of Siirt, which was in Diyarbakır ...
, an area of about with an overwhelming Armenian majority1,769 Armenian and 155 Kurdish householdswhich was traditionally considered their main operational area. The region was in "a state of revolutionary turmoil" because the local Armenians had refused to pay taxes for the past seven years. Andranik and tens of other ''fedayi''including Hrayr and Sebouhheld a meeting at Gelieguzan village in the third quarter of 1903 to manage the future defense of the Armenian villages from possible Turkish and Kurdish attacks. Andranik suggested a widespread uprising of the Armenians of Taron and Vaspurakan
Vaspurakan (, Western Armenian pronunciation: ''Vasbouragan'') was the eighth province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now southeast ...
; Hrayr opposed his view and suggested a small, local uprising in Sasun, because the Armenian irregulars lacked resources. Hrayr's suggestion was eventually approved by the ''fedayi'' meeting. Andranik was chosen as the main commander of the uprising.
 The first clashes took place in January 1904 between the ''fedayi'' and Kurdish irregulars supported by the Ottoman government. The Turkish offensive started in early April with an estimated 10,000 to 20,000 soldiers and 7,000 Kurdish irregulars put against 100 to 200 Armenian ''fedayi'' and 700 to 1,000 local Armenian men. Hrayr was killed during the intense fighting; Andranik survived and resumed the fight. Between 7,000 and 10,000 Armenian civilians were killed during the two months of the uprising, while about 9,000 were left homeless. Around 4,000 Sasun villagers were forced into exile after the uprising.
After weeks of fighting and cannon bombardment of the Armenian villages, the Ottoman forces and Kurdish irregulars suppressed the uprising by May 1904; they outnumbered the Armenian forces several times. Minor clashes occurred thereafter. According to Christopher J. Walker, the ''fedayi'' came "near to organising an uprising and shaking Ottoman power in Armenia," but "even then it was unthinkable that the empire would lose any of her territory, since the idea of intervention was far from Russia." Trotsky wrote that international attention was on the
The first clashes took place in January 1904 between the ''fedayi'' and Kurdish irregulars supported by the Ottoman government. The Turkish offensive started in early April with an estimated 10,000 to 20,000 soldiers and 7,000 Kurdish irregulars put against 100 to 200 Armenian ''fedayi'' and 700 to 1,000 local Armenian men. Hrayr was killed during the intense fighting; Andranik survived and resumed the fight. Between 7,000 and 10,000 Armenian civilians were killed during the two months of the uprising, while about 9,000 were left homeless. Around 4,000 Sasun villagers were forced into exile after the uprising.
After weeks of fighting and cannon bombardment of the Armenian villages, the Ottoman forces and Kurdish irregulars suppressed the uprising by May 1904; they outnumbered the Armenian forces several times. Minor clashes occurred thereafter. According to Christopher J. Walker, the ''fedayi'' came "near to organising an uprising and shaking Ottoman power in Armenia," but "even then it was unthinkable that the empire would lose any of her territory, since the idea of intervention was far from Russia." Trotsky wrote that international attention was on the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
and the uprising went largely unnoticed by the European powers and Russia.
In July–August 1904, Andranik and his ''fedayi'' reached Lake Van
Lake Van ( tr, Van Gölü; hy, Վանա լիճ, translit=Vana lič̣; ku, Gola Wanê) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the far east of Turkey, in the provinces of Van and Bitlis in the Armenian highlands. It is a saline soda lake ...
and got to Aghtamar Island with sailing ships. They escaped to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
via Van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
in September 1904, "leaving little more than a heroic memory." Trotsky states that they were forced to leave Turkish Armenia to avoid further killings of Armenians and to lower the tensions, while Tsatur Aghayan wrote that Andranik left the Ottoman Empire because he sought to "gather new resources and find practical programs" for the Armenian struggle.
Immigration and conflict with the ARF
 From Persia, Andranik moved to the Caucasus, where he met the Armenian leaders in
From Persia, Andranik moved to the Caucasus, where he met the Armenian leaders in Baku
Baku (, ; az, Bakı ) is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. Baku is located below sea level, which makes it the lowest lying national capital in the world an ...
and Tiflis. He then left Russia and traveled to Europe, where he was engaged in advocacy in support of the Armenians' national liberation struggle. In 1906 in Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situa ...
, he published a book on military tactics. Most of the work was about his activities and the strategies he used during the 1904 Sasun uprising.
In February–March 1907, Andranik went to Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
to participate in the fourth ARF Congress. The ARF, which had been collaborating with Turkish émigré political groups in Europe since 1902, discussed and approved the negotiations with the Young Turkswho later perpetrated the Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily through t ...
to overthrow Sultan Abdul Hamid II. Andranik strongly denounced this cooperation and left the party. In 1908, the ARF asked Andranik to move to Constantinople and nominate his candidacy in the Ottoman parliament election, but he declined the offer, saying "I don't want to sit there and do nothing." Andranik distanced himself from active political and military affairs for several years.
First Balkan War
 In 1907 Andranik settled in
In 1907 Andranik settled in Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
, where he met the leaders of the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization
The Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization (IMRO; bg, Вътрешна Македонска Революционна Организация (ВМРО), translit=Vatrešna Makedonska Revoljucionna Organizacija (VMRO); mk, Внатр� ...
including revolutionary Boris Sarafov
Boris Petrov Sarafov (Bulgarian and mk, Борис Петров Сарафов) (12 June 1872 in Libyahovo, Salonica Vilayet, Ottoman Empire, present-day Bulgaria – 28 November 1907 in Sofia, Bulgaria) was a Bulgarian Army officer an ...
and the two pledged to work jointly for the oppressed peoples of Armenia and Macedonia. During the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
(1912–13), Andranik led a company
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared ...
of 230 Armenian volunteers part of the Macedonian-Adrianopolitan Volunteer Corps
The Macedonian-Adrianopolitan Volunteer Corps ( bg, Македоно-одринско опълчение, ''Makedono-odrinsko opalchenie'') was a volunteer corps of the Bulgarian Army during the Balkan Wars. It was formed on 23 September 1912 ...
of Aleksandar Protogerov within the Bulgarian armyagainst the Ottoman Empire. He shared the command with Garegin Nzhdeh. On the opposite side, approximately 8,000 Armenians fought for the Ottoman Empire. Andranik was given the rank of a first lieutenant
First lieutenant is a commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces; in some forces, it is an appointment.
The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations, but in most forces it is sub-divided into a ...
by the Bulgarian government. He distinguished himself in several battles, including in the Battle of Merhamli
The Battle of Merhamli was part of the First Balkan War between the armies of Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire which took place on 14/27 November 1912. After a long chase throughout Western Thrace the Bulgarian troops led by General Nikola Genev a ...
, when he helped the Bulgarians to capture Turkish commander Yaver Pasha. Andranik was honored with the Order of Bravery by General Protogerov in 1913. However, Andranik disbanded his men in May 1913, and foreseeing the war between Bulgaria and Serbia he "retired to a village near Varna, and lived as a farmer until August 1914."
World War I

 With the outbreak of
With the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
in July 1914 between Russia, France and Britain on one side and Germany, the Ottoman Empire and Austria on the other, Andranik left Bulgaria for Russia. He was appointed the commander of the first Armenian volunteer battalion by the Russian government. From November 1914 to August 1915, Andranik took part in the Caucasus Campaign
The Caucasus campaign comprised armed conflicts between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, later including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus, the German Empire, the Central Caspian Dict ...
as the head commander of the first Armenian battalion of about 1,200 volunteers within the Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Ar ...
. Andranik's battalion particularly stood out at the Battle of Dilman in April 1915. By the victory at Dilman, the Russian and Armenian forces under the command of General Nazarbekian, effectively stopped the Turks from invading the Caucasus via Iranian Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan or Azarbaijan ( fa, آذربایجان, ''Āzarbāijān'' ; az-Arab, آذربایجان, ''Āzerbāyjān'' ), also known as Iranian Azerbaijan, is a historical region in northwestern Iran that borders Iraq, Turkey, the Nakhchivan ...
.
Through 1915, the Armenian genocide was underway in the Ottoman Empire. By the end of the war, virtually all Armenians living in their ancestral homeland were either dead or forced into exile by the Ottoman government. An estimated 1.5 million Armenians died in the process, ending the Armenian presence in Western Armenia
Western Armenia (Western Armenian: Արեւմտեան Հայաստան, ''Arevmdian Hayasdan'') is a term to refer to the eastern parts of Turkey (formerly the Ottoman Empire) that are part of the historical homeland of the Armenians. Weste ...
. The only major resistance to the Turkish atrocities took place in Van. The Turkish army besieged the city but the local Armenians, under the leadership of Aram Manukian
Aram Manukian, reformed spelling: Արամ Մանուկյան, and he is also referred to as simply Aram. (19 March 187929 January 1919), was an Armenian revolutionary, statesman, and a leading member of the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (D ...
, kept them out until the Armenian volunteers reached Van, forcing the Turks to retreat. Andranik with his unit entered Van on 19 May 1915. Andranik subsequently helped the Russian army to take control of Shatakh, Moks
Moxoene or Mokk' ( hy, Մոկք, translit=Mokkʿ, ku, Miks) was a territory of Kingdom of Armenia and later Sasanian Armenia, located east of Arzanene from south of Lake Van to north of Bohtan river. The territory was ruled by a local dynasty.
...
and Tatvan on the southern shore of Lake Van. During the summer of 1915, the Armenian volunteer units disintegrated and Andranik went to Tiflis
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million pe ...
to recruit more volunteers and continued the combat from November 1915 until March 1916. With Andranik's support, the city of Mush was captured by Russians in February 1916. In recognition of lieutenant general Theodore G. Chernozubov, the successes of Russian army in numerous locations were significantly associated with the fighting of the first Armenian battalion, headed by Andranik. Chernozubov praised Andranik as a brave and experienced chief, who well understood the combat situation; Chernozubov described him as always at the head of militia, enjoying great prestige among the volunteers.
The situation drastically changed in 1916 when the Russian government ordered the Armenian volunteer units to be demobilized and prohibited any Armenian civic activity. Andranik resigned as the commander of the first Armenian battalion. Despite the earlier Russian promises, their plan for the region was to make Western Armenia an integral part of Russia and "possibly repopulate by Russian peasants and Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
." Richard Hovannisian wrote that because the "Russian armies were in firm control of most of the Armenian plateau by the summer of 1916, there was no longer any need to expend niceties upon the Armenians." According to Tsatur Aghayan, Russia used the Armenian volunteers for its own interests. Andranik and other Armenian volunteers, disappointed by the Russian policy, left the front in July 1916.
Russian Revolution and Turkish reoccupation
 The
The February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and some ...
was positively accepted by the Armenians because it ended the autocratic rule of Nicholas II
Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov; spelled in pre-revolutionary script. ( 186817 July 1918), known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer,. was the last Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Pol ...
. The Special Transcaucasian Committee
The Special Transcaucasian Committee ( Russian: Особый Закавказский Комитет ''Osobyi Zakavkazskii Komitet'' (OZaKom, Ozakom or OZAKOM)) was established on March 9, 1917, with Member of the State Duma V. A. Kharlamov as C ...
(known as OZAKOM) was set up in the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
by the Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government ( rus, Временное правительство России, Vremennoye pravitel'stvo Rossii) was a provisional government of the Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately ...
. In April 1917, Andranik initiated the publication of the newspaper '' Hayastan'' (Armenia) in Tiflis. Vahan Totovents Vahan Hovhannesi Totovents ( hy, Վահան Հովհաննեսի Թոթովենց; September 1, 1889 – July 18, 1938) was an Armenian writer, poet and public activist.
Biography
Vahan Totovents was born on July 17, 1893 in the town of Mezre (no ...
became the editor of this non-partisan, Ottoman Armenian-orientated newspaper. Until December 1917, Andranik remained in the South Caucasus where he sought to help the Armenian refugees from the Ottoman Empire in their search for basic needs. The provisional government decree of 9 May 1917 put Turkish Armenia under civil administration, with Armenians holding key positions. About 150,000 local Armenians began to rebuild devastated Turkish Armenia; however the Russian army units gradually disintegrated and many soldiers deserted and returned to Russia.
After the 1917 October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
, the chaotic retreat of Russian troops from Western Armenia escalated. Bolshevik Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
and the Ottoman Empire signed the Armistice of Erzincan The Armistice of Erzincan (also spelled Erzindzhan or Erzinjan) was an agreement to suspend hostilities during World War I signed by the Ottoman Empire and Transcaucasian Commissariat in Erzincan on 18 December 1917 (5 December O.S.).Tadeusz Swiet ...
on 5 December 1917, ending the hostilities. The Soviet Russian government formally acknowledged the right of self-determination of the Ottoman Armenians in January 1918, but on 3 March 1918, Russia signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
with the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
, ceding Western Armenia and large areas in Eastern Europe to concentrate its forces against the Whites
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as ...
in the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
.
In December 1917, because the Russian divisions were deserting the region ''en masse'', the Russian command authorized the formation of the Armenian Army Corps under the Transcaucasian Commissariat
The Transcaucasian Commissariat was established at Tbilisi on 11 November 1917, as the first government of the independent Transcaucasia following the October Revolution in Petrograd. The Commissariat decided to strengthen the Georgian–Armenian� ...
. Under the command of General Nazarbekian, the Corps was positioned in the front line from Van to Erzincan
Erzincan (; ku, Erzîngan), historically Yerznka ( hy, Երզնկա), is the capital of Erzincan Province in Eastern Turkey. Nearby cities include Erzurum, Sivas, Tunceli, Bingöl, Elazığ, Malatya, Gümüşhane, Bayburt, and Giresun. The ...
a city of around about 20,000 people. Two of the Corps' three divisions were made up of Russian Armenians, while Andranik commanded the Turkish (Western) Armenian division. The Georgian forces patrolled the area between Erzincan and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
. Hovannisian states that the only "several thousand men now defended a 300-mile front formerly secured by a half million Russian regulars." Since December 1917, Andranik commanded the Armenian forces in Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses the double-headed eagle as ...
. In January 1918, he was appointed commander of the Western Armenian division of the Armenian Army Corps and given the rank of major-general by the Caucasus Front command. Andranik was unable to defend Erzurum for long and the outnumbering Turks captured the city on 12 March 1918, forcing the Armenians to evacuate.
While the Transcaucasian delegation and the Turks were holding a conference in Trebizond, through March and April the Turkish forces, according to Walker, "overran the temporary establishment of Armenian rule in Turkish Armenia, extinguishing the hope so recently raised." Hovannisian wrote, "the battle for Turkish Armenia had been quickly decided; the struggle for Russian Armenia was now at hand." After the Turks captured Erzurum, the largest city in Turkish Armenia, Andranik retreated through Kars
Kars (; ku, Qers; ) is a city in northeast Turkey and the capital of Kars Province. Its population is 73,836 in 2011. Kars was in the ancient region known as ''Chorzene'', (in Greek Χορζηνή) in classical historiography (Strabo), part of ...
, passed through Alexandropol
Gyumri ( hy, Գյումրի, ) is an urban municipal community and the second-largest city in Armenia, serving as the administrative center of Shirak Province in the northwestern part of the country. By the end of the 19th century, when the city w ...
and Jalaloghly, and arrived in Dsegh
Dsegh ( hy, Դսեղ), known as Tumanyan between 1938 and 1969, is a village in the Lori Province of Armenia. Dsegh is the birthplace of one of the most celebrated of Armenian poets Hovhannes Tumanyan from which took the name from 1938 to 1969. ...
by 18 May. By early April 1918, the Turkish forces had reached the pre-war international borders. Andranik and his unit in Dsegh were not able to take part in the battles of Sardarabad, Abaran and Karakilisa.
First Republic of Armenia
 After the Ottoman forces were effectively stopped at Sardarabad, the Armenian National Council declared the independence of the Russian Armenian lands on 28 May 1918. Andranik condemned this move and denounced the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. Angry with the Dashnaks, he favored good relations with Bolshevik Russia instead. Andranik refused to acknowledge the Republic of Armenia, which he regarded as little more than "a pawn in the grip of ttomanTurkey․" He condemned the singing of the
After the Ottoman forces were effectively stopped at Sardarabad, the Armenian National Council declared the independence of the Russian Armenian lands on 28 May 1918. Andranik condemned this move and denounced the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. Angry with the Dashnaks, he favored good relations with Bolshevik Russia instead. Andranik refused to acknowledge the Republic of Armenia, which he regarded as little more than "a pawn in the grip of ttomanTurkey․" He condemned the singing of the Treaty of Batum
The Treaty of Batum was signed in Batum on 4 June 1918, between the Ottoman Empire and the three Transcaucasian states: the First Republic of Armenia, the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and the Democratic Republic of Georgia. It was the first ...
(by which the Ottoman Empire recognized the independence of a greatly reduced Armenia and imposed a number of humiliating conditions) as an act of treason. As Christopher Walker notes, many Turkish Armenians saw the new republic as "only a dusty province without Turkish Armenia whose salvation Armenians had been seeking for 40 years." In early June, Andranik departed from Dilijan
Dilijan ( hy, Դիլիջան) is a spa town and urban municipal community in the Tavush Province of Armenia. The town is one of the most important resorts in Armenia, situated within the Dilijan National Park. The forested town is home to nume ...
with thousands of refugees; they traveled through Sevan, Nor Bayazet and Vayots Dzor, and arrived in Nakhichevan on 17 June. He subsequently tried to help the Armenian refugees from Van at Khoy
Khoy (Persian and az, خوی; ; ; also Romanized as Khoi), is a city and capital of Khoy County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran. At the 2012 census, its population was 200,985.
Khoy is located north of the province's capital and largest ci ...
, Iran. He sought to join the British forces in northern Iran, but after encountering a large number of Turkish soldiers he retreated to Nakhichevan. On 14 July 1918, he proclaimed Nakhichevan an integral part of (Soviet) Russia. His move was welcomed by Armenian Bolshevik leader Stepan Shahumyan and Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
.
Zangezur
 As the Turkish forces moved towards Nakhichevan, Andranik with his Armenian Special Striking Division moved to the mountainous region of
As the Turkish forces moved towards Nakhichevan, Andranik with his Armenian Special Striking Division moved to the mountainous region of Zangezur
Zangezur ( hy, Զանգեզուր) is a historical and geographical region in Eastern Armenia on the slopes of the Zangezur Mountains which largely corresponds to the Syunik Province of the Republic of Armenia. It was ceded to Russia by Qajar I ...
to set up a defense. By mid-1918, the relations between the Armenians and Azerbaijanis in Zangezur had deteriorated. Andranik arrived in Zangezur at a critical moment with around 30,000 refugees and an estimated force of between 3,000 and 5,000 men. He established effective control of the region by September. The role of Zangezur was crucial because it was a connection point between Turkey and Azerbaijan. Under Andranik, the region became one of the last centers of Armenian resistance after the Treaty of Batum.
Andranik's irregulars remained in Zangezur surrounded by Muslim villages that controlled the key routes connecting the different parts of Zangezur. According to Donald Bloxham
Donald Bloxham FRHistS is a Professor of Modern History, specialising in genocide, war crimes and other mass atrocities studies. He is the editor of the ''Journal of Holocaust Education''.
He completed his undergraduate studies at Keele and pos ...
, Andranik initiated the change of Zangezur into a solidly Armenian land by destroying Muslim villages and trying to ethnically homogenize key areas of the Armenian state. In late 1918, Azerbaijan accused Andranik of killing innocent Azerbaijani peasants in Zangezur and demanded that he withdraw Armenian units from the area. Antranig Chalabian
Antranig Chalabian (March 11, 1922, Kessab, Syria – April 12, 2011, Southfield, Michigan) was a medical illustrator, cartographer and historian, an author of several volumes on Armenian history. He is best known for his biography of General A ...
wrote that, "Without the presence of General Andranik and his Special Striking Division, what is now the Zangezur district of Armenia would be party of Azerbaijan today. Without General Andranik and his men, only a miracle could have saved the sixty thousand Armenian inhabitants of the Zangezur district from complete annihilation by the Turko-Tatar forces in the fall of 1918"; he further stated that Andranik "did not massacre peaceful Tatars." Andranik's activities in Zangezur were protested by Ottoman general Halil Pasha
Halil Pasha (also known as Bostancı Halil Pasha) was an Ottoman statesman who served as the governor of Ottoman Egypt from 1631 to 1633. He was known for his "gentle, impartial, and prosperous administration"d'Avennes, Prisse (1983) ''Arab art ...
, who threatened the Dashnak government with retaliation for Andranik's actions. Armenia's Prime Minister Hovhannes Katchaznouni
Hovhannes Kajaznuni or Katchaznouni (; 14 February 1868 – 15 January 1938) was an Armenian architect and politician who served as the first Prime Minister of the First Republic of Armenia from June 6, 1918 to August 7, 1919. He was a member of ...
said he had no control over Andranik and his forces.
Karabakh
 The Ottoman Empire was officially defeated in the First World War and the
The Ottoman Empire was officially defeated in the First World War and the Armistice of Mudros
Concluded on 30 October 1918 and taking effect at noon the next day, the Armistice of Mudros ( tr, Mondros Mütarekesi) ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed by th ...
was signed on 30 October 1918. The Ottoman forces evacuated Karabakh in November 1918 and by the end of October of that year, Andranik's forces were concentrated between Zangezur and Karabakh
Karabakh ( az, Qarabağ ; hy, Ղարաբաղ, Ġarabaġ ) is a geographic region in present-day southwestern Azerbaijan and eastern Armenia, extending from the highlands of the Lesser Caucasus down to the lowlands between the rivers Kura and ...
. Before moving towards Karabakh, Andranik made sure that the local Armenians would support him in fighting the Azerbaijanis. In mid-November 1918, he received letters from Karabakh Armenian officials asking him to postpone the offensive for 10 days to allow negotiations with the Muslims of the region. According to Hovannisian, "the time lost proved crucial." In late November, Andranik's forces headed towards Shushi
/ hy, Շուշի
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline = ShushaCollection2021.jpg
, image_caption = Landmarks of Shusha, from top left:Ghazanchetsots Cathedral • Yukhari Govha ...
the main city of Karabakh and a major Armenian cultural center. After an intense fight against the local Kurds, his forces broke through Abdallyar (Lachin
Lachin ( az, Laçın, , ; hy, Բերձոր, translit=Berdzor; ku, Laçîn) is a town in Azerbaijan and the administrative center of the Lachin District. It is located within the strategic Lachin corridor, which links the disputed region of N ...
) and the surrounding villages.
By early December, Andranik was away from Shushi when he received a message from British General W. M. Thomson in Baku, suggesting that he retreat from Karabakh because the World War was over and any further Armenian military activity would adversely affect the solution of the Armenian question, which was soon to be considered by the 1919 peace conference in Paris. Trusting the British, Andranik returned to Zangezur.
The region was left under limited control of the Armenian Karabakh Council
The Karabakh Council () was the unrecognised government over Mountainous Karabagh (Nagorno-Karabakh) in eastern Armenia between 1918 and 1920. The council's body was elected by the assembly of Mountainous Karabakh—the representative body of t ...
. The British mission under command of Thomson arrived in Karabakh in December 1918. Thomson insisted the council "act only in local, nonpolitical matters," which sparked discontent among the Armenians. An "ardent pan-Turkist" Khosrov bey Sultanov
Khosrov bey Alipasha bey oghlu Sultanov ( az, Xosrov bəy Əlipaşa bəy oğlu Sultanov; 1879 – 1943), also spelled as Khosrow Sultanov, was an Azerbaijani statesman, General Governor of Karabakh and Minister of Defense of the Azerbaijani Democ ...
was soon appointed the governor of Karabakh and Zangezur by Thomson to "squash any unrest in the region." Christopher J. Walker wrote that " arabakhwith its large Armenian majority remained Azerbaijani throughout the pre-Soviet and Soviet period" because of "Andranik's trust of the word of a British officer."
Departure
 During the winter of 1918–19, Zangezur was isolated from Karabakh and Yerevan by snow. The refugees intensified the famine and epidemic conditions and gave way to inflation. In December 1918, Andranik withdrew from Karabakh to
During the winter of 1918–19, Zangezur was isolated from Karabakh and Yerevan by snow. The refugees intensified the famine and epidemic conditions and gave way to inflation. In December 1918, Andranik withdrew from Karabakh to Goris
Goris ( hy, Գորիս) is a town and the centre of the urban community of Goris, in Syunik Province at the south of Armenia. Located in the valley of the Goris (or Vararak) River, it is 254 km from the Armenian capital Yerevan and 67 ...
. On his way, he met with British officers who suggested the Armenian units stay in Zangezur for the winter. Andranik agreed to such a proposal and on 23 December 1918, a group of Armenian leaders met in a conference and concluded that Zangezur could not cope with the influx of refugees until spring. They agreed that the first logical step in relieving the tension was the reparation of more than 15,000 refugees from Nakhichevanthe adjoining district that had been evacuated by the Ottoman armies. Andranik and the conference called upon the British to provide for the refugees in the interim. Major W. D. Gibbon arrived with limited supplies and money donated by the Armenians of Baku, but this was not enough to support the refugees.
 At the end of February 1919, Andranik was ready to leave Zangezur. Gibbon suggested Andranik and his soldiers leave by Baku-Tiflis railway at
At the end of February 1919, Andranik was ready to leave Zangezur. Gibbon suggested Andranik and his soldiers leave by Baku-Tiflis railway at Yevlakh
Yevlakh ( az, Yevlax, ) is a city in Azerbaijan, 265 km west of capital Baku. It is surrounded by, but administratively separate from, the Yevlakh District.
Etymology
The settlement is mentioned by the 13th century Armenian historian Step ...
station. Andranik rejected this plan and on 22 March 1919, he left Goris and traveled across Sisian through deep snowdrifts to Daralagyaz, then moved to the Ararat plain with his few thousand irregulars. After a three-week march, his men and horses reached the railway station of Davalu. He was met by Dro, the Assistant Minister of Military Affairs and Sargis Manasian, the Assistant Minister of Internal Affairs, who offered to take him to visit Yerevan, but he rejected their invitation as he believed the Dashnak government had betrayed the Armenians and was responsible for the loss of his homeland and the annihilation of his people. Zangezur became more vulnerable to Azerbaijani threats after Andranik left the district. Earlier, before Andranik's and his soldiers' dismissal, the local Armenian forces had requested support from Yerevan.
On 13 April 1919, Andranik reached Etchmiadzin
Vagharshapat ( hy, Վաղարշապատ ) is the 4th-largest city in Armenia and the most populous municipal community of Armavir Province, located about west of the capital Yerevan, and north of the closed Turkish-Armenian border. It is com ...
, the seat of Catholicos of All Armenians
The Catholicos of All Armenians (plural Catholicoi) ( hy, Ամենայն Հայոց Կաթողիկոս; see #Other names), is the chief bishop and spiritual leader of Armenia's national church, the Armenian Apostolic Church, and the worldwide Arme ...
and the religious center of the Armenians, who helped the troops prepare for disbanding. His 5,000-strong division had dwindled to 1,350 soldiers. As a result of Andranik's disagreements with the Dashnak government and the diplomatic machinations of the British in the Caucasus, Andranik disbanded his division and handed his belongings and weapons to the Catholicos George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother ...
. On 27 April 1919, he left Etchmiadzin accompanied by 15 officers, and went to Tiflis on a special train; according to Blackwood, "news of his journey traveled before him. At every station crowds were waiting to get a glimpse of their national hero." He left Armenia for the last time; in Tiflis he met with Georgia's Foreign Minister Evgeni Gegechkori
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Martvili, Kutais Governorate, Russian Empire
, death_date =
, death_place = Paris, France
, nationality = Georgian
, occupation = Politician
, known_for ...
and discussed the Georgian–Armenian War
The Armeno-Georgian War was a short border dispute that was fought in December 1918 between the newly-independent Democratic Republic of Georgia and the First Republic of Armenia, largely over the control of former districts of Tiflis Governorat ...
. The Tbilisi-based writer Hovhannes Tumanyan
Hovhannes Tumanyan ( hy, Հովհաննես Թումանյան, classical spelling: Յովհաննէս Թումանեան, – March 23, 1923) was an Armenian poet, writer, translator, and literary and public activist. He is the nationa ...
served as their interpreter.
Last years
 From 1919 to 1922, Andranik traveled around Europe and the United States seeking support for the Armenian refugees. He visited Paris and London, where he tried to persuade the Allied powers to occupy Turkish Armenia. In 1919, during his visit to France, Andranik was bestowed the title of
From 1919 to 1922, Andranik traveled around Europe and the United States seeking support for the Armenian refugees. He visited Paris and London, where he tried to persuade the Allied powers to occupy Turkish Armenia. In 1919, during his visit to France, Andranik was bestowed the title of Legion of Honor
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon ...
Officier by President Raymond Poincaré
Raymond Nicolas Landry Poincaré (, ; 20 August 1860 – 15 October 1934) was a French statesman who served as President of France from 1913 to 1920, and three times as Prime Minister of France.
Trained in law, Poincaré was elected deputy in ...
. In late 1919, Andranik led a delegation to the United States to lobby its support for a mandate for Armenia and fund-raising for the Armenian army. He was accompanied by General Jaques Bagratuni and Hovhannes Katchaznouni
Hovhannes Kajaznuni or Katchaznouni (; 14 February 1868 – 15 January 1938) was an Armenian architect and politician who served as the first Prime Minister of the First Republic of Armenia from June 6, 1918 to August 7, 1919. He was a member of ...
. In Fresno, he directed a campaign which raised for the relief of Armenian war refugees.
 When he returned to Europe, Andranik married Nevarte Kurkjian in Paris on 15 May 1922;
When he returned to Europe, Andranik married Nevarte Kurkjian in Paris on 15 May 1922; Boghos Nubar
Boghos Nubar ( hyw, Պօղոս Նուպար), also known as Boghos Nubar Pasha () (2 August 1851 – 25 June 1930), was a chairman of the Armenian National Delegation, and the founder, alongside ten other Armenian national movement leaders, of th ...
was their best man. Andranik and Nevarte moved to the United States and settled in Fresno, California
Fresno () is a major city in the San Joaquin Valley of California, United States. It is the county seat of Fresno County and the largest city in the greater Central Valley region. It covers about and had a population of 542,107 in 2020, maki ...
in 1922. In his 1936 short story, ''Antranik of Armenia'', Armenian-American writer William Saroyan
William Saroyan (; August 31, 1908 – May 18, 1981) was an Armenian-American novelist, playwright, and short story writer. He was awarded the Pulitzer Prize for Drama in 1940, and in 1943 won the Academy Award for Best Story for the film ''T ...
described Andranik's arrival. He wrote, "It looked as if all Armenians of California were at the Southern Pacific depot at the day he arrived." He said Andranik "was a man of about fifty in a neat Armenians suit of clothes. He was a little under six feet tall, very solid and very strong. He had an old-style Armenian mustache that was white. The expression of his face was both ferocious and kind." Andranik lived with the family of Armen Alchian
Armen Albert Alchian (; April 12, 1914February 19, 2013) was an American economist. He spent almost his entire career at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). A major microeconomic theorist, he is known as one of the founders of new i ...
, who later became a prominent economist, in Fresno for several months.
In his novel ''Call of the Plowmen'' («Ռանչպարների կանչը», 1979), where Andranik is called Shapinand, Khachik Dashtents Khachik Dashtents ( hy, Խաչիկ Դաշտենց; ''Khachik Tonoyi Tonoyan'', May 25, 1910 – March 9, 1974) was an ethnic Armenian Soviet writer, poet and translator.classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA Worl ...
describes his life in Fresno:
Death
In February 1926, Andranik left Fresno to reside in San Francisco in an unsuccessful attempt to regain his health.''The Fresno Bee
''The Fresno Bee'' is a daily newspaper serving Fresno, California, and surrounding counties in that U.S. state's central San Joaquin Valley. It is owned by The McClatchy Company and ranks fourth in circulation among the company's newspaper ...
'', Death Claims Famous General, Once of Fresno, 31 August 1927 According to his death certificate found in the Butte County, California
Butte County () is a county located in the northern part of the U.S. state of California. In the 2020 census, its population was 211,632. The county seat is Oroville.
Butte County comprises the Chico, CA metropolitan statistical area. It is ...
records, Andranik died from angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of obstr ...
on 31 August 1927 at Richardson Springs, California
Richardson Springs (formerly, Mud Springs) is an unincorporated community in Butte County, California. It is located on Mud Creek north-northeast of Chico, at an elevation of 620 feet (189 m). The place is named for J.H. and Lee Richardson, ...
. On 7 September 1927, citywide public attention was accorded to him for his funeral in the Ararat Cemetery, Fresno. On October 9 more than 2,500 members of the Armenian community attended memorial services at Carnegie Hall
Carnegie Hall ( ) is a concert venue in Midtown Manhattan in New York City. It is at 881 Seventh Avenue, occupying the east side of Seventh Avenue between West 56th and 57th Streets. Designed by architect William Burnet Tuthill and built ...
in New York.
He was initially buried at Ararat Cemetery in Fresno. After his first funeral, it was planned to take Andranik's remains to Armenia for final burial; however, when they arrived in France, the Soviet authorities refused permission to allow his remains to enter Soviet Armenia. Instead they remained in France and, after a second funeral service held in the Armenian Church of Paris, were buried in Père Lachaise Cemetery
Père Lachaise Cemetery (french: Cimetière du Père-Lachaise ; formerly , "East Cemetery") is the largest cemetery in Paris, France (). With more than 3.5 million visitors annually, it is the most visited necropolis in the world. Notable figure ...
in Paris on 29 January 1928. In early 2000, the Armenian and French governments arranged the transfer of Andranik's body from Paris to Yerevan. ''Asbarez
''Asbarez'' ( hy, Ասպարէզ "Arena") is an Armenian-American bilingual daily newspaper published in Armenian and English in Los Angeles, California, formerly by the Western USA Central Committee of the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. A ...
'' wrote that the transfer was initiated by Armenia's Prime Minister Vazgen Sargsyan
Vazgen Zaveni Sargsyan ( hy, Վազգեն Զավենի Սարգսյան, ; 5 March 1959 – 27 October 1999) was an Armenian military commander and politician. He was the first Defence Minister of Armenia from 1991 to 1992 and then from ...
. Andranik's body was moved to Armenia on 17 February 2000. It was placed in the Sport & Concert Complex in Yerevan for two days and was then taken to Etchmiadzin Cathedral
Etchmiadzin Cathedral) or simply Etchmiadzin. Alternatively spelled as Echmiadzin, Ejmiatsin, and Edjmiadsin. ( hy, Էջմիածնի մայր տաճար, Ēǰmiatsni mayr tačar) is the mother church of the Armenian Apostolic Church, located ...
, where Karekin II
Catholicos Karekin II ( hy, Գարեգին Բ, also spelled Garegin; born 21 August 1951) is the current Catholicos of All Armenians, the supreme head of the Armenian Apostolic Church. In 2013 he was unanimously elected the Oriental Orthodox he ...
officiated the funeral service. Andranik was re-interred at Yerablur military cemetery in Yerevan on 20 February 2000, next to Vazgen Sargsyan. In his speech during the reburial ceremony, Armenia's President Robert Kocharyan described Andranik as "one of the greatest sons of the Armenian nation." Prime Minister Aram Sargsyan, Foreign Minister Vartan Oskanian
Vartan Minasi Oskanian ( hy, Վարդան Մինասի Օսկանյան; born February 7, 1954) is the former Foreign Minister of Armenia (1998–2008) and founder of the Civilitas Foundation.
Early life and career
Born into a wealthy Armenian ...
, and one of Andranik's soldiers, 102-year-old Grigor Ghazarian, were also in attendance. A memorial was built on his grave with the phrase ''Zoravar Hayots''"General of the Armenians"engraved on it.
Legacy and recognition
Public image
Andranik was considered a hero during his lifetime. ''The Literary Digest
''The Literary Digest'' was an influential American general interest weekly magazine published by Funk & Wagnalls. Founded by Isaac Kaufmann Funk in 1890, it eventually merged with two similar weekly magazines, ''Public Opinion'' and '' Current Op ...
'' described Andranik in 1920 as "the Armenian's Robin Hood, Garibaldi, and Washington, all in one." ''The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publish ...
'' wrote that he is "worshiped by his countrymen for his heroic fighting in their defense against the Turks." Andranik was praised by the noted Armenian writer Hovhannes Tumanyan
Hovhannes Tumanyan ( hy, Հովհաննես Թումանյան, classical spelling: Յովհաննէս Թումանեան, – March 23, 1923) was an Armenian poet, writer, translator, and literary and public activist. He is the nationa ...
, while Armenian Bolshevik Anastas Mikoyan
Anastas Ivanovich Mikoyan (; russian: Анаста́с Ива́нович Микоя́н; hy, Անաստաս Հովհաննեսի Միկոյան; 25 November 1895 – 21 October 1978) was an Armenian Communist revolutionary, Old Bolshevik an ...
wrote in his memoirs that "the name Andranik was surrounded by halo of glory."
 Andranik is considered a national hero by Armenians worldwide. He is also seen as a legendary figure in Armenian culture. In a series of polls in 2006–08, Andranik consistently placed second after Vazgen Sargsyan in the list of Armenian national heroes and leaders.
During the Soviet period, his legacy and those of other Armenian national heroes were diminished and "any reference to them would be dangerous since they represented the strive for independence," especially prior to the
Andranik is considered a national hero by Armenians worldwide. He is also seen as a legendary figure in Armenian culture. In a series of polls in 2006–08, Andranik consistently placed second after Vazgen Sargsyan in the list of Armenian national heroes and leaders.
During the Soviet period, his legacy and those of other Armenian national heroes were diminished and "any reference to them would be dangerous since they represented the strive for independence," especially prior to the Khrushchev Thaw
The Khrushchev Thaw ( rus, хрущёвская о́ттепель, r=khrushchovskaya ottepel, p=xrʊˈɕːɵfskəjə ˈotʲ:ɪpʲɪlʲ or simply ''ottepel'')William Taubman, Khrushchev: The Man and His Era, London: Free Press, 2004 is the period ...
. Paruyr Sevak, a prominent Soviet Armenian author, wrote an essay about Andranik in 1963 after reading one of his soldier's notes. Sevak wrote that his generation knew "little about Andranik, almost nothing." He continued, "knowing nothing about Andranik means to know nothing about modern Armenian history." In 1965, Andranik's 100th anniversary was celebrated in Soviet Armenia.
Criticism
Andranik's activities have also attracted occasional criticism. Andranik, generally seen as a pro-Russian (and pro-Soviet) figure, was criticized by the scholar-turned-political activistRafael Ishkhanyan
Rafayel Avetisi Ishkhanyan ( hy, Ռաֆայել Ավետիսի Իշխանյան, 9 March 1922 – 6 February 1995) was an Armenian linguist, philologist and historian. He was a professor of the Yerevan State University.
Biography
Ishkhanyan was ...
for his constant reliance on Russia. Ishkhanyan characterized Andranik and Hakob Zavriev
Hakob Zavriev ( hy, Հակոբ Զավրիև), also known as Yakov Zavriev, was an Armenian politician.
Zavriev was a graduate of the St. Petersburg Army Medical Academy. He later joined the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. The viceroy of the ...
as leaders of the stream within Armenian political thought unconditionally reliant on Russia. He contrasted them with Aram Manukian
Aram Manukian, reformed spelling: Արամ Մանուկյան, and he is also referred to as simply Aram. (19 March 187929 January 1919), was an Armenian revolutionary, statesman, and a leading member of the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (D ...
and his self-reliant stance.First published in English in The poet spoke out against the erection of Andranik's statue in Yerevan. He opined that Andranik "doesn't have the right" to have a statue in the capital, because he did not do "anything real" for the First Republic and left Armenia. He called Andranik a popular hero and finds calling him a national hero unacceptable.
Memorials
Statues and memorials of Andranik have been erected around the world, including inBucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north o ...
, Romania (1936), Père Lachaise Cemetery in Paris (1945), Melkonian Educational Institute
The Melkonian Educational Institute (MEI) ( hy, Մելգոնեան Կրթական Հաստատութիւն (ՄԿՀ)) was an Armenian boarding school of high academic standard located in Nicosia, Cyprus.
Established in 1926 by the Melkonian brot ...
, Nicosia
Nicosia ( ; el, Λευκωσία, Lefkosía ; tr, Lefkoşa ; hy, Նիկոսիա, romanized: ''Nikosia''; Cypriot Arabic: Nikusiya) is the largest city, capital, and seat of government of Cyprus. It is located near the centre of the Mesaori ...
, Cyprus (1990), Le Plessis-Robinson
Le Plessis-Robinson () is a commune in the southwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the center of Paris. , it has 29,100 inhabitants.
History
Plessis was first mentioned in 839 as ''Plessiacus apud Castanetum'', meaning ''ples ...
, Paris (2005), Varna, Bulgaria (2011), and Armavir, Russia. A memorial exists in Richardson Springs, California, where Andranik died. In May 2011, a statue of Andranik was erected in Volonka village near Sochi
Sochi ( rus, Со́чи, p=ˈsotɕɪ, a=Ru-Сочи.ogg) is the largest resort city in Russia. The city is situated on the Sochi River, along the Black Sea in Southern Russia, with a population of 466,078 residents, up to 600,000 residents i ...
, Russia; however, it was removed the same day, apparently under pressure from Turkey, which earlier announced that they would boycott the 2014 Sochi Winter Olympics if the statue remained standing.
 The first statue of Andranik in Armenia was erected in 1967 in the village of Ujan. Another early statue in Armenia was erected in Voskehask, near Gyumri, in 1969. More statues have been erected after Armenia's independence from the Soviet Union in 1991; three of which can be found in the Armenian capital of Yerevan—in
The first statue of Andranik in Armenia was erected in 1967 in the village of Ujan. Another early statue in Armenia was erected in Voskehask, near Gyumri, in 1969. More statues have been erected after Armenia's independence from the Soviet Union in 1991; three of which can be found in the Armenian capital of Yerevan—in Malatia-Sebastia
Malatia-Sebastia ( hy, Մալաթիա-Սեբաստիա վարչական շրջան, ), also nicknamed colloquially as Bangladesh, is one of the 12 districts of Yerevan, the capital of Armenia, located in the western part of the city. As of the 20 ...
district (2000); near the St. Gregory Cathedral (by Ara Shiraz, 2002); and outside the Fedayi Movement Museum (2006) in the Armenian capital Yerevan. Elsewhere in Armenia, Andranik's statues stand in Voskevan
Voskevan ( hy, Ոսկեվան) is a village in the Tavush Province of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of wor ...
and Navur
Navur ( hy, Նավուր) is a village in the Berd Municipality of the Tavush Province of Armenia.
Gallery
Navur Tavush.jpg, A view of Navur
Mariam Mayri vank-02.JPG, Mariam Mayri Vank in Navur
General Andranik, Navour (1).JPG, Statue of Gene ...
villages of Tavush, in Gyumri
Gyumri ( hy, Գյումրի, ) is an urban municipal community and the second-largest city in Armenia, serving as the administrative center of Shirak Province in the northwestern part of the country. By the end of the 19th century, when the city w ...
's Victory Park (1994), Arteni
Arteni ( hy, Արտենի;) is a town in the Aragatsotn province of Armenia.
The town contains a wine factory.
See also
*Aragatsotn Province
Aragatsotn ( hy, Արագածոտն, ) is a province ('' marz'') of Armenia. It is located in the ...
, and Angeghakot
Angeghakot ( hy, Անգեղակոթ) is a village in the Sisian Municipality of the Syunik Province in Armenia. A large reservoir, the Angeghakot Reservoir, spanning more than the entire length of the village lies to the south.
Demographics
I ...
, among other places.
Numerous streets and squares both inside and outside Armenia, including in Córdoba, Argentina, Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the ...
and Varna in Bulgaria, Meudon
Meudon () is a municipality in the southwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is in the département of Hauts-de-Seine. It is located from the center of Paris. The city is known for many historic monuments and some extraordinary trees. One of t ...
, Paris and a section of Connecticut Route 314 state highway running entirely within Wethersfield, Connecticut
Wethersfield is a town located in Hartford County, Connecticut. It is located immediately south of Hartford along the Connecticut River. Its population was 27,298 at the time of the 2020 census.
Many records from colonial times spell the nam ...
are named after Andranik. General Andranik Station of the Yerevan Metro
The Karen Demirchyan Yerevan Subway ( hy, Կարեն Դեմիրճյանի անվան Երևանի մետրոպոլիտեն, ''Karen Demirchyani anvan Yerevani metropoliten''; since December 1999), colloquially known as the Yerevan Metro ( hy, � ...
was opened in 1989 as Hoktemberyan Station and was renamed for Andranik in 1992. In 1995, General Andranik's Museum was founded in Komitas Park of Yerevan, but was soon closed because the building was privatized. It was reopened on 16 September 2006, by Ilyich Beglarian as the Museum of Armenian Fedayi Movement, named after Andranik.
According to Patrick Wilson, during the First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War, referred to in Armenia as the Artsakh Liberation War ( hy, Արցախյան ազատամարտ, Artsakhyan azatamart) was an ethnic conflict, ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 t ...
Andranik "inspired a new generation of Armenians." A volunteer regiment from Masis named "General Andranik" operated in Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh during the conflict.
Many organizations and groups in the Armenian diaspora
The Armenian diaspora refers to the communities of Armenians outside Armenia and other locations where Armenians are considered an indigenous population. Since antiquity, Armenians have established communities in many regions throughout the world. ...
are named after Andranik. On 11 September 2012, during the Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
vs. Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
football match in Sofia's Levski National Stadium, Armenian fans brought a giant poster with pictures of General Andranik and Armenian officer Gurgen Margaryan
On 19 February 2004, Gurgen Margaryan ( hy, Գուրգեն Մարգարյան; 26 September 1978 – 19 February 2004), a lieutenant in the Armenian army, was murdered in Budapest, Hungary, by Ramil Safarov, a lieutenant in the Azerbaijani army.
...
, who was murdered in 2004 by Azerbaijani lieutenant Ramil Safarov. The text on the poster read, "Andranik's children are also heroes ... The work will be done."
The 65 page manuscripts of General Andranik, the only known memoir written by him, were returned to Armenia in May 2014 and sent to the History Museum of Armenia
The History Museum of Armenia (armenian: Հայաստանի պատմության թանգարան) is a museum in Armenia with departments of Archaeology, Numismatics, Ethnography, Modern History and Restoration. It has a national collection of ...
through Culture Minister Hasmik Poghosyan, almost a century after Andranik had parted with them.
In culture

 Andranik has been figured prominently in the Armenian literature, sometimes as a fictional character. The Western Armenian writer Siamanto wrote a poem entitled "Andranik", which was published in Geneva in 1905. The first book about Andranik was published during his lifetime. In 1920, Vahan Totovents, under the pen name Arsen Marmarian, published the book ''Gen. Andranik and His Wars'' (Զոր. Անդրանիկ և իր պատերազմները) in Entente-occupied Constantinople. The famed Armenian-American writer William Saroyan wrote a short story titled ''Antranik of Armenia'', which was included in his collection of short stories ''Inhale and Exhale'' (1936). Another US-based Armenian writer Hamastegh's novel ''The White Horseman'' (Սպիտակ Ձիավորը, 1952) was based on Andranik and other ''fedayi''. Hovhannes Shiraz, one of the most prominent Armenian poets of the 20th century, wrote at least two poems about Andranik; one in 1963 and another in 1967. The latter one, titled ''Statue to Andranik'' (Արձան Անդրանիկին), was published in 1991 after Shiraz's death.
Andranik has been figured prominently in the Armenian literature, sometimes as a fictional character. The Western Armenian writer Siamanto wrote a poem entitled "Andranik", which was published in Geneva in 1905. The first book about Andranik was published during his lifetime. In 1920, Vahan Totovents, under the pen name Arsen Marmarian, published the book ''Gen. Andranik and His Wars'' (Զոր. Անդրանիկ և իր պատերազմները) in Entente-occupied Constantinople. The famed Armenian-American writer William Saroyan wrote a short story titled ''Antranik of Armenia'', which was included in his collection of short stories ''Inhale and Exhale'' (1936). Another US-based Armenian writer Hamastegh's novel ''The White Horseman'' (Սպիտակ Ձիավորը, 1952) was based on Andranik and other ''fedayi''. Hovhannes Shiraz, one of the most prominent Armenian poets of the 20th century, wrote at least two poems about Andranik; one in 1963 and another in 1967. The latter one, titled ''Statue to Andranik'' (Արձան Անդրանիկին), was published in 1991 after Shiraz's death. Sero Khanzadyan
Sero Nikolayi Khanzadyan ( hy, Սերո Նիկոլայի Խանզադյան, , 1915 – June 26, 1998) was an Armenian writer and novelist.
Early life and education
Sero Khanzadyan was born in 1915 to a peasant family in the town of Goris locate ...
's novel ''Andranik'' was suppressed for years and was published in 1989 when the tight Soviet control over publications was relaxed. Between the 1960s and the 1980s, author Suren Sahakyan collected folk stories and completed a novel, "Story about Andranik" (Ասք Անդրանիկի մասին). It was first published in Yerevan in 2008.
Andranik's name has been memorialized in numerous songs. In 1913, Leon Trotsky described Andranik as "a hero of song and legend." Italian diplomat and historian Luigi Villari
Luigi Villari (1876–1959), son of Pasquale Villari and Linda White Mazini Villari, was an Italian historian, traveler and diplomat. He worked in the Minister of Foreign Affairs (Italy), Italian Foreign Office and was later a newspaper corresponde ...
wrote in 1906 that he met a priest from Turkish Armenia in Erivan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and ...
who "sang the war-song of Antranik, the leader of Armenian revolutionary bands in Turkey." Andranik is one of the main figures featured in Armenian patriotic songs, performed by Nersik Ispiryan
Nersik Ispiryan ( hy, Ներսիկ Իսպիրյան, born May 15, 1963) is an Armenian singer best known for his Armenian nationalistic songs.
Biography
Nersik Ispiryan was born in Yerevan, Armenian SSR, Soviet Union. He graduated from Schoo ...
, Harout Pamboukjian
Harout Pamboukjian ( hy, Հարութ Փամբուկչյան; hyw, Յարութ Փամպուքճեան; born July 1, 1950), known as Dzakh Harut ( hy, Ձախ Հարութ, literally "Left Harout"), is an Armenian pop singer living in Los Ang ...
and others. There are dozens of songs dedicated to him, including ''Like an Eagle'' by '' gusan'' Sheram, 1904 and ''Andranik pasha'' by ''gusan'' Hayrik. Andranik also features in the popular song ''The Bravehearts of the Caucasus'' (Կովկասի քաջեր) and other pieces of Armenian patriotic folklore.
Several documentaries about Andranik have been produced; these include '' Andranik'' (1929) by Armena-Film in France, directed by Asho Shakhatuni, who also played the main role; ''General Andranik'' (1990) directed by Levon Mkrtchyan
Levon Mkrtchyan ( hy, Լևոն Մկրտչյան; russian: Левон Гайкович Мкртчян; born February 25, 1953 in Leninakan (now Gyumri) is an Armenian director, known for his documentaries, "Davit Anhaght", "Charentz: Known and Unk ...
, narrated by Khoren Abrahamyan
Khoren Babkeni Abrahamyan ( hy, Խորեն Բաբկենի Աբրահամյան, April 1, 1930, Yerevan – December 10, 2004) was an Armenian actor and director, and People's Artist of the USSR. Abrahamyan was honored with the title People’s Ar ...
; and ''Andranik Ozanian'', a 53-minute-long documentary by the Public Television of Armenia.
Awards
 Through his military career, Andranik was awarded with a number of medals and orders by governments of four countries. Andranik's medals and sword were moved to Armenia and given to the
Through his military career, Andranik was awarded with a number of medals and orders by governments of four countries. Andranik's medals and sword were moved to Armenia and given to the History Museum of Armenia
The History Museum of Armenia (armenian: Հայաստանի պատմության թանգարան) is a museum in Armenia with departments of Archaeology, Numismatics, Ethnography, Modern History and Restoration. It has a national collection of ...
in 2006.
Published works
* * * * Memoirs of Andranik written down by Levon K. Lyulejian.