Alcohol (chemistry) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Alcohols have a long history of myriad uses. For simple mono-alcohols, which is the focus on this article, the following are most important industrial alcohols:.
*methanol, mainly for the production of formaldehyde and as a
Alcohols have a long history of myriad uses. For simple mono-alcohols, which is the focus on this article, the following are most important industrial alcohols:.
*methanol, mainly for the production of formaldehyde and as a
Al(C2H5)3 + 9 C2H4 -> Al(C8H17)3
:Al(C8H17)3 + 3O + 3 H2O -> 3 HOC8H17 + Al(OH)3
The process generates a range of alcohols that are separated by distillation.
Many higher alcohols are produced by hydroformylation of alkenes followed by hydrogenation. When applied to a terminal alkene, as is common, one typically obtains a linear alcohol:
:RCH=CH2 + H2 + CO -> RCH2CH2CHO
:RCH2CH2CHO + 3 H2 -> RCH2CH2CH2OH
Such processes give
 The hydroboration-oxidation and oxymercuration-reduction of alkenes are more reliable in organic synthesis. Alkenes react with N-bromosuccinimide and water in halohydrin formation reaction.
The hydroboration-oxidation and oxymercuration-reduction of alkenes are more reliable in organic synthesis. Alkenes react with N-bromosuccinimide and water in halohydrin formation reaction.
2 R-OH + 2 NaH -> 2 R-O-Na+ + 2 H2
: 2 R-OH + 2 Na -> 2 R-O-Na+ + H2
The acidity of alcohols is strongly affected by solvation. In the gas phase, alcohols are more acidic than in water. In DMSO, alcohols (and water) have a p''K''a of around 29–32. As a consequence, alkoxides (and hydroxide) are powerful bases and nucleophiles (e.g., for the Williamson ether synthesis) in this solvent. In particular, or in DMSO can be used to generate significant equilibrium concentrations of acetylide ions through the deprotonation of alkynes (see
 Alcohols may, likewise, be converted to alkyl bromides using hydrobromic acid or phosphorus tribromide, for example:
:
Alcohols may, likewise, be converted to alkyl bromides using hydrobromic acid or phosphorus tribromide, for example:
: 3 R-OH + PBr3 -> 3 RBr + H3PO3
In the Barton-McCombie deoxygenation an alcohol is deoxygenated to an
 Upon treatment with strong acids, alcohols undergo the E1 elimination reaction to produce alkenes. The reaction, in general, obeys Zaitsev's Rule, which states that the most stable (usually the most substituted) alkene is formed. Tertiary alcohols eliminate easily at just above room temperature, but primary alcohols require a higher temperature.
This is a diagram of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to produce
Upon treatment with strong acids, alcohols undergo the E1 elimination reaction to produce alkenes. The reaction, in general, obeys Zaitsev's Rule, which states that the most stable (usually the most substituted) alkene is formed. Tertiary alcohols eliminate easily at just above room temperature, but primary alcohols require a higher temperature.
This is a diagram of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to produce 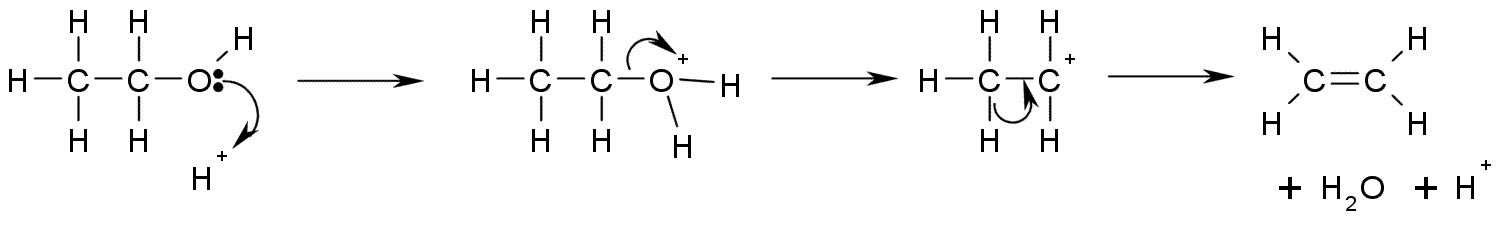 A more controlled elimination reaction requires the formation of the
A more controlled elimination reaction requires the formation of the
R-OH + R'-CO2H -> R'-CO2R + H2O
Other types of ester are prepared in a similar manner for example, tosyl (tosylate) esters are made by reaction of the alcohol with p-
 Reagents useful for the transformation of primary alcohols to aldehydes are normally also suitable for the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones. These include Collins reagent and Dess-Martin periodinane. The direct oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids can be carried out using potassium permanganate or the Jones reagent.
Reagents useful for the transformation of primary alcohols to aldehydes are normally also suitable for the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones. These include Collins reagent and Dess-Martin periodinane. The direct oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids can be carried out using potassium permanganate or the Jones reagent.
 In
In chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols.
The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior ...
or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compounds that contain hydroxyl functional groups have ''trivial names'' which do not include the suffix ''-ol'' or the prefix ''hydroxy-'', e.g. the sugars glucose and sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
.
History
The inflammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such asAristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
(384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt
, conventional_long_name = Roman Egypt
, common_name = Egypt
, subdivision = Province
, nation = the Roman Empire
, era = Late antiquity
, capital = Alexandria
, title_leader = Praefectus Augustalis
, image_map = Roman E ...
. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Ḥayyān (ninth century CE), was that by adding salt to boiling wine, which increases the wine's relative volatility, the flammability of the resulting vapors may be enhanced. The distillation of wine is attested in Arabic works attributed to al-Kindī (–873 CE) and to al-Fārābī
Abu Nasr Muhammad Al-Farabi ( fa, ابونصر محمد فارابی), ( ar, أبو نصر محمد الفارابي), known in the West as Alpharabius; (c. 872 – between 14 December, 950 and 12 January, 951)PDF version was a renowned early Isla ...
(–950), and in the 28th book of al-Zahrāwī's (Latin: Abulcasis, 936–1013) ''Kitāb al-Taṣrīf'' (later translated into Latin as ''Liber servatoris''). In the twelfth century, recipes for the production of ''aqua ardens'' ("burning water", i.e., alcohol) by distilling wine with salt started to appear in a number of Latin works, and by the end of the thirteenth century it had become a widely known substance among Western European chemists.
The works of Taddeo Alderotti (1223–1296) describe a method for concentrating alcohol involving repeated fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to ...
through a water-cooled still, by which an alcohol purity of 90% could be obtained. The medicinal properties of ethanol were studied by Arnald of Villanova (1240–1311 CE) and John of Rupescissa (–1366), the latter of whom regarded it as a life-preserving substance able to prevent all diseases (the ''aqua vitae
''Aqua vitae'' (Latin for "water of life") or aqua vita is an archaic name for a concentrated aqueous solution of ethanol. These terms could also be applied to weak ethanol without rectification. Usage was widespread during the Middle Ages a ...
'' or "water of life", also called by John the ''quintessence
Quintessence, or fifth essence, may refer to:
Cosmology
* Aether (classical element), in medieval cosmology and science, the fifth element that fills the universe beyond the terrestrial sphere
* Quintessence (physics), a hypothetical form of da ...
'' of wine).
Nomenclature
Etymology
The word "alcohol" derives from the Arabic '' kohl'' ( ar, الكحل, al-kuḥl), a powder used as an eyeliner. The first part of the word () is the Arabic definite article, equivalent to ''the'' in English. The second part of the word () has several antecedents in Semitic languages, ultimately deriving from theAkkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system
* Akkadian myt ...
𒎎𒋆𒁉𒍣𒁕 (guḫlum), meaning stibnite or antimony.
Like its antecedents in Arabic and older languages, the term ''alcohol'' was originally used for the very fine powder produced by the sublimation
Sublimation or sublimate may refer to:
* ''Sublimation'' (album), by Canvas Solaris, 2004
* Sublimation (phase transition), directly from the solid to the gas phase
* Sublimation (psychology), a mature type of defense mechanism
* Sublimate of mer ...
of the natural mineral stibnite to form antimony trisulfide . It was considered to be the essence or "spirit" of this mineral. It was used as an antiseptic, eyeliner, and cosmetic
Cosmetic may refer to:
* Cosmetics, or make-up, substances to enhance the beauty of the human body, apart from simple cleaning
*Cosmetic, an adjective describing beauty, aesthetics, or appearance, especially concerning the human body
*Cosmetic, ...
. Later the meaning of alcohol was extended to distilled substances in general, and then narrowed again to ethanol, when "spirits" was a synonym for hard liquor.
Bartholomew Traheron, in his 1543 translation of John of Vigo, introduces the word as a term used by "barbarous" authors for "fine powder." Vigo wrote: "the barbarous auctours use alcohol, or (as I fynde it sometymes wryten) alcofoll, for moost fine poudre."
The 1657 ''Lexicon Chymicum'', by William Johnson glosses the word as "antimonium sive stibium." By extension, the word came to refer to any fluid obtained by distillation, including "alcohol of wine," the distilled essence of wine. Libavius
Andreas Libavius or Andrew Libavius was born in Halle, Germany c. 1550 and died in July 1616. Libavius was a renaissance man who spent time as a professor at the University of Jena teaching history and poetry. After which he became a physician at ...
in ''Alchymia'' (1594) refers to "vini alcohol vel vinum alcalisatum". Johnson (1657) glosses ''alcohol vini'' as "quando omnis superfluitas vini a vino separatur, ita ut accensum ardeat donec totum consumatur, nihilque fæcum aut phlegmatis in fundo remaneat." The word's meaning became restricted to "spirit of wine" (the chemical known today as ethanol) in the 18th century and was extended to the class of substances so-called as "alcohols" in modern chemistry after 1850.
The term ''ethanol'' was invented in 1892, blending " ethane" with the "-ol" ending of "alcohol", which was generalized as a libfix.
Systematic names
IUPAC nomenclature is used in scientific publications and where precise identification of the substance is important. In naming simple alcohols, the name of the alkane chain loses the terminal ''e'' and adds the suffix ''-ol'', ''e.g.'', as in "ethanol" from the alkane chain name "ethane". When necessary, the position of the hydroxyl group is indicated by a number between the alkane name and the ''-ol'': propan-1-ol for , propan-2-ol for . If a higher priority group is present (such as analdehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group ...
, ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ...
, or carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
), then the prefix ''hydroxy-''is used, e.g., as in 1-hydroxy-2-propanone (). Compounds having more than one hydroxy group are called polyols. They are named using suffixes -diol, -triol, etc., following a list of the position numbers of the hydroxyl groups, as in propane-1,2-diol
Propylene glycol ( IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid, which is nearly odorless but possesses a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH.
Containing two alcohol groups, it is classed as a diol. It is ...
for CH3CH(OH)CH2OH (propylene glycol).
In cases where the hydroxy group is bonded to an sp2 carbon on an aromatic ring, the molecule is classified separately as a phenol and is named using the IUPAC rules for naming phenols. Phenols have distinct properties and are not classified as alcohols.
Common names
In other less formal contexts, an alcohol is often called with the name of the corresponding alkyl group followed by the word "alcohol", e.g.,methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many ...
alcohol, ethyl
Ethyl may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Cold Ethyl, a Swedish rock band
*Ethyl Sinclair, a character in the ''Dinosaurs'' television show
Science and technology
* Ethyl group, an organic chemistry moiety
* Ethyl alcohol (or ethanol)
* E ...
alcohol. Propyl alcohol may be ''n''-propyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, depending on whether the hydroxyl group is bonded to the end or middle carbon on the straight propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used a ...
chain. As described under systematic naming, if another group on the molecule takes priority, the alcohol moiety is often indicated using the "hydroxy-" prefix.
In archaic nomenclature, alcohols can be named as derivatives of methanol using "-carbinol" as the ending. For instance, can be named trimethylcarbinol.
Primary, secondary, and tertiary
Alcohols are then classified into primary, secondary (''sec-'', ''s-''), and tertiary (''tert-'', ''t-''), based upon the number of carbon atoms connected to the carbon atom that bears the hydroxyl functional group. (The respective numeric shorthands 1°, 2°, and 3° are sometimes used in informal settings.) The primary alcohols have general formulas . The simplest primary alcohol is methanol (), for which R=H, and the next is ethanol, for which , the methyl group. Secondary alcohols are those of the form RR'CHOH, the simplest of which is 2-propanol (). For the tertiary alcohols the general form is RR'R"COH. The simplest example is tert-butanol (2-methylpropan-2-ol), for which each of R, R', and R" is . In these shorthands, R, R', and R" represent substituents, alkyl or other attached, generally organic groups.Examples
Applications
 Alcohols have a long history of myriad uses. For simple mono-alcohols, which is the focus on this article, the following are most important industrial alcohols:.
*methanol, mainly for the production of formaldehyde and as a
Alcohols have a long history of myriad uses. For simple mono-alcohols, which is the focus on this article, the following are most important industrial alcohols:.
*methanol, mainly for the production of formaldehyde and as a fuel additive
Petrol additives increase petrol's octane rating or act as corrosion inhibitors or lubricants, thus allowing the use of higher compression ratios for greater efficiency and power. Types of additives include metal deactivators, corrosion inhibitors, ...
*ethanol, mainly for alcoholic beverages, fuel additive, solvent
*1-propanol, 1-butanol, and isobutyl alcohol for use as a solvent and precursor to solvents
*C6–C11 alcohols used for plasticizers, e.g. in polyvinylchloride
*fatty alcohol (C12–C18), precursors to detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are more ...
s
Methanol is the most common industrial alcohol, with about 12 million tons/y produced in 1980. The combined capacity of the other alcohols is about the same, distributed roughly equally.
Toxicity
With respect to acute toxicity, simple alcohols have low acute toxicities. Doses of several milliliters are tolerated. Forpentanol
An amyl alcohol is any of eight alcohols with the formula C5H12O. A mixture of amyl alcohols (also called amyl alcohol) can be obtained from fusel alcohol. Amyl alcohol is used as a solvent and in esterification, by which is produced amyl acetate a ...
s, hexanols, octanols and longer alcohols, LD50 range from 2–5 g/kg (rats, oral). Ethanol is less acutely toxic. All alcohols are mild skin irritants.
The metabolism of methanol (and ethylene glycol) is affected by the presence of ethanol, which has a higher affinity for liver alcohol dehydrogenase. In this way methanol will be excreted intact in urine.
Physical properties
In general, thehydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
makes alcohols polar. Those groups can form hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
s to one another and to most other compounds. Owing to the presence of the polar OH alcohols are more water-soluble than simple hydrocarbons. Methanol, ethanol, and propanol are miscible
Miscibility () is the property of two substances to mix in all proportions (that is, to fully dissolve in each other at any concentration), forming a homogeneous mixture (a solution). The term is most often applied to liquids but also applies ...
in water. Butanol, with a four-carbon chain, is moderately soluble.
Because of hydrogen bonding, alcohols tend to have higher boiling points than comparable hydrocarbons and ethers. The boiling point of the alcohol ethanol is 78.29 °C, compared to 69 °C for the hydrocarbon hexane, and 34.6 °C for diethyl ether.
Occurrence in nature
Simple alcohols are found widely in nature. Ethanol is the most prominent because it is the product of fermentation, a major energy-producing pathway. Other simple alcohols, chieflyfusel alcohols
Fusel alcohols or fuselol, also sometimes called fusel oils in Europe, are mixtures of several higher alcohols (those with more than two carbons, chiefly amyl alcohol) produced as a by-product of alcoholic fermentation. The word ''Fusel'' is Ger ...
, are formed in only trace amounts. More complex alcohols however are pervasive, as manifested in sugars, some amino acids, and fatty acids.
Production
Ziegler and oxo processes
In the Ziegler process, linear alcohols are produced from ethylene and triethylaluminium followed by oxidation and hydrolysis. An idealized synthesis of1-octanol
1-Octanol, also known as octan-1-ol, is the organic compound with the molecular formula CH3(CH2)7OH. It is a fatty alcohol. Many other isomers are also known generically as octanols. 1-Octanol is manufactured for the synthesis of esters for use ...
is shown:
:fatty alcohol
Fatty alcohols (or long-chain alcohols) are usually high-molecular-weight, straight-chain primary alcohols, but can also range from as few as 4–6 carbons to as many as 22–26, derived from natural fats and oils. The precise chain length varies ...
s, which are useful for detergents.
Hydration reactions
Some low molecular weight alcohols of industrial importance are produced by the addition of water to alkenes. Ethanol, isopropanol, 2-butanol, and tert-butanol are produced by this general method. Two implementations are employed, the direct and indirect methods. The direct method avoids the formation of stable intermediates, typically using acid catalysts. In the indirect method, the alkene is converted to thesulfate ester
Organosulfates are a class of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the structure R-O-SO3−. The SO4 core is a sulfate group and the R group is any organic residue. All organosulfates are formally esters derived from alcohols ...
, which is subsequently hydrolyzed. The direct hydration using ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
( ethylene hydration) or other alkenes from cracking of fractions of distilled crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
.
Hydration is also used industrially to produce the diol ethylene glycol from ethylene oxide.
Biological routes
Ethanol is obtained byfermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
using glucose produced from sugar from the hydrolysis of starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
, in the presence of yeast and temperature of less than 37 °C to produce ethanol. For instance, such a process might proceed by the conversion of sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
by the enzyme invertase into glucose and fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
, then the conversion of glucose by the enzyme complex zymase into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Several species of the benign bacteria in the intestine use fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
as a form of anaerobic metabolism. This metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
reaction produces ethanol as a waste product. Thus, human bodies contain some quantity of alcohol endogenously produced by these bacteria. In rare cases, this can be sufficient to cause "auto-brewery syndrome
Auto-brewery syndrome (ABS) (also known as gut fermentation syndrome, endogenous ethanol fermentation or drunkenness disease) is a condition characterized by the fermentation of ingested carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract of the body cause ...
" in which intoxicating quantities of alcohol are produced.
Like ethanol, butanol can be produced by fermentation processes. ''Saccharomyces'' yeast are known to produce these higher alcohols at temperatures above . The bacterium '' Clostridium acetobutylicum'' can feed on cellulose to produce butanol on an industrial scale.
Substitution
Primary alkyl halides react with aqueous NaOH or KOH mainly to primary alcohols in nucleophilic aliphatic substitution. (Secondary and especially tertiary alkyl halides will give the elimination (alkene) product instead).Grignard reagent
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide ...
s react with carbonyl groups to secondary and tertiary alcohols. Related reactions are the Barbier reaction and the Nozaki-Hiyama reaction.
Reduction
Aldehydes orketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ...
s are reduced with sodium borohydride or lithium aluminium hydride
Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li Al H4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic ...
(after an acidic workup). Another reduction by aluminiumisopropylates is the Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction. Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation is the asymmetric reduction of β-keto-esters.
Hydrolysis
Alkenes engage in an acid catalysedhydration reaction
In chemistry, a hydration reaction is a chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, che ...
using concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst that gives usually secondary or tertiary alcohols. Formation of a secondary alcohol via alkene reduction and hydration is shown on the right:
:Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent su ...
s can be converted to diazonium salts, which are then hydrolyzed.
Reactions
Deprotonation
With aqueous p''K''a values of around 16–19, they are, in general, slightly weakeracid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
s than water. With strong bases such as sodium hydride or sodium they form salts called ''alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, whe ...
s'', with the general formula (where R is an alkyl and M is a metal).
: Favorskii reaction
The Favorskii reaction is an organic chemistry reaction between an alkyne and a carbonyl group, under basic conditions. The reaction was discovered in the early 1900s by the Russian chemist Alexei Yevgrafovich Favorskii.
When the carbonyl is ...
).
Nucleophilic substitution
The OH group is not a good leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions, so neutral alcohols do not react in such reactions. However, if the oxygen is first protonated to give , the leaving group ( water) is much more stable, and the nucleophilic substitution can take place. For instance, tertiary alcohols react with hydrochloric acid to produce tertiary alkyl halides, where thehydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
is replaced by a chlorine atom by unimolecular nucleophilic substitution. If primary or secondary alcohols are to be reacted with hydrochloric acid, an activator such as zinc chloride is needed. In alternative fashion, the conversion may be performed directly using thionyl chloride.
alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which ...
with tributyltin hydride or a trimethylborane-water complex in a radical substitution reaction.
Dehydration
Meanwhile, the oxygen atom haslone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone ...
s of nonbonded electrons that render it weakly basic
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College ...
in the presence of strong acids such as sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
. For example, with methanol:
ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
:
 A more controlled elimination reaction requires the formation of the
A more controlled elimination reaction requires the formation of the xanthate ester
150px, Sodium salt of ethyl xanthate
Xanthate usually refers to a salt with the formula (R = alkyl; M+ = Na+, K+), thus they are the metal-thioate/''O''-esters of dithiocarbonate. The name ''xanthates'' is derived from Ancient Greek ''xanthos'' ...
.
Protonolysis
Tertiary alcohols react with strong acids to generate carbocations. The reaction is related to their dehydration, e.g. isobutylene from tert-butyl alcohol. A special kind of dehydration reaction involves triphenylmethanol and especially its amine-substituted derivatives. When treated with acid, these alcohols lose water to give stable carbocations, which are commercial dyes. 322px, Preparation of crystal violet by protonolysis of the tertiary alcohol.Esterification
Alcohol andcarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
s react in the so-called Fischer esterification
Fischer is a German occupational surname, meaning fisherman. The name Fischer is the fourth most common German surname. The English version is Fisher.
People with the surname A
* Abraham Fischer (1850–1913) South African public official
* Ad ...
. The reaction usually requires a catalyst, such as concentrated sulfuric acid:
: toluenesulfonyl
In organic chemistry, a toluenesulfonyl group (tosyl group, abbreviated Ts or Tos) is a univalent functional group with the chemical formula –. It consists of a tolyl group, –, joined to a sulfonyl group, ––, with the open valence on s ...
chloride in pyridine.
Oxidation
Primary alcohols () can be oxidized either toaldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group ...
s () or to carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
s (). The oxidation of secondary alcohols () normally terminates at the ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo ...
() stage. Tertiary alcohols () are resistant to oxidation.
The direct oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids normally proceeds via the corresponding aldehyde, which is transformed via an ''aldehyde hydrate'' () by reaction with water before it can be further oxidized to the carboxylic acid.
 Reagents useful for the transformation of primary alcohols to aldehydes are normally also suitable for the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones. These include Collins reagent and Dess-Martin periodinane. The direct oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids can be carried out using potassium permanganate or the Jones reagent.
Reagents useful for the transformation of primary alcohols to aldehydes are normally also suitable for the oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones. These include Collins reagent and Dess-Martin periodinane. The direct oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids can be carried out using potassium permanganate or the Jones reagent.
See also
* Enol * Ethanol fuel *Fatty alcohol
Fatty alcohols (or long-chain alcohols) are usually high-molecular-weight, straight-chain primary alcohols, but can also range from as few as 4–6 carbons to as many as 22–26, derived from natural fats and oils. The precise chain length varies ...
* Index of alcohol-related articles
Alcohol is any organic compound in which a hydroxyl functional group (- O H) is bound to a carbon atom, usually connected to other carbon or hydrogen atoms. An important class are the simple acyclic alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2 ...
* List of alcohols
This list is ordered by the number of carbon atoms in an alcohol.
C1
* Methanol
C2
* Ethanol
C3
* 1-Propanol
* Allyl alcohol
* Isopropyl alcohol
C4
* n-Butanol
* Isobutanol
* sec-Butanol
* tert-Butyl alcohol
C5
* 1-Pentanol
* Isoamyl alco ...
* Lucas test
* Polyol
* Rubbing alcohol
* Sugar alcohol
* Transesterification
Notes
Citations
General references
* {{Authority control Antiseptics Functional groups