Aberdare St John The Baptist Church on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aberdare ( ; cy, Aberdâr) is a town in the
 With the ecclesiastical parishes of St Fagan's (Trecynon) and Aberaman carved out of the ancient parish, Aberdare had 12 Anglican churches and one
With the ecclesiastical parishes of St Fagan's (Trecynon) and Aberaman carved out of the ancient parish, Aberdare had 12 Anglican churches and one
 The Aberdare population at the 2001 census was 31,705 (ranked 13th largest in Wales). By 2011 it was 29,748, though the figure includes the surrounding populations of
The Aberdare population at the 2001 census was 31,705 (ranked 13th largest in Wales). By 2011 it was 29,748, though the figure includes the surrounding populations of
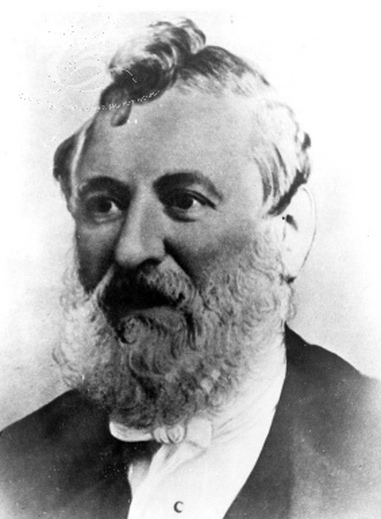 This evidence helped inform the findings of the report which would go on to stigmatise Welsh people as "ignorant", "lazy" and "immoral" and found the reason for this was the continued use of the Welsh language, which it described as "evil". The controversial reports allowed the local non-conformist minister Thomas Price of Calfaria to arrange public meetings, from which he would emerge as a leading critic of the vicar's evidence and, by implication, a defender of both the Welsh language and the morality of the local population, It is still contended that Griffiths was made vicar of
This evidence helped inform the findings of the report which would go on to stigmatise Welsh people as "ignorant", "lazy" and "immoral" and found the reason for this was the continued use of the Welsh language, which it described as "evil". The controversial reports allowed the local non-conformist minister Thomas Price of Calfaria to arrange public meetings, from which he would emerge as a leading critic of the vicar's evidence and, by implication, a defender of both the Welsh language and the morality of the local population, It is still contended that Griffiths was made vicar of
 On 11 May 1919, an extensive fire broke out on Cardiff Street, Aberdare.
With the decline of both iron and coal, Aberdare has become reliant on commercial businesses as a major source of employment. Its industries include cable manufacture, smokeless fuels, and tourism.
On 11 May 1919, an extensive fire broke out on Cardiff Street, Aberdare.
With the decline of both iron and coal, Aberdare has become reliant on commercial businesses as a major source of employment. Its industries include cable manufacture, smokeless fuels, and tourism.

 At the
At the
 Aberdare, during its boom years, was considered a centre of Welsh culture: it hosted the first National Eisteddfod in 1861, with which David Williams (Alaw Goch) was closely associated. The town erected a monument in the local park to commemorate the occasion. A number of local eisteddfodau had long been held in the locality, associated with figures such as William Williams (Carw Coch) The Eisteddfod was again held in Aberdare in 1885, and also in 1956 at Aberdare Park where the Gorsedd standing stones still exist. At the last National Eisteddfod held in Aberdare in 1956 Mathonwy Hughes won the chair. From the mid nineteenth century, Aberdare was an important publishing centre where a large number of books and journals were produced, the majority of which were in the Welsh language. A newspaper entitled
Aberdare, during its boom years, was considered a centre of Welsh culture: it hosted the first National Eisteddfod in 1861, with which David Williams (Alaw Goch) was closely associated. The town erected a monument in the local park to commemorate the occasion. A number of local eisteddfodau had long been held in the locality, associated with figures such as William Williams (Carw Coch) The Eisteddfod was again held in Aberdare in 1885, and also in 1956 at Aberdare Park where the Gorsedd standing stones still exist. At the last National Eisteddfod held in Aberdare in 1956 Mathonwy Hughes won the chair. From the mid nineteenth century, Aberdare was an important publishing centre where a large number of books and journals were produced, the majority of which were in the Welsh language. A newspaper entitled
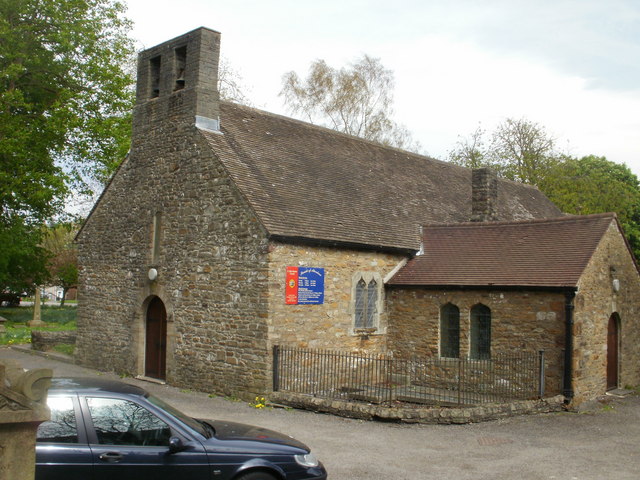 With the development of Aberdare as an industrial centre in the nineteenth century it became increasingly apparent that the ancient church was far too small to service the perceived spiritual needs of an urban community, particularly in view of the rapid growth of nonconformity from the 1830s onwards. Eventually, John Griffith, the rector of Aberdare undertook to raise funds to build a new church, leading to the rapid construction of St Elvan's Church in the town centre between 1851 and 1852. This
With the development of Aberdare as an industrial centre in the nineteenth century it became increasingly apparent that the ancient church was far too small to service the perceived spiritual needs of an urban community, particularly in view of the rapid growth of nonconformity from the 1830s onwards. Eventually, John Griffith, the rector of Aberdare undertook to raise funds to build a new church, leading to the rapid construction of St Elvan's Church in the town centre between 1851 and 1852. This  John Griffith, vicar of Aberdare, who built St Elvan's, transformed the role of the Anglican church in the valley by building a number of other churches, including St Fagan's,
John Griffith, vicar of Aberdare, who built St Elvan's, transformed the role of the Anglican church in the valley by building a number of other churches, including St Fagan's,
 Of the other Independent chapels in the valley Saron, in Davis Street, Aberaman, was used for regular services by a small group of members until 2011. For many years, these were held in a small side-room, and not the chapel itself. The chapel has a large vestry comprising rows of two-way-facing wooden benches and a stage, with a side entrance onto Beddoe Street and back entrance to Lewis Street. Although the building is not in good repair, the interior, including pulpit and balcony seating area (back & sides), was in good order but the chapel eventually closed due to the very small number of members remaining. In February 1999, Saron was made a Grade II Listed Building.
Of the other Independent chapels in the valley Saron, in Davis Street, Aberaman, was used for regular services by a small group of members until 2011. For many years, these were held in a small side-room, and not the chapel itself. The chapel has a large vestry comprising rows of two-way-facing wooden benches and a stage, with a side entrance onto Beddoe Street and back entrance to Lewis Street. Although the building is not in good repair, the interior, including pulpit and balcony seating area (back & sides), was in good order but the chapel eventually closed due to the very small number of members remaining. In February 1999, Saron was made a Grade II Listed Building.
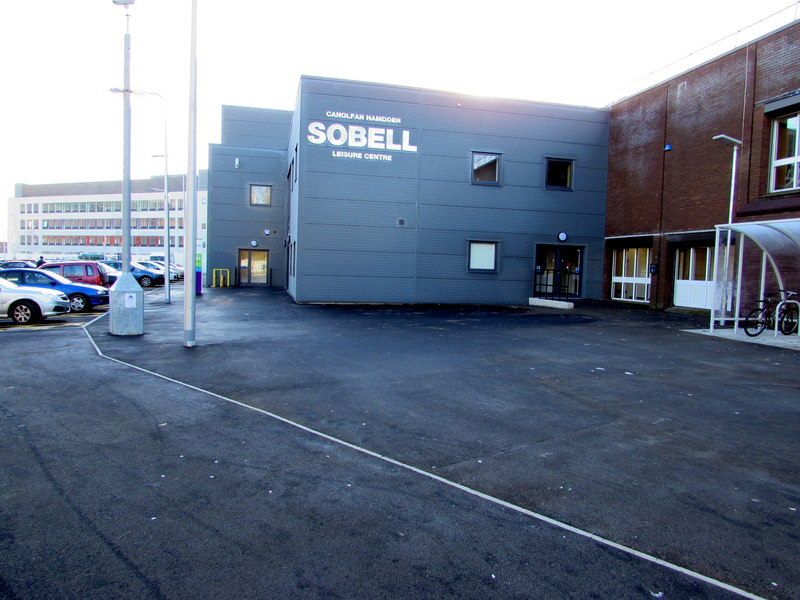 Aberdare is home to '' Yr Ynys'', an historic sports ground which has the distinction of hosting the first Rugby League international, a professional Rugby League team, a football League side and an All Blacks' tour match. Today the Ynys hosts the town's Rugby Union and Cricket teams, as well as the Sobell Leisure Centre and the Ron Jones Athletics Stadium, a 263-seat stadium with
Aberdare is home to '' Yr Ynys'', an historic sports ground which has the distinction of hosting the first Rugby League international, a professional Rugby League team, a football League side and an All Blacks' tour match. Today the Ynys hosts the town's Rugby Union and Cricket teams, as well as the Sobell Leisure Centre and the Ron Jones Athletics Stadium, a 263-seat stadium with
 The Northern Union hired the Ynys on the 1 January 1908 to host what would be the first ever international rugby league match. Played on a near frozen pitch, the match between
The Northern Union hired the Ynys on the 1 January 1908 to host what would be the first ever international rugby league match. Played on a near frozen pitch, the match between
 A rugby club representing Aberdare was recorded as early as 1876, but the modern Aberdare RFC traces its history back to a foundation of 1890. The club had great success in the early twentieth century with local star Dai 'Tarw' Jones captaining the club from 1905 to 1907. Jones gained recognition as a player in club, representative and international games. Most notably, Jones played an important part in the "'' Match of the century''", when Wales defeated the New Zealand All Blacks. In 1907, Jones and the Aberdare club played a pivotal role in the professionalism scandal, with the Welsh Rugby Union permanently suspending the club's entire committee and a number of players (including a lifetime ban for Jones). These events would quickly lead to many of the town's players and fans switching to rugby league, with the first ever rugby league international and the founding of Aberdare RLFC in 1908.
Despite the suspensions, rugby union continued in the town as the club (renamed Aberaman RFC) moved to Aberaman Park. The Ynys Stadium would host its first international rugby union side on 12 December 1935, when the 1935-36 All Blacks played a tour match against a Mid-Districts side. The All Blacks won the match 31–10 in front of a crowd of 6,000.
Aberaman RFC returned to the Ynys in the 1960s. In February 1971, a clubhouse was opened at the old Crown Hotel in Gloucester Street, this was followed by the construction of a grand stand at the Ynys costing £20,000. Following the advent of professionalism in rugby union, the WRU sanctions against Aberdare were no longer applicable. As such, the club took the name Aberdare RUFC once again. Aberdare is also home to Abercwmboi RFC and Hirwaun RFC.
A rugby club representing Aberdare was recorded as early as 1876, but the modern Aberdare RFC traces its history back to a foundation of 1890. The club had great success in the early twentieth century with local star Dai 'Tarw' Jones captaining the club from 1905 to 1907. Jones gained recognition as a player in club, representative and international games. Most notably, Jones played an important part in the "'' Match of the century''", when Wales defeated the New Zealand All Blacks. In 1907, Jones and the Aberdare club played a pivotal role in the professionalism scandal, with the Welsh Rugby Union permanently suspending the club's entire committee and a number of players (including a lifetime ban for Jones). These events would quickly lead to many of the town's players and fans switching to rugby league, with the first ever rugby league international and the founding of Aberdare RLFC in 1908.
Despite the suspensions, rugby union continued in the town as the club (renamed Aberaman RFC) moved to Aberaman Park. The Ynys Stadium would host its first international rugby union side on 12 December 1935, when the 1935-36 All Blacks played a tour match against a Mid-Districts side. The All Blacks won the match 31–10 in front of a crowd of 6,000.
Aberaman RFC returned to the Ynys in the 1960s. In February 1971, a clubhouse was opened at the old Crown Hotel in Gloucester Street, this was followed by the construction of a grand stand at the Ynys costing £20,000. Following the advent of professionalism in rugby union, the WRU sanctions against Aberdare were no longer applicable. As such, the club took the name Aberdare RUFC once again. Aberdare is also home to Abercwmboi RFC and Hirwaun RFC.
 The Ynys stadium was also home to
The Ynys stadium was also home to
BBC website on AberdareWebsite of the Parish of St Fagans Aberdare
www.geograph.co.uk : photos of Aberdare and surrounding area
{{authority control Towns in Rhondda Cynon Taf Former communities of Rhondda Cynon Taf
Cynon Valley
Cynon Valley () is a former coal mining valley in Wales. Cynon Valley lies between Rhondda and the Merthyr Valley and takes its name from the River Cynon. Aberdare is located in the north of the valley and Mountain Ash is in the south of th ...
area of Rhondda Cynon Taf
Rhondda Cynon Taf (; RCT; also spelt as Rhondda Cynon Taff) is a county borough in the south-east of Wales. It consists of five valleys: the Rhondda Fawr, Rhondda Fach, Cynon, Taff (Welsh: ''Taf'') and Ely valleys, plus a number of towns and vill ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, at the confluence of the Rivers Dare (Dâr) and Cynon. Aberdare has a population of 39,550 (mid-2017 estimate). Aberdare is south-west of Merthyr Tydfil, north-west of Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingd ...
and east-north-east of Swansea. During the 19th century it became a thriving industrial settlement, which was also notable for the vitality of its cultural life and as an important publishing centre.
Etymology
The name ''Aberdare'' means "mouth/confluence of the river dare", as the town is located where the Dare river ( cy, Afon Dâr) meets the Cynon ( cy, afon Cynon). While the town's Welsh spelling uses formal conventions, the English spelling of the name reflects the town's pronunciation in the localGwenhwyseg
Gwenhwyseg (also called "Gwentian") is a Welsh dialect of South East Wales. The name derives from an old term for the inhabitants of the area, ''y Gwennwys''.
One of Gwenhwyseg's characteristics is the change in the long a vowel sound of the di ...
dialect of South East Wales.
''Dâr'' is an archaic Welsh word for oaks (the plural of ''derwen''), and the valley was noted for its large and fine oaks as late as the nineteenth century. In ancient times, the river may have been associated with ''Daron'', an ancient Celtic goddess
The gods and goddesses of the pre-Christian Celtic peoples are known from a variety of sources, including ancient places of worship, statues, engravings, cult objects and place or personal names. The ancient Celts appear to have had a pantheon ...
of oak. As such, the town would share an etymology with Aberdaron and the Daron river. As with many Welsh toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s, it is likely that the locality was known by this name long before the development of the town.
History
Early history
There are several cairns and the remains of a circularBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
encampment on the mountain between Aberdare and Merthyr
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after Tydf ...
. This may have led to the mountain itself being named ''Bryn-y-Beddau'' (hill of graves) although other local traditions associate the name with the Battle of Hirwaun Wrgant.
Middle Ages
The area is traditionally given as the scene of the ''battle of Hirwaun Wrgant'', where the allied forces of theNorman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
Robert Fitzhamon
Robert Fitzhamon (died March 1107), or Robert FitzHamon (literally, 'Robert, son of Hamon'), Seigneur de Creully in the Calvados region and Torigny in the Manche region of Normandy, was the first Norman feudal baron of Gloucester and the Nor ...
and Iestyn ap Gwrgant
Iestyn ap Gwrgant (or Jestyn ap Gwrgant) ( eng, Iestyn, son of Gwrgant) (1014 – 1093) was the last ruler of the Welsh kingdom of Morgannwg, which encompassed the counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire.
Lineage
Iestyn ap Gwrgant was the las ...
, the last Welsh prince of Glamorgan defeated Rhys ap Tewdwr, prince of Dyfed
Dyfed () is a preserved county in southwestern Wales. It is a mostly rural area with a coastline on the Irish Sea and the Bristol Channel.
Between 1974 and 1996, Dyfed was also the name of the area's county council and the name remains in use f ...
. The battle is thought to have started at Aberdare, with the areas now known as upper and lower ''Gadlys'' (The battle Court(s)), traditionally given as each armies' headquarters.
The settlement of Aberdare dates from at least this period, with the first known reference being in a monastic chapter of 1203 concerning grazing right on Hirwaun Common. It was originally a small village in an agricultural district, centred around the Church of St John the Baptist, said to date from at least 1189. By the middle of the 15th century, Aberdare contained a water mill in addition to a number of thatched cottages, of which no evidence remains., pp.9–11
Industrial Aberdare
Aberdare grew rapidly in the early nineteenth century through two major industries: first iron, then coal. A branch of theGlamorganshire Canal
The Glamorganshire Canal in South Wales, UK, was begun in 1790. It ran along the valley of the River Taff from Merthyr Tydfil to the sea at Cardiff. The final section of canal was closed in 1951.
History
Construction started in 1790; being ...
(1811) was opened to transport these products; then the railway became the main means of transport to the South Wales coast. From the 1870s onwards, the economy of the town was dominated by the coal mining industry, with only a small tinplate
Tinplate consists of sheets of steel coated with a thin layer of tin to impede rusting. Before the advent of cheap milled steel, the backing metal was wrought iron. While once more widely used, the primary use of tinplate now is the manufacture ...
works. There were also several brickworks and breweries. During the latter half of the 19th century, considerable improvements were made to the town, which became a pleasant place to live, despite the nearby collieries. A postgraduate theological college opened in connection with the Church of England in 1892, but in 1907 it moved to Llandaff
Llandaff (; cy, Llandaf ; from 'church' and ''River Taff, Taf'') is a district, Community (Wales), community and coterminous electoral ward in the north of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It was incorporated into the city in 1922. It is the seat of ...
.
 With the ecclesiastical parishes of St Fagan's (Trecynon) and Aberaman carved out of the ancient parish, Aberdare had 12 Anglican churches and one
With the ecclesiastical parishes of St Fagan's (Trecynon) and Aberaman carved out of the ancient parish, Aberdare had 12 Anglican churches and one Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
church, built in 1866 in Monk Street near the site of a cell attached to Penrhys monastery; and at one time there were over 50 Nonconformist chapels (including those in surrounding settlements such as Cwmaman
Cwmaman () is a former coal mining village near Aberdare, Wales. The name is Welsh for "Aman Valley" and the River Aman flows through the village. Cwmaman literally means: valley of the river Aman. It lies in the valley of several mountains. ...
and Llwydcoed). The services in the majority of the chapels were in Welsh. Most of these chapels have now closed, with many converted to other uses. The urban district includes what were once the separate villages of Aberaman
Aberaman is a village near Aberdare in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, south Wales. It was heavily dependent on the coal industry and the population, as a result, grew rapidly in the late nineteenth century. Most of the industry has now ...
, Abernant, Cwmaman
Cwmaman () is a former coal mining village near Aberdare, Wales. The name is Welsh for "Aman Valley" and the River Aman flows through the village. Cwmaman literally means: valley of the river Aman. It lies in the valley of several mountains. ...
, Cwmbach
Cwmbach is a village and Community (Wales), community (and electoral ward) near Aberdare, in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. Cwmbach means 'Little Valley' in Welsh language, Welsh (Cwm = valley, Bach = little). Cwmbach has a popul ...
, Cwmdare, Llwydcoed, Penywaun
Penywaun (also in ) is a community, electoral ward and north-western suburb of Aberdare in the Cynon Valley within the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. At the 2011 census, the population of the ward was registered as 3,063.
Etymolog ...
and Trecynon
Trecynon is a village near Aberdare situated in the Cynon Valley, in Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. It dates from the early nineteenth century and developed as a result of the opening of the Aberdare Ironworks at Llwydcoed in 1800.
Etymology
The s ...
.
Population growth
In 1801, the population of the parish of Aberdare was just 1,486, but the early 19th century saw rapid industrial growth, first through the ironworks, and later through the iron andsteam coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
industries. By the 1840s the parish population was increasing by 1,000 people every year, almost exclusively migrant workers from west Wales, which was suffering from an agricultural depression. This growth was increasingly concentrated in the previously agricultural areas of Blaengwawr and Cefnpennar to the south of the town. The population of the Aberdare District (centred on the town) was 9,322 in 1841, 18,774 in 1851, and 37,487 in 1861.
Despite a small decline in the 1870s, population levels continued to increase, with the first decade of the 20th century seeing a notably sharp increase, largely as a result of the steam coal trade, reaching 53,779 in 1911. The population has since declined owing to the loss of most of the heavy industry.
 The Aberdare population at the 2001 census was 31,705 (ranked 13th largest in Wales). By 2011 it was 29,748, though the figure includes the surrounding populations of
The Aberdare population at the 2001 census was 31,705 (ranked 13th largest in Wales). By 2011 it was 29,748, though the figure includes the surrounding populations of Aberaman
Aberaman is a village near Aberdare in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, south Wales. It was heavily dependent on the coal industry and the population, as a result, grew rapidly in the late nineteenth century. Most of the industry has now ...
, Abercwmboi, Cwmbach
Cwmbach is a village and Community (Wales), community (and electoral ward) near Aberdare, in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. Cwmbach means 'Little Valley' in Welsh language, Welsh (Cwm = valley, Bach = little). Cwmbach has a popul ...
and Llwydcoed.
Language
Welsh was the prominent language until the mid 20th century and Aberdare was an important centre of Welsh language publishing. A large proportion of the early migrant population were Welsh speaking, and in 1851 only ten per cent of the population had been born outside of Wales. In his controversial evidence to the 1847 Inquiry into the State of Education in Wales - the report of which is known in Wales as the ''Brad y Llyfrau Gleision'' (''Treason of the Blue Books''), the Anglican vicar of Aberdare, John Griffith, stated that the English language was "generally understood" and referred to the arrival of people from anglicised areas such as Radnorshire and south Pembrokeshire. Griffith also made allegations about the Welsh speaking population and what he considered to be the degraded character of the women of Aberdare, alleging sexual promiscuity was an accepted social convention, that drunkenness and improvidence amongst the miners was common and attacking what he saw as exaggerated emotion in the religious practices of the Nonconformists.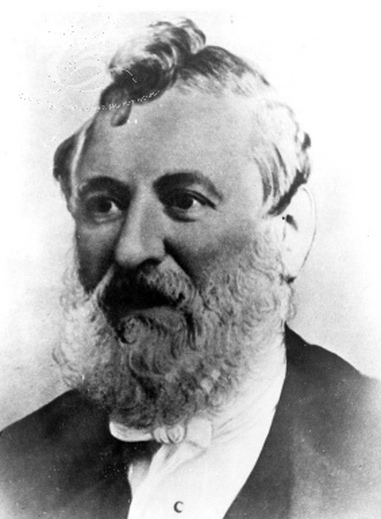 This evidence helped inform the findings of the report which would go on to stigmatise Welsh people as "ignorant", "lazy" and "immoral" and found the reason for this was the continued use of the Welsh language, which it described as "evil". The controversial reports allowed the local non-conformist minister Thomas Price of Calfaria to arrange public meetings, from which he would emerge as a leading critic of the vicar's evidence and, by implication, a defender of both the Welsh language and the morality of the local population, It is still contended that Griffiths was made vicar of
This evidence helped inform the findings of the report which would go on to stigmatise Welsh people as "ignorant", "lazy" and "immoral" and found the reason for this was the continued use of the Welsh language, which it described as "evil". The controversial reports allowed the local non-conformist minister Thomas Price of Calfaria to arrange public meetings, from which he would emerge as a leading critic of the vicar's evidence and, by implication, a defender of both the Welsh language and the morality of the local population, It is still contended that Griffiths was made vicar of Merthyr
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after Tydf ...
in the neighbouring valley to escape local anger, even though it was over ten years before he left Aberdare. The reports and subsequent defence would maintain the perceptions of Aberdare, the Cynon Valley
Cynon Valley () is a former coal mining valley in Wales. Cynon Valley lies between Rhondda and the Merthyr Valley and takes its name from the River Cynon. Aberdare is located in the north of the valley and Mountain Ash is in the south of th ...
and even the wider area as proudly nonconformist and defiantly Welsh speaking throughout its industrialised history.
By 1901, the census recorded that 71.5% of the population of Aberdare Urban District spoke Welsh, but this fell to 65.2% in 1911., p.229 The 1911 data shows that Welsh was more widely spoken among the older generation compared to the young, and amongst women compared to men. A shift in language was expedited with the loss of men during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the resulting economic turmoil. English gradually began to replace Welsh as the community language, as shown by the decline of the Welsh language press in the town. This pattern continued after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
despite the advent of Welsh medium education. Ysgol Gymraeg Aberdâr, the Welsh-medium primary school, was established in the 1950s with Idwal Rees as head teacher.
According to the 2011 Census, 11.6% of Aberdare residents aged three years and over can speak Welsh, with 24.8% of 3- to 15-year-olds stating that they can speak it.
Industry
Iron Industry
Ironworks were established at Llwydcoed and Abernant in 1799 and 1800 respectively, followed by others at Gadlys andAberaman
Aberaman is a village near Aberdare in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, south Wales. It was heavily dependent on the coal industry and the population, as a result, grew rapidly in the late nineteenth century. Most of the industry has now ...
in 1827 and 1847. The iron industry began to expand in a significant way around 1818 when the Crawshay family of Merthyr purchased the Hirwaun ironworks and place them under independent management. In the following year, Rowland Fothergill
Rowland Fothergill (1794- 19 September 1871) was an ironmaster in South Wales, whose main industrial interests lay in the Aberdare district. He was high sheriff of Glamorgan in 1850.
He was the son of Richard Fothergill.
Prior to acquiring prop ...
took over the ironworks at Abernant and a few years later did the same at Llwydcoed. Both concerns later fell into the hands of his nephew Richard Fothergill. The Gadlys Ironworks was established in 1827 by Matthew Wayne, who had previously managed the Cyfarthfa
Cyfarthfa is a community and electoral ward in the west of the town of Merthyr Tydfil in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales.
Community
Cyfarthfa mainly consists of the settlements of Gellideg and Heolgerrig and Rhyd-y-car area just west of Mer ...
ironworks at Merthyr. The Gadlys works, now considered an important archaeological site, originally comprised four blast furnaces, inner forges, rowing mills and puddling furnaces. The development of these works provided impetus to the growth of Aberdare as a nucleated town. The iron industry was gradually superseded by coal and all the five iron works had closed by 1875, as the local supply of iron ore was inadequate to meet the ever-increasing demand created by the invention of steel, and as a result the importing of ore proved more profitable.
Coal industry
The iron industry had a relatively small impact upon the economy of Aberdare and in 1831 only 1.2% of the population was employed in manufacturing, as opposed to 19.8% in neighbouring Merthyr Tydfil. In the early years of Aberdare's development, most of the coal worked in the parish was coking coal, and was consumed locally, chiefly in the ironworks. Although the Gadlys works was small in comparison with the other ironworks it became significant as the Waynes also became involved in the production of sale coal. In 1836, this activity led to the exploitation of the "Four-foot Seam" of high- calorific valuesteam coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
began, and pits were sunk in rapid succession.
In 1840, Thomas Powell sank a pit at Cwmbach
Cwmbach is a village and Community (Wales), community (and electoral ward) near Aberdare, in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. Cwmbach means 'Little Valley' in Welsh language, Welsh (Cwm = valley, Bach = little). Cwmbach has a popul ...
, and during the next few years he opened another four pits. In the next few years, other local entrepreneurs now became involved in the expansion of the coal trade, including David Williams at Ynysgynon and David Davis at Blaengwawr, as well as the latter's son David Davis, Maesyffynnon. They were joined by newcomers such as Crawshay Bailey
Crawshay Bailey (1789 – 9 January 1872) was an English industrialist who became one of the great iron-masters of Wales.
Early life
Bailey was born in 1789 in Great Wenham, Suffolk, the son of John Bailey, of Wakefield and his wife Susannah ...
at Aberaman and, in due course, George Elliot in the lower part of the valley. This coal was valuable for steam railways and steam ship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
s, and an export trade began, via the Taff Vale Railway
The Taff Vale Railway (TVR) was a standard gauge railway in South Wales, built by the Taff Vale Railway Company to serve the iron and coal industries around Merthyr Tydfil and to connect them with docks in Cardiff. It was opened in st ...
and the port of Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingd ...
. The population of the parish rose from 6,471 in 1841 to 14,999 in 1851 and 32,299 in 1861 and John Davies described it as "the most dynamic place in Wales". In 1851, the Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
decided to use Welsh steam coal in ships of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
, and this decision boosted the reputation of Aberdare's product and launched a huge international export market.Davies, ''op cit'', p 400 Coal mined in Aberdare parish rose from in 1844 to in 1850, and the coal trade, which after 1875 was the chief support of the town, soon reached huge dimensions.
The growth of the coal trade inevitably led to a number of industrial disputes, some of which were local and others which affected the wider coalfield. Trade unionism began to appear in the Aberdare Valley at intervals from the 1830s onwards but the first significant manifestation occurred during the Aberdare Strike of 1857–8. The dispute was initiated by the depression in trade which followed the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
and saw the local coal owners successfully impose a reduction in wages. The dispute did, however, witness an early manifestation of mass trade unionism amongst the miners of the valley and although unsuccessful the dispute saw the emergence of a stronger sense of solidarity amongst the miners.
Steam coal was subsequently found in the Rhondda
Rhondda , or the Rhondda Valley ( cy, Cwm Rhondda ), is a former coal mining, coalmining area in South Wales, historically in the county of Glamorgan. It takes its name from the River Rhondda, and embraces two valleys – the larger Rhondda Fa ...
and further west, but many of the great companies of the Welsh coal industry's Gilded Age started operation in Aberdare and the lower Cynon Valley, including those of
Samuel Thomas, David Davies and Sons, Nixon's Navigation and Powell Duffryn
Powell may refer to:
People
* Powell (surname)
* Powell (given name)
* Powell baronets, several baronetcies
*Colonel Powell (disambiguation), several military officers
*General Powell (disambiguation), several military leaders
* Governor Powell ...
.
During the early years of the twentieth century, the Aberdare valley became the focus of increased militancy among the mining workforce and an unofficial strike by 11,000 miners in the district from 20 October 1910 unyil 2 February 1911 attracted much attention at the time, although it was ultimately overshadowed by the Cambrian dispute in the neighbouring Rhondda valley which became synonymous with the so-called Tonypandy Riots.
In common with the rest of the South Wales coalfield, Aberdare's coal industry commenced a long decline after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, and the last two deep mines still in operation in the 1960s were the small Aberaman and Fforchaman collieries, which closed in 1962 and 1965 respectively.
 On 11 May 1919, an extensive fire broke out on Cardiff Street, Aberdare.
With the decline of both iron and coal, Aberdare has become reliant on commercial businesses as a major source of employment. Its industries include cable manufacture, smokeless fuels, and tourism.
On 11 May 1919, an extensive fire broke out on Cardiff Street, Aberdare.
With the decline of both iron and coal, Aberdare has become reliant on commercial businesses as a major source of employment. Its industries include cable manufacture, smokeless fuels, and tourism.
Government
As a small village in the upland valleys of Glamorgan, Aberdare did not play any significant part in political life until its development as an industrial settlement. It was part of the lordship of Miskin, and the ancient office of High Constable continued in ceremonial form until relatively recent times.Parliamentary elections
In 1832, Aberdare was removed from the Glamorgan county constituency and became part of the parliamentary borough (constituency) of Merthyr Tydfil. For much of the nineteenth century, the representation was initially controlled by the ironmasters of Merthyr, notably the Guest family. From 1852 until 1868 the seat was held by Henry Austen Bruce whose main industrial interests lay in the Aberdare valley. Bruce was a Liberal but was viewed with suspicion by the more radical faction which became increasingly influential within Welsh Liberalism in the 1860s. The radicals supported such policies as the disestablishment of the Church of England and were closely allied to theLiberation Society
The Liberation Society was an organisation in Victorian England that campaigned for disestablishment of the Church of England. It was founded in 1844 by Edward Miall as the British Anti-State Church Association and was renamed in 1853 as the Soci ...
.
1868 general election
Nonconformist ministers played a prominent role in this new politics and, at Aberdare, they found an effective spokesman in the Rev Thomas Price minister of Calfaria, Aberdare. Following the granting of a second parliamentary seat to the borough of Merthyr Tydfil in 1867, the Liberals of Aberdare sought to ensure that a candidate from their part of the constituency was returned alongside the sitting member, Henry Austen Bruce. Their choice fell upon Richard Fothergill, owner of the ironworks at Abernant, who was enthusiastically supported by the Rev Thomas Price. Shortly before the election, however, Henry Richard intervened as a radical Liberal candidate, invited by the radicals of Merthyr. To many people's surprise, Price was lukewarm about his candidature and continued to support Fothergill. Ultimately, Henry Richard won a celebrated victory with Fothergill in second place and Bruce losing his seat. Richard thus became one of the-first radical MPs from Wales.1874–1914
At the 1874 General Election, both Richard and Fothergill were again returned, although the former was criticised for his apparent lack of sympathy towards the miners during the industrial disputes of the early 1870s. This led to the emergence of Thomas Halliday as the first labour or working-class candidate to contest a Welsh constituency. Although he polled well, Halliday fell short of being elected. For the remainder of the nineteenth century, the constituency was represented by industrialists, most notably David Alfred Thomas. In 1900, however, Thomas was joined byKeir Hardie
James Keir Hardie (15 August 185626 September 1915) was a Scottish trade unionist and politician. He was a founder of the Labour Party, and served as its first parliamentary leader from 1906 to 1908.
Hardie was born in Newhouse, Lanarkshire. ...
, the ILP
''ilp.'' () is the debut album by record producer and musician Kwes. It was released on 14 October 2013 on Warp Records. The release is a follow up to his second EP release '' Meantime''. The record's title ''ilp'' refers literally to the record ...
candidate, who became the first labour representative to be returned for a Welsh constituency independent of the Liberal Party.
Twentieth century
The Aberdare constituency came into being at the 1918 election. The first representative wasCharles Butt Stanton
Charles Butt Stanton (7 April 1873 – 6 December 1946) was a British politician, who served as an Member of Parliament (MP) from 1915 to 1922. He entered Parliament by winning one of the two seats for Merthyr Tydfil at a by-election on 25 No ...
who had been elected at a by-election following Hardie's death in 1915. However, in 1922, Stanton was defeated by a Labour candidate and the party has held the seat ever since. The only significant challenge came from Plaid Cymru
Plaid Cymru ( ; ; officially Plaid Cymru – the Party of Wales, often referred to simply as Plaid) is a centre-left to left-wing, Welsh nationalist political party in Wales, committed to Welsh independence from the United Kingdom.
Plaid wa ...
at the 1970 and February 1974 General Elections but this performance has not since been repeated. From 1984 until 2019 the parliamentary seat, now known as Cynon Valley
Cynon Valley () is a former coal mining valley in Wales. Cynon Valley lies between Rhondda and the Merthyr Valley and takes its name from the River Cynon. Aberdare is located in the north of the valley and Mountain Ash is in the south of th ...
was held by Ann Clwyd of Labour.

Local government
Aberdare was an ancient parish within Glamorgan. Until the mid-nineteenth century the local government of Aberdare and its locality remained in the hands of traditional structures such as the parishvestry
A vestry was a committee for the local secular and ecclesiastical government for a parish in England, Wales and some English colonies which originally met in the vestry or sacristy of the parish church, and consequently became known colloquiall ...
and the High Constable, who was chosen on an annual basis. However, the rapid industrial development of the parish resulted in the situation where these traditional bodies could not cope with the realities of an urbanised, industrial community which had developed without any planning or facilities. During the early decades of the century the iron masters gradually imposed their influence over local affairs and this remained the case following the formation of the Merthyr Board of Guardians
Boards of guardians were ''ad hoc'' authorities that administered Poor Law in the United Kingdom from 1835 to 1930.
England and Wales
Boards of guardians were created by the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834, replacing the parish overseers of the po ...
in 1836. During the 1850s and early 1860s, however, as coal displaced iron as the main industry in the valley, the ironmasters were displaced as the dominant group in local government and administration by an alliance between mostly indigenous coal owners, shopkeepers and tradesmen, professional men and dissenting ministers. A central figure in this development was the Rev Thomas Price. The growth of this alliance was rooted in the reaction to the 1847 Education Reports and the subsequent efforts to establish a British School at Aberdare.
In the 1840s there were no adequate sanitary facilities or water supply and life expectancy was low. Outbreaks of cholera and typhus were commonplace. Against this background, Thomas Webster Rammell prepared a report for the General Board of Health on the sanitary condition of the parish, which recommended that a local board of health
Local boards or local boards of health were local authorities in urban areas of England and Wales from 1848 to 1894. They were formed in response to cholera epidemics and were given powers to control sewers, clean the streets, regulate environmenta ...
be established. The whole parish of Aberdare was formally declared a local board district on 31 July 1854, to be governed by the Aberdare Local Board of Health
Aberdare Local Board of Health was established in 1854 in response to the 1848 Public Health Act, and a report on the sanitary condition of the town conducted by Thomas Webster Rammell. It was eventually replaced in 1894 by Aberdare Urban Distric ...
. Its first chairman was Richard Fothergill and the members included David Davis, Blaengwawr, David Williams (''Alaw Goch''), Rees Hopkin Rhys and the Rev. Thomas Price. It was followed by the Aberdare School Board in 1871.
By 1889, the Local Board of Health had initiated a number of developments which included the purchase of local reservoirs from the Aberdare Waterworks Company for £97,000, a sewerage scheme costing £35,000, as well as the opening of Aberdare Public Park and a local fever hospital. The lack of a Free Library, however, remained a concern.
Later, the formation of the Glamorgan County Council
Glamorgan County Council was established in 1889 together with the administrative county of Glamorganshire under the Local Government Act 1888. The first elections to the council were held in January 1889. The council was abolished under the Local ...
(upon which Aberdare had five elected members) in 1889, followed by the Aberdare Urban District Council
Aberdare Urban District Council was a local authority in Aberdare, Wales.
History
It was created in 1894 as a result of the 1894 Local Government of England and Wales Act and the 1894 Aberdare Urban District Council election saw the election of ...
, which replaced the Local Board in 1894, transformed the local politics of the Aberdare valley.
 At the
At the 1889 Glamorgan County Council Elections
The first election to the Glamorgan County Council was held on 17 January 1889. Results were announced over several days. They were followed by the 1892 election. The authority, by far the largest county in Wales in terms of population, was est ...
most of the elected representatives were coalowners and industrialists and the only exception in the earlier period was the miners' agent David Morgan (Dai o'r Nant), elected in 1892 as a labour representative. From the early 1900s, however, Labour candidates began to gain ground and dominated local government from the 1920s onwards. The same pattern was seen on the Aberdare UDC.
Aberdare Urban District was abolished in 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972. The area became part of the borough of Cynon Valley
Cynon Valley () is a former coal mining valley in Wales. Cynon Valley lies between Rhondda and the Merthyr Valley and takes its name from the River Cynon. Aberdare is located in the north of the valley and Mountain Ash is in the south of th ...
within the new county of Mid Glamorgan
, Government= Mid Glamorgan County Council
, Status= Non-metropolitan county (1974–1996) Preserved county (1996–)
, Start= 1974
, End= 1996
, Arms= ''Coat of arms of Mid ...
. The area of the former urban district was made a community
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, ...
, later being subdivided in 1982 into five communities: Aberaman
Aberaman is a village near Aberdare in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, south Wales. It was heavily dependent on the coal industry and the population, as a result, grew rapidly in the late nineteenth century. Most of the industry has now ...
, Cwmbach
Cwmbach is a village and Community (Wales), community (and electoral ward) near Aberdare, in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. Cwmbach means 'Little Valley' in Welsh language, Welsh (Cwm = valley, Bach = little). Cwmbach has a popul ...
, Llwydcoed, Penywaun
Penywaun (also in ) is a community, electoral ward and north-western suburb of Aberdare in the Cynon Valley within the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. At the 2011 census, the population of the ward was registered as 3,063.
Etymolog ...
, and a smaller Aberdare community. The Aberdare community was further divided in 2017 into two communities called Aberdare East and Aberdare West. Aberdare East includes Aberdare town centre and the village of Abernant. Aberdare West includes Cwmdare, Cwm Sian and Trecynon
Trecynon is a village near Aberdare situated in the Cynon Valley, in Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. It dates from the early nineteenth century and developed as a result of the opening of the Aberdare Ironworks at Llwydcoed in 1800.
Etymology
The s ...
. No community council exists for either of the Aberdare communities.
Cynon Valley Borough Council and Mid Glamorgan County Council
Mid Glamorgan County Council () was the upper-tier authority for the Welsh county of Mid Glamorgan between its creation in 1974 and its abolition in 1996.
History
Local government in England and Wales was reorganised in 1974 under the Local Gover ...
were both abolished in 1996, since when Aberdare has been governed by Rhondda Cynon Taf County Borough Council. The town lies mainly in the Aberdare East ward, represented by two county councillors. Nearby Cwmdare, Llwydcoed and Trecynon
Trecynon is a village near Aberdare situated in the Cynon Valley, in Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. It dates from the early nineteenth century and developed as a result of the opening of the Aberdare Ironworks at Llwydcoed in 1800.
Etymology
The s ...
are represented by the Aberdare West/Llwydcoed ward. Both wards have been represented by the Labour Party since 2012.
Culture
 Aberdare, during its boom years, was considered a centre of Welsh culture: it hosted the first National Eisteddfod in 1861, with which David Williams (Alaw Goch) was closely associated. The town erected a monument in the local park to commemorate the occasion. A number of local eisteddfodau had long been held in the locality, associated with figures such as William Williams (Carw Coch) The Eisteddfod was again held in Aberdare in 1885, and also in 1956 at Aberdare Park where the Gorsedd standing stones still exist. At the last National Eisteddfod held in Aberdare in 1956 Mathonwy Hughes won the chair. From the mid nineteenth century, Aberdare was an important publishing centre where a large number of books and journals were produced, the majority of which were in the Welsh language. A newspaper entitled
Aberdare, during its boom years, was considered a centre of Welsh culture: it hosted the first National Eisteddfod in 1861, with which David Williams (Alaw Goch) was closely associated. The town erected a monument in the local park to commemorate the occasion. A number of local eisteddfodau had long been held in the locality, associated with figures such as William Williams (Carw Coch) The Eisteddfod was again held in Aberdare in 1885, and also in 1956 at Aberdare Park where the Gorsedd standing stones still exist. At the last National Eisteddfod held in Aberdare in 1956 Mathonwy Hughes won the chair. From the mid nineteenth century, Aberdare was an important publishing centre where a large number of books and journals were produced, the majority of which were in the Welsh language. A newspaper entitled Y Gwladgarwr
''Y Gwladgarwr'' ("The Patriot") was a liberal Welsh language newspaper, established in 1858, published weekly in Aberdare by Abraham Mason, and distributed around the districts of South Wales. Devoted to Welsh literature, the paper provided poet ...
(the Patriot) was published at Aberdare from 1856 until 1882 and was circulated widely throughout the South Wales valleys. From 1875 a more successful newspaper, Tarian y Gweithiwr (the Workman's Shield) was published at Aberdare by John Mills. Y Darian, as it was known, strongly supported the trade union movements among the miners and ironworkers of the valleys. The miners' leader, William Abraham, derived support from the newspaper, which was also aligned with radical nonconformist liberalism. The rise of the political labour movement and the subsequent decline of the Welsh language in the valleys, ultimately led to its decline and closure in 1934.
The Coliseum Theatre
The London Coliseum (also known as the Coliseum Theatre) is a theatre in St Martin's Lane, Westminster, built as one of London's largest and most luxurious "family" variety theatres. Opened on 24 December 1904 as the London Coliseum Theatre ...
is Aberdare's main arts venue, containing a 600-seat auditorium
An auditorium is a room built to enable an audience to hear and watch performances. For movie theatres, the number of auditoria (or auditoriums) is expressed as the number of screens. Auditoria can be found in entertainment venues, community ...
and cinema. It is situated in nearby Trecynon
Trecynon is a village near Aberdare situated in the Cynon Valley, in Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. It dates from the early nineteenth century and developed as a result of the opening of the Aberdare Ironworks at Llwydcoed in 1800.
Etymology
The s ...
and was built in 1938 using miners' subscriptions.
The Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
poet Alun Lewis, was born near Aberdare in the village Cwmaman
Cwmaman () is a former coal mining village near Aberdare, Wales. The name is Welsh for "Aman Valley" and the River Aman flows through the village. Cwmaman literally means: valley of the river Aman. It lies in the valley of several mountains. ...
and there is a plaque commemorating him, including a quotation from his poem ''The Mountain over Aberdare''.
The founding members of the rock band Stereophonics originated from the nearby village of Cwmaman
Cwmaman () is a former coal mining village near Aberdare, Wales. The name is Welsh for "Aman Valley" and the River Aman flows through the village. Cwmaman literally means: valley of the river Aman. It lies in the valley of several mountains. ...
. It is also the hometown of guitarist Mark Parry of Vancouver rock band The Manvils
The Manvils are a Canadian rock band from Vancouver. The band consists of the singer, songwriter and guitarist Mikey Manville, bass guitarist Dave Fenton and drummer Jay Koenderman.
The Manvils have appeared on stage with Stereophonics, Suici ...
. Famed anarchist-punk band Crass
Crass were an English art collective and punk rock band formed in Epping, Essex in 1977, who promoted anarchism as a political ideology, a lifestylism, way of life, and a resistance movement. Crass popularised the anarcho-punk movement of the ...
played their last live show for striking miners in Aberdare during the UK miners' strike.
Griffith Rhys Jones − or Caradog as he was commonly known − was the Conductor of the famous 'Côr Mawr' of some 460 voices (the South Wales Choral Union), which twice won first prize at Crystal Palace choral competitions in London in the 1870s. He is depicted in the town's most prominent statue by sculptor Goscombe John
Sir William Goscombe John (21 February 1860 – 15 December 1952) was a prolific Welsh sculptor known for his many public memorials. As a sculptor, John developed a distinctive style of his own while respecting classical traditions and forms of ...
, unveiled on Victoria Square in 1920.
Aberdare was culturally twinned with the German town of Ravensburg.
Religion
Anglican Church
The original parish church ofSt John the Baptist
John the Baptist or , , or , ;Wetterau, Bruce. ''World history''. New York: Henry Holt and Company. 1994. syc, ܝܘܿܚܲܢܵܢ ܡܲܥܡܕ݂ܵܢܵܐ, Yoḥanān Maʿmḏānā; he, יוחנן המטביל, Yohanān HaMatbil; la, Ioannes Bapti ...
was originally built in 1189. Some of its original architecture is still intact.
 With the development of Aberdare as an industrial centre in the nineteenth century it became increasingly apparent that the ancient church was far too small to service the perceived spiritual needs of an urban community, particularly in view of the rapid growth of nonconformity from the 1830s onwards. Eventually, John Griffith, the rector of Aberdare undertook to raise funds to build a new church, leading to the rapid construction of St Elvan's Church in the town centre between 1851 and 1852. This
With the development of Aberdare as an industrial centre in the nineteenth century it became increasingly apparent that the ancient church was far too small to service the perceived spiritual needs of an urban community, particularly in view of the rapid growth of nonconformity from the 1830s onwards. Eventually, John Griffith, the rector of Aberdare undertook to raise funds to build a new church, leading to the rapid construction of St Elvan's Church in the town centre between 1851 and 1852. This Church in Wales
The Church in Wales ( cy, Yr Eglwys yng Nghymru) is an Anglican church in Wales, composed of six dioceses.
The Archbishop of Wales does not have a fixed archiepiscopal see, but serves concurrently as one of the six diocesan bishops. The p ...
church still stands the heart of the parish of Aberdare and has had extensive work since its erection.Newman (1995), p.133 The church has a modern electrical, two-manual and pedal board pipe organ, that is still used in services.
 John Griffith, vicar of Aberdare, who built St Elvan's, transformed the role of the Anglican church in the valley by building a number of other churches, including St Fagan's,
John Griffith, vicar of Aberdare, who built St Elvan's, transformed the role of the Anglican church in the valley by building a number of other churches, including St Fagan's, Trecynon
Trecynon is a village near Aberdare situated in the Cynon Valley, in Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. It dates from the early nineteenth century and developed as a result of the opening of the Aberdare Ironworks at Llwydcoed in 1800.
Etymology
The s ...
. Other churches in the parish are St Luke's ( Cwmdare), St James's ( Llwydcoed) and St Matthew's Church (1891) ( Abernant).Newman (1995), p. 134
In the parish of Aberaman and Cwmaman is St Margaret's Church, with an old, but beautiful, pipe organ with two manuals and a pedal board. Also in this parish is St Joseph's Church, Cwmaman. St Joseph's has recently undergone much recreational work, almost converting the church into a community centre, surrounded by a beautiful, floral garden and leading to the Cwmaman Sculpture Trail. However, regular church services still take place. Here, there is a two-manual and pedal board electric organ, with speakers at the front and sides of the church.
In 1910 there were 34 Anglican churches in the Urban District of Aberdare. A survey of the attendance at places of worship on a particular Sunday in that year recorded that 17.8% of worshippers attended church services, with the remainder attending nonconformist chapels.
Nonconformity
The Aberdare Valley was a stronghold of Nonconformity from the mid-nineteenth century until the inter-war years. In the aftermath of the 1847 Education Reports nonconformists became increasingly active in the political and educational life of Wales and in few places was this as prevalent as at Aberdare. The leading figure was Thomas Price, minister of Calfaria, Aberdare. Aberdare was a major centre of the 1904–05 Religious Revival, which had begun atLoughor
Loughor () ( cy, Casllwchwr) is a Welsh town in the City and County of Swansea, within the Historic counties of Wales, historic county boundaries of Glamorgan, Wales. It lies on the estuary of the River Loughor. The town has a community (Wales), ...
near Swansea. The revival aroused alarm among ministers for the revolutionary, even anarchistic, impact it had upon chapel congregations and denominational organisation. In particular, it was seen as drawing attention away from pulpit preaching and the role of the minister. The local newspaper, the ''Aberdare Leader'', regarded the revival with suspicion from the outset, objecting to the 'abnormal heat' which it engendered. Trecynon
Trecynon is a village near Aberdare situated in the Cynon Valley, in Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. It dates from the early nineteenth century and developed as a result of the opening of the Aberdare Ironworks at Llwydcoed in 1800.
Etymology
The s ...
was particularly affected by the revival, and the meetings held there were sais to have aroused more emotion and excitement than the more restrained meetings in Aberdare itself. The impact of the revival was significant in the short term, but in the longer term was fairly transient.
Once the immediate impact of the revival had faded, it was clear from the early twentieth century that there was a gradual decline in the influence of the chapels. This can be explained by several factors, including the rise of socialism and the process of linguistic change which saw the younger generation increasingly turn to the English language. There were also theological controversies such as that over the New Theology propounded by R.J. Campbell.
Of the many chapels, few are still used for their original purpose and a number of closed since the turn of the millennium. Many have been converted for housing or other purposes (including one at Robertstown which has become a mosque), and others demolished. Among the notable chapels were Calfaria, Aberdare and Seion, Cwmaman (Baptist); Saron, Aberaman and Siloa, Aberdare
Siloa Chapel was the largest of the Welsh Independent, or Congregationalist, chapels in Aberdare. Services are held in the Welsh language. Established in 1844, Siloa is one of the few Welsh-language chapels in the locality to remain open today. ...
(Independent); and Bethania, Aberdare (Calvinistic Methodist).
Independents
The earliest Welsh Independent, or Congregationalist chapel in the Aberdare area was Ebenezer, trecynon, although meetings had been held from the latter years of the eighteenth century in dwelling houses in the locality, for example at Hirwaun. During the nineteenth century, the Independents showed the biggest increases in terms of places of worship: from two in 1837 to twenty-five (four of them being English causes), in 1897.Rees, Chapels in the Valley, p.169 By 1910 there were 35 Independent chapels, with a total membership of 8,612. Siloa Chapel was the largest of the Independent chapels in Aberdare and is one of the few that remain open today, having been 're-established' as a Welsh language chapel. The Independent ministers of nineteenth-century Aberdare included some powerful personalities but none had the kind of wider social authority which Thomas Price enjoyed amongst the Baptists. Of the other Independent chapels in the valley Saron, in Davis Street, Aberaman, was used for regular services by a small group of members until 2011. For many years, these were held in a small side-room, and not the chapel itself. The chapel has a large vestry comprising rows of two-way-facing wooden benches and a stage, with a side entrance onto Beddoe Street and back entrance to Lewis Street. Although the building is not in good repair, the interior, including pulpit and balcony seating area (back & sides), was in good order but the chapel eventually closed due to the very small number of members remaining. In February 1999, Saron was made a Grade II Listed Building.
Of the other Independent chapels in the valley Saron, in Davis Street, Aberaman, was used for regular services by a small group of members until 2011. For many years, these were held in a small side-room, and not the chapel itself. The chapel has a large vestry comprising rows of two-way-facing wooden benches and a stage, with a side entrance onto Beddoe Street and back entrance to Lewis Street. Although the building is not in good repair, the interior, including pulpit and balcony seating area (back & sides), was in good order but the chapel eventually closed due to the very small number of members remaining. In February 1999, Saron was made a Grade II Listed Building.
Baptists
The Baptists were the most influential of the nonconformist denominations in Aberdare and their development was led by the Rev. Thomas Price who came to Aberdare in the early 1840s as minister of Calfaria Chapel.Jones, Explorations and Explanations, p.197−8 In 1837 the Baptists had three chapels, but in 1897 there were twenty, seventeen of them being Welsh. By 1910 the number of chapels had increased to 30, with a total membership of 7,422. Most of these Baptist chapels were established under the influence of Thomas Price who encouraged members to establish branch chapels to attract migrants who flocked to the town and locality from rural Wales. The chapels came together for regular gatherings, including baptismal services which were held in theRiver Cynon
The River Cynon ( cy, Afon Cynon) in South Wales is a main tributary of the Taff. Its source is the rising of Llygad Cynon (OS grid ref SN 95240 07740) at above sea level at Penderyn, Rhondda Cynon Taf and flows roughly southeast, into the Ta ...
As a result, Price exerted an influence in the religious life of the locality which was far greater than that of any other minister.
Calvinistic Methodists
By 1910 there were 24 Calvinistic Methodist chapels in the Aberdare Urban District with a total membership of 4,879. The most prominent of these was Bethania, Aberdare, once the largest chapel in Aberdare. Derelict for many years, it was demolished in 2015. The Methodists were numerically powerful and while some of their ministers such as William James of Bethania served on the Aberdare School Board and other public bodies, their constitution militated against the sort of active political action which came more naturally to the Baptists and Independents.Other denominations
The other denominations were weaker, including the Wesleyan Methodists who had 14 places of worship by 1910. There was also a significant Unitarian tradition in the valley and three places of worship by 1910. Highland Place Unitarian Church celebrated its 150th anniversary in 2010, with a number of lectures on its history and the history of Unitarianism in Wales taking place there. The church has a two-manual pipe organ with pedal board that is used to accompany all services. The current organist is Grace Jones, the sister of the former organist Jacob Jones. The connected schoolroom is used for post-service meetings and socialising.Judaism
Seymour Street was once home to a synagogue which opened its doors in the late 1800s and which closed in 1957. The site now has a blue plaque.Education
The state of education in the parish was a cause for concern during the early industrial period as is illustrated by the reaction to the 1847 Education Reports. Initially, there was an outcry, led by the Rev Thomas Price against the comments made by the vicar of Aberdare in his submission to the commissioners. However, on closer reflection, the reports related the deficiencies of educational provision, not only in Aberdare itself but also in the communities of the valleys generally. In so doing they not only criticised the ironmasters for their failure to provide schools for workers' children but also the nonconformists for not establishing British Schools. At the ten schools in Aberdare there was accommodation for only 1,317 children, a small proportion of the population. Largely as a result of these criticisms, the main nonconformist denominations worked together to establish a British School, known locally as Ysgol y Comin, which was opened in 1848, accommodating 200 pupils. Funds were raised which largely cleared the debts and the opening of the school was marked by a public meeting addressed by Price and David Williams (''Alaw Goch''). Much energy was expended during this period on conflicts between Anglicans and nonconformists over education. The establishment of the Aberdare School Board in 1871 brought about an extension of educational provision but also intensified religious rivalries. School Board elections were invariably fought on religious grounds. Despite these tensions the Board took over a number of existing schools and established new ones. By 1889, fourteen schools were operated by the Board but truancy and lack of attendance remained a problem, as in many industrial districts. In common with other public bodies at the time (see 'Local Government' above), membership of the School Board was dominated by coal owners and colliery officials, nonconformist ministers, professional men and tradesmen. Only occasionally was an Anglican clergyman elected and, with the exception of David Morgan (''Dai o'r Nant''), no working class candidates were elected for more than one term.Colleges
* Coleg y CymoeddSecondary schools
* Aberdare Community School * St. John the Baptist School (Aberdare) *Ysgol Gyfun Rhydywaun
Ysgol Gyfun Rhydywaun is a Welsh-medium comprehensive school in the Cynon Valley in the village of Penywaun, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales, to the northwest of the town of Aberdare.
The school was established on 1 September 1995. It provides a Welsh ...
Transport
The town is served by Aberdare railway station and Aberdare bus station, opposite each other in the town centre. The town has also been subject to an extensive redevelopment scheme during 2012–13.Sports
 Aberdare is home to '' Yr Ynys'', an historic sports ground which has the distinction of hosting the first Rugby League international, a professional Rugby League team, a football League side and an All Blacks' tour match. Today the Ynys hosts the town's Rugby Union and Cricket teams, as well as the Sobell Leisure Centre and the Ron Jones Athletics Stadium, a 263-seat stadium with
Aberdare is home to '' Yr Ynys'', an historic sports ground which has the distinction of hosting the first Rugby League international, a professional Rugby League team, a football League side and an All Blacks' tour match. Today the Ynys hosts the town's Rugby Union and Cricket teams, as well as the Sobell Leisure Centre and the Ron Jones Athletics Stadium, a 263-seat stadium with crumb rubber
Crumb rubber is recycled rubber produced from automotive and truck scrap tires. During the recycling process, steel and tire cord (fluff) are removed, leaving tire rubber with a granular consistency. Continued processing with a granulator or c ...
track and field sports facilities, home to Aberdare Valley AAC.
Cricket
A cricket club was re-established at the Ynys in 1968 and was named Riverside Cricket Club in reference to its location on the banks of the river Dare. The club would later be renamed Dare Valley CC, before finally changing its name to Aberdare CC. In 2008 the club was granted a 25-year lease on the land outside the boundary of the Ynys' pitch 1, where a club house and training nets were soon constructed. This was followed by the building of a Community Hub and Café in the 2010s. Today, the club runs 3 adult teams and 4 junior sides.Rugby League
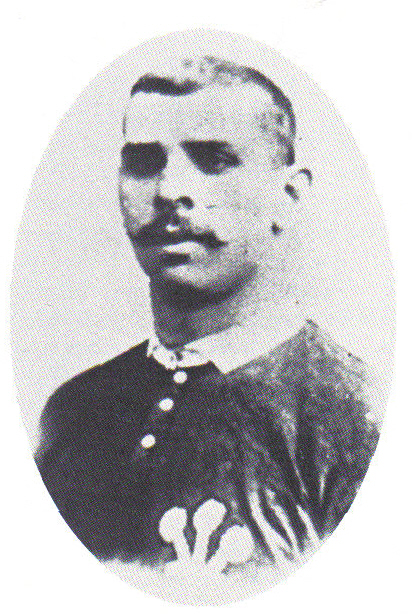
 The Northern Union hired the Ynys on the 1 January 1908 to host what would be the first ever international rugby league match. Played on a near frozen pitch, the match between
The Northern Union hired the Ynys on the 1 January 1908 to host what would be the first ever international rugby league match. Played on a near frozen pitch, the match between Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
and the New Zealand All Golds proved to be a close and exciting game. The decisive score came from local star and former Aberdare RFC player, Dai "Tarw" Jones, who scored a try just minutes before the final whistle, giving Wales a 9–8 victory.
The match attracted 15,000 paying spectators, with the gate receipts of £560 highlighting the commercial potential of rugby league at the Ynys. This took place at a time when the Northern Union was looking to establish professional teams across south Wales and just months after the Welsh Rugby Union had sanctioned Aberdare RFC for professionalism (banning Jones for life). As such, discussions on the establishment of a Rugby League club in Aberdare advanced quickly and on 21 July 1908, Aberdare RLFC were admitted to the Northern Union's Rugby League. On 5 September 1908 the new team played their first match against Wigan
Wigan ( ) is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, on the River Douglas. The town is midway between the two cities of Manchester, to the south-east, and Liverpool, to the south-west. Bolton lies to the north-east and Warrington t ...
in front of a crowd of 3,000 at the Ynys.
The potential for crowd support was again demonstrated when on the 10th November 1908 the Ynys hosted its second international side as 5,000 spectators watched Aberdare take on the first touring Australian team. However the Aberdare club side could not replicate the heroics of the Welsh team, losing the match 10–37. Indeed, Aberdare struggled under Northern Union rules and initially high crowd numbers deteriorate with the poor results, which saw Aberdare finishing their only season in the Rugby Football League as the bottom club. Finally on 10 July 1909, Aberdare reported 'unexpected difficulties' in its finances and resigned from the Northern Rugby League.
Rugby Union
 A rugby club representing Aberdare was recorded as early as 1876, but the modern Aberdare RFC traces its history back to a foundation of 1890. The club had great success in the early twentieth century with local star Dai 'Tarw' Jones captaining the club from 1905 to 1907. Jones gained recognition as a player in club, representative and international games. Most notably, Jones played an important part in the "'' Match of the century''", when Wales defeated the New Zealand All Blacks. In 1907, Jones and the Aberdare club played a pivotal role in the professionalism scandal, with the Welsh Rugby Union permanently suspending the club's entire committee and a number of players (including a lifetime ban for Jones). These events would quickly lead to many of the town's players and fans switching to rugby league, with the first ever rugby league international and the founding of Aberdare RLFC in 1908.
Despite the suspensions, rugby union continued in the town as the club (renamed Aberaman RFC) moved to Aberaman Park. The Ynys Stadium would host its first international rugby union side on 12 December 1935, when the 1935-36 All Blacks played a tour match against a Mid-Districts side. The All Blacks won the match 31–10 in front of a crowd of 6,000.
Aberaman RFC returned to the Ynys in the 1960s. In February 1971, a clubhouse was opened at the old Crown Hotel in Gloucester Street, this was followed by the construction of a grand stand at the Ynys costing £20,000. Following the advent of professionalism in rugby union, the WRU sanctions against Aberdare were no longer applicable. As such, the club took the name Aberdare RUFC once again. Aberdare is also home to Abercwmboi RFC and Hirwaun RFC.
A rugby club representing Aberdare was recorded as early as 1876, but the modern Aberdare RFC traces its history back to a foundation of 1890. The club had great success in the early twentieth century with local star Dai 'Tarw' Jones captaining the club from 1905 to 1907. Jones gained recognition as a player in club, representative and international games. Most notably, Jones played an important part in the "'' Match of the century''", when Wales defeated the New Zealand All Blacks. In 1907, Jones and the Aberdare club played a pivotal role in the professionalism scandal, with the Welsh Rugby Union permanently suspending the club's entire committee and a number of players (including a lifetime ban for Jones). These events would quickly lead to many of the town's players and fans switching to rugby league, with the first ever rugby league international and the founding of Aberdare RLFC in 1908.
Despite the suspensions, rugby union continued in the town as the club (renamed Aberaman RFC) moved to Aberaman Park. The Ynys Stadium would host its first international rugby union side on 12 December 1935, when the 1935-36 All Blacks played a tour match against a Mid-Districts side. The All Blacks won the match 31–10 in front of a crowd of 6,000.
Aberaman RFC returned to the Ynys in the 1960s. In February 1971, a clubhouse was opened at the old Crown Hotel in Gloucester Street, this was followed by the construction of a grand stand at the Ynys costing £20,000. Following the advent of professionalism in rugby union, the WRU sanctions against Aberdare were no longer applicable. As such, the club took the name Aberdare RUFC once again. Aberdare is also home to Abercwmboi RFC and Hirwaun RFC.
Soccer
 The Ynys stadium was also home to
The Ynys stadium was also home to Aberdare Athletic F.C.
Aberdare Athletic Football Club were a Welsh football club founded in 1893 and based in Aberdare. They joined the Football League in 1921 but were replaced by Torquay United after failing to be re-elected in 1927.
History
Founded in 1893, ...
, members of the Football League between 1921 and 1927. Aberdare finished bottom in their final season and folded in 1928 after failing to be re-elected to the league.
Aberaman Athletic F.C.
Aberdare Town Football Club is a Welsh football club that currently play in the South Wales Alliance League Premier Division. Their ground is situated on Cardiff Road, Aberdare, between the suburb of Aberaman and the village of Abercwmboi. They ...
continued to play until World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, and was succeeded by Aberdare & Aberaman Athletic in 1945 and Aberdare Town F.C. in 1947. The club continue to play in the Welsh Football League
The Welsh Football League (also known as the Nathaniel Car Sales Welsh Football League for sponsorship reasons) was a club football league in Wales. For its final season in 2019–20 season it operated at levels 3 and 4 of the Welsh football leag ...
. Today, Aberdare Town plays in the South Wales Alliance League
The South Wales Alliance League is a football league structure in South Wales, currently known for sponsorship reasons as ''The Highadmit Projects South Wales Alliance League''. The top tier of the league, the Premier Division is at the fourt ...
and are based at Aberaman Park.
Notable people
:''See also :People from Aberdare'' Notable current and former residents and natives of Aberdare include: * Henry Austin Bruce – 1st Baron Aberdare &Home Secretary
The secretary of state for the Home Department, otherwise known as the home secretary, is a senior minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom. The home secretary leads the Home Office, and is responsible for all national s ...
(1868–1873)
* Les Cartwright - Former Association Footballer and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
international, played for Coventry City
Coventry City Football Club is a professional association football club based in Coventry, West Midlands, England. The team currently compete in the Championship, the second tier of the English football league system. The club is nicknamed t ...
and Wrexham AFC
Wrexham Association Football Club ( cy, Clwb Pêl-droed Wrecsam) is a Welsh professional association football club based in Wrexham, Wales. The team competes in the National League, the fifth tier of the English football league system. Formed ...
* Rose Davies – Labour politician and feminist
* Ian Evans – Former Rugby Union Player and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
international, played for Ospreys and Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
. Currently coaching at the Dragons
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
*Lyn Evans
Lyn Evans CBE (born Lyndon Rees Evans in 1945), is a Welsh scientist who served as the project leader of the Large Hadron Collider in Switzerland. Based at CERN, in 2012 he became the director of the Linear Collider Collaboration, an internat ...
– particle physicist and project leader of the Large Hadron Collider
*Ioan Gruffudd
Ioan Gruffudd (; (born 6 October 1973) is a Welsh actor. He first came to public attention as Fifth Officer Harold Lowe in ''Titanic'' (1997), and then for his portrayal of Horatio Hornblower in the ''Hornblower (TV series), Hornblower'' seri ...
– actor, born in Llwydcoed, Aberdare
*Patrick Hannan (presenter)
Patrick Hannan MBE (26 September 1941 – 11 October 2009) was a Welsh political journalist, author and television and radio presenter.
The son of an Irish doctor who migrated to Wales in the 1930s, he was born and raised in Aberaman, near A ...
– broadcaster
* David "Tarw" Jones – Dual code rugby international
* Alun Lewis – War poet
*Arthur Linton
Arthur Vincent Linton (28 November 1868 – 23 July 1896) was a British road bicycle racer. He is best known for sharing victory in the Bordeaux–Paris road race in 1896 and for breaking the Welsh one-hour paced cycling record. His death just t ...
- cyclist
* Lee Lucas - Association Footballer, played for Swansea City and Motherwell.
*Jimmy Michael
Jimmy Michael (18 August 1877 – 21 November 1904) was a Welsh world cycling champion and one of the top riders in the sport for several years.
Origins
Jimmy Michael was tall. He was born in Aberaman, Cynon Valley, Wales. His parents had a ...
– World cycling champion
* 'Big' Jim Mills – Wales & Great Britain rugby league international
* John Morgan – Canadian comedian, Royal Canadian Air Farce
The Royal Canadian Air Farce was a comedy troupe that was active from 1973 to 2019. It is best known for their various Canadian Broadcasting Corporation series, first on CBC Radio and later on CBC Television. Although their weekly radio series ...
* Mihangel Morgan – Welsh language writer, born in Trecynon
Trecynon is a village near Aberdare situated in the Cynon Valley, in Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales. It dates from the early nineteenth century and developed as a result of the opening of the Aberdare Ironworks at Llwydcoed in 1800.
Etymology
The s ...
, some of his literary works feature Aberdare
* Roy Noble – Welsh broadcaster, has lived near Aberdare for the past 30 years
* R. Ifor Parry – Congregationalist Minister and schoolteacher
* Jason Price - Former Association Footballer, played for Swansea City and Doncaster Rovers
Doncaster Rovers Football Club is a professional association football club based in Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England. The team compete in League Two, the fourth tier of the English football league system. The club play their home games at ...
* Thomas Price (Baptist minister) – Baptist Minister and radical politician
*Ieuan Rhys
Ieuan Rhys (born 24 December 1961) is a Welsh actor. His television work has included thirteen years in the BBC Cymru soap opera ''Pobol y Cwm'', Seargent Tom Swann in the last series of ''A Mind to Kill'' (for Fiction Factory/ Channel 5) and s ...
– actor, from Trecynon
* Rhys Hopkin Rhys – 19th century industrialist and prominent local figure
*Rhian Samuel
Rhian Samuel (born Aberdare, Wales, 1944) is a Welsh woman composer who resided in the USA for many years. She has composed over 140 published works, including orchestral, chamber, vocal, and choral music. She now divides her time between mid-W ...
– composer and professor of music
* Bethan Sayed – member of the Senedd for the South Wales (West) Region
* Stereophonics – all three original members, Kelly Jones
Kelly Jones (born 3 June 1974) is a Welsh singer-songwriter and a founding member, lead singer, and guitarist of the rock band Stereophonics.
Early life and debut
Kelly Jones was born youngest of three boys for Beryl and Arwyn Jones in the s ...
, Richard Jones and Stuart Cable
Stuart James Cable (19 May 1970 – 7 June 2010) was a Welsh rock drummer and broadcaster, best known as the original drummer for the band Stereophonics.
Early life
Cable was born in Aberdare, Rhondda Cynon Taf, on 19 May 1970. When he was 1 ...
were brought up in Cwmaman
Cwmaman () is a former coal mining village near Aberdare, Wales. The name is Welsh for "Aman Valley" and the River Aman flows through the village. Cwmaman literally means: valley of the river Aman. It lies in the valley of several mountains. ...
, Aberdare
*Rees Thomas
Rees Thomas (1882–14 June 1926) was a Welsh international rugby union back row player who was utilised usually as a flanker or Number 8. Thomas played club rugby for Pontypool and county rugby for Monmouthshire. He won eight caps for Wales ...
- Former Association Footballer, played for Cardiff City, Bournemouth & Boscombe Athletic and Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
*Jo Walton
Jo Walton (born 1964) is a Welsh and Canadian fantasy and science fiction writer and poet. She is best known for the fantasy novel ''Among Others'', which won the Hugo and Nebula Awards in 2012, and '' Tooth and Claw'', a Victorian era novel ...
– fantasy novelist, now living in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, Quebec
* David Young – rugby player and coach, raised in Penywaun
See also
*List of twin towns and sister cities in the United Kingdom
__NOTOC__
This is a list of places in the United Kingdom having standing links to local communities in other countries. In most cases, the association, especially when formalised by local government, is known as "town twinning" (though other terms ...
* Aberdare Park
References
Sources
Books
* * * * * * *Journals
* * * * * *Newspapers
*Aberdare Leader *Cardiff and Merthyr GuardianOnline
*External sources
BBC website on Aberdare
External links
www.geograph.co.uk : photos of Aberdare and surrounding area
{{authority control Towns in Rhondda Cynon Taf Former communities of Rhondda Cynon Taf