Axolotl Paludarium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The axolotl (; from nci, āxōlōtl ), ''Ambystoma mexicanum'', is a paedomorphic salamander closely related to the tiger salamander. Axolotls are unusual among
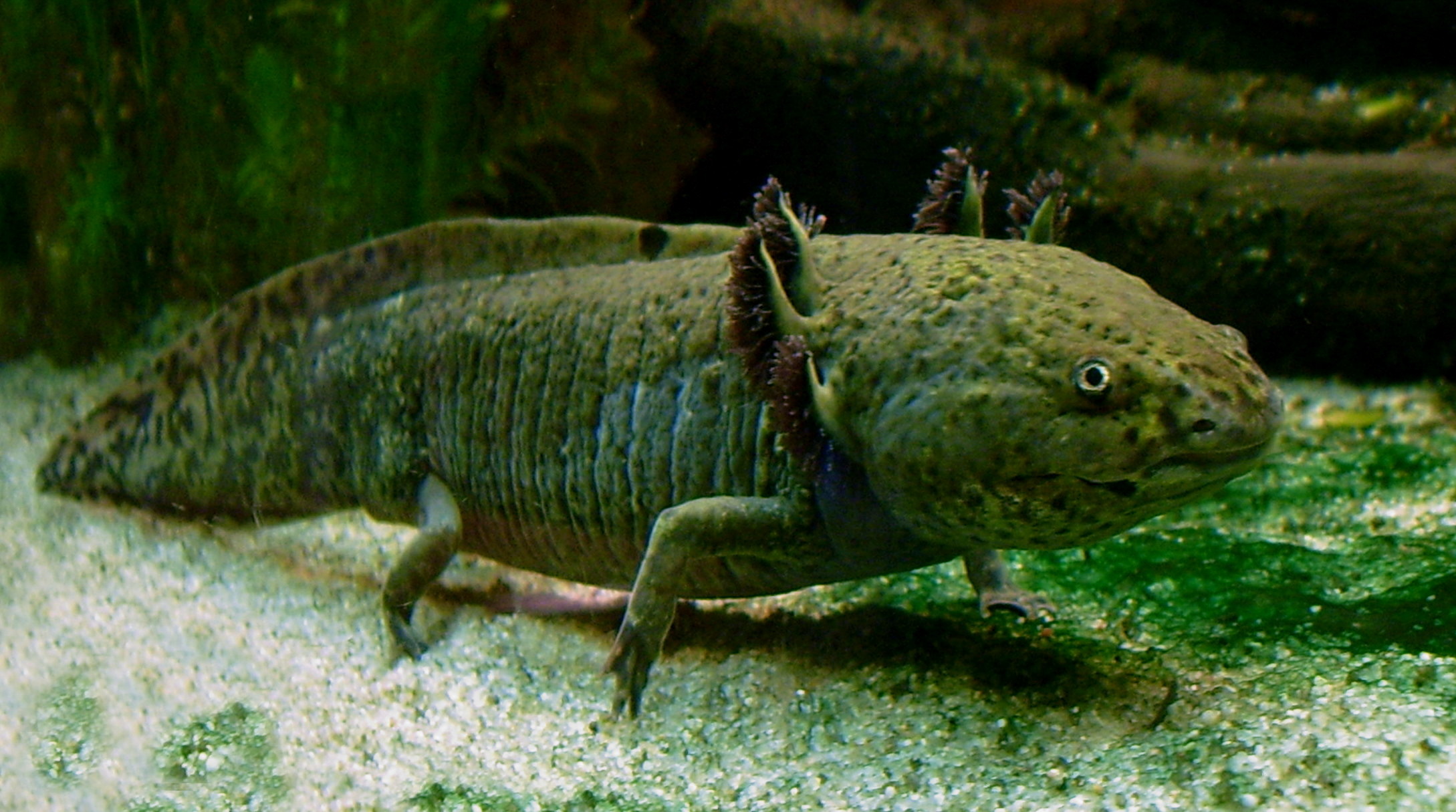


 A sexually mature adult axolotl, at age 18–27 months, ranges in length from , although a size close to is most common and greater than is rare. Axolotls possess features typical of salamander larvae, including external gills and a caudal fin extending from behind the head to the vent. External gills are usually lost when salamander species mature into adulthood, although the axolotl maintains this feature. This is due to their neoteny evolution, where axolotls are much more aquatic than other salamander species.
Their heads are wide, and their eyes are lidless. Their limbs are underdeveloped and possess long, thin digits. Males are identified by their swollen
A sexually mature adult axolotl, at age 18–27 months, ranges in length from , although a size close to is most common and greater than is rare. Axolotls possess features typical of salamander larvae, including external gills and a caudal fin extending from behind the head to the vent. External gills are usually lost when salamander species mature into adulthood, although the axolotl maintains this feature. This is due to their neoteny evolution, where axolotls are much more aquatic than other salamander species.
Their heads are wide, and their eyes are lidless. Their limbs are underdeveloped and possess long, thin digits. Males are identified by their swollen 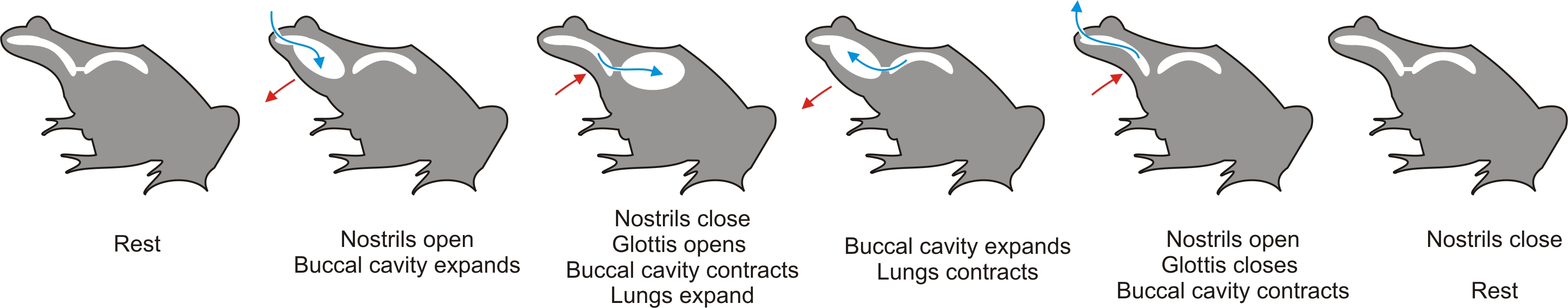
 Axolotls have four pigmentation genes; when mutated they create different color variants. The normal wild-type animal is brown/tan with gold speckles and an olive undertone. The five more common mutant colors are leucistic (pale pink with black eyes), golden albino (golden with gold eyes), xanthic (grey with black eyes), albino (pale pink/white with red eyes) which is more common in axolotls than some other creatures, and melanoid (all black/dark blue with no gold speckling or olive tone). In addition, there is wide individual variability in the size, frequency, and intensity of the gold speckling and at least one variant that develops a black and white piebald appearance on reaching maturity. Because pet breeders frequently cross the variant colors, double homozygous mutants are common in the pet trade, especially white/pink animals with pink eyes that are double homozygous mutants for both the albino and leucistic trait. Axolotls also have some limited ability to alter their color to provide better camouflage by changing the relative size and thickness of their melanophores.
Axolotls have four pigmentation genes; when mutated they create different color variants. The normal wild-type animal is brown/tan with gold speckles and an olive undertone. The five more common mutant colors are leucistic (pale pink with black eyes), golden albino (golden with gold eyes), xanthic (grey with black eyes), albino (pale pink/white with red eyes) which is more common in axolotls than some other creatures, and melanoid (all black/dark blue with no gold speckling or olive tone). In addition, there is wide individual variability in the size, frequency, and intensity of the gold speckling and at least one variant that develops a black and white piebald appearance on reaching maturity. Because pet breeders frequently cross the variant colors, double homozygous mutants are common in the pet trade, especially white/pink animals with pink eyes that are double homozygous mutants for both the albino and leucistic trait. Axolotls also have some limited ability to alter their color to provide better camouflage by changing the relative size and thickness of their melanophores.
 The axolotl is native only to the freshwater of
The axolotl is native only to the freshwater of
 Today, the axolotl is still used in research as a
Today, the axolotl is still used in research as a
 The axolotl is a popular exotic pet like its relative, the tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum''). As for all poikilothermic organisms, lower temperatures result in slower metabolism and a very unhealthily reduced appetite. Temperatures at approximately to are suggested for captive axolotls to ensure sufficient food intake; stress resulting from more than a day's exposure to lower temperatures may quickly lead to disease and death, and temperatures higher than may lead to metabolic rate increase, also causing stress and eventually death. Chlorine, commonly added to
The axolotl is a popular exotic pet like its relative, the tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum''). As for all poikilothermic organisms, lower temperatures result in slower metabolism and a very unhealthily reduced appetite. Temperatures at approximately to are suggested for captive axolotls to ensure sufficient food intake; stress resulting from more than a day's exposure to lower temperatures may quickly lead to disease and death, and temperatures higher than may lead to metabolic rate increase, also causing stress and eventually death. Chlorine, commonly added to  Salts, such as
Salts, such as
Follow the Eggs, Hatchlings and Juveniles
Mating Dance and Laying Eggs
Follow the Eggs and Hatchlings (2nd Batch)
University of KY Axolotl Colony
The animal that’s everywhere and nowhere
*
"The Tao of Axolotl"
– thetolteciching.com; on folklore {{Authority control Amphibians described in the 18th century Animal models Animal testing on amphibians Animals bred for albinism on a large scale Critically endangered biota of Mexico Critically endangered fauna of North America Endemic amphibians of Mexico Mole salamanders Population genetics Regenerative biomedicine Taxa named by Frederick Polydore Nodder Taxa named by George Shaw Valley of Mexico
amphibians
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbore ...
in that they reach adulthood without undergoing metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
. Instead of taking to the land, adults remain aquatic and gilled. The species was originally found in several lakes underlying what is now Mexico City, such as Lake Xochimilco
Lake Xochimilco (; nah, Xōchimīlco, ) is an ancient endorheic lake, located in the present-day Borough of Xochimilco in southern Mexico City.
The lake is within the Valley of Mexico hydrological basin, in central Mexico.
History
Geolo ...
and Lake Chalco
Lake Chalco was an endorheic lake formerly located in the Valley of Mexico, and was important for Mesoamerican cultural development in central Mexico. The lake was named after the ancient city of Chalco on its former eastern shore.
Geography
L ...
. These lakes were drained by Spanish settlers after the conquest of the Aztec Empire, leading to the destruction of much of the axolotl’s natural habitat.
Axolotls should not be confused with the larval stage of the closely related tiger salamander (''A. tigrinum''), which are widespread in much of North America and occasionally become paedomorphic. Neither should they be confused with mudpuppies (''Necturus'' spp.), fully aquatic salamanders from a different family that are not closely related to the axolotl but bear a superficial resemblance.
, wild axolotls were near extinction due to urbanization in Mexico City and consequent water pollution, as well as the introduction of invasive species such as tilapia and perch. They are listed as critically endangered in the wild, with a decreasing population of around 50 to 1,000 adult individuals, by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) and are listed under Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES).regenerate limbs, gills and parts of their eyes and brains. Axolotls were also sold as food in Mexican markets and were a staple in the Aztec diet.
Description



 A sexually mature adult axolotl, at age 18–27 months, ranges in length from , although a size close to is most common and greater than is rare. Axolotls possess features typical of salamander larvae, including external gills and a caudal fin extending from behind the head to the vent. External gills are usually lost when salamander species mature into adulthood, although the axolotl maintains this feature. This is due to their neoteny evolution, where axolotls are much more aquatic than other salamander species.
Their heads are wide, and their eyes are lidless. Their limbs are underdeveloped and possess long, thin digits. Males are identified by their swollen
A sexually mature adult axolotl, at age 18–27 months, ranges in length from , although a size close to is most common and greater than is rare. Axolotls possess features typical of salamander larvae, including external gills and a caudal fin extending from behind the head to the vent. External gills are usually lost when salamander species mature into adulthood, although the axolotl maintains this feature. This is due to their neoteny evolution, where axolotls are much more aquatic than other salamander species.
Their heads are wide, and their eyes are lidless. Their limbs are underdeveloped and possess long, thin digits. Males are identified by their swollen cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, a ...
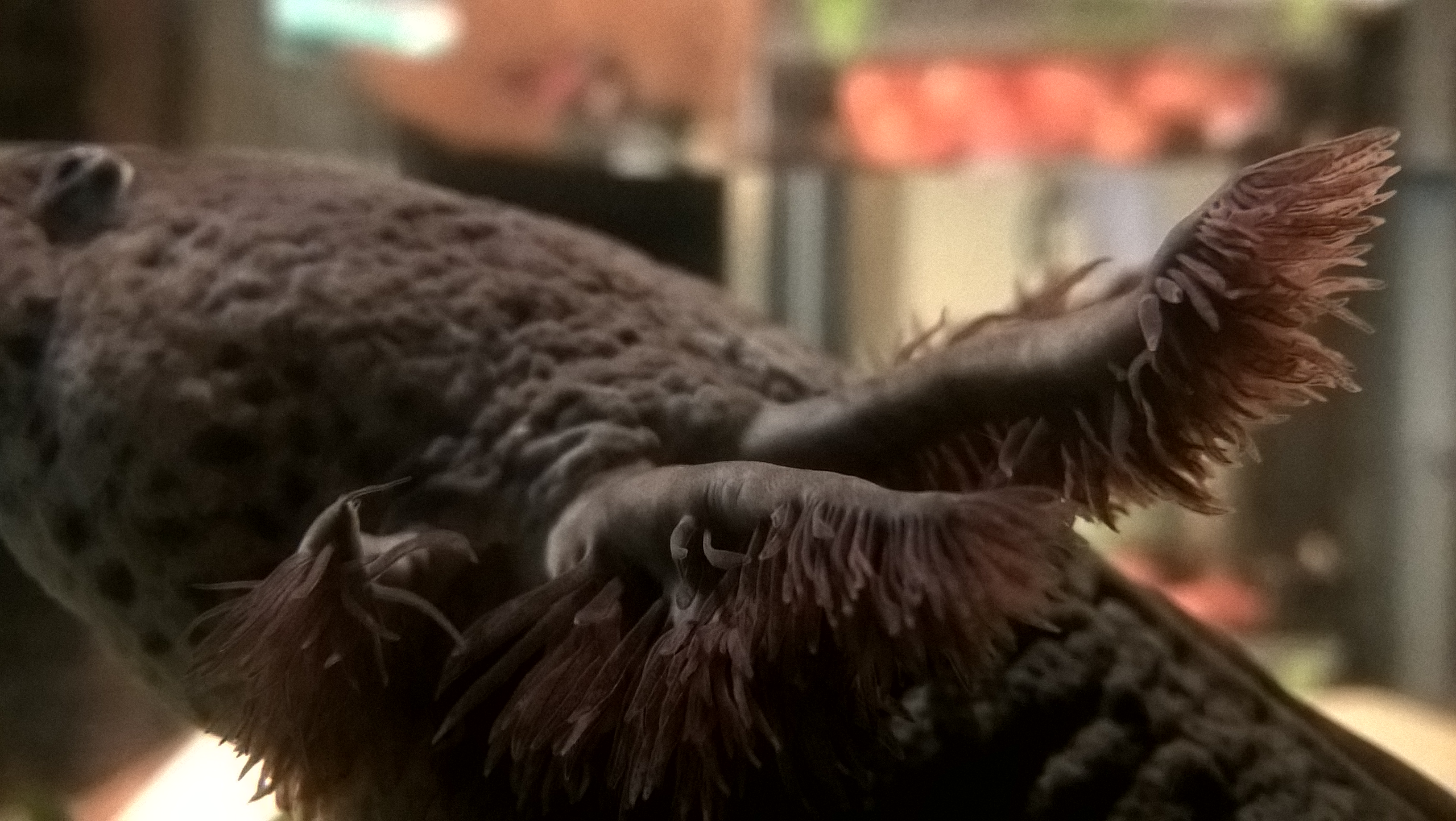
e lined with papillae, while females are noticeable for their wider bodies full of eggs. Three pairs of external gill stalks (rami) originate behind their heads and are used to move oxygenated water. The external gill rami are lined with filaments (fimbriae) to increase surface area for gas exchange. Four-gill slits lined with gill rakers are hidden underneath the external gills, which prevent food from entering and allow particles to filter through.
Axolotls have barely visible vestigial teeth, which develop during metamorphosis. The primary method of feeding is by suction
Suction is the colloquial term to describe the air pressure differential between areas.
Removing air from a space results in a pressure differential. Suction pressure is therefore limited by external air pressure. Even a perfect vacuum cannot ...
, during which their rakers interlock to close the gill slits. External gills are used for respiration, although buccal pumping (gulping air from the surface) may also be used to provide oxygen to their lungs. Buccal pumping can occur in a two-stroke manner that pumps air from the mouth to the lungs, and with four-stroke that reverses this pathway with compression forces.
 Axolotls have four pigmentation genes; when mutated they create different color variants. The normal wild-type animal is brown/tan with gold speckles and an olive undertone. The five more common mutant colors are leucistic (pale pink with black eyes), golden albino (golden with gold eyes), xanthic (grey with black eyes), albino (pale pink/white with red eyes) which is more common in axolotls than some other creatures, and melanoid (all black/dark blue with no gold speckling or olive tone). In addition, there is wide individual variability in the size, frequency, and intensity of the gold speckling and at least one variant that develops a black and white piebald appearance on reaching maturity. Because pet breeders frequently cross the variant colors, double homozygous mutants are common in the pet trade, especially white/pink animals with pink eyes that are double homozygous mutants for both the albino and leucistic trait. Axolotls also have some limited ability to alter their color to provide better camouflage by changing the relative size and thickness of their melanophores.
Axolotls have four pigmentation genes; when mutated they create different color variants. The normal wild-type animal is brown/tan with gold speckles and an olive undertone. The five more common mutant colors are leucistic (pale pink with black eyes), golden albino (golden with gold eyes), xanthic (grey with black eyes), albino (pale pink/white with red eyes) which is more common in axolotls than some other creatures, and melanoid (all black/dark blue with no gold speckling or olive tone). In addition, there is wide individual variability in the size, frequency, and intensity of the gold speckling and at least one variant that develops a black and white piebald appearance on reaching maturity. Because pet breeders frequently cross the variant colors, double homozygous mutants are common in the pet trade, especially white/pink animals with pink eyes that are double homozygous mutants for both the albino and leucistic trait. Axolotls also have some limited ability to alter their color to provide better camouflage by changing the relative size and thickness of their melanophores.
Habitat and ecology

 The axolotl is native only to the freshwater of
The axolotl is native only to the freshwater of Lake Xochimilco
Lake Xochimilco (; nah, Xōchimīlco, ) is an ancient endorheic lake, located in the present-day Borough of Xochimilco in southern Mexico City.
The lake is within the Valley of Mexico hydrological basin, in central Mexico.
History
Geolo ...
and Lake Chalco
Lake Chalco was an endorheic lake formerly located in the Valley of Mexico, and was important for Mesoamerican cultural development in central Mexico. The lake was named after the ancient city of Chalco on its former eastern shore.
Geography
L ...
in the Valley of Mexico. Lake Chalco no longer exists, having been drained as a flood control measure, and Lake Xochimilco remains a remnant of its former self, existing mainly as canals. The water temperature in Xochimilco rarely rises above , although it may fall to in the winter, and perhaps lower.
Surveys in 1998, 2003, and 2008 found 6,000, 1,000, and 100 axolotls per square kilometer in its Lake Xochimilco habitat, respectively. A four-month-long search in 2013, however, turned up no surviving individuals in the wild. Just a month later, two wild ones were spotted in a network of canals leading from Xochimilco.
The wild population has been put under heavy pressure by the growth of Mexico City. The axolotl is currently on the International Union for Conservation of Nature's annual Red List of threatened species. Non-native fish, such as African tilapia and Asian carp, have also recently been introduced to the waters. These new fish have been eating the axolotls' young, as well as their primary source of food.
Axolotls are members of the tiger salamander, or ''Ambystoma tigrinum
The tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum'') is a species of mole salamander and one of the largest terrestrial salamanders in North America.
Description
These salamanders usually grow to a length of with a lifespan of around 12–15 years. ...
'', species complex, along with all other Mexican species of ''Ambystoma''. Their habitat is like that of most neotenic species—a high-altitude body of water surrounded by a risky terrestrial environment. These conditions are thought to favor neoteny. However, a terrestrial population of Mexican tiger salamanders occupies and breeds in the axolotl's habitat.
The axolotl is carnivorous, consuming small prey such as mollusks, worms, insects, other arthropods, and small fish in the wild. Axolotls locate food by smell, and will "snap" at any potential meal, sucking the food into their stomachs with vacuum force.
Use as a model organism
 Today, the axolotl is still used in research as a
Today, the axolotl is still used in research as a model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
, and large numbers are bred in captivity. They are especially easy to breed compared to other salamanders in their family, which are rarely captive-bred due to the demands of terrestrial life. One attractive feature for research is the large and easily manipulated embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
, which allows viewing of the full development of a vertebrate. Axolotls are used in heart defect studies due to the presence of a mutant gene that causes heart failure in embryos. Since the embryos survive almost to hatching with no heart function, the defect is very observable. The axolotl is also considered an ideal animal model for the study of neural tube closure due to the similarities between human and axolotl neural plate and tube formation; the axolotl's neural tube, unlike the frog's, is not hidden under a layer of superficial epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
. There are also mutations affecting other organ systems some of which are not well characterized and others that are. The genetics of the color variants of the axolotl have also been widely studied.
Regeneration
The feature of the axolotl that attracts most attention is its healing ability: the axolotl does not heal by scarring and is capable of theregeneration
Regeneration may refer to:
Science and technology
* Regeneration (biology), the ability to recreate lost or damaged cells, tissues, organs and limbs
* Regeneration (ecology), the ability of ecosystems to regenerate biomass, using photosynthesis
...
of entire lost appendages in a period of months, and, in certain cases, more vital structures, such as tail, limb, central nervous system, and tissues of the eye and heart. They can even restore less vital parts of their brains. They can also readily accept transplants from other individuals, including eyes and parts of the brain—restoring these alien organs to full functionality. In some cases, axolotls have been known to repair a damaged limb, as well as regenerating an additional one, ending up with an extra appendage that makes them attractive to pet owners as a novelty. In metamorphosed individuals, however, the ability to regenerate is greatly diminished. The axolotl is therefore used as a model for the development of limbs in vertebrates. There are three basic requirements for regeneration of the limb: the wound epithelium, nerve signaling, and the presence of cells from the different limb axes. A wound epidermis is quickly formed by the cells to cover up the site of the wound. In the following days, the cells of the wound epidermis divide and grow quickly forming a blastema, which means the wound is ready to heal and undergo patterning to form the new limb.
It is believed that during limb generation, axolotls have a different system to regulate their internal macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
level and suppress inflammation, as scarring prevents proper healing and regeneration. However, this belief has been questioned by other studies. Axolotl’s regenerative properties leave the species as the perfect model to study the process of stem cells and its own neoteny feature. Current research can record specific examples of these regenerative properties through tracking cell fates and behaviors, lineage tracing skin triploid cell grafts, pigmentation imaging, electroporation, tissue clearing and lineage tracing from dye labeling. The newer technologies of germline modification and transgenesis are better suited for live imaging the regenerative processes that occur for axolotls.
Genome
The 32 billionbase pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
long sequence of the axolotl's genome was published in 2018 and was the largest animal genome completed at the time. It revealed species-specific genetic pathways that may be responsible for limb regeneration. Although the axolotl genome is about 10 times as large as the human genome, it encodes a similar number of proteins, namely 23,251 (the human genome encodes about 20,000 proteins). The size difference is mostly explained by a large fraction of repetitive sequences, but such repeated elements also contribute to increased median intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene. ...
sizes (22,759 bp) which are 13, 16 and 25 times that observed in human (1,750 bp), mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
(1,469 bp) and Tibetan frog (906 bp), respectively.
Neoteny
When most amphibians are young, they live in water, and they use gills that can breathe in the water. When they become adults, they go through a process calledmetamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
, in which they lose their gills and start living on land. However, the axolotl is unusual in that it has a lack of thyroid stimulating hormone, which is needed for the thyroid to produce thyroxine in order for the axolotl to go through metamorphosis; therefore, it keeps its gills and lives in water all its life, even after it becomes an adult and is able to reproduce. Its body has the capacity to go through metamorphosis if given the necessary hormone, but axolotls do not produce it, and must be exposed to it from an external source, after which an axolotl undergoes an artificially-induced metamorphosis and begins living on land. One method of artificial metamorphosis induction is through an injection of iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
, which is used in the production of thyroid hormones.
An axolotl undergoing metamorphosis experiences a number of physiological changes that help them adapt to life on land. These include increased muscle tone in limbs, the absorption of gills and fins into the body, the development of eyelids, and a reduction in the skin's permeability to water, allowing the axolotl to stay more easily hydrated when on land. The lungs of an axolotl, though present alongside gills after reaching non-metamorphosed adulthood, develop further during metamorphosis.
An axolotl that has gone through metamorphosis resembles an adult plateau tiger salamander, though the axolotl differs in its longer toes. The process of artificially inducing metamorphosis can often result in death during or even following a successful attempt, and so casual hobbyists are generally discouraged from attempting to induce metamorphosis in pet axolotls.
Neoteny is the term for reaching sexual maturity without undergoing metamorphosis. Many other species within the axolotl's genus are also either entirely neotenic or have neotenic populations. Siren
Siren or sirens may refer to:
Common meanings
* Siren (alarm), a loud acoustic alarm used to alert people to emergencies
* Siren (mythology), an enchanting but dangerous monster in Greek mythology
Places
* Siren (town), Wisconsin
* Siren, Wisco ...
s and '' Necturus'' are other neotenic salamanders, although unlike axolotls, they cannot be induced to metamorphose by an injection of iodine or thyroxine hormone.
The genes responsible for neoteny in laboratory animals may have been identified; however, they are not linked in wild populations, suggesting artificial selection
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
is the cause of complete neoteny in laboratory and pet axolotls.
Six adult axolotls (including a leucistic specimen) were shipped from Mexico City to the '' Jardin des Plantes'' in Paris in 1863. Unaware of their neoteny, Auguste Duméril
Auguste Henri André Duméril (30 November 1812 – 12 November 1870) was a French zoologist. His father, André Marie Constant Duméril (1774-1860), was also a zoologist. In 1869 he was elected as a member of the Académie des sciences.
Duméril ...
was surprised when, instead of the axolotl, he found in the vivarium a new species, similar to the salamander. This discovery was the starting point of research about neoteny. It is not certain that '' Ambystoma velasci'' specimens were not included in the original shipment. Vilem Laufberger in Prague used thyroid hormone injections to induce an axolotl to grow into a terrestrial adult salamander. The experiment was repeated by Englishman Julian Huxley
Sir Julian Sorell Huxley (22 June 1887 – 14 February 1975) was an English evolutionary biologist, eugenicist, and internationalist. He was a proponent of natural selection, and a leading figure in the mid-twentieth century modern synthesis. ...
, who was unaware the experiment had already been done, using ground thyroids. Since then, experiments have been done often with injections of iodine or various thyroid hormones used to induce metamorphosis.
Neoteny has been observed in all salamander families in which it seems to be a survival mechanism, in aquatic environments only of mountain and hill, with little food and, in particular, with little iodine. In this way, salamanders can reproduce and survive in the form of a smaller larval stage, which is aquatic and requires a lower quality and quantity of food compared to the big adult, which is terrestrial. If the salamander larvae ingest a sufficient amount of iodine, directly or indirectly through cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
, they quickly begin metamorphosis and transform into bigger terrestrial adults, with higher dietary requirements. In fact, in some high mountain lakes there live dwarf forms of salmonids that are caused by deficiencies in food and, in particular, iodine, which causes cretinism and dwarfism
Dwarfism is a condition wherein an organism is exceptionally small, and mostly occurs in the animal kingdom. In humans, it is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than , regardless of sex; the average adult height among people with dw ...
due to hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
, as it does in humans.
Captive care
 The axolotl is a popular exotic pet like its relative, the tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum''). As for all poikilothermic organisms, lower temperatures result in slower metabolism and a very unhealthily reduced appetite. Temperatures at approximately to are suggested for captive axolotls to ensure sufficient food intake; stress resulting from more than a day's exposure to lower temperatures may quickly lead to disease and death, and temperatures higher than may lead to metabolic rate increase, also causing stress and eventually death. Chlorine, commonly added to
The axolotl is a popular exotic pet like its relative, the tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum''). As for all poikilothermic organisms, lower temperatures result in slower metabolism and a very unhealthily reduced appetite. Temperatures at approximately to are suggested for captive axolotls to ensure sufficient food intake; stress resulting from more than a day's exposure to lower temperatures may quickly lead to disease and death, and temperatures higher than may lead to metabolic rate increase, also causing stress and eventually death. Chlorine, commonly added to tapwater
Tap water (also known as faucet water, running water, or municipal water) is water supplied through a tap, a water dispenser valve. In many countries, tap water usually has the quality of drinking water. Tap water is commonly used for drinking, ...
, is harmful to axolotls. A single axolotl typically requires a tank. Axolotls spend the majority of the time at the bottom of the tank.
 Salts, such as
Salts, such as Holtfreter's solution
Holtfreter's solution (Holtfreter's medium) is a balanced salt solution that was developed by the developmental biologist Johannes Holtfreter for studying amphibian embryos and to reduce bacterial infections. As a specialised aqueous solution, it f ...
, are often added to the water to prevent infection.
In captivity, axolotls eat a variety of readily available foods, including trout and salmon pellets, frozen or live bloodworm Blood worm or bloodworm is an ambiguous term and can refer to:
* Larvae of a non-biting midge (family Chironomidae) containing hemoglobin
* ''Glycera'' (annelid), a polychaete often used for fishing bait
* Species of the Polychaeta subclass Scole ...
s, earthworms, and waxworms. Axolotls can also eat feeder fish, but care should be taken as fish may contain parasites.
Substrates are another important consideration for captive axolotls, as axolotls (like other amphibians and reptiles) tend to ingest bedding material together with food and are commonly prone to gastrointestinal obstruction and foreign body ingestion. Some common substrates used for animal enclosures can be harmful for amphibians and reptiles. Gravel (common in aquarium use) should not be used, and is recommended that any sand consists of smooth particles with a grain size of under 1mm. One guide to axolotl care for laboratories notes that bowel obstructions are a common cause of death, and recommends that no items with a diameter below 3 cm (or approximately the size of the animal's head) should be available to the animal.
There is some evidence that axolotls might seek out appropriately-sized gravel for use as gastroliths
A gastrolith, also called a stomach stone or gizzard stone, is a rock held inside a gastrointestinal tract. Gastroliths in some species are retained in the muscular gizzard and used to grind food in animals lacking suitable grinding teeth. In oth ...
based on experiments conducted at the University of Manitoba axolotl colony, but these studies are outdated and not conclusive. As there is no conclusive evidence pointing to gastrolith use, gravel should be avoided due to the high risk of impaction.
Cultural significance
The species is named after the Aztec deity Xolotl, who transformed himself into an axolotl. They continue to play an outsized cultural role in Mexico, and have appeared in cartoons and murals. In 2020, it was announced that the axolotl will be featured on the new design for Mexico's 50- peso banknote, along with images of maize andchinampa
Chinampa ( nah, chināmitl ) is a technique used in Mesoamerican agriculture which relies on small, rectangular areas of fertile arable land to grow crops on the shallow lake beds in the Valley of Mexico. They are built up on wetlands of a lake o ...
s.
See also
* Mudpuppies * Olm *Texas salamander
''Eurycea neotenes'', also known as the Texas salamander, Bexar County salamander, Edwards Plateau salamander, or Texas neotenic salamander, is a species of entirely aquatic, lungless salamander native to the United States. It is endemic to centr ...
* Texas blind salamander
The Texas blind salamander (''Eurycea rathbuni'') is a rare cave-dwelling troglobite amphibian native to San Marcos, Hays County, Texas, specifically the San Marcos Pool of the Edwards Aquifer.
Description
The species has a broad, flat, snout ...
* Lake Patzcuaro salamander
The Lake Patzcuaro salamander, locally known as achoque, ''Ambystoma dumerilii'', is a neotenic salamander species.
This salamander is found in Lake Pátzcuaro, a high-altitude lake in the Mexican state of Michoacán. This is located in the Mesa ...
* Barred tiger salamander
* Amphibious fish
Amphibious fish are fish that are able to leave water for extended periods of time. About 11 distantly related genera of fish are considered amphibious. This suggests that many fish genera independently evolved amphibious traits, a process known ...
* Handfish
* Regenerative biomedicine
References
External links
*Follow the Eggs, Hatchlings and Juveniles
Mating Dance and Laying Eggs
Follow the Eggs and Hatchlings (2nd Batch)
University of KY Axolotl Colony
The animal that’s everywhere and nowhere
*
"The Tao of Axolotl"
– thetolteciching.com; on folklore {{Authority control Amphibians described in the 18th century Animal models Animal testing on amphibians Animals bred for albinism on a large scale Critically endangered biota of Mexico Critically endangered fauna of North America Endemic amphibians of Mexico Mole salamanders Population genetics Regenerative biomedicine Taxa named by Frederick Polydore Nodder Taxa named by George Shaw Valley of Mexico