Avicranium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Avicranium'' is a 
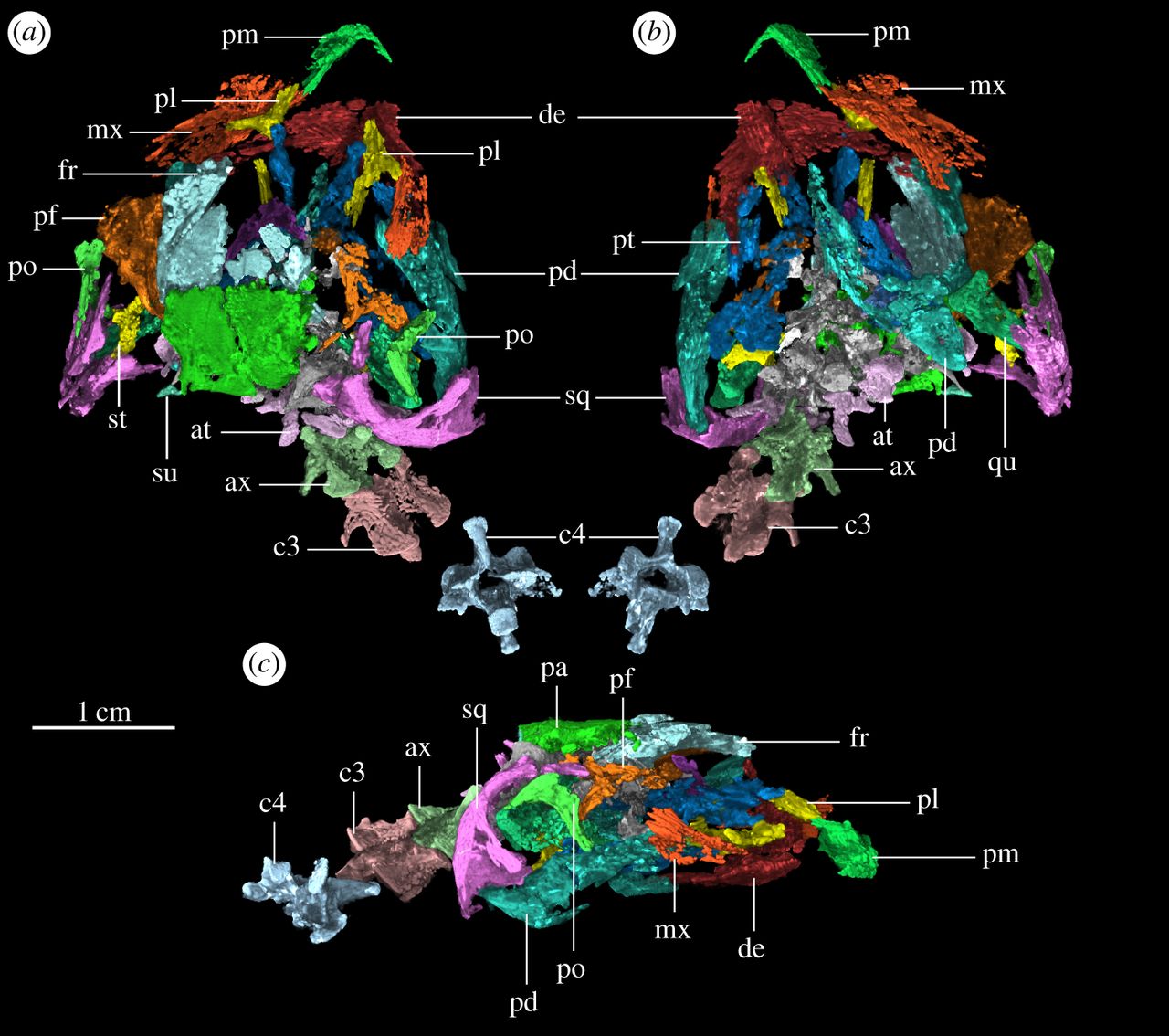 AMNH FARB 30834 can be recognized as a drepanosaur due to several traits of its vertebrae. The articular surfaces of its vertebral centres are heterocoelous (saddle-shaped). The neural spines are anteroposteriorly short and strongly anterodorsally inclined. These features closely resemble those of ''
AMNH FARB 30834 can be recognized as a drepanosaur due to several traits of its vertebrae. The articular surfaces of its vertebral centres are heterocoelous (saddle-shaped). The neural spines are anteroposteriorly short and strongly anterodorsally inclined. These features closely resemble those of ''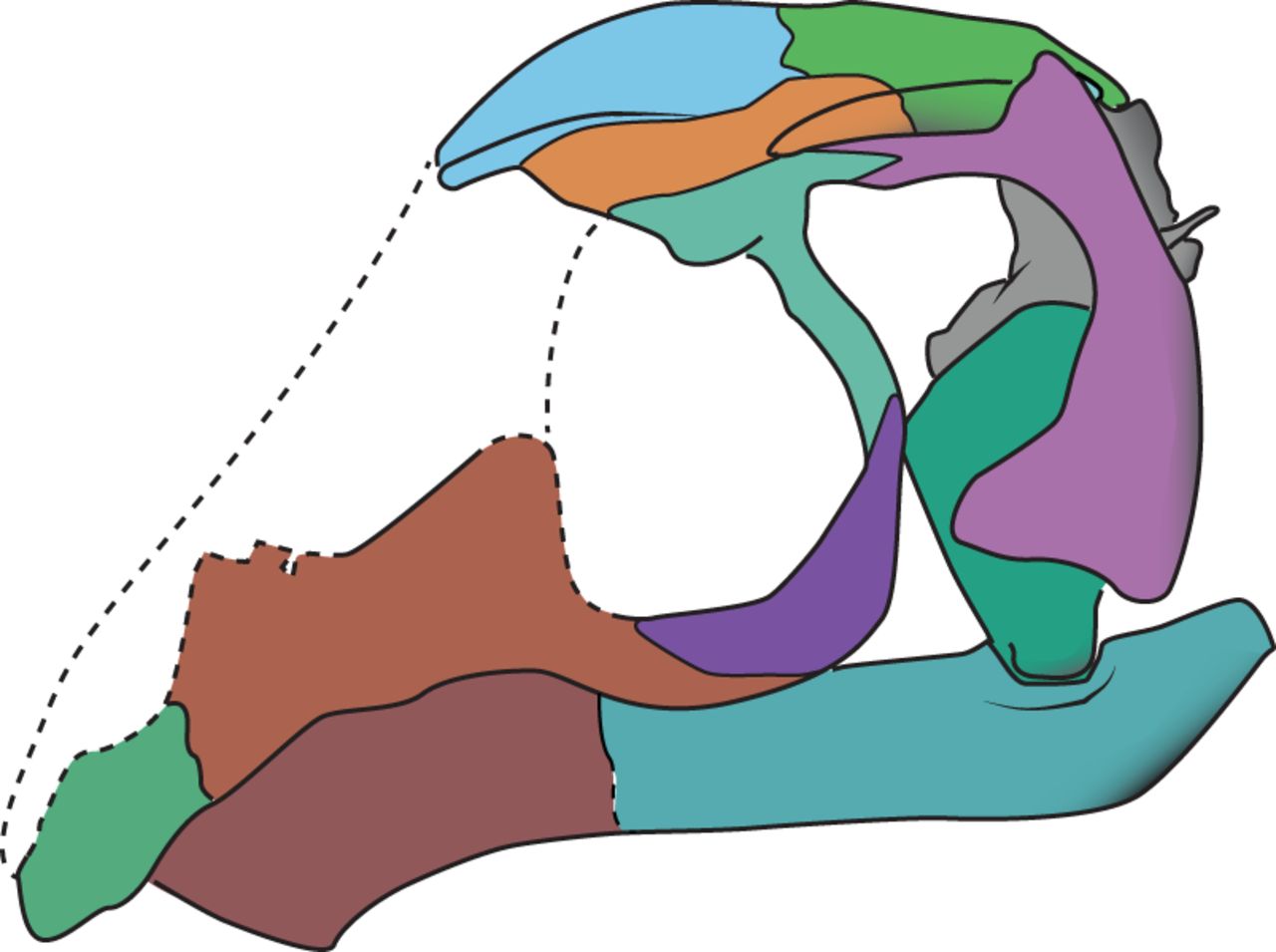 However, the most notable feature of AMNH FARB 30834 is its skull, which shares many similarities with the skulls of modern birds. The snout is slender and tapering, similar to that of ''
However, the most notable feature of AMNH FARB 30834 is its skull, which shares many similarities with the skulls of modern birds. The snout is slender and tapering, similar to that of ''
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of extinct drepanosaur
Drepanosaurs (members of the clade Drepanosauromorpha) are a group of extinct reptiles that lived between the Carnian and Rhaetian stages of the late Triassic Period, approximately between 230 and 210 million years ago. The various species of dre ...
reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
known from the Chinle Formation
The Chinle Formation is an Upper Triassic continental geological formation of fluvial, lacustrine, and palustrine to eolian deposits spread across the U.S. states of Nevada, Utah, northern Arizona, western New Mexico, and western Colorado. In Ne ...
of the late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch ...
. The type species of ''Avicranium'' is ''Avicranium renestoi''. "''Avicranium''" is Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for "bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ...
cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
", in reference to its unusual bird-like skull, while "''renestoi''" references Silvio Renesto, a paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
known for studies of Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
drepanosaurs.
Discovery
Theholotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
and only known specimen of ''Avicranium'' is AMNH FARB 30834, a disarticulated skull attached to a few cervical (neck) vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
e. This specimen hails from the ''Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period from t ...
'' (or Whitaker) quarry at Ghost Ranch
Ghost Ranch is a retreat and education center located close to the village of Abiquiú in Rio Arriba County in north central New Mexico, United States. It was the home and studio of Georgia O'Keeffe, as well as the subject of many of her painti ...
in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
, USA
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. This quarry belongs to the ' siltstone member' of the Chinle formation, which corresponds to the late Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic Period. It has the rank of an age (geochronology) or stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227 to million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian.
Stratigraphic defi ...
to early Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age ...
stages of the Triassic. Various unprepared blocks from this locality were excavated by American Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 inter ...
field parties during the 1940s. Long believed to only contain multiple specimens of the early dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
''Coelophysis'', these blocks are now known to contain a multitude of different Triassic reptiles. AMNH FARB 30834 was uncovered during the preparation of a block containing the holotype of ''Effigia okeeffeae
''Effigia'' was an extinct genus of shuvosaurid known from the Late Triassic of New Mexico, south-western USA. With a bipedal stance, long neck, and a toothless beaked skull, ''Effigia'' and other shuvosaurids bore a resemblance to the ornithomim ...
'', a large shuvosaurid
Shuvosauridae is an extinct family (biology), family of theropod-like pseudosuchians within the clade Poposauroidea. Shuvosaurids existed in North America (United States) and South America (Argentina) during the Late Triassic period (late Carnian ...
pseudosuchia
Pseudosuchia is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs". Prior to ...
n. Multiple other drepanosaur vertebrae and limb fragments have also been found in the block, although it is unclear whether they belong to the same specimen as AMNH FARB 308344.
Despite AMNH FARB 30834 being disarticulated and partially covered by the rock matrix, many of its bones are well-preserved and the specimen as a whole was micro-CT
X-ray microtomography, like tomography and X-ray computed tomography, uses X-rays to create cross-sections of a physical object that can be used to recreate a virtual model (3D model) without destroying the original object. The prefix ''micro-'' ...
scanned, revealing elements hidden under rock. This scan allowed the skull to be reconstructed in 3D using digital software. An endocast
An endocast is the internal cast of a hollow object, often referring to the cranial vault in the study of brain development in humans and other organisms. Endocasts can be artificially made for examining the properties of a hollow, inaccessible sp ...
of the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
was also digitally constructed from the skull. ''Avicranium'' has the most well-preserved skull material of any drepanosaur.
Description
 AMNH FARB 30834 can be recognized as a drepanosaur due to several traits of its vertebrae. The articular surfaces of its vertebral centres are heterocoelous (saddle-shaped). The neural spines are anteroposteriorly short and strongly anterodorsally inclined. These features closely resemble those of ''
AMNH FARB 30834 can be recognized as a drepanosaur due to several traits of its vertebrae. The articular surfaces of its vertebral centres are heterocoelous (saddle-shaped). The neural spines are anteroposteriorly short and strongly anterodorsally inclined. These features closely resemble those of ''Drepanosaurus
''Drepanosaurus'' (; "sickle lizard") is a genus of arboreal (tree-dwelling) reptile that lived during the Triassic Period. It is a member of the Drepanosauridae, a group of diapsid reptiles known for their prehensile tails. ''Drepanosaurus'' wa ...
''.
 However, the most notable feature of AMNH FARB 30834 is its skull, which shares many similarities with the skulls of modern birds. The snout is slender and tapering, similar to that of ''
However, the most notable feature of AMNH FARB 30834 is its skull, which shares many similarities with the skulls of modern birds. The snout is slender and tapering, similar to that of ''Megalancosaurus
''Megalancosaurus'' is a genus of extinct reptile from the Late Triassic Dolomia di Forni Formation and Zorzino Limestone of northern Italy, and one of the best known drepanosaurids. The type species is ''M. preonensis''; a translation of the ...
'', although it differs from ''Megalancosaurus'' by being completely toothless. The frontal
Front may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film
* ''The Front'', 1976 film
Music
*The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and ea ...
, postfrontal, and postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ve ...
bones (above and behind the eyes) project outwards, forcing the orbits to face forwards. The frontal and parietal bones are both broad and thick, creating a high and domed cranium. According to the digital endocast of the specimen, this domed cranium held an enlarged brain with large optic lobes.
On the other hand, the skull also possesses many primitive features. The squamosal The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including ...
is tall and anteroposteriorly broad, and possesses bony plates which frame the quadrate from the side and rear. This is similar to the condition in captorhinids
Captorhinidae (also known as cotylosaurs) is an extinct family of tetrapods, traditionally considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea.
Description
C ...
and ''Araeoscelis
''Araeoscelis'' (from el, αραιά , 'thin' and el, σκελίς , 'ribs of beef') is an extinction, extinct genus of reptile, and one of the earliest diapsids. Fossils have been found in the Nocona Formation, Nocona, Arroyo Formation, Arroyo ...
'', but unlike that of neodiapsids
Neodiapsida is a clade, or major branch, of the reptilian family tree, typically defined as including all diapsids apart from some early primitive types known as the araeoscelidians. Modern reptiles and birds belong to the neodiapsid subclade Sau ...
, which only have the quadrate framed from the side. The quadrate itself is also stouter than that of neodiapsids and lacks a concave rear edge and a dorsal extension which articulates with the squamosal. The occipital condyle
The occipital condyles are undersurface protuberances of the occipital bone in vertebrates, which function in articulation with the superior facets of the atlas vertebra.
The condyles are oval or reniform (kidney-shaped) in shape, and their anteri ...
of the braincase possesses a deep pit, while the foramen ovale is very large.
The stapes
The ''stapes'' or stirrup is a bone in the middle ear of humans and other animals which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the foot ...
is massive, similar to the condition in other early reptiles. Combined with a straight quadrate without a tympanic crest, this indicates that ''Avicranium'' (and presumably other drepanosaurs) lacked a tympanic membrane
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air ...
(eardrum), and that the drepanosauromorph lineage evolved before more advanced diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years ago ...
s (such as sauria
Sauria is the clade containing the most recent common ancestor of archosaurs (such as crocodilians, dinosaurs, etc.) and lepidosaurs ( lizards and kin), and all its descendants. Since most molecular phylogenies recover turtles as more closely re ...
ns) acquired tympanic membranes.
Avicranium can be distinguished from ''Hypuronector
''Hypuronector'' is a genus of extinct drepanosaur reptile from the Triassic Period that lived in what is now New Jersey. The etymology of the name translates as "deep-tailed swimmer from the lake," in reference to its assumed aquatic habits hypo ...
'', ''Megalancosaurus'', and '' Vallesaurus'' (the only other drepanosaurs with preserved skulls) due to the following features:
* The complete absence of teeth.
* A tall and triangular retroarticular process.
* Cervical neural spines which are approximately as wide as they are long.
Paleobiology
The binocular eyes and enlarged brain of Avicranium are likely adaptations to anarboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the Animal locomotion, locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. Th ...
lifestyle, as such a lifestyle requires advanced sensory processing, such as depth perception
Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions. Depth perception happens primarily due to stereopsis an ...
and three-dimensional navigation. It is very likely that these features convergently evolved
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
with those of pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to ...
s and modern birds, which would require similar sensory processing during flight
Flight or flying is the process by which an object moves through a space without contacting any planetary surface, either within an atmosphere (i.e. air flight or aviation) or through the vacuum of outer space (i.e. spaceflight). This can be a ...
. An arboreal lifestyle has been previously proposed for other members of the drepanosauromorph lineage.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q47454090 Drepanosaurs Late Triassic reptiles of North America Fossil taxa described in 2017 Prehistoric reptile genera