Autumn Colors (4099639400) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Autumn leaf color is a phenomenon that affects the normal green leaves of many

 During the summer growing season, phosphate is at a high level. It has a vital role in the breakdown of the sugars manufactured by chlorophyll, but in autumn, phosphate, along with the other chemicals and nutrients, moves out of the leaf into the
During the summer growing season, phosphate is at a high level. It has a vital role in the breakdown of the sugars manufactured by chlorophyll, but in autumn, phosphate, along with the other chemicals and nutrients, moves out of the leaf into the
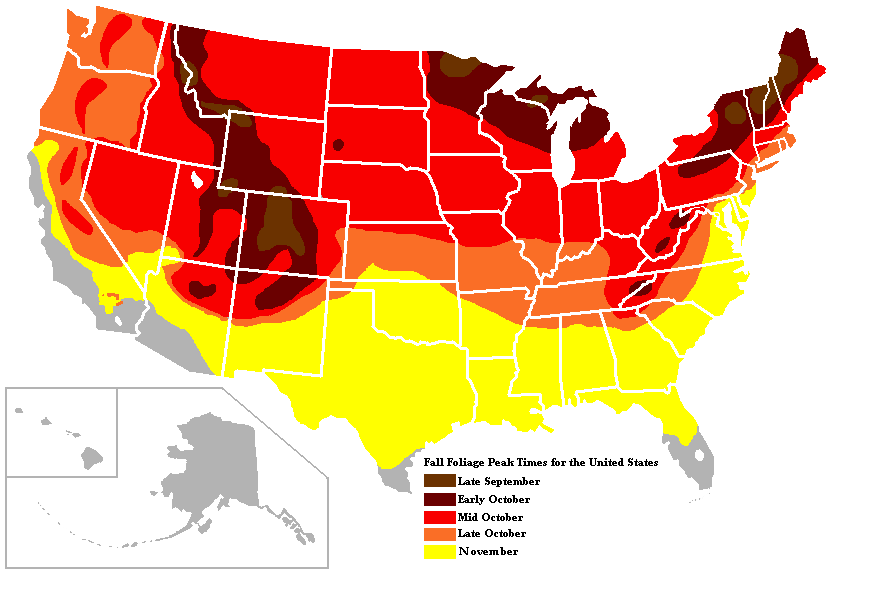 According to the
According to the
 In the southern hemisphere, colorful autumn foliage can be observed in southern and central
In the southern hemisphere, colorful autumn foliage can be observed in southern and central
Autumnal tints by Henry David ThoreauIdentifying Common trees in Autumn by their colors
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Autumn Leaf Color Leaf songs Plant physiology Leaves Pigmentation
deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
s and shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees ...
s by which they take on, during a few weeks in the autumn season, various shades of yellow, orange, red, purple, and brown. The phenomenon is commonly called autumn colours or autumn foliage in British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
and fall colors, fall foliage, or simply foliage in American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ...
.
In some areas of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, "leaf peeping
__NOTOC__
Leaf peeping is an informal term in the United States and Canada for the activity in which people travel to view and photograph the fall foliage in areas where leaves change colors in autumn,
particularly in northern New England, Appalac ...
" tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
is a major contribution to economic activity. This tourist activity occurs between the beginning of color changes and the onset of leaf fall, usually around September and October in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
and April to May in the Southern Hemisphere.
Chlorophyll and the green/yellow/orange colors
A greenleaf
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, ste ...
is green because of the presence of a pigment known as chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
, which is inside an organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
called a chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
. When abundant in the leaf's cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
, as during the growing season, the chlorophyll's green color dominates and masks out the colors of any other pigments that may be present in the leaf. Thus, the leaves of summer are characteristically green.
Chlorophyll has a vital function: it captures solar rays and uses the resulting energy in the manufacture of the plant's food simple sugars which are produced from water and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
. These sugars are the basis of the plant's nourishment the sole source of the carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
s needed for growth and development. In their food-manufacturing process, the chlorophylls break down, thus are being continually "used up". During the growing season, however, the plant replenishes the chlorophyll so that the supply remains high and the leaves stay green.
In late summer, with daylight hours shortening and temperatures cooling, the vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated b ...
s that carry fluids into and out of the leaf are gradually closed off as a layer of special cork
Cork or CORK may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
***Wine cork
Places Ireland
* Cork (city)
** Metropolitan Cork, also known as G ...
cells forms at the base of each leaf. As this cork layer develops, water and mineral intake into the leaf is reduced, slowly at first, and then more rapidly. During this time, the amount of chlorophyll in the leaf begins to decrease. Often, the veins are still green after the tissues between them have almost completely changed color.
Chlorophyll is located in the thylakoid
Thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thyl ...
membrane of the chloroplast and it is composed of an apoprotein along with several ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
s, the most important of which are chlorophylls a and b. In the autumn, this complex is broken down. Chlorophyll degradation is thought to occur first. Research suggests that the beginning of chlorophyll degradation is catalyzed by chlorophyll b reductase, which reduces chlorophyll b to 7‑hydroxymethyl chlorophyll a, which is then reduced to chlorophyll a. This is believed to destabilize the complex, at which point breakdown of the apoprotein occurs. An important enzyme in the breakdown of the apoprotein is FtsH6, which belongs to the FtsH family of protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
s.
Chlorophylls degrade into colorless tetrapyrrole
Tetrapyrroles are a class of chemical compounds that contain four pyrrole or pyrrole-like rings. The pyrrole/pyrrole derivatives are linked by ( =- or -- units), in either a linear or a cyclic fashion. Pyrroles are a five-atom ring with four car ...
s known as nonfluorescent chlorophyll catabolites.
As the chlorophylls degrade, the hidden pigments of yellow xanthophyll
Xanthophylls (originally phylloxanthins) are yellow pigments that occur widely in nature and form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group; the other division is formed by the carotenes. The name is from Greek (, "yellow") and (, "l ...
s and orange beta-carotene are revealed.
Pigments that contribute to other colors

Carotenoids
Carotenoid
Carotenoids (), also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic compound, organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and Fungus, fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpki ...
s are present in the leaves throughout the year, but their orange-yellow colors are usually masked by green chlorophyll. As autumn approaches, certain influences both inside and outside the plant cause the chlorophylls to be replaced at a slower rate than they are being used up. During this period, with the total supply of chlorophylls gradually dwindling, the "masking" effect slowly fades away. Then other pigments present (along with the chlorophylls) in the leaf's cells begin to show through. These are carotenoids and they provide colorations of yellow, brown, orange, and the many hues in between.
The carotenoids occur, along with the chlorophyll pigments, in tiny structures called plastid
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosy ...
s, within the cells of leaves. Sometimes, they are in such abundance in the leaf that they give a plant a yellow-green color, even during the summer. Usually, however, they become prominent for the first time in autumn, when the leaves begin to lose their chlorophyll.
Carotenoids are common in many living things, giving characteristic color to carrot
The carrot ('' Daucus carota'' subsp. ''sativus'') is a root vegetable, typically orange in color, though purple, black, red, white, and yellow cultivars exist, all of which are domesticated forms of the wild carrot, ''Daucus carota'', nat ...
s, corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
, canaries, and daffodil
''Narcissus'' is a genus of predominantly spring flowering perennial plants of the amaryllis family, Amaryllidaceae. Various common names including daffodil,The word "daffodil" is also applied to related genera such as '' Sternbergia'', ''Is ...
s, as well as egg yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example bec ...
s, rutabaga
Rutabaga (; North American English) or swede (British English and some Commonwealth English) is a root vegetable, a form of ''Brassica napus'' (which also includes rapeseed). Other names include Swedish turnip, neep (Scots), and turnip (Scott ...
s, buttercup
''Ranunculus'' is a large genus of about almost 1700 to more than 1800 species of flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae. Members of the genus are known as buttercups, spearworts and water crowfoots.
The genus is distributed in Europe, ...
s, and banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", distinguis ...
s.
Their brilliant yellows and oranges tint the leaves of such hardwood species as hickories, ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non- gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
, maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http ...
, yellow poplar
''Liriodendron tulipifera''—known as the tulip tree, American tulip tree, tulipwood, tuliptree, tulip poplar, whitewood, fiddletree, and yellow-poplar—is the North American representative of the two-species genus ''Liriodendron'' (the other ...
, aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species; some, but not all, are classified by botanists in the section ''Populus'', of the ''Populus'' genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
*'' Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (China ...
, birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech-oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 30 ...
, black cherry
''Prunus serotina'', commonly called black cherry,World Economic Plants: A Standard Reference, Second Edition'. CRC Press; 19 April 2016. . p. 833–. wild black cherry, rum cherry, or mountain black cherry, is a deciduous tree or shrub of the g ...
, sycamore
Sycamore is a name which has been applied to several types of trees, but with somewhat similar leaf forms. The name derives from the ancient Greek ' (''sūkomoros'') meaning "fig-mulberry".
Species of trees known as sycamore:
* ''Acer pseudoplata ...
, cottonwood, sassafras
''Sassafras'' is a genus of three extant and one extinct species of deciduous trees in the family Lauraceae, native to eastern North America and eastern Asia.Wolfe, Jack A. & Wehr, Wesley C. 1987. The sassafras is an ornamental tree. "Middle Eoc ...
, and alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few sp ...
. Carotenoids are the dominant pigment in coloration of about 15-30% of tree species.
Anthocyanins
The reds, the purples, and their blended combinations that decorate autumn foliage come from another group of pigments in the cells calledanthocyanin
Anthocyanins (), also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart gave the name Anthokyan to a chemical compo ...
s. Unlike the carotenoids, these pigments are not present in the leaf throughout the growing season, but are actively produced towards the end of summer. They develop in late summer in the sap
Sap is a fluid transported in xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a separa ...
of the cells of the leaf, and this development is the result of complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
interactions of many influences both inside and outside the plant. Their formation depends on the breakdown of sugars in the presence of bright light as the level of phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
in the leaf is reduced.
 During the summer growing season, phosphate is at a high level. It has a vital role in the breakdown of the sugars manufactured by chlorophyll, but in autumn, phosphate, along with the other chemicals and nutrients, moves out of the leaf into the
During the summer growing season, phosphate is at a high level. It has a vital role in the breakdown of the sugars manufactured by chlorophyll, but in autumn, phosphate, along with the other chemicals and nutrients, moves out of the leaf into the stem
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushro ...
of the plant. When this happens, the sugar-breakdown process changes, leading to the production of anthocyanin pigments. The brighter the light during this period, the greater the production of anthocyanins and the more brilliant the resulting color display. When the days of autumn are bright and cool, and the nights are chilly but not freezing, the brightest colorations usually develop.
Anthocyanins temporarily color the edges of some of the very young leaves as they unfold from the bud
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be spec ...
s in early spring. They also give the familiar color to such common fruits as cranberries
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry m ...
, red apples, blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bi ...
, cherries
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The nam ...
, strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
, and plums
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
.
Anthocyanins are present in about 10% of tree species in temperate regions, although in certain areas most famously northern New England up to 70% of tree species may produce the pigment. In autumn forests, they appear vivid in the maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http ...
s, oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
s, sourwood
''Oxydendrum arboreum'', the sourwood or sorrel tree, is the sole species in the genus ''Oxydendrum'', in the family Ericaceae. It is native to eastern North America, from southern Pennsylvania south to northwest Florida and west to southern I ...
, sweetgums, dogwood
''Cornus'' is a genus of about 30–60 species of woody plants in the family Cornaceae, commonly known as dogwoods, which can generally be distinguished by their blossoms, berries, and distinctive bark. Most are deciduous trees or shrub ...
s, tupelo
Tupelo , genus ''Nyssa'' , is a small genus of deciduous trees with alternate, simple leaves. It is sometimes included in the subfamily Nyssoideae of the dogwood family, Cornaceae, but is placed by other authorities in the family Nyssaceae. In ...
s, cherry trees
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The na ...
, and persimmon
The persimmon is the edible fruit of a number of species of trees in the genus ''Diospyros''. The most widely cultivated of these is the Oriental persimmon, ''Diospyros kaki'' ''Diospyros'' is in the family Ebenaceae, and a number of non-pers ...
s. These same pigments often combine with the carotenoids' colors to create the deeper orange, fiery reds, and bronzes typical of many hardwood species.
Function of autumn colors
Deciduous plants were traditionally believed to shed their leaves in autumn primarily because the high costs involved in their maintenance would outweigh the benefits from photosynthesis during the winter period of low light availability and cold temperatures. In many cases, this turned out to be oversimplistic other factors involved include insect predation, water loss, and damage from high winds or snowfall. Anthocyanins, responsible for red-purple coloration, are actively produced in autumn, but not involved in leaf-drop. A number of hypotheses on the role of pigment production in leaf-drop have been proposed, and generally fall into two categories: interaction with animals, and protection from nonbiological factors.Photoprotection
According to the photoprotection theory, anthocyanins protect the leaf against the harmful effects of light at low temperatures. The leaves are about to fall, so protection is not of extreme importance for the tree. Photo-oxidation and photoinhibition, however, especially at low temperatures, make the process of reabsorbing nutrients less efficient. By shielding the leaf with anthocyanins, according to the photoprotection theory, the tree manages to reabsorb nutrients (especially nitrogen) more efficiently.Coevolution
coevolution
In biology, coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection. The term sometimes is used for two traits in the same species affecting each other's evolution, as well ...
theory, the colors are warning signals to insects like aphids that use trees as a host for the winter. If the colors are linked to the amount of chemical defenses against insects, then the insects will avoid red leaves and increase their fitness; at the same time, trees with red leaves have an advantage because they reduce their parasite load. This has been shown in the case of apple tree
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ' ...
s where some domesticated apple varieties, unlike wild ones, lack red leaves in autumn. A greater proportion of aphids that avoid apple trees with red leaves manage to grow and develop compared to those that do not. A trade-off, moreover, exists between fruit size, leaf color, and aphids resistance as varieties with red leaves have smaller fruits, suggesting a cost to the production of red leaves linked to a greater need for reduced aphid infestation.
Consistent with red-leaved trees providing reduced survival for aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A t ...
s, tree species with bright leaves tend to select for more specialist aphid pests than do trees lacking bright leaves (autumn colors are useful only in those species coevolving with insect pests in autumn). One study found that simulating insect herbivory (leaf-eating damage) on maple trees showed earlier red coloration than trees that were not damaged.
The coevolution theory of autumn colors was proposed by W. D. Hamilton
William Donald Hamilton (1 August 1936 – 7 March 2000) was a British evolutionary biologist, recognised as one of the most significant evolutionary theorists of the 20th century.
Hamilton became known for his theoretical work expounding a ...
in 2001 as an example of evolutionary signalling theory
Within evolutionary biology, signalling theory is a body of theoretical work examining communication between individuals, both within species and across species. The central question is when organisms with conflicting interests, such as in sex ...
. With biological signals such as red leaves, it is argued that because they are costly to produce, they are usually honest, so signal the true quality of the signaller with low-quality individuals being unable to fake them and cheat. Autumn colors would be a signal if they are costly to produce, or be impossible to fake (for example if autumn pigments were produced by the same biochemical pathway that produces the chemical defenses against the insects).
The change of leaf colors prior to fall have also been suggested as adaptations that may help to undermine the camouflage of herbivores.
Many plants with berries attract birds with especially visible berry and/or leaf color, particularly bright red. The birds get a meal, while the shrub, vine, or typically small tree gets undigested seeds carried off and deposited with the birds' manure. Poison ivy is particularly notable for having bright-red foliage drawing birds to its off-white seeds (which are edible for birds, but not most mammals).
Allelopathy
The brilliant red autumn color of some species of maple is created by processes separate from those in chlorophyll breakdown. When the tree is struggling to cope with the energy demands of a changing and challenging season, maple trees are involved in an additional metabolic expenditure to create anthocyanins. These anthocyanins, which create the visual red hues, have been found to aid in interspecific competition by stunting the growth of nearby saplings (allelopathy
Allelopathy is a biological phenomenon by which an organism produces one or more biochemicals that influence the germination, growth, survival, and reproduction of other organisms. These biochemicals are known as allelochemicals and can have be ...
).
Tourism
Although some autumn coloration occurs wherever deciduous trees are found, the most brightly colored autumn foliage is found in the northern hemisphere, including most of southern mainlandCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, some areas of the northern United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, Northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ra ...
and Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
north of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
, the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
region of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
near the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
, and Eastern Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
(including much of northern and eastern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, and as well as Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
).
 In the southern hemisphere, colorful autumn foliage can be observed in southern and central
In the southern hemisphere, colorful autumn foliage can be observed in southern and central Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
, the south
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
and southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
regions of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, and southeastern Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
(including Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
).
Climate influences
Compared to Western Europe (excluding Southern Europe), North America provides many more arbor species (more than 800 species and about 70 oaks, compared to 51 and three, respectively, in Western Europe) which adds many more different colors to the spectacle. The main reason is the different effect of theIce age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
s while in North America, species were protected in more southern regions along north–south ranging mountains, this was not the case in much of Europe.
Global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
and rising carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere may delay the usual autumn spectacle of changing colors and falling leaves in northern hardwood forests in the future, and increase forest productivity. Specifically, higher autumn temperatures in the Northeastern United States is delaying the color change. Experiments with poplar trees showed that they stayed greener longer with higher CO2 levels, independent of temperature changes. However, the experiments over two years were too brief to indicate how mature forests may be affected over time. Other studies using 150 years of herbarium
A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a collection of preserved plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study.
The specimens may be whole plants or plant parts; these will usually be in dried form mounted on a sheet of paper (called ...
specimens found more than a one month delay in the onset of autumn since the 19th century, and found that insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
, viral, and drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
stress can also affect the timing of fall coloration in maple trees. Also, other factors, such as increasing ozone levels close to the ground (tropospheric ozone
Ground-level ozone (O3), also known as surface-level ozone and tropospheric ozone, is a trace gas in the troposphere (the lowest level of the Earth's atmosphere), with an average concentration of 20–30 parts per billion by volume (ppbv), with cl ...
pollution), can negate the beneficial effects of elevated carbon dioxide.
References
Notes
Further reading
*External links
Autumnal tints by Henry David Thoreau
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Autumn Leaf Color Leaf songs Plant physiology Leaves Pigmentation