Austin is the
capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, Department (country subdivision), department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city ...
of the
U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sover ...
of
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, as well as the
seat
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair (furniture), ...
and largest city of
Travis County
Travis County is located in south central Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,290,188. It is the fifth-most populous county in Texas. Its county seat is Austin, the capital of Texas. The county was established in 1840 and is na ...
, with portions extending into
Hays and
Williamson counties. Incorporated on December 27, 1839, it is the
11th-most-populous city in the United States,
the
fourth-most-populous city in Texas, the
second-most-populous state capital city, and the most populous state capital that is not also the most populous city in its state.
It has been one of the fastest growing large cities in the United States since 2010.
Downtown Austin
Downtown Austin is the central business district of Austin, Texas. Downtown is located on the north bank of the Colorado River. The approximate borders of Downtown include Lamar Boulevard to the west, Martin Luther King Jr. Boulevard and the Un ...
and
Downtown San Antonio
Downtown San Antonio is the central business district of San Antonio, Texas, United States. It also serves as the urban core of Greater San Antonio, a metropolitan area with nearly 2.5 million people.
In addition to being encircled by Loops 1604 ...
are approximately apart, and both fall along the
Interstate 35
Interstate 35 (I-35) is a major Interstate Highway in the central United States. As with most primary Interstates that end in a five, it is a major cross-country, north–south route. It stretches from Laredo, Texas, near the Mexican border ...
corridor. Some observers believe that the two regions may some day form a new "metroplex" similar to
Dallas and Fort Worth. Austin is the southernmost state capital in the
contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
and is considered a "
Beta −"
global city as categorized by the
Globalization and World Cities Research Network
The Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) is a think tank that studies the relationships between world cities in the context of globalization. It is based in the geography department of Loughborough University in Leicestershi ...
.
As of 2021, Austin had an estimated population of 964,177,
up from 961,855 at the
2020 census. The city is the cultural and economic center of the metropolitan statistical area, which had an estimated population of 2,295,303 , a roughly 84% increase from the year 2000.
Located in within the greater
Texas Hill Country
The Texas Hill Country is a geographic region of Central and South Texas, forming the southeast part of the Edwards Plateau. Given its location, climate, terrain, and vegetation, the Hill Country can be considered the border between the Ameri ...
, it is home to numerous lakes, rivers, and waterways, including
Lady Bird Lake
Lady Bird Lake (formerly, and still colloquially referred to as Town Lake) is a river-like reservoir on the Colorado River in Austin, Texas, United States. The City of Austin created the reservoir in 1960 as a cooling pond for a new city power p ...
and
Lake Travis
Lake Travis is a reservoir on the Colorado River in central Texas in the United States.
Serving principally as a flood-control reservoir, Lake Travis' historical minimum to maximum water height change is nearly 100 feet. In 2018 alone, it saw ...
on the
Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid drainage basin, watershed that encompasses parts of ...
,
Barton Springs
Barton Springs is a set of four natural water springs located at Barton Creek on the grounds of Zilker Park in Austin, Texas, resulting from water flowing through the Edwards Aquifer. The largest spring, Main Barton Spring (also known as Partheni ...
,
McKinney Falls, and
Lake Walter E. Long
Lake Walter E. Long (also known as Decker Lake) is a power plant cooling reservoir on Decker Creek in Austin, Texas. The reservoir was officially impounded in 1967 and serves to provide water for turbines used in the production of electricity ...
.
Residents of Austin are known as
Austinites.
They include a diverse mix of government employees, college students, musicians, high-tech workers, digital marketers, and
blue-collar worker
A blue-collar worker is a working class person who performs manual labor. Blue-collar work may involve skilled or unskilled labor. The type of work may involving manufacturing, warehousing, mining, excavation, electricity generation and powe ...
s. The city's official slogan promotes Austin as "The Live Music Capital of the World", a reference to the city's many musicians and live music venues, as well as the long-running
PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcasting, public broadcaster and Non-commercial activity, non-commercial, Terrestrial television, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly fu ...
TV concert series ''
Austin City Limits
''Austin City Limits'' is an American live music television program recorded and produced by Austin PBS. The show helped Austin become widely known in the United States as the "Live Music Capital of the World", and is the only television show t ...
''.
The city also adopted "
Silicon Hills
Silicon Hills is a nickname for the cluster of high-tech companies in the Austin metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Texas. Silicon Hills has been a nickname for Austin since the mid-1990s. The name is analogous to Silicon Valley, but refers ...
" as a nickname in the 1990s due to a rapid influx of technology and development companies. In recent years, some Austinites have adopted the unofficial slogan "
Keep Austin Weird
''Keep Austin Weird'' is the slogan adopted by the Austin Independent Business Alliance to promote small businesses in Austin, Texas. It is intended to promote local businesses and is inspired by comments made by Red Wassenich in 2000 while givin ...
", which refers to the desire to protect small, unique, and local businesses from being overrun by large corporations.
Since the late 19th century, Austin has also been known as the "
City of the Violet Crown
City of the Violet Crown is a term for at least two cities, Athens, Greece and Austin, Texas.
Athens, Greece
In one of his surviving fragments (fragment 76), the lyric poet Pindar wrote of Athens:
The climate of Attica is characterised by low h ...
", because of the colorful glow of light across the hills just after sunset.
In 1987, Austin originated and remains the site for
South by Southwest
South by Southwest, abbreviated as SXSW and colloquially referred to as South By, is an annual conglomeration of parallel film, interactive media, and music festivals and Convention (meeting), conferences organized jointly that take place in m ...
(stylized as SXSW and colloquially referred to as ''South By''), an annual conglomeration of parallel
film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
,
interactive media
Interactive media normally refers to products and services on digital computer-based systems which respond to the user's actions by presenting content such as text, moving image, animation, video and audio. Since its early conception, various fo ...
, and
music festival
A music festival is a community event with performances of singing and instrument playing that is often presented with a theme such as musical genre (e.g., rock, blues, folk, jazz, classical music), nationality, locality of musicians, or h ...
s and
conferences
A conference is a meeting of two or more experts to discuss and exchange opinions or new information about a particular topic.
Conferences can be used as a form of group decision-making, although discussion, not always decisions, are the main pu ...
that take place in mid-March.
Emerging from a strong economic focus on government and education, since the 1990s, Austin has become a center for technology and business.
The technology roots in Austin can be traced back to the 1960s when Tracor (now BAE Systems), a major defense electronics contractor, began operation in the city in 1962. IBM followed in 1967, opening a facility to produce its Selectric typewriters. Texas Instruments setup in Austin two years later, Motorola (now NXP Semiconductors) started semiconductor chip manufacturing in 1974. BAE Systems, IBM, and NXP Semiconductors still have campuses and manufacturing operations in Austin as of 2022. A number of
Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for their respective fiscal years. The list includes publicly held companies, along ...
companies have headquarters or regional offices in Austin, including
3M,
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD),
Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology c ...
,
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
,
Facebook (Meta),
Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...
,
IBM,
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
,
NXP Semiconductors
NXP Semiconductors N.V. (NXP) is a Dutch semiconductor designer and manufacturer with headquarters in Eindhoven, Netherlands. The company employs approximately 31,000 people in more than 30 countries. NXP reported revenue of $11.06 billion in 2 ...
,
Oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word '' ...
,
Tesla,
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globall ...
, and
Whole Foods Market
Whole Foods Market IP, Inc., a subsidiary of Amazon, is an upscale American multinational supermarket chain headquartered in Austin, Texas, which sells products free from hydrogenated fats and artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. A US ...
.
Dell
Dell is an American based technology company. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies.
Dell sells personal computers (PCs), servers, data ...
's worldwide headquarters is located in the nearby suburb of
Round Rock
Round Rock is a city in the U.S. state of Texas, in Williamson County, Texas, Williamson County (with a small part in Travis County, Texas, Travis County), which is a part of the Greater Austin metropolitan area. Its population is 119,468 as of ...
. With regard to education, Austin is the home of the
University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
, which is one of the largest universities in the U.S., with over 50,000 students. In 2021, Austin became home to the
Austin FC
Austin FC is an American professional soccer club based in Austin, Texas. The club competes in Major League Soccer (MLS) as a member of the Western Conference. Founded in 2018, the club began play in the 2021 season. Their home stadium is Q2 ...
, the first (and currently only)
major professional sports league in the city.
History
Austin, Travis County and Williamson County have been the site of human habitation since at least 9200 BC. The area's earliest known inhabitants lived during the late
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
(Ice Age) and are linked to the
Clovis culture
The Clovis culture is a prehistoric Paleoamerican culture, named for distinct stone and bone tools found in close association with Pleistocene fauna, particularly two mammoths, at Blackwater Locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, in 1936 ...
around 9200 BC (over 11,200 years ago), based on evidence found throughout the area and documented at the much-studied
Gault Site, midway between
Georgetown and
Fort Hood
Fort Hood is a United States Army post located near Killeen, Texas. Named after Confederate General John Bell Hood, it is located halfway between Austin and Waco, about from each, within the U.S. state of Texas. The post is the headquarters ...
.
When settlers arrived from Europe, the
Tonkawa
The Tonkawa are a Native American tribe indigenous to present-day Oklahoma. Their Tonkawa language, now extinct, is a linguistic isolate.
Today, Tonkawa people are enrolled in the federally recognized Tonkawa Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma.
...
tribe inhabited the area. The
Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in La ...
s and
Lipan Apaches
Lipan Apache are a band of Apache, a Southern Athabaskan Indigenous people, who have lived in the Southwest and Southern Plains for centuries. At the time of European and African contact, they lived in New Mexico, Colorado, Oklahoma, Texas, a ...
were also known to travel through the area. Spanish colonists, including the
Espinosa-
Olivares-
Aguirre expedition, traveled through the area, though few permanent settlements were created for some time.
In 1730, three
Catholic missions
Missionary work of the Catholic Church has often been undertaken outside the geographically defined parishes and dioceses by religious orders who have people and material resources to spare, and some of which specialized in missions. Eventually, p ...
from
East Texas
East Texas is a broadly defined cultural, geographic, and ecological region in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Texas that comprises most of 41 counties. It is primarily divided into Northeast and Southeast Texas. Most of the region consi ...
were combined and reestablished as one mission on the south side of the Colorado River, in what is now
Zilker Park
Zilker Metropolitan Park is a recreational area in south Austin, Texas at the juncture of Barton Creek and the Colorado River that comprises over of publicly owned land. It is named after its benefactor, Andrew Jackson Zilker, who donated the la ...
, in Austin. The mission was in this area for only about seven months, and then was moved to
San Antonio de Béxar
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, subdivision_t ...
and split into three missions.
During the 1830s, pioneers began to settle the area in central Austin along the
Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid drainage basin, watershed that encompasses parts of ...
. Spanish forts were established in what are now
Bastrop and
San Marcos
San Marcos is the Spanish name of Saint Mark. It may also refer to:
Towns and cities Argentina
* San Marcos, Salta
Colombia
* San Marcos, Antioquia
* San Marcos, Sucre
Costa Rica
* San Marcos, Costa Rica (aka San Marcos de Tarrazú)
...
.
Following
Mexico's independence, new settlements were established in
Central Texas
Central Texas is a region in the U.S. state of Texas surrounding Austin and roughly bordered by San Saba to Bryan and San Marcos to Hillsboro. Central Texas overlaps with and includes part of the Texas Hill Country and corresponds to a ph ...
, but growth in the region was stagnant because of conflicts with the regional Native Americans.

In 1835–1836, Texans fought and won
independence from Mexico. Texas thus became an independent country with its own president, congress, and monetary system. In 1839, the Texas Congress formed a commission to seek a site for a new capital of the
Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
to replace
Houston
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in ...
.
When he was Vice President of Texas,
Mirabeau B. Lamar
Mirabeau Buonaparte Lamar (August 16, 1798 – December 25, 1859) was an Lawyer, attorney born in Georgia,
who became a Texas politician, poet, diplomat, and soldier. He was a leading Texas political figure during the Republic of Texas, Texas ...
had visited the area during a
buffalo-hunting expedition between 1837 and 1838. He advised the commissioners to consider the area on the north bank of the
Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid drainage basin, watershed that encompasses parts of ...
(near the present-day
Congress Avenue Bridge
The Ann W. Richards Congress Avenue Bridge (formerly known simply as the Congress Avenue Bridge) crosses over Lady Bird Lake in Austin, Texas. Before construction of the Longhorn Dam was completed in 1960, the bridge crossed the Colorado Ri ...
), noting the area's hills, waterways, and pleasant surroundings.
It was seen as a convenient crossroads for trade routes between
Santa Fe and
Galveston Bay
Galveston Bay ( ) is a bay in the western Gulf of Mexico along the upper coast of Texas. It is the seventh-largest estuary in the United States, and the largest of seven major estuaries along the Texas Gulf Coast. It is connected to the Gulf of ...
, as well as routes between northern Mexico and the
Red River.
In 1839, the site was chosen, and was briefly incorporated under the name "Waterloo". Shortly afterward, the name was changed to Austin in honor of
Stephen F. Austin
Stephen Fuller Austin (November 3, 1793 – December 27, 1836) was an American-born empresario. Known as the "Father of Texas" and the founder of Anglo Texas,Hatch (1999), p. 43. he led the second and, ultimately, the successful colonization ...
, the "Father of Texas" and the republic's first secretary of state.
The city grew throughout the 19th century and became a center for government and education with the construction of the
Texas State Capitol
The Texas State Capitol is the capitol and seat of government of the American state of Texas. Located in downtown Austin, Texas, the structure houses the offices and chambers of the Texas Legislature and of the Governor of Texas. Designed in 18 ...
and the
University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
.

Edwin Waller
Edwin Waller (November 4, 1800 – January 3, 1881) was an entrepreneur, signer of the Texas Declaration of Independence, the first mayor of Austin, Texas, and the designer of its downtown grid plan.
Texas independence
He was born in Spotsyl ...
was picked by Lamar to survey the village and draft a plan laying out the new capital.
The original site was narrowed to that fronted the Colorado River between two creeks, Shoal Creek and Waller Creek, which was later named in his honor. Waller and a team of surveyors developed Austin's first
city plan
Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water, ...
, commonly known as the
Waller Plan
The 1839 Austin city plan (commonly known as the Waller Plan) is the original city plan for the development of Austin, Texas, which established the grid plan for what is now downtown Austin. It was commissioned in 1839 by the government of the Re ...
, dividing the site into a 14-block grid plan bisected by a broad north–south thoroughfare, Congress Avenue, running up from the river to Capital Square, where the new Texas State Capitol was to be constructed. A temporary one-story capitol was erected on the corner of Colorado and 8th Streets. On August 1, 1839, the first auction of 217 out of 306 lots total was held.
The Waller Plan designed and surveyed now forms the basis of downtown Austin.
In 1840, a series of conflicts between the
Texas Rangers and the
Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in La ...
s, known as the
Council House Fight
The Council House Fight, often referred to as the Council House Massacre, was a fight between soldiers and officials of the Republic of Texas and a delegation of Comanche chiefs during a peace conference in San Antonio on March 19, 1840. The mee ...
and the
Battle of Plum Creek
The Battle of Plum Creek was a clash between allied Tonkawa, militia, and Rangers of the Republic of Texas and a huge Comanche war party under Chief Buffalo Hump, which took place near Lockhart, Texas, on August 12, 1840, following the Great Rai ...
, pushed the Comanches westward, mostly ending conflicts in Central Texas. Settlement in the area began to expand quickly. Travis County was established in 1840, and the surrounding counties were mostly established within the next two decades.
Initially, the new capital thrived but Lamar's political enemy,
Sam Houston
Samuel Houston (, ; March 2, 1793 – July 26, 1863) was an American general and statesman who played an important role in the Texas Revolution. He served as the first and third president of the Republic of Texas and was one of the first two i ...
, used two Mexican army incursions to
San Antonio
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= U.S. state, State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, s ...
as an excuse to move the government. Sam Houston fought bitterly against Lamar's decision to establish the capital in such a remote wilderness. The men and women who traveled mainly from Houston to conduct government business were intensely disappointed as well. By 1840, the population had risen to 856, nearly half of whom fled Austin when Congress recessed. The resident
African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
population listed in January of this same year was 176. The fear of Austin's proximity to the Indians and Mexico, which still considered Texas a part of their land, created an immense motive for Sam Houston, the first and third President of the Republic of Texas, to relocate the capital once again in 1841. Upon threats of Mexican troops in Texas, Houston raided the Land Office to transfer all official documents to Houston for safe keeping in what was later known as the
Archive War
The Texas Archive War was an 1842 dispute over an attempted move of the Republic of Texas national archives from Austin, Texas, Austin to Houston, Texas, Houston and, more broadly, over President Sam Houston's efforts to make Houston the capital of ...
, but the people of Austin would not allow this unaccompanied decision to be executed. The documents stayed, but the capital would temporarily move from Austin to Houston to
Washington-on-the-Brazos
Washington-on-the-Brazos is an unincorporated community along the Brazos River in Washington County, Texas, United States. The town is best known for being the site of the Convention of 1836 and the signing of the Texas Declaration of Independenc ...
. Without the governmental body, Austin's population declined to a low of only a few hundred people throughout the early 1840s. The voting by the fourth President of the Republic,
Anson Jones
Anson Jones (January 20, 1798 – January 09, 1858) was a doctor, businessman, member of Congress, and the fourth and last President of the Republic of Texas.
Early life
Jones was born on January 20, 1798, in Great Barrington, Massachus ...
, and Congress, who reconvened in Austin in 1845, settled the issue to keep Austin the seat of government, as well as annex the Republic of Texas into the United States.
In 1860, 38% of Travis County residents were
slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. In 1861, with the outbreak of the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, voters in Austin and other Central Texas communities voted against secession.
However, as the war progressed and fears of attack by
Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
forces increased, Austin contributed hundreds of men to the
Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
forces. The African American population of Austin swelled dramatically after the enforcement of the
Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the Civil War. The Proclamation changed the legal sta ...
in Texas by
Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
General
Gordon Granger
Gordon Granger (November 6, 1821 – January 10, 1876) was a career U.S. Army officer and a Union general during the American Civil War, where he distinguished himself at the Battle of Chickamauga.
Granger is best remembered for his part in the ...
at Galveston, in an event commemorated as
Juneteenth
Juneteenth is a federal holiday in the United States commemorating the emancipation of enslaved African Americans. Deriving its name from combining "June" and "nineteenth", it is celebrated on the anniversary of General Order No. 3, i ...
. Black communities such as
Wheatville, Pleasant Hill, and Clarksville were established, with Clarksville being the oldest surviving freedomtown ‒ the original post-Civil War settlements founded by former African-American slaves ‒ west of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
.
In 1870, blacks made up 36.5% of Austin's population.

The postwar period saw dramatic population and economic growth. The opening of the
Houston and Texas Central Railway
The Houston and Texas Central Railway (H&TC), was an 872-mile (1403-km) railway system chartered in Texas in 1848, with construction beginning in 1856. The line eventually stretched from Houston northward to Dallas and Denison, Texas. with branch ...
(H&TC) in 1871 turned Austin into the major trading center for the region, with the ability to transport both cotton and cattle. The
Missouri, Kansas & Texas (MKT) line followed close behind. Austin was also the terminus of the southernmost leg of the
Chisholm Trail
The Chisholm Trail was a trail used in the post-Civil War era to drive cattle overland from ranches in Texas to Kansas railheads. The trail was established by Black Beaver, a Lenape guide and rancher, and his friend Jesse Chisholm, a Cheroke ...
, and "drovers" pushed cattle north to the railroad. Cotton was one of the few crops produced locally for export, and a
cotton gin
A cotton gin—meaning "cotton engine"—is a machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from their seeds, enabling much greater productivity than manual cotton separation.. Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (); a ...
engine was located downtown near the trains for "ginning" cotton of its seeds and turning the product into bales for shipment. However, as other new railroads were built through the region in the 1870s, Austin began to lose its primacy in trade to the surrounding communities.
In addition, the areas east of Austin took over cattle and cotton production from Austin, especially in towns like
Hutto
Hutto is a city in Williamson County, Texas, United States. It is part of the Greater Austin, Austin–Round Rock metropolitan area. The population was 27,577 at the 2020 census.
Geography
Hutto is located at (30.544517, −97.545198), about sev ...
and
Taylor
Taylor, Taylors or Taylor's may refer to:
People
* Taylor (surname)
**List of people with surname Taylor
* Taylor (given name), including Tayla and Taylah
* Taylor sept, a branch of Scottish clan Cameron
* Justice Taylor (disambiguation)
Plac ...
that sit over the
blackland prairie, with its deep, rich soils for producing cotton and hay.
In September 1881, Austin public schools held their first classes. The same year, Tillotson Collegiate and Normal Institute (now part of
Huston–Tillotson University
Huston–Tillotson University (HT) is a private historically black university in Austin, Texas. Established in 1875, Huston–Tillotson University was the first institution of higher learning in Austin. The university is affiliated with the Unite ...
) opened its doors. The
University of Texas
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
held its first classes in 1883, although classes had been held in the original wooden state capitol for four years before.
During the 1880s, Austin gained new prominence as the
state capitol building was completed in 1888 and claimed as the seventh largest building in the world.
In the late 19th century, Austin expanded its city limits to more than three times its former area, and the first granite dam was built on the Colorado River to power a new street car line and the new "
moon towers".
The first dam washed away in a flood on April 7, 1900.
In the late 1920s and 1930s, Austin implemented the
1928 Austin city plan
The 1928 Austin city plan (also known as the 1928 Austin master plan) was commissioned in 1927 by the City Council of Austin, Texas. It was developed by consulting firm Koch & Fowler, which presented the final proposal early the next year. The maj ...
through a series of civic development and beautification projects that created much of the city's infrastructure and many of its parks. In addition, the state legislature established the
Lower Colorado River Authority
The Lower Colorado River Authority (LCRA) is a nonprofit public utility created in November 1934 by the Texas Legislature. LCRA's mission is to enhance the lives of the Texans it serves through water stewardship, energy and community service. LCR ...
(LCRA) that, along with the city of Austin, created the system of dams along the Colorado River to form the
Highland Lakes. These projects were enabled in large part because the
Public Works Administration
The Public Works Administration (PWA), part of the New Deal of 1933, was a large-scale public works construction agency in the United States headed by Secretary of the Interior Harold L. Ickes. It was created by the National Industrial Recove ...
provided Austin with greater funding for municipal construction projects than other Texas cities.
During the early twentieth century, a three-way system of social segregation emerged in Austin, with Anglos, African Americans and Mexicans being separated by custom or law in most aspects of life, including housing, health care, and education. Many of the municipal improvement programs initiated during this period—such as the construction of new roads, schools, and hospitals—were deliberately designed to institutionalize this system of segregation. Deed restrictions also played an important role in
residential segregation
Residential segregation in the United States is the physical separation of two or more groups into different neighborhoods—a form of segregation that "sorts population groups into various neighborhood contexts and shapes the living environment a ...
. After 1935 most housing deeds prohibited African Americans (and sometimes other nonwhite groups) from using land. Combined with the system of segregated public services, racial segregation increased in Austin during the first half of the twentieth century, with African Americans and Mexicans experiencing high levels of discrimination and social marginalization.
In 1940, the destroyed granite dam on the Colorado River was finally replaced by a hollow concrete dam that formed Lake McDonald (now called
Lake Austin
Lake Austin, formerly Lake McDonald, is a water reservoir on the Colorado River in Austin, Texas. The reservoir was formed in 1939 by the construction of Tom Miller Dam by the Lower Colorado River Authority. Lake Austin is one of the seven High ...
) and which has withstood all floods since. In addition, the much larger Mansfield Dam was built by the LCRA upstream of Austin to form
Lake Travis
Lake Travis is a reservoir on the Colorado River in central Texas in the United States.
Serving principally as a flood-control reservoir, Lake Travis' historical minimum to maximum water height change is nearly 100 feet. In 2018 alone, it saw ...
, a flood-control reservoir.
In the early 20th century, the
Texas Oil Boom
The Texas oil boom, sometimes called the gusher age, was a period of dramatic change and economic growth in the U.S. state of Texas during the early 20th century that began with the discovery of a large petroleum reserve near Beaumont, Texas. T ...
took hold, creating tremendous economic opportunities in Southeast Texas and North Texas. The growth generated by this boom largely passed by Austin at first, with the city slipping from fourth largest to tenth largest in Texas between 1880 and 1920.
After a severe lull in economic growth from the
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, Austin resumed its steady development. Following the mid-20th century, Austin became established as one of Texas' major metropolitan centers. In 1970, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Austin's population as 14.5% Hispanic, 11.9% black, and 73.4% non-Hispanic white.
In the late 20th century, Austin emerged as an important high tech center for
semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glas ...
s and software. The
University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
emerged as a major university.
The 1970s saw Austin's emergence in the national music scene, with local artists such as
Willie Nelson
Willie Hugh Nelson (born April 29, 1933) is an American country musician. The critical success of the album ''Shotgun Willie'' (1973), combined with the critical and commercial success of ''Red Headed Stranger'' (1975) and '' Stardust'' (197 ...
,
Asleep at the Wheel
Asleep at the Wheel is an American Western swing group that was formed in Paw Paw, West Virginia, and is based in Austin, Texas. The band has won nine Grammy Awards since their 1970 inception, released over twenty albums, and has charted more t ...
, and
Stevie Ray Vaughan
Stephen Ray Vaughan (October 3, 1954 – August 27, 1990) was an American musician, best known as the guitarist and frontman of the blues rock trio Stevie Ray Vaughan and Double Trouble. Although his mainstream career spanned only seven years, ...
and iconic music venues such as the
Armadillo World Headquarters
Armadillo World Headquarters (The 'Dillo or Armadillo WHQ) was an influential Texas music hall and beer garden in Austin at 525 Barton Springs Road – at South First Street – just south of the Colorado River and downtown Austin. The 'Dillo f ...
. Over time, the long-running television program ''Austin City Limits'', its namesake Austin City Limits Festival, and the
South by Southwest
South by Southwest, abbreviated as SXSW and colloquially referred to as South By, is an annual conglomeration of parallel film, interactive media, and music festivals and Convention (meeting), conferences organized jointly that take place in m ...
music festival solidified the city's place in the music industry.
Geography

Austin, the southernmost state capital of the contiguous 48 states, is located in
Central Texas
Central Texas is a region in the U.S. state of Texas surrounding Austin and roughly bordered by San Saba to Bryan and San Marcos to Hillsboro. Central Texas overlaps with and includes part of the Texas Hill Country and corresponds to a ph ...
on the
Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid drainage basin, watershed that encompasses parts of ...
. Austin is northwest of
Houston
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in ...
, south of
Dallas
Dallas () is the List of municipalities in Texas, third largest city in Texas and the largest city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of metropolitan statistical areas, fourth-largest metropolitan area in the United States at 7.5 ...
and northeast of
San Antonio
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= U.S. state, State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, s ...
.
Austin occupies a total area of . Approximately of this area is water.
Austin is situated at the foot of the
Balcones Escarpment
The Balcones Fault or Balcones Fault Zone is an area of largely normal faulting Edwards Aquifer in the U.S. state of Texas that runs roughly from the southwest part of the state near Del Rio to the north-central region near Dallas along Inte ...
, on the
Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid drainage basin, watershed that encompasses parts of ...
, with three artificial lakes within the city limits:
Lady Bird Lake
Lady Bird Lake (formerly, and still colloquially referred to as Town Lake) is a river-like reservoir on the Colorado River in Austin, Texas, United States. The City of Austin created the reservoir in 1960 as a cooling pond for a new city power p ...
(formerly known as Town Lake),
Lake Austin
Lake Austin, formerly Lake McDonald, is a water reservoir on the Colorado River in Austin, Texas. The reservoir was formed in 1939 by the construction of Tom Miller Dam by the Lower Colorado River Authority. Lake Austin is one of the seven High ...
(both created by dams along the Colorado River), and
Lake Walter E. Long
Lake Walter E. Long (also known as Decker Lake) is a power plant cooling reservoir on Decker Creek in Austin, Texas. The reservoir was officially impounded in 1967 and serves to provide water for turbines used in the production of electricity ...
that is partly used for cooling water for the Decker Power Plant.
Mansfield Dam
Mansfield Dam (formerly Marshall Ford Dam) is a dam located across a canyon at Marshall Ford on the Colorado River, northwest of Austin, Texas. The groundbreaking ceremony occurred on February 19, 1937, with United States Secretary of the Interi ...
and the foot of
Lake Travis
Lake Travis is a reservoir on the Colorado River in central Texas in the United States.
Serving principally as a flood-control reservoir, Lake Travis' historical minimum to maximum water height change is nearly 100 feet. In 2018 alone, it saw ...
are located within the city's limits.
Lady Bird Lake, Lake Austin, and Lake Travis are each on the Colorado River.
The elevation of Austin varies from to approximately above sea level.
Due to the fact it straddles the
Balcones Fault
The Balcones Fault or Balcones Fault Zone is an area of largely normal faulting Edwards Aquifer in the U.S. state of Texas that runs roughly from the southwest part of the state near Del Rio to the north-central region near Dallas along Inte ...
, much of the eastern part of the city is flat, with heavy clay and loam soils, whereas the western part and western suburbs consist of rolling hills on the edge of the
Texas Hill Country
The Texas Hill Country is a geographic region of Central and South Texas, forming the southeast part of the Edwards Plateau. Given its location, climate, terrain, and vegetation, the Hill Country can be considered the border between the Ameri ...
.
Because the hills to the west are primarily
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
rock with a thin covering of topsoil, portions of the city are frequently subjected to
flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing o ...
s from the runoff caused by thunderstorms. To help control this runoff and to generate hydroelectric power, the
Lower Colorado River Authority
The Lower Colorado River Authority (LCRA) is a nonprofit public utility created in November 1934 by the Texas Legislature. LCRA's mission is to enhance the lives of the Texans it serves through water stewardship, energy and community service. LCR ...
operates a series of dams that form the
Texas Highland Lakes
The Texas Highland Lakes is a chain of fresh water reservoirs in Central Texas formed by dams on the lower Colorado River. The Texas Colorado River winds southeast from West Texas to Matagorda Bay and the Gulf of Mexico.
The lower Colorado River ...
. The lakes also provide venues for boating, swimming, and other forms of recreation within several parks on the lake shores.
Austin is located at the intersection of four major ecological regions, and is consequently a temperate-to-hot green oasis with a highly variable climate having some characteristics of the desert, the tropics, and a wetter climate. The area is very diverse ecologically and biologically, and is home to a variety of animals and plants.
Notably, the area is home to many types of wildflowers that blossom throughout the year but especially in the spring. This includes the popular
bluebonnets, some planted by
"Lady Bird" Johnson, wife of former President
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
.
The soils of Austin range from shallow, gravelly clay loams over limestone in the western outskirts to deep, fine sandy loams, silty clay loams, silty clays or clays in the city's eastern part. Some of the clays have pronounced shrink-swell properties and are difficult to work under most moisture conditions. Many of Austin's soils, especially the clay-rich types, are slightly to moderately alkaline and have free
calcium carbonate.
Cityscape
Austin's skyline historically was modest, dominated by the Texas State Capitol and the University of Texas
Main Building. However, since the 2000s, many new high-rise towers have been constructed. Austin is currently undergoing a skyscraper boom, which includes recent construction on new office, hotel and residential buildings. Downtown's buildings are somewhat spread out, partly due to a set of
zoning
Zoning is a method of urban planning in which a municipality or other tier of government divides land into areas called zones, each of which has a set of regulations for new development that differs from other zones. Zones may be defined for a si ...
restrictions that preserve the view of the
Texas State Capitol
The Texas State Capitol is the capitol and seat of government of the American state of Texas. Located in downtown Austin, Texas, the structure houses the offices and chambers of the Texas Legislature and of the Governor of Texas. Designed in 18 ...
from various locations around Austin, known as the
Capitol View Corridors.

At night, parts of Austin are lit by "artificial moonlight" from
moonlight tower
A moonlight tower or moontower is a lighting structure designed to illuminate areas of a town or city at night.
The towers were popular in the late 19th century in cities across the United States and Europe; they were most common in the 1880s and ...
s built to illuminate the central part of the city. The moonlight towers were built in the late 19th century and are now recognized as historic landmarks. Only 15 of the 31 original innovative towers remain standing in Austin, but none remain in any of the other cities where they were installed. The towers are featured in the 1993 film ''
Dazed and Confused''.
Downtown
The central business district of Austin is home to the tallest condo towers in the state, with
The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publis ...
(58 stories and tall) and
The Austonian
The Austonian is a residential skyscraper in Downtown Austin, Texas, USA. At tall with 56 floors, the building is the second tallest in Austin, overtaking the 360 Condominiums and behind The Independent. It is also the second tallest building i ...
(topping out at 56 floors and tall). The Independent became the tallest all-residential building in the U.S. west of
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
when topped out in 2018. In 2005, then-Mayor Will Wynn set out a goal of having 25,000 people living downtown by 2015. Although downtown's growth did not meet this goal, downtown's residential population did surge from an estimated 5,000 in 2005 to 12,000 in 2015. The skyline has drastically changed in recent years, and the residential real estate market has remained relatively strong. , there were 31 high rise projects either under construction, approved or planned to be completed in Austin's downtown core between 2017 and 2020. Sixteen of those were set to rise above tall, including four above 600', and eight above 500'. An additional 15 towers were slated to stand between 300' and 399' tall.
Climate
Austin is located within the middle of a unique, narrow transitional zone between the dry deserts of the American Southwest and the lush, green, more humid regions of the American Southeast. Its climate, topography, and vegetation share characteristics of both. Officially, Austin has a
humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
under the
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
. This climate is typified by long, very hot summers, short, mild winters, and warm to hot spring and fall seasons in-between. Austin averages of annual rainfall distributed mostly evenly throughout the year, though spring and fall are the wettest seasons. Sunshine is common during all seasons, with 2,650 hours, or 60.3% of the possible total, of bright sunshine per year.
Summers in Austin are very hot, with average July and August highs frequently reaching the high-90s (34–36 °C) or above. Highs reach on 123 days per year, of which 29 days reach ; all years in the 1991-2020 period recorded at least 1 day of the latter.
The average daytime high is or warmer between March 1 and November 21, rising to or warmer between April 14 and October 24, and reaching or warmer between May 30 and September 18.
The highest ever recorded temperature was occurring on September 5, 2000, and August 28, 2011. An uncommon characteristic of Austin's climate is its highly variable humidity, which fluctuates frequently depending on the shifting patterns of air flow and wind direction. It is common for a lengthy series of warm, dry, low-humidity days to be occasionally interrupted by very warm and humid days, and vice versa. Humidity rises with winds from the east or southeast, when the air drifts inland from the
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
, but decreases significantly with winds from the west or southwest, bringing air flowing from
Chihuahuan Desert
The Chihuahuan Desert ( es, Desierto de Chihuahua, ) is a desert ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of far West Texas, the middle to lower Rio Grande Valley and the lower P ...
areas of
West Texas
West Texas is a loosely defined region in the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the arid and semiarid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Abilene, and Del Rio.
No consensus exists on the boundary betwee ...
or northern Mexico.
Winters in Austin are mild, although occasional short-lived bursts of cold weather known as "
Blue Northers" can occur. January is the coolest month with an average daytime high of . The overnight low drops to or below freezing 12 times per year,
and sinks below during 76 evenings per year, mostly between mid-December and mid-February. The average first and last dates for a freeze are December 1 and February 15, giving Austin an average growing season of 288 days, and the coldest temperature of the year is normally about under the 1991-2020 climate normals, putting Austin in USDA zone 9a.
Conversely, winter months also produce warm days on a regular basis. On average, 10 days in January reach or exceed and 1 day reaches ; during the 1991-2020 period, all Januarys had at least 1 day with a high of or more, and most (60%) had at least 1 day with a high of or more.
The lowest ever recorded temperature in the city was on January 31, 1949. Roughly every two years Austin experiences an
ice storm
An ice storm, also known as a glaze event or a silver storm is a type of winter storm characterized by freezing rain. The U.S. National Weather Service defines an ice storm as a storm which results in the accumulation of at least of ice on ex ...
that freezes roads over and cripples travel in the city for 24 to 48 hours. When Austin received of ice on January 24, 2014, there were 278 vehicular collisions. Similarly, snowfall is rare in Austin. A snow event of on February 4, 2011, caused more than 300 car crashes. The most recent snow event occurred February 14–15, 2021, when of snow fell at Austin's
Camp Mabry
Camp Mabry (ICAO: KATT) is a military installation in Austin, Texas, that houses the headquarters of the Texas Military Department, Texas Military Forces, and Texas Military Forces Museum. Established in 1892, Camp Mabry is the third-oldest activ ...
, the largest two-day snowfall since records began being kept in 1948.
Typical of
Central Texas
Central Texas is a region in the U.S. state of Texas surrounding Austin and roughly bordered by San Saba to Bryan and San Marcos to Hillsboro. Central Texas overlaps with and includes part of the Texas Hill Country and corresponds to a ph ...
, severe weather in Austin is a threat that can strike during any season. However, it is most common during the spring. According to most classifications, Austin lies within the extreme southern periphery of
Tornado Alley
Tornado Alley is a loosely defined area of the central United States where tornadoes are most frequent. The term was first used in 1952 as the title of a research project to study severe weather in areas of Texas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Kansas, So ...
, although many sources place Austin outside of Tornado Alley altogether.
Consequently, tornadoes strike Austin less frequently than areas farther to the north.
However, severe weather and/or
supercell thunderstorms
A supercell is a thunderstorm characterized by the presence of a mesocyclone: a deep, persistently rotating updraft. Due to this, these storms are sometimes referred to as rotating thunderstorms. Of the four classifications of thunderstorms (s ...
can occur multiple times per year, bringing damaging winds, lightning, heavy rain, and occasional flash flooding to the city. The deadliest storm to ever strike city limits was the
twin tornadoes storm of May 4, 1922, while the deadliest
tornado outbreak
__NOTOC__
A tornado outbreak is the occurrence of multiple tornadoes spawned by the same synoptic scale weather system. The number of tornadoes required to qualify as an outbreak typically are at least six to ten, with at least two rotational l ...
to ever strike the metro area was the
Central Texas tornado outbreak of May 27, 1997.
2011 drought

From October 2010 through September 2011, both major reporting stations in Austin, Camp Mabry and Bergstrom Int'l, had the least rainfall of a
water year
A water year (also called ''hydrological year'', ''discharge year'' or ''flow year'') is a term commonly used in hydrology to describe a time period of 12 months for which precipitation totals are measured. Its beginning differs from the calendar ...
on record, receiving less than a third of normal precipitation.
This was a result of
La Niña
La Niña (; ) is an oceanic and atmospheric phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of as part of the broader El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern. The name ''La Niña'' originates from Spanish for "the girl", by an ...
conditions in the eastern Pacific Ocean where water was significantly cooler than normal. David Brown, a regional official with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, explained that "these kinds of droughts will have effects that are even more extreme in the future, given a warming and drying regional climate." The drought, coupled with exceedingly high temperatures throughout the summer of 2011, caused many wildfires throughout Texas, including notably the
Bastrop County Complex Fire
The Bastrop County Complex fire was a conflagration that engulfed parts of Bastrop County, Texas, in September and October 2011. The wildfire was the costliest and most destructive wildfire in Texas history and among the costliest in U.S. hi ...
in neighboring Bastrop, Texas.
2018 flooding and water crisis
In the fall of 2018, Austin and surrounding areas received heavy rainfall and
flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing o ...
ing following
Hurricane Sergio The name Sergio has been used for four tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
* Tropical Storm Sergio (1978) – threatened Baja California.
* Hurricane Sergio (1982) – never threatened land.
* Hurricane Sergio (2006) – never threatened ...
.
The
Lower Colorado River Authority
The Lower Colorado River Authority (LCRA) is a nonprofit public utility created in November 1934 by the Texas Legislature. LCRA's mission is to enhance the lives of the Texans it serves through water stewardship, energy and community service. LCR ...
opened four
floodgates
Floodgates, also called stop gates, are adjustable gates used to control water flow in flood barriers, reservoir, river, stream, or levee systems. They may be designed to set spillway crest heights in dams, to adjust flow rates in sluices and ...
of the
Mansfield Dam
Mansfield Dam (formerly Marshall Ford Dam) is a dam located across a canyon at Marshall Ford on the Colorado River, northwest of Austin, Texas. The groundbreaking ceremony occurred on February 19, 1937, with United States Secretary of the Interi ...
after Lake Travis was recorded at 146% full at . From October 22 to October 29, 2018, the City of Austin issued a mandatory citywide
boil-water advisory
A boil-water advisory, boil-water notice, boil-water warning, boil-water order, or boil order is a public-health advisory or directive issued by governmental or other health authorities to consumers when a community's drinking water is or could b ...
after the
Highland Lakes, home to the city's main water supply, became overwhelmed by unprecedented amounts of silt, dirt, and debris that washed in from the
Llano River
The Llano River ( ) is a tributary of the Colorado River (Texas), Colorado River, about long, in Texas in the United States. It drains part of the Edwards Plateau in Texas Hill Country northwest of Austin, Texas, Austin.
Two spring-fed tributa ...
. Austin Water, the city's water utility, has the capacity to process up to 300 million gallons of water per day; however, the elevated level of
turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids can ...
reduced output to only 105 million gallons per day. Since Austin residents consumed an average of 120 million gallons of water per day, the infrastructure was not able to keep up with demand.
2021 winter storm

In February 2021,
Winter Storm Uri
Winter is the coldest season of the year in Polar regions of Earth, polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring (season), spring. The tilt of Axial tilt#Earth, Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a Hemi ...
dropped prolific amounts of snow across Texas and Oklahoma, including Austin. The Austin area received a total of of snowfall between February 14 and 15, with snow cover persisting until February 20.
This marked the longest time the area had had more than of snow, with the previous longest time being three days in
January 1985.
Lack of
winterization
Winterization is the process of preparing something for winter.
Humanitarian aid
In emergency or disaster response situations, such as managed by the UNHCR, winterization activities include the distribution of items including blankets, quilts, ...
in
natural gas power plants, which supply a large amount of power to the
Texas grid, and increased energy demand caused
ERCOT
The Electric Reliability Council of Texas, Inc. (ERCOT) is an American organization that operates Texas's electrical grid, the Texas Interconnection, which supplies power to more than 25 million Texas customers and represents 90 percent of the sta ...
and
Austin Energy
Austin Energy is a publicly owned utility providing electrical power to the city of Austin, Texas and surrounding areas. Established in 1895, the utility is a department of the City of Austin and returns its profits to the city's general fund to ...
to enact
rolling blackouts
A rolling blackout, also referred to as rota or rotational load shedding, rota disconnection, feeder rotation, or a rotating outage, is an intentionally engineered electrical power shutdown in which electricity delivery is stopped for non-overla ...
in order to avoid total grid collapse between February 15 and February 18. Initial rolling blackouts were to last for a maximum of 40 minutes, however lack of energy production caused many blackouts to last for much longer, at the peak of the blackouts an estimated 40% of Austin Energy homes were without power.
Starting on February 15, Austin Water received reports of pipe breaks, hourly water demand increased from 150 million gallons per day (MGD) on February 15 to a peak hourly demand of 260 MGD on February 16. On the morning of February 17 demand increased to 330 MGD, the resulting drop of water pressure caused the Austin area to enter into a
boil-water advisory
A boil-water advisory, boil-water notice, boil-water warning, boil-water order, or boil order is a public-health advisory or directive issued by governmental or other health authorities to consumers when a community's drinking water is or could b ...
which would last until water pressure was restored on February 23.
Demographics
In 2020, there were 961,855 people, up from the
2000 United States census
The United States census of 2000, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States on April 1, 2000, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2 percent over the 248,709,873 people enumerated during the 1990 ce ...
tabulation where there were people, households, and families residing in the city. In 2000, the population density was . There were dwelling units at an average density of . There were households, out of which 26.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 38.1% were married couples living together, 10.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 46.7% were non-families. 32.8% of all households were made up of individuals, and 4.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.40 and the average family size was 3.14.
In the city, 22.5% of the population was under the age of 18, 16.6% was from 18 to 24, 37.1% from 25 to 44, 17.1% from 45 to 64, and 6.7% were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 30 years. For every 100 females, there were 105.8 males.
The median income for a household in the city was , and the median income for a family was $. Males had a median income of $ compared to $ for females. The per capita income for the city was $. About 9.1% of families and 14.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 16.5% of those under age 18 and 8.7% of those age 65 or over. The median house price was $ in 2009, and it has increased every year since 2004. The median value of a house which the owner occupies was $318,400 in 2019—higher than the average American home value of $240,500.
According to a survey completed in 2014 by
Gallup, it is estimated that 5.3% of residents in the
Austin metropolitan area identify as
lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. The Austin metropolitan area had the third-highest rate in the nation.
Race and ethnicity
According to the
2010 United States census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servin ...
, the racial composition of Austin was 68.3%
White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
(48.7%
non-Hispanic whites
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Amer ...
), 35.1%
Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
(29.1%
Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
, 0.5%
Puerto Rican, 0.4%
Cuban
Cuban may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Cuba, a country in the Caribbean
* Cubans, people from Cuba, or of Cuban descent
** Cuban exile, a person who left Cuba for political reasons, or a descendant thereof
* Cuban citizen, a perso ...
, 5.1% Other), 8.1%
African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 6.3%
Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
(1.9%
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, 1.5%
Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, 1.0%
Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
, 0.7%
Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
, 0.3%
Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
, 0.2%
Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, 0.8% Other), 0.9%
American Indian, 0.1%
Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander, and 3.4%
two or more races
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultur ...
.
According to the
2020 United States census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to of ...
, the racial composition of Austin was 72.6%
White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
(48.3%
non-Hispanic whites
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Amer ...
), 33.9%
Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
, 7.8%
African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 7.6%
Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
, 0.7%
American Indian, 0.1%
Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander, and 3.4%
two or more races
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultur ...
.
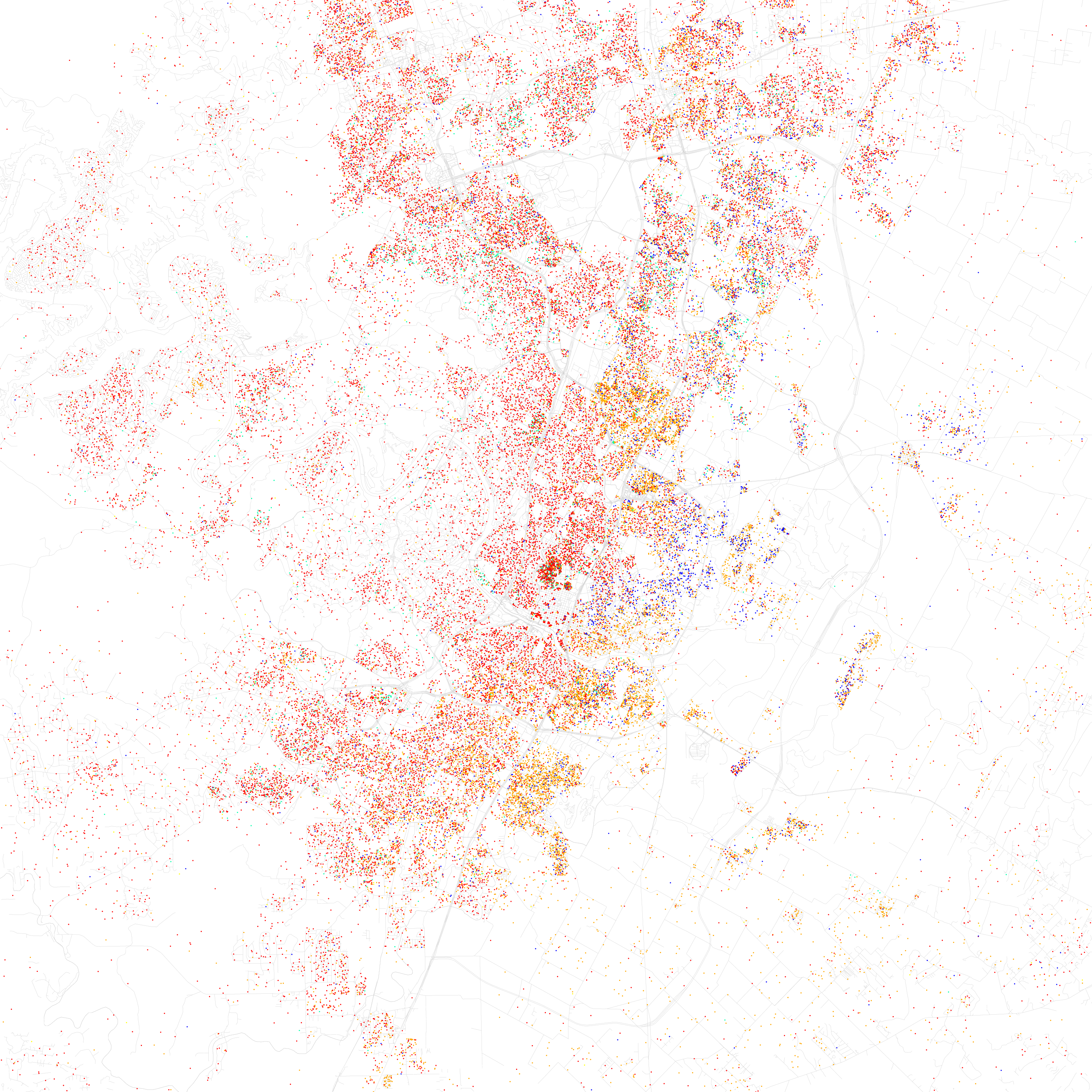
A 2014 University of Texas study stated that Austin was the only U.S. city with a fast growth rate between 2000 and 2010 with a net loss in African Americans. , Austin's African American and non-Hispanic white percentage share of the total population was declining despite the actual numbers of both ethnic groups increasing, as the rapid growth of the Latino or Hispanic and Asian populations has outpaced all other ethnic groups in the city. Austin's non-Hispanic white population first dropped below 50% in 2005.
Religion
According to
Sperling's BestPlaces
Bertrand T. Sperling (born 1950 in Brooklyn, New York) is an author and researcher. His books and studies on quality of life in America have made him "an internationally recognized expert on cities."
Work Studies
Sperling is commissioned to c ...
, 52.4% of Austin's population are religious.
The majority of Austinites identified themselves as
Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
, about 25.2% of whom claimed affiliation with the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
.
The city's Catholic population is served by the
Roman Catholic Diocese of Austin
The Diocese of Austin ( la, Dioecesis Austiniensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church comprising 25 counties of Central Texas in the United States. The diocese includes 123 parishes and missions and six ...
, headquartered at the
Cathedral of Saint Mary. Nationwide, 23% of Americans identified as Catholic in 2016. Other significant Christian groups in Austin include
Baptists
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compe ...
(8.7%), followed by Methodism, Methodists (4.3%), Latter Day Saint movement, Latter-Day Saints (1.5%), Anglicanism, Episcopalians or Anglicans (1.0%), Lutheranism, Lutherans (0.8%), Presbyterianism, Presbyterians (0.6%), Pentecostalism, Pentecostals (0.3%), and other Christians such as the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Disciples of Christ and Eastern Orthodox Church (7.1%).
The second largest religion Austinites identify with is Islam (1.7%); roughly 0.8% of Americans nationwide claimed affiliation with the Islamic faith.
The dominant branch of Islam is Sunni Islam. Established in 1977, the largest mosque in Austin is the Islamic Center of Greater Austin. The community is affiliated with the Islamic Society of North America. The same study says that Eastern religions, eastern faiths including Buddhism, Sikhism, and Hinduism made up 0.9% of the city's religious population.
Several Hindu temples exist in the Austin Metropolitan area with the most notable one being Radha Madhav Dham. Judaism forms less than 0.1% of the religious demographic in Austin. Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox, Reform Judaism, Reform, and Conservative Judaism, Conservative congregations are present in the community.
In addition to those religious groups, Austin is also home to an active secular humanist community, hosting nationwide television shows and charity work.
Homelessness
As of 2019, there were 2,255 individuals experiencing homelessness in Travis County. Of those, 1,169 were sheltered and 1,086 were unsheltered. In September 2019, the Austin City Council approved $62.7 million for programs aimed at homelessness, which includes housing displacement prevention, crisis mitigation, and affordable housing; the city council also earmarked $500,000 for crisis services and encampment cleanups.
In June 2019, following a federal court ruling on homelessness sleeping in public, the Austin City Council lifted a 25-year-old ban on camping, sitting, or lying down in public unless doing so causes an obstruction. The resolution also included the approval of a new housing-focused shelter in South Austin. In early October 2019, Texas Governor Greg Abbott sent a letter to Mayor Steve Adler threatening to deploy state resources to combat the camping ban repeal.
On October 17, 2019, the City Council revised the camping ordinance, which imposed increased restrictions on sidewalk camping.
In November 2019, the State of Texas opened a temporary homeless encampment on a former vehicle storage yard owned by the Texas Department of Transportation.
In May 2021, the camping ban was reinstated after a referendum, ballot proposition was approved by 57% of voters. The ban introduces penalties for camping, sitting, or lying down on a public sidewalk or sleeping outdoors in or near Downtown Austin or the area around the University of Texas campus. The ordinance would also prohibit solicitation at certain locations.
Economy

The Greater Austin metropolitan statistical area had a gross domestic product (GDP) of $86 billion in 2010. Austin is considered to be a major center for high tech.
Thousands of graduates each year from the engineering and computer science programs at the
University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
provide a steady source of employees that help to fuel Austin's technology and defense industry sectors. The region's rapid growth has led ''Forbes'' to rank the Austin metropolitan area number one among all big cities for jobs for 2012 in their annual survey and WSJ Marketwatch to rank the area number one for growing businesses. As a result of the high concentration of high-tech companies in the region, Austin was strongly affected by the Dot-com bubble, dot-com boom in the late 1990s and subsequent bust.
Austin's largest employers include the Austin Independent School District, the City of Austin,
Dell
Dell is an American based technology company. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies.
Dell sells personal computers (PCs), servers, data ...
, the Federal government of the United States, U.S. Federal Government,
NXP Semiconductors
NXP Semiconductors N.V. (NXP) is a Dutch semiconductor designer and manufacturer with headquarters in Eindhoven, Netherlands. The company employs approximately 31,000 people in more than 30 countries. NXP reported revenue of $11.06 billion in 2 ...
,
IBM, St. David's Healthcare Partnership, Seton Family of Hospitals, the Texas, State of Texas, the Texas State University, and the University of Texas at Austin.
Other high-tech companies with operations in Austin include
3M,
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
, Amazon (company), Amazon, Advanced Micro Devices, AMD, Apartment Ratings, Applied Materials, Arm Holdings, Bigcommerce, BioWare, Blizzard Entertainment, Buffalo Technology, Cirrus Logic, Cisco Systems, Dropbox (service), Dropbox, eBay, Electronic Arts, Flextronics, Facebook,
Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...
, Hewlett-Packard, Hoover's, HomeAway, HostGator, Intel Corporation, National Instruments, Nintendo, Nvidia,
Oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word '' ...
, PayPal, Polycom, Qualcomm, Inc., Qualcomm, Rackspace, RetailMeNot, Inc., RetailMeNot, Rooster Teeth, Samsung, Samsung Group, Silicon Labs, Spansion,
Tesla, United Devices, VMware, Xerox, and Zoho Corporation. In 2010, Facebook accepted a grant to build a downtown office that could bring as many as 200 jobs to the city. The proliferation of technology companies has led to the region's nickname, "Silicon Hills", and spurred development that greatly expanded the city.
Austin is also emerging as a hub for Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies; the city is home to about 85 of them.
In 2004, the city was ranked by the Milken Institute as the #12 biotech and life science center in the United States and in 2018, CBRE Group ranked Austin as #3 emerging life sciences cluster. Companies such as Hospira, Pharmaceutical Product Development, and ArthroCare, ArthroCare Corporation are located there.
Whole Foods Market
Whole Foods Market IP, Inc., a subsidiary of Amazon, is an upscale American multinational supermarket chain headquartered in Austin, Texas, which sells products free from hydrogenated fats and artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. A US ...
, an international grocery store chain specializing in fresh and packaged food products, was founded and is headquartered in Austin.
Other companies based in Austin include
NXP Semiconductors
NXP Semiconductors N.V. (NXP) is a Dutch semiconductor designer and manufacturer with headquarters in Eindhoven, Netherlands. The company employs approximately 31,000 people in more than 30 countries. NXP reported revenue of $11.06 billion in 2 ...
, GoodPop, Temple-Inland, Sweet Leaf Tea Company, Keller Williams Realty, National Western Life, GSD&M, Dimensional Fund Advisors, Golfsmith, Forestar Group, EZCorp, Outdoor Voices, Tito's Vodka, Indeed, Speak Social, and YETI (company), YETI.
In 2018, Austin metro-area companies saw a total of $1.33 billion invested. Austin's VC numbers were so strong in 2018 that they accounted for more than 60 percent of Texas' total investments.
Culture and contemporary life


"Keep Austin Weird" has been a local motto for years, featured on bumper stickers and T-shirts. This motto has not only been used in promoting Austin's eccentricity and diversity, but is also meant to bolster support of local independent businesses.
According to the 2010 book ''Weird City'' the phrase was begun by a local Austin Community College librarian, Red Wassenich, and his wife, Karen Pavelka, who were concerned about Austin's "rapid descent into commercialism and overdevelopment."
The slogan has been interpreted many ways since its inception, but remains an important symbol for many Austinites who wish to voice concerns over rapid growth and development. Austin has a long history of vocal citizen resistance to development projects perceived to degrade the environment, or to threaten the natural and cultural landscapes.
According to the Nielsen Company, adults in Austin read and contribute to blogs more than those in any other U.S. metropolitan area.
Austin residents have the highest Internet usage in all of Texas.
In 2013, Austin was the most active city on Reddit, having the largest number of views per capita.
Austin was selected as the No. 2 Best Big City in "Best Places to Live" by ''Money (magazine), Money'' magazine in 2006, and No. 3 in 2009, and also the "Sustainability, Greenest City in America" by MSN.
South Congress is a shopping district stretching down South Congress Avenue from Downtown. This area is home to coffee shops, eccentric stores, restaurants, food trucks, trailers, and festivals. It prides itself on "Keeping Austin Weird," especially with development in the surrounding area(s). Many Austinites attribute its enduring popularity to the magnificent and unobstructed Texas Capitol View Corridors, view of the Texas State Capitol.
The Rainey Street Historic District is a neighborhood in Downtown Austin formerly consisting of bungalow style homes built in the early 20th century. Since the early 2010s, the former working class residential street has turned into a popular nightlife district. Much of the historic homes have been renovated into hotels, condominiums, bars and restaurants, many of which feature large porches and outdoor yards for patrons. The Rainey Street district is also home to the Emma S. Barrientos Mexican American Cultural Center.
Austin has been part of the Creative Cities Network, UNESCO Creative Cities Network under Media arts, Media Arts the category.
Old Austin

"Old Austin" is an adage often used by nostalgic natives. The term "Old Austin" refers to a time when the city was smaller and more Bohemianism, bohemian with a considerably lower cost of living and better known for its lack of traffic, Hipster (contemporary subculture), hipsters, and urban sprawl. It is often employed by longtime residents expressing displeasure at the rapidly changing culture, or when referencing nostalgia of Austin culture.
The growth and popularity of Austin can be seen by the expansive development taking place in its downtown landscape. This growth can have a negative impact on longtime small businesses that cannot keep up with the expenses associated with gentrification and the rising cost of real estate. A former Austin musician, Dale Watson (singer), Dale Watson, described his move away from Austin, "I just really feel the city has sold itself. Just because you're going to get $45 million for a company to come to town – if it's not in the best interest of the town, I don't think they should do it. This city was never about money. It was about quality of life." Though much is changing rapidly in Austin, businesses such as Thundercloud Subs are thought by many to maintain classic Austin business cultural sentiments unique to the history of the city; as Diana Burgess stated, "I definitely appreciate that they haven't raised their prices a ton or made things super fancy. I think it speaks to that
original Old Austin vibe. A lot of us that grew up here really appreciate that."
Annual cultural events

The William Sidney Porter House, O. Henry House Museum hosts the annual O. Henry Pun-Off, a pun contest where the successful contestants exhibit wit akin to that of the author William Sydney Porter.
Other annual events include Eeyore's Birthday Party, Spamarama, Austin gay pride, Pride Festival & Parade in August, the Austin Reggae Festival in April, Kite Festival, Texas Craft Brewers Festival in September, Art City Austin in April, East Austin Studio Tour in November, and Carnaval Brasileiro in Austin, Texas, Carnaval Brasileiro in February. Sixth Street features annual festivals such as the Pecan Street Festival and Halloween night. The three-day Austin City Limits Music Festival has been held in
Zilker Park
Zilker Metropolitan Park is a recreational area in south Austin, Texas at the juncture of Barton Creek and the Colorado River that comprises over of publicly owned land. It is named after its benefactor, Andrew Jackson Zilker, who donated the la ...
every year since 2002. Every year around the end of March and the beginning of April, Austin is home to "Texas Relay Weekend."
Austin's Zilker Park Tree is a Christmas display made of lights strung from the top of a Moonlight tower in Zilker Park. The Zilker Tree is lit in December along with the "Trail of Lights," an Austin Christmas tradition. The Trail of Lights was canceled four times, first starting in 2001 and 2002 due to the September 11 Attacks, and again in 2010 and 2011 due to budget shortfalls, but the trail was turned back on for the 2012 holiday season.
Cuisine and breweries
Austin is perhaps best known for its Texas barbecue and Tex-Mex cuisine. Franklin Barbecue is perhaps Austin's most famous barbecue restaurant; the restaurant has sold out of brisket every day since its establishment. Breakfast tacos and Chili con queso, queso are popular food items in the city; Austin is sometimes called the "home of the breakfast taco." Kolach (cake), Kolaches are a common pastry in Austin bakeries due to the large Czech Americans, Czech and German Americans, German immigrant population in Texas. The Oasis Restaurant is the largest outdoor restaurant in Texas, which promotes itself as the "Sunset Capital of Texas" with its terraced views looking West over
Lake Travis
Lake Travis is a reservoir on the Colorado River in central Texas in the United States.
Serving principally as a flood-control reservoir, Lake Travis' historical minimum to maximum water height change is nearly 100 feet. In 2018 alone, it saw ...
. P. Terry's, an Austin-based fast food burger chain, has a loyal following among Austinites. Some other Austin-based chain restaurants include Amy's Ice Creams, Bush's Chicken, Chuy's, DoubleDave's Pizzaworks, and Schlotzky's.
Austin is also home to a large number of food trucks, with 1,256 food trucks operating in 2016.
The city of Austin has the second-largest number of food trucks per capita in the United States.
Austin's first food hall, "Fareground," features a number of Austin-based food vendors and a bar in the ground level and courtyard of One Congress Plaza.
Austin has a large craft beer scene, with over 50 microbreweries in the metro area. Drinks publication VinePair named Austin as the "top beer destination in the world" in 2019. Notable Austin-area breweries include Jester King Brewery, Live Oak Brewing Company, and Real Ale Brewing Company.
Music

As Austin's official slogan is ''The Live Music Capital of the World'', the city has a vibrant live Music of Austin, music scene with more music venues per capita than any other U.S. city.
Austin's music revolves around the many nightclubs on 6th Street and an annual film/music/interactive festival known as
South by Southwest
South by Southwest, abbreviated as SXSW and colloquially referred to as South By, is an annual conglomeration of parallel film, interactive media, and music festivals and Convention (meeting), conferences organized jointly that take place in m ...
(SXSW). The concentration of restaurants, bars, and music venues in the city's downtown core is a major contributor to Austin's live music scene, as the ZIP Code encompassing the downtown entertainment district hosts the most bar or alcohol-serving establishments in the U.S.
The longest-running concert music program on American television, ''
Austin City Limits
''Austin City Limits'' is an American live music television program recorded and produced by Austin PBS. The show helped Austin become widely known in the United States as the "Live Music Capital of the World", and is the only television show t ...
'', is recorded at ACL Live at The Moody Theater, located in the bottom floor of the W Hotels in Austin. ''Austin City Limits'' and C3 Presents produce the Austin City Limits Music Festival, an annual music and art festival held at
Zilker Park
Zilker Metropolitan Park is a recreational area in south Austin, Texas at the juncture of Barton Creek and the Colorado River that comprises over of publicly owned land. It is named after its benefactor, Andrew Jackson Zilker, who donated the la ...
in Austin. Other music events include the Urban Music Festival, Fun Fun Fun Fest, Chaos In Tejas and Old Settler's Music Festival. Austin Lyric Opera performs multiple operas each year (including the 2007 opening of Philip Glass's ''Waiting for the Barbarians (opera), Waiting for the Barbarians'', written by University of Texas at Austin alumnus J. M. Coetzee).
The Austin Symphony Orchestra performs a range of classical, pop and family performances and is led by music director and conductor Peter Bay. The Austin Baroque Orchestra and La Follia Austin Baroque ensembles both give historically informed performances of Baroque music.
Film
Austin hosts several film festivals, including the South by Southwest Film Conference, SXSW (South by Southwest) Film Festival and the Austin Film Festival, which hosts international films. A movie theater chain by the name of Alamo Drafthouse Cinema was founded in Austin in 1997; the South Lamar location of which is home to the annual week-long Fantastic Fest film festival. In 2004 the city was first in ''MovieMaker Magazine's'' annual top ten cities to live and make movies.
Austin has been the location for a number of motion pictures, partly due to the influence of The University of Texas at Austin College of Communication, University of Texas at Austin Department of Radio-Television-Film. Films produced in Austin include ''The Texas Chain Saw Massacre'' (1974), ''Songwriter'' (1984), ''Man of the House (2005 crime comedy film), Man of the House'', ''Secondhand Lions'', ''Texas Chainsaw Massacre 2'', ''Nadine (1987 film), Nadine'', ''Waking Life'', ''Spy Kids (film), Spy Kids'', ''The Faculty'', Dazed and Confused (film), ''Dazed and Confused'', ''The Guards Themselves'', ''Wild Texas Wind'', ''Office Space'', ''The Life of David Gale'', ''Miss Congeniality (film), Miss Congeniality'', ''Doubting Thomas'', ''Slacker (film), Slacker'', ''Idiocracy'', ''Death Proof'', ''The New Guy'', ''Hope Floats'', ''The Alamo (2004 film), The Alamo'', ''Blank Check (film), Blank Check'', ''The Wendall Baker Story'', ''School of Rock'', ''A Slipping-Down Life'', ''A Scanner Darkly (film), A Scanner Darkly'', ''Saturday Morning Massacre'', and most recently, the Coen brothers' ''True Grit (2010 film), True Grit'', ''Grindhouse (film), Grindhouse'', ''Machete (2010 film), Machete'', ''How to Eat Fried Worms (film), How to Eat Fried Worms'', ''Bandslam'' and ''Lazer Team''. In order to draw future film projects to the area, the Austin Film Society has converted several airplane hangars from the former Mueller Airport into filmmaking center Austin Studios. Projects that have used facilities at Austin Studios include music videos by The Flaming Lips and feature films such as ''25th Hour'' and ''Sin City (film), Sin City''.
Austin also hosted the MTV series, ''The Real World: Austin'' in 2005. Fear the Walking Dead (season 4), Season 4 of the AMC (TV channel), AMC show ''Fear the Walking Dead'' was filmed in various locations around Austin in 2018. The film review websites Spill.com and Ain't It Cool News are based in Austin. Rooster Teeth Productions, creator of popular web series such as ''Red vs. Blue'' and ''RWBY'', is also located in Austin.
Theater

Austin has a strong theater culture, with dozens of itinerant and resident companies producing a variety of work. The Church of the Friendly Ghost is a volunteer-run arts organization supporting creative expression and counter-culture community. The city also has live performance theater venues such as the Zachary Scott Theatre Center, Vortex Repertory Company, Salvage Vanguard Theater, Rude Mechanicals' the Off Center, Austin Playhouse, Scottish Rite Children's Theater, Hyde Park Theatre, the Blue Theater, The Hideout Theatre, and Esther's Follies. The Victory Grill was a renowned venue on the Chitlin' Circuit. Public art and performances in the parks and on bridges are popular. Austin hosts the Fuse Box Festival each April featuring theater artists.
The Paramount Theatre (Austin, Texas), Paramount Theatre, opened in downtown Austin in 1915, contributes to Austin's theater and film culture, showing classic films throughout the summer and hosting regional premieres for films such as ''Miss Congeniality (film), Miss Congeniality''. The
Zilker Park
Zilker Metropolitan Park is a recreational area in south Austin, Texas at the juncture of Barton Creek and the Colorado River that comprises over of publicly owned land. It is named after its benefactor, Andrew Jackson Zilker, who donated the la ...
Summer Musical is a long-running outdoor musical.
The Long Center for the Performing Arts is a 2,300-seat theater built partly with materials reused from the old Lester E. Palmer Auditorium.
Ballet Austin is among the fifteen largest ballet academies in the country. Each year Ballet Austin's 20-member professional company performs ballets from a wide variety of choreographers, including their international award-winning artistic director, Stephen Mills. The city is also home to the Ballet East Dance Company, a modern dance ensemble, and the Tapestry Dance Company which performs a variety of dance genres.
The Austin improvisational theatre scene has several theaters: ColdTowne Theater, The Hideout Theater, The Fallout Theater, and The Institution Theater. Austin also hosts the Out of Bounds Comedy Festival, which draws comedic artists in all disciplines to Austin.
Libraries

The Austin Public Library is a public library system operated by the City of Austin and consists of the Central Library on Cesar Chavez Street (Austin), César Chávez Street, the Austin History Center, 20 branches and the Recycled Reads bookstore and upcycling facility. The APL library system also has mobile libraries – bookmobile buses and a human-powered trike and trailer called "unbound: sin fronteras."
The Central Library, which is an anchor to the redevelopment of the former Seaholm Power Plant site and the Shoal Creek, Austin, Texas, Shoal Creek Walk, opened on October 28, 2017. The six-story Central Library contains a living rooftop garden, reading porches, an indoor reading room, bicycle parking station, large indoor and outdoor event spaces, a gift shop, an art gallery, café, and a "technology petting zoo" where visitors can play with next-generation gadgets like 3D printing, 3D printers. In 2018, Time (magazine), Time magazine named the Austin Central Library on its list of "World's Greatest Places."
Museums and other points of interest

Museums in Austin include the Texas Memorial Museum, the George Washington Carver Museum and Cultural Center, Thinkery, the Blanton Museum of Art (reopened in 2006), the Bob Bullock Texas State History Museum across the street (which opened in 2000), The Contemporary Austin, the Elisabet Ney Museum and the galleries at the Harry Ransom Center. The
Texas State Capitol
The Texas State Capitol is the capitol and seat of government of the American state of Texas. Located in downtown Austin, Texas, the structure houses the offices and chambers of the Texas Legislature and of the Governor of Texas. Designed in 18 ...
itself is also a major tourist attraction.
The Driskill Hotel, built in 1886, once owned by George W. Littlefield, and located at 6th and Brazos streets, was finished just before the construction of the Capitol building. 6th Street (Austin), Sixth Street is a musical hub for the city. The Enchanted Forest, a multi-acre outdoor music, art, and performance art space in South Austin hosts events such as fire-dancing and circus-like-acts. Austin is also home to the Lyndon Baines Johnson Library and Museum, which houses documents and artifacts related to the Johnson administration, including LBJ's limousine and a re-creation of the Oval Office.

Locally produced art is featured at the South Austin Museum of Popular Culture. The Mexic-Arte Museum is a Mexican and Mexican-American art museum founded in 1983. Austin is also home to the O. Henry House Museum, which served as the residence of O. Henry from 1893 to 1895. Farmers' markets are popular attractions, providing a variety of locally grown and often organic foods.
Austin also has many odd statues and landmarks, such as the ''Stevie Ray Vaughan Memorial'', the Willie Nelson statue, ''Willie Nelson'' statue, the Mangia dinosaur, the Loca Maria lady at Taco Xpress, the Hyde Park Gym's giant flexed arm, and Daniel Johnston's ''Hi, How are You?'' Jeremiah the Innocent frog mural.
The Ann W. Richards Congress Avenue Bridge houses the world's largest urban population of Mexican free-tailed bats. Starting in March, up to 1.5 million bats take up residence inside the bridge's expansion and contraction zones as well as in long horizontal grooves running the length of the bridge's underside, an environment ideally suited for raising their young. Every evening around sunset, the bats emerge in search of insects, an exit visible on weather radar. Watching the bat emergence is an event that is popular with locals and tourists, with more than 100,000 viewers per year. The bats migrate to Mexico each winter.
The Austin Zoo, located in unincorporated area, unincorporated western
Travis County
Travis County is located in south central Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,290,188. It is the fifth-most populous county in Texas. Its county seat is Austin, the capital of Texas. The county was established in 1840 and is na ...
, is a Rescue coordination centre, rescue zoo that provides sanctuary to displaced animals from a variety of situations, including those involving neglect.
The HOPE Outdoor Gallery is a public, three-story outdoor street art project located on Baylor Street in the Clarksville, Austin, Texas, Clarksville neighborhood. The gallery, which consists of the foundations of a failed multifamily development, is a constantly-evolving canvas of graffiti and murals. Also known as "Castle Hill" or simply "Graffiti Park," the site on Baylor Street was closed to the public in early January 2019 but remained intact, behind a fence and with an armed guard, in mid-March 2019. The gallery will build a new art park at Carson Creek Ranch in Southeast Austin.
Sports


Many Austinites support the athletic programs of the University of Texas at Austin known as the Texas Longhorns. During the 2005–2006 academic term, Texas Longhorns football, Longhorns football team was named the NCAA Division I FBS National Football Championship, NCAA Division I FBS National Football Champion, and Texas Longhorns baseball, Longhorns baseball team won the 2005 College World Series, College World Series. The Texas Longhorns play home games in the state's second-largest sports stadium, Darrell K Royal–Texas Memorial Stadium, seating over 101,000 fans. Baseball games are played at UFCU Disch–Falk Field.
Austin was the most populous city in the United States without a Major professional sports leagues of the United States and Canada, major-league professional sports team, which changed in 2021 with
Austin FC
Austin FC is an American professional soccer club based in Austin, Texas. The club competes in Major League Soccer (MLS) as a member of the Western Conference. Founded in 2018, the club began play in the 2021 season. Their home stadium is Q2 ...
's entry to MLS. Minor-league professional sports came to Austin in 1996, when the Austin Ice Bats began playing at the Travis County Expo Center; they were later replaced by the American Hockey League, AHL Texas Stars. Austin has hosted a number of other professional teams, including the Austin Spurs of the NBA G League, the Austin Aztex of the United Soccer League, the Austin Outlaws in Women's Football Alliance, WFA football, and the Austin Aces in World TeamTennis, WTT tennis.
Natural features like the bicycle-friendly
Texas Hill Country
The Texas Hill Country is a geographic region of Central and South Texas, forming the southeast part of the Edwards Plateau. Given its location, climate, terrain, and vegetation, the Hill Country can be considered the border between the Ameri ...
and generally mild #Climate, climate make Austin the home of several endurance and multi-sport races and communities. The Capitol 10,000 is the largest race in Texas, and approximately fifth largest in the United States. The Austin Marathon has been run in the city every year since 1992. Additionally, the city is home to the largest 5 mile race in Texas, named the Turkey Trot as it is run annually on thanksgiving. Started in 1991 by Thundercloud Subs, a local sandwich chain (who still sponsors the event), the event has grown to host over 20,000 runners. All proceeds are donated to Caritas of Austin, a local charity.
The Austin-founded American Swimming Association hosts several swim races around town. Austin is also the hometown of several cycling groups and the disgraced cyclist Lance Armstrong. Combining these three disciplines is a growing crop of triathlons, including the Capital of Texas Triathlon held every Memorial Day on and around Lady Bird Lake, Auditorium Shores, and
Downtown Austin
Downtown Austin is the central business district of Austin, Texas. Downtown is located on the north bank of the Colorado River. The approximate borders of Downtown include Lamar Boulevard to the west, Martin Luther King Jr. Boulevard and the Un ...
.
Austin is home to the Circuit of the Americas (COTA), a grade 1 Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile specification motor racing facility which hosts the Formula One United States Grand Prix. The State of Texas has pledged $25 million in public funds annually for 10 years to pay the sanctioning fees for the race. Built at an estimated cost of $250 to $300 million, the circuit opened in 2012 and is located just east of the Austin Bergstrom International Airport. In August 2017, a new soccer-specific stadium was announced to be built between the Austin360 Amphitheater and the Grand Plaza at COTA. A professional soccer team known as Austin Bold FC will start playing in the United Soccer League in 2019.
The summer of 2014 marked the inaugural season for World TeamTennis team Austin Aces, formerly Orange County Breakers of the southern California region. The Austin Aces played their matches at the Cedar Park Center northwest of Austin, and featured former professionals Andy Roddick and Marion Bartoli, as well as current WTA tour player Vera Zvonareva. The team left after the 2015 season.
In 2017, Anthony Precourt, Precourt Sports Ventures announced a plan to move the Columbus Crew SC soccer franchise from Columbus, Ohio to Austin. Precourt negotiated an agreement with the City of Austin to build a $200 million privately funded stadium on public land at 10414 McKalla Place, following initial interest in Butler Shores Metropolitan Park and Roy G. Guerrero Colorado River Park. As part of an arrangement with the league, operational rights of Columbus Crew SC were sold in late 2018, and Austin FC was announced as Major League Soccer's 27th franchise on January 15, 2019, with the expansion team starting play in 2021.
Parks and recreation
The Austin Parks and Recreation Department received the Excellence in Aquatics award in 1999 and the Gold Medal Awards in 2004 from the National Recreation and Park Association.
To strengthen the region's parks system, which spans more than , The Austin Parks Foundation (APF) was established in 1992 to develop and improve parks in and around Austin. APF works to fill the city's park funding gap by leveraging volunteers, philanthropists, park advocates, and strategic collaborations to develop, maintain and enhance Austin's parks, trails and green spaces.
Lady Bird Lake
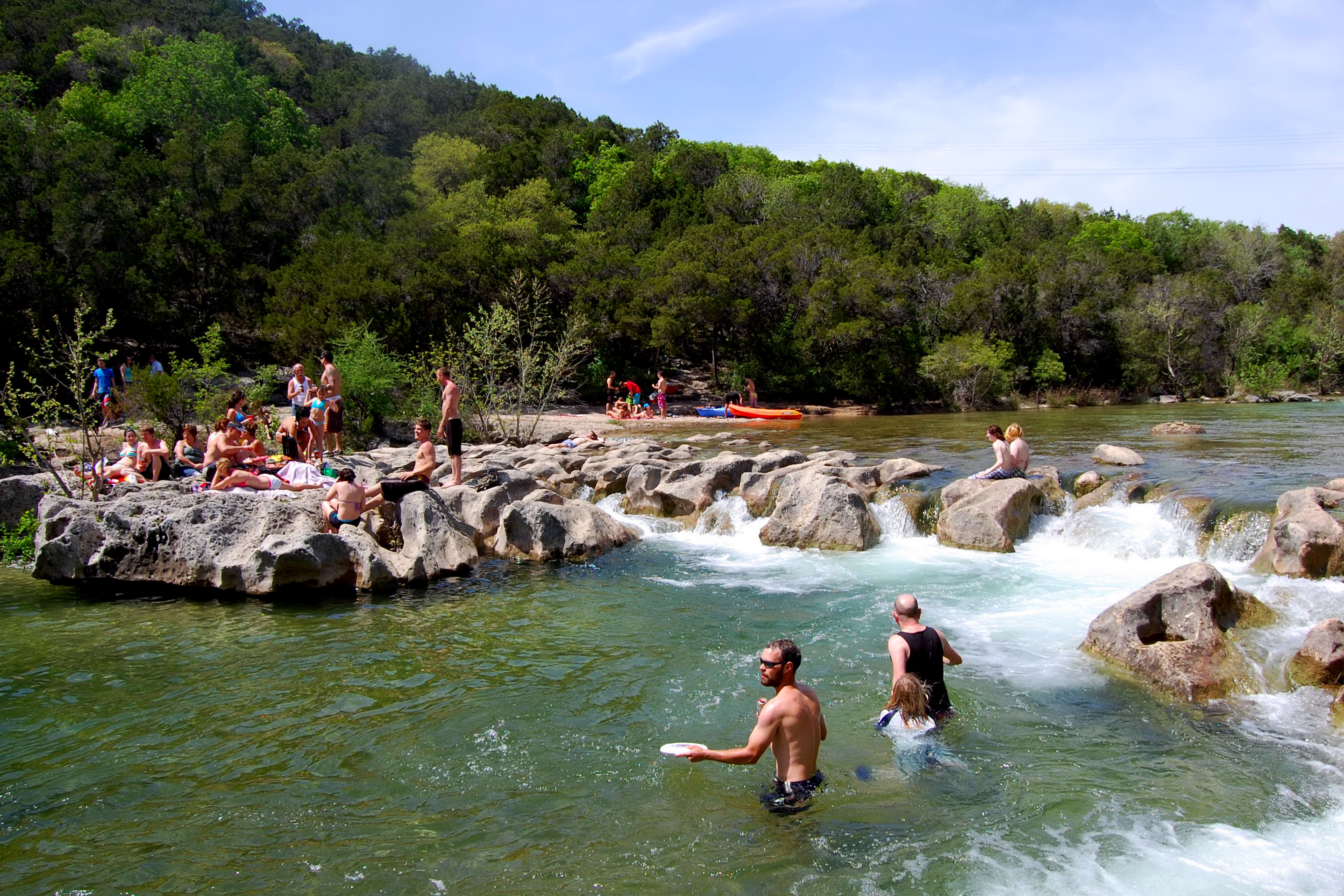





Lady Bird Lake
Lady Bird Lake (formerly, and still colloquially referred to as Town Lake) is a river-like reservoir on the Colorado River in Austin, Texas, United States. The City of Austin created the reservoir in 1960 as a cooling pond for a new city power p ...
(formerly Town Lake) is a river-like reservoir on the Colorado River. The lake is a popular recreational area for Paddleboarding, paddleboards, kayaks, canoes, dragon boats, and rowing (sport), rowing shells. Austin's warm climate and the river's calm waters, nearly length and straight courses are especially popular with sport rowing, crew teams and clubs. Other recreational attractions along the shores of the lake include swimming in Deep Eddy Pool, the oldest swimming pool in Texas, and Red Bud Isle, a small island formed by the 1900 Austin Dam failure (Texas), collapse of the McDonald Dam that serves as a recreation area with a dog park and access to the lake for canoeing and fishing. The Ann and Roy Butler Hike and Bike Trail forms a complete circuit around the lake. A local nonprofit, The Trail Foundation, is the Trail's private steward and has built amenities and infrastructure including trailheads, lakefront gathering areas, restrooms, exercise equipment, as well as doing Trailwide ecological restoration work on an ongoing basis. The Butler Trail loop was completed in 2014 with the public-private partnership 1-mile Boardwalk project.
Along the shores of Lady Bird Lake is the 350 acre (142 ha)
Zilker Park
Zilker Metropolitan Park is a recreational area in south Austin, Texas at the juncture of Barton Creek and the Colorado River that comprises over of publicly owned land. It is named after its benefactor, Andrew Jackson Zilker, who donated the la ...
, which contains large open lawns, sports fields, cross country courses, historical markers, concession stands, and picnic areas. Zilker Park is also home to numerous attractions, including the Zilker Botanical Garden, the Umlauf Sculpture Garden, Zilker Hillside Theater, the Austin Nature & Science Center, and the Zilker Zephyr, a gauge Ridable miniature railway, miniature railway carries passengers on a tour around the park. Auditorium Shores, an urban park along the lake, is home to the Palmer Auditorium, the Long Center for the Performing Arts, and an Dog park, off-leash dog park on the water. Both Zilker Park and Auditorium Shores have a direct view of the Downtown skyline.
Barton Creek Greenbelt
The Barton Creek Greenbelt is a public green belt managed by the City of Austin's Park and Recreation Department. The Greenbelt, which begins at
Zilker Park
Zilker Metropolitan Park is a recreational area in south Austin, Texas at the juncture of Barton Creek and the Colorado River that comprises over of publicly owned land. It is named after its benefactor, Andrew Jackson Zilker, who donated the la ...
and stretches South/Southwest to the Woods of Westlake subdivision (land), subdivision, is characterized by large
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
cliffs, dense foliage, and shallow bodies of water. Popular activities include rock climbing, mountain biking, and hiking. Some well known naturally forming swimming holes along Austin's greenbelt include Twin Falls, Sculpture Falls, Gus Fruh Pool, and Campbell's Hole. During years of heavy rainfall, the water level of the creek rises high enough to allow human swimming, swimming, High diving, cliff diving, kayaking, Paddleboarding, paddle boarding, and tubing (recreation), tubing.
Swimming holes
Austin is home to more than 50 public pools and swimming holes. These include Deep Eddy Pool, Texas' oldest man-made swimming pool, and Barton Springs Pool, the nation's largest natural swimming pool in an urban area. Barton Springs Pool is spring-fed while Deep Eddy is well-fed. Both range in temperature from about during the winter to about during the summer. Hippie Hollow Park, a county park situated along Lake Travis, is the only officially sanctioned nude beach, clothing-optional public park in Texas. Hamilton Pool Preserve is a natural pool that was created when the dome of an underground river collapsed due to massive erosion thousands of years ago. The pool, located about 23 miles (37 km) west of Austin, is a popular summer swimming spot for visitors and residents. Hamilton Pool Preserve consists of 232 acres (0.94 km2) of protected natural habitat featuring a jade green pool into which a 50-foot (15 m) waterfall flows.
Other parks and recreation
Camping is legal on all public property except in front of City Hall since 2019. However, "Other areas where camping remains banned include any city park space, under Austin Parks and Recreation rules. That includes downtown green spaces as well as trails and greenbelts such as along Barton Creek."
McKinney Falls State Park is a state park administered by the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department, located at the confluence of Onion Creek (Texas), Onion Creek and Williamson Creek. The park includes several designated hiking trails and campground, campsites with water and electric. The namesake features of the park are the scenic upper and lower falls along Onion Creek. The Emma Long Metropolitan Park is a municipal park along the shores of
Lake Austin
Lake Austin, formerly Lake McDonald, is a water reservoir on the Colorado River in Austin, Texas. The reservoir was formed in 1939 by the construction of Tom Miller Dam by the Lower Colorado River Authority. Lake Austin is one of the seven High ...
, originally constructed by the Civilian Conservation Corps. The Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center is a botanical garden and arboretum that features more than 800 species of native Texas plants in both garden and natural settings; the Wildflower Center is located southwest of Downtown in Circle C Ranch. Roy G. Guerrero Park is located along the Colorado River in East Riverside-Oltorf, Austin, Texas, East Riverside and contains miles of wooded trails, a sandy beach along the river, and a disc golf course.
Covert Park, located on the top of Mount Bonnell, is a popular tourist destination overlooking Lake Austin and the Colorado River. The mount provides a vista for viewing the city of Austin, Lake Austin, and the surrounding hills. It was designated a Recorded Texas Historic Landmark in 1969, bearing Marker number 6473, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2015.
The Austin Country Club is a private golf club located along the shores of the Colorado River, right next to the Pennybacker Bridge. Founded in 1899, the club moved to its third and present site in 1984, which features a challenging layout designed by noted course architect Pete Dye.
Government
Crime
As of 2021, Austin is one of the safest large cities in the United States. In 2019, the FBI named Austin the 11th safest city on a list of 22 American cities with a population above 400,000.
FBI statistics show that overall violent and property crimes dropped in Austin in 2015, but increased in suburban areas of the city. One such southeastern suburb, Del Valle, Texas, Del Valle, reported eight homicides within two months in 2016. According to 2016 Austin Police Department, APD crime statistics, the 78723 census tract had the most violent crime, with 6 murders, 25 rapes, and 81 robberies. The city had 39 homicides in 2016, the most since 1997.
Notable incidents
One of the first American Mass shootings in the United States, mass school shooting incidents took place in Austin on August 1, 1966, when Charles Whitman shot 43 people, killing 13 from the top of the University of Texas tower.
The University of Texas tower shooting led to the formation of the SWAT team of the Austin Police Department.
In 1991, 1991 Austin yogurt shop murders, four teenage girls were murdered in a yogurt shop by an unknown assailant(s). A police officer responded to reports of a fire at the I Can't Believe It's Yogurt! store on Anderson Lane and discovered the girls' bodies in a back room. The murders remain unsolved.
In 2010, Andrew Joseph Stack III deliberately crashed his Piper PA-28 Cherokee into Echelon 1, a building in which the Internal Revenue Service, housing 190 employees was a lessee of. The resulting explosion killed 1 and injured 13 IRS employees, completely destroyed the building and cost the IRS a total of $38.6 million. ''(see 2010 Austin suicide attack)''
A Austin serial bombings, series of bombings occurred in Austin in March 2018. Over the course of 20 days, five Letter bomb, package bombs exploded, killing two people and injuring another five. The suspect, 23-year-old Mark Anthony Conditt of Pflugerville, Texas, suicide bombing, blew himself up inside his vehicle after he was pulled over by police on March 21, also injuring a police officer.
In 2020, Austin was the victim of a cyberattack by the Russian group Berserk Bear, possibly related to the 2020 United States federal government data breach, U.S. federal government data breach earlier that year.
On April 18, 2021, a shooting occurred at the Arboretum Oaks Apartments near The Arboretum (Austin, Texas), The Arboretum shopping center, in which a former Travis County Sheriff's Office detective killed his ex-wife, his adoptive daughter, and his daughter's boyfriend.
The suspect, who was previously charged with child sexual assault, was arrested in Manor, Texas, Manor after a 20-hour manhunt.
A mass shooting took place in the early morning of June 12, 2021, on Sixth Street (Austin, Texas), Sixth Street, which resulted in 14 people injured and one dead. The man killed was believed to be an innocent bystander who was struck as he was standing outside a bar. A 19-year-old suspect was formally charged and arrested in Killeen, Texas, Killeen nearly two weeks after the shooting.
City government

Austin is administered by an 11-member city council (10 council members elected by geographic district plus a mayor elected at large). The council is accompanied by a hired city manager under the manager-council system of municipal governance. Council and mayoral elections are non-partisan, with a runoff in case there is no majority winner. A referendum approved by voters on November 6, 2012, changed the council composition from six council members plus a mayor elected at large to the current "10+1" district system. November 2014 marked the first election under the new system. The Federal government of the United States, Federal government had forced San Antonio and Dallas to abandon at-large systems before 1987; however, the court could not show a racist pattern in Austin and upheld the city's at-large system during a 1984 lawsuit. In five elections between 1973 and 1994 Austin voters rejected single-member districts.
Austin formerly operated its city hall at 128 West 8th Street. Antoine Predock and Cotera Kolar Negrete & Reed Architects designed a new city hall building, which was intended to reflect what ''The Dallas Morning News'' referred to as a "crazy-quilt vitality, that embraces everything from country music to environmental protests and high-tech swagger." The new city hall, built from recycled materials, has solar panels in its garage. The city hall, at 301 West Second Street, opened in November 2004. Steve Adler (lawyer), Steve Adler assumed the office of mayor on January 6, 2015.
Law enforcement in Austin is provided by the Austin Police Department, except for state government buildings, which are patrolled by the Texas Department of Public Safety. The University of Texas Police operate from the
University of Texas
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
.
Fire protection within the city limits is provided by the Austin Fire Department, while the surrounding county is divided into twelve geographical areas known as emergency services districts, which are covered by separate regional fire departments. Emergency medical services are provided for the whole county by Austin-Travis County Emergency Medical Services.
Mayor Steve Adler (politician), Steve Adler (Democratic Party (U.S.), D)
Other levels of government
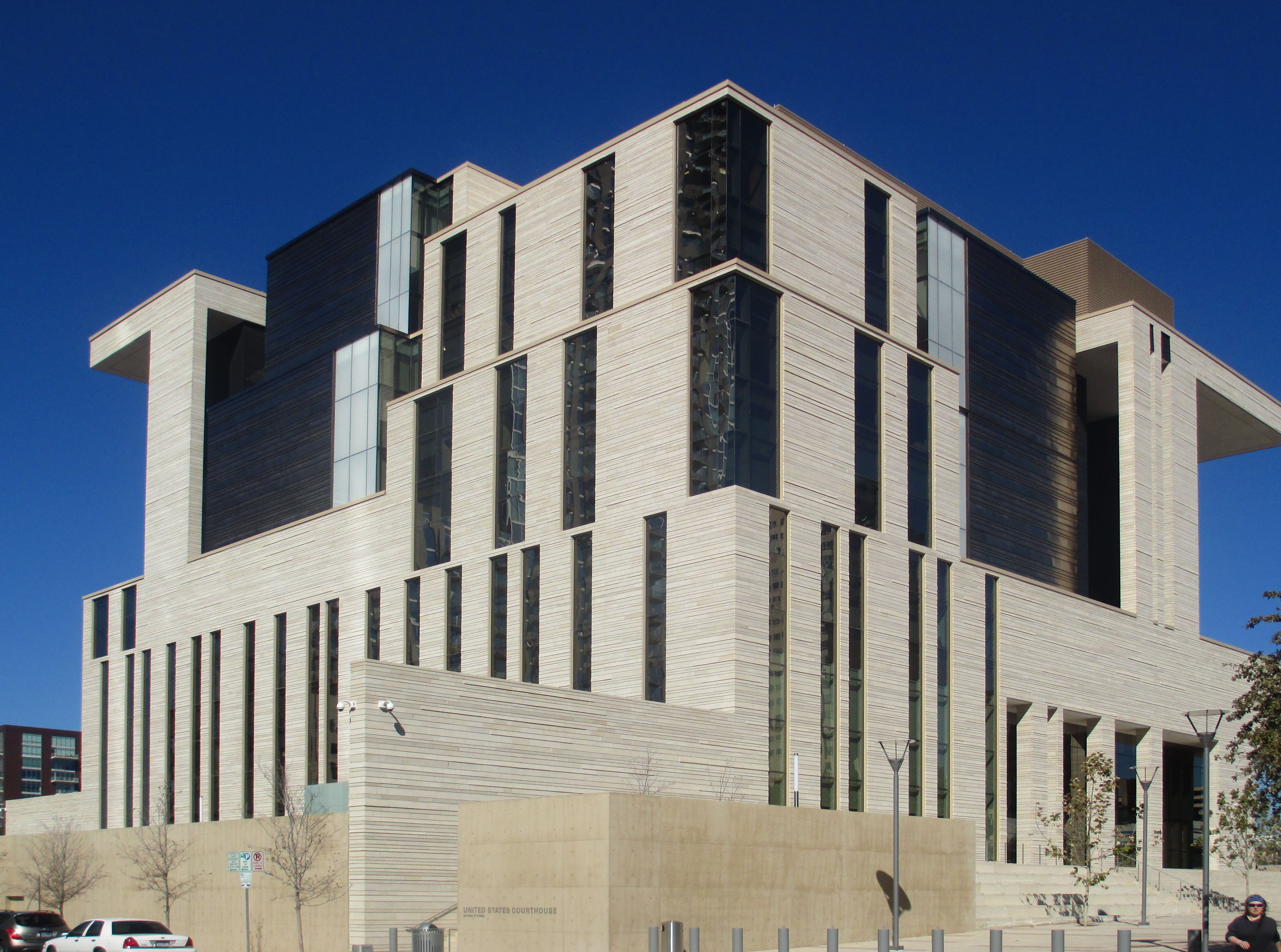

Austin is the county seat of
Travis County
Travis County is located in south central Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,290,188. It is the fifth-most populous county in Texas. Its county seat is Austin, the capital of Texas. The county was established in 1840 and is na ...
and hosts the Heman Marion Sweatt Travis County Courthouse downtown, as well as other county government offices.
The Texas Department of Transportation operates the Austin District Office in Austin.
The Texas Department of Criminal Justice (TDCJ) operates the Austin I and Austin II district parole offices in Austin.
The United States Postal Service operates several post offices in Austin.
Politics
Austin is known as an enclave of Modern liberalism in the United States, liberal politics in an otherwise conservative state—so much so, that the city is sometimes sarcastically called the "People's Republic of Austin" by residents of other parts of Texas, and conservatives in the Texas Legislature. Former Governor Rick Perry referred to it as a "blueberry in the tomato soup," meaning it is a Democratic city in a Republican state.
Since redistricting following the 2010 United States census, Austin has been divided between six congressional districts at the federal level: Texas's 35th congressional district, Texas's 35th, Texas's 25th congressional district, Texas's 25th, Texas's 10th congressional district, Texas's 10th, Texas's 21st congressional district, Texas's 21st, Texas's 17th congressional district, Texas's 17th, and Texas's 31st congressional district, Texas's 31st. Texas's 35th congressional district is represented by Democrat Lloyd Doggett. The other five districts are represented by Republicans, of whom only one, Michael McCaul of the 10th district, lives in
Travis County
Travis County is located in south central Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,290,188. It is the fifth-most populous county in Texas. Its county seat is Austin, the capital of Texas. The county was established in 1840 and is na ...
.
As a result of the major party realignment that began in the 1970s, central Austin became a stronghold of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, while the suburbs tend to vote Republican Party (United States), Republican. Overall, the city is a blend of downtown liberalism and suburban conservatism but leans to the political left as a whole. The city last went to a Republican candidate in 2000 when former Texas Governor George W. Bush successfully ran for president. In 2004, the Democrats rebounded strongly as John Kerry enjoyed a 14.0% margin over Bush, who once again won Texas.
City residents have been supportive of alternative candidates; for example, Ralph Nader presidential campaign, 2000, Ralph Nader won 10.4% of the vote in Austin in 2000.
In 2003, the city adopted a resolution against the USA PATRIOT Act that reaffirmed constitutionally guaranteed rights.
As of 2018, all six of Austin's state legislative districts are held by Democrats.
Travis County was also the only county in Texas to reject Texas Constitutional Amendment Proposition 2 that effectively outlawed gay marriage and status equal or similar to it and did so by a wide margin (40% for, 60% against).
Two of the candidates for president in the 2004 race called Austin home. Michael Badnarik, the Libertarian Party candidate, and David Cobb (activist), David Cobb of the Green Party of the United States, Green Party both had lived in Austin. During the run up to the election in November, a presidential debate was held at the
University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
student union involving the two candidates. While the Commission on Presidential Debates only invites Democrats and Republicans to participate in televised debates, the debate at UT was open to all presidential candidates. Austin also hosted one of the last presidential debates between Barack Obama and Hillary Clinton during their heated race for the Democratic nomination in 2008.
In the 2016 presidential election, Travis County, which contains the majority of Austin, voted for Hillary Clinton (D) by a 38.9-point margin (66.3% to 27.4%).
Gerrymandering
A controversial turning point in the political history of the Austin area was the 2003 Texas redistricting. Before then, Austin had been entirely or almost entirely within the borders of a single congressional district–what was then the 10th District–for over a century. Opponents characterized the resulting district layout as excessively partisan gerrymandering, and the plan was challenged in court by Democratic and minority activists. The Supreme Court of the United States has never struck down a redistricting plan for being excessively partisan. The plan was subsequently upheld by a three-judge federal panel in late 2003, and on June 28, 2006, the matter was largely settled when the Supreme Court, in a 7–2 decision, upheld the entire congressional redistricting plan with the exception of a Hispanic-majority district in southwest Texas. This affected Austin's districting, as U.S. Rep. Lloyd Doggett's district (U.S. Congressional District 25) was found to be insufficiently compact to compensate for the reduced minority influence in the southwest district; it was redrawn so that it took in most of southeastern Travis County and several counties to its south and east.
Environmental movement
The distinguishing political movement of Austin politics has been that of the environmental movement, which spawned the parallel neighborhood movement, then the more recent conservationist movement (as typified by the Hill Country Conservancy), and eventually the current ongoing debate about "sense of place" and preserving the Austin quality of life. Much of the environmental movement has matured into a debate on issues related to saving and creating an Austin "sense of place."
In 2012, Austin became just one of a few cities in
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
to ban the sale and use of plastic bags. However, the ban ended in 2018 due to a court ruling that regarded all bag bans in the state to contravene the Texas Solid Waste Disposal Act.
Education
According to the 2015–2019 Census estimates, 51.7% of Austin residents ages 25 and over have earned at least a bachelor's degree, compared to the national figure of 32.1%. 19.4% hold a Graduate degree, graduate or professional degree, compared to the national figure of 12.4%.
Higher education



Austin is home to the
University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
, the flagship institution of the University of Texas System with over 40,000 undergraduate students and 11,000 graduate students.
Other institutions of higher learning in Austin include St. Edward's University,
Huston–Tillotson University
Huston–Tillotson University (HT) is a private historically black university in Austin, Texas. Established in 1875, Huston–Tillotson University was the first institution of higher learning in Austin. The university is affiliated with the Unite ...
, Austin Community College, Concordia University Texas, Concordia University, the Seminary of the Southwest, the Acton School of Business, Texas Health and Science University, University of St. Augustine for Health Sciences, Austin Graduate School of Theology, Austin Presbyterian Theological Seminary, Virginia College's Austin Campus, The Art Institute of Austin, Southern Careers Institute of Austin, Austin Conservatory and a branch of Park University.
The University of Texas System and Texas State University System are headquartered in downtown Austin.
Public primary and secondary education
Approximately half of the city by area is served by the Austin Independent School District. This district includes notable schools such as the magnet Liberal Arts and Science Academy High School of Austin, Texas (LASA), which, by test scores, has consistently been within the top thirty high schools in the nation, as well as The Ann Richards School for Young Women Leaders. The remaining portion of Austin is served by adjoining school districts, including Round Rock Independent School District, Round Rock ISD, Pflugerville Independent School District, Pflugerville ISD, Leander Independent School District, Leander ISD, Manor Independent School District, Manor ISD, Del Valle Independent School District, Del Valle ISD, Lake Travis Independent School District, Lake Travis ISD, Hays Consolidated Independent School District, Hays, and Eanes Independent School District, Eanes Independent school district, ISD.
Four of the metro's major public school systems, representing 54% of area enrollment, are included in ''Expansion Management'' magazine's latest annual education quality ratings of nearly 2,800 school districts nationwide. Two districts—Eanes and Round Rock—are rated "gold medal," the highest of the magazine's cost-performance categories.
Private and alternative education
The Austin metropolitan area is also served by 27 charter school districts and over 100 private schools.
Austin has a large network of private and alternative education institutions for children in PreK–12th grade exists. Austin is also home to child developmental institutions.
Media
Austin's main daily newspaper is the ''Austin American-Statesman''. ''The Austin Chronicle'' is Austin's alternative weekly, while ''The Daily Texan'' is the student newspaper of the
University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
. Austin's business newspaper is the weekly ''Austin Business Journal''. ''The Austin Monitor'' is an online outlet that specializes in insider reporting on City Hall, Travis County Commissioners Court, Austin Independent School District, AISD, and other related local civics beats. The ''Monitor'' is backed by the nonprofit Capital of Texas Media Foundation. Austin also has numerous smaller special interest or sub-regional newspapers such as the ''Oak Hill Gazette'', ''Westlake Picayune'', ''Hill Country News'', ''Round Rock Leader'', ''NOKOA'', and ''The Villager'' among others. ''Texas Monthly'', a major regional magazine, is also headquartered in Austin. The ''Texas Observer'', a muckraking biweekly political magazine, has been based in Austin for over five decades. The weekly ''Community Impact Newspaper'' published by John Garrett, former publisher of the ''Austin Business Journal'' has five regional editions and is delivered to every house and business within certain ZIP codes and all of the news is specific to those ZIP codes. Another statewide publication based in Austin is ''The Texas Tribune'', an on-line publication focused on Texas politics.
The ''Tribune'' is "user-supported" through donations, a business model similar to public radio. The editor is Evan Smith (journalist), Evan Smith, former editor of ''Texas Monthly''. Smith co-founded the ''Texas Tribune'', a nonprofit, non-partisan public media organization, with Austin venture capitalist John Thornton and veteran journalist Ross Ramsey.
Commercial radio stations include KASE-FM (Country music, country), KVET (AM), KVET (sports), KVET-FM (country), KKMJ-FM (adult contemporary), KLBJ (AM), KLBJ (talk), KLBJ-FM (classic rock), KFIT (variety hits), KFMK (contemporary Christian), KOKE-FM (progressive country) and KPEZ (rhythmic contemporary). KUT-FM is the leading Public broadcasting, public radio station in Texas and produces the majority of its content locally. KOOP (FM) is a volunteer-run radio station with more than 60 locally produced programs. KVRX is the student-run college radio station of the University of Texas at Austin with a focus on local and non-mainstream music and community programming. Other listener-supported stations include KAZI (urban contemporary), and KMFA (Classical music, classical).
Network television stations (affiliations in parentheses) include KTBC (TV), KTBC (Fox Owned-and-operated station, O&O), KVUE (ABC), KXAN (NBC), KEYE-TV (CBS), KLRU (PBS), KNVA (The CW), KBVO (TV), KBVO (MyNetworkTV), and KAKW (Univision Owned-and-operated station, O&O). KLRU produces several award-winning locally produced programs such as ''
Austin City Limits
''Austin City Limits'' is an American live music television program recorded and produced by Austin PBS. The show helped Austin become widely known in the United States as the "Live Music Capital of the World", and is the only television show t ...
''. Despite Austin's explosive growth, it is only a medium-sized market (currently 38th) because the suburban and rural areas are not much larger than the city proper. Additionally, the proximity of San Antonio truncates the potential market area.
Alex Jones, journalist, radio show host and filmmaker, produces his talk show ''The Alex Jones Show'' in Austin which broadcasts nationally on more than 60 AM and FM radio stations in the United States, WWCR Radio shortwave and XM Radio: Channel 166.
Transportation
In 2009, 72.7% of Austin (city) commuters drove alone, with other mode shares being: 10.4% carpool, 6% were remote workers, 5% use transit, 2.3% walk, and 1% bicycle. In 2016, the American Community Survey estimated modal shares for Austin (city) commuters of 73.5% for driving alone, 9.6% for carpooling, 3.6% for riding transit, 2% for walking, and 1.5% for cycling. The city of Austin has a lower than average percentage of households without a car. In 2015, 6.9 percent of Austin households lacked a car, and decreased slightly to 6 percent in 2016. The national average was 8.7 percent in 2016. Austin averaged 1.65 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8.
In mid-2019, TomTom ranked Austin as having the worst traffic congestion in Texas, as well as 19th nationally and 179th globally.
Highways

Central Austin lies between two major north–south freeways: Interstate 35 in Texas, Interstate 35 to the east and the State Highway Loop 1 (Texas), Mopac Expressway (Loop 1) to the west. U.S. Highway 183 (Texas), U.S. Highway 183 runs from northwest to southeast, and State Highway 71 (Texas), State Highway 71 crosses the southern part of the city from east to west, completing a rough "box" around central and north-central Austin. Austin is the largest city in the United States to be served by only one Interstate Highway.
U.S. Highway 290 (Texas), U.S. Highway 290 enters Austin from the east and merges into Interstate 35. Its highway designation continues south on I-35 and then becomes part of Highway 71, continuing to the west. Highway 290 splits from Highway 71 in southwest Austin, in an interchange known as "The Y." Highway 71 continues to Brady, Texas, and Highway 290 continues west to intersect Interstate 10 in Texas, Interstate 10 near Junction, Texas, Junction. Interstate 35 continues south through
San Antonio
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= U.S. state, State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, s ...
to Laredo, Texas, Laredo on the Texas-Mexico border. Interstate 35 is the highway link to the Dallas-Fort Worth metroplex in northern Texas. There are two links to Houston, Texas (Highway 290 and State Highway 71/Interstate 10). Highway 183 leads northwest of Austin toward Lampasas, Texas, Lampasas.
In the mid-1980s, construction was completed on State Highway Loop 360 (Texas), Loop 360, a scenic highway that curves through the hill country from near the 71/Mopac interchange in the south to near the 183/Mopac interchange in the north. The iconic Pennybacker Bridge, also known as the "360 Bridge," crosses Lake Austin to connect the northern and southern portions of Loop 360.
Tollways

State Highway 130 (Texas), State Highway 130 is a bypass route designed to relieve traffic congestion, starting from Interstate 35 just north of Georgetown and running along a parallel route to the east, where it bypasses
Round Rock
Round Rock is a city in the U.S. state of Texas, in Williamson County, Texas, Williamson County (with a small part in Travis County, Texas, Travis County), which is a part of the Greater Austin metropolitan area. Its population is 119,468 as of ...
, Austin,
San Marcos
San Marcos is the Spanish name of Saint Mark. It may also refer to:
Towns and cities Argentina
* San Marcos, Salta
Colombia
* San Marcos, Antioquia
* San Marcos, Sucre
Costa Rica
* San Marcos, Costa Rica (aka San Marcos de Tarrazú)
...
and New Braunfels, Texas, New Braunfels before ending at Interstate 10 east of Seguin, Texas, Seguin, where drivers could drive west to return to Interstate 35 in San Antonio, Texas, San Antonio. The first segment was opened in November 2006, which was located east of Austin–Bergstrom International Airport at Austin's southeast corner on State Highway 71 (Texas), State Highway 71. Highway 130 runs concurrently with Highway 45 from Pflugerville, Texas, Pflugerville on the north until it reaches US Highway 183, US 183 well south of Austin, at which point State Highway 45 (Texas), SR 45 continues west. The entire route of State Highway 130 is now complete. The final leg opened on November 1, 2012. The highway is noted for having a maximum speed limit of for the entire route. The section of the toll road between Mustang Ridge and Seguin has a posted speed limit of , the highest posted speed limits in the United States, speed limit in the United States.
State Highway 45 (Texas), State Highway 45 runs east–west from just south of Highway 183 in Cedar Park, Texas, Cedar Park to 130 inside Pflugerville, Texas, Pflugerville (just east of Round Rock). A tolled extension of State Highway Loop 1 was also created. A new southeast leg of Highway 45 has recently been completed, running from US 183 and the south end of Segment 5 of TX-130 south of Austin due west to I-35 at the FM 1327/Creedmoor exit between the south end of Austin and Buda, Texas, Buda. The 183A Toll Road opened in March 2007, providing a tolled alternative to U.S. 183 through the cities of Leander, Texas, Leander and Cedar Park, Texas, Cedar Park. Currently under construction is a change to East US 290 from US 183 to the town of Manor. Officially, the tollway will be dubbed Tollway 290 with "Manor Expressway" as nickname.
Despite the overwhelming initial opposition to the toll road concept when it was first announced, all three toll roads have exceeded revenue projections.

Airports
Austin's primary airport is Austin–Bergstrom International Airport (ABIA) (List of airports by IATA code: A#AU, IATA code AUS), located southeast of the city. The airport is on the site of the former Bergstrom Air Force Base, which was closed in 1993 as part of the Base Realignment and Closure process. Until 1999, Robert Mueller Municipal Airport was Austin's main airport until ABIA took that role and the old airport was shut down.
Austin Executive Airport, along with several smaller airports outside the city center, serves general aviation traffic.
Intercity transit
Amtrak's Austin (Amtrak station), Austin station is located in west downtown and is served by the ''Texas Eagle'' which runs daily between Chicago and San Antonio, continuing on to Los Angeles several times a week.
Railway segments between Austin and San Antonio have been evaluated for a proposed regional passenger rail project called "Lone Star Rail". However, failure to come to an agreement with the track's current owner, Union Pacific Railroad, ended the project in 2016.
Greyhound Lines operates the Austin Station north of downtown near Highland Mall.
Grupo Senda's Turimex Internacional service operates bus service from Austin to Nuevo Laredo and on to many destinations in Mexico from their station in East Austin.
Megabus (North America), Megabus offers daily service to San Antonio, Dallas/Fort Worth and Houston.
Public transportation

The Capital Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Capital Metro) provides public transportation to the city, primarily with its Capital MetroBus, MetroBus local bus service, the Capital MetroBus#MetroExpress, MetroExpress express bus system, as well as a bus rapid transit service, Capital MetroRapid, MetroRapid. Capital Metro opened a regional rail, commuter rail system, Capital MetroRail, in 2010.
The system consists of a single line serving downtown Austin, the neighborhoods of East Austin, North Central Austin, and Northwest Austin plus the suburb of Leander, Texas, Leander.
Since it began operations in 1985, Capital Metro has proposed adding light rail services to its network. Despite support from the City Council, voters rejected light rail proposals in 2000
and 2014.
However, in 2020, voters approved Capital Metro's transit expansion plan, Project Connect, by a comfortable margin. The plan proposes 2 new light rail lines, an additional bus rapid transit line (which could be converted to light rail in the future), a second commuter rail line, several new MetroRapid lines, more MetroExpress routes, and a number of other infrastructure, technology and service expansion projects.
Capital Area Rural Transportation System connects Austin with outlying suburbs and surrounding rural areas.
Ride sharing
Austin is served by several Ridesharing company, ride-sharing companies including Uber and Lyft.
On May 9, 2016, Uber and Lyft voluntarily ceased operations in Austin in response to a city ordinance that required ride sharing company drivers to get fingerprint checks, have their vehicles labeled, and not pick up or drop off in certain city lanes.
Uber and Lyft resumed service in the summer of 2017.
The city was previously served by Fasten (company), Fasten until they ceased all operations in the city in March 2018.
Austin is also served by Electric Cab of North America's six-passenger electric car, electric cabs that operate on a flexible route from the Kramer station, Kramer MetroRail Station to The Domain (Austin, Texas), Domain Northside and from the Downtown station (Capital MetroRail), Downtown MetroRail station and MetroRapid stops to locations between the Austin Convention Center and near Sixth and Bowie streets by Whole Foods.
Carsharing service Zipcar operates in Austin and, until 2019, the city was also served by Car2Go which kept its North American headquarters in the city even after pulling out.
Cycling and walking

The city's bike advocacy organization is Bike Austin. BikeTexas, a state-level advocacy organization, also has its main office in Austin.
Bicycles are a popular transportation choice among students, faculty, and staff at the University of Texas. According to a survey done at the University of Texas, 57% of commuters bike to campus.
The City of Austin and Capital Metro jointly own a bike-sharing service, Capital Metropolitan Transportation Authority#Other services, Capital MetroBike, which is available in and around downtown. The service is a franchise of BCycle, a national bike sharing network owned by Trek Bicycle, and is operated by local nonprofit organization Bike Share of Austin. Until 2020 the service was known as Austin BCycle. In 2018, LimeBike, Lime began offering dockless bikes, which do not need to be docked at a designated station.
In 2018, scooter-sharing system, scooter-sharing companies Lime (transportation company), Lime and Bird (company), Bird debuted Scooter-sharing system, rentable electric scooters in Austin. The city briefly banned the scooters — which began operations before the city could implement a permitting system — until the city completed development of their "dockless mobility" permitting process on May 1, 2018. Dockless electric scooters and bikes are banned from Austin city parks and the Lady Bird Lake#Ann and Roy Butler Hike-and-Bike Trail and Boardwalk, Ann and Roy Butler Trail and Boardwalk. For the 2018 Austin City Limits Music Festival, the city of Austin offered a designated parking area for dockless bikes and scooters.
Notable people
International relations
Austin has two types of relationships with other cities, Sister city, sister and friendship.
Sister cities

Austin's sister cities are:
* City of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia (1983)
* Angers, Pays de la Loire, France (2011)
* Antalya, Antalya Province, Turkey (2009)
* Gwangmyeong, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea (2001)
* London Borough of Hackney, Hackney, London, England, United Kingdom (2014)
* Koblenz, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany (1991)
* Lima, Peru (1981)
* Maseru, Lesotho (1978)
* Ōita (city), Ōita, Ōita Prefecture, Ōita, Japan (1990)
* Orlu, Imo, Orlu, South East (Nigeria), South East, Nigeria (2000)
* Pune, Maharashtra, India (2018)
* Saltillo, Coahuila, Mexico (1968)
* Taichung, Taiwan (1986)
* Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China (1997)
The cities of Belo Horizonte, Brazil and Elche, Spain were formerly sister cities, but upon a vote of the Austin City Council in 1991, their status was de-activated.
Friendship cities
Covenants between two city leaders:
* Siem Reap, Cambodia (2011)
* Tehuacán, Mexico (2019)
* Villefranche-sur-Mer, France (2010)
See also
* List of companies based in Austin, Texas
* List of people from Austin, Texas
* National Register of Historic Places listings in Travis County, Texas
* Williamson Creek Greenbelt
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
External links
AustinTexas.gov- official city website
Austin Chamber of CommerceHistoric photographs from the Austin History Center hosted by th
Portal to Texas History*
*
{{Authority control
Austin, Texas,
Cities in Texas
Cities in Hays County, Texas
Cities in Travis County, Texas
Cities in Williamson County, Texas
County seats in Texas
Cities in Greater Austin
Planned cities in the United States
Populated places established in 1835
1839 establishments in the Republic of Texas
Academic enclaves
Capitals of former nations
State capitals in the United States
 In 1835–1836, Texans fought and won independence from Mexico. Texas thus became an independent country with its own president, congress, and monetary system. In 1839, the Texas Congress formed a commission to seek a site for a new capital of the
In 1835–1836, Texans fought and won independence from Mexico. Texas thus became an independent country with its own president, congress, and monetary system. In 1839, the Texas Congress formed a commission to seek a site for a new capital of the 
 The postwar period saw dramatic population and economic growth. The opening of the
The postwar period saw dramatic population and economic growth. The opening of the  Austin, the southernmost state capital of the contiguous 48 states, is located in
Austin, the southernmost state capital of the contiguous 48 states, is located in  At night, parts of Austin are lit by "artificial moonlight" from
At night, parts of Austin are lit by "artificial moonlight" from  From October 2010 through September 2011, both major reporting stations in Austin, Camp Mabry and Bergstrom Int'l, had the least rainfall of a
From October 2010 through September 2011, both major reporting stations in Austin, Camp Mabry and Bergstrom Int'l, had the least rainfall of a  In February 2021,
In February 2021,  A 2014 University of Texas study stated that Austin was the only U.S. city with a fast growth rate between 2000 and 2010 with a net loss in African Americans. , Austin's African American and non-Hispanic white percentage share of the total population was declining despite the actual numbers of both ethnic groups increasing, as the rapid growth of the Latino or Hispanic and Asian populations has outpaced all other ethnic groups in the city. Austin's non-Hispanic white population first dropped below 50% in 2005.
A 2014 University of Texas study stated that Austin was the only U.S. city with a fast growth rate between 2000 and 2010 with a net loss in African Americans. , Austin's African American and non-Hispanic white percentage share of the total population was declining despite the actual numbers of both ethnic groups increasing, as the rapid growth of the Latino or Hispanic and Asian populations has outpaced all other ethnic groups in the city. Austin's non-Hispanic white population first dropped below 50% in 2005.

 "Old Austin" is an adage often used by nostalgic natives. The term "Old Austin" refers to a time when the city was smaller and more Bohemianism, bohemian with a considerably lower cost of living and better known for its lack of traffic, Hipster (contemporary subculture), hipsters, and urban sprawl. It is often employed by longtime residents expressing displeasure at the rapidly changing culture, or when referencing nostalgia of Austin culture.
The growth and popularity of Austin can be seen by the expansive development taking place in its downtown landscape. This growth can have a negative impact on longtime small businesses that cannot keep up with the expenses associated with gentrification and the rising cost of real estate. A former Austin musician, Dale Watson (singer), Dale Watson, described his move away from Austin, "I just really feel the city has sold itself. Just because you're going to get $45 million for a company to come to town – if it's not in the best interest of the town, I don't think they should do it. This city was never about money. It was about quality of life." Though much is changing rapidly in Austin, businesses such as Thundercloud Subs are thought by many to maintain classic Austin business cultural sentiments unique to the history of the city; as Diana Burgess stated, "I definitely appreciate that they haven't raised their prices a ton or made things super fancy. I think it speaks to that original Old Austin vibe. A lot of us that grew up here really appreciate that."
"Old Austin" is an adage often used by nostalgic natives. The term "Old Austin" refers to a time when the city was smaller and more Bohemianism, bohemian with a considerably lower cost of living and better known for its lack of traffic, Hipster (contemporary subculture), hipsters, and urban sprawl. It is often employed by longtime residents expressing displeasure at the rapidly changing culture, or when referencing nostalgia of Austin culture.
The growth and popularity of Austin can be seen by the expansive development taking place in its downtown landscape. This growth can have a negative impact on longtime small businesses that cannot keep up with the expenses associated with gentrification and the rising cost of real estate. A former Austin musician, Dale Watson (singer), Dale Watson, described his move away from Austin, "I just really feel the city has sold itself. Just because you're going to get $45 million for a company to come to town – if it's not in the best interest of the town, I don't think they should do it. This city was never about money. It was about quality of life." Though much is changing rapidly in Austin, businesses such as Thundercloud Subs are thought by many to maintain classic Austin business cultural sentiments unique to the history of the city; as Diana Burgess stated, "I definitely appreciate that they haven't raised their prices a ton or made things super fancy. I think it speaks to that original Old Austin vibe. A lot of us that grew up here really appreciate that."
 The William Sidney Porter House, O. Henry House Museum hosts the annual O. Henry Pun-Off, a pun contest where the successful contestants exhibit wit akin to that of the author William Sydney Porter.
Other annual events include Eeyore's Birthday Party, Spamarama, Austin gay pride, Pride Festival & Parade in August, the Austin Reggae Festival in April, Kite Festival, Texas Craft Brewers Festival in September, Art City Austin in April, East Austin Studio Tour in November, and Carnaval Brasileiro in Austin, Texas, Carnaval Brasileiro in February. Sixth Street features annual festivals such as the Pecan Street Festival and Halloween night. The three-day Austin City Limits Music Festival has been held in
The William Sidney Porter House, O. Henry House Museum hosts the annual O. Henry Pun-Off, a pun contest where the successful contestants exhibit wit akin to that of the author William Sydney Porter.
Other annual events include Eeyore's Birthday Party, Spamarama, Austin gay pride, Pride Festival & Parade in August, the Austin Reggae Festival in April, Kite Festival, Texas Craft Brewers Festival in September, Art City Austin in April, East Austin Studio Tour in November, and Carnaval Brasileiro in Austin, Texas, Carnaval Brasileiro in February. Sixth Street features annual festivals such as the Pecan Street Festival and Halloween night. The three-day Austin City Limits Music Festival has been held in  As Austin's official slogan is ''The Live Music Capital of the World'', the city has a vibrant live Music of Austin, music scene with more music venues per capita than any other U.S. city. Austin's music revolves around the many nightclubs on 6th Street and an annual film/music/interactive festival known as
As Austin's official slogan is ''The Live Music Capital of the World'', the city has a vibrant live Music of Austin, music scene with more music venues per capita than any other U.S. city. Austin's music revolves around the many nightclubs on 6th Street and an annual film/music/interactive festival known as  Austin has a strong theater culture, with dozens of itinerant and resident companies producing a variety of work. The Church of the Friendly Ghost is a volunteer-run arts organization supporting creative expression and counter-culture community. The city also has live performance theater venues such as the Zachary Scott Theatre Center, Vortex Repertory Company, Salvage Vanguard Theater, Rude Mechanicals' the Off Center, Austin Playhouse, Scottish Rite Children's Theater, Hyde Park Theatre, the Blue Theater, The Hideout Theatre, and Esther's Follies. The Victory Grill was a renowned venue on the Chitlin' Circuit. Public art and performances in the parks and on bridges are popular. Austin hosts the Fuse Box Festival each April featuring theater artists.
The Paramount Theatre (Austin, Texas), Paramount Theatre, opened in downtown Austin in 1915, contributes to Austin's theater and film culture, showing classic films throughout the summer and hosting regional premieres for films such as ''Miss Congeniality (film), Miss Congeniality''. The
Austin has a strong theater culture, with dozens of itinerant and resident companies producing a variety of work. The Church of the Friendly Ghost is a volunteer-run arts organization supporting creative expression and counter-culture community. The city also has live performance theater venues such as the Zachary Scott Theatre Center, Vortex Repertory Company, Salvage Vanguard Theater, Rude Mechanicals' the Off Center, Austin Playhouse, Scottish Rite Children's Theater, Hyde Park Theatre, the Blue Theater, The Hideout Theatre, and Esther's Follies. The Victory Grill was a renowned venue on the Chitlin' Circuit. Public art and performances in the parks and on bridges are popular. Austin hosts the Fuse Box Festival each April featuring theater artists.
The Paramount Theatre (Austin, Texas), Paramount Theatre, opened in downtown Austin in 1915, contributes to Austin's theater and film culture, showing classic films throughout the summer and hosting regional premieres for films such as ''Miss Congeniality (film), Miss Congeniality''. The  The Austin Public Library is a public library system operated by the City of Austin and consists of the Central Library on Cesar Chavez Street (Austin), César Chávez Street, the Austin History Center, 20 branches and the Recycled Reads bookstore and upcycling facility. The APL library system also has mobile libraries – bookmobile buses and a human-powered trike and trailer called "unbound: sin fronteras."
The Central Library, which is an anchor to the redevelopment of the former Seaholm Power Plant site and the Shoal Creek, Austin, Texas, Shoal Creek Walk, opened on October 28, 2017. The six-story Central Library contains a living rooftop garden, reading porches, an indoor reading room, bicycle parking station, large indoor and outdoor event spaces, a gift shop, an art gallery, café, and a "technology petting zoo" where visitors can play with next-generation gadgets like 3D printing, 3D printers. In 2018, Time (magazine), Time magazine named the Austin Central Library on its list of "World's Greatest Places."
The Austin Public Library is a public library system operated by the City of Austin and consists of the Central Library on Cesar Chavez Street (Austin), César Chávez Street, the Austin History Center, 20 branches and the Recycled Reads bookstore and upcycling facility. The APL library system also has mobile libraries – bookmobile buses and a human-powered trike and trailer called "unbound: sin fronteras."
The Central Library, which is an anchor to the redevelopment of the former Seaholm Power Plant site and the Shoal Creek, Austin, Texas, Shoal Creek Walk, opened on October 28, 2017. The six-story Central Library contains a living rooftop garden, reading porches, an indoor reading room, bicycle parking station, large indoor and outdoor event spaces, a gift shop, an art gallery, café, and a "technology petting zoo" where visitors can play with next-generation gadgets like 3D printing, 3D printers. In 2018, Time (magazine), Time magazine named the Austin Central Library on its list of "World's Greatest Places."
 Museums in Austin include the Texas Memorial Museum, the George Washington Carver Museum and Cultural Center, Thinkery, the Blanton Museum of Art (reopened in 2006), the Bob Bullock Texas State History Museum across the street (which opened in 2000), The Contemporary Austin, the Elisabet Ney Museum and the galleries at the Harry Ransom Center. The
Museums in Austin include the Texas Memorial Museum, the George Washington Carver Museum and Cultural Center, Thinkery, the Blanton Museum of Art (reopened in 2006), the Bob Bullock Texas State History Museum across the street (which opened in 2000), The Contemporary Austin, the Elisabet Ney Museum and the galleries at the Harry Ransom Center. The  Locally produced art is featured at the South Austin Museum of Popular Culture. The Mexic-Arte Museum is a Mexican and Mexican-American art museum founded in 1983. Austin is also home to the O. Henry House Museum, which served as the residence of O. Henry from 1893 to 1895. Farmers' markets are popular attractions, providing a variety of locally grown and often organic foods.
Austin also has many odd statues and landmarks, such as the ''Stevie Ray Vaughan Memorial'', the Willie Nelson statue, ''Willie Nelson'' statue, the Mangia dinosaur, the Loca Maria lady at Taco Xpress, the Hyde Park Gym's giant flexed arm, and Daniel Johnston's ''Hi, How are You?'' Jeremiah the Innocent frog mural.
The Ann W. Richards Congress Avenue Bridge houses the world's largest urban population of Mexican free-tailed bats. Starting in March, up to 1.5 million bats take up residence inside the bridge's expansion and contraction zones as well as in long horizontal grooves running the length of the bridge's underside, an environment ideally suited for raising their young. Every evening around sunset, the bats emerge in search of insects, an exit visible on weather radar. Watching the bat emergence is an event that is popular with locals and tourists, with more than 100,000 viewers per year. The bats migrate to Mexico each winter.
The Austin Zoo, located in unincorporated area, unincorporated western
Locally produced art is featured at the South Austin Museum of Popular Culture. The Mexic-Arte Museum is a Mexican and Mexican-American art museum founded in 1983. Austin is also home to the O. Henry House Museum, which served as the residence of O. Henry from 1893 to 1895. Farmers' markets are popular attractions, providing a variety of locally grown and often organic foods.
Austin also has many odd statues and landmarks, such as the ''Stevie Ray Vaughan Memorial'', the Willie Nelson statue, ''Willie Nelson'' statue, the Mangia dinosaur, the Loca Maria lady at Taco Xpress, the Hyde Park Gym's giant flexed arm, and Daniel Johnston's ''Hi, How are You?'' Jeremiah the Innocent frog mural.
The Ann W. Richards Congress Avenue Bridge houses the world's largest urban population of Mexican free-tailed bats. Starting in March, up to 1.5 million bats take up residence inside the bridge's expansion and contraction zones as well as in long horizontal grooves running the length of the bridge's underside, an environment ideally suited for raising their young. Every evening around sunset, the bats emerge in search of insects, an exit visible on weather radar. Watching the bat emergence is an event that is popular with locals and tourists, with more than 100,000 viewers per year. The bats migrate to Mexico each winter.
The Austin Zoo, located in unincorporated area, unincorporated western 
 Many Austinites support the athletic programs of the University of Texas at Austin known as the Texas Longhorns. During the 2005–2006 academic term, Texas Longhorns football, Longhorns football team was named the NCAA Division I FBS National Football Championship, NCAA Division I FBS National Football Champion, and Texas Longhorns baseball, Longhorns baseball team won the 2005 College World Series, College World Series. The Texas Longhorns play home games in the state's second-largest sports stadium, Darrell K Royal–Texas Memorial Stadium, seating over 101,000 fans. Baseball games are played at UFCU Disch–Falk Field.
Austin was the most populous city in the United States without a Major professional sports leagues of the United States and Canada, major-league professional sports team, which changed in 2021 with
Many Austinites support the athletic programs of the University of Texas at Austin known as the Texas Longhorns. During the 2005–2006 academic term, Texas Longhorns football, Longhorns football team was named the NCAA Division I FBS National Football Championship, NCAA Division I FBS National Football Champion, and Texas Longhorns baseball, Longhorns baseball team won the 2005 College World Series, College World Series. The Texas Longhorns play home games in the state's second-largest sports stadium, Darrell K Royal–Texas Memorial Stadium, seating over 101,000 fans. Baseball games are played at UFCU Disch–Falk Field.
Austin was the most populous city in the United States without a Major professional sports leagues of the United States and Canada, major-league professional sports team, which changed in 2021 with 




 Central Austin lies between two major north–south freeways: Interstate 35 in Texas, Interstate 35 to the east and the State Highway Loop 1 (Texas), Mopac Expressway (Loop 1) to the west. U.S. Highway 183 (Texas), U.S. Highway 183 runs from northwest to southeast, and State Highway 71 (Texas), State Highway 71 crosses the southern part of the city from east to west, completing a rough "box" around central and north-central Austin. Austin is the largest city in the United States to be served by only one Interstate Highway.
U.S. Highway 290 (Texas), U.S. Highway 290 enters Austin from the east and merges into Interstate 35. Its highway designation continues south on I-35 and then becomes part of Highway 71, continuing to the west. Highway 290 splits from Highway 71 in southwest Austin, in an interchange known as "The Y." Highway 71 continues to Brady, Texas, and Highway 290 continues west to intersect Interstate 10 in Texas, Interstate 10 near Junction, Texas, Junction. Interstate 35 continues south through
Central Austin lies between two major north–south freeways: Interstate 35 in Texas, Interstate 35 to the east and the State Highway Loop 1 (Texas), Mopac Expressway (Loop 1) to the west. U.S. Highway 183 (Texas), U.S. Highway 183 runs from northwest to southeast, and State Highway 71 (Texas), State Highway 71 crosses the southern part of the city from east to west, completing a rough "box" around central and north-central Austin. Austin is the largest city in the United States to be served by only one Interstate Highway.
U.S. Highway 290 (Texas), U.S. Highway 290 enters Austin from the east and merges into Interstate 35. Its highway designation continues south on I-35 and then becomes part of Highway 71, continuing to the west. Highway 290 splits from Highway 71 in southwest Austin, in an interchange known as "The Y." Highway 71 continues to Brady, Texas, and Highway 290 continues west to intersect Interstate 10 in Texas, Interstate 10 near Junction, Texas, Junction. Interstate 35 continues south through  State Highway 130 (Texas), State Highway 130 is a bypass route designed to relieve traffic congestion, starting from Interstate 35 just north of Georgetown and running along a parallel route to the east, where it bypasses
State Highway 130 (Texas), State Highway 130 is a bypass route designed to relieve traffic congestion, starting from Interstate 35 just north of Georgetown and running along a parallel route to the east, where it bypasses  The Capital Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Capital Metro) provides public transportation to the city, primarily with its Capital MetroBus, MetroBus local bus service, the Capital MetroBus#MetroExpress, MetroExpress express bus system, as well as a bus rapid transit service, Capital MetroRapid, MetroRapid. Capital Metro opened a regional rail, commuter rail system, Capital MetroRail, in 2010. The system consists of a single line serving downtown Austin, the neighborhoods of East Austin, North Central Austin, and Northwest Austin plus the suburb of Leander, Texas, Leander.
Since it began operations in 1985, Capital Metro has proposed adding light rail services to its network. Despite support from the City Council, voters rejected light rail proposals in 2000 and 2014. However, in 2020, voters approved Capital Metro's transit expansion plan, Project Connect, by a comfortable margin. The plan proposes 2 new light rail lines, an additional bus rapid transit line (which could be converted to light rail in the future), a second commuter rail line, several new MetroRapid lines, more MetroExpress routes, and a number of other infrastructure, technology and service expansion projects.
Capital Area Rural Transportation System connects Austin with outlying suburbs and surrounding rural areas.
The Capital Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Capital Metro) provides public transportation to the city, primarily with its Capital MetroBus, MetroBus local bus service, the Capital MetroBus#MetroExpress, MetroExpress express bus system, as well as a bus rapid transit service, Capital MetroRapid, MetroRapid. Capital Metro opened a regional rail, commuter rail system, Capital MetroRail, in 2010. The system consists of a single line serving downtown Austin, the neighborhoods of East Austin, North Central Austin, and Northwest Austin plus the suburb of Leander, Texas, Leander.
Since it began operations in 1985, Capital Metro has proposed adding light rail services to its network. Despite support from the City Council, voters rejected light rail proposals in 2000 and 2014. However, in 2020, voters approved Capital Metro's transit expansion plan, Project Connect, by a comfortable margin. The plan proposes 2 new light rail lines, an additional bus rapid transit line (which could be converted to light rail in the future), a second commuter rail line, several new MetroRapid lines, more MetroExpress routes, and a number of other infrastructure, technology and service expansion projects.
Capital Area Rural Transportation System connects Austin with outlying suburbs and surrounding rural areas.
 The city's bike advocacy organization is Bike Austin. BikeTexas, a state-level advocacy organization, also has its main office in Austin.
Bicycles are a popular transportation choice among students, faculty, and staff at the University of Texas. According to a survey done at the University of Texas, 57% of commuters bike to campus.
The City of Austin and Capital Metro jointly own a bike-sharing service, Capital Metropolitan Transportation Authority#Other services, Capital MetroBike, which is available in and around downtown. The service is a franchise of BCycle, a national bike sharing network owned by Trek Bicycle, and is operated by local nonprofit organization Bike Share of Austin. Until 2020 the service was known as Austin BCycle. In 2018, LimeBike, Lime began offering dockless bikes, which do not need to be docked at a designated station.
In 2018, scooter-sharing system, scooter-sharing companies Lime (transportation company), Lime and Bird (company), Bird debuted Scooter-sharing system, rentable electric scooters in Austin. The city briefly banned the scooters — which began operations before the city could implement a permitting system — until the city completed development of their "dockless mobility" permitting process on May 1, 2018. Dockless electric scooters and bikes are banned from Austin city parks and the Lady Bird Lake#Ann and Roy Butler Hike-and-Bike Trail and Boardwalk, Ann and Roy Butler Trail and Boardwalk. For the 2018 Austin City Limits Music Festival, the city of Austin offered a designated parking area for dockless bikes and scooters.
The city's bike advocacy organization is Bike Austin. BikeTexas, a state-level advocacy organization, also has its main office in Austin.
Bicycles are a popular transportation choice among students, faculty, and staff at the University of Texas. According to a survey done at the University of Texas, 57% of commuters bike to campus.
The City of Austin and Capital Metro jointly own a bike-sharing service, Capital Metropolitan Transportation Authority#Other services, Capital MetroBike, which is available in and around downtown. The service is a franchise of BCycle, a national bike sharing network owned by Trek Bicycle, and is operated by local nonprofit organization Bike Share of Austin. Until 2020 the service was known as Austin BCycle. In 2018, LimeBike, Lime began offering dockless bikes, which do not need to be docked at a designated station.
In 2018, scooter-sharing system, scooter-sharing companies Lime (transportation company), Lime and Bird (company), Bird debuted Scooter-sharing system, rentable electric scooters in Austin. The city briefly banned the scooters — which began operations before the city could implement a permitting system — until the city completed development of their "dockless mobility" permitting process on May 1, 2018. Dockless electric scooters and bikes are banned from Austin city parks and the Lady Bird Lake#Ann and Roy Butler Hike-and-Bike Trail and Boardwalk, Ann and Roy Butler Trail and Boardwalk. For the 2018 Austin City Limits Music Festival, the city of Austin offered a designated parking area for dockless bikes and scooters.