Atrial septal defect on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a
 A patent foramen ovale (PFO) is a remnant opening of the fetal foramen ovale, which often closes after a person's birth. This remnant opening is caused by the incomplete fusion of the septum primum and the septum secundum; in healthy hearts, this fusion forms the fossa ovalis, a portion of the interatrial septum which corresponds to the location of the foramen ovale in the fetus. In medical use, the term "patent" means open or unobstructed. In about 25% of people, the foramen ovale does not close, leaving them with a PFO or at least with what some physicians classify as a "pro-PFO", which is a PFO that is normally closed, but can open under increased right atrial pressure. On echocardiography, shunting of blood may not be noted except when the patient coughs.
PFO is linked to
A patent foramen ovale (PFO) is a remnant opening of the fetal foramen ovale, which often closes after a person's birth. This remnant opening is caused by the incomplete fusion of the septum primum and the septum secundum; in healthy hearts, this fusion forms the fossa ovalis, a portion of the interatrial septum which corresponds to the location of the foramen ovale in the fetus. In medical use, the term "patent" means open or unobstructed. In about 25% of people, the foramen ovale does not close, leaving them with a PFO or at least with what some physicians classify as a "pro-PFO", which is a PFO that is normally closed, but can open under increased right atrial pressure. On echocardiography, shunting of blood may not be noted except when the patient coughs.
PFO is linked to
Image:Gray468.png, Heart of human
 Most individuals with a significant ASD are diagnosed ''
Most individuals with a significant ASD are diagnosed ''
File:UOTW 54 - Ultrasound of the Week 1.webm, ASD with pulmonary embolism resulting in a right-to-left shunting of blood
File:UOTW 54 - Ultrasound of the Week 2.webm, ASD with pulmonary embolism resulting in a right-to-left shunting of blood
File:UOTW 54 - Ultrasound of the Week 3.webm, ASD with pulmonary embolism resulting in a right-to-left shunting of blood
 Until recently, patients with PFO and cryptogenic stroke were treated with antiplatelet therapy only. Previous studies did not identify a clear benefit of PFO closure over antiplatelet therapy in reducing recurrent ischemic stroke. However, based on new evidence and systematic review in the field, percutaneous PFO closure in addition to antiplatelet therapy is suggested for all who meet all the following criteria:
* Age ≤ 60 years at onset of first stroke,
* Embolic-appearing cryptogenic
Until recently, patients with PFO and cryptogenic stroke were treated with antiplatelet therapy only. Previous studies did not identify a clear benefit of PFO closure over antiplatelet therapy in reducing recurrent ischemic stroke. However, based on new evidence and systematic review in the field, percutaneous PFO closure in addition to antiplatelet therapy is suggested for all who meet all the following criteria:
* Age ≤ 60 years at onset of first stroke,
* Embolic-appearing cryptogenic 
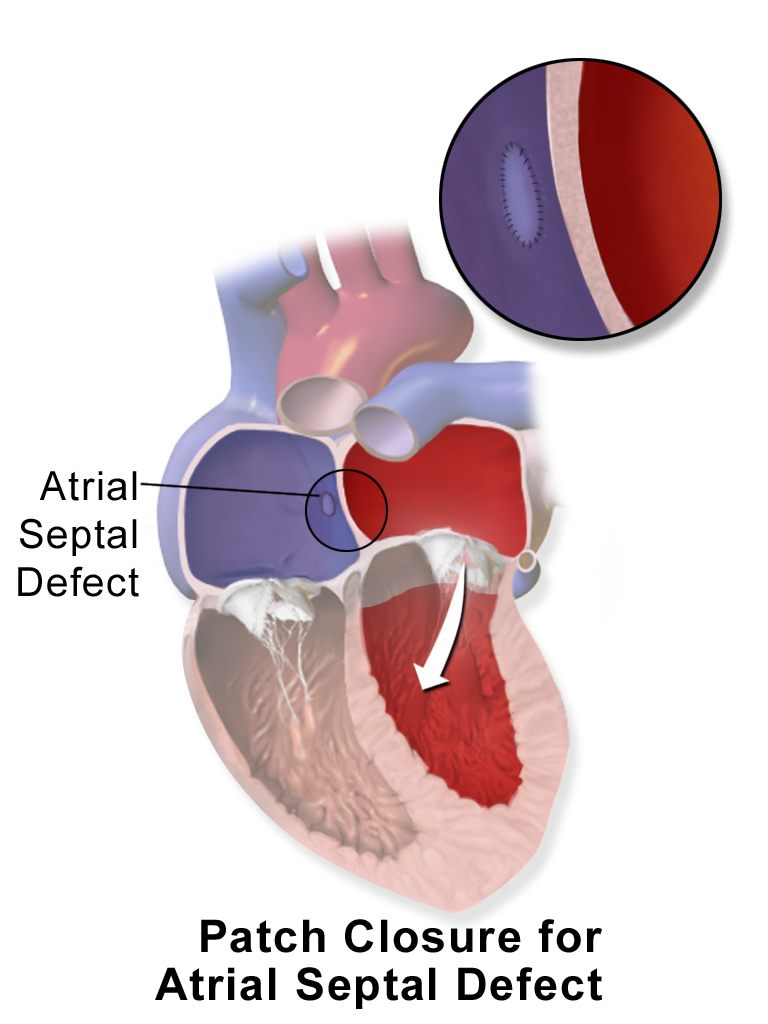 Surgical closure of an ASD involves opening up at least one atrium and closing the defect with a patch under direct visualization.
Surgical closure of an ASD involves opening up at least one atrium and closing the defect with a patch under direct visualization.
 Percutaneous device closure involves the passage of a catheter into the heart through the femoral vein guided by fluoroscopy and echocardiography. An example of a percutaneous device is a device which has discs that can expand to a variety of diameters at the end of the catheter. The catheter is placed in the right femoral vein and guided into the right atrium. The catheter is guided through the atrial septal wall and one disc (left atrial) is opened and pulled into place. Once this occurs, the other disc (right atrial) is opened in place and the device is inserted into the septal wall. This type of PFO closure is more effective than drug or other medical therapies for decreasing the risk of future thromboembolism.
The most common adverse effect of PFO device closure is new-onset atrial fibrillation. Other complications, all rare, include device migration, erosion and embolization and device thrombosis or formation of an inflammatory mass with risk for recurrent ischemic stroke.
Percutaneous closure of an ASD is currently only indicated for the closure of secundum ASDs with a sufficient rim of tissue around the septal defect so that the closure device does not impinge upon the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, or the
Percutaneous device closure involves the passage of a catheter into the heart through the femoral vein guided by fluoroscopy and echocardiography. An example of a percutaneous device is a device which has discs that can expand to a variety of diameters at the end of the catheter. The catheter is placed in the right femoral vein and guided into the right atrium. The catheter is guided through the atrial septal wall and one disc (left atrial) is opened and pulled into place. Once this occurs, the other disc (right atrial) is opened in place and the device is inserted into the septal wall. This type of PFO closure is more effective than drug or other medical therapies for decreasing the risk of future thromboembolism.
The most common adverse effect of PFO device closure is new-onset atrial fibrillation. Other complications, all rare, include device migration, erosion and embolization and device thrombosis or formation of an inflammatory mass with risk for recurrent ischemic stroke.
Percutaneous closure of an ASD is currently only indicated for the closure of secundum ASDs with a sufficient rim of tissue around the septal defect so that the closure device does not impinge upon the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, or the
Atrial septal defect
information for parents. {{DEFAULTSORT:Atrial Septal Defect Congenital heart defects Underwater diving medicine
congenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital h ...
in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward :wikt:bulge, bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also b ...
(ASA).
After PFO closure the atria normally are separated by a dividing wall, the interatrial septum
The interatrial septum is the wall of tissue that separates the right and left atria of the heart.
Structure
The interatrial septum is a that lies between the left atrium and right atrium of the human heart. The interatrial septum lies at ang ...
. If this septum is defective or absent, then oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
-rich blood can flow directly from the left side of the heart to mix with the oxygen-poor blood in the right side of the heart; or the opposite, depending on whether the left or right atrium has the higher blood pressure. In the absence of other heart defects, the left atrium has the higher pressure. This can lead to lower-than-normal oxygen levels in the arterial blood that supplies the brain, organs, and tissues. However, an ASD may not produce noticeable signs or symptoms, especially if the defect is small. Also, in terms of health risks, people who have had a cryptogenic stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
are more likely to have a PFO than the general population.
A cardiac shunt is the presence of a net flow of blood through a defect, either from left to right or right to left. The amount of shunting present, if any, determines the hemodynamic significance of the ASD. A right-to-left-shunt results in venous blood entering the left side of the heart and into the arterial circulation without passing through the pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lun ...
to be oxygenate
In the liquid fuel industry, oxygenates are hydrocarbon-derived fuel additives containing at least one oxygen atom to promote complete combustion. Absent oxygenates, fuel combustion is usually incomplete, and the exhaust stream pollutes the air ...
d. This may result in the clinical finding of cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
, the presence of bluish-colored skin, especially of the lips and under the nails.
During development of the baby, the interatrial septum develops to separate the left
Left may refer to:
Music
* ''Left'' (Hope of the States album), 2006
* ''Left'' (Monkey House album), 2016
* ''Left'' (Helmet album), 2023
* "Left", a song by Nickelback from the album ''Curb'', 1996
Direction
* Left (direction), the relativ ...
and right atria. However, a hole in the septum called the foramen ovale allows blood from the right atrium to enter the left atrium during fetal development. This opening allows blood to bypass the nonfunctional fetal lungs while the fetus obtains its oxygen from the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
. A layer of tissue called the septum primum acts as a valve over the foramen ovale during fetal development. After birth, the pressure in the right side of the heart drops as the lungs open and begin working, causing the foramen ovale to close entirely. In about 25% of adults, the foramen ovale does not entirely seal. In these cases, any elevation of the pressure in the pulmonary circulatory system (due to pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swell ...
, temporarily while cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex fol ...
ing, etc.) can cause the foramen ovale to remain open.
Types
The six types of atrial septal defects are differentiated from each other by whether they involve other structures of the heart and how they are formed during the developmental process during earlyfetal
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a ...
development.
Ostium secundum
The ''ostium secundum atrial septal defect'' is the most common type of atrial septal defect and comprises 6–10% of all congenital heart diseases. It involves a patent ostium secundum (that is, a patent foramen secundum). The secundum atrial septal defect usually arises from an enlarged foramen ovale, inadequate growth of the septum secundum, or excessive absorption of the septum primum. About 10 to 20% of individuals with ostium secundum ASDs also havemitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the atria of the heart, left atrium during Systole (medicine), systole. It is the primary form of myxom ...
.
An ostium secundum ASD accompanied by an acquired mitral valve stenosis
Mitral stenosis is a valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the opening of the mitral valve of the heart. It is almost always caused by rheumatic valvular heart disease. Normally, the mitral valve is about 5 cm2 during di ...
is called Lutembacher's syndrome.
Natural history
Most individuals with an uncorrected secundum ASD do not have significant symptoms through early adulthood. More than 70% develop symptoms by about 40 years of age. Symptoms are typically decreased exercise tolerance, easy fatigability, palpitations, and syncope. Complications of an uncorrected secundum ASD includepulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swell ...
, right-sided congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically pr ...
.
While pulmonary hypertension is unusual before 20 years of age, it is seen in 50% of individuals above the age of 40. Progression to Eisenmenger's syndrome
Eisenmenger syndrome or Eisenmenger's syndrome is defined as the process in which a long-standing left-to-right cardiac shunt caused by a congenital heart defect (typically by a ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, or less commonly, pa ...
occurs in 5 to 10% of individuals late in the disease process.
Patent foramen ovale
 A patent foramen ovale (PFO) is a remnant opening of the fetal foramen ovale, which often closes after a person's birth. This remnant opening is caused by the incomplete fusion of the septum primum and the septum secundum; in healthy hearts, this fusion forms the fossa ovalis, a portion of the interatrial septum which corresponds to the location of the foramen ovale in the fetus. In medical use, the term "patent" means open or unobstructed. In about 25% of people, the foramen ovale does not close, leaving them with a PFO or at least with what some physicians classify as a "pro-PFO", which is a PFO that is normally closed, but can open under increased right atrial pressure. On echocardiography, shunting of blood may not be noted except when the patient coughs.
PFO is linked to
A patent foramen ovale (PFO) is a remnant opening of the fetal foramen ovale, which often closes after a person's birth. This remnant opening is caused by the incomplete fusion of the septum primum and the septum secundum; in healthy hearts, this fusion forms the fossa ovalis, a portion of the interatrial septum which corresponds to the location of the foramen ovale in the fetus. In medical use, the term "patent" means open or unobstructed. In about 25% of people, the foramen ovale does not close, leaving them with a PFO or at least with what some physicians classify as a "pro-PFO", which is a PFO that is normally closed, but can open under increased right atrial pressure. On echocardiography, shunting of blood may not be noted except when the patient coughs.
PFO is linked to stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, sleep apnea
Sleep apnea (sleep apnoea or sleep apnœa in British English) is a sleep-related breathing disorder in which repetitive Apnea, pauses in breathing, periods of shallow breathing, or collapse of the upper airway during sleep results in poor vent ...
, migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
with aura, cluster headache, decompression sickness
Decompression sickness (DCS; also called divers' disease, the bends, aerobullosis, and caisson disease) is a medical condition caused by dissolved gases emerging from Solution (chemistry), solution as bubbles inside the body tissues during D ...
, Raynaud's phenomenon, hyperventilation syndrome, transient global amnesia (TGA), and leftsided carcinoid heart disease (mitral valve). No cause is established for a foramen ovale to remain open instead of closing, but heredity and genetics may play a role. In rats research showed a link to the amount of Cryptosporidium infestation and the number of newborn rats that failed to close their foramen ovale. PFO is not treated in the absence of other symptoms.
The mechanism by which a PFO may play a role in stroke is called paradoxical embolism. In the case of PFO, a blood clot from the venous circulatory system is able to pass from the right atrium directly into the left atrium via the PFO, rather than being filtered by the lungs, and thereupon into systemic circulation toward the brain. Also multiple substances – including the prothrombotic agent serotonin – are shunted bypassing the lungs. PFO is common in patients with an atrial septal aneurysm (ASA), a much rarer condition, which is also linked to cryptogenic (i.e., of unknown cause) stroke.
PFO is more common in people with cryptogenic stroke than in those with a stroke of known cause. While PFO is present in 25% in the general population, the probability of someone having a PFO increases to about 40 to 50% in those who have had a cryptogenic stroke, and more so in those who have a stroke before the age of 55. Treatment with anticoagulant
An anticoagulant, commonly known as a blood thinner, is a chemical substance that prevents or reduces the coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some occur naturally in blood-eating animals, such as leeches and mosquitoes, which ...
and antiplatelet
An antiplatelet drug (antiaggregant), also known as a platelet agglutination inhibitor or platelet aggregation inhibitor, is a member of a class of pharmaceuticals that decrease platelet aggregation and inhibit thrombus formation. They are effectiv ...
medications in this group appear similar.
Ostium primum
A defect in theostium primum
In the developing heart, the atria are initially open to each other, with the opening known as the primary interatrial foramen or ostium primum (or interatrial foramen primum). The foramen lies beneath the edge of septum primum and the endocardia ...
is occasionally classified as an atrial septal defect, but it is more commonly classified as an atrioventricular septal defect
Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" or "endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the heart that c ...
. Ostium primum defects are less common than ostium secundum defects. This type of defect is usually associated with Down syndrome.
Sinus venosus
A sinus venosus ASD is a type of atrial septum defect in which the defect involves the venous inflow of either thesuperior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vei ...
or the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
.
A sinus venosus ASD that involves the superior vena cava makes up 2 to 3% of all interatrial communication. It is located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. It is frequently associated with anomalous drainage of the right-sided pulmonary vein
The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer Blood#Oxygen transport, oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four ''main pulmonary veins'', two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the h ...
s into the right atrium (instead of the normal drainage of the pulmonary veins into the left atrium).
Common or single atrium
Common (or single) atrium is a failure of development of the embryologic components that contribute to the atrial septal complex. It is frequently associated withheterotaxy syndrome
Situs ambiguus (), or heterotaxy, is a rare congenital defect in which the major visceral Organ (anatomy), organs are distributed abnormally within the chest and abdomen. Clinically, heterotaxy spectrum generally refers to any defect of left-righ ...
.
Mixed
The interatrial septum can be divided into five septal zones. If the defect involves two or more of the septal zones, then the defect is termed a mixed atrial septal defect.Presentation
Complications
Due to the communication between the atria that occurs in ASDs, disease entities or complications from the condition are possible. Patients with an uncorrected atrial septal defect may be at increased risk for developing a cardiac arrhythmia, as well as more frequent respiratory infections.Decompression sickness
ASDs, and particularly PFOs, are a predisposing venous blood carrying inert gases, such ashelium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
or nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
does not pass through the lungs.
The only way to release the excess inert gases from the body is to pass the blood carrying the inert gases through the lungs to be exhaled. If some of the inert gas-laden blood passes through the PFO, it avoids the lungs and the inert gas is more likely to form large bubbles in the arterial blood stream causing decompression sickness.
Eisenmenger's syndrome
If a net flow of blood exists from the left atrium to the right atrium, called a left-to-right shunt, then an increase in the blood flow through the lungs happens. Initially, this increased blood flow is asymptomatic, but if it persists, the pulmonary blood vessels may stiffen, causing pulmonary hypertension, which increases the pressures in the right side of the heart, leading to the reversal of the shunt into a right-to-left shunt. Reversal of the shunt occurs, and the blood flowing in the opposite direction through the ASD is called Eisenmenger's syndrome, a rare and late complication of an ASD.Paradoxical embolus
Venousthrombus
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
(clots in the veins) are quite common. Embolizations (dislodgement of thrombi) normally go to the lung and cause pulmonary emboli
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathin ...
. In an individual with ASD, these emboli can potentially enter the arterial system, which can cause any phenomenon attributed to acute loss of blood to a portion of the body, including cerebrovascular accident
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop ...
(stroke), infarction of the spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
or intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. T ...
s, or even a distal extremity (i.e., finger or toe).
This is known as a paradoxical embolus because the clot material paradoxically enters the arterial system instead of going to the lungs.
Migraine
Some recent research has suggested that a proportion of cases of migraine may be caused by PFO. While the exact mechanism remains unclear, closure of a PFO can reduce symptoms in certain cases. This remains controversial; 20% of the general population has a PFO, which for the most part, is asymptomatic. About 20% of the female population has migraines, and theplacebo effect
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials ...
in migraine typically averages around 40%. The high frequency of these facts make finding statistically significant relationships between PFO and migraine difficult (i.e., the relationship may just be chance or coincidence). In a large randomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical ...
, the higher prevalence of PFO in migraine patients was confirmed, but migraine headache cessation was not more prevalent in the group of migraine patients who underwent closure of their PFOs.
Causes
* Down syndrome – patients with Down syndrome have higher rates of ASDs, especially a particular type that involves the ventricular wall. As many as one half of Down syndrome patients have some type of septal defect. * Ebstein's anomaly – about 50% of individuals with Ebstein anomaly have an associated shunt between the right and left atria, either an atrial septal defect or a patent foramen ovale. *Fetal alcohol syndrome
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person who is exposed to alcohol during gestation. FASD affects 1 in 20 Americans, but is highly misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed.
The several forms of the ...
– about one in four patients with fetal alcohol syndrome has either an ASD or a ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. It's a common heart problem present at birth ( congenital heart defect). The extent of the opening may vary ...
.
* Holt–Oram syndrome
Holt–Oram syndrome (also called atrio-digital syndrome, atriodigital dysplasia, cardiac-limb syndrome, heart-hand syndrome type 1, HOS, ventriculo-radial syndrome) is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects bones in the arms and hands (th ...
– both the osteium secundum and osteum primum types of ASD are associated with Holt–Oram syndrome
* Lutembacher's syndrome – the presence of a congenital ASD along with acquired mitral stenosis
Mechanisms
In unaffected individuals, the chambers of the left side of the heart are under higher pressure than the chambers of the right side because the left ventricle has to produce enough pressure to pump blood throughout the entire body, while the right ventricle needs only to produce enough pressure to pump blood to thelung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s.
In the case of a large ASD (> 9 mm), which may result in a clinically remarkable left-to-right shunt, blood shunts from the left atrium to the right atrium. This extra blood from the left atrium may cause a volume overload of both the right atrium and the right ventricle. If untreated, this condition can result in enlargement of the right side of the heart and ultimately heart failure.
Any process that increases the pressure in the left ventricle can cause worsening of the left-to-right shunt. This includes hypertension, which increases the pressure that the left ventricle has to generate to open the aortic valve during ventricular systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. Its contrasting phase is diastole, the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling ...
, and coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up ...
which increases the stiffness of the left ventricle, thereby increasing the filling pressure of the left ventricle during ventricular diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricul ...
. The left-to-right shunt increases the filling pressure of the right heart ( preload) and forces the right ventricle to pump out more blood than the left ventricle. This constant overloading of the right side of the heart causes an overload of the entire pulmonary vasculature. Eventually, pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swell ...
may develop.
The pulmonary hypertension will cause the right ventricle to face increased afterload
Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole (ventricular contraction). Afterload is proportional to the average arterial pressure. As aortic and pulmonary pressures increase, the afterload increases on ...
. The right ventricle is forced to generate higher pressures to try to overcome the pulmonary hypertension. This may lead to right ventricular failure (dilatation and decreased systolic function of the right ventricle).
If the ASD is left uncorrected, the pulmonary hypertension progresses and the pressure in the right side of the heart becomes greater than the left side of the heart. This reversal of the pressure gradient across the ASD causes the shunt to reverse – a right-to-left shunt. This phenomenon is known as Eisenmenger's syndrome
Eisenmenger syndrome or Eisenmenger's syndrome is defined as the process in which a long-standing left-to-right cardiac shunt caused by a congenital heart defect (typically by a ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, or less commonly, pa ...
. Once right-to-left shunting occurs, a portion of the oxygen-poor blood gets shunted to the left side of the heart and ejected to the peripheral vascular system. This causes signs of cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
.
embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
of about 35 days
Image:Atrial septal defect-en.png, Atrial septal defect with left-to-right shunt
File:Blausen 0069 AtrialSeptalDefect 02.png, Illustration depicting atrial septal defect
Diagnosis
 Most individuals with a significant ASD are diagnosed ''
Most individuals with a significant ASD are diagnosed ''in utero
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more fertilized eggs until bir ...
'' or in early childhood with the use of ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, ...
or auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory system, circulatory and resp ...
of the heart sounds
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stetho ...
during physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
. Some individuals with an ASD have surgical correction of their ASD during childhood. The development of signs and symptoms due to an ASD are related to the size of the intracardiac shunt. Individuals with a larger shunt tend to present with symptoms at a younger age.
Adults with an uncorrected ASD present with symptoms of dyspnea on exertion (shortness of breath with minimal exercise), congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically pr ...
, or cerebrovascular accident
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop ...
(stroke). They may be noted on routine testing to have an abnormal chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
or an abnormal ECG
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles.
It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of ...
and may have atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
. If the ASD causes a left-to-right shunt, the pulmonary vasculature in both lungs may appear dilated on chest X-ray, due to the increase in pulmonary blood flow.
Physical examination
The physical findings in an adult with an ASD include those related directly to the intracardiac shunt and those that are secondary to the right heart failure that may be present in these individuals. In unaffected individuals, respiratory variations occur in the splitting of the second heart sound (S2). During respiratory inspiration, the negative intrathoracic pressure causes increased blood return into the right side of the heart. The increased blood volume in the right ventricle causes the pulmonic valve to stay open longer during ventricular systole. This causes a normal delay in the P2 component of S2. During expiration, the positive intrathoracic pressure causes decreased blood return to the right side of the heart. The reduced volume in the right ventricle allows the pulmonic valve to close earlier at the end of ventricular systole, causing P2 to occur earlier. In individuals with an ASD, a fixed splitting of S2 occurs because the extra blood return during inspiration gets equalized between the left and right atria due to the communication that exists between the atria in individuals with ASD. The right ventricle can be thought of as continuously overloaded because of the left-to-right shunt, producing a widely split S2. Because the atria are linked via the atrial septal defect, inspiration produces no net pressure change between them, and has no effect on the splitting of S2. Thus, S2 is split to the same degree during inspiration as expiration, and is said to be "fixed".Echocardiography
In transthoracicechocardiography
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ec ...
, an atrial septal defect may be seen on color flow imaging as a jet of blood from the left atrium to the right atrium.
If agitated saline is injected into a peripheral vein during echocardiography, small air bubbles can be seen on echocardiographic imaging. Bubbles traveling across an ASD may be seen either at rest or during a cough. (Bubbles only flow from right atrium to left atrium if the right atrial pressure is greater than left atrial). Because better visualization of the atria is achieved with transesophageal echocardiography, this test may be performed in individuals with a suspected ASD which is not visualized on transthoracic imaging.
Newer techniques to visualize these defects involve intracardiac imaging with special catheters typically placed in the venous system and advanced to the level of the heart. This type of imaging is becoming more common and involves only mild sedation for the patient typically.
If the individual has adequate echocardiographic windows, use of the echocardiogram to measure the cardiac output of the left ventricle and the right ventricle independently is possible. In this way, the shunt fraction can be estimated using echocardiography.
Transcranial doppler bubble study
A less invasive method for detecting a PFO or other ASDs than transesophagal ultrasound is transcranial Doppler with bubble contrast. This method reveals the cerebral impact of the ASD or PFO.Electrocardiogram
The ECG findings in atrial septal defect vary with the type of defect the individual has. Individuals with atrial septal defects may have a prolonged PR interval (a first-degree heart block). The prolongation of the PR interval is probably due to the enlargement of the atria common in ASDs and the increased distance due to the defect itself. Both of these can cause an increased distance of internodal conduction from the SA node to theAV node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the ...
.
In addition to the PR prolongation, individuals with a primum ASD have a left axis deviation of the QRS complex, while those with a secundum ASD have a right axis deviation of the QRS complex. Individuals with a sinus venosus ASD exhibit a left axis deviation of the P wave (not the QRS complex).
A common finding in the ECG is the presence of incomplete right bundle branch block
A right bundle branch block (RBBB) is a heart block in the Bundle branches#Structure, right bundle branch of the Electrical conduction system of the heart, electrical conduction system.
During a right bundle branch block, the right ventricle (h ...
, which is so characteristic that if it is absent, the diagnosis of ASD should be reconsidered.
Treatment
Patent foramen ovale
Most patients with a PFO are asymptomatic and do not require any specific treatment. However, those who develop a stroke require further workup to identify the etiology. In those where a comprehensive evaluation is performed and an obvious etiology is not identified, they are defined as having a cryptogenic stroke. The mechanism for stroke is such individuals is likely embolic due to paradoxical emboli, a left atrial appendage clot, a clot on the inter-atrial septum, or within the PFO tunnel.PFO closure
 Until recently, patients with PFO and cryptogenic stroke were treated with antiplatelet therapy only. Previous studies did not identify a clear benefit of PFO closure over antiplatelet therapy in reducing recurrent ischemic stroke. However, based on new evidence and systematic review in the field, percutaneous PFO closure in addition to antiplatelet therapy is suggested for all who meet all the following criteria:
* Age ≤ 60 years at onset of first stroke,
* Embolic-appearing cryptogenic
Until recently, patients with PFO and cryptogenic stroke were treated with antiplatelet therapy only. Previous studies did not identify a clear benefit of PFO closure over antiplatelet therapy in reducing recurrent ischemic stroke. However, based on new evidence and systematic review in the field, percutaneous PFO closure in addition to antiplatelet therapy is suggested for all who meet all the following criteria:
* Age ≤ 60 years at onset of first stroke,
* Embolic-appearing cryptogenic ischemic stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop ...
(i.e., no evident source of stroke despite a comprehensive evaluation), and
* PFO with a right-to-left interatrial shunt detected by bubble study (echocardiogram)
A variety of PFO closure devices may be implanted via catheter-based procedures.

Medical therapy
Based on the most up to date evidence, PFO closure is more effective at reducing recurrent ischemic stroke when compared to medical therapy. In most of these studies, antiplatelet and anticoagulation were combined in the medical therapy arm. Although there is limited data on the effectiveness of anticoagulation in reducing stroke in this population, it is hypothesized that based on the embolic mechanism, that anticoagulation should be superior to antiplatelet therapy at reducing risk of recurrent stroke. A recent review of the literature supports this hypothesis recommending anticoagulation over the use of antiplatelet therapy in patients with PFO and cryptogenic stroke. However, more evidence is required comparing of PFO closure with anticoagulation or anticoagulation with antiplatelet therapy.Atrial septal defect
Once someone is found to have an atrial septal defect, a determination of whether it should be corrected is typically made. If the atrial septal defect is causing the right ventricle to enlarge a secundum atrial septal defect should generally be closed. If the ASD is not causing problems the defect may simply be checked every two or three years. Methods of closure of an ASD include surgical closure and percutaneous closure.Evaluation prior to correction
Prior to correction of an ASD, an evaluation is made of the severity of the individual's pulmonary hypertension (if present at all) and whether it is reversible (closure of an ASD may be recommended for prevention purposes, to avoid such a complication in the first place. Pulmonary hypertension is not always present in adults who are diagnosed with an ASD in adulthood). If pulmonary hypertension is present, the evaluation may include a right heart catheterization. This involves placing a catheter in the venous system of the heart and measuring pressures and oxygen saturations in the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, and pulmonary artery, and in the wedge position. Individuals with a pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) less than 7 wood units show regression of symptoms (including NYHA functional class). However, individuals with a PVR greater than 15 wood units have increased mortality associated with closure of the ASD. If the pulmonary arterial pressure is more than two-thirds of the systemic systolic pressure, a net left-to-right shunt should occur at least 1.5:1 or evidence of reversibility of the shunt when given pulmonary artery vasodilators prior to surgery. (If Eisenmenger's physiology has set in, the right-to-left shunt must be shown to be reversible with pulmonary artery vasodilators prior to surgery.) Surgical mortality due to closure of an ASD is lowest when the procedure is performed prior to the development of significant pulmonary hypertension. The lowest mortality rates are achieved in individuals with a pulmonary artery systolic pressure less than 40 mmHg. IfEisenmenger's syndrome
Eisenmenger syndrome or Eisenmenger's syndrome is defined as the process in which a long-standing left-to-right cardiac shunt caused by a congenital heart defect (typically by a ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, or less commonly, pa ...
has occurred, a significant risk of mortality exists regardless of the method of closure of the ASD. In individuals who have developed Eisenmenger's syndrome, the pressure in the right ventricle has raised high enough to reverse the shunt in the atria. If the ASD is then closed, the afterload
Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole (ventricular contraction). Afterload is proportional to the average arterial pressure. As aortic and pulmonary pressures increase, the afterload increases on ...
that the right ventricle has to act against has suddenly increased. This may cause immediate right ventricular failure, since it may not be able to pump the blood against the pulmonary hypertension.
Surgical closure
 Surgical closure of an ASD involves opening up at least one atrium and closing the defect with a patch under direct visualization.
Surgical closure of an ASD involves opening up at least one atrium and closing the defect with a patch under direct visualization.
Catheter procedure
 Percutaneous device closure involves the passage of a catheter into the heart through the femoral vein guided by fluoroscopy and echocardiography. An example of a percutaneous device is a device which has discs that can expand to a variety of diameters at the end of the catheter. The catheter is placed in the right femoral vein and guided into the right atrium. The catheter is guided through the atrial septal wall and one disc (left atrial) is opened and pulled into place. Once this occurs, the other disc (right atrial) is opened in place and the device is inserted into the septal wall. This type of PFO closure is more effective than drug or other medical therapies for decreasing the risk of future thromboembolism.
The most common adverse effect of PFO device closure is new-onset atrial fibrillation. Other complications, all rare, include device migration, erosion and embolization and device thrombosis or formation of an inflammatory mass with risk for recurrent ischemic stroke.
Percutaneous closure of an ASD is currently only indicated for the closure of secundum ASDs with a sufficient rim of tissue around the septal defect so that the closure device does not impinge upon the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, or the
Percutaneous device closure involves the passage of a catheter into the heart through the femoral vein guided by fluoroscopy and echocardiography. An example of a percutaneous device is a device which has discs that can expand to a variety of diameters at the end of the catheter. The catheter is placed in the right femoral vein and guided into the right atrium. The catheter is guided through the atrial septal wall and one disc (left atrial) is opened and pulled into place. Once this occurs, the other disc (right atrial) is opened in place and the device is inserted into the septal wall. This type of PFO closure is more effective than drug or other medical therapies for decreasing the risk of future thromboembolism.
The most common adverse effect of PFO device closure is new-onset atrial fibrillation. Other complications, all rare, include device migration, erosion and embolization and device thrombosis or formation of an inflammatory mass with risk for recurrent ischemic stroke.
Percutaneous closure of an ASD is currently only indicated for the closure of secundum ASDs with a sufficient rim of tissue around the septal defect so that the closure device does not impinge upon the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, or the tricuspid
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
or mitral
The mitral valve ( ), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two Cusps of heart valves, cusps or flaps and lies between the atrium (heart), left atrium and the ventricle (heart), ...
valves. The Amplatzer Septal Occluder (ASO) is commonly used to close ASDs. The ASO consists of two self-expandable round discs connected to each other with a 4-mm waist, made up of 0.004– to 0.005-inch Nitinol wire mesh filled with Dacron fabric. Implantation of the device is relatively easy. The prevalence of residual defect is low. The disadvantages are a thick profile of the device and concern related to a large amount of nitinol (a nickel-titanium compound) in the device and consequent potential for nickel toxicity.
Percutaneous closure is the method of choice in most centres. Studies evaluating percutaneous ASD closure among pediatric and adult population show that this is relatively safer procedure and has better outcomes with increasing hospital volume.
Epidemiology
As a group, atrial septal defects are detected in one child per 1500 live births. PFOs are quite common (appearing in 10–20% of adults), but when asymptomatic go undiagnosed. ASDs make up 30 to 40% of all congenital heart diseases that are seen in adults. The ostium secundum atrial septal defect accounts for 7% of all congenital heart lesions. This lesion shows a male:female ratio of 1:2.References
Additional references
*Further reading
*External links
Atrial septal defect
information for parents. {{DEFAULTSORT:Atrial Septal Defect Congenital heart defects Underwater diving medicine