|
Oxygenate
In the liquid fuel industry, oxygenates are hydrocarbon-derived fuel additives containing at least one oxygen atom to promote complete combustion. Absent oxygenates, fuel combustion is usually incomplete, and the exhaust stream pollutes the air with carbon monoxide, soot particles, aromatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and nitrated polyaromatic hydrocarbons. The most common oxygenates are either alcohols or ethers, but ketones and aldehydes are also included in this distinction. Carboxylic acids and esters can be grouped with oxygenates in the simple definition that they contain at least one oxygen atom. However, they are usually unwanted in oils, and therefore likely fuels, due to their environmental toxicity and tendency to cause catalyst poisoning and corrosion during oil production and refining. * Alcohols: ** Methanol (MeOH) ** Ethanol (EtOH); see also Common ethanol fuel mixtures ** Isopropyl alcohol (IPA) ** ''n''-Butanol (BuOH) ** Gasoline grade ''tert''-buta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Tert-butyl Ether
Methyl ''tert''-butyl ether (MTBE), also known as ''tert''-butyl methyl ether, is an organic compound with a structural formula (CH3)3COCH3. MTBE is a volatile, flammable, and colorless liquid that is sparingly soluble in water. Primarily used as a fuel additive, MTBE is blended into gasoline to increase its octane rating and knock resistance, and reduce unwanted emissions. Production and properties MTBE is manufactured via the chemical reaction of methanol and isobutylene. Methanol is primarily derived from natural gas, where steam reforming converts the various light hydrocarbons in natural gas (primarily methane) into carbon monoxide and hydrogen. The resulting gases then further react in the presence of a catalyst to form methanol. Isobutylene can be produced through a variety of methods. ''n''-butane can be isomerized into isobutane which can be dehydrogenated to isobutylene. In the Halcon process, ''t''-Butyl hydroperoxide derived from isobutane oxygenation is tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
A Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is any member of a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple fused aromatic rings. Most are produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter— by engine exhaust fumes, tobacco, incinerators, in roasted meats and cereals, or when biomass burns at lower temperatures as in forest fires. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are also found in fossil fuel deposits such as coal and in petroleum. Exposure to PAHs can lead to different types of cancer, to fetal development complications, and to cardiovascular issues. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon, or polynuclear aromatic hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tert-Butanol
''tert''-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as ''t''-BuOH). Its isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and butan-2-ol. ''tert''-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether. Natural occurrence ''tert''-Butyl alcohol has been identified in beer and chickpeas. It is also found in cassava, which is used as a fermentation ingredient in certain alcoholic beverages. Preparation ''tert''-Butyl alcohol is derived commercially from isobutane as a coproduct of propylene oxide production. It can also be produced by the catalytic hydration of isobutylene, or by a Grignard reaction between acetone Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone) is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly Volatile organic compound, volatile, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tert-Amyl Methyl Ether
''tert''-Amyl methyl ether (TAME) is an ether used as a fuel oxygenate. TAME derives from C5 distillation fractions of naphtha. It has an ethereous odor. Unlike most ethers, it does not require a stabilizer as it does not form peroxides on storage. Other names: * 2-Methoxy-2-methylbutane * Butane, 2-methoxy-2-methyl- * 1,1-Dimethylpropyl methyl ether * Methyl tert-pentyl ether * Methyl tert-Amyl ether * 2-Methyl-2-methoxybutane * Methyl 2-methyl-2-butyl ether * tert-Pentyl methyl ether * Tertiary amyl methyl ether * Methyl 1,1-dimethylpropyl ether * 2-Methoxy-2-methylbutane Uses TAME is mostly used as an oxygenate to gasoline. It is added for three reasons: to increase octane enhancement, to replace banned tetraethyl lead, and to raise the oxygen content in gasoline. It is known that TAME in fuel reduces exhaust emissions of some volatile organic compounds. TAME is also used as a solvent in organic synthesis as a more environmentally friendly alternative to some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Additive
Gasoline additives may increase gasoline's octane rating, thus allowing the use of higher compression ratios for greater efficiency and power, or act as corrosion inhibitors or lubricants. Other additives include metal deactivators, oxygenates and antioxidants. Some additives are harmful and are regulated or banned in some countries. Fictional additives *Sugar, as seen in '' The Passionate Stranger'' (1957) and popularly believed to damage the engine. Additives * Oxygenates ** Alcohols: *** Methanol (MeOH) *** Ethanol (EtOH); see also common ethanol fuel mixtures *** Isopropyl alcohol (IPA) *** ''n''-butanol (BuOH) *** Gasoline grade ''t''-butanol (GTBA) ** Ethers: *** Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), now outlawed in many states of the U.S. for road use because of water contamination. *** Tertiary amyl methyl ether (TAME) *** Tertiary hexyl methyl ether (THEME) *** Ethyl tertiary butyl ether (ETBE) *** Tertiary amyl ethyl ether (TAEE) *** Diisopropyl ether (DIPE) * Antiox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diisopropyl Ether
Diisopropyl ether is a secondary ether that is used as a solvent. It is a colorless liquid that is slightly soluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. It is used as an extractant and an oxygenate gasoline additive. It is obtained industrially as a byproduct in the production of isopropanol by hydration of propylene. Diisopropyl ether is sometimes represented by the abbreviation DIPE. Uses Whereas at 20 °C, diethyl ether will dissolve 1% by weight water, diisopropyl ether dissolves 0.88%. Diisopropyl ether is used as a specialized solvent to remove or extract polar organic compounds from aqueous solutions, e.g. phenols, ethanol, acetic acid. It has also been used as an antiknock agent. In the laboratory, diisopropyl ether is useful for recrystallizations because it has a wide liquid range. Diisopropyl ether is used for converting bromoboranes, which are thermally labile, into isopropoxy derivatives. Safety Diisopropyl ether forms explosive peroxides upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tert-Amyl Ethyl Ether
''tert''-Amyl ethyl ether (TAEE) is a chemical compound, classified as an ether, with the molecular formula C7H16O. It is used as an additive in gasoline fuels as an oxygenate and also as a solvent in organic chemistry. TAEE is prepared by acid-catalyzed addition of ethanol to 2-methyl-2-butene. See also * List of gasoline additives References {{DEFAULTSORT:Amyl ethyl ether, tert- Ether solvents Oxygenates Ethoxy compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest oxocarbon, carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called ''metal carbonyl, carbonyl''. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds. Numerous environmental and biological sources generate carbon monoxide. In industry, carbon monoxide is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Indoors CO is one of the most acutely toxic contaminants affecting indoor air quality. CO may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel-burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel-burning heating systems (wood, oil, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Tert-butyl Ether
Ethyl ''tertiary''-butyl ether (ETBE), also known as ethyl ''tert''-butyl ether, is commonly used as an oxygenate gasoline additive in the production of gasoline from crude oil. ETBE offers equal or greater air quality benefits than ethanol, while being technically and logistically less challenging. Unlike ethanol, ETBE does not induce evaporation of gasoline, which is one of the causes of smog, and does not absorb moisture from the atmosphere. Production Ethyl tert-butyl ether is manufactured industrially by the acidic etherification of isobutylene with ethanol at a temperature of 30–110 °C and a pressure of 0,8–1,3 MPa. The reaction is carried out with an acidic ion-exchange resin as a catalyst. Suitable reactors are fixed-bed reactors such as tube bundle or circulation reactors in which the reflux can be cooled optionally. Ethanol, produced by fermentation and distillation, is more expensive than methanol, which is derived from natural gas. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
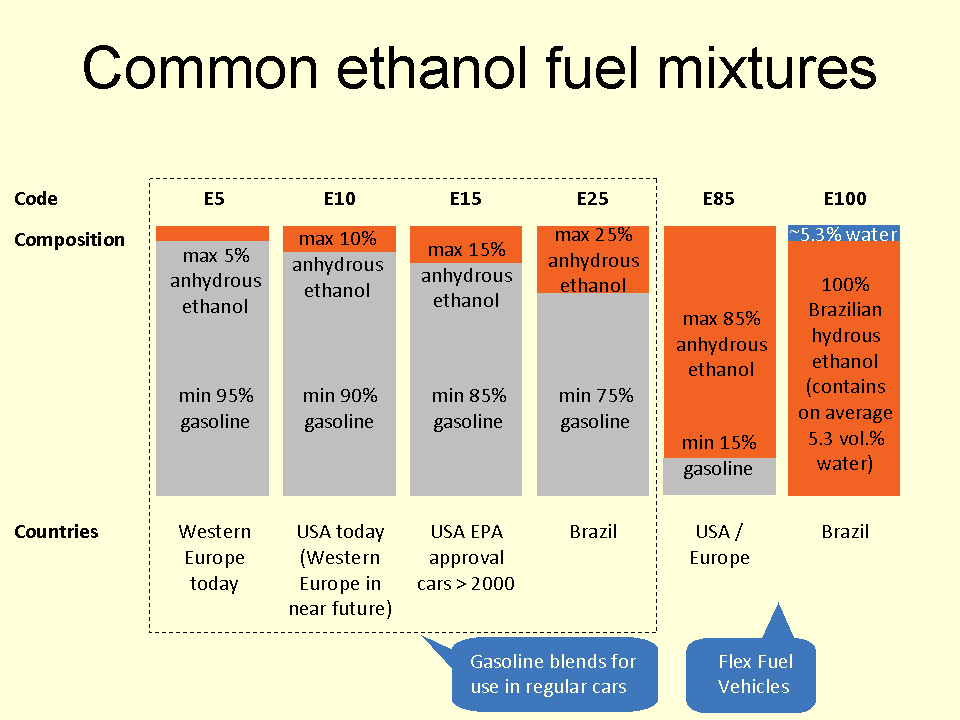
Common Ethanol Fuel Mixtures
Several common ethanol fuel mixtures are in use around the world. The use of pure anhydrous, hydrous or anhydrous ethanol in internal combustion engines (ICEs) is only possible if the engines are designed or modified for that purpose, and used only in automobiles, light-duty trucks and motorcycles. Anhydrous ethanol can be blended with :gasoline (petrol) for use in gasoline engines, but with high ethanol content only after engine modifications to meter increased fuel volume since pure ethanol contains only 2/3 of the BTUs of an equivalent volume of pure gasoline. High percentage ethanol mixtures are used in some racing engine applications as the very high octane rating of ethanol is compatible with very high compression ratios. Ethanol fuel mixtures have "E" numbers which describe the percentage of ethanol fuel in the mixture by volume, for example, E85 is 85% anhydrous ethanol and 15% gasoline. Low-ethanol blends are typically from E5 to E25, although internationally the most c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |