Army ROTC on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Army Reserve Officer Training Corps (AROTC) is the
 ; Basic course qualification requirements
A candidate for freshman and sophomore level ROTC training must:
*Be of good moral character
*Be a
; Basic course qualification requirements
A candidate for freshman and sophomore level ROTC training must:
*Be of good moral character
*Be a
 Leadership labs place cadets in leadership positions, teach and provide practical experience in military drill and ceremonies, troop leading procedures, small unit tactical operations, rappelling and water survival. Labs are held during the week and run for approximately two hours.
Leadership labs place cadets in leadership positions, teach and provide practical experience in military drill and ceremonies, troop leading procedures, small unit tactical operations, rappelling and water survival. Labs are held during the week and run for approximately two hours.
 Cadets may compete for training opportunities conducted at active army schools. This training is usually conducted during the summer months, but some allocations are available during the winter holidays. Cadets are selected to attend this training based on their overall standing within the program. Since the number of allocations are limited, selection for schools is competitive and based on factors including ROTC grades, academic grades, participation in ROTC activities, APFT scores and advisor recommendations.
Cadets may compete for training opportunities conducted at active army schools. This training is usually conducted during the summer months, but some allocations are available during the winter holidays. Cadets are selected to attend this training based on their overall standing within the program. Since the number of allocations are limited, selection for schools is competitive and based on factors including ROTC grades, academic grades, participation in ROTC activities, APFT scores and advisor recommendations.
Cadets are trained in airmobile operations, including rappelling from helicopters, airmobile tactics and rigging air mobile cargo. This is a two-week course taught at Fort Campbell, Kentucky. Upon successful completion, the cadet is awarded the
Army airborne training is conducted for three weeks at
 Ranger Challenge is the varsity sport of Army ROTC. A Ranger Challenge team is made up of 9 people, 8 active participant and 1 reserved. They compete against other colleges throughout the nation in events such as patrolling, weapons assembly, one-rope bridge, Army Physical Fitness Test, land navigation and a ten-kilometer road march.
Ranger Challenge is the varsity sport of Army ROTC. A Ranger Challenge team is made up of 9 people, 8 active participant and 1 reserved. They compete against other colleges throughout the nation in events such as patrolling, weapons assembly, one-rope bridge, Army Physical Fitness Test, land navigation and a ten-kilometer road march.
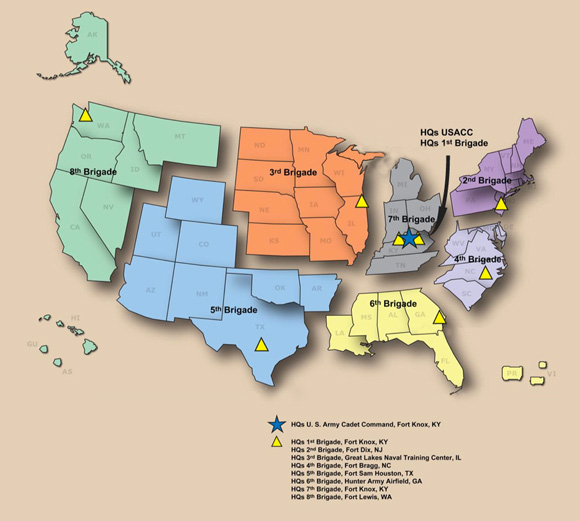 ROTC is composed of eight
ROTC is composed of eight
U.S. Army Cadet Command Homepage
{{Authority control Reserve Officers' Training Corps Fort Knox 1916 establishments in the United States
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
component of the Reserve Officers' Training Corps
The Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC; or ) is a group of college- and university-based officer-training programs for training commissioned officers of the United States Armed Forces.
While ROTC graduate officers serve in all branches o ...
. It is the largest Reserve Officer Training Corps
The Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC; or ) is a group of college- and university-based officer-training programs for training commissioned officers of the United States Armed Forces.
While ROTC graduate officers serve in all branches o ...
(ROTC) program which is a group of college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further education institution, or a secondary sc ...
and university
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
-based officer training programs for training commissioned officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer (NCO), or a warrant officer. However, absent ...
s for the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
and its reserves components: the Army Reserves and the Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG) is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States Army. It is simultaneously part of two differen ...
. There are over 30,000 Army ROTC cadets enrolled in 274 ROTC programs at colleges and universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
throughout the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. These schools are categorized as Military Colleges (MC), Military Junior Colleges (MJC) and Civilian Colleges (CC).
All of these units are commanded by the U.S. Army Cadet Command, whose mission is "to select, educate, train, and commission college students to be officers and leaders of character in the Total Army and form partnerships with high schools to conduct JROTC
The Junior Reserve Officers' Training Corps (JROTC) is a Federal government of the United States, federal program sponsored by the United States Armed Forces in high schools and also in some middle schools across the United States and at US mil ...
programs to develop citizens of character for a lifetime of commitment and service to the nation."
The first college to offer military training was Norwich University
Norwich University is a private university in Northfield, Vermont, United States. The university was founded in 1819 as the "American Literary, Scientific and Military Academy". It is the oldest of six senior military college, senior militar ...
, founded in 1819 in Vermont, followed by various state-chartered military schools and finally post-Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
civilian land grant colleges that required military training. The modern Army Reserve Officers' Training Corps was created by the National Defense Act of 1916
The National Defense Act of 1916, , was a United States federal law that updated the Militia Act of 1903, which related to the organization of the military, particularly the National Guard. The principal change of the act was to supersede provi ...
and commissioned its first class of lieutenants in 1920.
ROTC progression
For a cadet who only completes the first two years of ROTC (Basic Course), there is no military obligation, unless the student is a 3- to 4-year scholarship cadet or has other specific scholarships. If a cadet has accepted a scholarship, service commitments may vary. With some exceptions, in order to progress to the last two years of the program (Advanced Course) the cadet must contract with the United States Army. To do so, the student enlists in the United States Army Reserve Control Group (ROTC) as a cadet and elects to serve on either active duty or in a reserve component (Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG) is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States Army. It is simultaneously part of two differen ...
or Army Reserve).
Course of instruction
The following is an outline of a general military science program.Basic Course
 ; Basic course qualification requirements
A candidate for freshman and sophomore level ROTC training must:
*Be of good moral character
*Be a
; Basic course qualification requirements
A candidate for freshman and sophomore level ROTC training must:
*Be of good moral character
*Be a citizen of the United States
Citizenship of the United States is a legal status that entails Americans with specific rights, duties, protections, and benefits in the United States. It serves as a foundation of fundamental rights derived from and protected by the Constit ...
*Be under 35 years of age by December 31 of the year of your graduation
*Be physically able to participate in the program of instruction
*Meet other entrance requirements as determined by the departmental chair, current army regulations and university policies
A student who does not meet all of the above requirements should consult with the Department of Military Science and Leadership to determine if waivers can be granted.
; Military Science I year (MSI)
This year serves as the cadets' first introduction to the Army. Topics covered include military courtesy, military history, basic first aid, basic rifle marksmanship, basic hand grenade use, land navigation, rappelling, fundamentals of leadership, map orienteering, field training, military procedures, radio operations, rank structures and drill and ceremony.
; Military Science II year (MSII)
The second year is an expansion of the topics taught in the first year of the program. Cadets are introduced to tactics, troop leading procedures, basics of operations orders and ethics.
; Basic Camp
Basic Camp, formerly Cadet Initial Entry Training (CIET) and Leader's Training Course (LTC) before that, is a four-week (28-day) introduction to Army life and leadership training of the ROTC, held at Fort Knox, Kentucky
Fort Knox is a United States Army installation in Kentucky, south of Louisville and north of Elizabethtown, Kentucky, Elizabethtown. It is adjacent to the United States Bullion Depository (also known as Fort Knox), which is used to house a larg ...
each summer. The aim of this training is to motivate and qualify cadets for entry into the Senior ROTC program. Basic Camp is a summary version of the first two years of leadership development training that cadets receive at their university for the basic course. This course is designed for college students, either in the summer between freshman and sophomore year or between sophomore and junior year, qualifying these cadets for enrollment in the Military Science III year and Advanced Course.
Advanced Course
; Military Science III year (MSIII) The third year marks the beginning of the Advanced Course. This is where most cadets must contract with the Army to continue in the program. Cadets may be eligible for the Advanced Course if the following criteria are met: *The cadet has prior military service or *The cadet has completed the first two years of the program (Basic Course) or *The cadet has graduated the Leaders Training Course (formerly Basic Camp) at Ft. Knox, Kentucky and *The cadet has completed 54 credits (at least 60 preferred) of college coursework The course sequence in this year is mainly focused on the application of leadership and small-unit tactics. Cadets are assigned rotating leadership positions within the School Battalion and are evaluated on their performance and leadership abilities while in those positions. Third-year cadets practice briefing operations orders, executing small-unit tactics, leading and participating in physical training and preparing for successful performance at the four-week Cadet Leader Course during the summer following the third year. Under current regulations, attendance at the course is mandatory (in the past,Ranger School
The Ranger School is a 62-day United States Army small unit tactics and leadership course that develops functional skills directly related to units whose mission is to engage the enemy in close combat and direct fire battles. Ranger training w ...
was offered as an alternative to select cadets).
; Leadership Development Program
During MSIII year and continuing through Advanced Camp, cadets are introduced to the Leadership Development Program (LDP). The LDP is a structured set of rotations where MSIII cadets are assigned to specific roles in an organization consisting of companies, platoons and squads. Some of the roles traditionally filled are that of a company commander, company XO, first sergeant, platoon leader, platoon sergeant and squad leader.
While filling these positions, the MSIII is evaluated according to the Army Leadership Requirements Model (ALRM) which centers on what a leader is (attributes) and what a leader does (competencies), outlined by the following model.
The evaluation is usually given by an MS IV and is delivered in writing using a Developmental Counseling form, DA 4856. Cadets are counseled on their performance through the ALRM attributes and competencies. At the end of the MSIII school year, these counselings are collected and help determine a cadet's ranking on the Order of Merit List (OML), a ranking of all ROTC Cadets in the nation that impacts how Cadets receive their component and branch when they commission.
; Advanced Camp
Advanced Camp is a paid 35 day leadership course conducted at Fort Knox, Kentucky
Fort Knox is a United States Army installation in Kentucky, south of Louisville and north of Elizabethtown, Kentucky, Elizabethtown. It is adjacent to the United States Bullion Depository (also known as Fort Knox), which is used to house a larg ...
each summer. It was formerly conducted at Fort Lewis, Washington, Fort Bragg, North Carolina
Fort Bragg (formerly Fort Liberty from 2023–2025) is a United States Army, U.S. Army Military base, military installation located in North Carolina. It ranks among the largest military bases in the world by population, with more than 52,000 m ...
and Fort Riley, Kansas
Fort Riley is a United States Army installation located in North Central Kansas, on the Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, between Junction City and Manhattan. The Fort Riley Military Reservation covers 101,733 acres (41,170 ha) in Ge ...
. In 2014, Advanced Camp (then LDAC) was consolidated with Basic Camp at Fort Knox, Kentucky. This was a period of upheaval for the training event due to the rapid change of locations and new Cadet Command Commanding General stripping Advanced Camp of its graded portion. For 2014, Advanced Camp, then LDAC, retained its graded portions, but in 2015 it was changed to Cadet Leadership Camp (CLC). During the time it was called CLC, all the graded portions of were taken out and the 4 week period was pass/no pass. In 2016 a new commanding general took over Cadet Command, on his first day CLC became Advanced Camp and in 2017 the old style of graded events will be brought back. This includes a graded PT test, graded rifle qualification and graded training lanes. Typically, cadets attend Advanced Camp during the summer between their first and second years in the Advanced Course (junior and senior year of college). At Advanced Camp, cadets take on various leadership roles and are evaluated on their performance and leadership abilities in those positions. Cadets also participate in adventure training to include: confidence and obstacle courses, rappelling, water safety, weapons firing and patrolling. While at Advanced Camp, cadets take a series of standardized tests including the Cadet Development Assessment (CDA). The CDA assesses the state of a MSIII cadet's development in preparation for the MSIV year with a focus on mission-context problem solving. Cadets must attend and complete Advanced Camp to earn an Army commission.
; Military Science IV year (MSIV)
This is the final year of the ROTC program and the main focus is towards preparing cadets to become successful lieutenants in the Army upon graduation and commissioning. Senior cadets apply for their branches (career fields). Senior cadets apply before end of their third year, but have until mid September to make any changes before they are locked in. In early November, cadets are notified of which branch and status they were granted (e.g., Regular Army, Army Reserve, Army National Guard). For those cadets selected for the reserve component (Army Reserve or Army National Guard), they are responsible for locating a unit with which to serve. Cadets selected for active duty (Regular Army) are notified of their first duty assignment in the spring semester, typically in early April. Throughout their senior year, MSIV cadets are assigned cadet battalion staff positions and are responsible for evaluating MS III cadets, planning and coordinating training operations and missions. The primary purpose of the MSIV year is to learn how to manage and evaluate training in the field while learning officership in the classroom.
Branch assignment
Branch assignments are made according to the needs of the Army. Consideration is given to the cadet's area of academic specialty and their individual desires. Army policy is to assign graduating cadets to a branch and specialty code based on the following: *Army branch/specialty strength requirements *Academic disciplines *Personal preference *Recommendation of the Professor of Military Science *Demonstrated performance and potential *Prior military experience *Other experienceLab
 Leadership labs place cadets in leadership positions, teach and provide practical experience in military drill and ceremonies, troop leading procedures, small unit tactical operations, rappelling and water survival. Labs are held during the week and run for approximately two hours.
Leadership labs place cadets in leadership positions, teach and provide practical experience in military drill and ceremonies, troop leading procedures, small unit tactical operations, rappelling and water survival. Labs are held during the week and run for approximately two hours.
Physical fitness training
Physical fitness training builds physical conditioning, teamwork, and self-confidence. Physical fitness training sessions are typically scheduled for approximately one-hour and the intensity, time and type of exercises varies. All ROTC Cadets must pass the Army Combat Fitness Test (ACFT) with at least the minimum (60 points) in each of the six exercises according to the standards for their age and sex. Each program may further make its own standards. For example, a program may set a standard of scoring no less than 70% (10% more than the Army requires) in each category. Failure to reach the program standard may require increased physical fitness training on otherwise days of rest (commonly known as "incentive” or “remedial” PT). Physical fitness is also a graded component of the Order of Merit List in the branching process. Cadets with higher scores on the ACFT during their MSIII year and at Advanced Camp receive more points in this category, which places them higher on the OML and makes performing well in physical fitness necessary for Cadets to receive their preferred branch and component.College life
ROTC cadets must train for the military at the same time that they complete their college degree. This entails numerous commitments during and outside the school year. Cadets are typically (situation may vary in military colleges) mandated to wear military uniforms to college classes one day per week, take military science classes as one of their regular course requirements, attend physical fitness training during the week and participate in field training exercises on some weekends. The summers following Cadets' sophomore and junior years typically involve training courses atFort Knox
Fort Knox is a United States Army installation in Kentucky, south of Louisville and north of Elizabethtown, Kentucky, Elizabethtown. It is adjacent to the United States Bullion Depository (also known as Fort Knox), which is used to house a larg ...
or other military installations, at a time when other students might typically pursue internships
An internship is a period of work experience offered by an organization for a limited period of time. Once confined to medical graduates, internship is used to practice for a wide range of placements in businesses, non-profit organizations and g ...
or research
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to ...
opportunities.
Cadre
The cadre at each university consist of military personnel and civilian technical assistants who run the ROTC program. It is the cadre's job to teach the military science classes and oversee the day-to-day operations of the ROTC program. Every Army ROTC program has a professor of military science, usually a lieutenant colonel; it is his/her job to instruct the MSIVs as they make the transition from cadet to second lieutenant. Depending on the size of the program, there are typically other cadre members including an assistant professor of military science, usually a senior captain or a major who teaches younger cadets, and a senior military instructor, usually a senior NCO who teaches basic military skills and tactics.Scholarships
The United States Army offers ROTC scholarships that assist students with financing their education. There are numerous types of Army ROTC scholarships available for both high school and college students.: There are three different types of scholarships available to high school students. These scholarships are won through the national ROTC scholarship selection board which convenes on three different dates that vary slightly each school year. *Four-year scholarships offered to candidates pay for full tuition for all four years of their undergraduate degree. *Three-year advanced designee scholarships require students to enroll in a college ROTC program and be a full-time college student, for which the student's freshmen year will not be paid for by the Army. If the student displays academic competence and receives a recommendation by the program's Professor of Military Science, the remaining three years will be paid for in full. *Two-year scholarships are known as Early Commissioning Program scholarships (ECP), or Ike Skelton scholarships. These scholarships enable a student to commission into the Army Reserves or the Army National Guard in two years instead of the usual four. Students are required to attend a Military Junior College (MJC) for two years and will commission after. As students will have an associates rather than the required bachelors for the Basic Officer Leaders Course (BOLC), students will have up to three years to earn their bachelors and are eligible for the Educational Assistance Program which can pay for up to two years of tuition. If students wish to go Active Duty on the ECP route, they will have to do so through their respective MJC. ROTC scholarships for those already attending college will cover the remaining years of their college. *The three-year scholarship is available for students who have three academic years of college remaining. *The two-year scholarship is available for students who have two academic years of college remaining. The Army ROTC scholarship entitles its recipients to full-tuition assistance, as well as a textbook/fee allowance and a monthly stipend to cover the student's living expenses. Typically, cadets receive tuition assistance. However, they also have the option to apply the scholarship to their 'room and board' expenses instead of school tuition. The Simultaneous Membership Program (SMP) is an alternative route to receive military scholarship benefits. The program requires cadets to enlist in a reserve unit (Army Reserve or National Guard) while enrolled in ROTC. ECP cadets are required to enlist in the Army Reserves or the Army National Guard during their two years at a Military Junior College, and will be in the SMP program. SMP cadets are not required to complete Basic Combat Training (BCT) or Advanced Individual Training (AIT), but it is necessary to receive specific benefits. The benefits are as follows: *Drill pay at E-5 or higher *Cadet rank *GI Bill *Federal tuition assistance *GI Bill Kicker (If qualified) *National Guard members may be eligible for various state-offered benefits, including additional tuition assistance Once contracted, SMP cadets cannot be deployed. However, they are required to attend all drill events with their unit. This includes drill weekend and advanced training.Training opportunities
Air Assault Badge
The Air Assault Badge, U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry, dated 18 January 1978, last accessed 16 October 2020 is awarded by the U.S. Army for successful completion of the United States Army Air Assault School, Air Assault School. The course includes ...
.
Fort Moore
Fort Benning (named Fort Moore from 2023–2025) is a United States Army post in the Columbus, Georgia area. Located on Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia's border with Alabama, Fort Benning supports more than 120,000 active-duty military, family me ...
, Georgia. Upon successful completion, cadets are awarded the Parachutist Badge.
The Cadet Intern Program
An initiative of ASA/MRA, allows cadets to work with a variety of programs across the nation, such as Department of the Army (DA), the Office of the Chief of the Army Reserve (OCAR), National Guard Bureau (NGB), Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), European Command (EUCOM), Africa Command (AFRICOM), or the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) for 3–8 weeks.Cadet Troop Leadership Training
Cadet Troop Leadership Training is an optional program for MSIII cadets during the summer following completion of LDAC. This three-week CONUS or four-week OCONUS program trains cadets in lieutenant positions with active army units. Assignments are available in nearly all branches and with units worldwide.Drill Cadet Leadership Training
Drill Cadet Leadership Training is very similar to Cadet Troop Leadership training but it takes place at Fort Jackson, South Carolina. During the three weeks, cadets will follow around drill sergeants and the officers of each basic training company.Northern Warfare Training Course
The Northern Warfare Training course is a three-week course covering tactical operations in a cold weather climate. The course is taught atFort Greely
Fort Greely is a United States Army launch site for anti-ballistic missiles located about southeast of Fairbanks, Alaska, Fairbanks, Alaska. It is also the home of the Cold Regions Test Center (CRTC), as Fort Greely is one of the coldest areas ...
in Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
. Cadets are trained in winter survival techniques, skiing, snowshoeing and cold weather patrolling.
Mountain Warfare Training Course
The Army Mountain Warfare course is taught at the Ethan Allen Firing Range inJericho, Vermont
Jericho is a town in Chittenden County, Vermont, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 5,104. The town was named after the ancient city of Jericho.
History
Ira Allen and Remember Baker began surveying the town of Jericho ...
. It is taught in two phases, each lasting two weeks. The summer phase teaches and tests cadets on military mountaineering operations including rock climbing, rappelling and orienteering. The winter phase teaches and tests on similar tasks, but in the winter environment. It includes ice climbing, cross-country skiing and cold weather operations.
Sapper Leader Course
The Sapper Leader Course is a 28-day United States Army small unit tactics and leadership course that develops soldiers in critical skills and teaches advanced combat engineer techniques needed across the Army. Sapper training began developmen ...
The Sapper Leader Course focuses on the application of a mixture of infantry and combat engineer small unit tactics to forces composed of one or more branch of service. Additionally, this course focuses on advancing the leadership skills of its students within these environments. The course is taught in two sections which each focus on different tasks. The first consists of general information including combat lifesaving, meeting physical fitness standards, demolitions, explosive hazard recognition, land navigation, knot tying, as well as air, mountain and water operations training. The second phase consists of tactics which relate specifically to patrolling and combat operations with topics covering movement formations, intelligence gathering, planning operations, MOUT, and a field training. The course as a whole lasts for 28 days. Phase one makes up the first thirteen days of training while phase two training takes up the remaining 15 days. Of these last 15 days, the field training exercise takes 9 to complete. To be accepted into the program, a prospective student must show proficiency in multiple areas of physical fitness, as well as knowledge of battle drills. To meet the minimum physical standards, a candidate must pass the APFT as well as the height and weight measures. Additionally, the results of the Combat Water Survival Test are required. All training is conducted on the U.S. Army installation of Ft. Leonard Wood, Missouri. On graduation, successful students will be awarded the sapper tab.
Robin Sage
For ROTC cadets, participation in the Robin Sage exercise is the opportunity to train in guerilla tactics with Special Forces candidates conducting the exercise. During the training, cadets act as a guerrilla force in Pineland, a fictional independent state which has been invaded, who are trained by special forces candidates. The training opportunity covers a variety of battle drills all focused around fieldcraft for small units. Some general items such as operations planning, medical procedures, troop movements and demolitions are among the more prominent skills taught in this environment. The exercise encompasses 20 days of training. For ROTC cadets, selection for training is dependent upon performance academically, and physically. The training is conducted in the civilian areas around Ft Bragg, North Carolina. During training, the 15 counties in central North Carolina are used to represent the independent state of Pineland. For ROTC candidates, no awards are received as this is part of a training exercise and not an independent school.Activities and clubs
Ranger Challenge
 Ranger Challenge is the varsity sport of Army ROTC. A Ranger Challenge team is made up of 9 people, 8 active participant and 1 reserved. They compete against other colleges throughout the nation in events such as patrolling, weapons assembly, one-rope bridge, Army Physical Fitness Test, land navigation and a ten-kilometer road march.
Ranger Challenge is the varsity sport of Army ROTC. A Ranger Challenge team is made up of 9 people, 8 active participant and 1 reserved. They compete against other colleges throughout the nation in events such as patrolling, weapons assembly, one-rope bridge, Army Physical Fitness Test, land navigation and a ten-kilometer road march.
Color guard
A color guard is responsible for posting the colors for ceremonial events (football games, dining ins and dining outs, military balls and commencements), as well as cannon detail at football games, in order to show honor towards flag and country.Military ball
These formal social events are designed to allow cadets to experience the type of social gathering and military etiquette they can expect as future commissioned officers. Cadets are encouraged to bring spouses or dates. Many dignitaries are invited, including the school president, certain university officials and representatives of veterans' societies, parents and relatives.Organization
 ROTC is composed of eight
ROTC is composed of eight brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military unit, military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute ...
s which command 273 ROTC units, referred to as battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of up to one thousand soldiers. A battalion is commanded by a lieutenant colonel and subdivided into several Company (military unit), companies, each typically commanded by a Major (rank), ...
s (though these units are typically much smaller than regular army battalions). The brigades command ROTC units throughout different regions of the country:
* 1st Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade (responsible for 10 Senior Military Colleges and Military Junior Colleges)
* 2nd Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade (CT, MA, ME, NH, NJ, NY, PA, RI, VT, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
)
* 3rd Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade (IA, IL, KS, MN, MO, ND, NE, SD, WI)
* 4th Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade (DC, DE, MD, NC, SC, VA, WV)
* 5th Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade (AR, AZ, CO, NM, OK, TX, UT, WY)
* 6th Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade (AL, FL, GA, LA, MS, PR, VI)
* 7th Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade (IN, KY, MI, OH, TN)
*8th Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade
The 8th Reserve Officers' Training Corps Brigade is a United States Army Reserve Officers' Training Corps brigade based at Joint Base Lewis-McChord, Washington (state), Washington.
Battalions Alaska
* University of Alaska Fairbanks
Californ ...
(AK, AS, CA, GU, HI, ID, MP, MT, NV, OR, WA, Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
)
List of commanding generals
The commander of the Reserve Officers' Training Corps is dual-hatted as the commanding general of U.S. Army Cadet Command since 2011.Notable graduates
In 1960, General George H. Decker became the first ROTC graduate named Chief of Staff of the Army. GeneralColin Powell
Colin Luther Powell ( ; – ) was an Americans, American diplomat, and army officer who was the 65th United States secretary of state from 2001 to 2005. He was the first African-American to hold the office. He was the 15th National Security ...
was the first ROTC graduate named Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (CJCS) is the presiding officer of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS). The chairman is the highest-ranking and most senior military officer in the United States Armed Forces Chairman: appointment; gra ...
, who was a graduate of the City College of New York
The City College of the City University of New York (also known as the City College of New York, or simply City College or CCNY) is a Public university, public research university within the City University of New York (CUNY) system in New York ...
and later served as the United States secretary of state
The United States secretary of state (SecState) is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State.
The secretary of state serves as the principal advisor to the ...
.
Chiefs of staff of the Army or chairmen of the Joint Chiefs of Staff to graduate from Army ROTC include:
*Chiefs of Staff of the Army
**General George H. Decker (Lafayette College
Lafayette College is a private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Easton, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1826 by James Madison Porter and other citizens in Easton, the college first held classes in 18 ...
)
** General Fred Weyand (University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Berkeley, California, United States. Founded in 1868 and named after t ...
)
** General Gordon R. Sullivan (Norwich University
Norwich University is a private university in Northfield, Vermont, United States. The university was founded in 1819 as the "American Literary, Scientific and Military Academy". It is the oldest of six senior military college, senior militar ...
)
** General Peter Schoomaker (University of Wyoming
The University of Wyoming (UW) is a Public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in Laramie, Wyoming, United States. It was founded in March 1886, four years before the territory was admitted as the 44th state, ...
)
** General George Casey (Georgetown University
Georgetown University is a private university, private Jesuit research university in Washington, D.C., United States. Founded by Bishop John Carroll (archbishop of Baltimore), John Carroll in 1789, it is the oldest Catholic higher education, Ca ...
)
** General Mark Milley (Princeton University
Princeton University is a private university, private Ivy League research university in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth, New Jersey, Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the List of Colonial ...
)
*Chairmen of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
**General Colin Powell
Colin Luther Powell ( ; – ) was an Americans, American diplomat, and army officer who was the 65th United States secretary of state from 2001 to 2005. He was the first African-American to hold the office. He was the 15th National Security ...
(City College of New York)
** General Hugh Shelton (North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State, North Carolina State, NC State University, or NCSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina, United States. Founded in 1887 and p ...
)
** General Mark Milley (Princeton University
Princeton University is a private university, private Ivy League research university in Princeton, New Jersey, United States. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth, New Jersey, Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the List of Colonial ...
)
*Other notable graduates
** Charlie Beckwith (University of Georgia
The University of Georgia (UGA or Georgia) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university with its main campus in Athens, Georgia, United States. Chartered in 1785, it is the oldest public university in th ...
)
** Patrick Murphy (King's College)
** Lou Holtz ( Kent State)
**Sam Walton
Samuel Moore Walton (March 29, 1918 – April 5, 1992) was an American business magnate best known for Co-founding the retailers Walmart and Sam's Club, which he started in Rogers, Arkansas, and Midwest City, Oklahoma, in 1962 and 1983 res ...
(University of Missouri
The University of Missouri (Mizzou or MU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Columbia, Missouri, United States. It is Missouri's largest university and the flagship of the four-campus Univers ...
)
** Earl Graves (Morgan State University
Morgan State University (Morgan State or MSU) is a Public university, public historically black colleges and universities, historically black research university in Baltimore, Baltimore, Maryland. It is the largest of Maryland's historically bla ...
)
**James Earl Jones
James Earl Jones (January 17, 1931 – September 9, 2024) was an American actor. A pioneer for black actors in the entertainment industry, Jones is known for his extensive and acclaimed roles on stage and screen. Jones is one of the few perfor ...
(University of Michigan
The University of Michigan (U-M, U of M, or Michigan) is a public university, public research university in Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest institution of higher education in the state. The University of Mi ...
)
**Samuel Alito
Samuel Anthony Alito Jr. ( ; born April 1, 1950) is an American jurist who serves as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was Samuel Alito Supreme Court ...
( Princeton)
**Frank Wells
Franklin G. Wells (March 4, 1932 – April 3, 1994) was an American businessman who served as President and Chief Operating Officer of The Walt Disney Company from 1984 until his death in 1994.
Life and career
Wells was born in Coronado, Califo ...
(Pomona College
Pomona College ( ) is a private university, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Claremont, California. It was established in 1887 by a group of Congregationalism in the United States, Congregationalists ...
)
**Dean Rusk
David Dean Rusk (February 9, 1909December 20, 1994) was the United States secretary of state from 1961 to 1969 under presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson, the second-longest serving secretary of state after Cordell Hull from the ...
(Davidson College
Davidson College is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Davidson, North Carolina, United States. It was established in 1837 by the Concord Presbytery and named after American Revolutiona ...
)
** Nancy Currie (Ohio State
The Ohio State University (Ohio State or OSU) is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio, United States. A member of the University System of Ohio, it was founded in 1870. It is one of the largest universities by enrollme ...
)
** Leon Panetta (Santa Clara University
Santa Clara University is a private university, private Jesuit university in Santa Clara, California, United States. Established in 1851, Santa Clara University is the oldest operating institution of higher learning in California. The university' ...
)
**Darrell Issa
Darrell Edward Issa ( ; born November 1, 1953) is an American businessman and politician serving as the U.S. representative for California's 48th congressional district. He represented the 50th congressional district from 2021 to 2023. A memb ...
( Kent State)
** Ernest Frederick "Fritz" Hollings (The Citadel
The Citadel Military College of South Carolina (simply known as The Citadel) is a public senior military college in Charleston, South Carolina, United States. Established in 1842, it is the third oldest of the six senior military colleges ...
)
** Robert L. Stewart ( The University of Southern Mississippi)
** James Earl Rudder (Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University (Texas A&M, A&M, TA&M, or TAMU) is a public university, public, Land-grant university, land-grant, research university in College Station, Texas, United States. It was founded in 1876 and became the flagship institution of ...
)
The Citadel
The Citadel Military College of South Carolina (simply known as The Citadel) is a public senior military college in Charleston, South Carolina, United States. Established in 1842, it is the third oldest of the six senior military colleges ...
has produced 293 general and flag officers
A flag officer is a commissioned officer in a nation's armed forces senior enough to be entitled to fly a flag to mark the position from which that officer exercises command.
Different countries use the term "flag officer" in different ways:
* ...
as of June 30, 2017. VMI had produced 265 as of 2006. The University of Oregon
The University of Oregon (UO, U of O or Oregon) is a Public university, public research university in Eugene, Oregon, United States. Founded in 1876, the university is organized into nine colleges and schools and offers 420 undergraduate and gra ...
has produced the highest number of general officers out of the civilian ROTC schools, with a total of 47.
Awards
There are three Department of the Army decorations authorized exclusively to cadets: * ROTC Medal for Heroism * Superior Cadet Decoration Award * Ranger Challenge Tab Outside these, cadets are eligible for numerous U.S. Army awards and decorations, as well as awards and decorations sponsored by various military societies and organizations.Distinguished Military Graduate Award
Cadets who demonstrated academic and leadership excellence can be designated as a distinguished military student (DMS) or distinguished military graduate (DMG). A Distinguished Military Graduate (DMG) is a cadet who has: * Maintained high scholastic standards * Successfully completed ROTC Advanced Camp at Fort Knox, KY * Graduated with a baccalaureate degree or that the degree will be conferred at the next regular commencement * Designated as a DMG by the Professor of Military Science * Ranked in the top 20% of Army ROTC Cadets nationwideSee also
* Early Commissioning Program * Naval Reserve Officers Training Corps * Air Force Reserve Officer Training Corps *Army University
The Army University is a professional military education university system of the United States Army. It is the largest professional military education system in the world, with over 150,000 soldiers educated in more than 88 occupations across ...
* Military Junior College
* Senior Military College
* Army Officer Candidate School
Notes
References
External links
U.S. Army Cadet Command Homepage
{{Authority control Reserve Officers' Training Corps Fort Knox 1916 establishments in the United States