Archaea Taxonomic Families on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a
 For much of the 20th century, prokaryotes were regarded as a single group of organisms and classified based on their
For much of the 20th century, prokaryotes were regarded as a single group of organisms and classified based on their
 The classification of archaea, and of prokaryotes in general, is a rapidly moving and contentious field. Current classification systems aim to organize archaea into groups of organisms that share structural features and common ancestors. These classifications rely heavily on the use of the sequence of
The classification of archaea, and of prokaryotes in general, is a rapidly moving and contentious field. Current classification systems aim to organize archaea into groups of organisms that share structural features and common ancestors. These classifications rely heavily on the use of the sequence of
 Archaeal membranes are made of molecules that are distinctly different from those in all other life forms, showing that archaea are related only distantly to bacteria and eukaryotes. In all organisms,
Archaeal membranes are made of molecules that are distinctly different from those in all other life forms, showing that archaea are related only distantly to bacteria and eukaryotes. In all organisms,
 Other archaea use in the atmosphere as a source of carbon, in a process called carbon fixation (they are autotrophs). This process involves either a highly modified form of the Calvin cycle or another metabolic pathway called the 3-hydroxypropionate/ 4-hydroxybutyrate cycle. The Thermoproteota also use the reverse Krebs cycle while the "Euryarchaeota" also use the reductive acetyl-CoA pathway. Carbon fixation is powered by inorganic energy sources. No known archaea carry out photosynthesis (Halobacterium is the only known phototroph archeon but it uses an alternative process to photosynthesis). Archaeal energy sources are extremely diverse, and range from the oxidation of
Other archaea use in the atmosphere as a source of carbon, in a process called carbon fixation (they are autotrophs). This process involves either a highly modified form of the Calvin cycle or another metabolic pathway called the 3-hydroxypropionate/ 4-hydroxybutyrate cycle. The Thermoproteota also use the reverse Krebs cycle while the "Euryarchaeota" also use the reductive acetyl-CoA pathway. Carbon fixation is powered by inorganic energy sources. No known archaea carry out photosynthesis (Halobacterium is the only known phototroph archeon but it uses an alternative process to photosynthesis). Archaeal energy sources are extremely diverse, and range from the oxidation of
 Archaea are genetically distinct from bacteria and eukaryotes, with up to 15% of the proteins encoded by any one archaeal genome being unique to the domain, although most of these unique genes have no known function. Of the remainder of the unique proteins that have an identified function, most belong to the Euryarchaeota and are involved in methanogenesis. The proteins that archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes share form a common core of cell function, relating mostly to Transcription (genetics), transcription, Translation (biology), translation, and nucleotide, nucleotide metabolism. Other characteristic archaeal features are the organization of genes of related function – such as enzymes that catalyze steps in the same
Archaea are genetically distinct from bacteria and eukaryotes, with up to 15% of the proteins encoded by any one archaeal genome being unique to the domain, although most of these unique genes have no known function. Of the remainder of the unique proteins that have an identified function, most belong to the Euryarchaeota and are involved in methanogenesis. The proteins that archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes share form a common core of cell function, relating mostly to Transcription (genetics), transcription, Translation (biology), translation, and nucleotide, nucleotide metabolism. Other characteristic archaeal features are the organization of genes of related function – such as enzymes that catalyze steps in the same
 Archaea exist in a broad range of
Archaea exist in a broad range of
 The well-characterized interactions between archaea and other organisms are either Mutualism (biology), mutual or commensalism, commensal. There are no clear examples of known archaeal
The well-characterized interactions between archaea and other organisms are either Mutualism (biology), mutual or commensalism, commensal. There are no clear examples of known archaeal
Introduction to the Archaea, ecology, systematics and morphology
Oceans of Archaea
nbsp;– E.F. DeLong, ''ASM News'', 2003
NCBI taxonomy page on Archaea
nbsp;– list of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature
Shotgun sequencing finds nanoorganisms
nbsp;– discovery of the ARMAN group of archaea
Browse any completed archaeal genome at UCSC
Comparative Analysis of Archaeal Genomes
(at United States Department of Energy, DOE's Integrated Microbial Genomes System, IMG system) {{Authority control Archaea, Extremophiles Domains (biology) Systems of bacterial taxonomy
domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
**Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* Do ...
of single-celled organisms. These microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s lack cell nuclei
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
and are therefore prokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
), but this term has fallen out of use.
Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the ...
. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phyl ...
. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated
Isolation is the near or complete lack of social contact by an individual.
Isolation or isolated may also refer to:
Sociology and psychology
*Isolation (health care), various measures taken to prevent contagious diseases from being spread
**Is ...
in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples.
Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi
''Haloquadratum walsbyi'' is of the genus ''Haloquadratum,'' within the archaea domain known for its square halophilic nature. First discovered in a brine pool in the Sinai peninsula of Egypt, ''H. walsbyi'' is noted for its flat, square-shaped ...
''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
s and several metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reac ...
s that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s involved in transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
and translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
. Other aspects of archaeal biochemistry are unique, such as their reliance on ether lipid
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
s in their cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
s, including archaeol
Archaeol is composed of two phytanyl chains linked to the sn-2 and sn-3 positions of glycerol. As its phosphate ester, it is a common component of the membranes of archaea.
Structure and contrast with other lipids
Archaeol is a diether.
The 2 ...
s. Archaea use more diverse energy sources than eukaryotes, ranging from organic compounds
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The s ...
such as sugars, to ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
, metal ions
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
or even hydrogen gas
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, a ...
. The salt-tolerant
Halotolerance is the adaptation of living organisms to conditions of high salinity. Halotolerant species tend to live in areas such as hypersaline lakes, coastal dunes, saline deserts, salt marshes, and inland salt seas and springs. Halophiles a ...
Haloarchaea
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of th ...
use sunlight as an energy source, and other species of archaea fix carbon (autotrophy), but unlike plants and cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
, no known species of archaea does both. Archaea reproduce asexually
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the fu ...
by binary fission
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that t ...
, fragmentation, or budding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is know ...
; unlike bacteria, no known species of Archaea form endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., no ...
s.
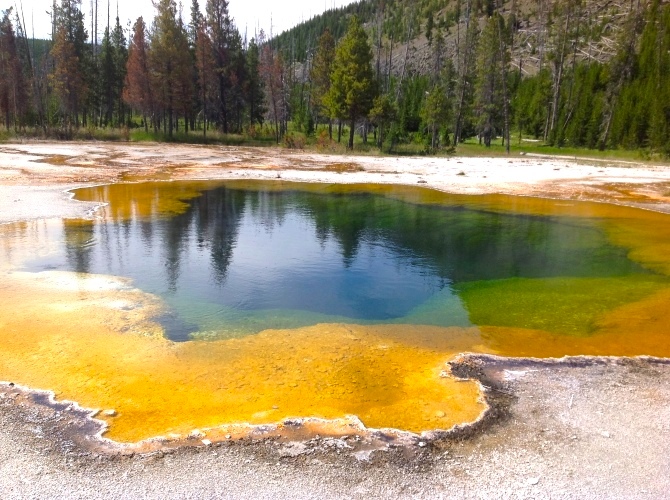
The first observed archaea were extremophile
An extremophile (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "love") is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e. environments that make survival challenging such as due to extreme temper ...
s, living in extreme environments such as hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
s and salt lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). ...
s with no other organisms. Improved molecular detection tools led to the discovery of archaea in almost every habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
, including soil, oceans, and marshland
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at ...
s. Archaea are particularly numerous in the oceans, and the archaea in plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
may be one of the most abundant groups of organisms on the planet.
Archaea are a major part of Earth's life. They are part of the microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found t ...
of all organisms. In the human microbiome
The human microbiome is the aggregate of all microbiota that reside on or within human tissues and biofluids along with the corresponding anatomical sites in which they reside, including the skin, mammary glands, seminal fluid, uterus, ovarian ...
, they are important in the gut, mouth, and on the skin. Their morphological, metabolic, and geographical diversity permits them to play multiple ecological roles: carbon fixation; nitrogen cycling
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biolog ...
; organic compound turnover; and maintaining microbial symbiotic
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
and syntrophic In biology, syntrophy, synthrophy, or cross-feeding (from Greek ''syn'' meaning together, ''trophe'' meaning nourishment) is the phenomenon of one species feeding on the metabolic products of another species to cope up with the energy limitations by ...
communities, for example.
No clear examples of archaeal pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
s or parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s are known. Instead they are often mutualists
Mutualism describes the ecological Biological interaction, interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of ecological interaction. Prominent examples include most vascular plants engag ...
or commensals
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fro ...
, such as the methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are com ...
s (methane-producing strains) that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
in humans and ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally ...
s, where their vast numbers facilitate digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intest ...
. Methanogens are also used in biogas
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. It is a ...
production and sewage treatment
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding envir ...
, and biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
exploits enzymes from extremophile archaea that can endure high temperatures and organic solvents
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for p ...
.
Classification
Early concept
 For much of the 20th century, prokaryotes were regarded as a single group of organisms and classified based on their
For much of the 20th century, prokaryotes were regarded as a single group of organisms and classified based on their biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
, morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
and metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
. Microbiologists tried to classify microorganisms based on the structures of their cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
s, their shapes, and the substances they consume. In 1965, Emile Zuckerkandl
Émile Zuckerkandl (July 4, 1922 – November 9, 2013) was an Austrian-born French biologist considered one of the founders of the field of molecular evolution. He introduced, with Linus Pauling, the concept of the "molecular clock", which enabl ...
and Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling (; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist, biochemist, chemical engineer, peace activist, author, and educator. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific top ...
instead proposed using the sequences of the gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
s in different prokaryotes to work out how they are related to each other. This phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
approach is the main method used today.
Archaea – at that time only the methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are com ...
s were known – were first classified separately from bacteria in 1977 by Carl Woese
Carl Richard Woese (; July 15, 1928 – December 30, 2012) was an American microbiologist and biophysicist. Woese is famous for defining the Archaea (a new domain of life) in 1977 through a pioneering phylogenetic taxonomy of 16S ribosomal RNA, ...
and George E. Fox
George Edward Fox (born December 17, 1945) is an astrobiologist, a Professor Emeritus and researcher at the University of Houston. He is an elected fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology, the American Association for the Advancement of Sc ...
based on their ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
(rRNA) genes. They called these groups the ''Urkingdoms'' of Archaebacteria and Eubacteria, though other researchers treated them as kingdoms
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
or subkingdoms. Woese and Fox gave the first evidence for Archaebacteria as a separate "line of descent": 1. lack of peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ...
in their cell walls, 2. two unusual coenzymes, 3. results of 16S ribosomal RNA
16 S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome (SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.
The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rRNA ...
gene sequencing. To emphasize this difference, Woese, Otto Kandler
Otto Kandler (23 October 1920 in Deggendorf – 29 August 2017 in Munich, Bavaria)
was a German botanist and microbiologist. Until his retirement in 1986 he was professor of botany at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
His most importa ...
and Mark Wheelis Mark L. Wheelis is an American microbiologist. Wheelis is currently a professor in the College of Biological Sciences, University of California, Davis. Carl Woese and Otto Kandler with Wheelis wrote the important paper '' Towards a natural system of ...
later proposed reclassifying organisms into three natural domains known as the three-domain system
The three-domain system is a biological classification introduced by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler, and Mark Wheelis in 1990 that divides cellular life forms into three domains, namely Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryota or Eukarya. The key difference fr ...
: the Eukarya
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
, the Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and the Archaea, in what is now known as the Woesian Revolution.
The word ''archaea'' comes from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
, meaning "ancient things", as the first representatives of the domain Archaea were methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are com ...
s and it was assumed that their metabolism reflected Earth's primitive atmosphere and the organisms' antiquity, but as new habitats were studied, more organisms were discovered. Extreme halophilic
The halophiles, named after the Greek word for "salt-loving", are extremophiles that thrive in high salt concentrations. While most halophiles are classified into the domain Archaea, there are also bacterial halophiles and some eukaryotic species, ...
and hyperthermophilic
A hyperthermophile is an organism that thrives in extremely hot environments—from 60 °C (140 °F) upwards. An optimal temperature for the existence of hyperthermophiles is often above 80 °C (176 °F). Hyperthermophiles are often within the doma ...
microbes were also included in Archaea. For a long time, archaea were seen as extremophiles that exist only in extreme habitats such as hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
s and salt lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). ...
s, but by the end of the 20th century, archaea had been identified in non-extreme environments as well. Today, they are known to be a large and diverse group of organisms abundantly distributed throughout nature. This new appreciation of the importance and ubiquity of archaea came from using polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) t ...
(PCR) to detect prokaryotes from environmental samples (such as water or soil) by multiplying their ribosomal genes. This allows the detection and identification of organisms that have not been cultured
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor ...
in the laboratory.
Classification
 The classification of archaea, and of prokaryotes in general, is a rapidly moving and contentious field. Current classification systems aim to organize archaea into groups of organisms that share structural features and common ancestors. These classifications rely heavily on the use of the sequence of
The classification of archaea, and of prokaryotes in general, is a rapidly moving and contentious field. Current classification systems aim to organize archaea into groups of organisms that share structural features and common ancestors. These classifications rely heavily on the use of the sequence of ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
genes to reveal relationships among organisms (molecular phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
). Most of the culturable and well-investigated species of archaea are members of two main phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phyl ...
, the "Euryarchaeota
Euryarchaeota (from Ancient Greek ''εὐρύς'' eurús, "broad, wide") is a phylum of archaea. Euryarchaeota are highly diverse and include methanogens, which produce methane and are often found in intestines, halobacteria, which survive extre ...
" and the Thermoproteota
The Thermoproteota (also known as crenarchaea) are archaea that have been classified as a phylum of the Archaea domain. Initially, the Thermoproteota were thought to be sulfur-dependent extremophiles but recent studies have identified characteris ...
(formerly Crenarchaeota). Other groups have been tentatively created, like the peculiar species ''Nanoarchaeum equitans
''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains of th ...
'', which was discovered in 2003 and has been given its own phylum, the "Nanoarchaeota
Nanoarchaeota (Greek, "dwarf or tiny ancient one") are a phylum of the Archaea. This phylum currently has only one representative, ''Nanoarchaeum equitans''.
Taxonomy
53 marker proteins based GTDB 07-RS207 phylogeny.
The currently accepted ...
". A new phylum "Korarchaeota
In alpha taxonomy, taxonomy, the Korarchaeota are a phylum (biology), phylum of the Archaea. The name is derived from the Greek noun koros or kore, meaning ''young man'' or ''young woman,'' and the Greek adjective archaios which means ''ancient.' ...
" has also been proposed. It contains a small group of unusual thermophilic species that shares features of both of the main phyla, but is most closely related to the Thermoproteota. Other recently detected species of archaea are only distantly related to any of these groups, such as the Archaeal Richmond Mine acidophilic nanoorganisms
Archaeal Richmond Mine acidophilic nanoorganisms (ARMAN) were first discovered in an extremely acidic mine located in northern California ( Richmond Mine at Iron Mountain) by Brett Baker in Jill Banfield's laboratory at the University of Califor ...
(ARMAN, comprising Micrarchaeota
DPANN is a superphylum of Archaea first proposed in 2013. Many members show novel signs of horizontal gene transfer from other domains of life. They are known as nanoarchaea or ultra-small archaea due to their smaller size (nanometric) compared t ...
and Parvarchaeota), which were discovered in 2006 and are some of the smallest organisms known.
A superphylum – TACK – which includes the Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota
The Nitrososphaerota (syn. Thaumarchaeota) are a phylum of the Archaea proposed in 2008 after the genome of ''Cenarchaeum symbiosum'' was sequenced and found to differ significantly from other members of the hyperthermophilic phylum Thermoprote ...
), "Aigarchaeota
The "Aigarchaeota" are a proposed archaeal phylum of which the main representative is '' Caldiarchaeum subterraneum''.. It is not yet clear if this represents a new phylum or a and order of the Nitrososphaerota, since the genome of ''Caldiarchaeu ...
", Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota
The Thermoproteota (also known as crenarchaea) are archaea that have been classified as a phylum of the Archaea domain. Initially, the Thermoproteota were thought to be sulfur-dependent extremophiles but recent studies have identified characteris ...
), and "Korarchaeota
In alpha taxonomy, taxonomy, the Korarchaeota are a phylum (biology), phylum of the Archaea. The name is derived from the Greek noun koros or kore, meaning ''young man'' or ''young woman,'' and the Greek adjective archaios which means ''ancient.' ...
" was proposed in 2011 to be related to the origin of eukaryotes. In 2017, the newly discovered and newly named Asgard
In Nordic mythology, Asgard (Old Norse: ''Ásgarðr'' ; "enclosure of the Æsir") is a location associated with the gods. It appears in a multitude of Old Norse sagas and mythological texts. It is described as the fortified home of the Æsir ...
superphylum was proposed to be more closely related to the original eukaryote and a sister group to TACK.
In 2013 the superphylum DPANN was proposed to group "Nanoarchaeota
Nanoarchaeota (Greek, "dwarf or tiny ancient one") are a phylum of the Archaea. This phylum currently has only one representative, ''Nanoarchaeum equitans''.
Taxonomy
53 marker proteins based GTDB 07-RS207 phylogeny.
The currently accepted ...
", "Nanohaloarchaeota
Nanohaloarchaea is a clade of diminutive archaea with small genomes and limited metabolic capabilities, belonging to the DPANN archaea. They are ubiquitous in hypersaline habitats, which they share with the extremely halophilic haloarchaea.
Nano ...
", Archaeal Richmond Mine acidophilic nanoorganisms
Archaeal Richmond Mine acidophilic nanoorganisms (ARMAN) were first discovered in an extremely acidic mine located in northern California ( Richmond Mine at Iron Mountain) by Brett Baker in Jill Banfield's laboratory at the University of Califor ...
(ARMAN, comprising "Micrarchaeota
DPANN is a superphylum of Archaea first proposed in 2013. Many members show novel signs of horizontal gene transfer from other domains of life. They are known as nanoarchaea or ultra-small archaea due to their smaller size (nanometric) compared t ...
" and "Parvarchaeota
Parvarchaeota is a phylum of archaea belonging to the DPANN archaea. They have been discovered in acid mine drainage waters and later in marine sediments. The cells of these organisms are extremely small consistent with small genomes. Metagenomic ...
"), and other similar archaea. This archaeal superphylum encompasses at least 10 different lineages and includes organisms with extremely small cell and genome sizes and limited metabolic capabilities. Therefore, many members of DPANN may be obligately dependent on symbiotic interactions with other organisms and may even include novel parasites. However, in other phylogenetic analyses it was found that DPANN does not form a monophyletic group and that it is caused by the long branch attraction
In phylogenetics, long branch attraction (LBA) is a form of systematic error whereby distantly related lineages are incorrectly inferred to be closely related. LBA arises when the amount of molecular or morphological change accumulated within a lin ...
(LBA), suggesting that all these lineages belong to "Euryarchaeota".
Cladogram
According to Tom A. Williams ''et al.'' (2017), Castelle & Banfield (2018) andGTDB
The Genome Taxonomy Database (GTDB) is an online database that maintains information on a proposed nomenclature of prokaryotes, following a phylogenomic approach based on a set of conserved single-copy proteins. In addition to breaking up parap ...
release 07-RS207 (8th April 2022):
Concept of species
The classification of archaea into species is also controversial. Biology defines aspecies
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
as a group of related organisms. The familiar exclusive breeding criterion (organisms that can breed with each other but not with others) is of no help since archaea only reproduce asexually.
Archaea show high levels of horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offsprin ...
between lineages. Some researchers suggest that individuals can be grouped into species-like populations given highly similar genomes and infrequent gene transfer to/from cells with less-related genomes, as in the genus ''Ferroplasma
''Ferroplasma'' is a genus of Archaea that belong to the family Ferroplasmaceae. Members of the ''Ferroplasma'' are typically acidophillic, pleomorphic, irregularly shaped cocci.
The archaean family Ferroplasmaceae was first described in the ear ...
''. On the other hand, studies in ''Halorubrum
''Halorubrum'' is a genus in the family Halorubraceae. ''Halorubrum'' species areusually halophilic and can be found in waters with high salt concentration such as the Dead Sea or Lake Zabuye.
Genetic exchange
A population of the haloarchaea '' ...
'' found significant genetic transfer to/from less-related populations, limiting the criterion's applicability. Some researchers question whether such species designations have practical meaning.
Current knowledge on genetic diversity is fragmentary and the total number of archaeal species cannot be estimated with any accuracy. Estimates of the number of phyla range from 18 to 23, of which only 8 have representatives that have been cultured and studied directly. Many of these hypothesized groups are known from a single rRNA sequence, indicating that the diversity among these organisms remains obscure. The Bacteria also include many uncultured microbes with similar implications for characterization.
Phyla
Valid Phyla
The following phyla have been validly published according to theBacteriological Code
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC) governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea.P. H. A. Sneath, 2003. A short histor ...
:
* Nitrososphaerota
The Nitrososphaerota (syn. Thaumarchaeota) are a phylum of the Archaea proposed in 2008 after the genome of ''Cenarchaeum symbiosum'' was sequenced and found to differ significantly from other members of the hyperthermophilic phylum Thermoprote ...
* Thermoproteota
The Thermoproteota (also known as crenarchaea) are archaea that have been classified as a phylum of the Archaea domain. Initially, the Thermoproteota were thought to be sulfur-dependent extremophiles but recent studies have identified characteris ...
Provisional Phyla
The following phyla have been proposed, but have not been validly published according to the Bacteriological Code (including those that have ''candidatus
In prokaryote nomenclature, ''Candidatus'' (Latin for candidate of Roman office) is used to name prokaryotic phyla that are well characterized but yet-uncultured. Contemporary sequencing approaches, such as 16S sequencing or metagenomics, provide m ...
'' status):
* "''Candidatus'' Aenigmarchaeota
DPANN is a superphylum of Archaea first proposed in 2013. Many members show novel signs of horizontal gene transfer from other domains of life. They are known as nanoarchaea or ultra-small archaea due to their smaller size (nanometric) compared t ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Aigarchaeota
The "Aigarchaeota" are a proposed archaeal phylum of which the main representative is '' Caldiarchaeum subterraneum''.. It is not yet clear if this represents a new phylum or a and order of the Nitrososphaerota, since the genome of ''Caldiarchaeu ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Altiarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Asgardaeota
Asgard or Asgardarchaeota is a proposed superphylum consisting of a group of archaea that includes Lokiarchaeota, Thorarchaeota, Odinarchaeota, and Heimdallarchaeota. It appears the eukaryotes emerged within the Asgard, in a branch containing ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Bathyarchaeota
TACK is a group of archaea acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and Korarchaeota, the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic th ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Brockarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Diapherotrites
DPANN is a superphylum of Archaea first proposed in 2013. Many members show novel signs of horizontal gene transfer from other domains of life. They are known as nanoarchaea or ultra-small archaea due to their smaller size (nanometric) compared t ...
"
* "''Euryarchaeota
Euryarchaeota (from Ancient Greek ''εὐρύς'' eurús, "broad, wide") is a phylum of archaea. Euryarchaeota are highly diverse and include methanogens, which produce methane and are often found in intestines, halobacteria, which survive extre ...
''"
* "''Candidatus'' Geoarchaeota
TACK is a group of archaea acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and Korarchaeota, the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic ther ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Hadarchaeota
Hadesarchaea, formerly called the South-African Gold Mine Miscellaneous Euryarchaeal Group, are a class of thermophile microorganisms that have been found in deep mines, hot springs, marine sediments and other subterranean environments.
Nomencla ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Hadesarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Halobacterota"
* "''Candidatus'' Heimdallarchaeota
Asgard or Asgardarchaeota is a proposed superphylum consisting of a group of archaea that includes Lokiarchaeota, Thorarchaeota, Odinarchaeota, and Heimdallarchaeota. It appears the eukaryotes emerged within the Asgard, in a branch containing th ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Helarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Huberarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Hydrothermarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Korarchaeota
In alpha taxonomy, taxonomy, the Korarchaeota are a phylum (biology), phylum of the Archaea. The name is derived from the Greek noun koros or kore, meaning ''young man'' or ''young woman,'' and the Greek adjective archaios which means ''ancient.' ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Lokiarchaeia"
* "''Candidatus'' Lokiarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Mamarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Marsarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Methanobacteriota"
* "''Candidatus'' Micrarchaeota
DPANN is a superphylum of Archaea first proposed in 2013. Many members show novel signs of horizontal gene transfer from other domains of life. They are known as nanoarchaea or ultra-small archaea due to their smaller size (nanometric) compared t ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Nanoarchaeota
Nanoarchaeota (Greek, "dwarf or tiny ancient one") are a phylum of the Archaea. This phylum currently has only one representative, ''Nanoarchaeum equitans''.
Taxonomy
53 marker proteins based GTDB 07-RS207 phylogeny.
The currently accepted ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Nanohaloarchaeota
Nanohaloarchaea is a clade of diminutive archaea with small genomes and limited metabolic capabilities, belonging to the DPANN archaea. They are ubiquitous in hypersaline habitats, which they share with the extremely halophilic haloarchaea.
Nano ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Nezhaarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Odinarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Pacearchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Parvarchaeota
Parvarchaeota is a phylum of archaea belonging to the DPANN archaea. They have been discovered in acid mine drainage waters and later in marine sediments. The cells of these organisms are extremely small consistent with small genomes. Metagenomic ...
"
* "''Candidatus'' Thermoplasmatota"
* "''Candidatus'' Thorarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Undinarchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Verstraetearchaeota"
* "''Candidatus'' Woesearchaeota"
Origin and evolution
The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. Scientific evidence suggests that Abiogenesis, life began on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago. The earliest evidence for life, life on Earth is graphite found to be Biogenic substance, biogenic in 3.7-billion-year-old Metasediment, metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48-billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. In 2015, possible remains of Biotic material, biotic matter were found in 4.1-billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. Although probable prokaryotic cell fossils date to almost 3.5 bya, billion years ago, most prokaryotes do not have distinctive morphologies, and fossil shapes cannot be used to identify them as archaea. Instead, chemical fossils of unique lipids are more informative because such compounds do not occur in other organisms. Some publications suggest that archaeal or eukaryotic lipid remains are present in shales dating from 2.7 billion years ago, though such data have since been questioned. These lipids have also been detected in even older rocks from west Greenland. The oldest such traces come from the Isua greenstone belt, Isua district, which includes Earth's oldest known sediments, formed 3.8 billion years ago. The archaeal lineage may be the most ancient that exists on Earth. Woese argued that the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes represent separate lines of descent that diverged early on from an ancestral colony of organisms. One possibility is that this occurred before the evolution of cells, when the lack of a typical cell membrane allowed unrestricted lateral gene transfer, and that the common ancestors of the three domains arose by fixation of specific subsets of genes. It is possible that the last common ancestor of bacteria and archaea was a thermophile, which raises the possibility that lower temperatures are "extreme environments" for archaea, and organisms that live in cooler environments appeared only later. Since archaea and bacteria are no more related to each other than they are to eukaryotes, the term ''prokaryote'' may suggest a false similarity between them. However, structural and functional similarities between lineages often occur because of shared ancestral traits or Convergent evolution, evolutionary convergence. These similarities are known as a ''grade'', and prokaryotes are best thought of as a grade of life, characterized by such features as an absence of membrane-bound organelles.Comparison with other domains
The following table compares some major characteristics of the three domains, to illustrate their similarities and differences. Archaea were split off as a third domain because of the large differences in their ribosomal RNA structure. The particular molecule 16S rRNA is key to the production of proteins in all organisms. Because this function is so central to life, organisms with mutations in their 16S rRNA are unlikely to survive, leading to great (but not absolute) stability in the structure of this polynucleotide over generations. 16S rRNA is large enough to show organism-specific variations, but still small enough to be compared quickly. In 1977, Carl Woese, a microbiologist studying the genetic sequences of organisms, developed a new comparison method that involved splitting the RNA into fragments that could be sorted and compared with other fragments from other organisms. The more similar the patterns between species, the more closely they are related. Woese used his new rRNA comparison method to categorize and contrast different organisms. He compared a variety of species and happened upon a group of methanogens with rRNA vastly different from any known prokaryotes or eukaryotes. These methanogens were much more similar to each other than to other organisms, leading Woese to propose the new domain of Archaea. His experiments showed that the archaea were genetically more similar to eukaryotes than prokaryotes, even though they were more similar to prokaryotes in structure. This led to the conclusion that Archaea and Eukarya shared a common ancestor more recent than Eukarya and Bacteria. The development of the nucleus occurred after the split between Bacteria and this common ancestor. One property unique to archaea is the abundant use of ether-linked lipids in their cell membranes. Ether linkages are more chemically stable than the ester linkages found in bacteria and eukarya, which may be a contributing factor to the ability of many archaea to survive in extreme environments that place heavy stress on cell membranes, such as extreme heat and salinity. Comparative analysis of archaeal genomes has also identified several molecular conserved signature indels and signature proteins uniquely present in either all archaea or different main groups within archaea. Another unique feature of archaea, found in no other organisms, is methanogenesis (the metabolic production of methane). Methanogenic archaea play a pivotal role in ecosystems with organisms that derive energy from oxidation of methane, many of which are bacteria, as they are often a major source of methane in such environments and can play a role as primary producers. Methanogens also play a critical role in the carbon cycle, breaking down organic carbon into methane, which is also a major greenhouse gas. This difference in biochemical structure of Bacteria and Archaea has been explained by researchers that they originated at deep sea alkaline hydrothermal vents, where they independently developed lipid biosynthesis and cell wall biochemistry during their transition to Archaea and Bacteria. It has been suggested that the last universal common ancestor was a not free-living organism. However this view has been challenged by other researchers and is currently in dispute.Relationship to bacteria
The relationships among the three-domain system, three domains are of central importance for understanding the origin of life. Most of themetabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reac ...
s, which are the object of the majority of an organism's genes, are common between Archaea and Bacteria, while most genes involved in genome expression are common between Archaea and Eukarya. Within prokaryotes, archaeal cell structure is most similar to that of gram-positive bacteria, largely because both have a single lipid bilayer and usually contain a thick sacculus (exoskeleton) of varying chemical composition. In some phylogenetic trees based upon different gene/protein sequences of prokaryotic homologs, the archaeal homologs are more closely related to those of gram-positive bacteria. Archaea and gram-positive bacteria also share conserved indels in a number of important proteins, such as Hsp70 and glutamine synthetase I; but the phylogeny of these genes was interpreted to reveal interdomain gene transfer, and might not reflect the organismal relationship(s).
It has been proposed that the archaea evolved from gram-positive bacteria in response to antibiotic evolutionary pressure, selection pressure. This is suggested by the observation that archaea are resistant to a wide variety of antibiotics that are produced primarily by gram-positive bacteria, and that these antibiotics act primarily on the genes that distinguish archaea from bacteria. The proposal is that the selective pressure towards resistance generated by the gram-positive antibiotics was eventually sufficient to cause extensive changes in many of the antibiotics' target genes, and that these strains represented the common ancestors of present-day Archaea. The evolution of Archaea in response to antibiotic selection, or any other competitive selective pressure, could also explain their adaptation to extreme environments (such as high temperature or acidity) as the result of a search for unoccupied niches to escape from antibiotic-producing organisms; Thomas Cavalier-Smith, Cavalier-Smith has made a similar suggestion. This proposal is also supported by other work investigating protein structural relationships and studies that suggest that gram-positive bacteria may constitute the earliest branching lineages within the prokaryotes.
Relation to eukaryotes
The evolutionary relationship between archaea and eukaryotes remains unclear. Aside from the similarities in cell structure and function that are discussed below, many genetic trees group the two. Complicating factors include claims that the relationship between eukaryotes and the archaeal phylumThermoproteota
The Thermoproteota (also known as crenarchaea) are archaea that have been classified as a phylum of the Archaea domain. Initially, the Thermoproteota were thought to be sulfur-dependent extremophiles but recent studies have identified characteris ...
is closer than the relationship between the "Euryarchaeota
Euryarchaeota (from Ancient Greek ''εὐρύς'' eurús, "broad, wide") is a phylum of archaea. Euryarchaeota are highly diverse and include methanogens, which produce methane and are often found in intestines, halobacteria, which survive extre ...
" and the phylum Thermoproteota and the presence of archaea-like genes in certain bacteria, such as ''Thermotoga maritima'', from horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offsprin ...
. The standard hypothesis states that the ancestor of the eukaryotes diverged early from the Archaea, and that eukaryotes arose through fusion of an archaean and eubacterium, which became the nucleus and cytoplasm; this hypothesis explains the genetic similarities between the groups. The eocyte hypothesis instead posits that Eukaryota emerged relatively late from the Archaea.
A lineage of archaea discovered in 2015, ''Lokiarchaeum'' (of proposed new Phylum "Lokiarchaeota"), named for a hydrothermal vent called Loki's Castle in the Arctic Ocean, was found to be the most closely related to eukaryotes known at that time. It has been called a transitional organism between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Several sister phyla of "Lokiarchaeota" have since been found ("Thorarchaeota", "Odinarchaeota", "Heimdallarchaeota
Asgard or Asgardarchaeota is a proposed superphylum consisting of a group of archaea that includes Lokiarchaeota, Thorarchaeota, Odinarchaeota, and Heimdallarchaeota. It appears the eukaryotes emerged within the Asgard, in a branch containing th ...
"), all together comprising a newly proposed supergroup Asgard
In Nordic mythology, Asgard (Old Norse: ''Ásgarðr'' ; "enclosure of the Æsir") is a location associated with the gods. It appears in a multitude of Old Norse sagas and mythological texts. It is described as the fortified home of the Æsir ...
, which may appear as a sister taxon to Proteoarchaeota.
Details of the relation of Asgard members and eukaryotes are still under consideration, although, in January 2020, scientists reported that ''Candidatus Prometheoarchaeum syntrophicum'', a type of Asgard archaea, may be a possible link between simple prokaryotic and complex eukaryotic microorganisms about two billion years ago.
Morphology
Individual archaea range from 0.1 Micrometre, micrometers (μm) to over 15 μm in diameter, and occur in various shapes, commonly as spheres, rods, spirals or plates. Other morphologies in theThermoproteota
The Thermoproteota (also known as crenarchaea) are archaea that have been classified as a phylum of the Archaea domain. Initially, the Thermoproteota were thought to be sulfur-dependent extremophiles but recent studies have identified characteris ...
include irregularly shaped lobed cells in ''Sulfolobus'', needle-like filaments that are less than half a micrometer in diameter in ''Thermofilum'', and almost perfectly rectangular rods in ''Thermoproteus'' and ''Pyrobaculum''. Archaea in the genus ''Haloquadratum'' such as ''Haloquadratum walsbyi
''Haloquadratum walsbyi'' is of the genus ''Haloquadratum,'' within the archaea domain known for its square halophilic nature. First discovered in a brine pool in the Sinai peninsula of Egypt, ''H. walsbyi'' is noted for its flat, square-shaped ...
'' are flat, square specimens that live in hypersaline pools. These unusual shapes are probably maintained by both their cell walls and a prokaryotic cytoskeleton. Proteins related to the cytoskeleton components of other organisms exist in archaea, and filaments form within their cells, but in contrast with other organisms, these cellular structures are poorly understood. In ''Thermoplasma'' and ''Ferroplasma
''Ferroplasma'' is a genus of Archaea that belong to the family Ferroplasmaceae. Members of the ''Ferroplasma'' are typically acidophillic, pleomorphic, irregularly shaped cocci.
The archaean family Ferroplasmaceae was first described in the ear ...
'' the lack of a cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
means that the cells have irregular shapes, and can resemble Amoeboid, amoebae.
Some species form aggregates or filaments of cells up to 200 μm long. These organisms can be prominent in biofilms. Notably, aggregates of ''Thermococcus coalescens'' cells fuse together in culture, forming single giant cells. Archaea in the genus ''Pyrodictium'' produce an elaborate multicell colony involving arrays of long, thin hollow tubes called ''cannulae'' that stick out from the cells' surfaces and connect them into a dense bush-like agglomeration. The function of these cannulae is not settled, but they may allow communication or nutrient exchange with neighbors. Multi-species colonies exist, such as the "string-of-pearls" community that was discovered in 2001 in a German swamp. Round whitish colonies of a novel Euryarchaeota species are spaced along thin filaments that can range up to long; these filaments are made of a particular bacteria species.
Structure, composition development, and operation
Archaea and bacteria have generally similar Cell (biology), cell structure, but cell composition and organization set the archaea apart. Like bacteria, archaea lack interior membranes and organelles. Like bacteria, thecell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
s of archaea are usually bounded by a cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
and they swim using one or more flagella. Structurally, archaea are most similar to gram-positive bacteria. Most have a single plasma membrane and cell wall, and lack a periplasmic space; the exception to this general rule is ''Ignicoccus'', which possess a particularly large periplasm that contains membrane-bound vesicle (biology), vesicles and is enclosed by an outer membrane.
Cell wall and archaella
Most archaea (but not ''Thermoplasma'' and ''Ferroplasma
''Ferroplasma'' is a genus of Archaea that belong to the family Ferroplasmaceae. Members of the ''Ferroplasma'' are typically acidophillic, pleomorphic, irregularly shaped cocci.
The archaean family Ferroplasmaceae was first described in the ear ...
'') possess a cell wall. In most archaea the wall is assembled from surface-layer proteins, which form an S-layer. An S-layer is a rigid array of protein molecules that cover the outside of the cell (like chain mail). This layer provides both chemical and physical protection, and can prevent macromolecules from contacting the cell membrane. Unlike bacteria, archaea lack peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ...
in their cell walls. Methanobacteriales do have cell walls containing pseudopeptidoglycan, which resembles eubacterial peptidoglycan in morphology, function, and physical structure, but pseudopeptidoglycan is distinct in chemical structure; it lacks D-amino acids and N-acetylmuramic acid, substituting the latter with N-Acetyltalosaminuronic acid.
Archaeal flagella are known as archaellum, archaella, that operate like bacterial flagellum, flagella – their long stalks are driven by rotatory motors at the base. These motors are powered by a electrochemical gradient, proton gradient across the membrane, but archaella are notably different in composition and development. The two types of flagella evolved from different ancestors. The bacterial flagellum shares a common ancestor with the type III secretion system, while archaeal flagella appear to have evolved from bacterial type IV pili. In contrast with the bacterial flagellum, which is hollow and assembled by subunits moving up the central pore to the tip of the flagella, archaeal flagella are synthesized by adding subunits at the base.
Membranes
cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
s are made of molecules known as phospholipids. These molecules possess both a chemical polarity, polar part that dissolves in water (the phosphate "head"), and a "greasy" non-polar part that does not (the lipid tail). These dissimilar parts are connected by a glycerol moiety. In water, phospholipids cluster, with the heads facing the water and the tails facing away from it. The major structure in cell membranes is a double layer of these phospholipids, which is called a lipid bilayer.
The phospholipids of archaea are unusual in four ways:
* They have membranes composed of glycerol-ether lipid
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
s, whereas bacteria and eukaryotes have membranes composed mainly of glycerol-ester lipids. The difference is the type of bond that joins the lipids to the glycerol moiety; the two types are shown in yellow in the figure at the right. In ester lipids this is an ester, ester bond, whereas in ether lipids this is an ether, ether bond.
* The stereochemistry of the archaeal glycerol moiety is the mirror image of that found in other organisms. The glycerol moiety can occur in two forms that are mirror images of one another, called ''enantiomers''. Just as a right hand does not fit easily into a left-handed glove, enantiomers of one type generally cannot be used or made by enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s adapted for the other. The archaeal phospholipids are built on a backbone of ''sn''-glycerol-1-phosphate, which is an enantiomer of ''sn''-glycerol-3-phosphate, the phospholipid backbone found in bacteria and eukaryotes. This suggests that archaea use entirely different enzymes for synthesizing phospholipids as compared to bacteria and eukaryotes. Such enzymes developed very early in life's history, indicating an early split from the other two domains.
* Archaeal lipid tails differ from those of other organisms in that they are based upon long isoprene, isoprenoid chains with multiple side-branches, sometimes with cyclopropane or cyclohexane rings. By contrast, the fatty acids in the membranes of other organisms have straight chains without side branches or rings. Although isoprenoids play an important role in the biochemistry of many organisms, only the archaea use them to make phospholipids. These branched chains may help prevent archaeal membranes from leaking at high temperatures.
* In some archaea, the lipid bilayer is replaced by a monolayer. In effect, the archaea fuse the tails of two phospholipid molecules into a single molecule with two polar heads (a bolaamphiphile); this fusion may make their membranes more rigid and better able to resist harsh environments. For example, the lipids in ''Ferroplasma
''Ferroplasma'' is a genus of Archaea that belong to the family Ferroplasmaceae. Members of the ''Ferroplasma'' are typically acidophillic, pleomorphic, irregularly shaped cocci.
The archaean family Ferroplasmaceae was first described in the ear ...
'' are of this type, which is thought to aid this organism's survival in its highly acidic habitat.
Metabolism
Archaea exhibit a great variety of chemical reactions in theirmetabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
and use many sources of energy. These reactions are classified into primary nutritional groups, nutritional groups, depending on energy and carbon sources. Some archaea obtain energy from inorganic compounds such as sulfur or ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
(they are chemotrophs). These include nitrifying bacteria, nitrifiers, methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are com ...
s and anaerobic organism, anaerobic methane oxidisers. In these reactions one compound passes electrons to another (in a redox reaction), releasing energy to fuel the cell's activities. One compound acts as an electron donor and one as an electron acceptor. The energy released is used to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through chemiosmosis, the same basic process that happens in the mitochondrion of eukaryotic cells.
Other groups of archaea use sunlight as a source of energy (they are phototrophs), but oxygen–generating photosynthesis does not occur in any of these organisms. Many basic metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reac ...
s are shared among all forms of life; for example, archaea use a modified form of glycolysis (the Entner–Doudoroff pathway) and either a complete or partial citric acid cycle. These similarities to other organisms probably reflect both early origins in the history of life and their high level of efficiency.
Some Euryarchaeota are methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are com ...
s (archaea that produce methane as a result of metabolism) living in anaerobic environments, such as swamps. This form of metabolism evolved early, and it is even possible that the first free-living organism was a methanogen. A common reaction involves the use of carbon dioxide as an electron acceptor to oxidize hydrogen. Methanogenesis involves a range of coenzymes that are unique to these archaea, such as coenzyme M and methanofuran. Other organic compounds such as Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols, acetic acid or formic acid are used as alternative electron acceptors by methanogens. These reactions are common in Gut (zoology), gut-dwelling archaea. Acetic acid is also broken down into methane and carbon dioxide directly, by ''acetotrophic'' archaea. These acetotrophs are archaea in the order Methanosarcinales, and are a major part of the communities of microorganisms that produce biogas
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. It is a ...
.
 Other archaea use in the atmosphere as a source of carbon, in a process called carbon fixation (they are autotrophs). This process involves either a highly modified form of the Calvin cycle or another metabolic pathway called the 3-hydroxypropionate/ 4-hydroxybutyrate cycle. The Thermoproteota also use the reverse Krebs cycle while the "Euryarchaeota" also use the reductive acetyl-CoA pathway. Carbon fixation is powered by inorganic energy sources. No known archaea carry out photosynthesis (Halobacterium is the only known phototroph archeon but it uses an alternative process to photosynthesis). Archaeal energy sources are extremely diverse, and range from the oxidation of
Other archaea use in the atmosphere as a source of carbon, in a process called carbon fixation (they are autotrophs). This process involves either a highly modified form of the Calvin cycle or another metabolic pathway called the 3-hydroxypropionate/ 4-hydroxybutyrate cycle. The Thermoproteota also use the reverse Krebs cycle while the "Euryarchaeota" also use the reductive acetyl-CoA pathway. Carbon fixation is powered by inorganic energy sources. No known archaea carry out photosynthesis (Halobacterium is the only known phototroph archeon but it uses an alternative process to photosynthesis). Archaeal energy sources are extremely diverse, and range from the oxidation of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
by the Nitrosopumilales to the oxidation of hydrogen sulfide or elemental sulfur by species of ''Sulfolobus'', using either oxygen or metal ions as electron acceptors.
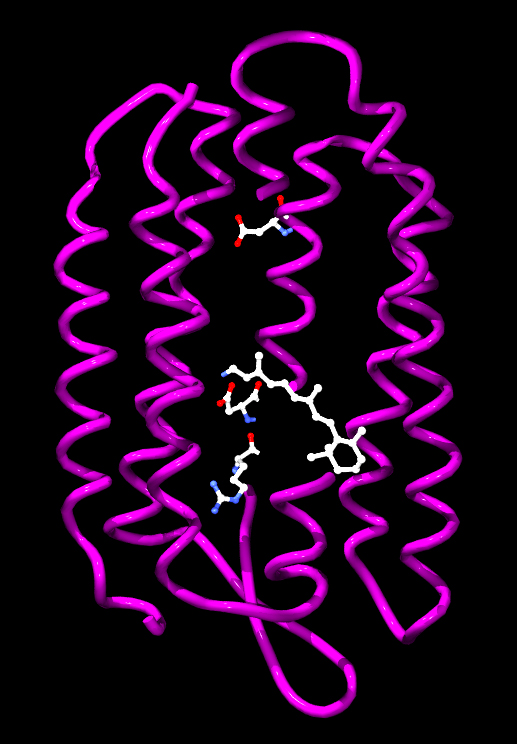
Phototrophic archaea use light to produce chemical energy in the form of ATP. In the Halobacteria, light-activated ion pumps like bacteriorhodopsin and halorhodopsin generate ion gradients by pumping ions out of and into the cell across the plasma membrane. The energy stored in these electrochemical gradients is then converted into ATP by ATP synthase. This process is a form of photophosphorylation. The ability of these light-driven pumps to move ions across membranes depends on light-driven changes in the structure of a retinol Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor buried in the center of the protein.
Genetics
Archaea usually have a single circular chromosome, with as many as 5,751,492 base pairs in ''Methanosarcina acetivorans'', the largest known archaeal genome. The tiny 490,885 base-pair genome of ''Nanoarchaeum equitans
''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains of th ...
'' is one-tenth of this size and the smallest archaeal genome known; it is estimated to contain only 537 protein-encoding genes. Smaller independent pieces of DNA, called ''plasmids'', are also found in archaea. Plasmids may be transferred between cells by physical contact, in a process that may be similar to bacterial conjugation.
 Archaea are genetically distinct from bacteria and eukaryotes, with up to 15% of the proteins encoded by any one archaeal genome being unique to the domain, although most of these unique genes have no known function. Of the remainder of the unique proteins that have an identified function, most belong to the Euryarchaeota and are involved in methanogenesis. The proteins that archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes share form a common core of cell function, relating mostly to Transcription (genetics), transcription, Translation (biology), translation, and nucleotide, nucleotide metabolism. Other characteristic archaeal features are the organization of genes of related function – such as enzymes that catalyze steps in the same
Archaea are genetically distinct from bacteria and eukaryotes, with up to 15% of the proteins encoded by any one archaeal genome being unique to the domain, although most of these unique genes have no known function. Of the remainder of the unique proteins that have an identified function, most belong to the Euryarchaeota and are involved in methanogenesis. The proteins that archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes share form a common core of cell function, relating mostly to Transcription (genetics), transcription, Translation (biology), translation, and nucleotide, nucleotide metabolism. Other characteristic archaeal features are the organization of genes of related function – such as enzymes that catalyze steps in the same metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reac ...
into novel operons, and large differences in tRNA genes and their aminoacyl tRNA synthetases.
Transcription in archaea more closely resembles eukaryotic than bacterial transcription, with the archaeal RNA polymerase being very close to its equivalent in eukaryotes, while archaeal translation shows signs of both bacterial and eukaryotic equivalents. Although archaea have only one type of RNA polymerase, its structure and function in transcription seems to be close to that of the eukaryotic RNA polymerase II, with similar protein assemblies (the general transcription factors) directing the binding of the RNA polymerase to a gene's promoter (biology), promoter, but other archaeal transcription factors are closer to those found in bacteria. Post-transcriptional modification is simpler than in eukaryotes, since most archaeal genes lack introns, although there are many introns in their transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
genes, and introns may occur in a few protein-encoding genes.
Gene transfer and genetic exchange
''Haloferax volcanii'', an extreme halophilic archaeon, forms cytoplasmic bridges between cells that appear to be used for transfer of DNA from one cell to another in either direction. When the hyperthermophilic archaea ''Sulfolobus solfataricus'' and ''Sulfolobus acidocaldarius'' are exposed to DNA-damaging UV irradiation or to the agents bleomycin or mitomycin C, species-specific cellular aggregation is induced. Aggregation in ''S. solfataricus'' could not be induced by other physical stressors, such as pH or temperature shift, suggesting that aggregation is induced specifically by DNA damage. Ajon et al. showed that UV-induced cellular aggregation mediates chromosomal marker exchange with high frequency in ''S. acidocaldarius''. Recombination rates exceeded those of uninduced cultures by up to three orders of magnitude. Frols et al. and Ajon et al. hypothesized that cellular aggregation enhances species-specific DNA transfer between ''Sulfolobus'' cells in order to provide increased repair of damaged DNA by means of homologous recombination. This response may be a primitive form of sexual interaction similar to the more well-studied bacterial transformation systems that are also associated with species-specific DNA transfer between cells leading to homologous recombinational repair of DNA damage.Archaeal viruses
Archaea are the target of a number of viruses in a diverse virosphere distinct from bacterial and eukaryotic viruses. They have been organized into 15-18 DNA-based families so far, but multiple species remain un-isolated and await classification. These families can be informally divided into two groups: archaea-specific and cosmopolitan. Archaeal-specific viruses target only archaean species and currently include 12 families. Numerous unique, previously unidentified viral structures have been observed in this group, including: bottle-shaped, spindle-shaped, coil-shaped, and droplet-shaped viruses. While the reproductive cycles and genomic mechanisms of archaea-specific species may be similar to other viruses, they bear unique characteristics that were specifically developed due to the morphology of host cells they infect. Their virus release mechanisms differ from that of other phages. Bacteriophages generally undergo either Lytic cycle, lytic pathways, Lysogenic cycle, lysogenic pathways, or (rarely) a mix of the two. Most archaea-specific viral strains maintain a stable, somewhat lysogenic, relationship with their hosts – appearing as a chronic infection. This involves the gradual, and continuous, production and release of Virus, virions without killing the host cell. Prangishyili (2013) noted that it has been hypothesized that tailed archaeal phages originated from bacteriophages capable of infecting haloarchaeal species. If the hypothesis is correct, it can be concluded that other double-stranded DNA viruses that make up the rest of the archaea-specific group are their own unique group in the global viral community. Krupovic et al. (2018) states that the high levels ofhorizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offsprin ...
, rapid mutation rates in viral genomes, and lack of universal gene sequences have led researchers to perceive the evolutionary pathway of archaeal viruses as a network. The lack of similarities among phylogenetic markers in this network and the global virosphere, as well as external linkages to non-viral elements, may suggest that some species of archaea specific viruses evolved from non-viral mobile genetic elements (MGE).
These viruses have been studied in most detail in thermophilics, particularly the orders Sulfolobales and Thermoproteales. Two groups of single-stranded DNA viruses that infect archaea have been recently isolated. One group is exemplified by the ''Halorubrum pleomorphic virus 1'' (''Pleolipoviridae'') infecting halophilic archaea, and the other one by the ''Aeropyrum coil-shaped virus'' (''Spiraviridae'') infecting a hyperthermophilic (optimal growth at 90–95 °C) host. Notably, the latter virus has the largest currently reported ssDNA genome. Defenses against these viruses may involve RNA interference from repetitive DNA sequences that are related to the genes of the viruses.
Reproduction
Archaea reproduce asexually by binary or multiple fission (biology), fission, fragmentation, orbudding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is know ...
; mitosis and meiosis do not occur, so if a species of archaea exists in more than one form, all have the same genetic material. Cell division is controlled in a cell cycle; after the cell's chromosome is replicated and the two daughter chromosomes separate, the cell divides. In the genus ''Sulfolobus'', the cycle has characteristics that are similar to both bacterial and eukaryotic systems. The chromosomes replicate from multiple starting points (origin of replication, origins of replication) using DNA polymerases that resemble the equivalent eukaryotic enzymes.
In Euryarchaeota the cell division protein FtsZ, which forms a contracting ring around the cell, and the components of the septum that is constructed across the center of the cell, are similar to their bacterial equivalents. In cren- and thaumarchaea, the cell division machinery Cdv fulfills a similar role. This machinery is related to the eukaryotic ESCRT-III machinery which, while best known for its role in cell sorting, also has been seen to fulfill a role in separation between divided cell, suggesting an ancestral role in cell division.
Both bacteria and eukaryotes, but not archaea, make spores. Some species of Haloarchaea
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of th ...
undergo phenotypic switching and grow as several different cell types, including thick-walled structures that are resistant to osmotic shock and allow the archaea to survive in water at low salt concentrations, but these are not reproductive structures and may instead help them reach new habitats.
Behavior
Communication
Quorum sensing was originally thought to not exist in Archaea, but recent studies have shown evidence of some species being able to perform cross-talk through quorum sensing. Other studies have shown syntrophic interactions between archaea and bacteria during biofilm growth. Although research is limited in archaeal quorum sensing, some studies have uncovered LuxR proteins in archaeal species, displaying similarities with bacteria LuxR, and ultimately allowing for the detection of small molecules that are used in high density communication. Similarly to bacteria, Archaea LuxR solos have shown to bind to AHLs (lactones) and non-AHLs ligans, which is a large part in performing intraspecies, interspecies, and interkingdom communication through quorum sensing.Ecology
Habitats
 Archaea exist in a broad range of
Archaea exist in a broad range of habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
s, and are now recognized as a major part of global ecosystems, and may represent about 20% of microbial cells in the oceans. However, the first-discovered archaeans were extremophile
An extremophile (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "love") is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e. environments that make survival challenging such as due to extreme temper ...
s. Indeed, some archaea survive high temperatures, often above , as found in geysers, black smokers, and oil wells. Other common habitats include very cold habitats and highly salt, saline, acidic, or alkaline water, but archaea include mesophiles that grow in mild conditions, in swamps and marshland, sewage, the oceans, the intestinal tract of animals, and soils. Similar to Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, PGPR, Archaea are now considered as a source of plant growth promotion as well.
Extremophile archaea are members of four main physiological groups. These are the halophiles, thermophiles, alkaliphiles, and Acidophile (organisms), acidophiles. These groups are not comprehensive or phylum-specific, nor are they mutually exclusive, since some archaea belong to several groups. Nonetheless, they are a useful starting point for classification.
Halophiles, including the genus ''Halobacterium'', live in extremely saline environments such as salt lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). ...
s and outnumber their bacterial counterparts at salinities greater than 20–25%. Thermophiles grow best at temperatures above , in places such as hot springs; ''hyperthermophilic'' archaea grow optimally at temperatures greater than . The archaeal ''Methanopyrus kandleri'' Strain 116 can even reproduce at , the highest recorded temperature of any organism.
Other archaea exist in very acidic or alkaline conditions. For example, one of the most extreme archaean acidophiles is ''Picrophilus, Picrophilus torridus'', which grows at pH 0, which is equivalent to thriving in 1.2 Molar concentration, molar sulfuric acid.
This resistance to extreme environments has made archaea the focus of speculation about the possible properties of extraterrestrial life. Some extremophile habitats are not dissimilar to those on Mars, leading to the suggestion that viable microbes could be transferred between planets in meteorites.
Recently, several studies have shown that archaea exist not only in mesophilic and thermophilic environments but are also present, sometimes in high numbers, at low temperatures as well. For example, archaea are common in cold oceanic environments such as polar seas. Even more significant are the large numbers of archaea found throughout the world's oceans in non-extreme habitats among the plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ...
community (as part of the picoplankton). Although these archaea can be present in extremely high numbers (up to 40% of the microbial biomass), almost none of these species have been isolated and studied in pure culture. Consequently, our understanding of the role of archaea in ocean ecology is rudimentary, so their full influence on global biogeochemistry, biogeochemical cycles remains largely unexplored. Some marine Thermoproteota are capable of nitrification, suggesting these organisms may affect the oceanic nitrogen cycle, although these oceanic Thermoproteota may also use other sources of energy.
Vast numbers of archaea are also found in the sediments that cover the sea floor, with these organisms making up the majority of living cells at depths over 1 meter below the ocean bottom. It has been demonstrated that in all oceanic surface sediments (from 1000- to 10,000-m water depth), the impact of viral infection is higher on archaea than on bacteria and virus-induced lysis of archaea accounts for up to one-third of the total microbial biomass killed, resulting in the release of ~0.3 to 0.5 gigatons of carbon per year globally.
Role in chemical cycling
Archaea recycle elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur through their various habitats. Archaea carry out many steps in the nitrogen cycle. This includes both reactions that remove nitrogen from ecosystems (such as nitrate-based respiration and denitrification) as well as processes that introduce nitrogen (such as nitrate assimilation and nitrogen fixation). Researchers recently discovered archaeal involvement inammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
oxidation reactions. These reactions are particularly important in the oceans. The archaea also appear crucial for ammonia oxidation in soils. They produce nitrite, which other microbes then oxidize to nitrate. Plants and other organisms consume the latter.
In the sulfur cycle, archaea that grow by oxidizing sulfur compounds release this element from rocks, making it available to other organisms, but the archaea that do this, such as ''Sulfolobus'', produce sulfuric acid as a waste product, and the growth of these organisms in abandoned mines can contribute to acid mine drainage and other environmental damage.
In the carbon cycle, methanogen archaea remove hydrogen and play an important role in the decay of organic matter by the populations of microorganisms that act as decomposers in anaerobic ecosystems, such as sediments, marshes, and sewage treatment, sewage-treatment works.
Interactions with other organisms
 The well-characterized interactions between archaea and other organisms are either Mutualism (biology), mutual or commensalism, commensal. There are no clear examples of known archaeal
The well-characterized interactions between archaea and other organisms are either Mutualism (biology), mutual or commensalism, commensal. There are no clear examples of known archaeal pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
s or parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s, but some species of methanogens have been suggested to be involved in periodontal disease, infections in the mouth, and ''Nanoarchaeum equitans
''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains of th ...
'' may be a parasite of another species of archaea, since it only survives and reproduces within the cells of the Crenarchaeon ''Ignicoccus, Ignicoccus hospitalis'', and appears to offer no benefit to its host (biology), host.
Mutualism
Mutualism is an interaction between individuals of different species that results in positive (beneficial) effects on per capita reproduction and/or survival of the interacting populations. One well-understood example of mutualism (biology), mutualism is the interaction between protozoa and methanogen, methanogenic archaea in the digestive tracts of animals that digest cellulose, such asruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally ...
s and termites. In these anaerobic environments, protozoa break down plant cellulose to obtain energy. This process releases hydrogen as a waste product, but high levels of hydrogen reduce energy production. When methanogens convert hydrogen to methane, protozoa benefit from more energy.
In anaerobic protozoa, such as ''Plagiopyla frontata'', archaea reside inside the protozoa and consume hydrogen produced in their hydrogenosomes. Archaea also associate with larger organisms. For example, the marine archaean ''Cenarchaeum, Cenarchaeum symbiosum'' lives within (is an endosymbiont of) the sponge ''Axinella, Axinella mexicana''.
Commensalism
Archaea can also be commensals, benefiting from an association without helping or harming the other organism. For example, the methanogen ''Methanobrevibacter smithii'' is by far the most common archaean in the human flora, making up about one in ten of all the prokaryotes in the human gut. In termites and in humans, these methanogens may in fact be mutualists, interacting with other microbes in the gut to aid digestion. Archaean communities also associate with a range of other organisms, such as on the surface of corals, and in the region of soil that surrounds plant roots (the Rhizosphere (ecology), rhizosphere).Parasitism
Although Archaea do not have a historical reputation of being pathogens, Archaea are often found with similar genomes to more common pathogen like ''E. coli,'' showing metabolic links and evolutionary history with today's pathogens. Archaea also has inconsistent detection within clinical studies because of the lack of categorization of Archaea into more specific species.Significance in technology and industry
Extremophile archaea, particularly those resistant either to heat or to extremes of acidity and alkalinity, are a source ofenzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s that function under these harsh conditions. These enzymes have found many uses. For example, thermostable DNA polymerases, such as the Pfu DNA polymerase from ''Pyrococcus furiosus'', revolutionized molecular biology by allowing the polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) t ...
to be used in research as a simple and rapid technique for cloning DNA. In industry, amylases, galactosidases and pullulanases in other species of ''Pyrococcus'' that function at over allow food processing at high temperatures, such as the production of low lactose milk and whey. Enzymes from these thermophilic archaea also tend to be very stable in organic solvents, allowing their use in environmentally friendly processes in green chemistry that synthesize organic compounds. This stability makes them easier to use in structural biology. Consequently, the counterparts of bacterial or eukaryotic enzymes from extremophile archaea are often used in structural studies.
In contrast with the range of applications of archaean enzymes, the use of the organisms themselves in biotechnology is less developed. Methanogen, Methanogenic archaea are a vital part of sewage treatment
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding envir ...
, since they are part of the community of microorganisms that carry out anaerobic digestion and produce biogas
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. It is a ...
. In mineral processing, acidophilic archaea display promise for the extraction of metals from ores, including gold, cobalt and copper.
Archaea host a new class of potentially useful antibiotics. A few of these archaeocins have been characterized, but hundreds more are believed to exist, especially within ''Haloarchaea
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of th ...
'' and ''Sulfolobus''. These compounds differ in structure from bacterial antibiotics, so they may have novel modes of action. In addition, they may allow the creation of new selectable markers for use in archaeal molecular biology.
See also
* Aerobic methane production * Earliest known life forms * List of Archaea genera * List of sequenced archaeal genomes * Nuclear localization sequence * ''The Surprising Archaea'' (book) * Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya * Unique properties of hyperthermophilic archaea * Branching order of bacterial phyla (Genome Taxonomy Database, 2018)References
Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
General
Introduction to the Archaea, ecology, systematics and morphology
Oceans of Archaea
nbsp;– E.F. DeLong, ''ASM News'', 2003
Classification
NCBI taxonomy page on Archaea
nbsp;– list of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature
Shotgun sequencing finds nanoorganisms
nbsp;– discovery of the ARMAN group of archaea
Genomics
Browse any completed archaeal genome at UCSC
Comparative Analysis of Archaeal Genomes
(at United States Department of Energy, DOE's Integrated Microbial Genomes System, IMG system) {{Authority control Archaea, Extremophiles Domains (biology) Systems of bacterial taxonomy